Module 6 Benzene and other arenes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
what are sigma bonds
strong bonds with 2 s orbitals overlapping
what are pi bonds
weaker bonds with 2 p orbitals overlapping
what does the ring on benzene signify
delocalised pi bonds above and below
what shape is benzene
planar (flat), a regular hexagon shape
what bond angles does benzene have
120 degrees
what do benzenes carbons make
each make 3 bonds
what happens to benzene in bromine water
does not decolourise (stays orange)
what are the 4 ways to tell you the root name is benzene
an alkyl group up to 7 carbons long (e.g. methyl ethyl), a halogen (bromo chloro fluoro), a nitro group (NO2), a carboxylic acid (COOH)
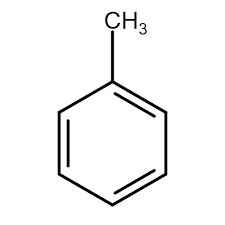
what is this
methylbenzene
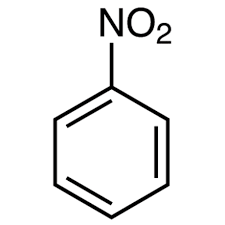
what is this
nitrobenzene
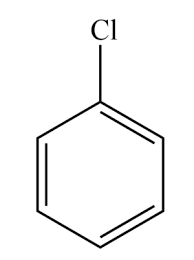
what is this
chlorobenzene
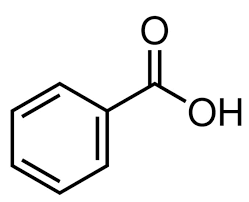
what is this
benzene carboxylic acid
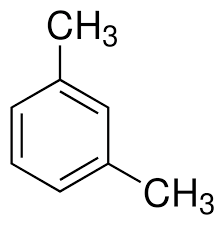
what is this
1,3-dimethylbenzene
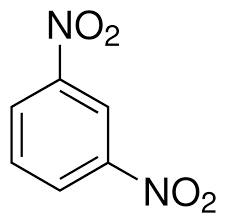
what is this
1,3-dinitrobenzene
when is the root name phenol
with most other functional groups or attached to chain with 7 or more carbon atoms
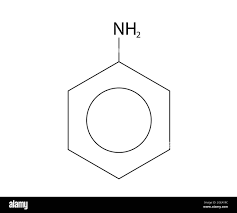
what is this
phenylamine
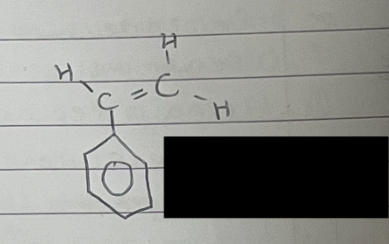
what is this
phenylethene
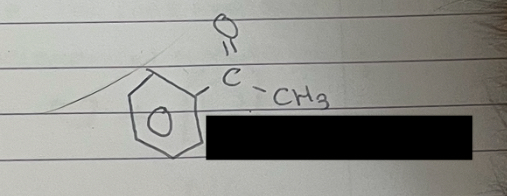
what is this
phenylethanone
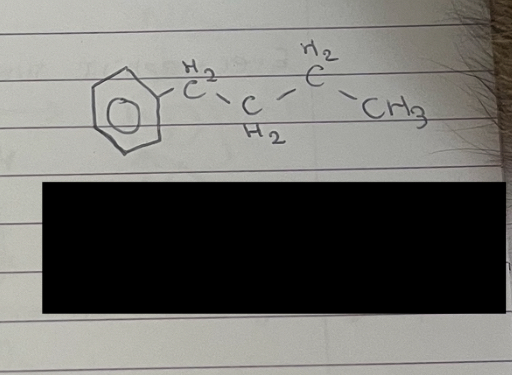
what is this
butylbenzene (carbon one of the butyl group is attached to the benzene)
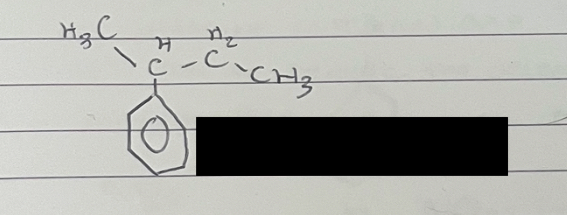
what is this
2-phenylbutane

what is this
phenyltmethanal
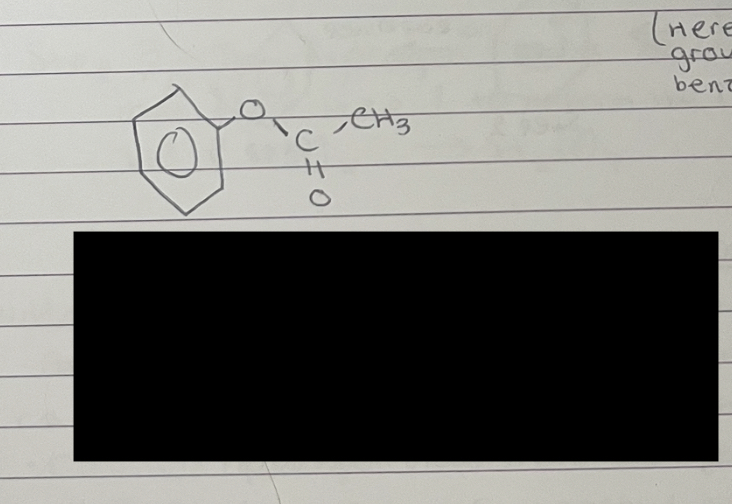
what is this
phenylethanoate (the benzene is on the -O section of the ester functional group so comes first in the name as a phenyl group)
what colour is benzene
colourless
what smell is benzene
sweet smelling
how flammable is benzene
highly flammable liquid
where is benzene found
found naturally in crude oil, component of petrol, found in cigarette smoke
what is benzene classified as
a carcinogen, can cause cancer
how reactive is benzene
unreactive
what are the derivatives of benzene
many aromatic compounds can be synthesised from benzene
what is the kekule model
structure of benzene based on 6 membered ring of carbon joined by alternate single and double bonds
why is the kekule model disaproved
not able to explain all its chemical and physical properties, lack of reactivity of benzene, length of C-C bonds, hydrogenation enthalpies
why does the lack of reactivity in benzene disapprove the kekule model
if it contained c=c bonds it should decolourise in brome in an electrophilic addition but it doesnt undergo electrophilic addition reaction and does not decolourise under normal conditions
why do the lengths of C-C bonds in benzene disapprove the kekule model
use xray diffraction to measure bond lengths in a molecule, single bond is 0.153nm and double bond is 0.134nm but bonds in benzene are 0-139nm,
why do hydrogenation enthalpies in benzene disapprove the kekule model
if benzene had kelule structure then it would have hydrogenation enthalpy 3x of cyclohexa-1,2,5-triene (kekule structure name) which is -120KJmol-1 so would be -360 but is -208
where in each carbon atoms of benzene are the electrons
1 electron is in p orbital at right angles to plane of bonded carbon and hydrogen atom
where do the p orbital electrons overlap in benzene
adjacent p orbital electrons overlap sideways above and below plane of carbon atoms to form ring of electron density
what do the overlapping p orbitals create in benzene
pi bonds which spread all over 6 carbon atoms in ring structure (the 6 electrons are delocalised)
what ones do i need to remember
benzoic acid (benzenecarboxylic acid), phenylamine, benzaldehyde (benzenecarbaldehyde)
what happens to compounds with more than 1 substituent group
ring is numbered just like a carbon chain starting in alphabetical order using smallest numbers possible