basu bio 112 final
1/252
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
253 Terms
theory
A well-tested explanation for a wide range of observations or experimental results.
monocot vs eudicot seed
monocot = one cotyledon
eudicot = two

monocot vs eudicot roots
monocot = fibrous root
eudicot = tap root
monocot vs eudicot vascular layout
monocot = scattered
eudicot = in a ring
monocot vs eudicot leaf
monocot = parallel veins
eudicot = net like vein
monocot vs eudicot flower
monocot = multiples of 3
eudicot = 4 or 5
prokaryotes that led to oxygenation of the atmosphere
cyanobacteria
how does cyanobacteria store food
as glycogen
who developed prokaryote staining
robert koch
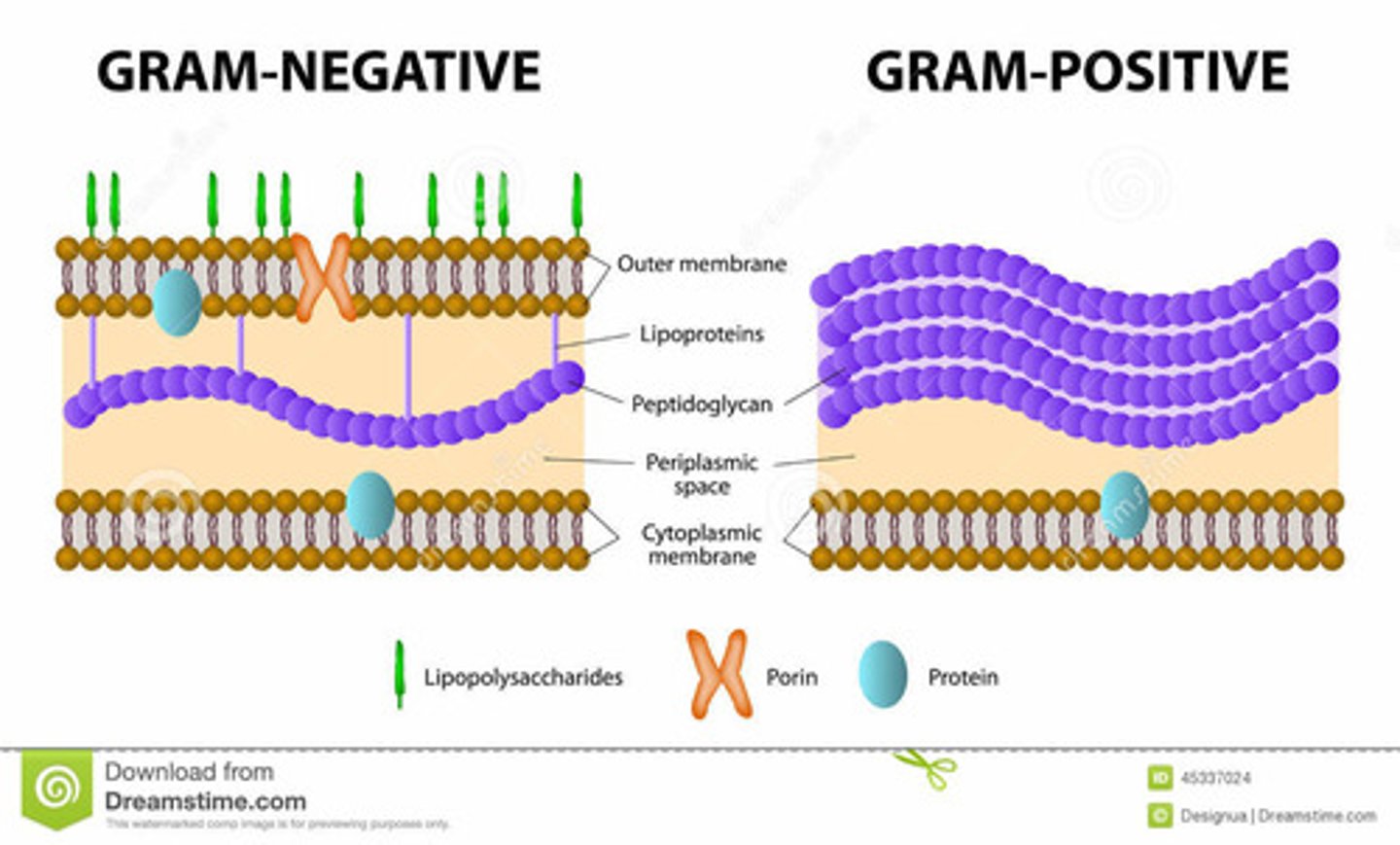
why does gram + bacteria stay purple while gram - turns pink?
gram + bacteria maintains the purple color of the stain bc/ it has a thicker peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall compared to gram -
method used in evolution to identify synapomorphies and arranging them into a clade
clade analysis
microevolution results in
change in allelic frequencies
4 mechanisms of microevoltuion
- mutation
- natural selection
- gene flow
- genetic drift
genetic drift
change in allelic frequency due to RANDOM events
(T/F) genetic drift has more effect in small populations
true
genetic drift can result in
loss or fixation of alleles
types of genetic drift
bottleneck effect and founder effect
gene flow
movement of alleles from one population to another
ex. migration
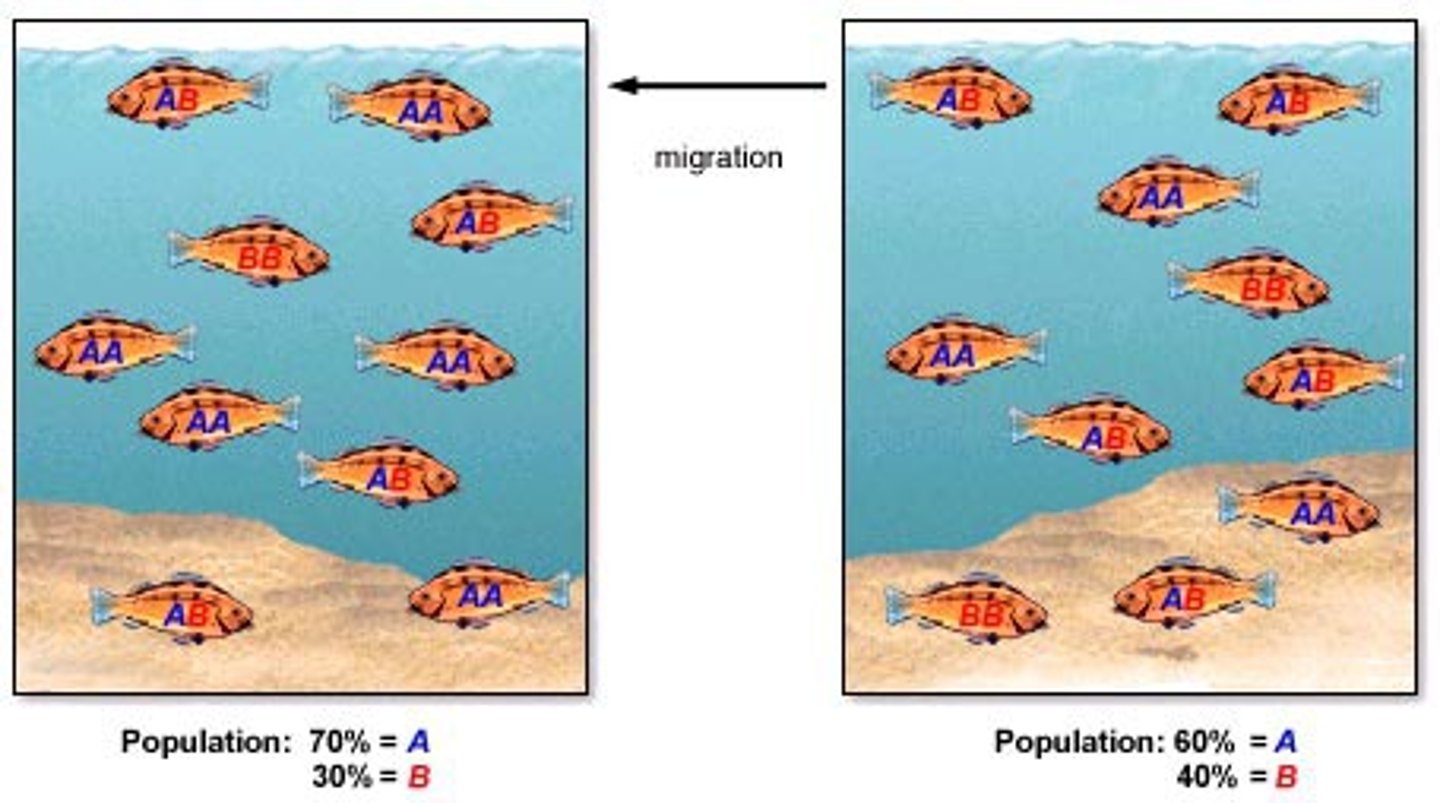
(T/F) gene flow tends to ADD diversity to populations
true
directional natural selection
chooses the extreme end of spectrum. shifts to newest fit phenotype
distruptive selection
middle of the spectrum is least fit. MAINTAINS DIVERSITY
Stabilizing selection
middle of the spectrum is considered more fit
frequency-dependent selection
most common trait is considered least fit
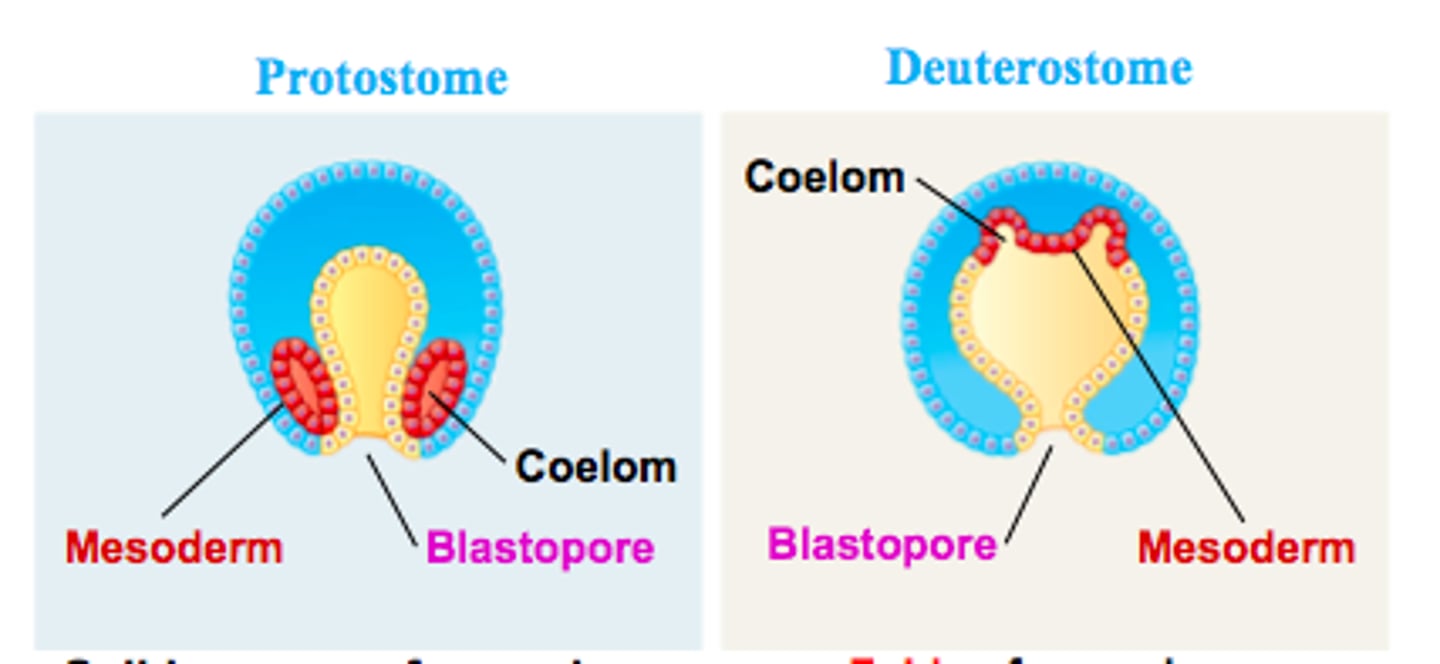
proteosome vs deuterostome cleavage
p = eight cell stage is spiral and determinate
d = radial and indeterminate
proteosome vs deuterostome blastophore fate
p = mouth
d = anus
proteosome vs deuterostome coelom formation
p = mesoderm splits
d = mesoderm pinches off
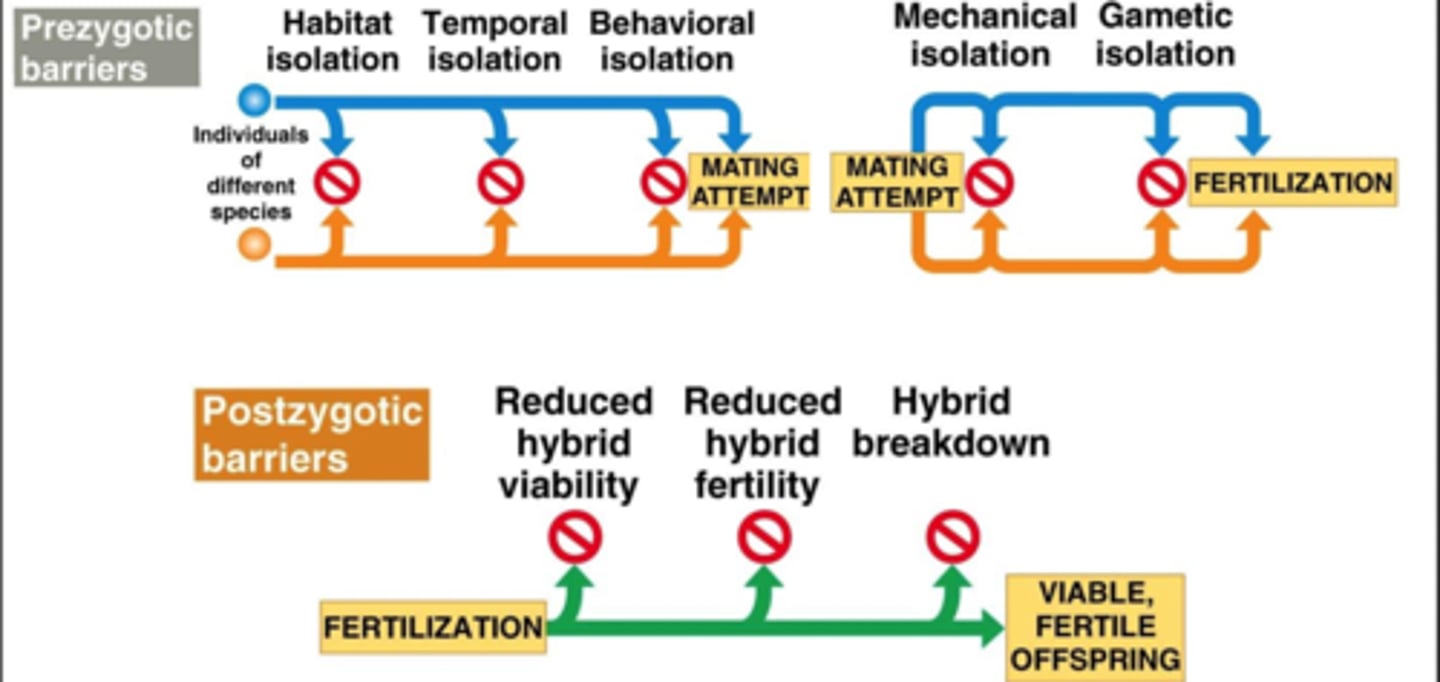
biological species concept
Definition of a species is a population or group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable, fertile offspring, but are not able to produce viable, fertile offspring with members of other populations.
prezygotic barriers vs postzygotic barriers
pre = zygote does not form
post = zygote has already formed
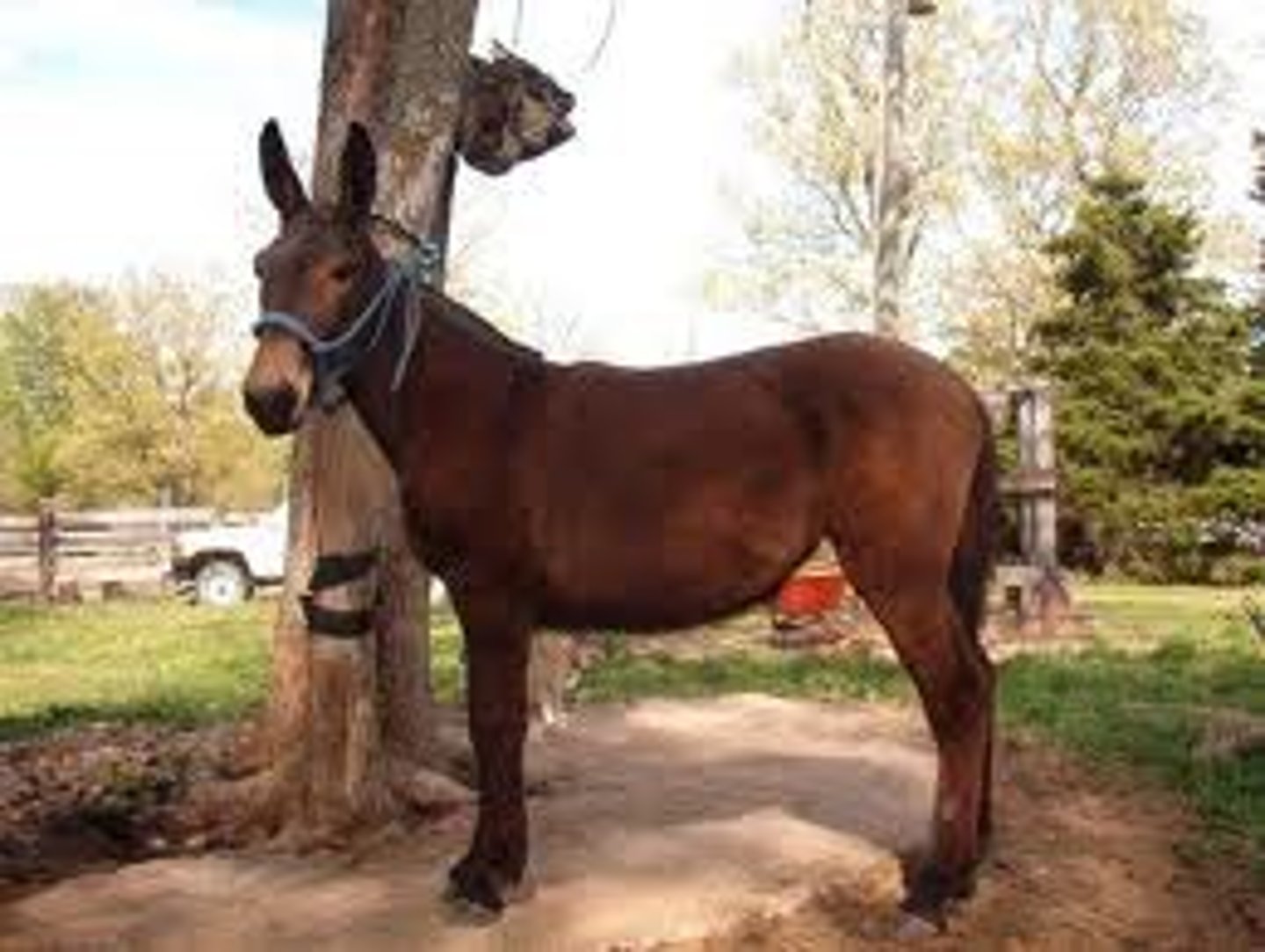
two hybrids mate. their offspring cannot produce offspring of its own.
hybrid sterility
ex. mule (horse mates w donkey)

2nd gen hybrids are weak
hybrid breakdown
Stramenopiles: (DOB)
- diatoms
- brown algae
- oomycetes
which stramenopile has silica cell walls
diatoms
(T/F) diatoms: only the gamete is flagellated
true
stramenopile that has algin and cellulose in the cell wall
brown algea
example of brown algea
kelp
which stramenopile is a photoautotroph
diatom
which stramenopile is an absorptive heterotroph
oomycetes
oomycetes has (blank) in its cell wall
cellulose
mycelia
networks of branched hyphae adapted for absorption
which stramenopile has mycelia and flagellated spores
oomycetes
amoebozoan : (SEG)
- slime mold
- entamoebas
- gymnameobas
what do all amoebozoan have in common
- all lack cell walls
- all use pseudopodia for movement
type of amoebozoan that aggregates into single body
slime mold

amoebozoan that has lobe-like pseudopodia
gymnamoebas
ameobozoan that is a parasite of animals
entameoabas
homologous structure
structures that are similar in different species of common ancestry

vestigial structures
a structure in a present day organism that no longer serves its natural purpose
homology
similarity resulting from common ancestry
convergence
similar traits having nothing to with similar conditions
Analogous Structures
similar adaptations due to similar conditions

charles darwin ideas
- descent w modification
- natural selection
- made first phylogenic tree
alfred wallace
published his own theory of evolution by natural selection about the same time as Charles Darwin
basal taxon
diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group
- autotroph =
carbon source is carbon dioxide

- heterotroph =
carbon source is organic compounds

Photo =
energy source is light

Chemo =
energy source is chemical compounds
Hardy-Weinberg conditions
-no mutations
-random mating
-no natural selection
-very large population size
-no gene flow
p+q = 1
allele frequency equation
p is dominant =A
q is recessive =a
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
genotype frequency equation
2pq = Aa
p = AA
q= aa
practice:
aa = 36%
find:
a. frequency of aa
b. frequency of a
c. frequency of A
d. frequency of AA and Aa
a. 36%
b. 60%
c. 40%
d. AA = 16% Aa = 48%
virus characteristics
- capsid
- DNA or RNA
- need host cell
- no cytoplasm
- some have envelope
(T/F) viruses can easily mutate
true
first step of viral infection
attachment
what happens in viral attachment
receptors in the surface of the host cell bind to virus capsid proteins or the envelope
[blank] is the basal clade with tissues and [blank] is the basal clade with no true tissue
Eumetazoa , animals
what do deuterostomes, lophotrochozoans, and ecdysozoa all have in common
bilateral symmetry
which protostome has acoelomate
platyhelminths

this phylum
- are sessile as adults and motile in youth
- no true tissue
- no cephalization
- no complex organ system
- aquatic
porifera
pores in sponges
ostia
large center cavity of sponge
spongocoel
where does water exit after the spongocoel in sponge
osculum
the jelly like substance that acts as sponge's endoskeleton
mesohyl
this sponge cell acts as valves and regulate flow of water through the ostia
porocyte
this sponge cell forms the outer covering of the sponge and assists in phagocytosis
pinacocyte
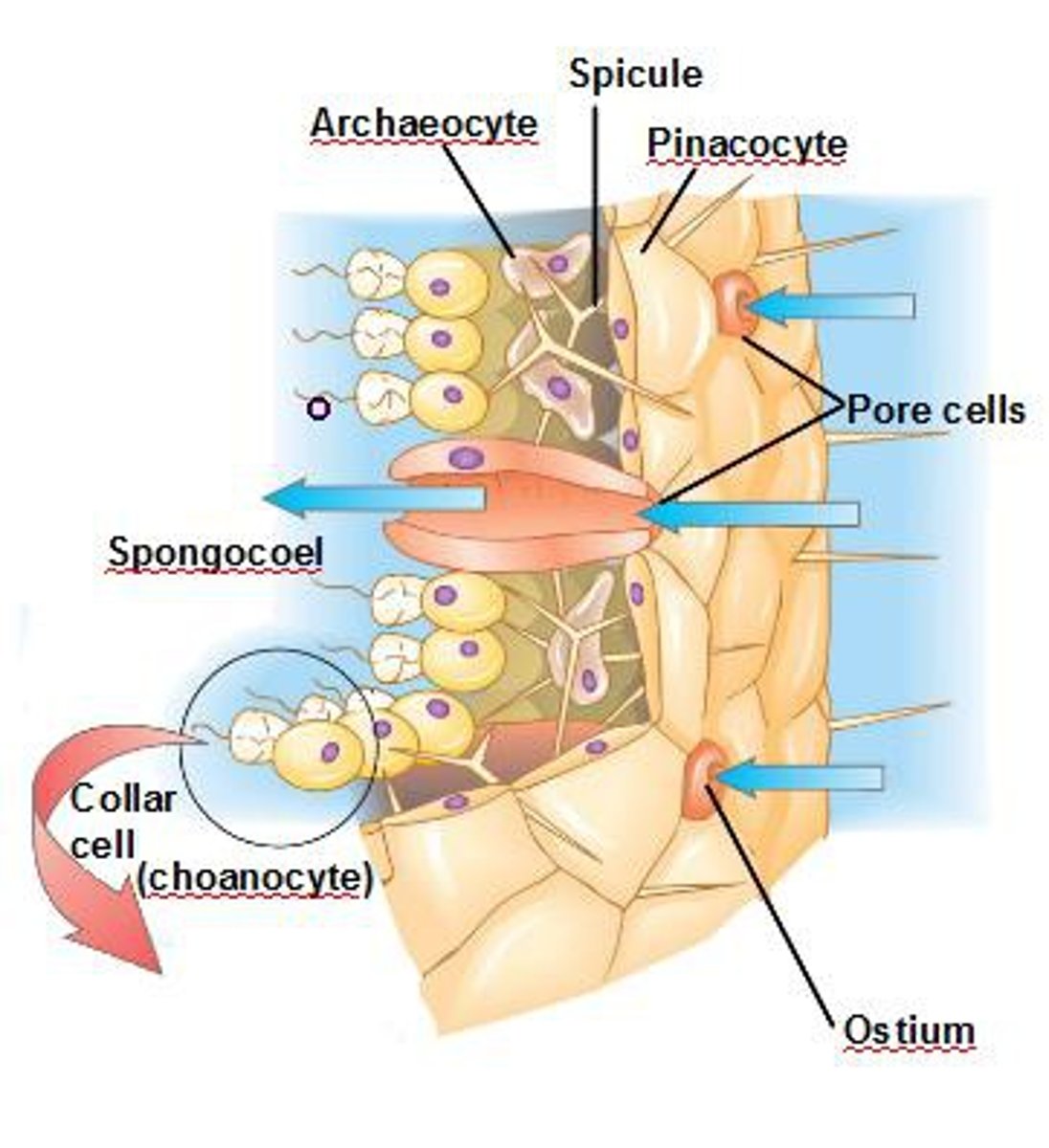
this sponge cell is the stem cell, meaning it can differentiate into other cell types. it can also deliver nutrients and gives rise to eggs for reproduction.
amoebocytes
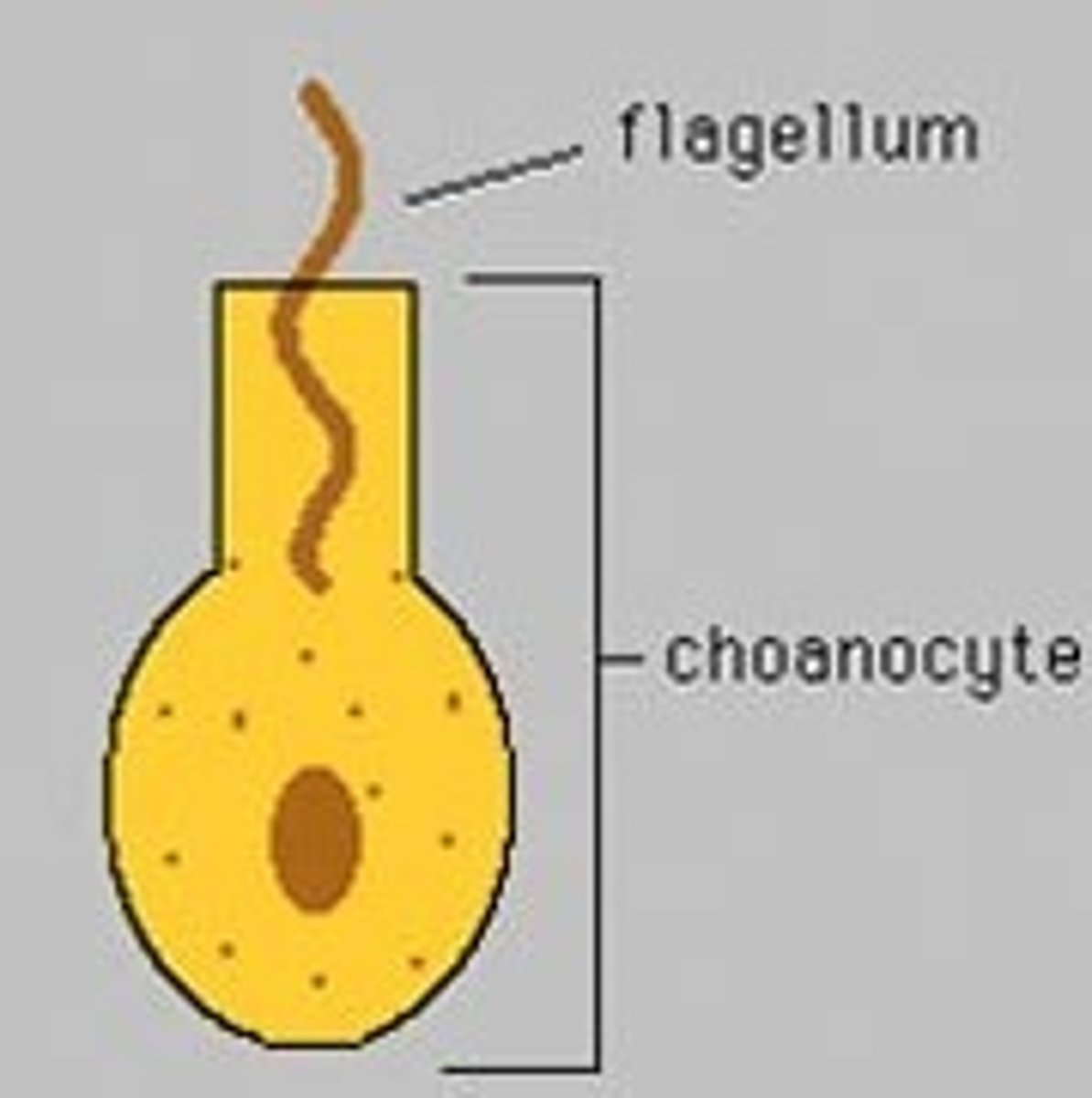
*defining cell of the sponge. can different into sperm. generate water current and filters food particles.
choanocyte
examples of cnidaria
jellyfish, hydra, sea anemones, coral
two body forms of cnidaria
- sessile polyp
- free swimming medusa
gastrovascular cavity
one opening for mouth and anus
alimentary canal
two openings for mouth and anus
non cellular layers functions as hydrostatic skeleton of cnidaria
mesoglea
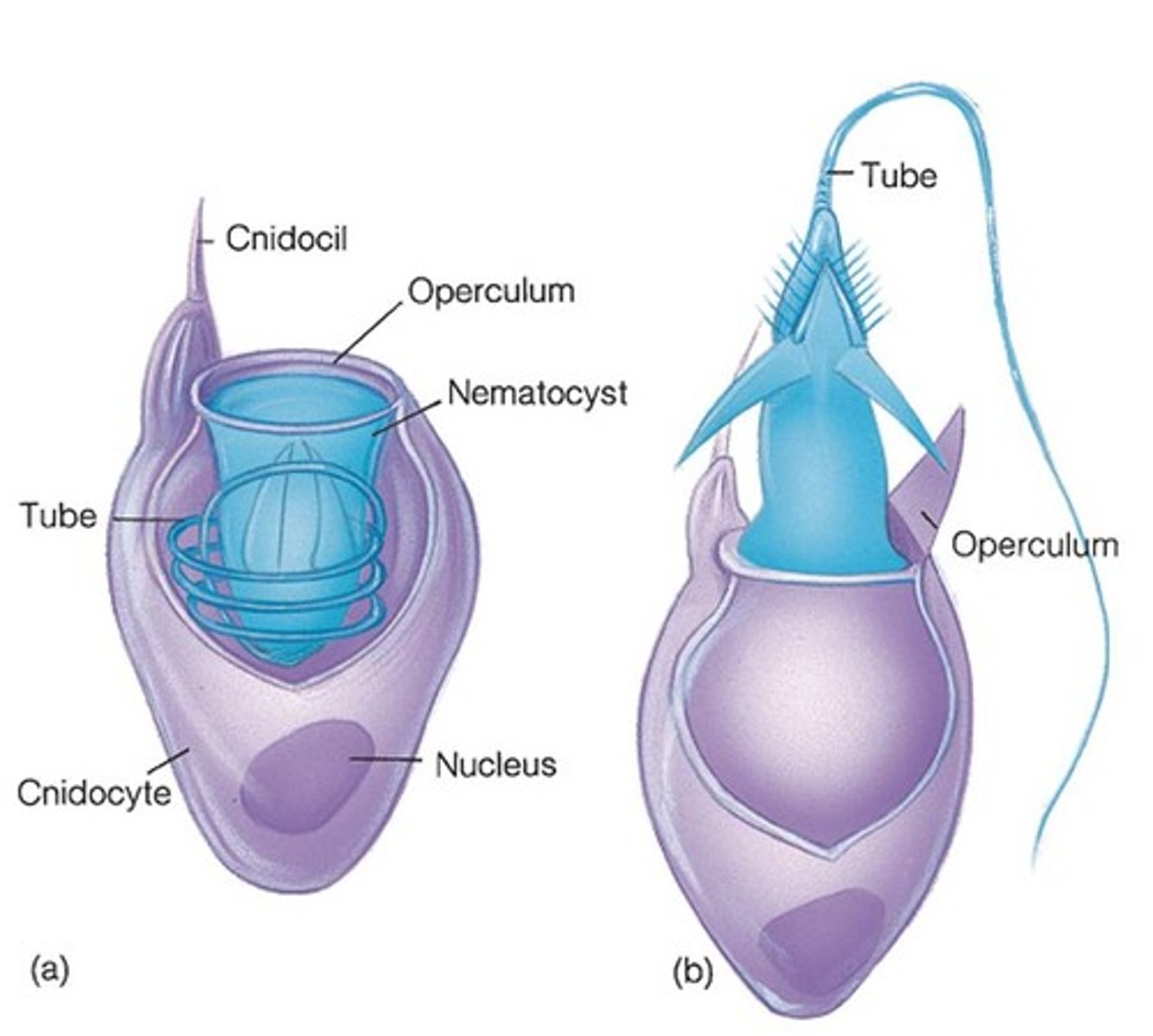
defining cell of cnidaria
cnidocyte
nematocyte and where its located
has cndiocele that are sensitive to touch - the nematocyte fires out barb and thread to sting the prey and cause cell lysis
what forms from ectoderm
skin and nerve
what forms from endoderm
gastrointestinal tissue, liver, pancreas, thyroid
what forms from mesoderm
muscle, bone, cardiovascular tissues
first example of cephalization
Platyhelminths
how to brachiopods feed
with a lophophore
how do Mollusca feed
they use their radula

three main parts of Mollusca and their function (MVM)
1. muscular foot = movement
2. visceral mass = contains most organs
3. mantle = covers visceral mass. mantle is where pearl comes from
hemolymph
fluid that is pumped in vessel and bathes tissues (like blood, but for open systems)
(T/F) Mollusca have an open system
true
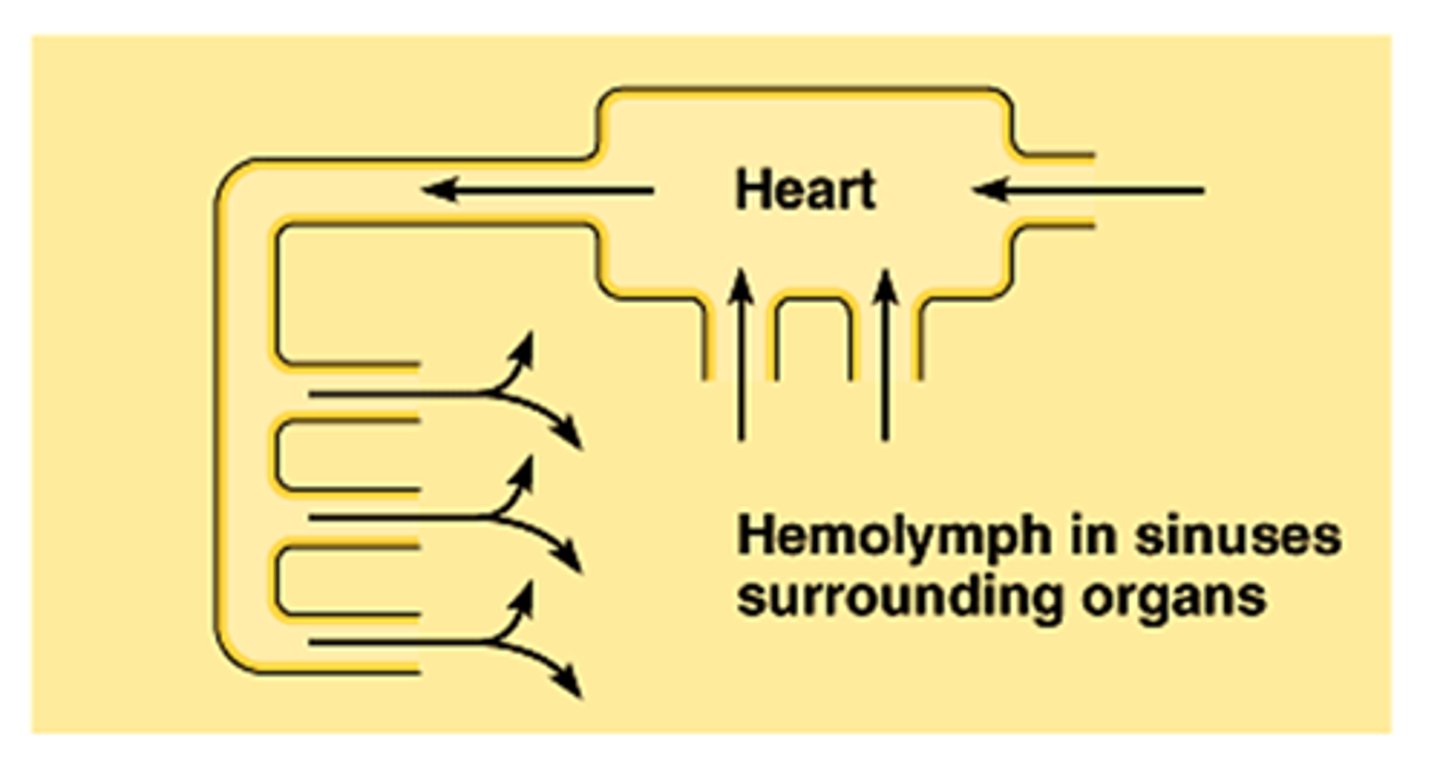
main body cavity of Mollusca
hemocoel
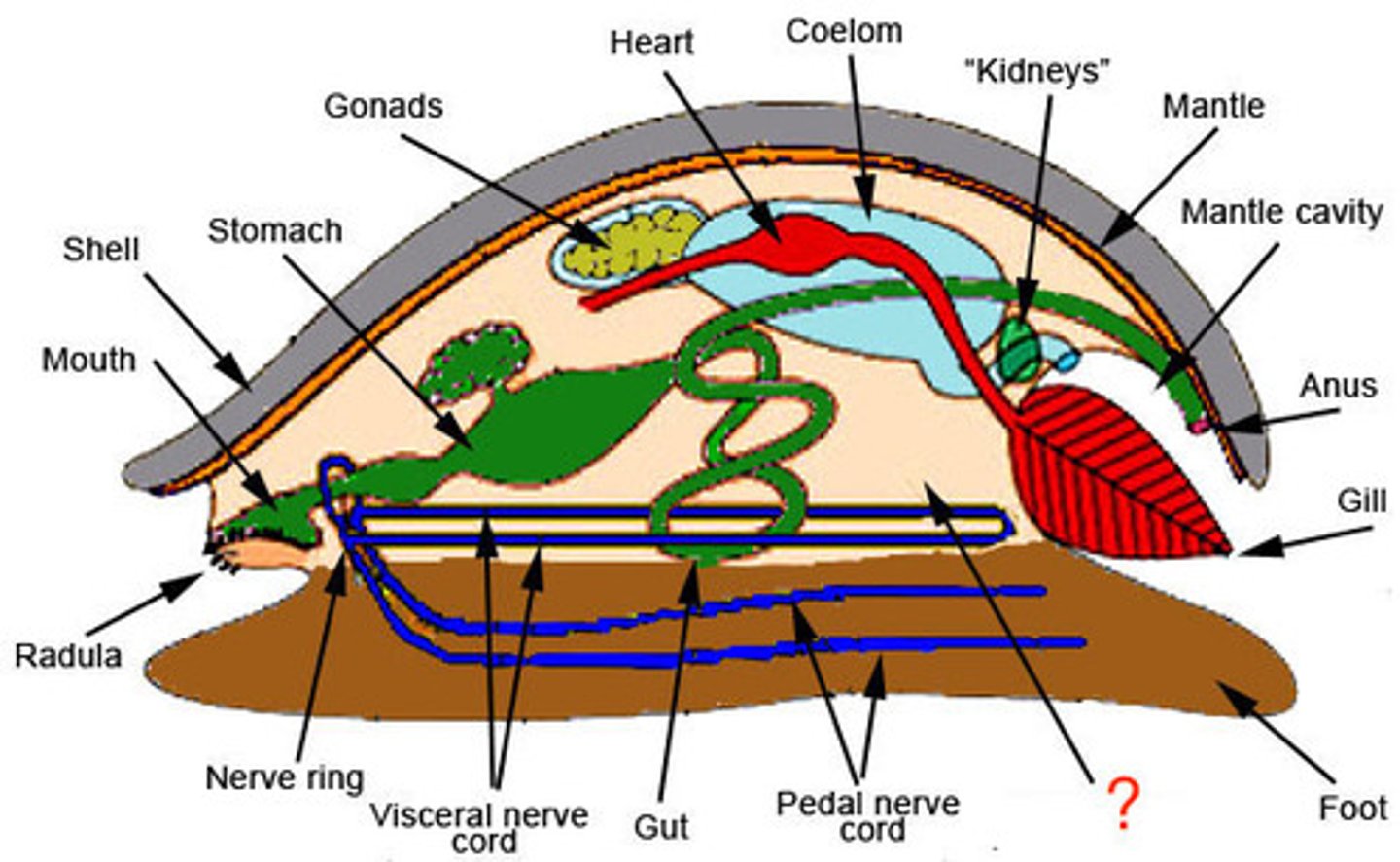
Mollusca have a reduced coelom that only covers
the heart and gonads
which is the only Mollusca to have a closed system
Cephalopoda
nacre and what its made of
mother of pearl is made of aragonite and conchiolin
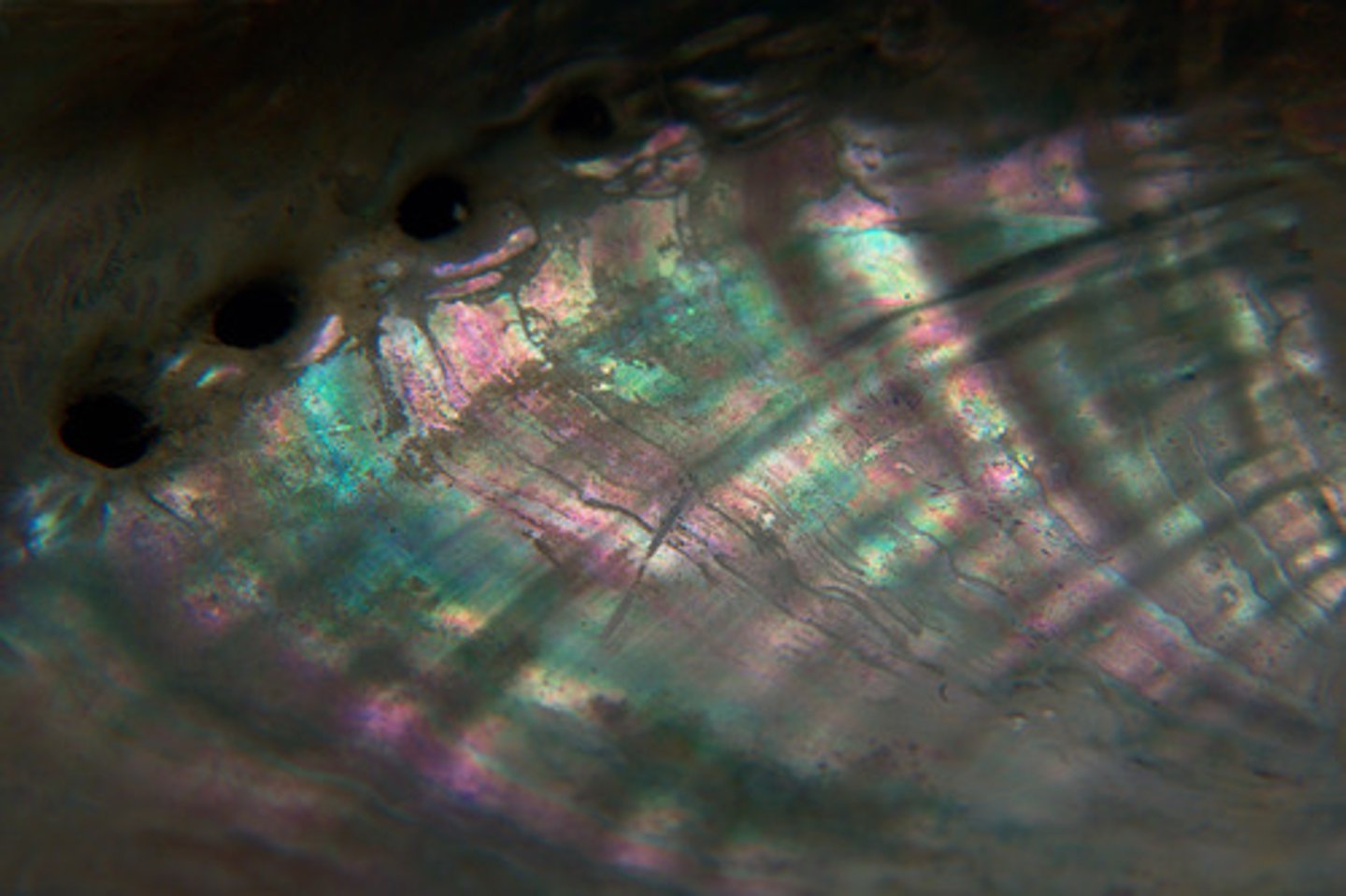
pearl function
defense mechanism for when irritants (ex. sand) enter their shell
*what kind of segmentation do Annelida have and what it does
metamerism is the repetition of structures in different segments. this allows the animal to have more efficient movement.
(T/F) Annelida have a closed system
true