Types and Features of Speech Sounds, Phonological Processes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
stop
airflow is completely blocked and then released
fricative
produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together.
affricate
consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative
nasal
blocking air in the mouth and releasing sound through the nose
liquid
the tongue produces a partial closure in the mouth, resulting in a resonant, vowel-like consonant
glide
vowel-like qualities; immediately precedes a vowel
aspirated sounds
voiceless sounds in which there is a puff of air
Dentalization
marked by a [┌┐] ; occurring dentalized sounds in children include: /d/, /s/, /z/
Palatalization
tail-like appendix added to the IPA symbol; sounds for which the palate is not the place of articulation
Velarization
it's making a sound go further back, the movement of the tongue placement in the direction of the velum
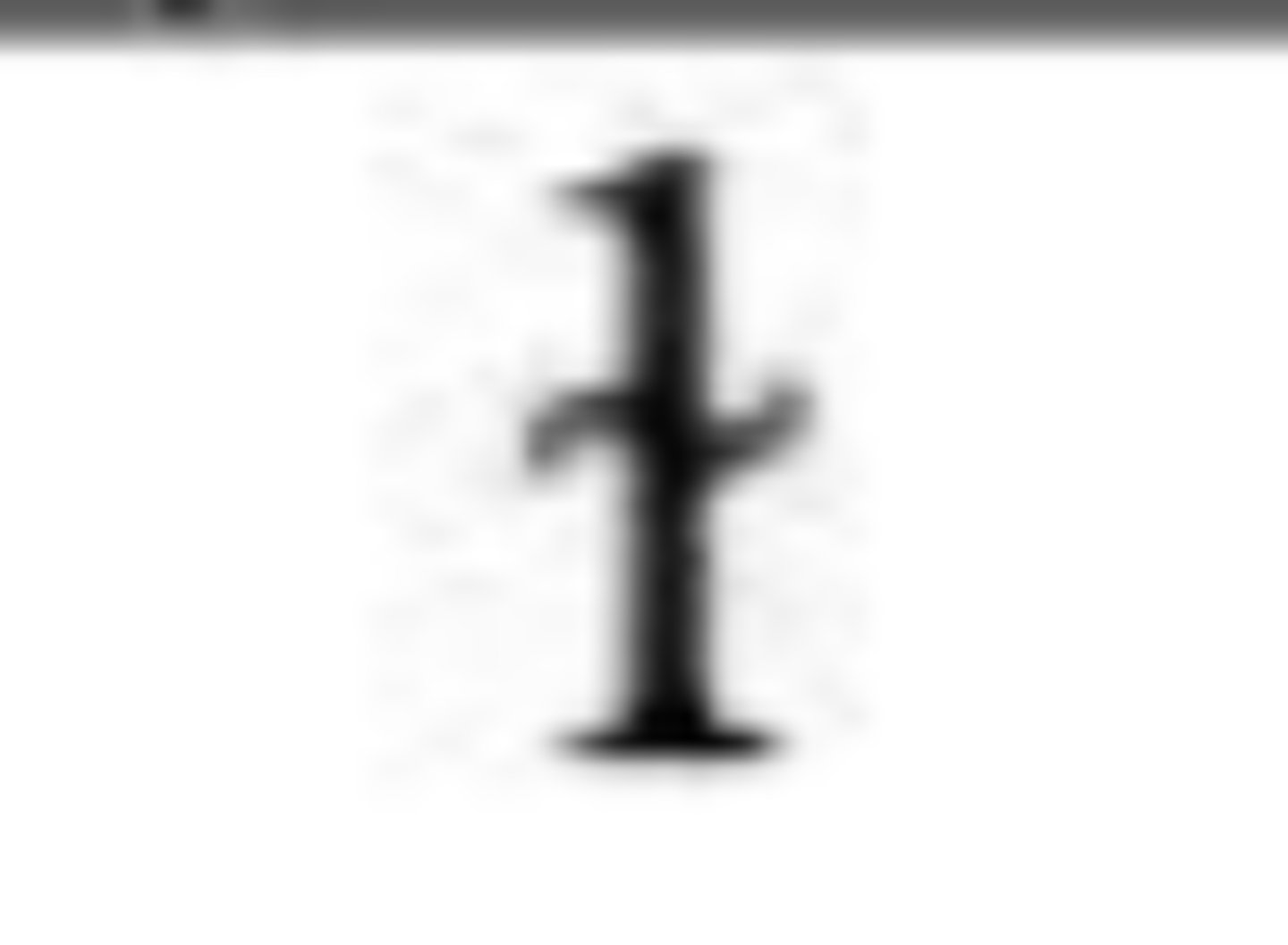
Lateralization
variation in which the airstream is released laterally; s -> th
unaspirated
no extra puff of air, ex: spin (immediate voicing)
unreleased
A stop with no audible release
fronting
When velar or palatal sounds like /k/, /g/, and sh, are substituted with alveolar sounds like /t/, /d/ and /s/
Nasal assimilation
A non-nasal sound becomes a nasal because of the influence of another nasal in the word
Deaffrication
substitution of an affricate with a fricative or stop
final consonant deletion
deletion of the final consonant in a word
cluster reduction
deletion of a consonant from a consonant cluster (poon for spoon)
gliding
Substituting liquids (/l/, /r/) with glides (/w/, /j/); wabbit
stopping
replacing fricatives or affricates with stop consonants (tun for sun or top for shop)
assimilation
sound changing to be more similar to neighboring sound (bapeball for baseball)
devoicing
Replacing voiced consonants at the end of a word with voiceless ones (e.g., "wep" for "web")
reduplication
repeating a whole syllable e.g. 'dada' and 'mama'
phonological processes
patterns of sound substitutions that young children use to simplify speech as they learn to talk.