AP Psych Unit 2: Cognitive Psychology
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds

Encoding
the processing of information so that it can be stored

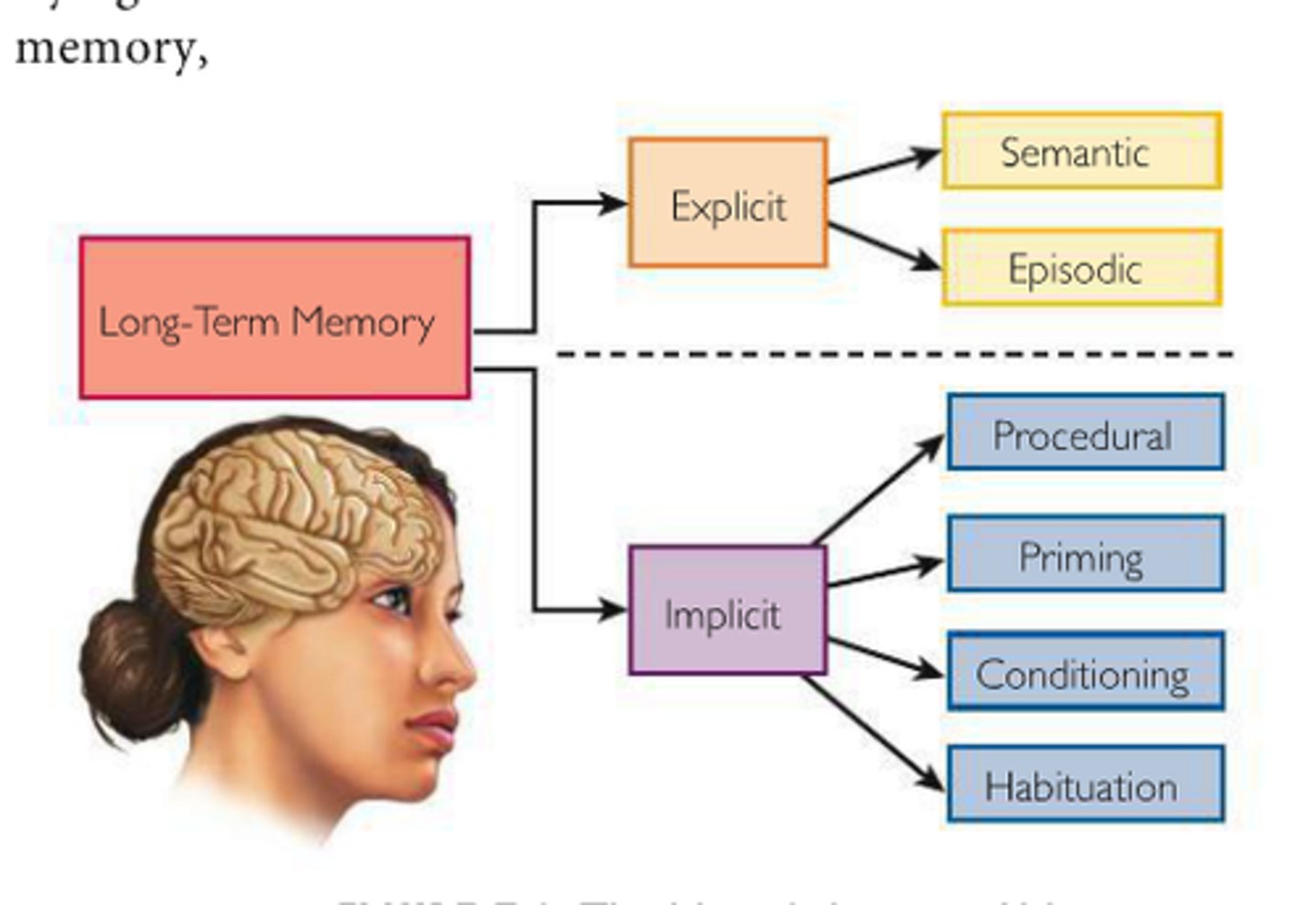
explicit memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
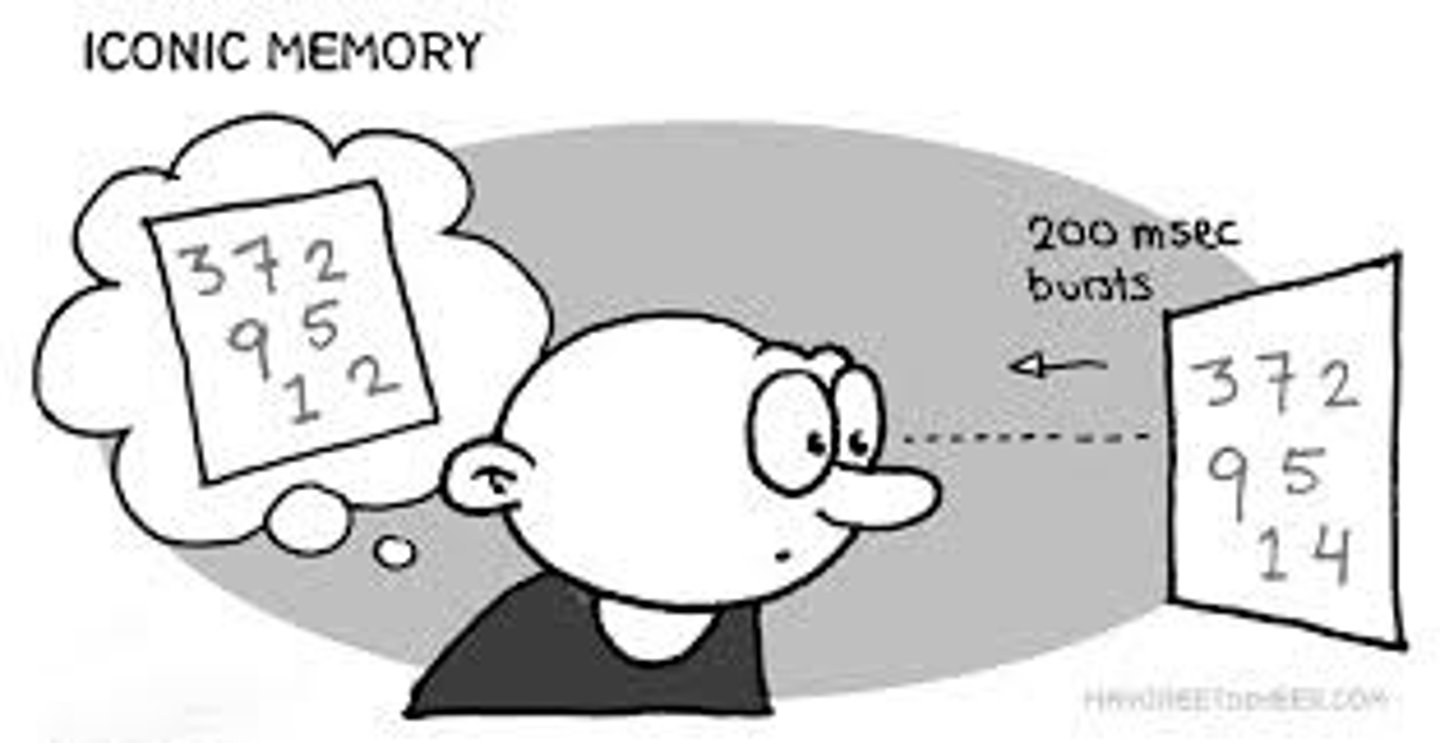
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
implicit memory
retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection; processed automatically
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences.

method of loci
A mnemonic technique that involves associating items on a list with a sequence of familiar physical locations
parallel processing
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions, including vision. Contrasts with the step-by-step (serial) processing of most computers and of conscious problem solving.

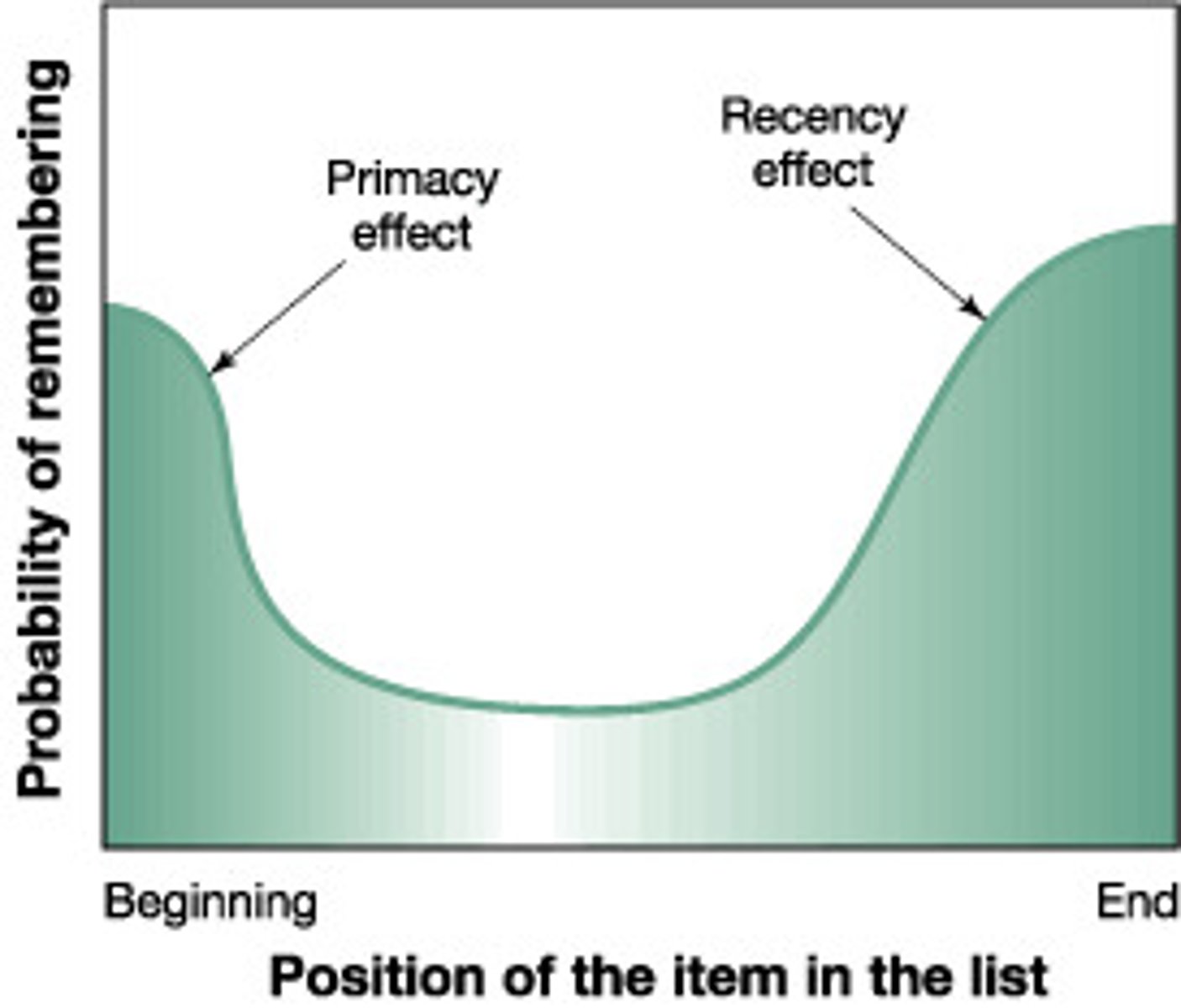
primacy effect
tendency to remember words at the beginning of a list especially well
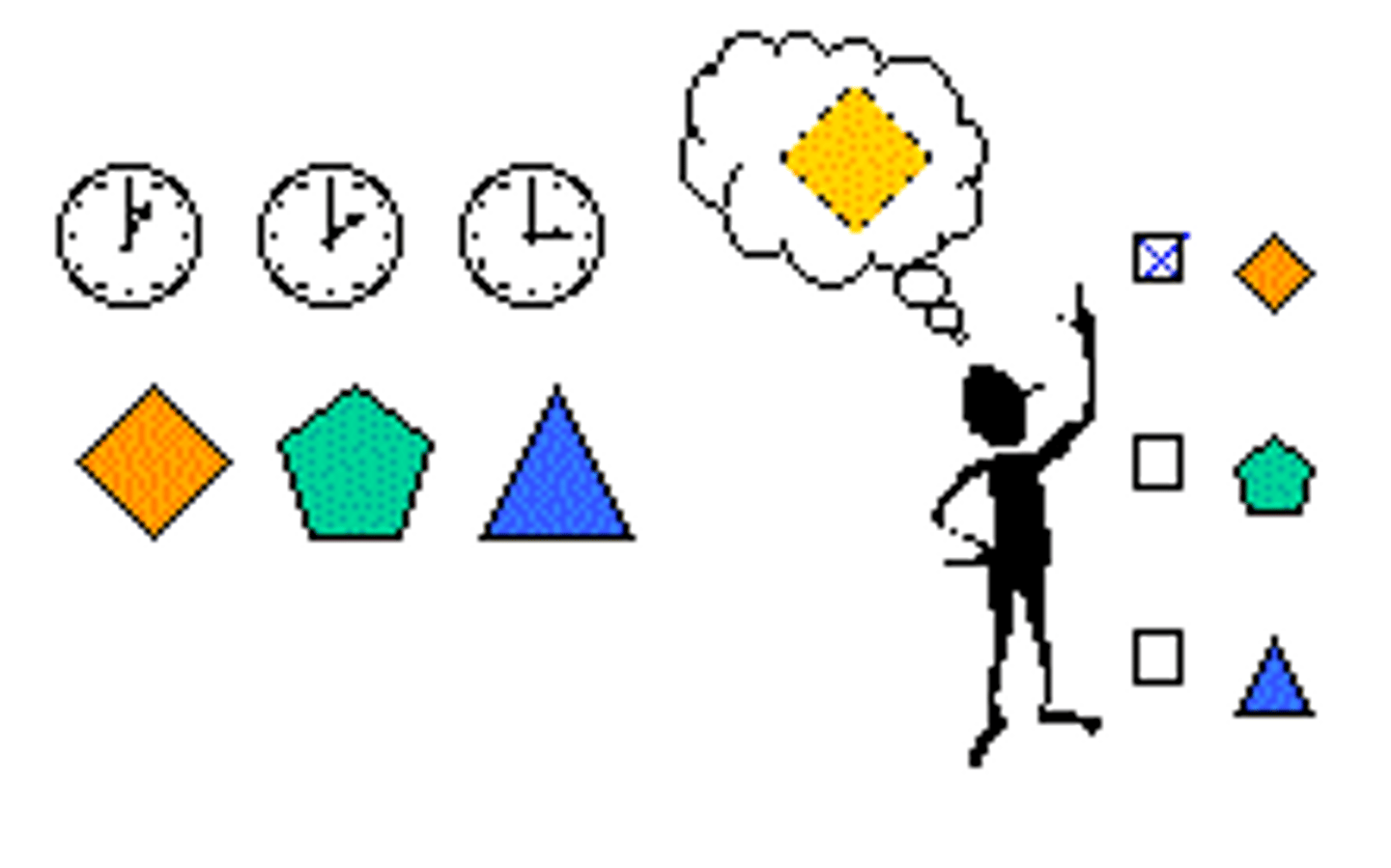
recall
A measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test.

recency effect
tendency to remember words at the end of a list especially well
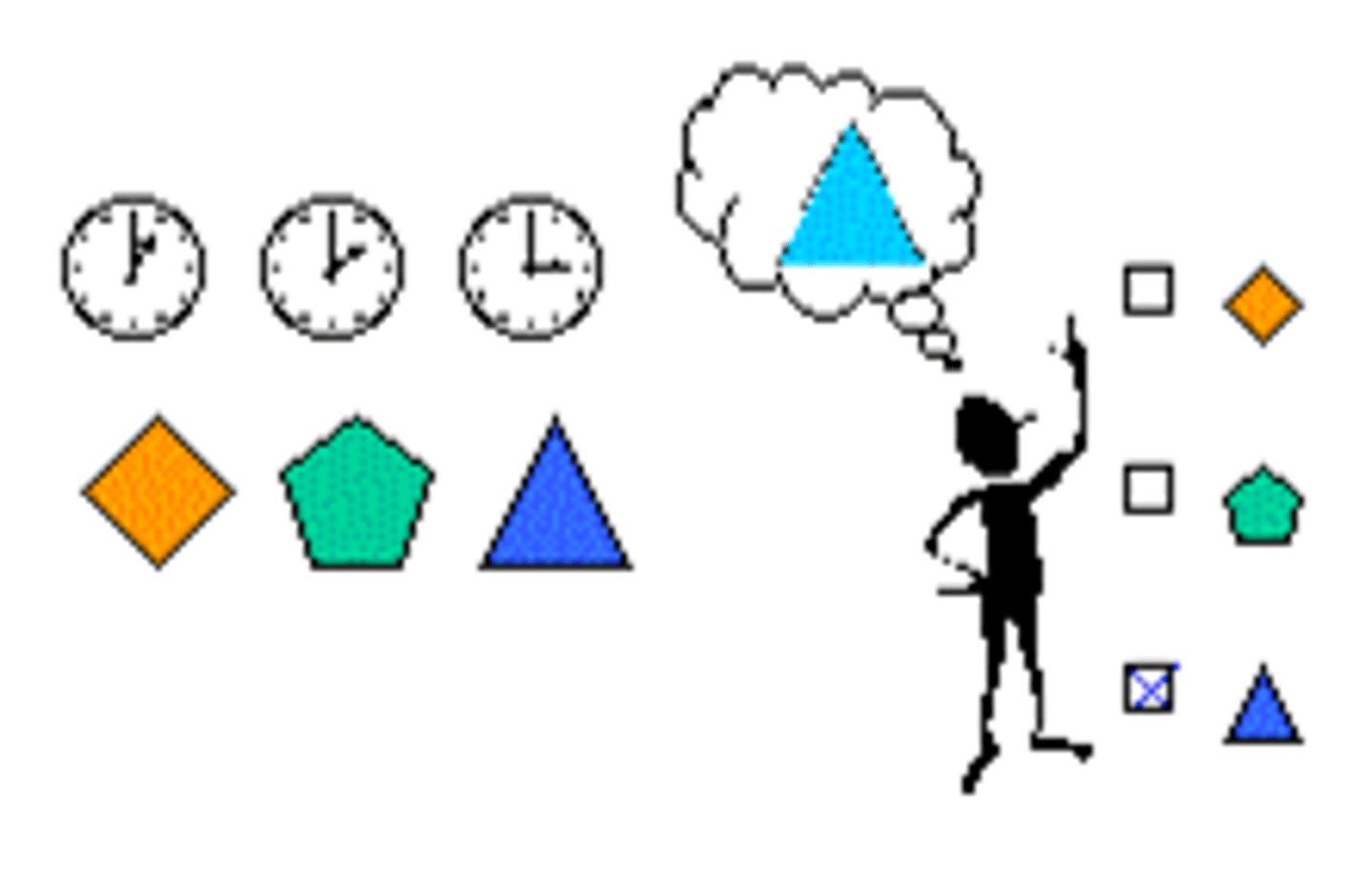
recognition
a measure of memory in which the person need only identify items previously learned, as on a multiple-choice test

Retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage

short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten

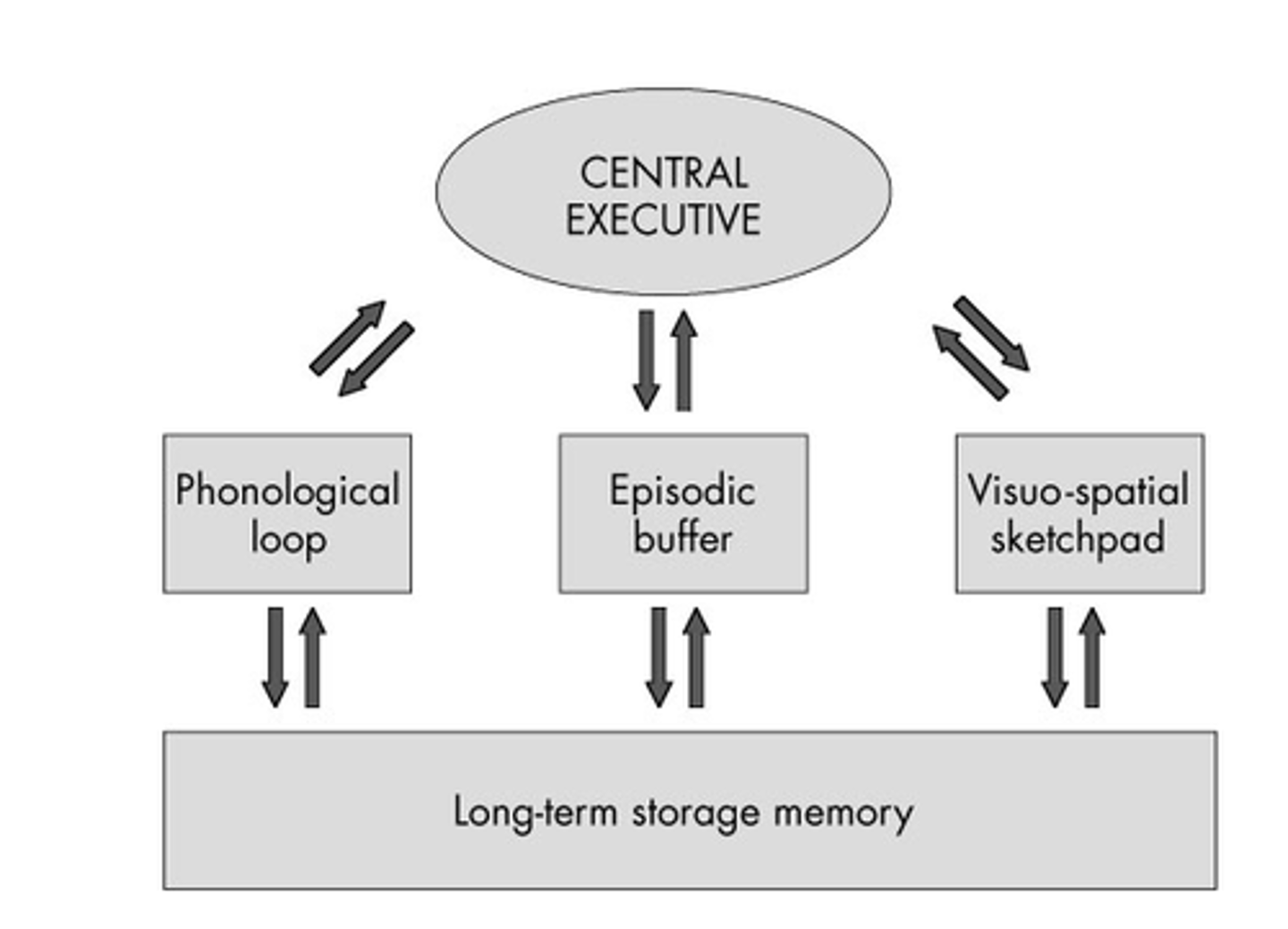
working memory
a newer understanding of short-term memory that focuses on conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual-spatial information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory
semantic memory
memory of general knowledge and information

episodic memory
the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at a particular time and place

memory consolidation
the gradual, physical process of converting new long-term memories to stable, enduring memory codes

infantile amnesia
inability of adults to remember personal experiences that took place before an early age; usually age 4

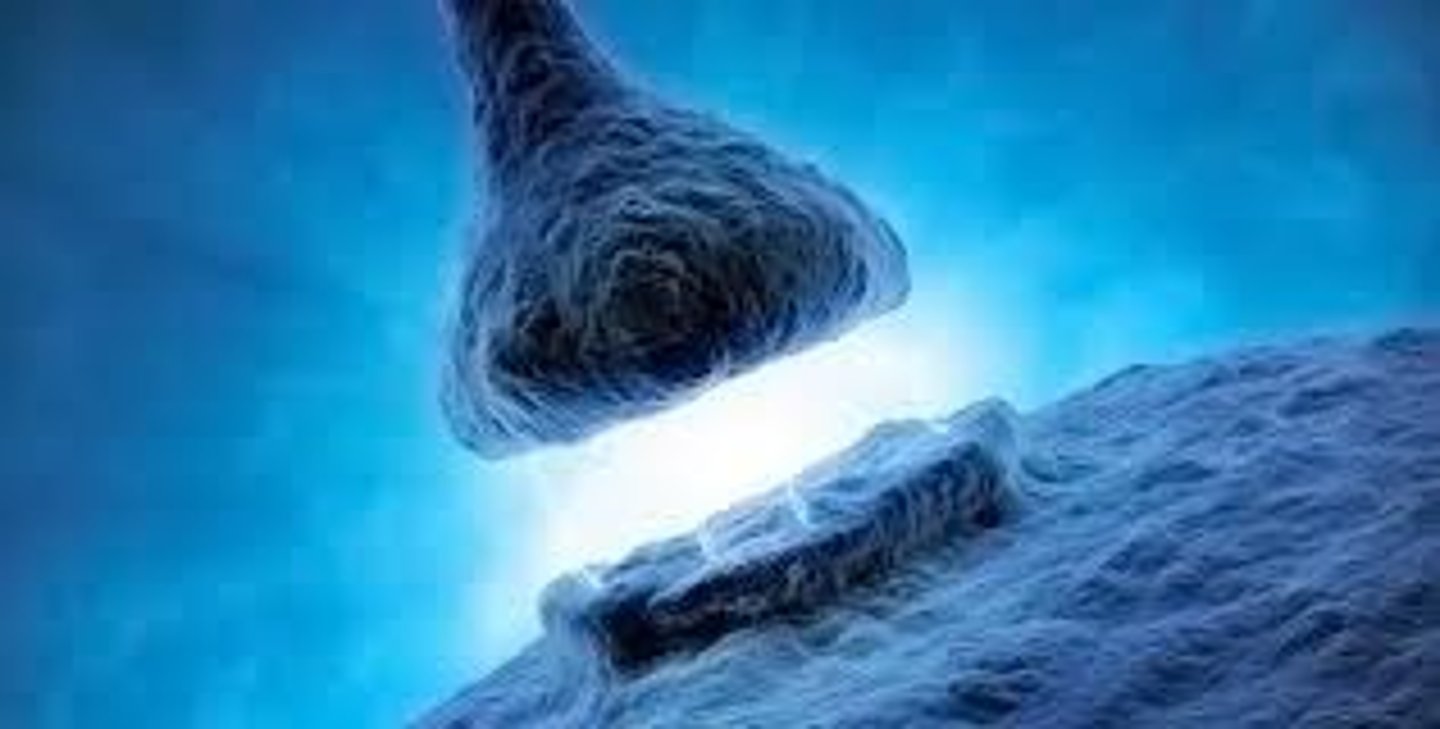
Long Term Potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory; strengthening of neural networks

serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list
anterograde amnesia
an inability to form new memories
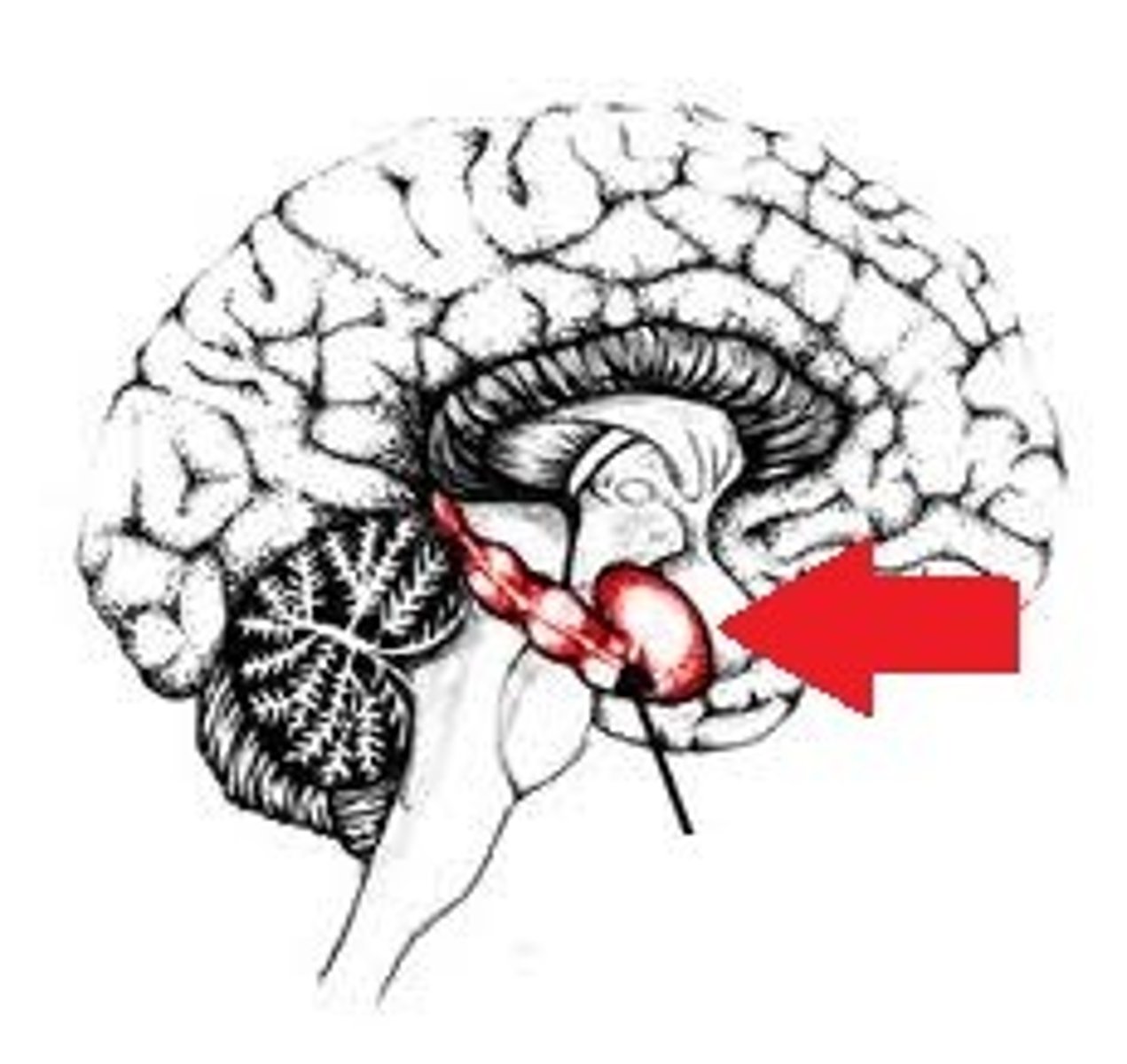
retrograde amnesia
loss of memories from our past

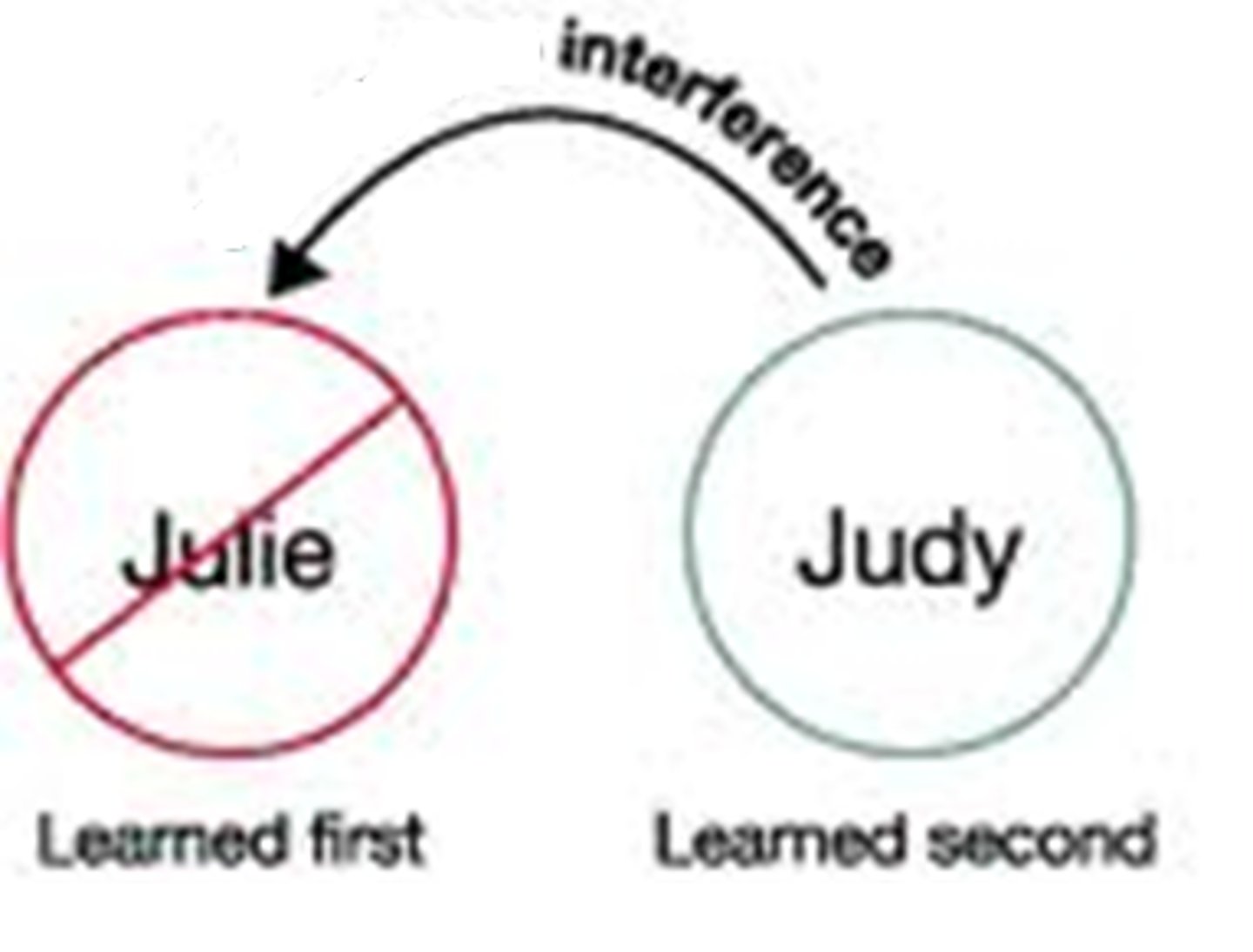
proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
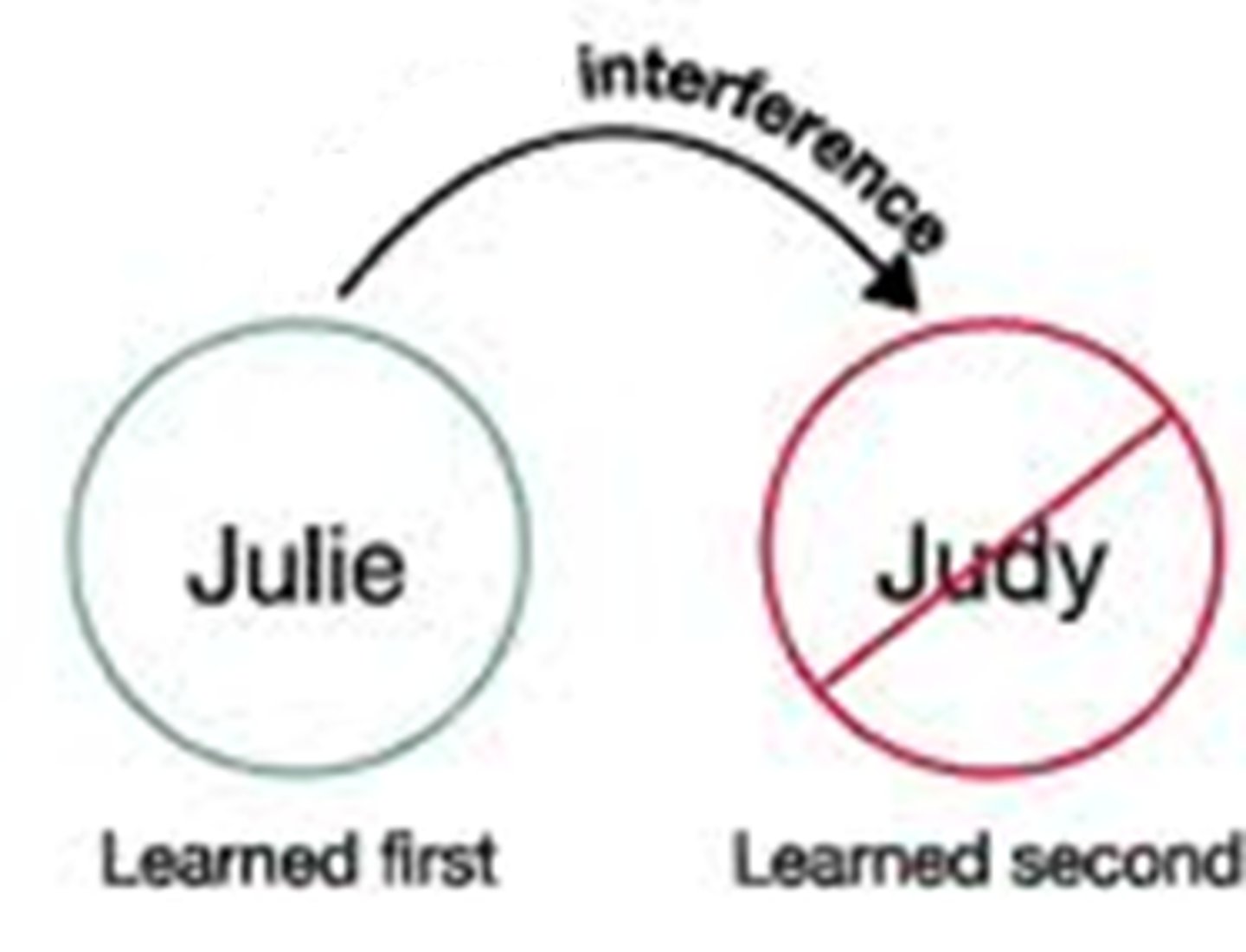
retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
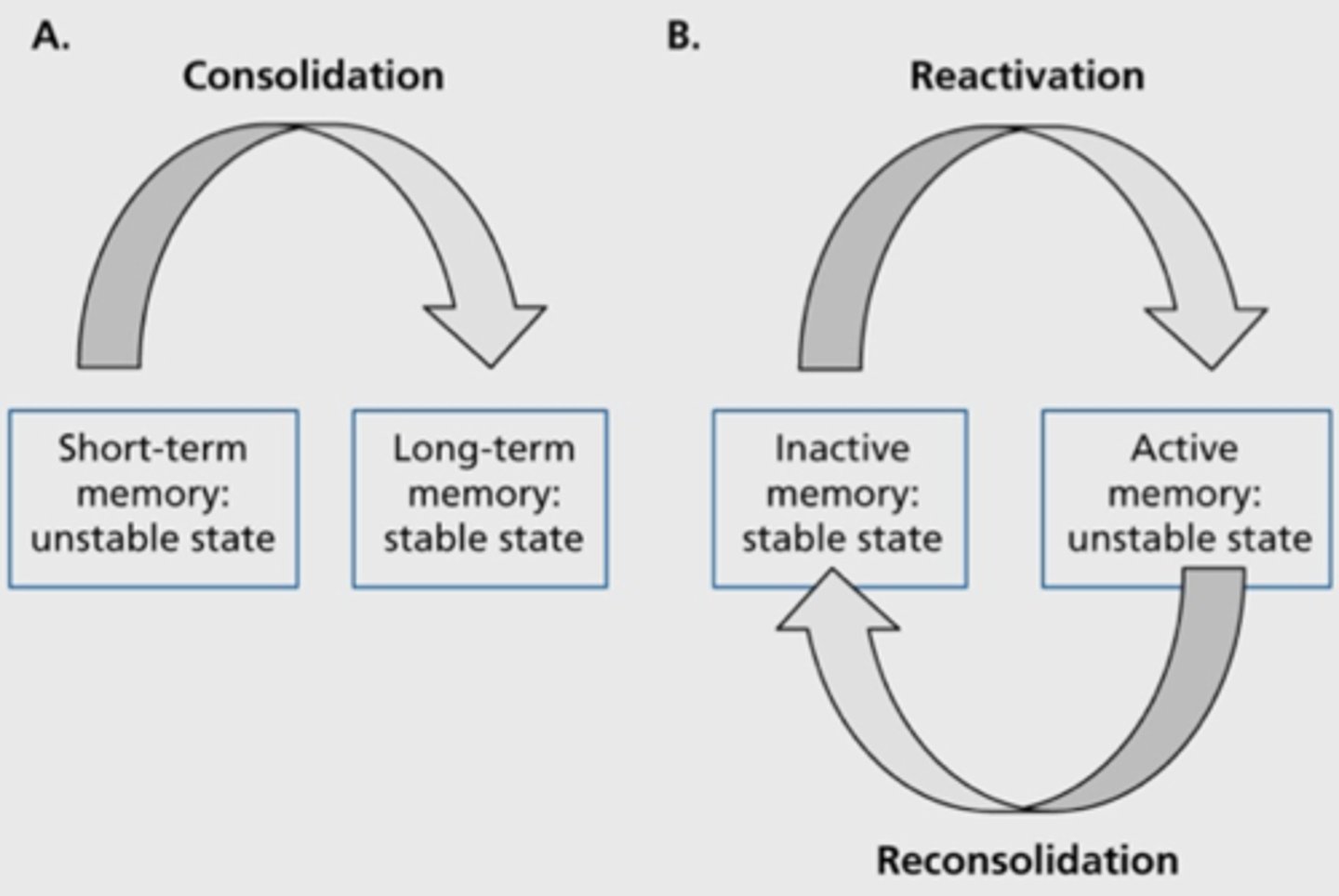
reconsolidation
a process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again
misinformation effect
when misleading information has corrupted one's memory of an event

source amnesia
faulty memory for how, when, or where information was learned or imagined

prototype
a mental image or best example of a category

convergent thinking
narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution

divergent thinking
expands the number of possible problem solutions

Algorithm
A methodical, logical rule or step-by-step procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem.

Heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms

confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence

representative heuristic
a mental shortcut whereby people classify something according to how similar it is to a typical case

availability heuristic
making a decision based on the answer that most easily comes to mind

belief perseverance
tendency to stick to our initial beliefs even when evidence contradicts them

Framing
the way an issue is posed; can significantly affect decisions and judgments.

functional fixedness
the tendency to perceive an item only in terms of its most common use

language
our spoken, written, or signed words and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning

phoneme
in language, the smallest distinctive sound unit

Morpheme
in a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or a part of a word (such as a prefix)

G-factor
A general ability, proposed by Spearman as the main factor underlying all intelligent mental activity

intelligence test
a method for assessing an individual's mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores such as the Wechsler Intelligence Scales and Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale
achievement test
a test designed to assess what a person has learned

IQ
measure of intelligence; the average is 100; there are many definitions of this attribute, including multiple and crystallized

Flynn effect
the worldwide phenomenon that shows intelligence test performance has been increasing over the years
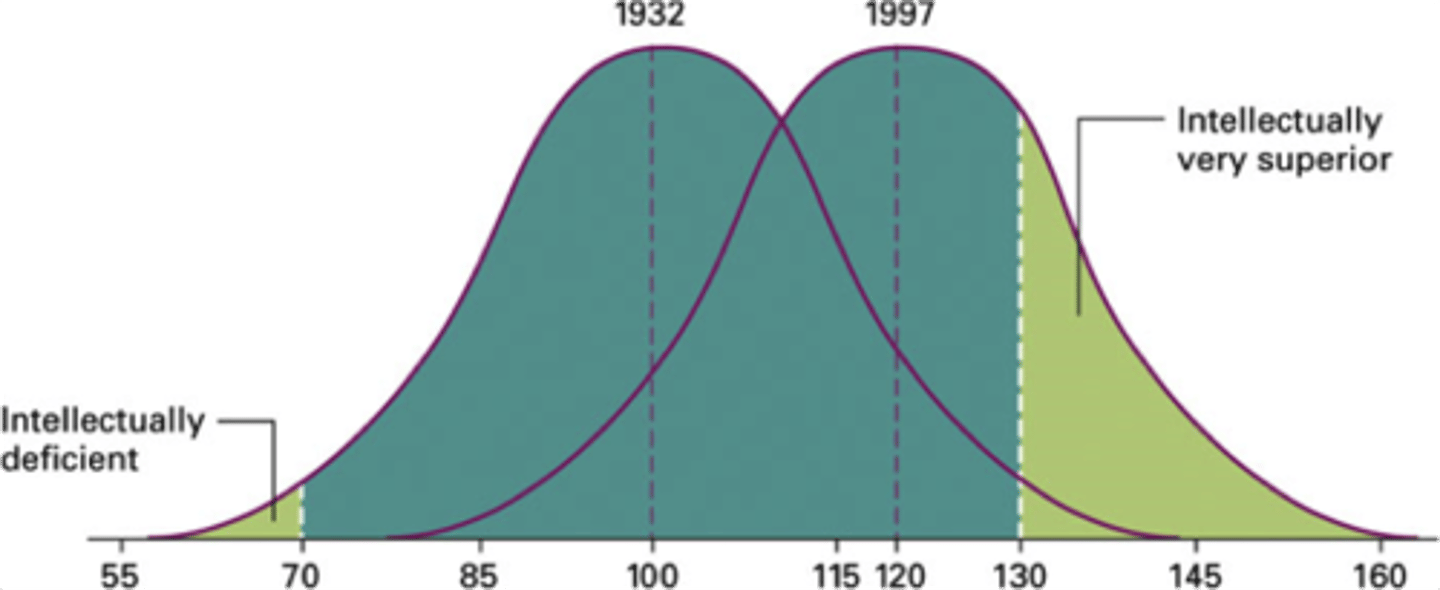
Reliability
consistency of measurement

Validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to

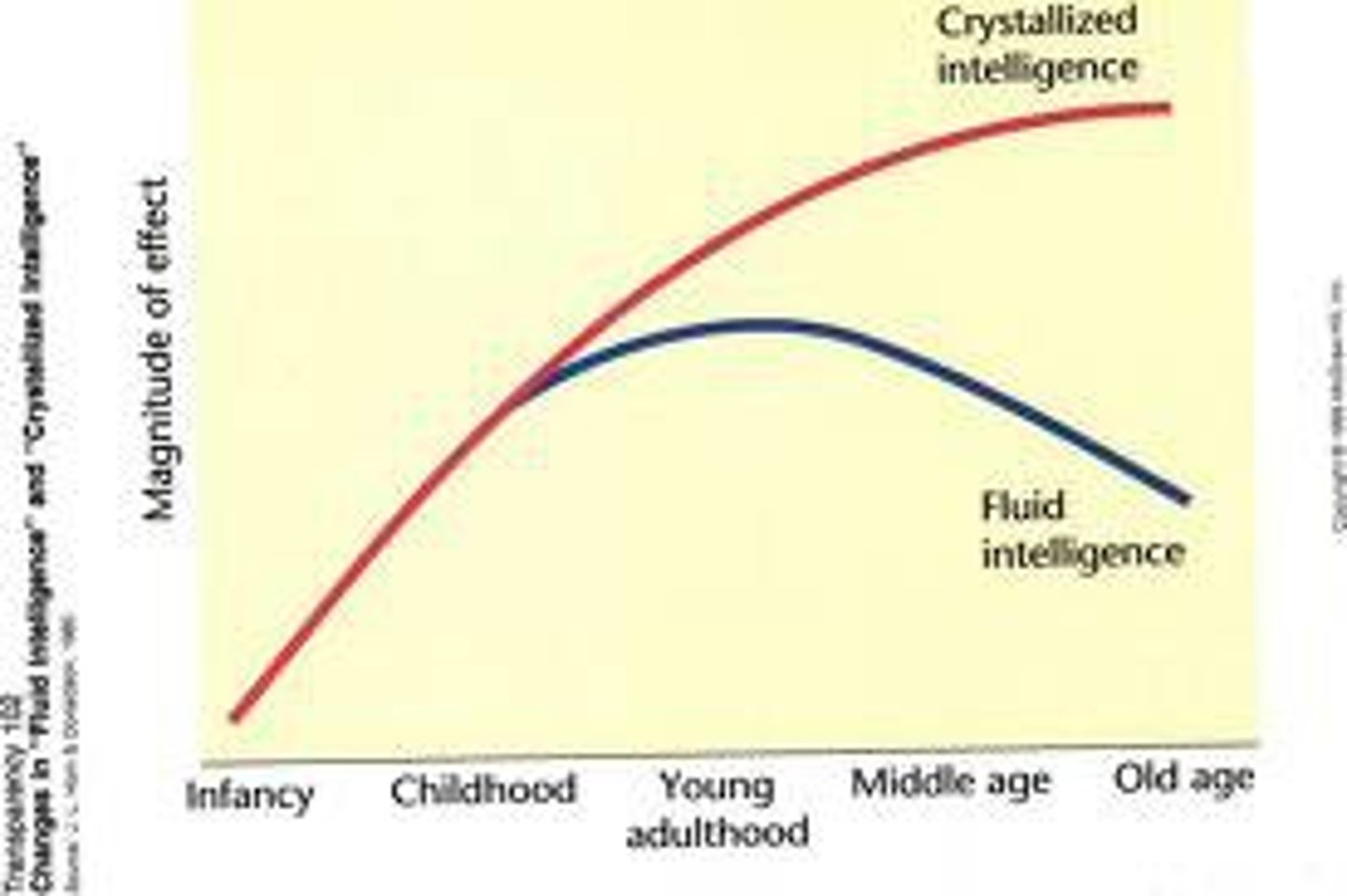
Crystalized intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
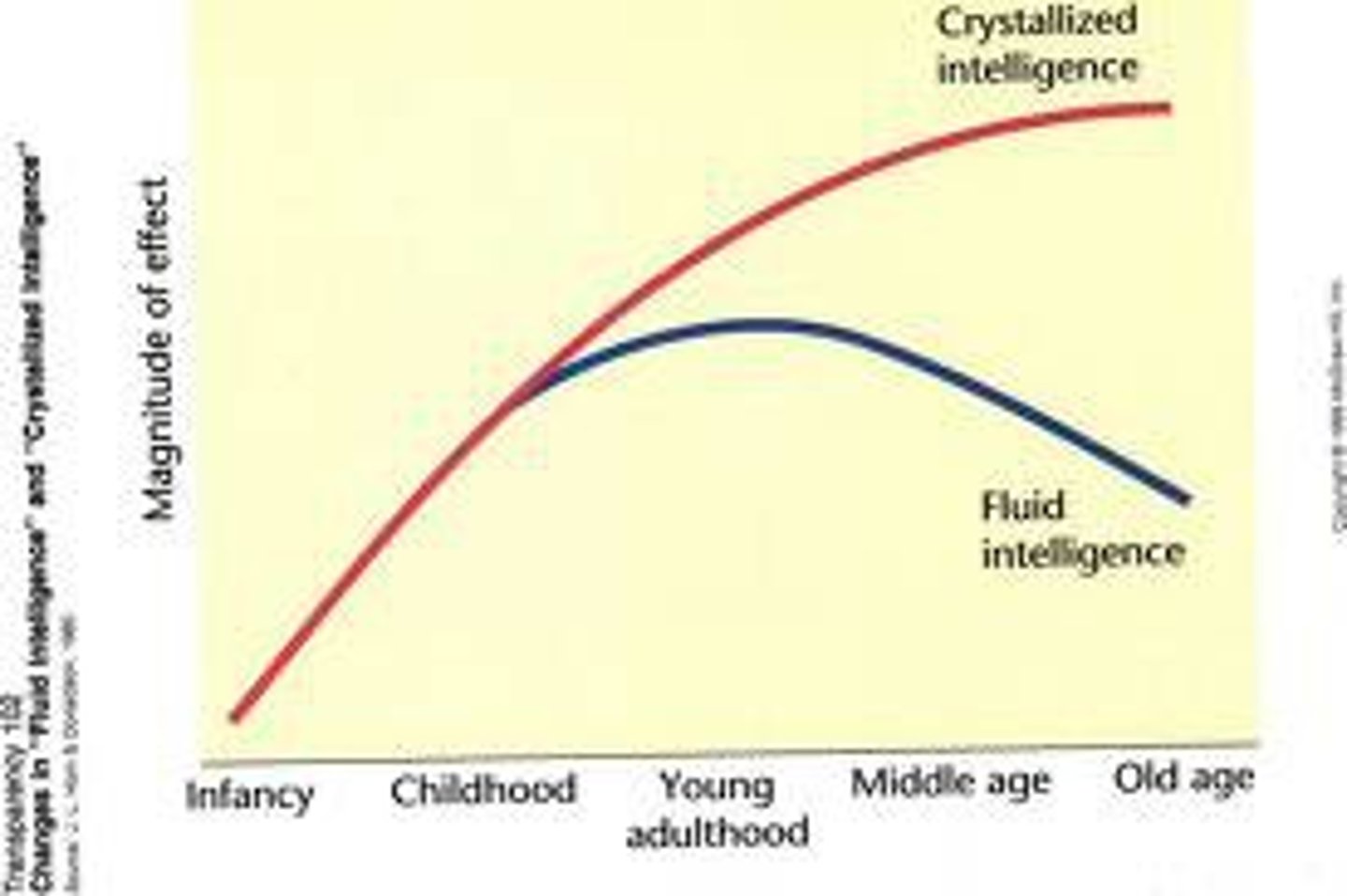
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood
aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person's future performance and capacity to learn

Effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort

Automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings

Procedural memory
the gradual acquisition of skills as a result of practice, or "knowing how" to do things
Sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
mnemonic devices
techniques for using associations to memorize and retrieve information

Categorization
a cognitive process used to organize information by placing it into larger groupings of information

Massed practice
a practice schedule in which studying continues for long periods, without interruption (cramming)

Distributed practice
spacing the study of material to be remembered by including breaks between study periods
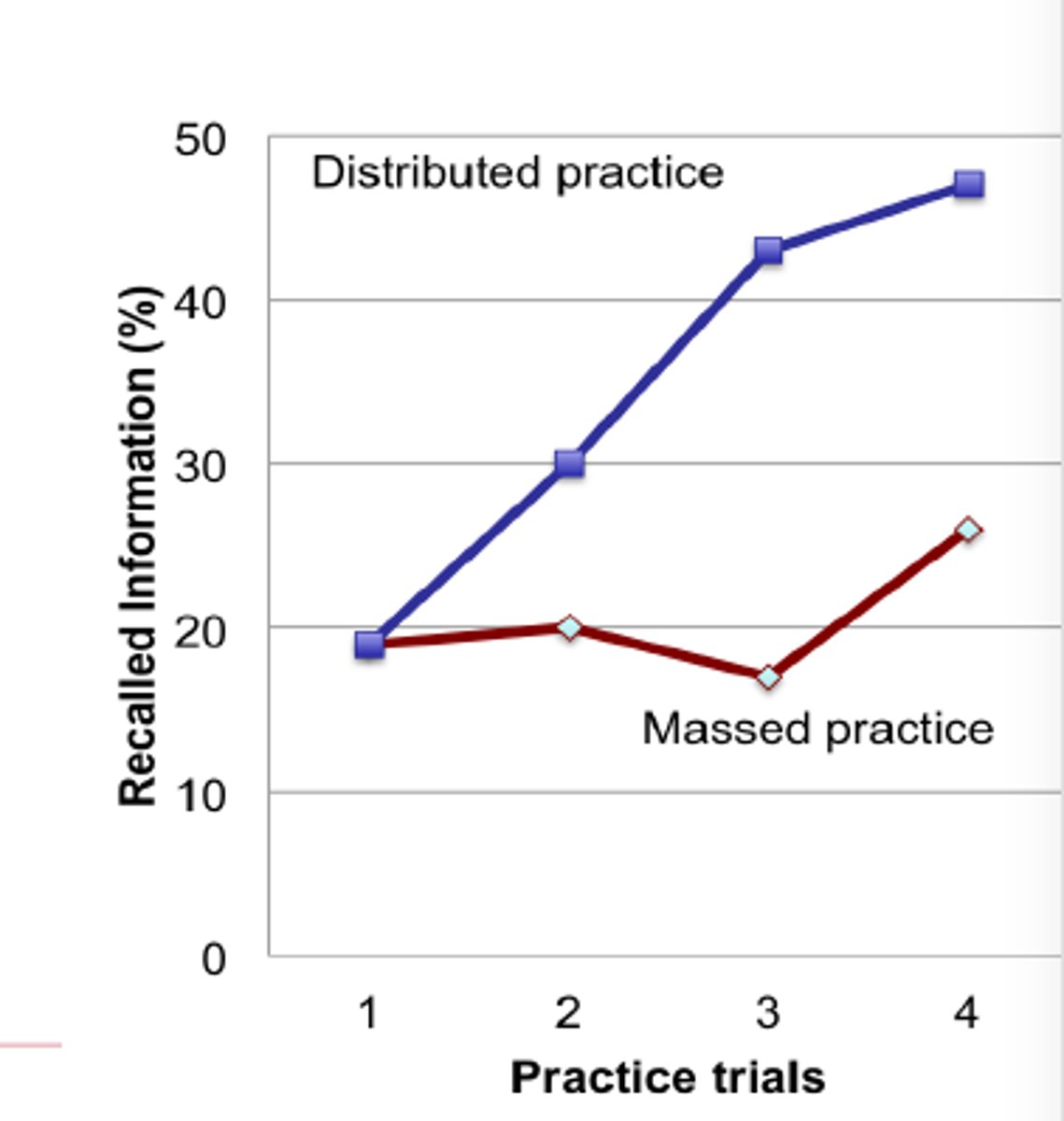
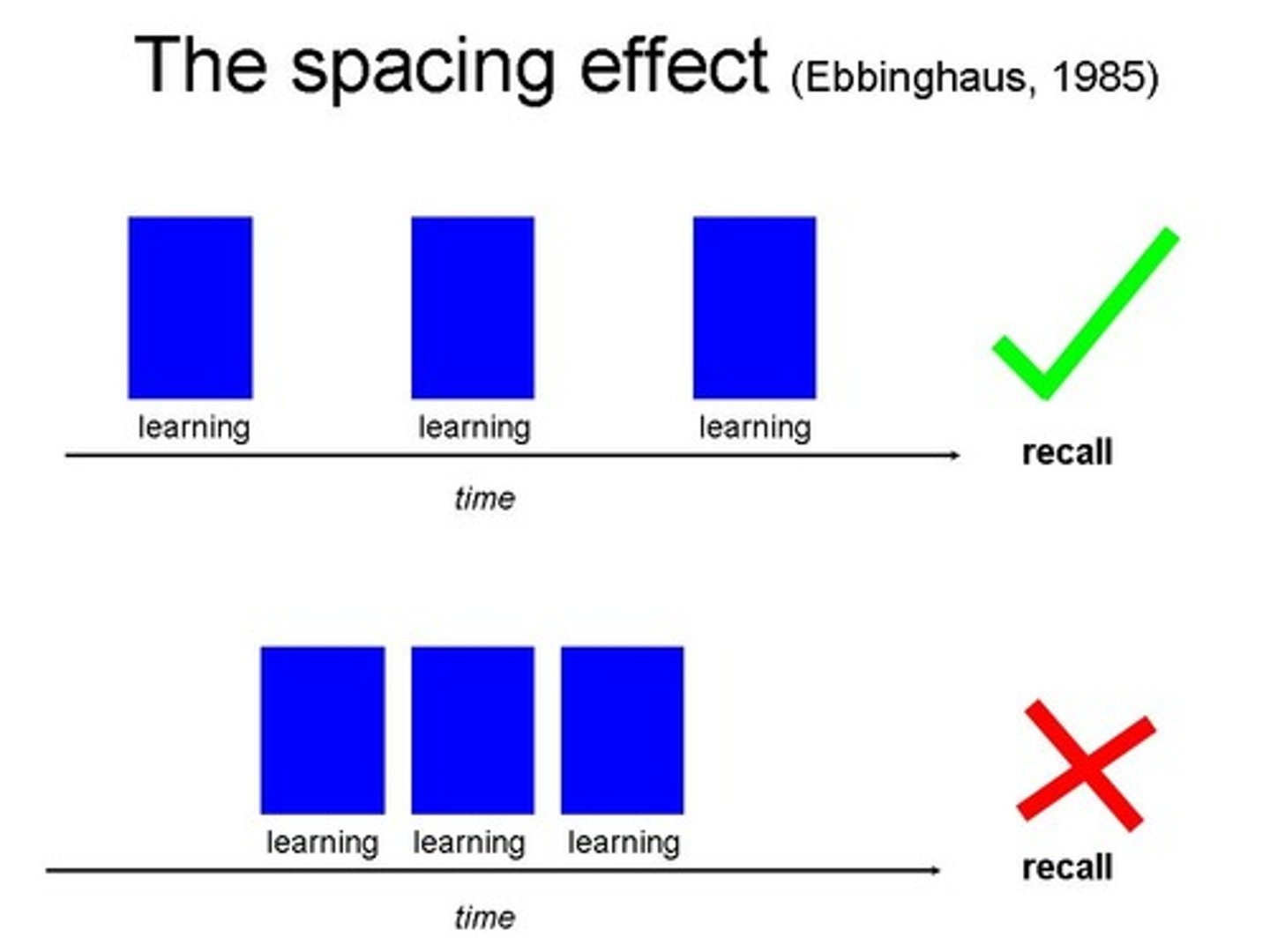
Spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically

Hierarchy
a system or organization in which people or groups are ranked one above the other according to status or authority.
rehearsal
the conscious repetition of information, either to maintain it in consciousness or to encode it for storage

autobiographical memory
the memory for events and facts related to one's personal life story

Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning

context dependent memory
The theory that information learned in a particular situation or place is better remembered when in that same situation or place.

Testing effect
Enhanced performance on a memory test caused by being tested on the material to be remembered.

State dependent memory
The theory that information learned in a particular state of mind (e.g., depressed, happy, somber) is more easily recalled when in that same state of mind.

Metacognition
thinking about thinking
Mood Congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood
Forgetting curve
a graphic depiction of how recall steadily declines over time

Dementia
a slowly progressive decline in mental abilities, including memory, thinking, and judgment, that is often accompanied by personality changes
Repression
keeping distressing thoughts and feelings buried in the unconscious

Imagination inflation
a memory phenomenon in which vividly imagining an event markedly increases confidence that the event actually occurred

Mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past

Creativity
the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas

Grammar
in a language, a system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others

Syntax
The arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language.

Semantics
the set of rules by which we derive meaning from morphemes, words, and sentences in a given language; also, the study of meaning

cooing stage
at about 2 months the infant begins to make vowel-like sounds

babbling stage
beginning at about 4 months, the stage of speech development in which the infant spontaneously utters various sounds at first unrelated to the household language

one word stage
the stage in speech development, from about age 1 to 2, during which a child speaks mostly in single words

Telegraphic stage
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram--'go car'--using mostly nouns and verbs and omitting 'auxiliary' words

Multiple Intelligence (ability) theory
Howard Gardener's theory that intelligence is composed of 7 different abilities or types of intelligence that individuals have varying degrees of competence in.

Mental age
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet; the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance

Growth mindset
the idea that our abilities are malleable qualities that we can cultivate and grow

Fixed mindset
the idea that we have a set amount of an ability that cannot change

Stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype

Predictive validity
The success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior.
