P&IA CLASS 2 TEST (Chest X-Ray)
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
PA CXR: Centering
CR enters MSP at the level of T7
• Top of IR will be 1½-2" above relaxed shoulders.
• MSP is perpendicular to IR.
• MCP is parallel to IR.
PA CXR: Marker
Marker in shoulder area out of AOl (left marker preferred).
PA CXR: Positioning
Patient will be upright- standing or seated facing IR- feet need to be shoulder width apart for a good base of support. MSP should be centered to IR. Have patient place hands on hips and roll shoulders forward to get scapulae out of lung field.
PA CXR: AOI
Heart and lungs (air-filled trachea, lungs, diaphragmatic domes, heart and aortic knob).
PA CXR: Collimation
14" x 17" (35 x 43 cm)
SID: 72" (183 cm)
PA CXR: Technique
Pulmonary Vascular Markings (PVM)
Lateral CXR: Centering
CR enters MCP at the level of T7.
• Top of IR will be 1½-2" above relaxed shoulders.
• MCP is perpendicular to IR.
• MSP is parallel to IR.
Lateral CXR: Marker
Left marker anterior to the patient - out of AOl (if Left Lateral CXR).
Lateral CXR: Positioning
Patient will be upright- standing or seated with left side against IR- feet need to be shoulder width apart for a good base of support. Make sure pt. is not rotated. Arms will be raised above head. MCP should be centered to IR.
Lateral CXR: AOI
Heart and lungs (heart, aorta and left-sided pulmonary lesions (if Left Lateral CXR)).
Lateral CXR: Collimation
14" x 17" (35 x 43 cm)
SID: 72" (183 cm)
Lateral CXR: Technique
Pulmonary Vascular Markings (PVM)
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): Marker
Marker in shoulder area out of AOl (mark side down).
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): Centering
CR enters approx. 2" lateral to MSP level of T7 (on elevated or "up" side)
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): Positioning
Patient will be upright- standing or seated facing IR- feet need to be shoulder width apart for a good base of support. Pt will then be placed in an oblique positon - coronal plane will be 45° to IR. One arm on hip- one arm up. Side of interest is side up.
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): AOI
Heart and lungs- side up.
• LAO- Maximum area of right lung field.
• RAO- Maximum area of left lung field.
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): Collimation
14" x 17" (35 x 43 cm)
SID: 72" (183 cm)
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): Technique
Pulmonary Vascular Markings (PVM)
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): Centering
CR enters MSP the level of mid-sternum.
• Top of IR will be approximately 3" above shoulders.
• MSP is perpendicular to IR.
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): Marker
Marker in shoulder area out of AOl.
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): Positioning
Patient upright facing tube with back against IR. MSP s/b centered to IR. Start with patient 1' in front of IR. Slowly lean patient back- MCP forms 15-20° angle with IR. Shoulders will be touching wall bucky.
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): AOI
Apices
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): Collimation
14" x 17" (35 x 43 cm)
SID: 72" (183 cm)
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): Technique
Pulmonary Vascular Markings (PVM)
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): Centering
CR enters MSP at the level of T7 (MSP and mid-sternum on AP).
• Top of IR will be 1½-2" above relaxed shoulders.
• MSP is perpendicular to IR.
• MCP is parallel to IR.
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): Marker
Marker in shoulder area out of AOl (mark side up).
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): Positioning
LLD: Patient will be lying on left side in lateral recumbent position against vertical IR. RLD: Patient will be lying on right side in lateral recumbent position against vertical IR.
MSP centered to IR. Build patient up on decub sponge. Make sure patient is level & spine is = to table with no backward /
forward leaning. Arms above head. CR will be horizontal.
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): AOI
Air-fluid levels or free air (air rises and fluid will gravitate down).
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): Collimation
14" x 17" (35 x 43 cm)
SID: 72" (183 cm)
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): Technique
Pulmonary Vascular Markings (PVM)
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Centering
CR is perpendicular.
CR enters MSP at manubrium/jugular notch.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Marker
Marker in light field out of AOl.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Positioning
Patient upright or supine. Shield patient based on facility protocol. Shoulders should be in the same horizontal plane - if patient is supine do not use pillow. Extend the patient's neck/chin slightly.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): AOI
Air-filled airway from mid-cervical to mid thoracic region.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Collimation
IR: 10" x 12" (25 x 30 cm)
12" LW and 1" beyond the skin shadow on sides.
SID: 40" (101 cm)
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway-Pharynx and Larynx): Centering
CR is perpendicular.
CR enters MSP at level of C4 (laryngeal prominence).
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway-Pharynx and Larynx): Marker
Marker in light field out of AOl.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway-Pharynx and Larynx): Positioning
Patient upright or supine. Shield patient based on facility protocol. Shoulders should be in the same horizontal plane - if patient is supine do not use pillow. Extend the patient's neck/chin slightly.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway-Pharynx and Larynx): AOI
Air-filled upper airway.
AP Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway-Pharynx and Larynx): Collimation
IR: 10" x 12" (25 x 30 cm)
12" LW and 1" beyond the skin shadow on sides.
SID: 40" (101 cm)
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway- Pharynx and Larynx): Centering
CR horizontal and perpendicular.
CR enters the midcoronal plane at the level of C4 (laryngeal prominence).
MCP is perpendicular to IR.
MSP is parallel to IR.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway- Pharynx and Larynx): Marker
Mark side closest to IR.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway- Pharynx and Larynx): Positioning
Patient upright- sitting or standing. Shield patient based on facility protocol. Patient should clasp the hands behind the body and rotate the shoulders posteriorly as far as possible. Extend the patient's neck/chin slightly.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway- Pharynx and Larynx): AOI
Air-filled upper airway.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway- Pharynx and Larynx): Collimation
IR: 10" x 12" (25 x 30 cm)
12" LW and 1" beyond the skin shadow on sides.
SID: 72" (183 cm)
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Centering
CR horizontal and perpendicular.
CR enters at the level of the manubrium (jugular notch), midway between the jugular notch and midcoronal plane.
• MCP is perpendicular to IR.
• MSP is parallel to IR.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Marker
Mark side closest to IR.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Positioning
Patient upright- sitting or standing. Shield patient based on facility protocol. Patient should clasp the hands behind the body and rotate the shoulders posteriorly as far as possible. Extend the patient's neck/chin slightly.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): AOI
Air-filled airway from mid-cervical to mid thoracic region.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Collimation
IR: 10" x 12" (25 x 30 cm)
12" LW and 1" beyond the skin shadow on sides.
SID: 72" (183 cm)
PA CXR: Respiration
take on second full inspiration.
Lateral CXR: Respiration
take on second full inspiration.
PA Oblique CXR (RAO or LAO): Respiration
take on second full inspiration.
AP Axial CXR (Lordotic position): Respiration
take on second full inspiration.
Lateral Decubitus CXR (RLD or LLD - AP or PA): Respiration
take on second full inspiration.
Lateral Soft Tissue Neck (Upper Airway- Pharynx and Larynx/Trachea and Superior Mediastinum): Respiration
exposure is made during slow inspiration to ensure the trachea is filled with air.
Select all that apply to a PA CXR:
1. Midsagittal plane is parallel to the image receptor
2. Midsagittal plane is perpendicular to the image receptor
3. SID is 72"
4. SID is 40"
5. Hands on hips, with shoulders rolled forward
2. Midsagittal plane is perpendicular to the image receptor, 3. SID is 72", 5. Hands on hips, with shoulders rolled forward
Select the body habitus that is the most common:
1. Hypersthenic
2. Sthenic
3. Hyposthenic
4. Asthenic
2. Sthenic
The left lateral decubitis position best demonstrates:
1. Apices
2. Right lung
3. Air in left lung
4. Fluid in left lung
4. Fluid in left lung
The lordotic position best demonstrates:
1. The apices
2. The right lung
3. Air in left lung
4. Fluid in left lung
1. The apices
A PA oblique CXR, LAO position, best demonstrates:
1. The Apices
2. The right lung
3. The left lung
4. Fluid in the left lung
5. Fluid in the right lung
2. The right lung
Chest x-rays are done upright whenever possible to (select all that apply):
1. Prevent engorement of the pulmonary vessels
2. Lower the diaphragm
3. Raise the diaphragm
4. Demonstrate air/fluid levels
5. Show engorgement of the vessels
1. Prevent engorement of the pulmonary vessels, 2. Lower the diaphragm, 4. Demonstrate air/fluid levels
What phase(s) of respiration best demonstrate a pneumothorax?
1. Inspiration
2. Expiration
3. Both inspiration and expiration
4. Just suspend breathing
3. Both inspiration and expiration
Why should a routine CXR be done on full inspiration? (select all that apply)
1. More air is inhaled on the second breath for maximum expansion of the lungs
2. Full inspiration causes the diaphragm to move inferiorly and expand more fully.
3. The costal muscles pull ribs superiorly and laterally causing the thorax to expand on inspiration.
4. Full inspiration causes the diaphragm to move superiorly
5. Minimum expansion of the lungs
1. More air is inhaled on the second breath for maximum expansion of the lungs, 2. Full inspiration causes the diaphragm to move inferiorly and expand more fully, 3. The costal muscles pull ribs superiorly and laterally causing the thorax to expand on inspiration.
A PA oblique CXR, RAO position, best demonstrates:
1. The Apices
2. The right lung
3. The left lung
4. Fluid in the left lung
5. Fluid in the right lung
3. The left lung
Which body habitus would require the IR to be placed transverse instead of lengthwise?
1. Asthenic
2. Sthenic
3. Hyposthenic
4. Hypersthenic
4. Hypersthenic
Which body habitus has long, narrow lungs?
1. Asthenic
2. Sthenic
3. Hyposthenic
4. Hypersthenic
1. Asthenic
When critiquing a PA CXR for centering, you would:
1. Make sure that it is centered at MSP at the level of T7.
2. Check the medial ends of the clavicle for rotation
3. Make sure the apices are above the clavicles
4. Make sure the heart and lungs are shown in their entirety.
5. Check for vascular markings
1. Make sure that it is centered at MSP at the level of T7.
How many posterior ribs should be visible to indicate a good inspiration?
10
Which of the following would result in the most magnification of the heart?
1. Portable AP at 72"
2. PA upright at 72"
3. AP supine at 60"
4. AP supine at 40"
4. AP supine at 40"
T/F The shoulders should be rotated forward on a PA CXR to move the scapulae laterally and out of the lung field.
True
Which radiographic position is being used when the patient is lying on their right side with a horizontal beam?
RLD
Which radiographic position is being used when the patient is lying on their back with a horizontal beam?
Dorsal decubitis
The main criteria when checking a lateral CXR for rotation:
1. Make sure there is no forward or backward leaning.
2. Check to see if the posterior ribs are superimposed.
3. Make sure the collimation is correct.
4. Check for vascular markings.
2. Check to see if the posterior ribs are superimposed.
Which radiographic position is being used when the patient is lying face down with a horizontal beam?
Ventral decubitis
Which radiographic position is being used when the patient is lying on their left side with a horizontal beam?
LLD
When critiquing a PA CXR for AOI, you would:
1. Make sure that it is centered at MSP at the level of T7.
2. Check the medial ends of the clavicle for rotation
3. Make sure the apices are above the clavicles
4. Make sure the heart and lungs are shown in their entirety from the apices to the costophrenic angles.
5. Check for vascular markings
4. Make sure the heart and lungs are shown in their entirety from the apices to the costophrenic angles.
Why is a routine CXR done at 72"?
1. To decrease magnification of the heart
2. To increase magnification of the heart
3. To increase magnification of the lungs
4. To decrease magnification of the lungs
1. To decrease magnification of the heart
If a PA oblique (RAO or LAO) chest is ordered specifically for the heart, how many degrees should the patient be rotated/obliqued?5-60 degrees
55-60 degrees
Which body habitus has short and broad lungs?
Hypersthenic
When critiquing a PA CXR for positioning, you would (select all that apply):
1. Make sure that it is centered at MSP at the level of T7.
2. Check the medial ends of the clavicle to see if they are equidistance from the spine
3. Make sure the apices are above the clavicles
4. Make sure the heart and lungs are shown in their entirety.
5. Check for vascular markings
2. Check the medial ends of the clavicle to see if they are equidistance from the spine, 3. Make sure the apices are above the clavicles
A left lateral decubitus chest (LLD) best demonstrates:
Fluid in the left lung
If you are looking for free air on a lateral decbuitis chest- would you be interested in the side down or the side up?
side up
All the following structures are part of the respiratory system except the:
1. Trachea
2. Pharynx
3. Bronchi
4. Esophagus
4. Esophagus
T/F Chest exams should be done at 40".
False
For a PA CXR projection, which of the following postitions are required?
1. Upright or erect body position
2. Shoulders rolled backward
3. Arms elevated overhead
4. Shoulders rolled forward
1. Upright or erect body position, 4. Shoulders rolled forward
Which projections are "routine" for a chest x-ray?
1. PA
2. AP
3. Lateral
4. PA oblique
5. Right or Left Lateral decubitis
1. PA, 3. Lateral
The left lateral is most often used in chest radiography because:
The heart is less magnified in the left lateral projection.
The serous membrane surrounding the lungs is the:
1. Hilum
2. Lingula
3. Pleura
4. Peritoneum
3. Pleura
Which of the following would be used to best demonstrate a pneumothorax in the left lung when a patient cannot stand?
RLD
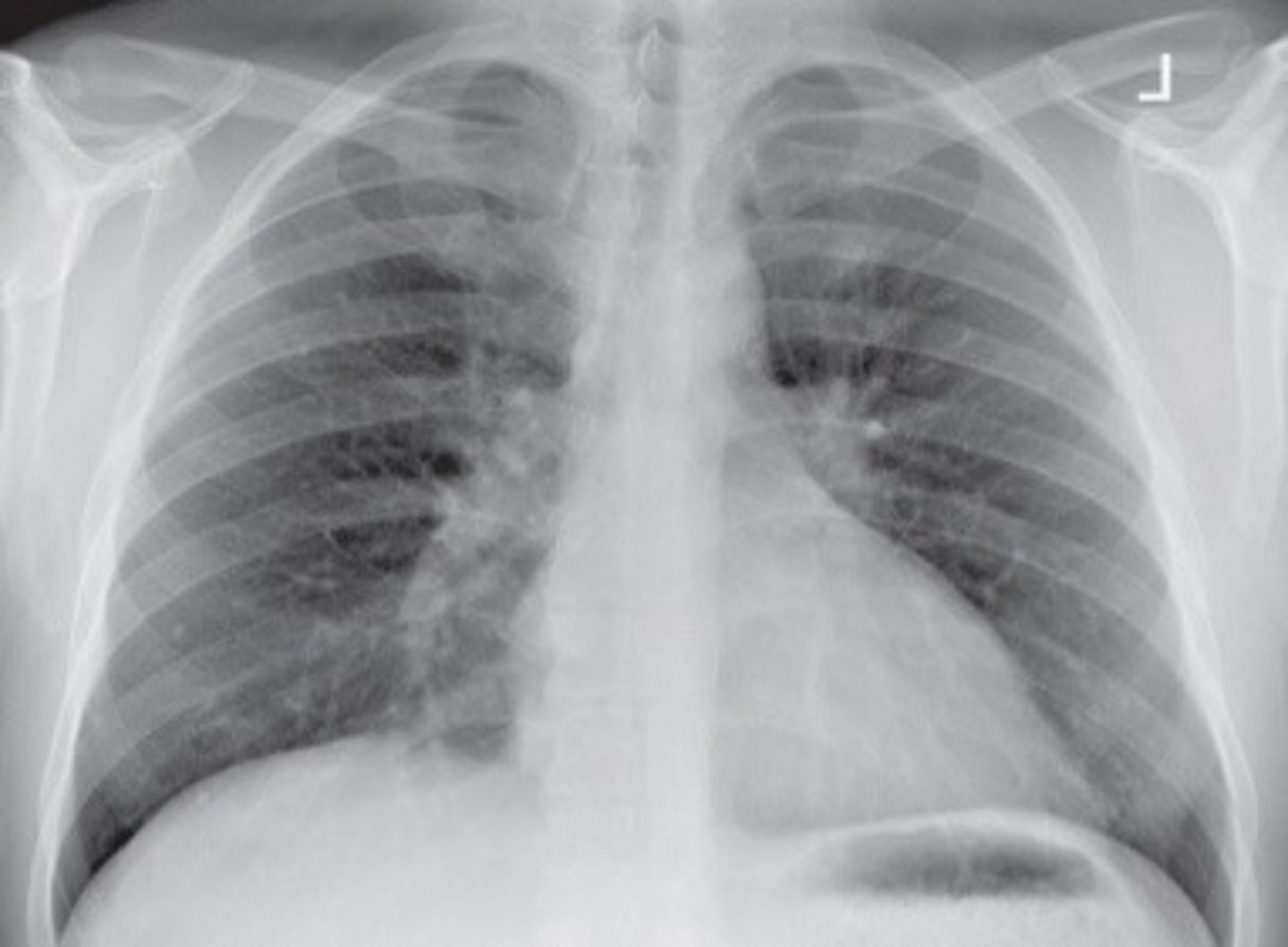
Hypersthenic
short and broad lungs, 5% of the population
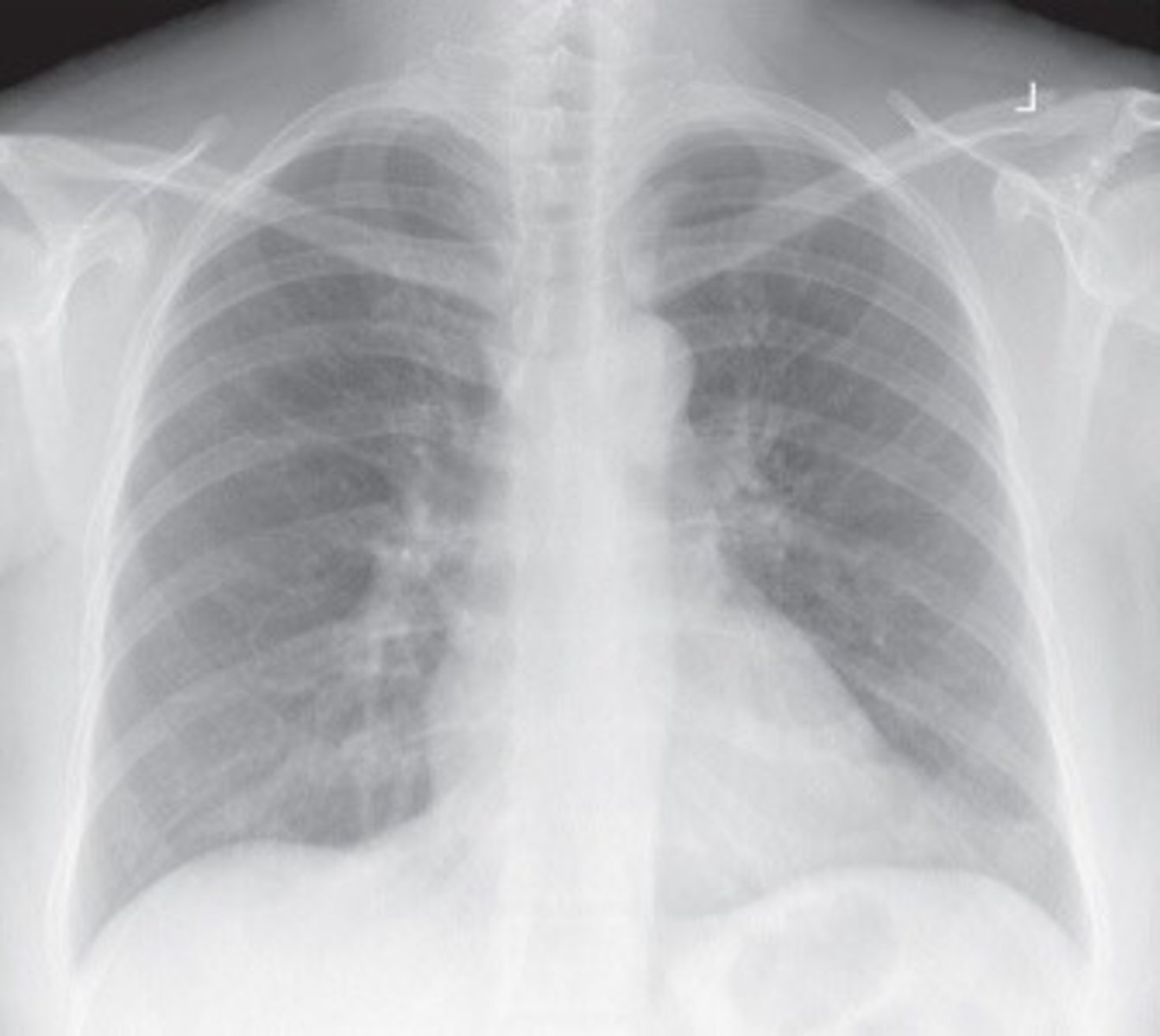
Sthenic
average, 50% of the population
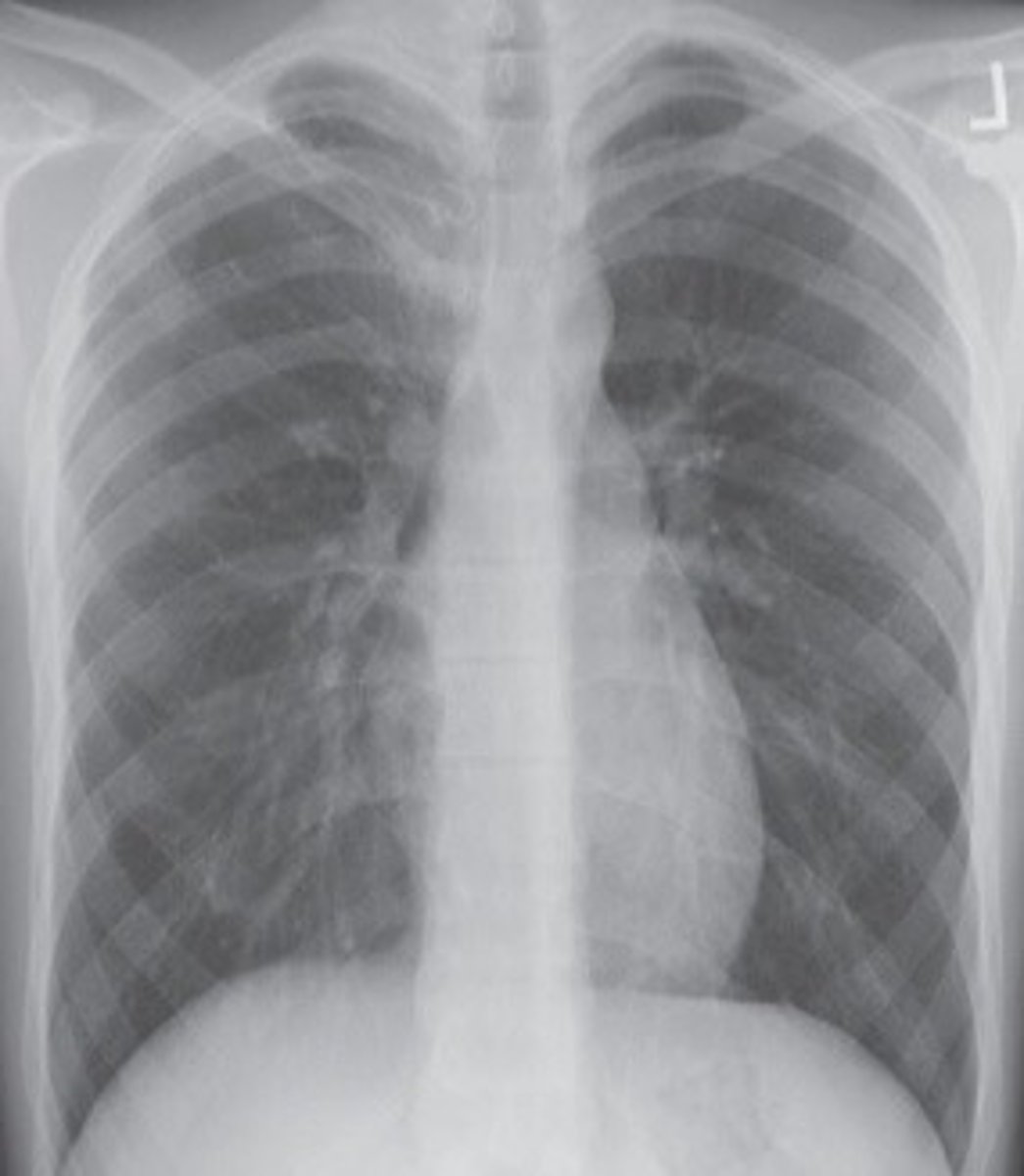
Asthenic
long and narrow lungs, 10% of the population
Which projection of the chest requires the patient to lean back 15-20 degrees and rest the posterior shoulders on the upright wall Bucky?
AP axial
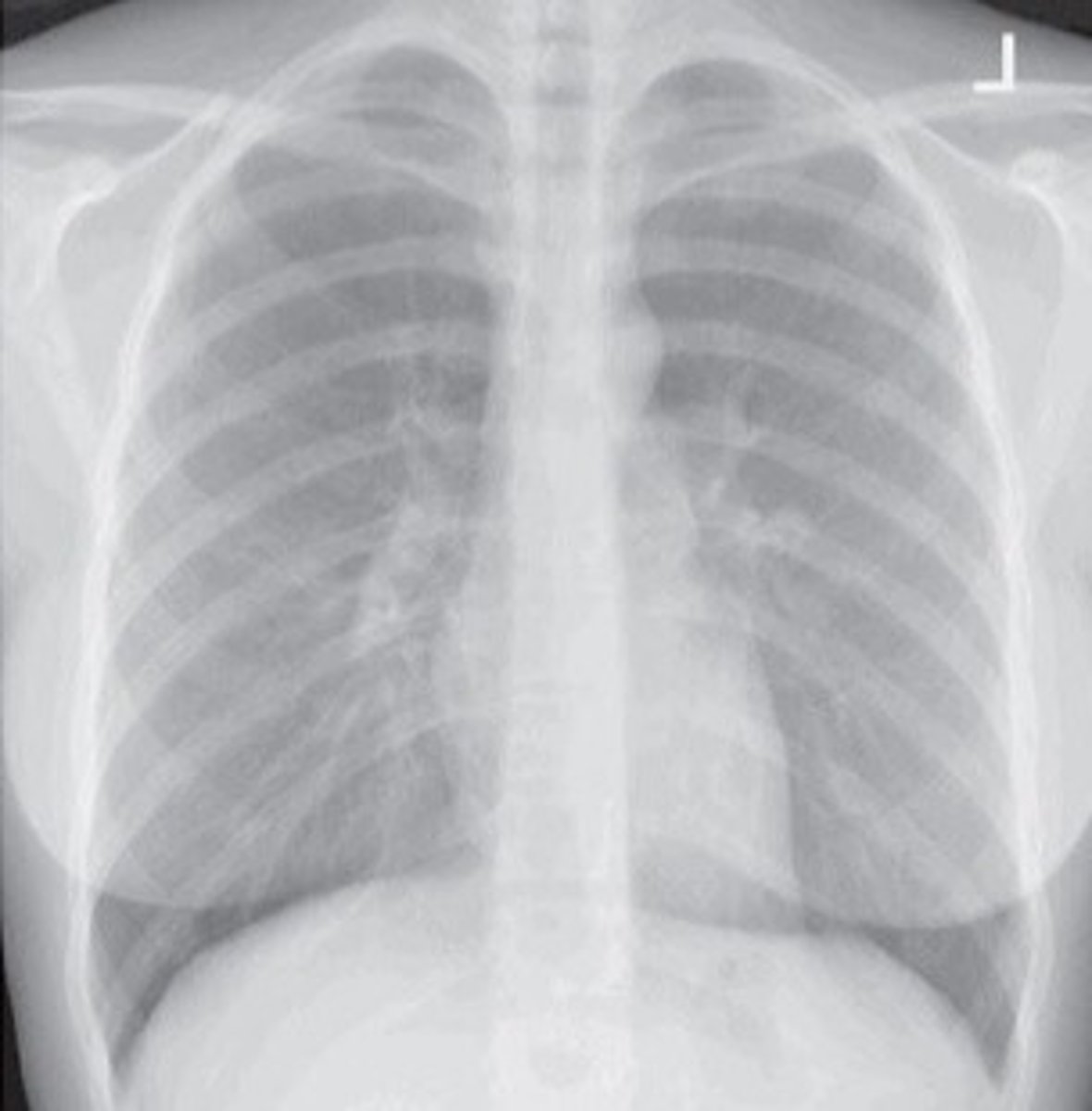
Hyposthenic
smaller than average, 35% of the population
The right lung has _________ lobes, and the left has ______ lobes.
three, two
Which lung is about 1" shorter than the other due to the position of the liver.
right
The ________ is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
diaphragm
The thoracic cavity is divided into right & left _______ cavities & a single ______________ cavity
pleural, pericardial
T/F The thoracic cavity is divided into three separate chambers.
True