Chem 211 - Titration Curve
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Describe the titration curve of strong acid
At equivalence point, pH = 7
Describe a titration curve of weak acid
pH is not 7 at equivalence point
at half-equivalence point, pH = pKa
larger Ka, smaller initial position
Write the Henderson Hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
What is a key characteristic of a titration with a weak diprotic acid?
Possesses 2+ equivalence points
What are some guidelines associated with weak diprotic acid titration
To see first endpoint: pKa2-pKa1 > 4
To see second endpoint Ka2 < 8
Equation for determining initial pH?
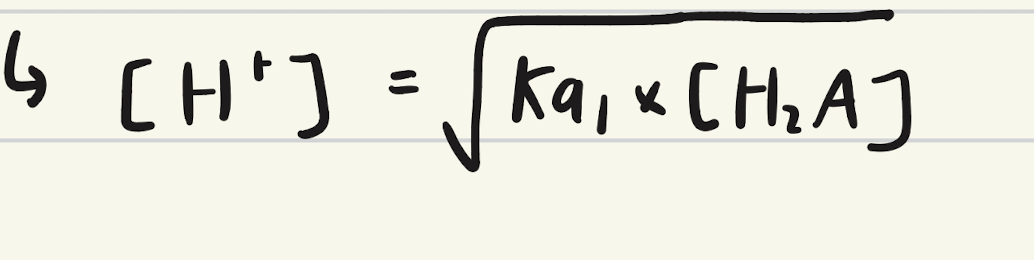
Equation for determining first equivalence point?
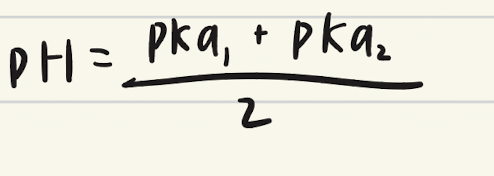
Equation for determining buffer region 1
pH = pKa1 + log [HA]/[H2A]
Equation for determining buffer region 2?
pH = pKa2 + log [A2-]/[HA]
Equation for determining endpoint 2?
Kb1 = K2/Ka2
Define what a buffer is
A mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base that resists changes in pH in addition of small amounts of another acid or base
Provide an example of a buffer
Tricine, acetate buffer
Explain how you would prepare a buffer of a certain pH of which reagents and what amounts
Use HH equation and get the ratio of A-/HA
How do we choose an indicator?
pKa of indicator dye should be larger than pKa of weak acid