OCR B Geography GCSE - Dynamic Development - Congo Case Study
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Environmental challenges?
Country is rich in resource but is so large they must be transported thousands of miles
Small amount of coastline limits ocean transport
The Congo river could supply hydroelectric power for Africa but the difficult terrain means setting up infrastructure is difficult
Dry seasons and droughts cause malnutrition and the destruction of infrastructure
How have some of the millennium development goals not been met?
NOT MET
Reduce hunger, malnutrition invcreased from 51% in 2000 to 66% in 2015
How have some of the millennium development goals Partially been met?
PARTIALLY MET
Promote Gender Equality, Girls finishing primary school doubles from 32% in 1999 to 65% in 2013, but amount of boys finishing primary school grew even more over the same period leading to higher inequality.
To provide water, 50% of population have access to clean water, a small increase since 2000
How have some of the millennium development goals been met?
Provide education for all, 35 % in 1999 to 72% in 2013
Stop the spread of disease, 70% are vaccinated against measles compared to 20% in 1999
what is Rostow's model?
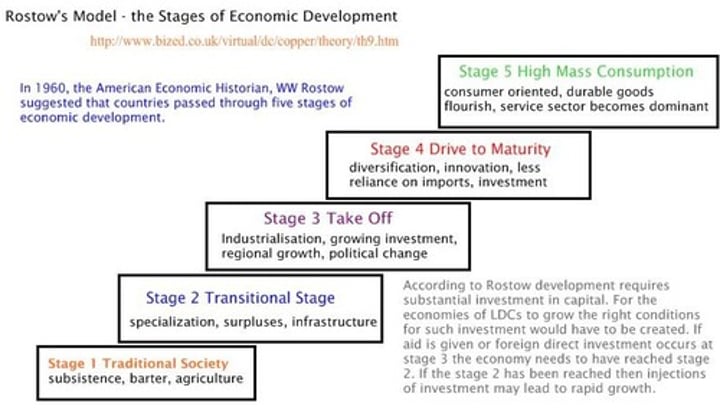
What stage of Rostow's model is the DRC?
Stage 2, preconditions for take off
(DRCs economy is based off of both primary and secondary goods)
Should be preparing for stage 3 of rapid industrialisation and increasing wealth
Why may the DRC not develop as Rowstow's model suggests?
Transport is very poor with few paved roads and limited railways, limiting potential exports
Only 10% have access to electricity, power cuts are common. Will hinder development.
Trade links?
Before now, DRC imported more than exported, it is now equal.
Mainly exports primary products , metals and minerals
Mainly imports manufactured goods like machinery
Human right violations and corruptions meant many countries were reluctant to trade until recently. Since 1997 trade links have increased.
Who are the main trading partners of the DRC?
Belgium, China, Italy, France and Australia
Pros and cons to trade?
PROS
Economy growth of 7% from 2010-2012, better standard of living
More likely to have investments or aid
CONS
Reliance on primary goods makes it vulnerable to falling prices e.g. global financial crisis
Reliance on secondary imports makes it vulnerable to increased prices
High demand for minerals can lead to exploitation like slavery
What is a TNC?
transnational corporation
A TNC is a large company which operates in countries all around the world.
What are the effects of TNCs like Banro operating in the DRC?
ADVANTAGE
employment - Banro employs at least 1500
Development projects- Banro built a market place in luhwindja to provide jobs and economy
Taxes - Banro contributes $120 million each year through spending
DISADVANTAGE
TNCs can pull out- mass unemployment
Some Profits will leave DRC and return to Canada
Some large mines have forced small mines shut
Environmental problems- deforestation
What are the effects of aid the DRC recieves?
PROS
Improves living conditions and infrastructure e.g. UK funded 1700 km of new road
Emergency aid provides food and shelter for those in conflicts
CONS
Early aid was the supply of weapons, this promoted violence
Some aid has conditions e.g. in 2008 China gave $9 billion but insisted development of mining and infrastructure. Doesn't benefit the extremely poor.
Top down development project?
Propsed construction of Grand Inga Dam on Congo river
Cost $80 billion
Donors - World Bank, African development bank and others
Effects of the grand Inga Dam?
PROS
Could Provide clean, cheap energy for all and to sell
Will promote industry and provide jobs
CONS
Money may be lost to corrupt officials/companies
Flooding of Bundi Valley and relocation of 30,000 people
Example of bottom up development project?
Involving teachers, students and parents in improving rural schools and increasing number of children in education
cost- £390,000
Donor - Comic Relief
Effects of bottom up plan?
PROS
-Local people have a say in how their school can be improved
-Better educated people earn more so contribute more to economic development
CONS
-Not enough funding to improve all schools
-Some families need children to earn money and cant afford to send them to school
-Doesn't tackle large scale issues
What?
-A nearly landlocked country in central Africa, one of the poorest in the World
-population of 79 million
-GNI per capita = $410
-life expectancy = 59 years
-Literacy rate = 61%
-Human Development Index= 0.43
Political and social factors affecting development?
When DRC gained independance from Belgium in 1960, by 1965 Mobutu Sese Seko seised power and prevented development
-Mobutu allowed armed forces to loot the country, leading to inequality in wealth
-Large companies paid bribes for access to mineral resources (most money earned from large companies would leave the country)
-Mobutu forces foreign companies to leave the country leading to loss of jobs.
-Refused to pay debt to Belgium who cancelled development projects in DRC
-Conflict over his leadership lead to damage to crops, property and infrastructure.
-Mobutu was overthrown in 1997 leading to a civil war which lasted until 2003
-Joseph Kabila (president from 2001) promised to improve Infrastructure, health, education, housing, jobs and access to resources
-Slow signs of economic growth
What are Conflict minerals?
Armed groups forced people to work in dangerous conditions to mine these minerals. Fighting over the ownership has caused millions of deaths
Many companies refuse to trade with the DRC due to their forced labour