Concepts & Applications Full
1/354
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
355 Terms
Define a catalyst
A catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction by reducing the energy barrier, without impacting the position of equilibrium. A catalyst is not consumed during the reaction.
What is the Arrhenius equation?
k = Ae(-Ea/RT)
What is the linearised Arrhenius equation?
lnk = lnA - Ea/RT
What is A in the Arrhenius equation?
A describes the collisions: the frequency of collision and the steric dependence for a successful collision
Convert the Eyring equation to include entropy and enthalpy
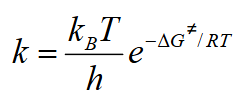
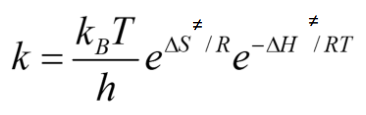
Linearise the Eyring equation
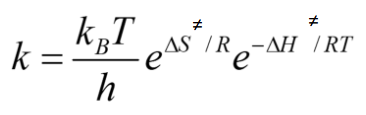
ln(k/T) = ln(kbolt/h) - ΔH‡/RT + ΔS‡/R
What is the significance of the ‡ symbol in the Eyring equation?
It shows that we are discussing the entropy and enthalpy of activation, which is used to inform about the transition state.
The equation does not describe the overall reaction entropy/enthalpy.
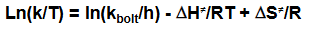
What do you plot to give a linear Eyring equation graph?
What is the gradient and intercept?
y axis: ln(k/T)
x axis: 1/T
Gradient: -ΔH‡/R
Intercept: ln(kbolt/h) + ΔS‡/R
What do ΔH‡ and ΔS‡ in the Eyring equation tell you about the mechanism of a reaction?
A large, positive ΔS‡ suggests an increase in disorder in the transition state, hence a dissociative mechanism.
A positive ΔH‡ suggests that there is bond breaking involved. To improve a catalyst you should aim to have a lower ΔH‡.
What is the equation for TOF?
What is the drawback of TOF?
number of cycles (turnovers) / number of centres x time
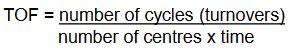
It doesn’t consider temperature or concentrations, so you have to be careful when comparing the values.
What is the equation for TON?
What is the benefit of TON over TOF?
moles of product / moles of catalyst

TON accounts for deactivation, gives a more realistic idea of the maximum yield
What is the equation for selectivity?
(quantity of desired products / amount of reactants consumed) x 100

What is the equation for efficiency?
(Mw(desired products) / Mw(all products of the reaction)) x 100

What is the equation for catalytic rate?
What are the units?
converted mol of substate / volume or mass of catalyst x time

molL-1h-1 or molkg-1h-1
What are the three types of catalyst?
Heterogeneous
Homogeneous
Enzymatic
What are the drawbacks of a heterogeneous catalyst?
Degradation over time due to leaching, poisoning or sintering
Can be difficult to control shape or size
Selectivity is often low
Activity depends on surface area
What are the benefits of a homogeneous catalyst?
Often selective and modifiable
Work at low temperatures and concentrations
Easier to obtain mechanistic information
Because the activity is linked to catalyst concentration, its easier to control
What are the drawbacks of a homogeneous catalyst?
Low thermal stability so often used under 200 degrees
Difficult to separate (expensive)
What are the benefits of an enzymamtic catalyst?
Highly specific
Work at low temperatures and concentrations
Enzymes can stabilise the transition state
What are the drawbacks of an enzymatic catalyst?
Can be deactivated by pH change/ extreme temperatures
Explain the impact of using water as a solvent on the rate of catalysis (acid/base)
Protons in hydrogen bonded systems move very rapidly because of their low mass.
This means that proton transfer in acid-base catalysis is very fast.
What is the equation for pH and proton concentration?
pH = -log[H+]
What is the first step in a specific acid catalysed process?
The acid protonates a reactant.
This is in equilibrium, so the concentration of the conjugate acid becomes finite.
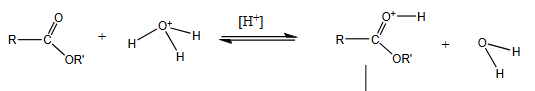
What is the catalyst in a specific acid catalysis process?
Protonated solvent (which fully transfers the proton the one of the reactants before the rate determining step)
How does the pH impact the rate of reaction in a specific acid catalysed reaction?
The pH ([H+]) impacts the position of equilibrium with the protonated reagent.
The reaction rate is then proportional to the concentration of this protonated reagent ([RH+]).
Therefore, rate ∝ pH
Define specific acid catalysis
When the substrate (reactant) is protonated by a strong acid prior to the rate determining step.
Define general acid catalysis
When every species that’s able to donate a proton contributes to the reaction rate (not just H3O+)
Write the equation for general acid catalysis rate
rate = kH[H+][AH] + k0[AH][sol] + k’0[A-][sol] + k’OH[A-][OH-]
How is general acid catalysis different to specific acid catalysis?
The proton donor in general acid catalysis is now the undissociated reagent.
This proton transfer is now slow, so is the rate limiting step
Describe this graph and the reasons for its shape
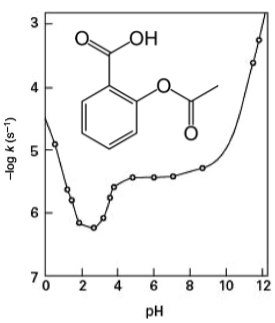
Linear regions below pH 2.5 and above 10.
This is where specific acid catalysis and specific base hydrolysis dominate, so rate is proportional to [H+].
The flat region in the middle is due to solvent catalysed reaction - this is flat because the solvent concentration doesn’t change.
How do you spot general acid catalysis vs specific acid catalysis?
The rate of reaction for specific acid catalysis will not change under varying concentrations of buffer, because rate is only dependent on pH.
Changing [buffer] in general acid catalysis will have an impact on rate because you are changing [HA].
Draw how an enzyme can use general acid catalysis to aid ester hydrolysis by water
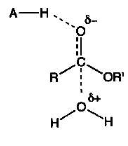
Draw how an enzyme can use general base catalysis to aid ester hydrolysis by water
Define mirco, meso and macropores
Misopore < 2 nm
Mesopore 2-50 nm
Macropore > 50 nm
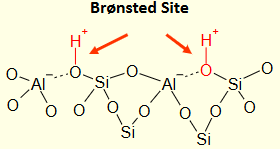
Draw a zeolite surface structure and clearly label the Bronsted acid site
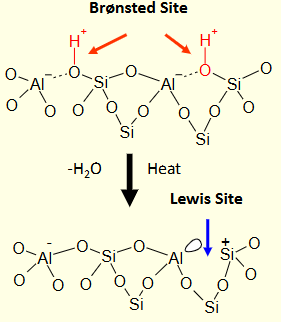
What happens to a zeolite surface when you heat it?
Water is lost, and the Bronsted acid site becomes a Lewis acid site.
The Lewis acid site has an empty orbital to accept an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct.
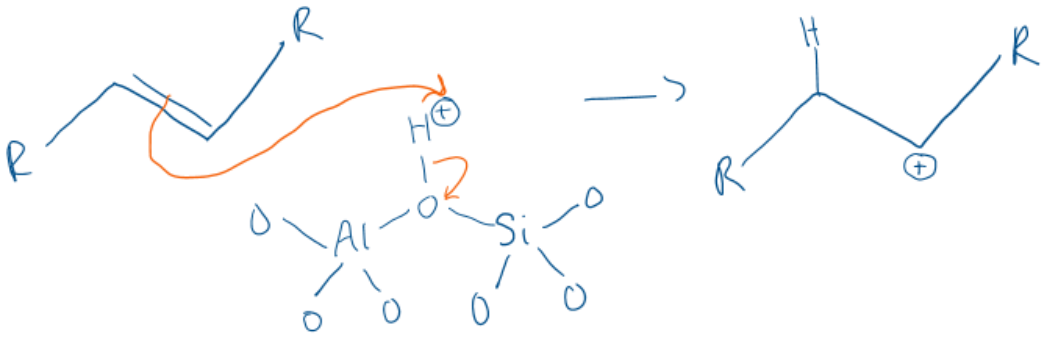
What are the two ways that a zeolite can produce a carbenium ion from hydrocarbons?
1) The Bronsted acid site can donate a proton to an alkene
2) The Lewis acid site can abstract H- from an alkane
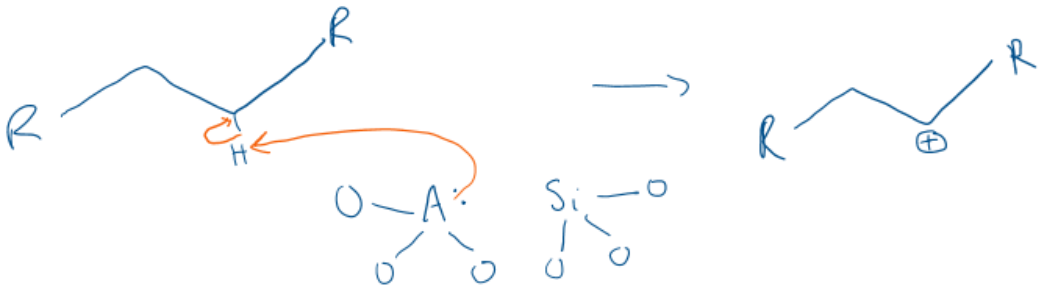
Give a general description of how zeolites cause catalytic cracking.
The zeolite either adds H+ to an alkene or removes H- from an alkane to give a carbenium ion.
The beta bond to the carbenium ion centre breaks heteolytically.
This gives an alkene and a carbenium ion.

Describe the two processes that a carbenium ion can undergo and why this is important.
It can undergo hydride shift and methyl shift to rearrange.
Methyl shift is slower than hydride shift
This allows the cation to rearrange to give the most stable products (tertiary carbocations).
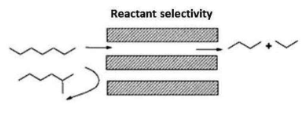
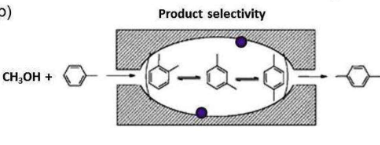
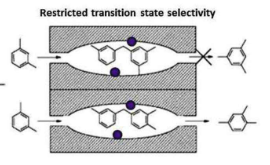
What are the three types of size selectivity? Give examples of each
1) Reactant selectivity: only linear alkanes are narrow enough to enter a pore so they are the only ones to react
2) Product selectivity: Only the 1,4-dimethyl product is narrow enough to leave the pore
3) Transition State selectivity: The 1,3,5-trisubstituted transiton state is too large for the pore, so only the 1,2,4 product is formed
What does the Ziegler Natta catalyst do?
Alkene polymerisation
Draw the mechanism for alkene polymerisation using a metallocene.
What is the evidence which supports this mechanism?
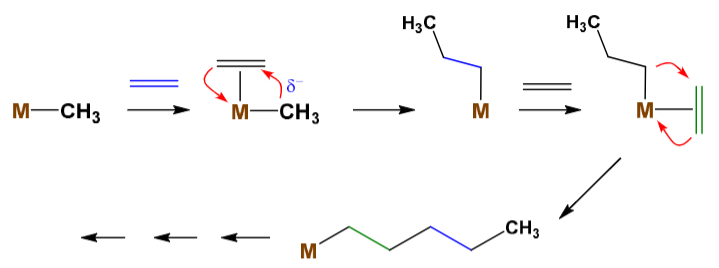
If you add fully deuterated ethene, there is no deuterium scrambling: The chain is (CD2CD2)n(CH2CH2)n
Give the words beneath the boxes
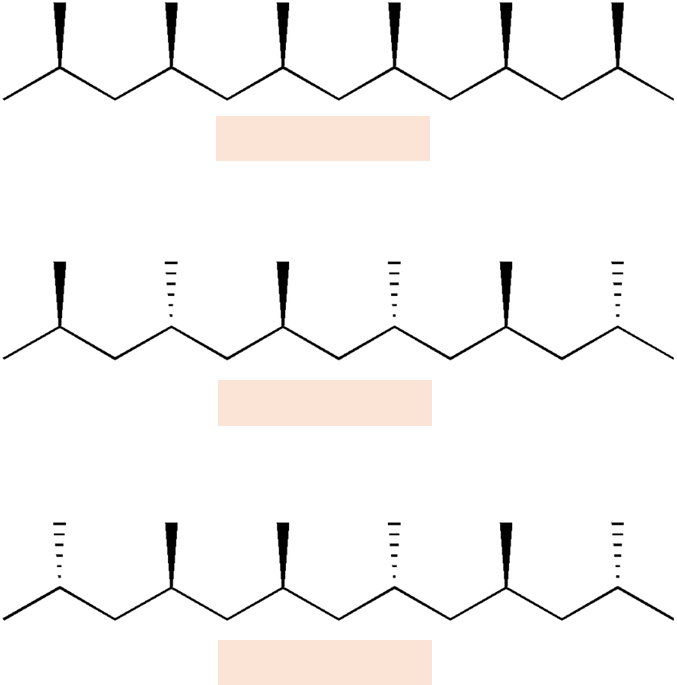
Isotactic
Syndiotactic
Atactic
How does the choice of transition metal in an alkene polymerisation catalyst impact the rate?
Late transition metals (RHS) are more electron rich so exhibit more backbonding to an alkene.
This makes the alkene more electron rich.
The migrating group is R-, so increased electron density on the alkene makes the migration slower
What does Mw/Mn tell you about polymer chain length?
High Mw/Mn = wider range of chain lengths
Low Mw/Mn suggests good selectivity (equal chain lengths)
What are the three methods of alkene polymerisation termination?
1) β-H transfer & alkene dissociation
2) Adding H2 (gives M-H and alkane)
3) Adding HX (gives M-X and alkane)
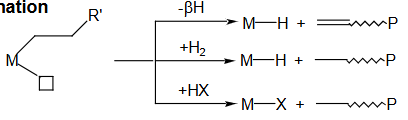
Draw a diagram to depict associative displacement

Draw a mechanism to show chain walking
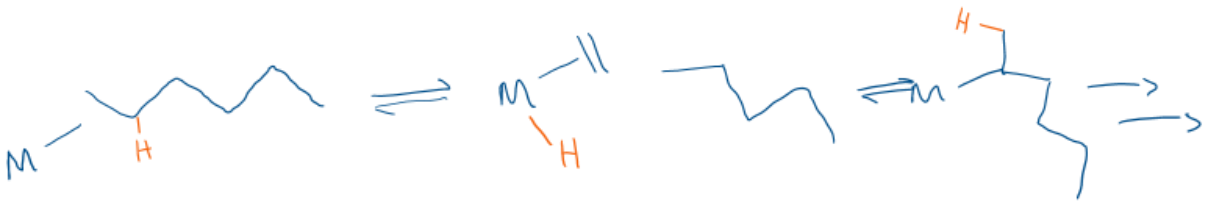
Name this type of Metathesis
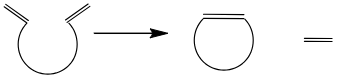
Ring closing metathesis
Name this type of Metathesis
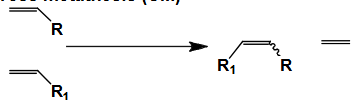
Cross metathesis
Name this type of Metathesis

Ring opening metathesis polymerisation (ROMP)
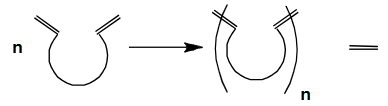
Name this type of Metathesis

Acyclic diene metathesis polymerisation (ADMET)
Name this type of Metathesis
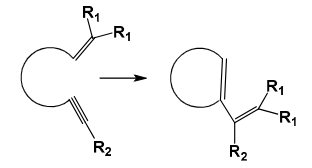
Enyne metathesis (EYM)
Name this type of Metathesis
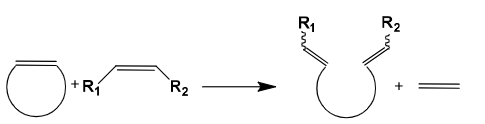
Ring-opening cross metathesis (ROCM)
Name this process of H2 activation

Oxidative addition
Name this process of H2 activation

Hydrogenolysis
Name this process of H2 activation

Heterolytic cleavage
What factors of an alkene/alkyne impact the rate of hydrogenation with Wilkinson’s catalyst?
Alkynes bind faster due to the higher electron density of the triple bond.
Electron donating groups (CN, OH) increase the rate of binding (& therefore hydrogenation), while electron withdrawing groups (R) decrease it
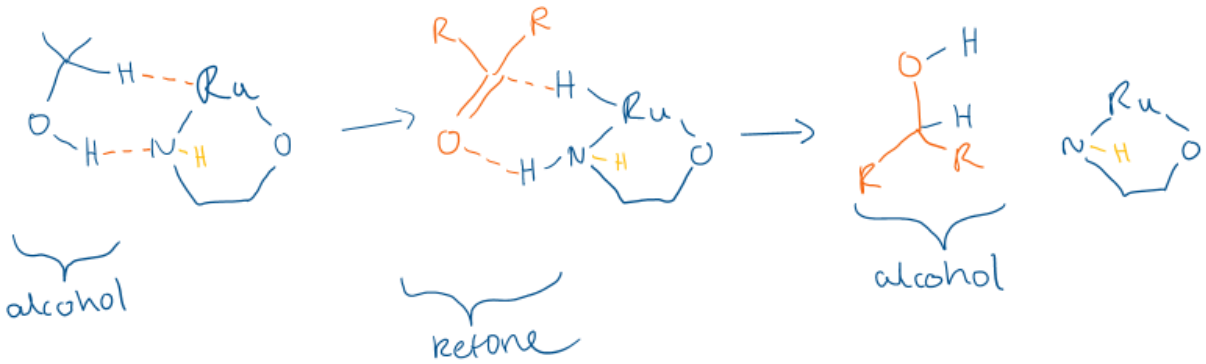
Describe transfer hydrogenation.
Draw the mechanism.
When a hydrogen donor (alcohol, amine) gives two protons to the catalyst, which are then transferred to another molecule like a ketone to reduce it to an alcohol
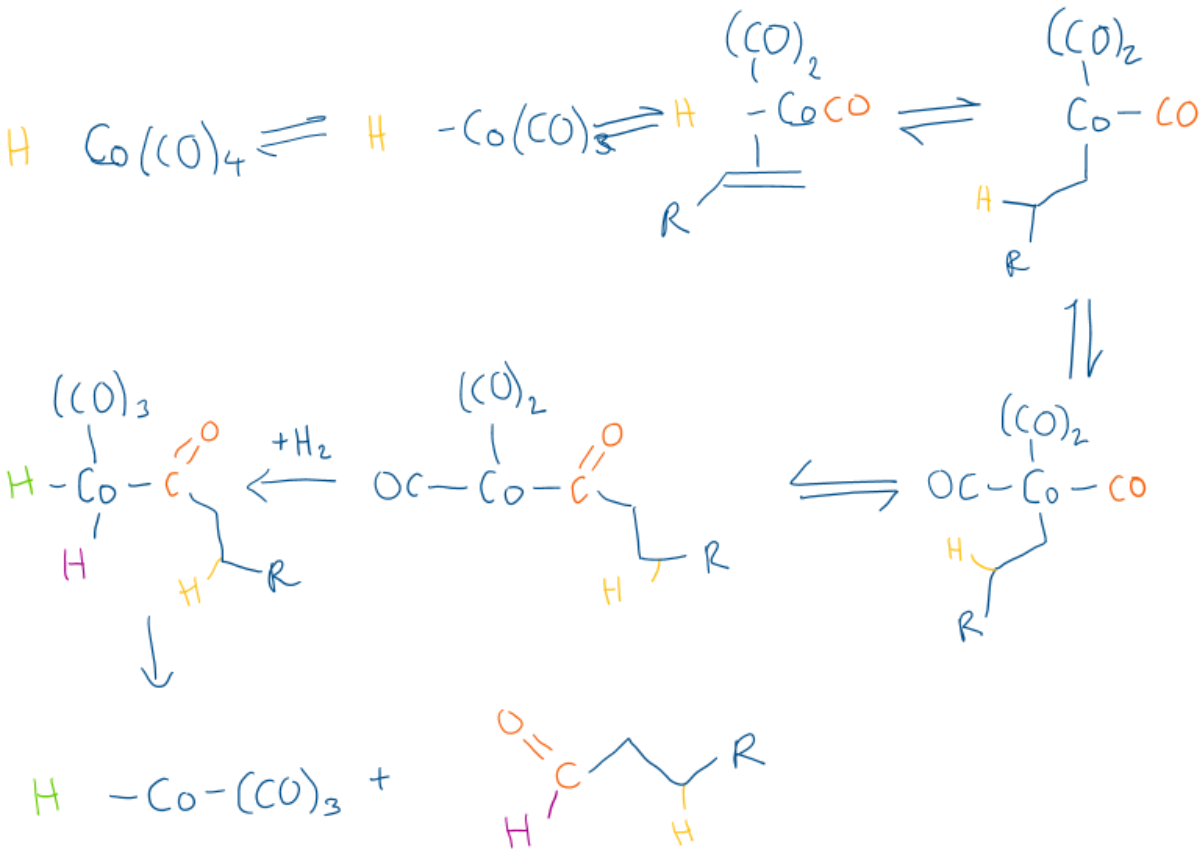
What is alkene hydroformylation?
Alkene + CO + H2 —> aldehyde
Draw the mechanism for hydroformylation of an alkene using Co(CO)4(H)
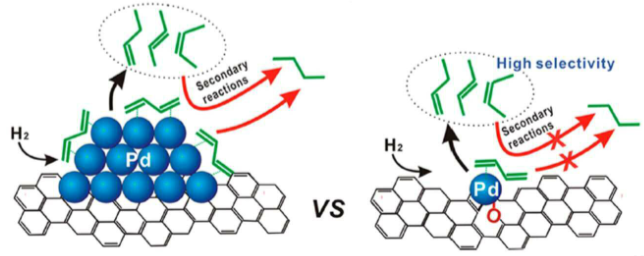
How can changing the loading of a metal on a support change the selectivity of hydrogenation?
Using single Pd atoms on a graphene support reduces the amount of full hydrogenation of a diene.
This is because only one alkene site can bind and react at a time
Describe the difference in bonding between physisorption and chemisorption.
Draw a diagram to depict this.
Physisorption: Van de Waals
Chemisorption: Chemical bonds
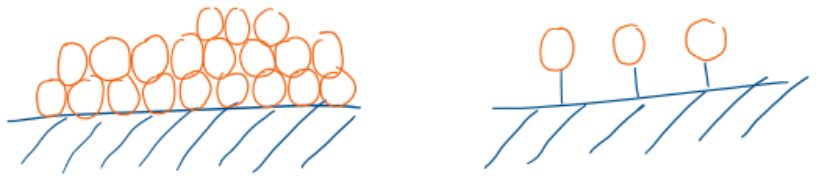
What is a monolayer?
When one layer of molecules physisorb onto a catalyst surface
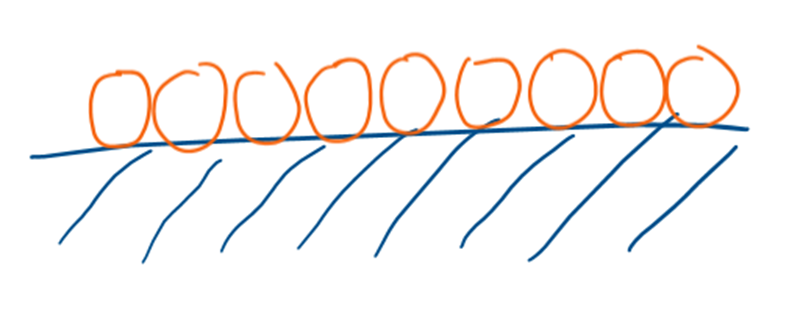
Describe and explain the entropy change that accompanies physisorption
ΔS < 0
For physisorption to be spontaneous, ΔG must be negative.
Therefore, ΔH must be negative (exothermic)
What volume does 1 mole of gas occupy at STP?
22,400 cm3
What are the 3 assumptions made in the Langmuir Isotherm?
1) The surface has a fixed number of identical sites
2) ΔHads is independent of coverage
3) Adsorbates do not interact
What is b in the Langmuir isotherm?
What is the equation for b
b is the equilibrium constant of binding of A to the M surface
b = [A-M] / [A][M]
What is the Langmuir Isotherm equation?
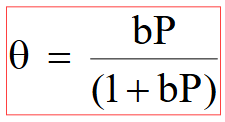
where θ is surface coverage
b is the binding equilibrium constant
P is the pressure
What is the linearised Langmuir isotherm equation?
What is the gradient and intercept?
P/n = 1/bnm + (1/nm)P
Because θ = n/nm
Where nm is the number of sites on the monolayer surface
Plotting P/n against P gives the gradient 1/nm
The intercept is 1/bnm
What improvements does the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) Adsorption Isotherm make on the Langmuir Adsorption isotherm?
What is the limitation of the BET isotherm?
Allows for multilayer adsorption
Accounts for different enthalpies of adsorption of multilayer and monolayers
Limitation: Only valid for a limited pressure range
What do you plot when using the BET isotherm?
What is the gradient?
What is the intercept?
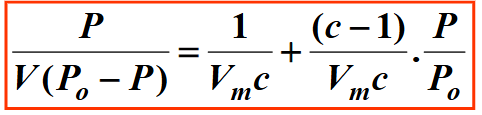
Plot P / V(P0-P) vs P/P0
Gradient = (c-1) / Vmc
Intercept = 1/Vmc
What is the equation for the rate of surface decomposition?
Rate = kθ
Rate = k(bP / (1+bP))
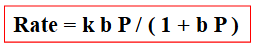
Discuss how changing the pressure impacts the rate using the rate equation:
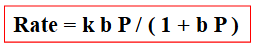
If low pressure: bP << 1, so rate = kbP
Therefore, rate is proportional to pressure at low pressures
If high pressure: bP >> 1, so rate = k
Zero order reaction, rate is constant with increasing pressure because the surface is fully occupied
What is a Langmuir-Hinshelwood type reaction?
Give the rate equation
A and B both adsorb, react while adsorbed then desorb as the product.
Rate = kθAθB
What is a negative order reaction?
When the rate of reaction relies upon two adsorbed species reacting, so increasing the concentration of one reduces the rate by inhibiting the other from adsorbing.
What is the equation for θA in a Langmuir-Hinshelwood reaction?
What does this tell you about A and B surface coverage?
θA = bAPA / ( 1 + bAPA + bBPB)
A and B surface coverage are inversely proportional to each other - the binding of one inhibits the other by occupying a binding site.
Using this equation, describe the two limits of a Langmuir Hinshelwood reaction
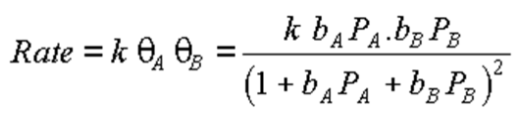
Limit 1:
Low pressure of A and B: rate = kbAPAbBPB
Rate is first order with respect to the pressures of A and B
Limit 2:
Low pressure of A, high pressure of B: rate = kbAPA / (bBPB)
Rate is first order with respect to A, and negative first order with respect to B
What is an Eley-Rideal type reaction?
Give the rate equation
A adsorbs and B reacts with adsorbed A
rate = kθA[B]
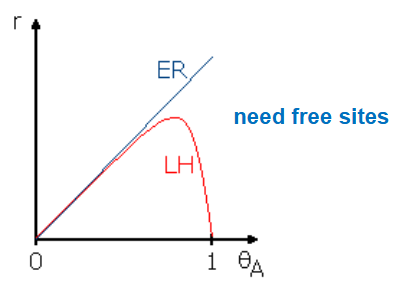
Draw a graph plotting rate against θA for both Langmuir-Hinshelwood and Eley-Rideal reactions.
Briefly describe the shape of these plots.
Name a method of activation of the C terminus
Converting to an acid chloride
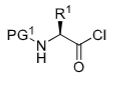
What is the drawback of C-terminus activation as an acid chloride
Reacts with Boc group to form oxazolone, which tautomerises to give a mixture of products
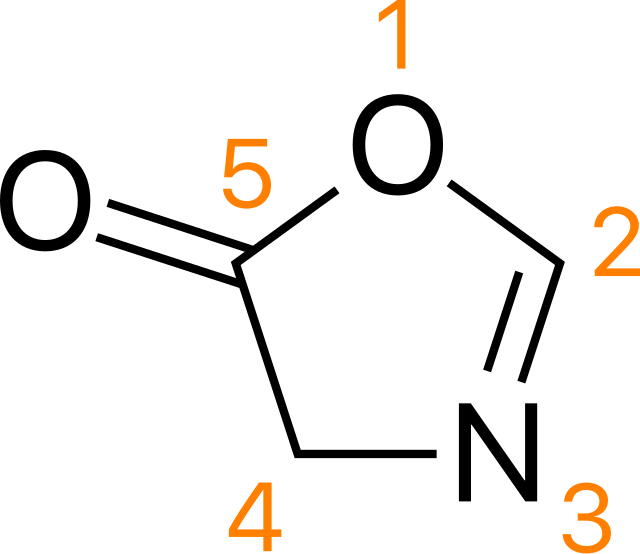
What is an alternative to activating the C-terminus?
Using a coupling reagent
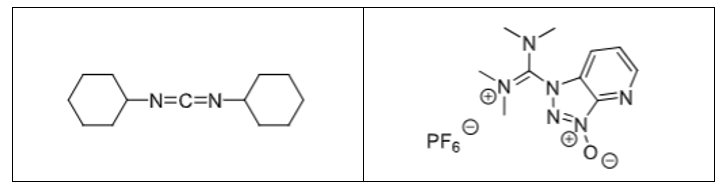
Give two examples of coupling reagents
DCC and HATU (+Base)
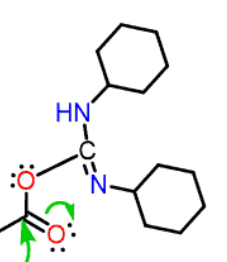
How does DCC activate a peptide? Draw the structure of the intermediate
Produces a good leaving group on the C-terminus
How does HATU activate a peptide? Draw the structure of the intermediate
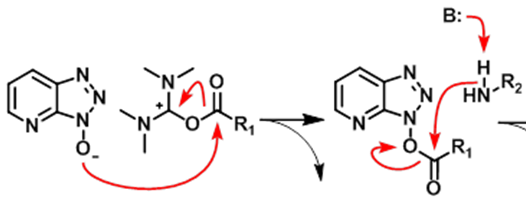
Adds a good leaving group
What is a protecting group for amines
carbamates
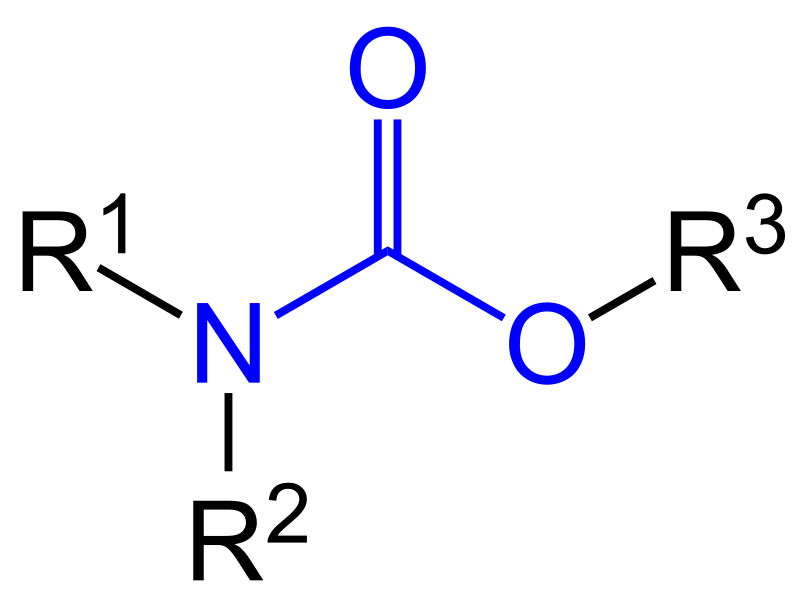
What is a protecting group for carboxylic acids
esters
What are the 3 protecting groups for hydroxyl groups
alkyl ethers
silyl ethers
esters
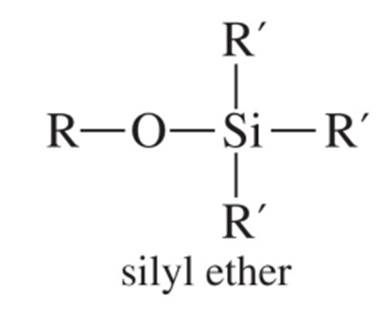
Give an example of a carbamate n-terminus protecting group and draw its structure
Boc
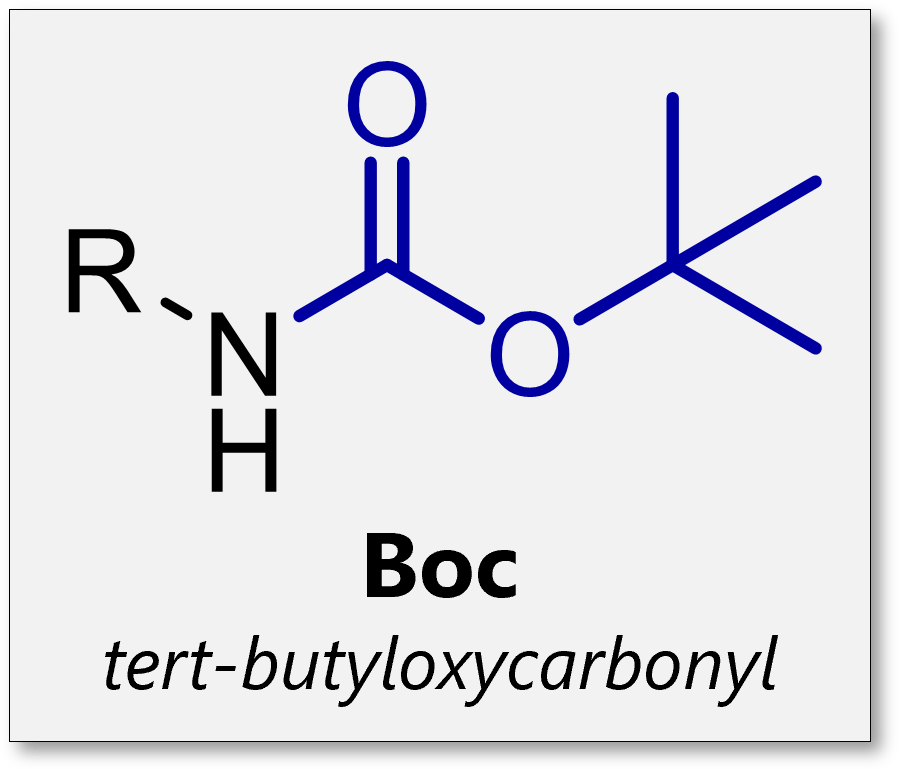
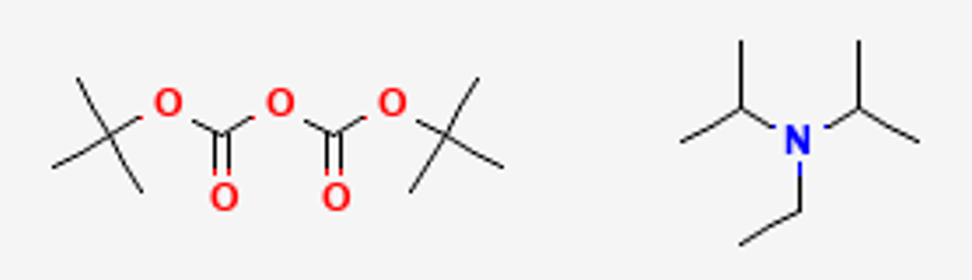
What are the reagents for adding a boc protecting group
Boc2O and a base (eg. DiPEA)
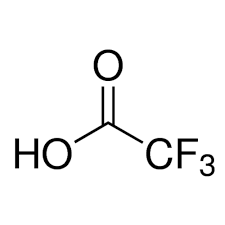
What are the reagents for removing Boc
Acid (TFA)
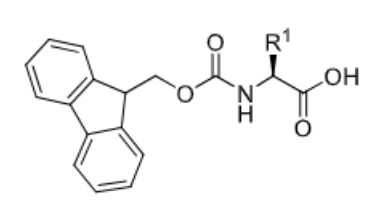
What is an alternative to Boc? Draw the structure
Fmoc
What is the deciding factor between Boc and Fmoc?
Boc is stable in basic conditions but removed with acid. Fmoc is stable in acidic conditions but removed with base
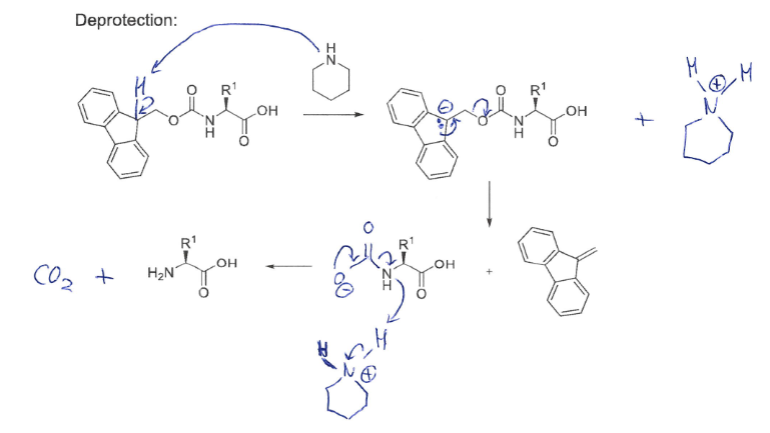
Draw the deprotection mechanism for Fmoc
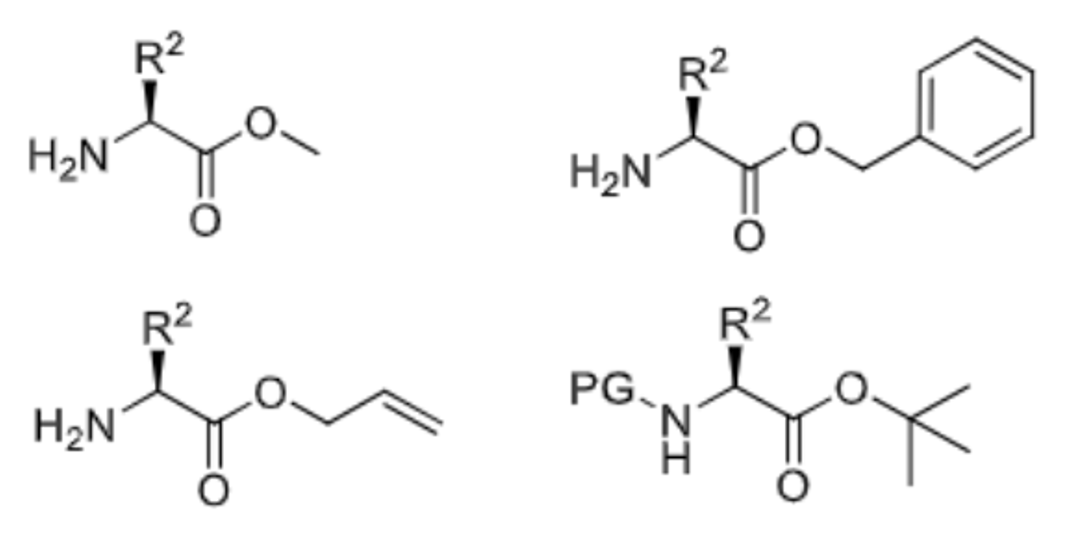
Give 4 examples of ester c-terminus protecting groups and draw their structures
Methyl ester
Benzyl ester
Allyl ester
Tert-butyl ester
What are the reagents for the removal of a methyl ester PG?
NaOH, H2O
What are the reagents for the removal of a benzyl ester PG?
H2, Pd/C
What are the reagents for the removal of an allyl ester PG?
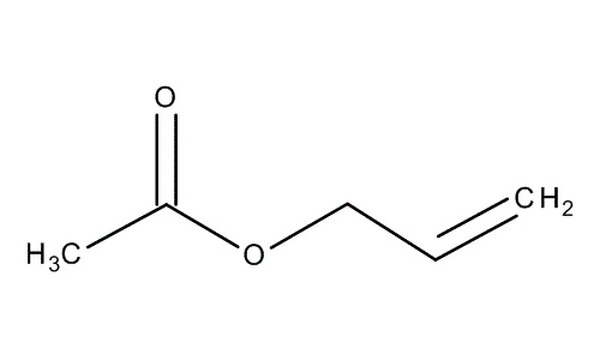
Pd(PPh3)4
What are the reagents for the removal of a tert-butyl ester PG?
TFA