Lab: Cow Eye Dissection
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Anterior Chamber

Ciliary Muscle
enabling changes in lens shape for light focusing
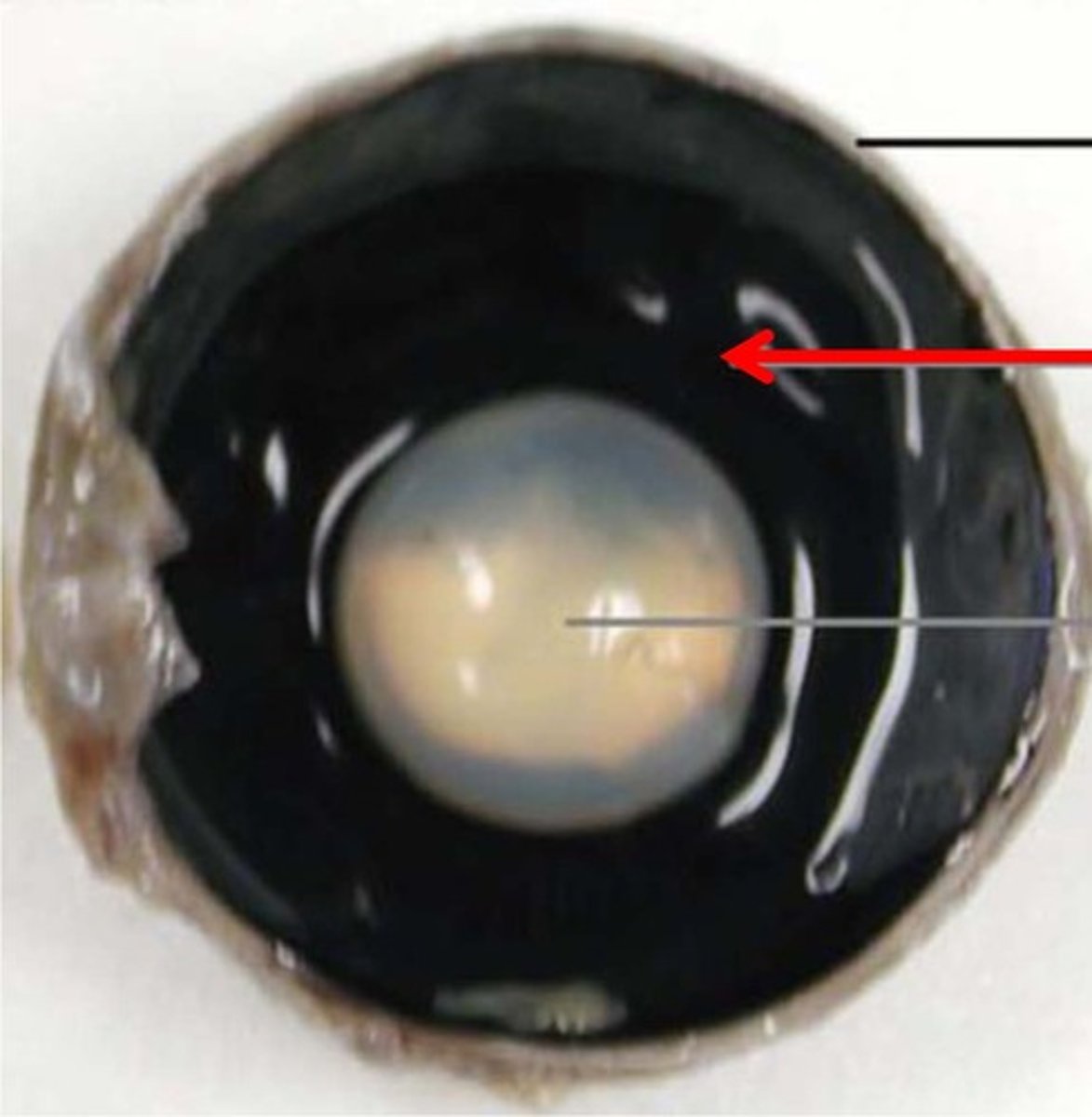
Retina
convert the light into neural signals, and send these signals on to the brain for visual recognition
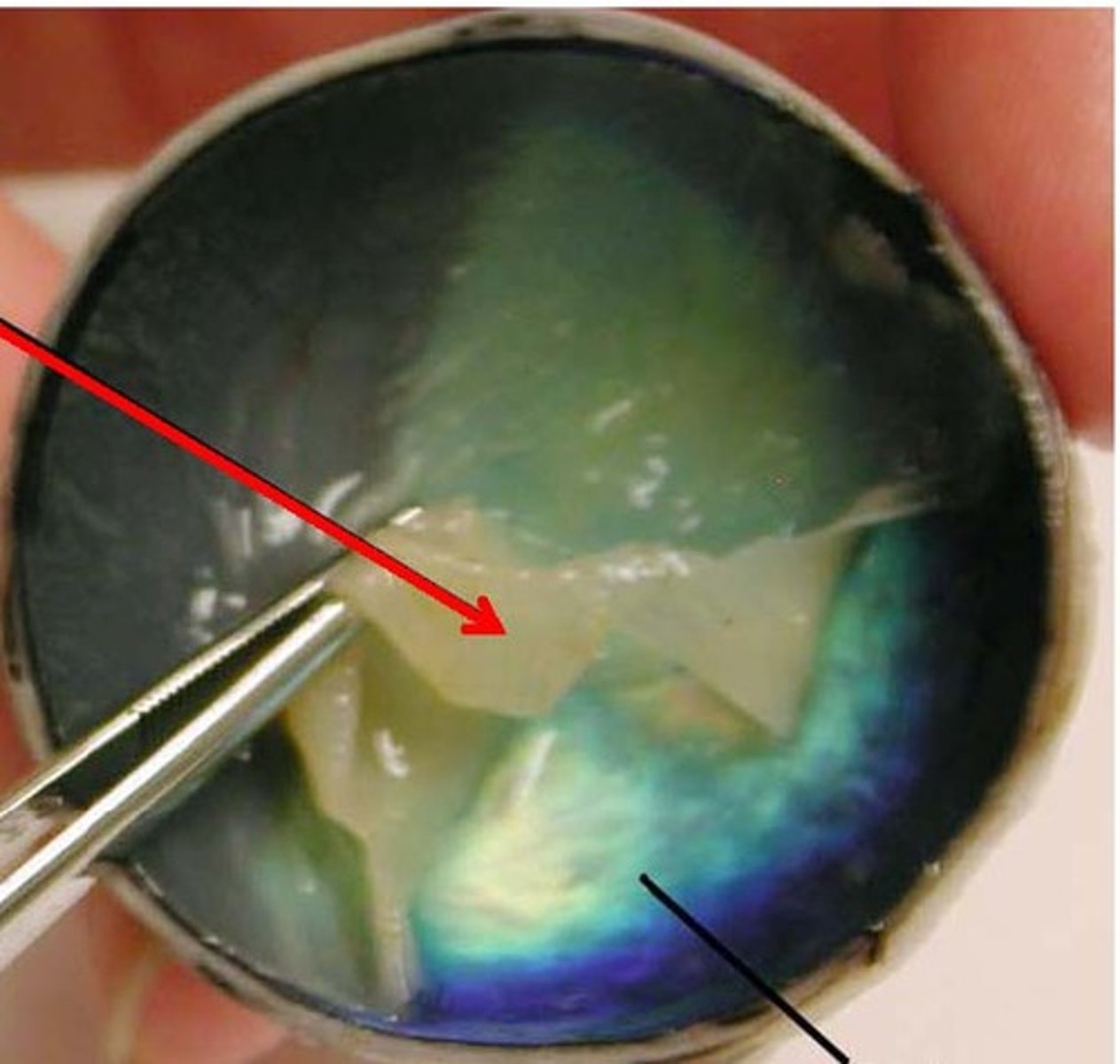
Choroid
the pigmented vascular layer of the eyeball between the retina and the sclera
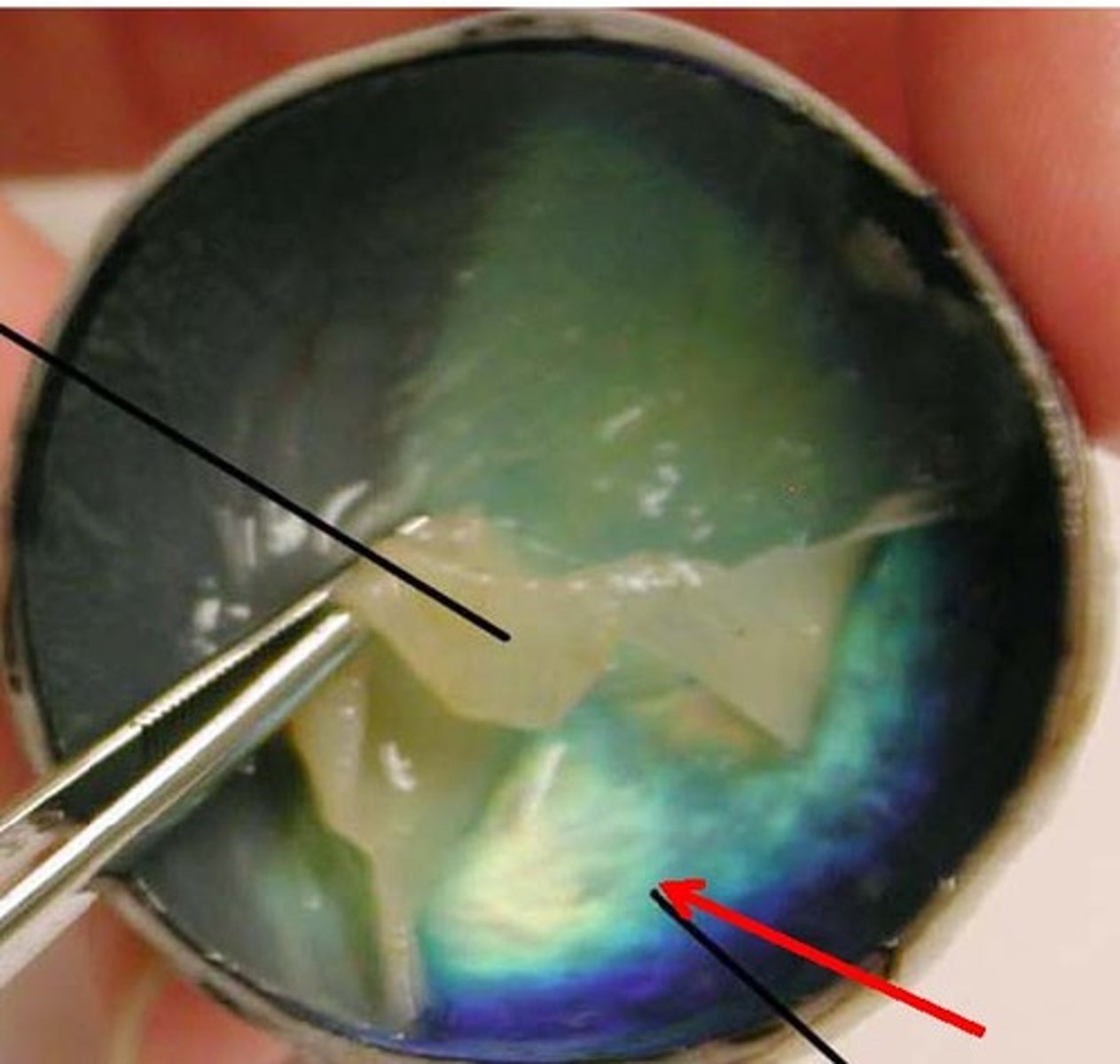
pupil
light opening that
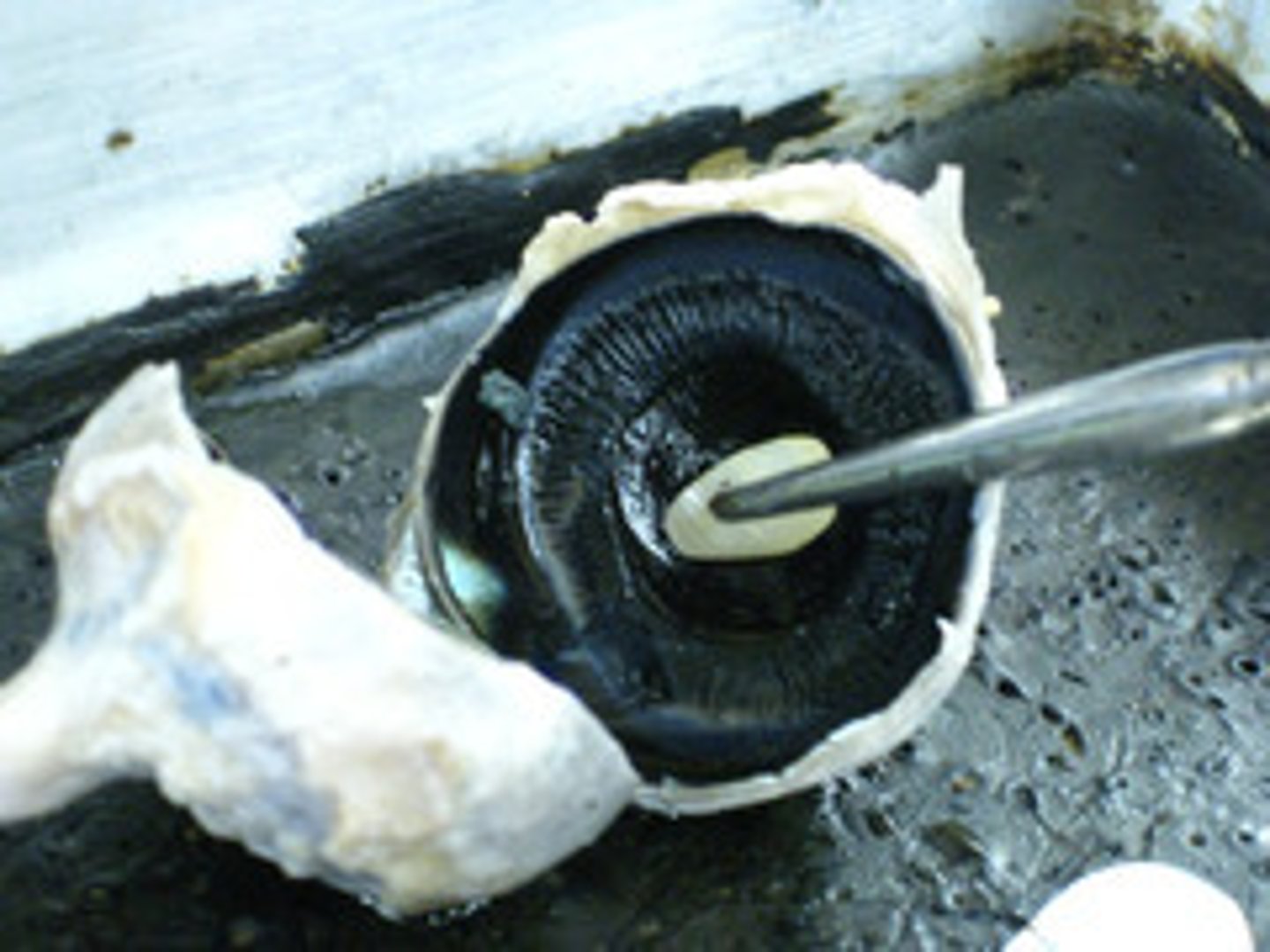
lens
focuses the light rays that pass through it (and onto the retina) in order to create clear images of objects that are positioned at various distances
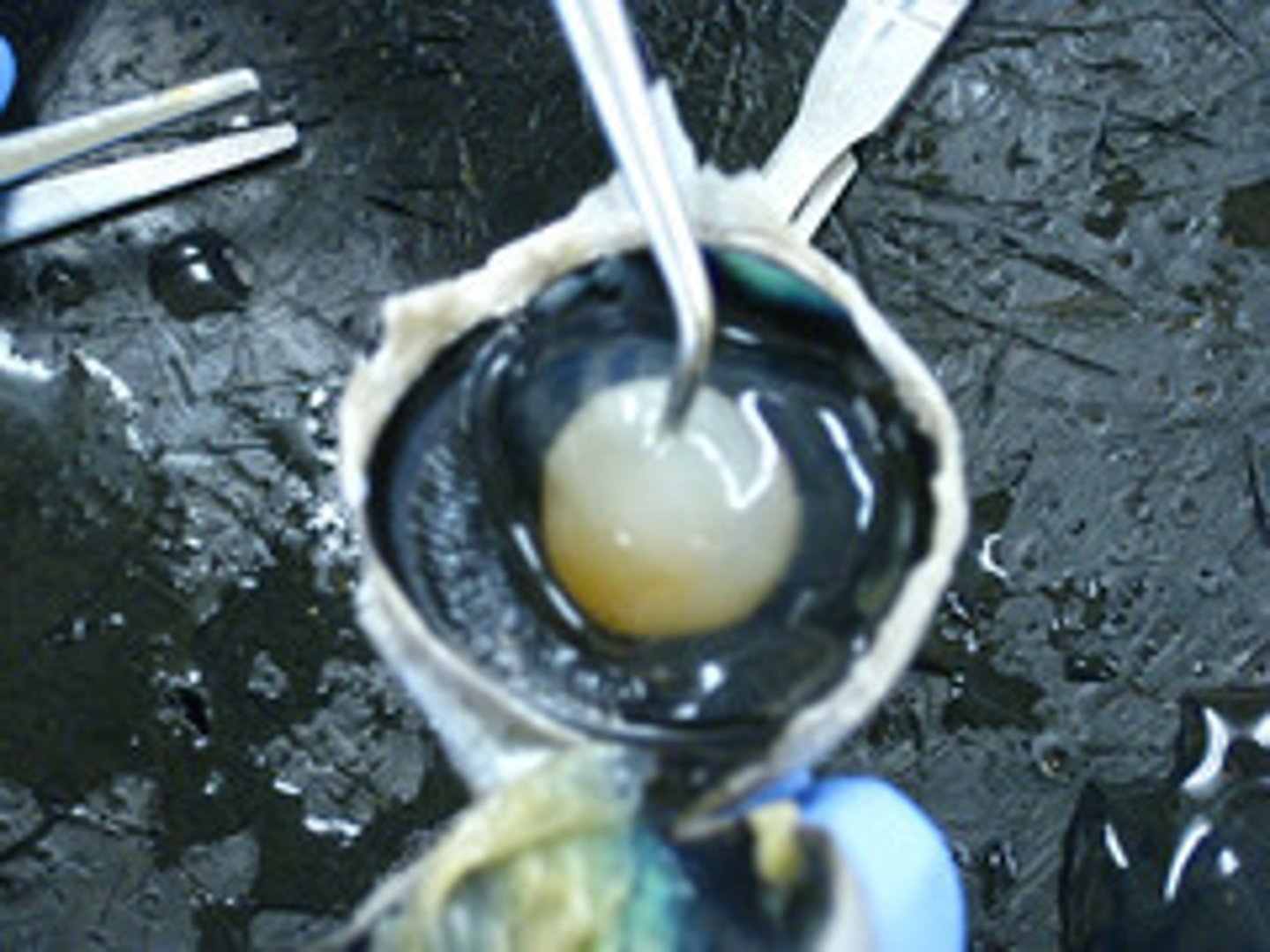
ciliary body
includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor

optic nerve
each of the second pair of cranial nerves, transmitting impulses to the brain from the retina at the back of the eye
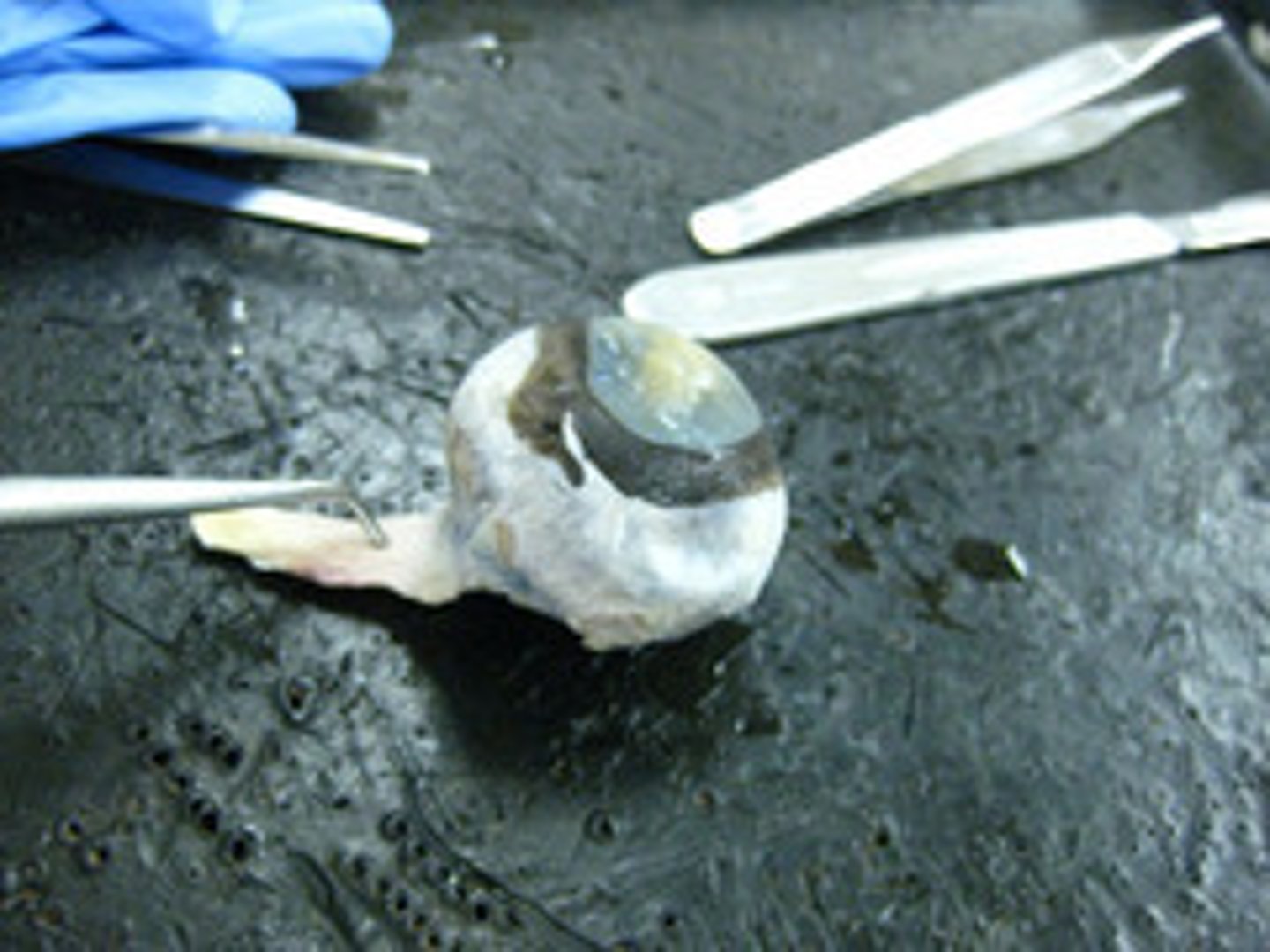
tapetum lucidum
night vision; reflects visible light back through the retina, increasing the light available to the photoreceptors
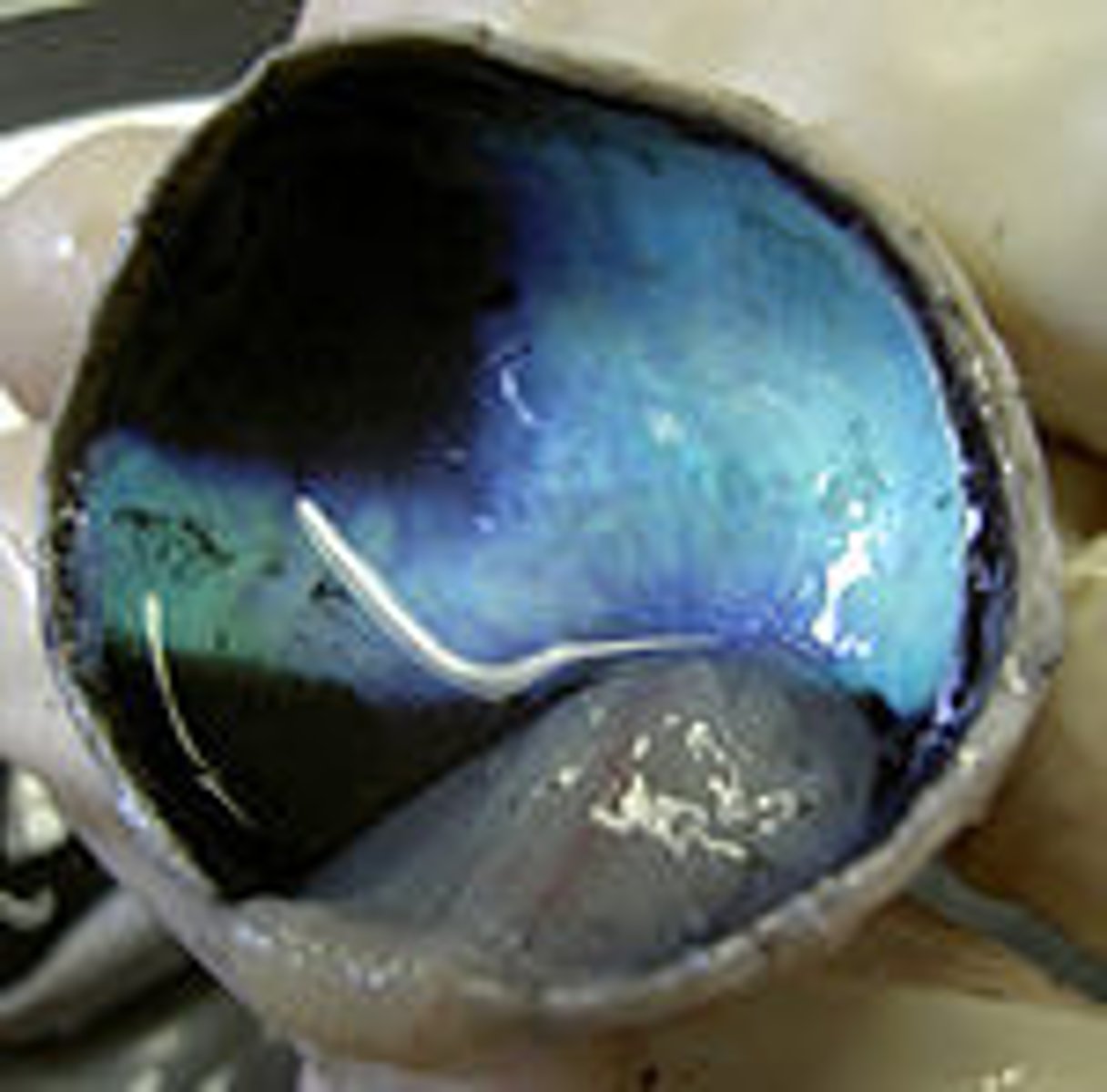
cornea
the transparent layer forming the front of the eye; controls and focuses the entry of light into the eye
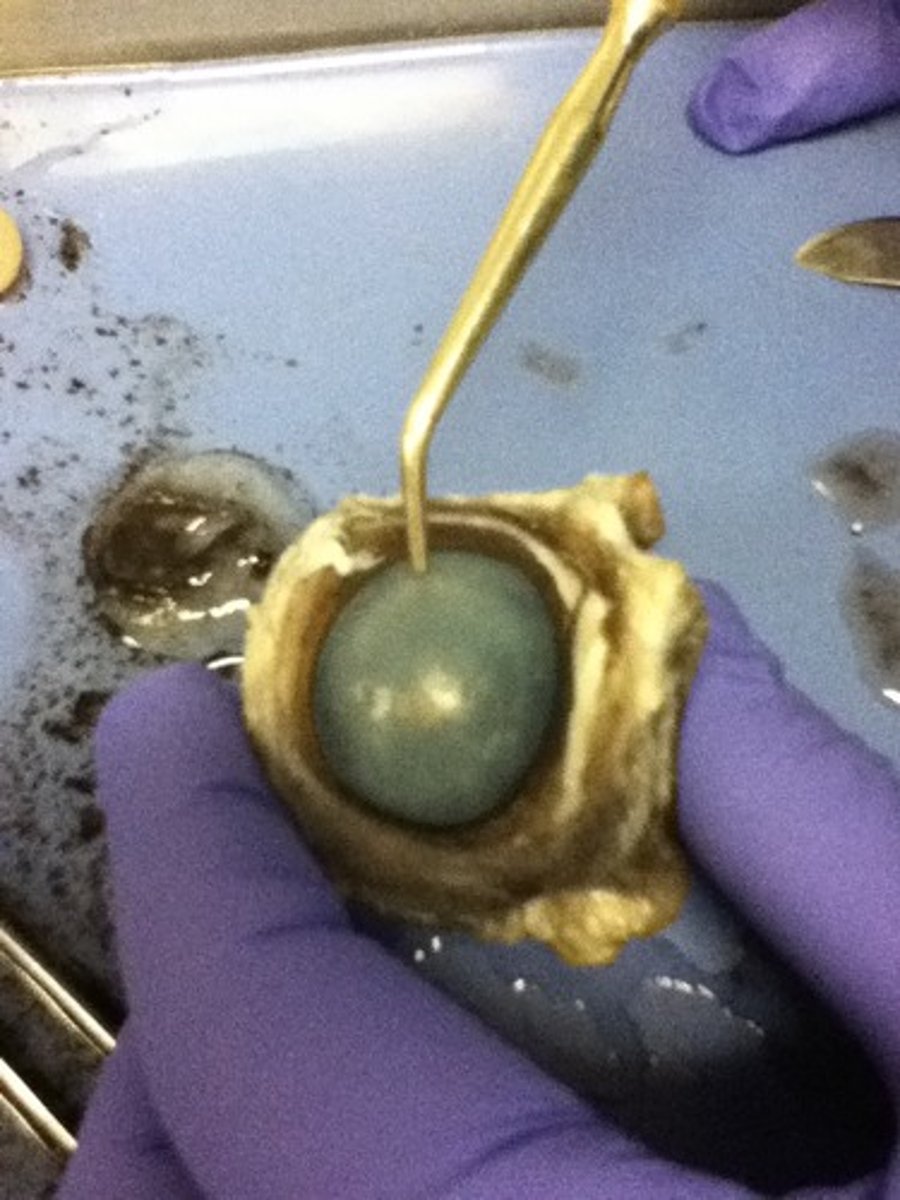
sclera
the white outer layer of the eyeball. At the front of the eye it is continuous with the cornea
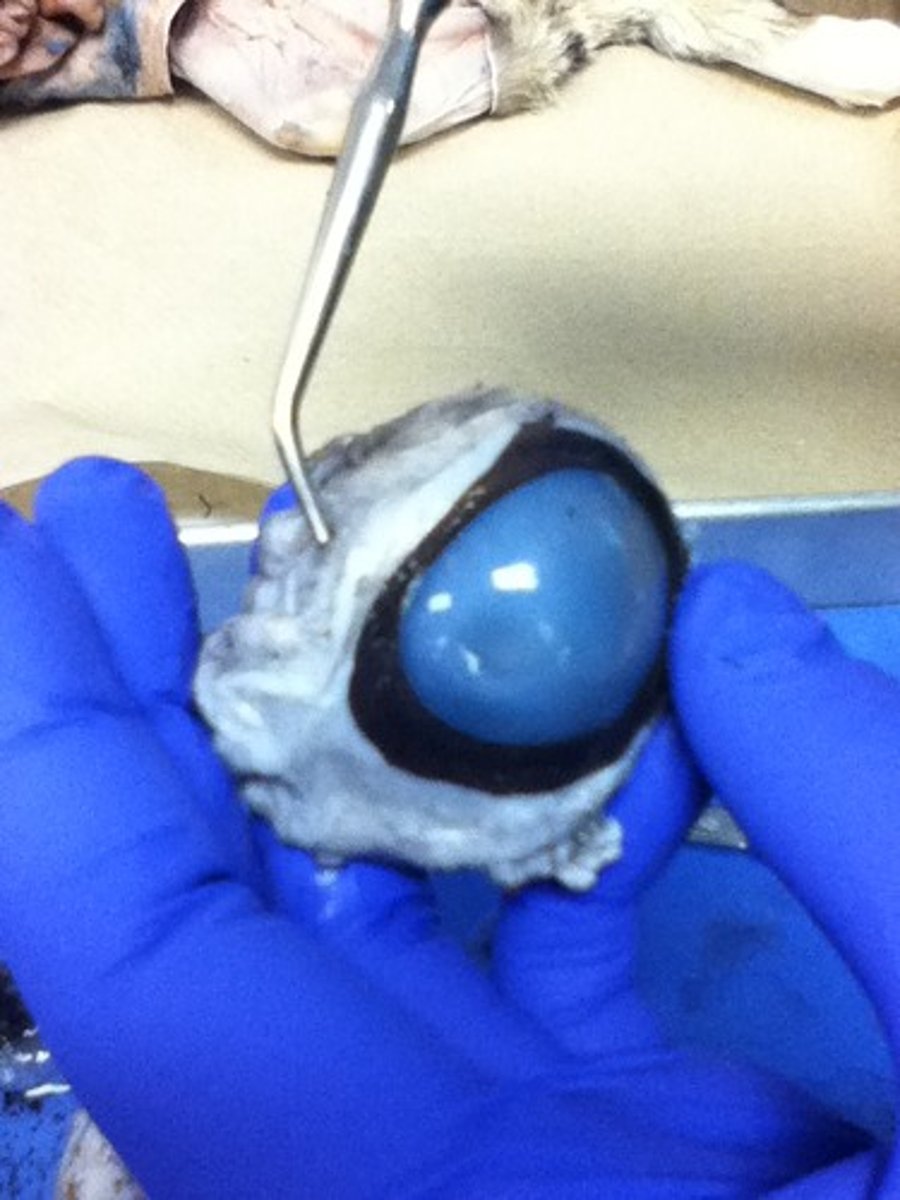
aqueous humor
transparent, watery fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary epithelium, a structure supporting the lens

vitreous humor
the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball of humans and other vertebrate

optic tract
continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm