Bio98 Lec 10 Glycolysis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
3 Primitive Functions of Metabolism
Generate chemical energy (ATP)
Transport electrons (NADH and NADPH)
Synthesize macromolecules needed for cell growth and survival.
2 Major types of metabolism
Anabolic and catabolic.
Anabolism
Making of macromolecules using NADPH and FADH2. (ATP & NADH are also required in the process.)
-Precursor molecules: amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, nitrogenous bases.
-They undergo anabolism to become cell macromolecules: proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids.
Catabolism
-Breakdown food into energy using NAD+ & FAD. NADP+ and ADP + HPO4²- are also involved.
-Energy containing nutrients (food): carbohydrates, fats, proteins.
-^^will undergo catabolism to turn into energy-depleted end products: CO2, H2O, and NH3.
SUMMARY: The metabolic process that breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy by converting nutrients into ATP and other energy carriers. It involves the degradation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into CO2, H2O, and NH3.
The Whole Glycolysis Pathway
Investment/Preparatory Phase: In this phase, energy is invested to convert glucose into a more reactive form. ATP is consumed to phosphorylate glucose and its derivatives, preparing them for subsequent reactions. (first 5 steps)
Payoff Phase: Oxidative conversion of glyceraldehyde 30phosphate into pyruvate. This phase results in the coupled formation of ATP and NADH, providing a net gain of energy for the cell. (last 5 steps)
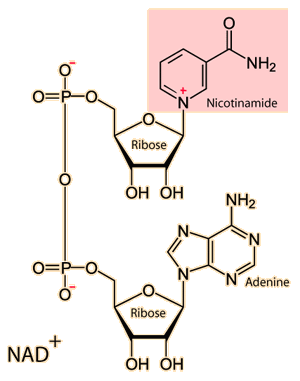
What is this?
NAD+ - one of 2 energy currencies
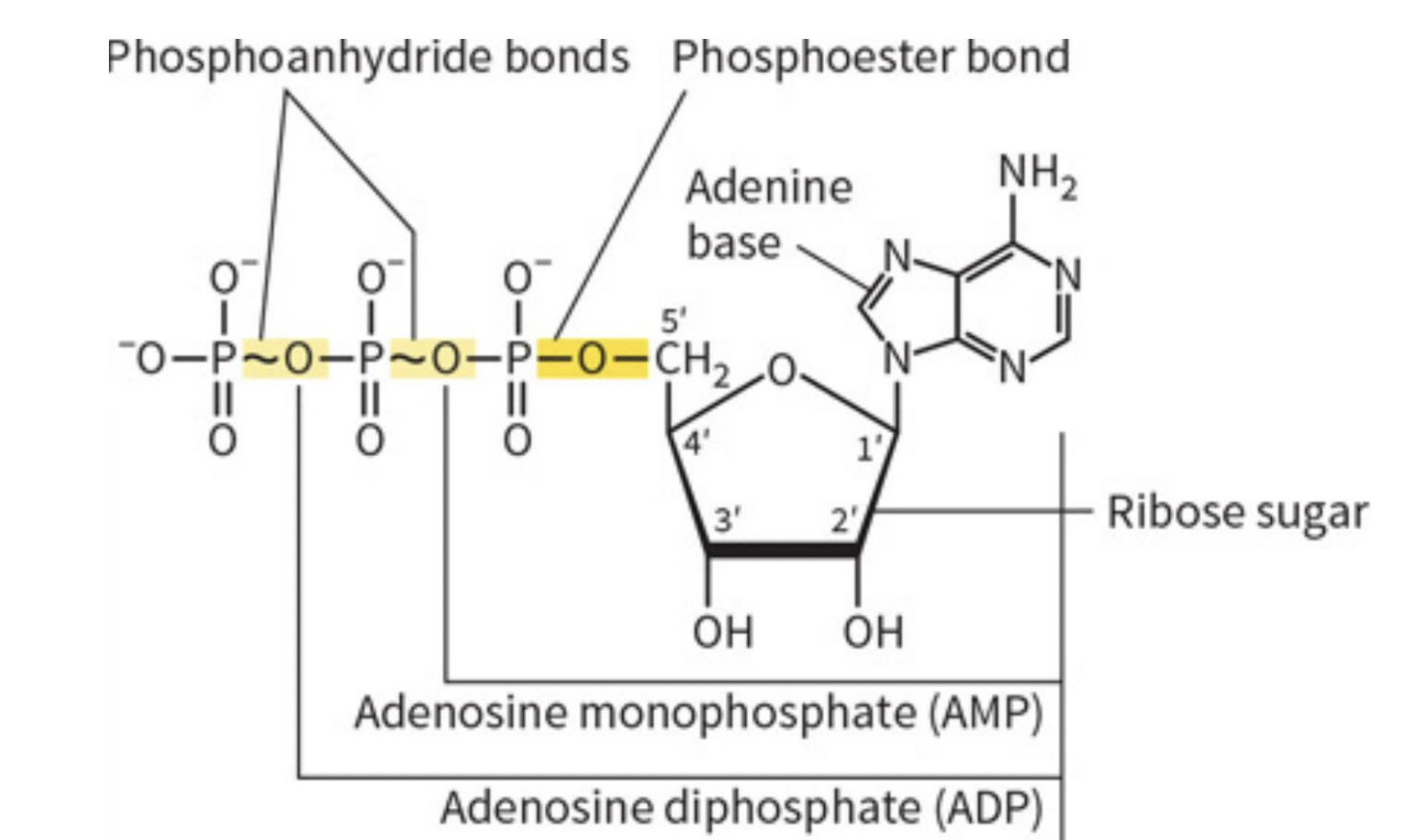
What is this?
ATP - one of 2 energy currencies
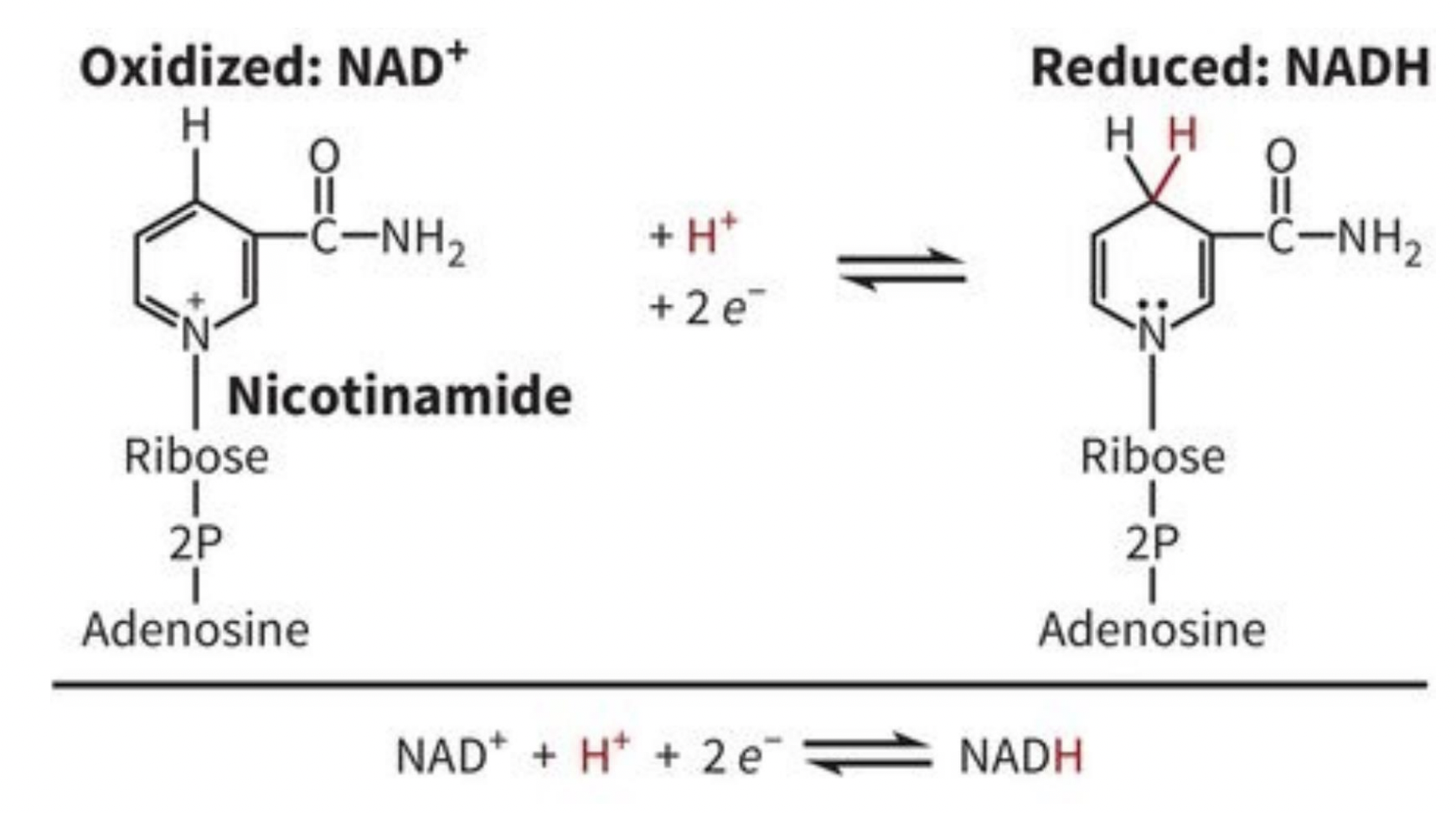
What is oxidation? What is reduction?
Oxidation: loss of electrons. (NAD+= loss of 2 electrons and H)
Reduction: gain of electrons. (NADH = gain of 2 electrons + H)
OIL RIG
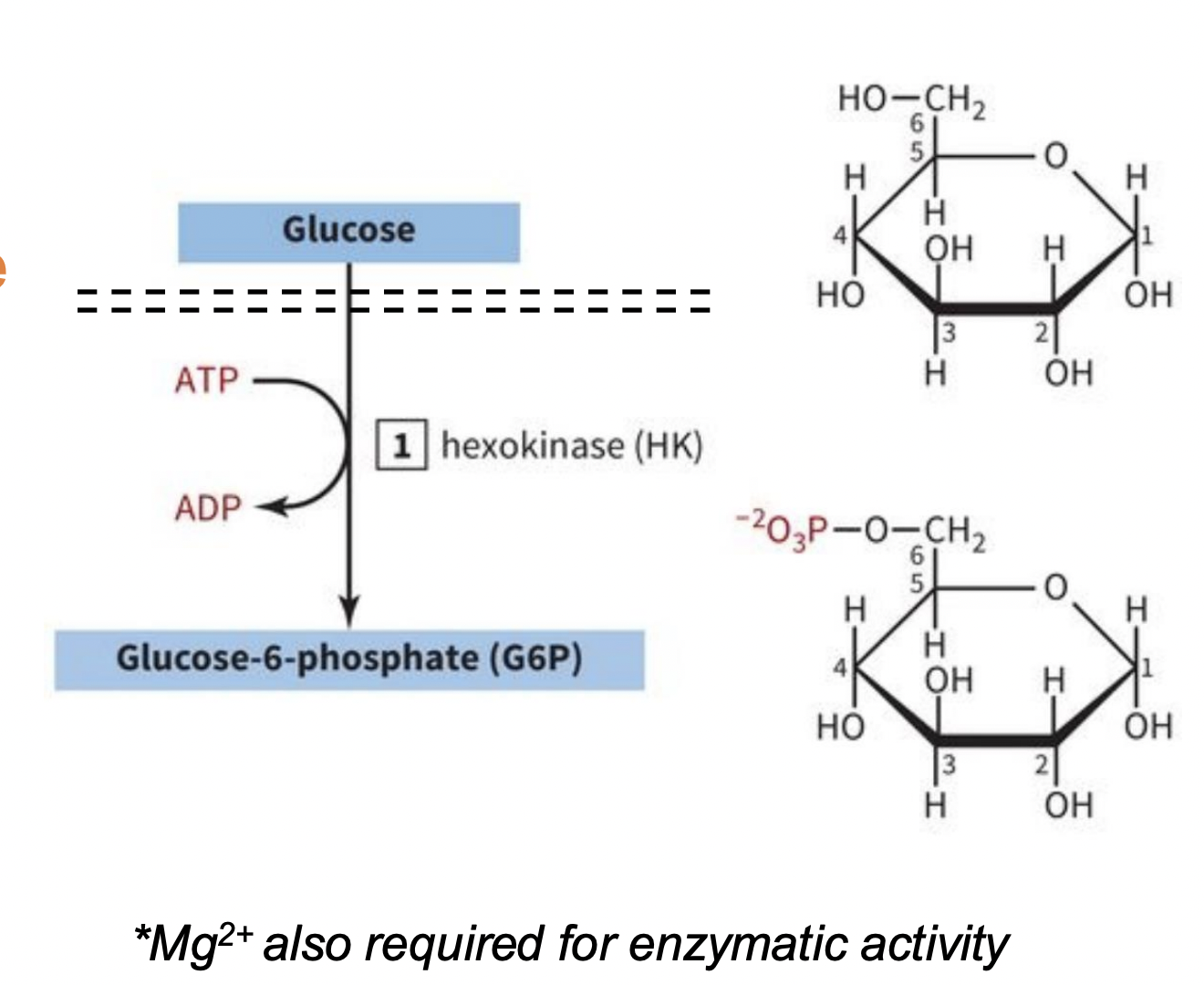
INVESTMENT/PREPARATORY PHASE STEP 1: Glucose Phosphorylation
-glucose is actively brought into cells through transporters
-hexokinase: enzyme that phosphorylates the glucose
-this traps glucose in the cell
-1st of 3 irreversible reactions in glycolysis
-uses 1 ATP per glucose molecule* (ATP → ADP through hexokinase; irreversible!!)
-kinase: enzyme that phosphorylates things
Mg2+ also required for enzymatic activity
what enzyme does step 1? what does it do?
hexokinase (HK): phosphorylates the glucose
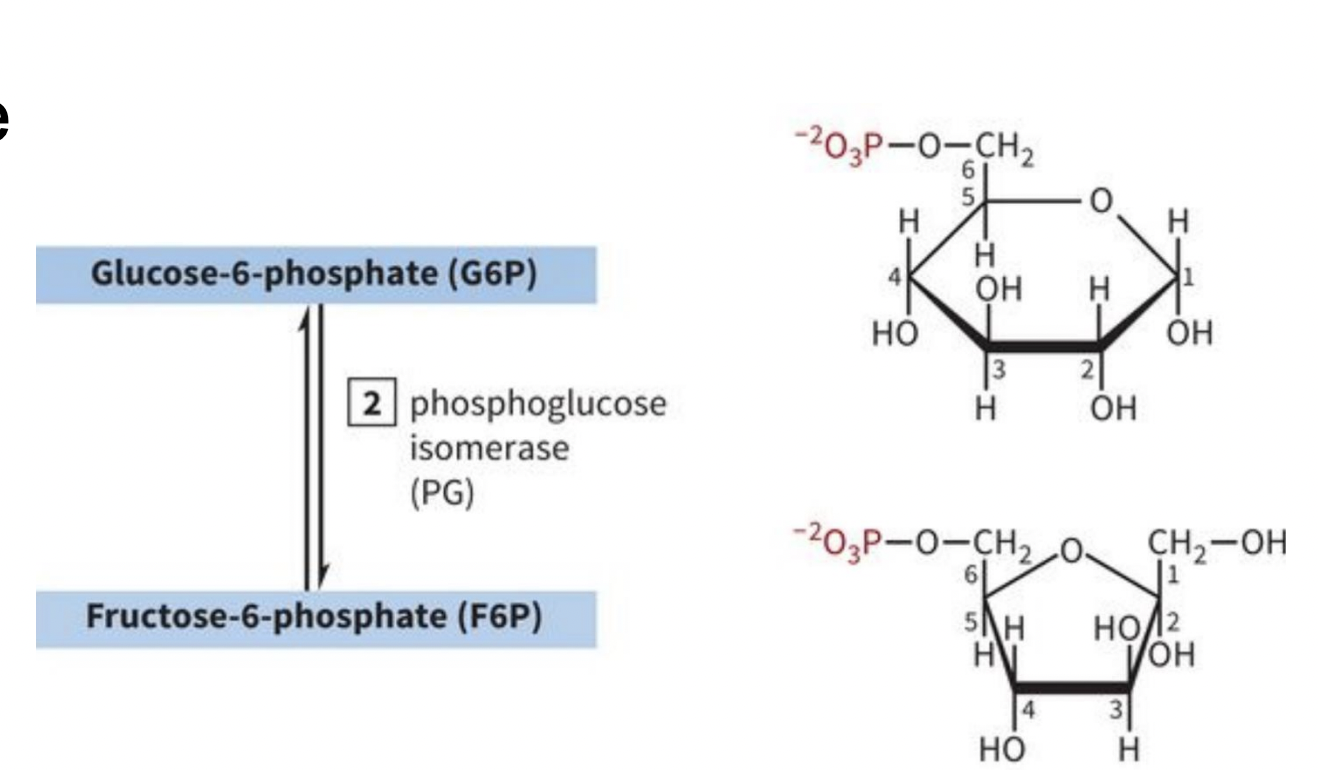
INVESTMENT/PREPARATORY PHASE STEP 2: Glucose Isomerization
-Isomerization= changing the shape, maintaining the same number of carbons
-Reversible rxn
-gets the sugar ready for next step
-Pyranose to furanose ring, fructose is less stable than glucose
-it basically converts glucose into fructose (G6P←→F6P ; reversible!!)
what does step 2?
phosphoglucose (or phosphohexose) isomerase (PGI): glucose isomerization (glucose to fructose)
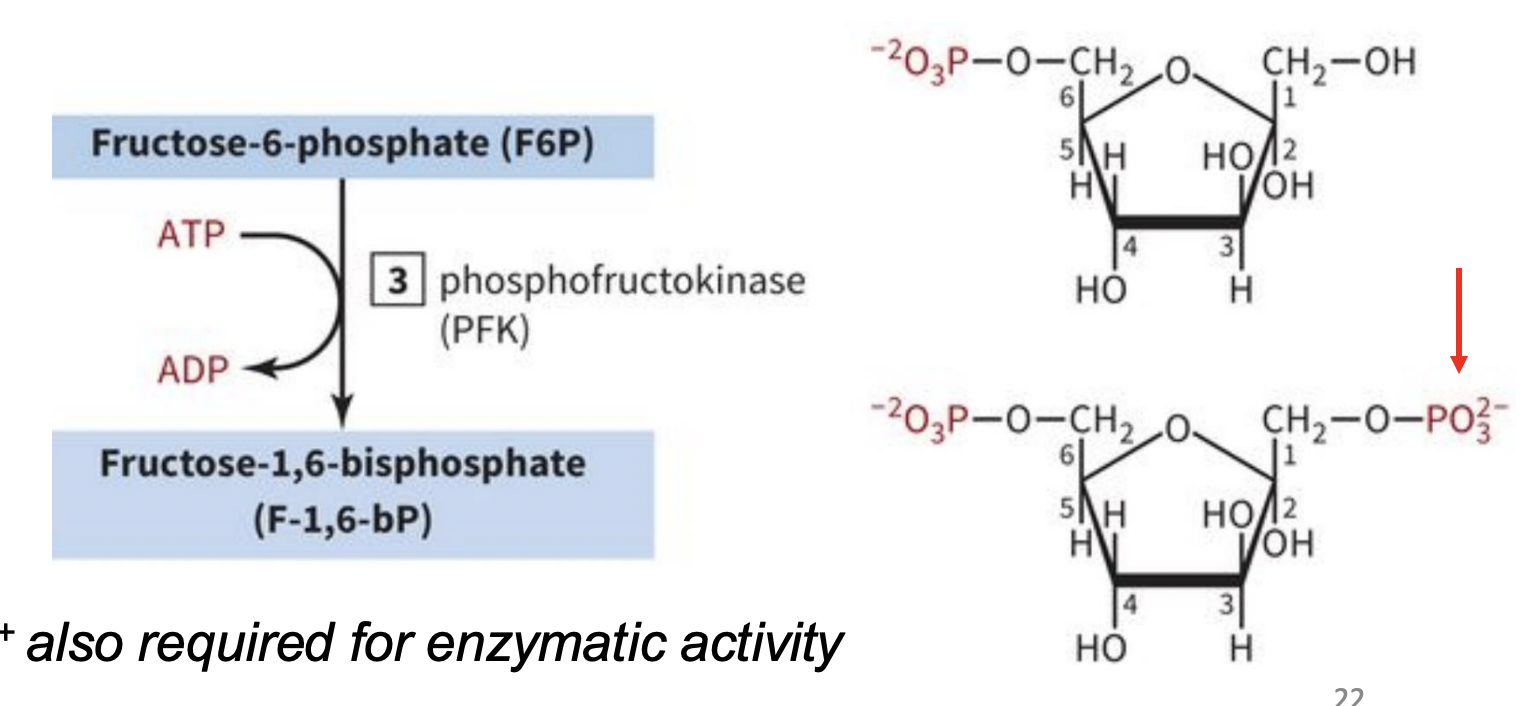
INVESTMENT/PREPARATORY PHASE STEP 3: Phosphorylation of Fructose
-Phosphate group added to carbon 1
-carried out by phosphofructokinase (F6P→F-1,6-bP)
-Uses ATP* (ATP→ADP bc^^)
-2nd irreverisible rxn
-highly negative ΔG
*Mg2+ also required for enzymatic activity
what enzyme does step 3?
phosphofructokinase: phosphorylates fructose into F-1,6-bP
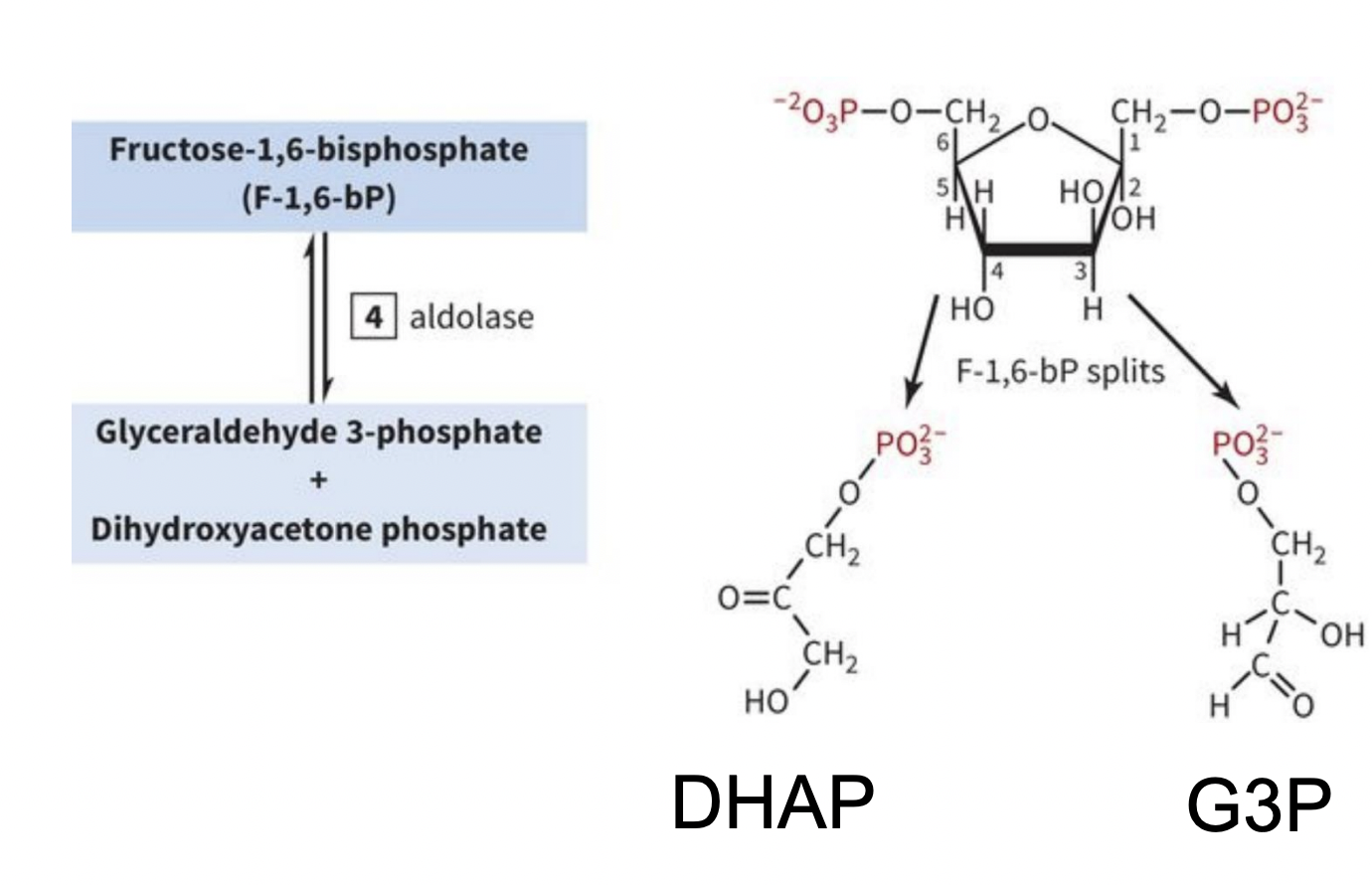
INVESTMENT/PREPARATORY PHASE STEP 4: Cleavage of 6-carbon Sugar to 2 3-carbon intermediates
-carried out by aldolase (F-1,6-bP → glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate OR G3P + DHAP)
lase = enzyme that breaks things down
-generates 2 different products, both cannot be further oxidized in that form (irreversible rxn)
what enzyme carries out step 4? what does it do?
aldolase: cleaves 6-carbon sugar to 2 3-carbon intermediates (that cannot be oxidized, ie DHAP + G3P)
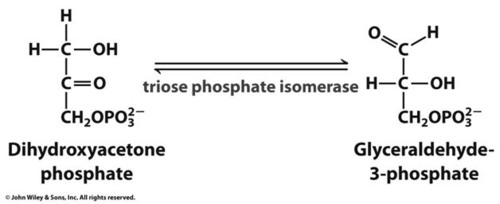
INVESTMENT/PREPARATORY PHASE STEP 5: Isomerization of DHAP to G3P
-For DHAP to be oxidized, it is converted to G3P by triose phosphate isomerase (TIM)
-Famous structure: TIM barrel
what does step 5?
triose phosphate isomerase (TIM/TPI): DHAP converts to or is isomerized into G3P
What is the overall ATP usage in the investment phase?
2 ATP
PAYOFF PHASE (to keep in mind)
-everything is in double amount because we have 2X G3P
-every intermediate has only 3 carbons in this phase
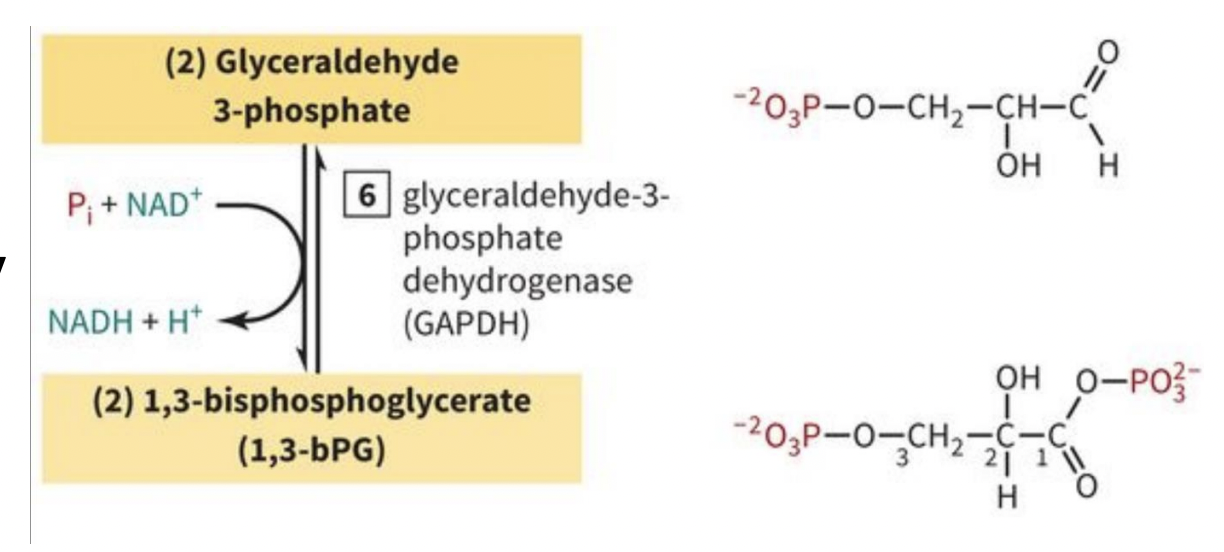
PAYOFF PHASE STEP 6: Oxidation of G3P to 1,3-BPG
-Inorganic phosphate (Pi) and oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+): used by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GADPH) to make 1,3-BPG
-this is an electron transfer
-stored energy that’s used in many other rxns
-this is why the process is starting to payoff
-REMINDER: 2 rxns per 1 glucose (2Pi, 2NAD+, 2 NADH + H+)
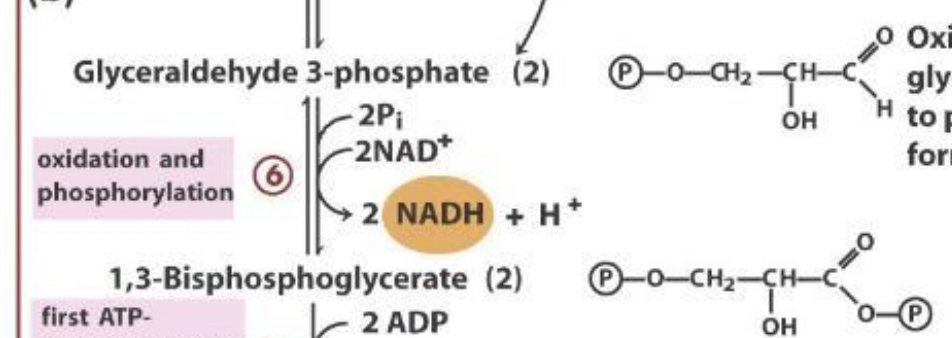
what’s in charge + used to make 1,3-BPG in step 6?
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GADPH) uses inorganic phosphate (Pi) and oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
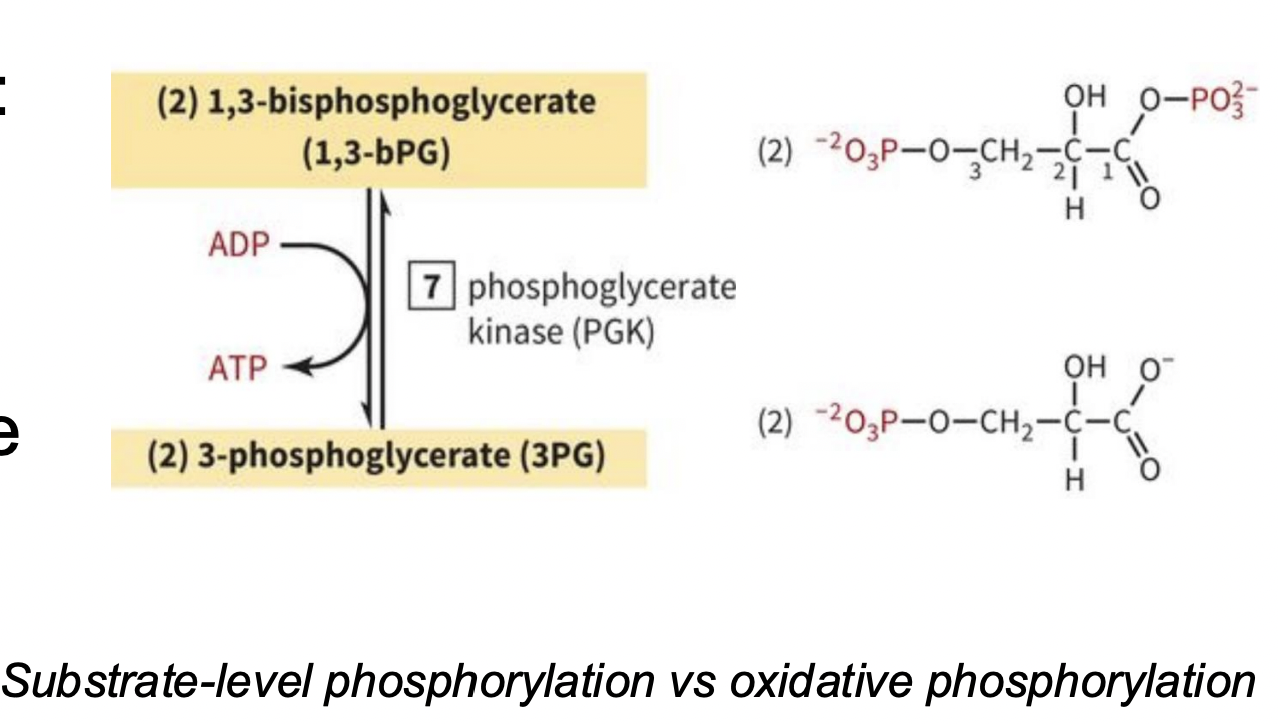
PAYOFF PHASE STEP 7: ADP is Phosphorylated to ATP using a phosphate from 1,3-BPG
-mediated by another kinase: phosphoglycerate kinase
-unusual that kinase removes a phosphate, but it can also do the reverse (which is where it gets its name)
-REMINDER: 2 rxns/1 glucose (2 ADP→2 ATP)

kinase used in step 7?
phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK): ADP is phosphorylated to ATP w/ a phosphate from 1,3-BPG
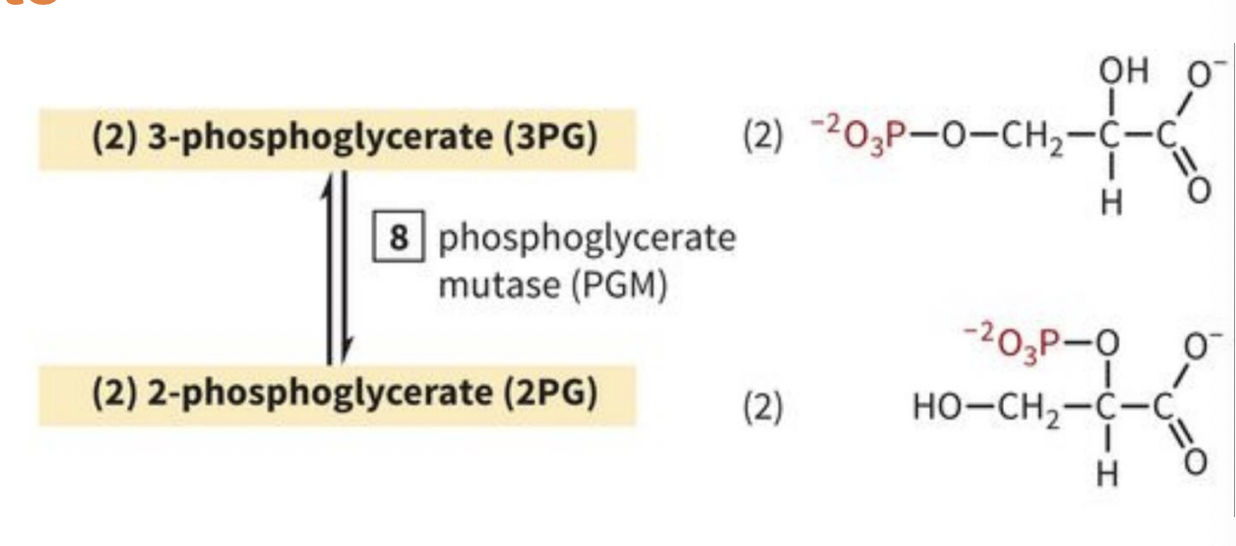
PAYOFF PHASE STEP 8: 3PG is isomerized to 2PG
-mediated by phosphoglycerate mutase
-the 3-phosphate’s moved to 2-position
-costs no energy, creates no energy, but needed for next step
REMINDER: 2 rxns/1 glucose
what’s used for step 8?
phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM): isomerizes 3PG to 2PG

PAYOFF PHASE STEP 9: 2PG is dehydrated to phosphoenolpryuvate (PEP)
-mediated by enolase
-loss of water (dehydration)
REMINDER: 2 rxns/ 1 glucose (2 H2O gone)
what’s used in step 9?
enolase: 2PG gets hydrated to phosphoenolpyruvate
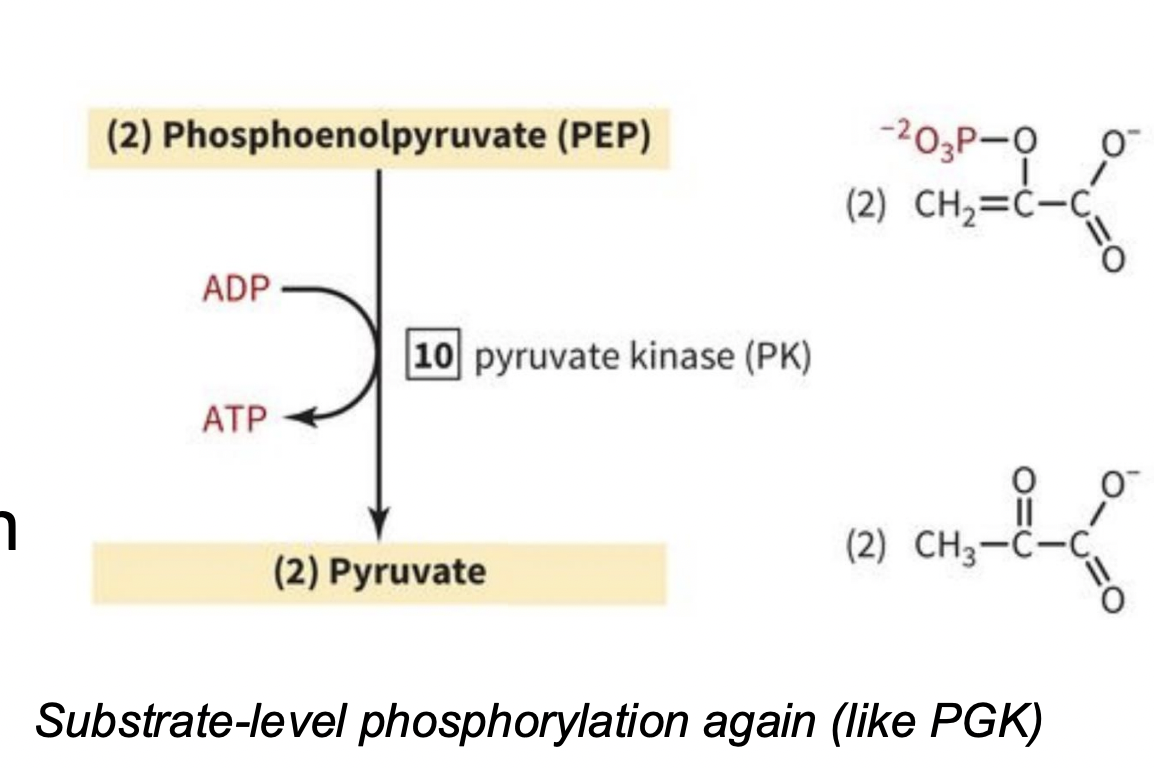
PAYOFF PHASE STEP 10: PEP is converted to pyruvate
Pyruvate kinase: takes the phosphate off PEP and phosphorylates ADP to ATP
-LAST irreversible step
-Phosphorylation of nucleotide (NOT protein)
-REMINDER: 2 rxns/1 glucose (2 pyruvates, 2ADP→2 ATP)
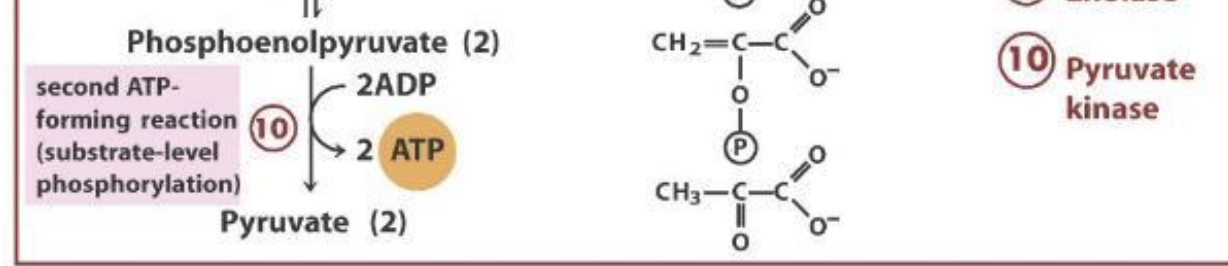
what does step 10?
pyruvate kinase (PK): takes the phosphate off PEP and phosphorylates ADP to ATP (2); makes 2 pyruvates too
GLYCOLYSIS RECAP
1 Glucose => 2Xs Pyruvate + 2Xs NADH + 2ATP (net)
uses 2 ATP but generates 4
Pyruvate isn’t the end product of metabolism (is either further oxidized or fermented)