Module 20: Hearing, Skin, Chemical, and Body Senses
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Audition
Hearing
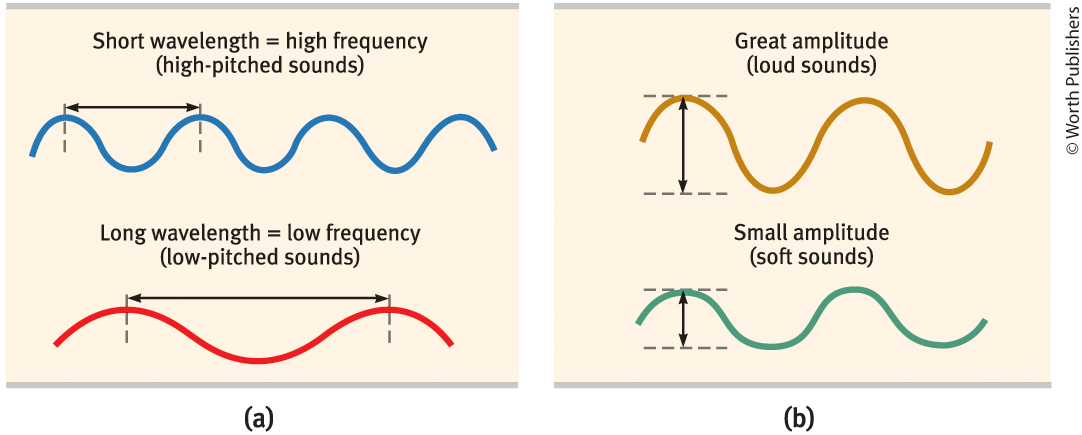
Pitch
A tone’s experiences highness or lowness, depends on frequency
Frequency
The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time (measured in hertz)
Decibels
Measure of sound intensity
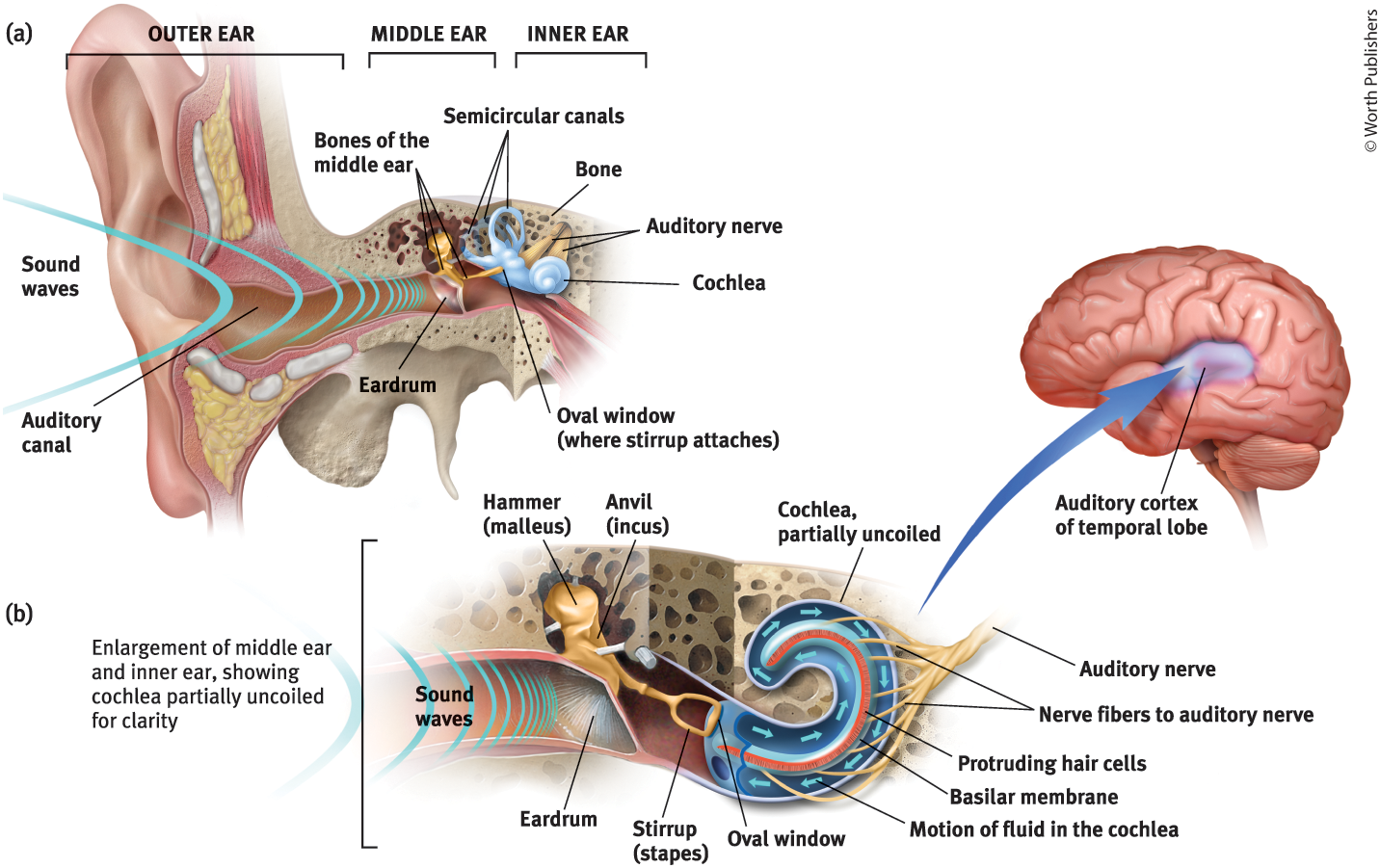
Middle Ear
The chamber between the eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window
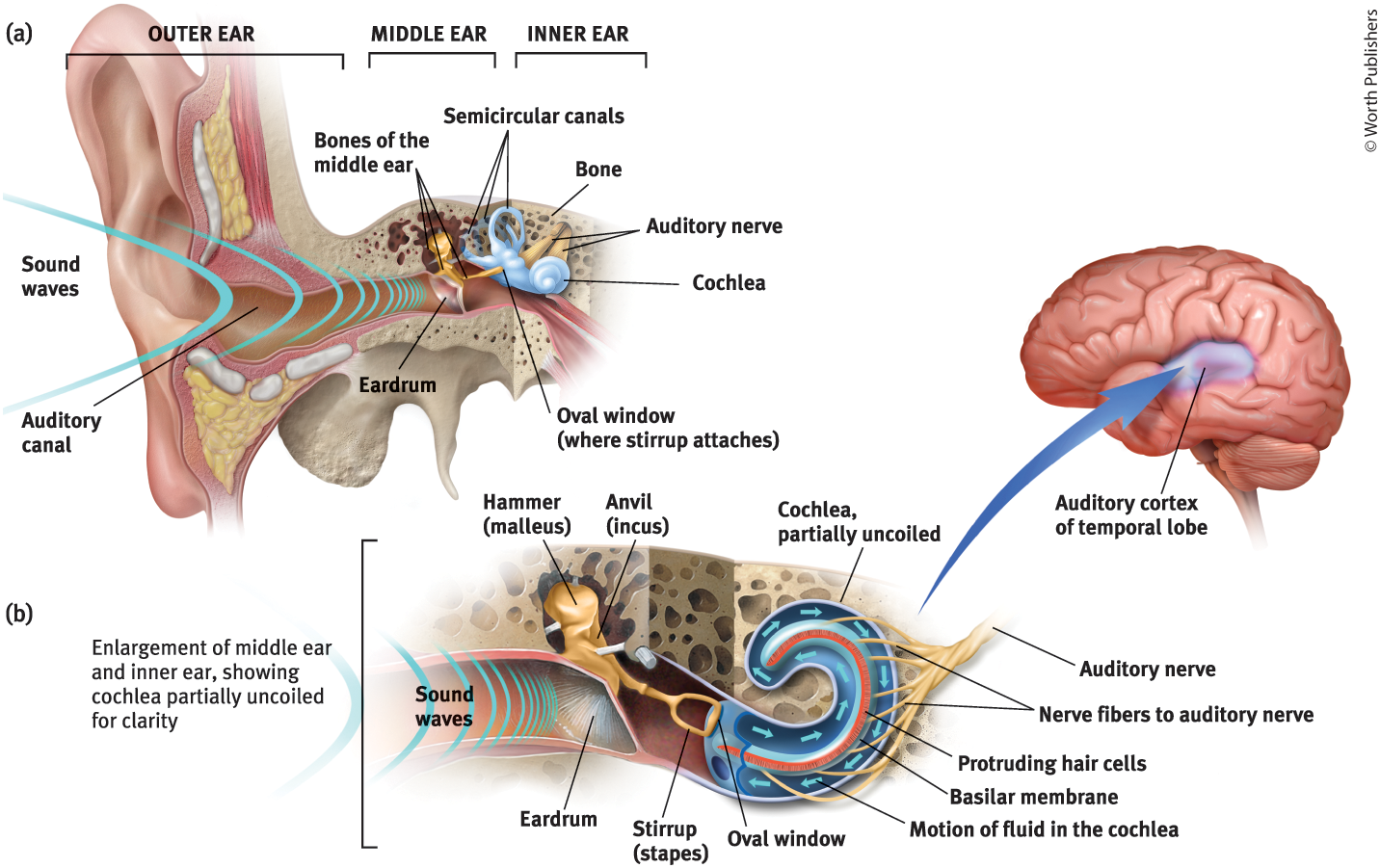
What are the 3 tiny bones in the middle ear?
Hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), and stirrup (staples)
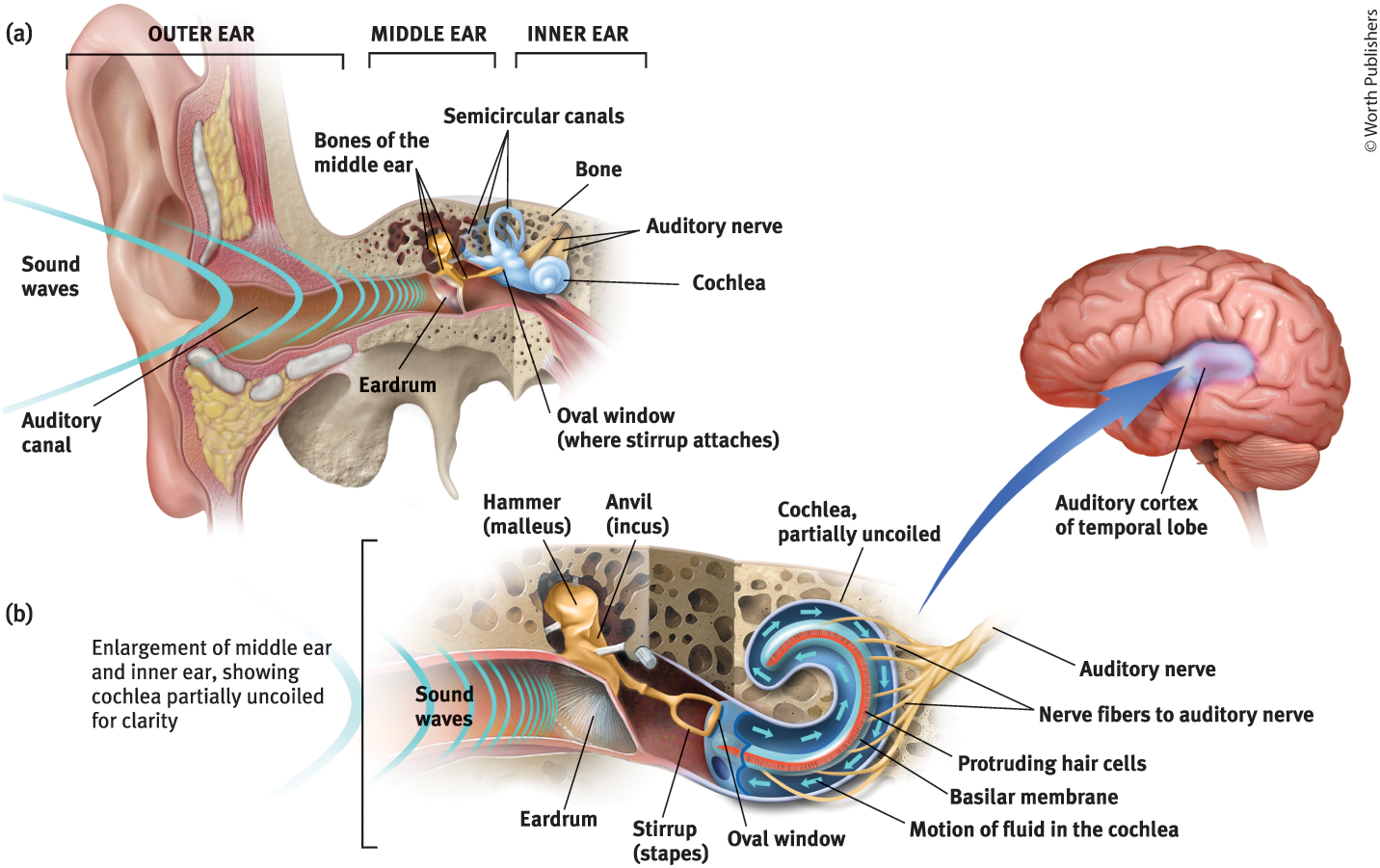
What is the purpose of the three tiny bones in the middle ear?
They pick up the vibrations of sound and transmit them to the cochlea

Cochlea
Coiled, boney fluid-filled tube in the inner ear
Sound waves traveling through the cochlear fluid trigger…
nerve impulses
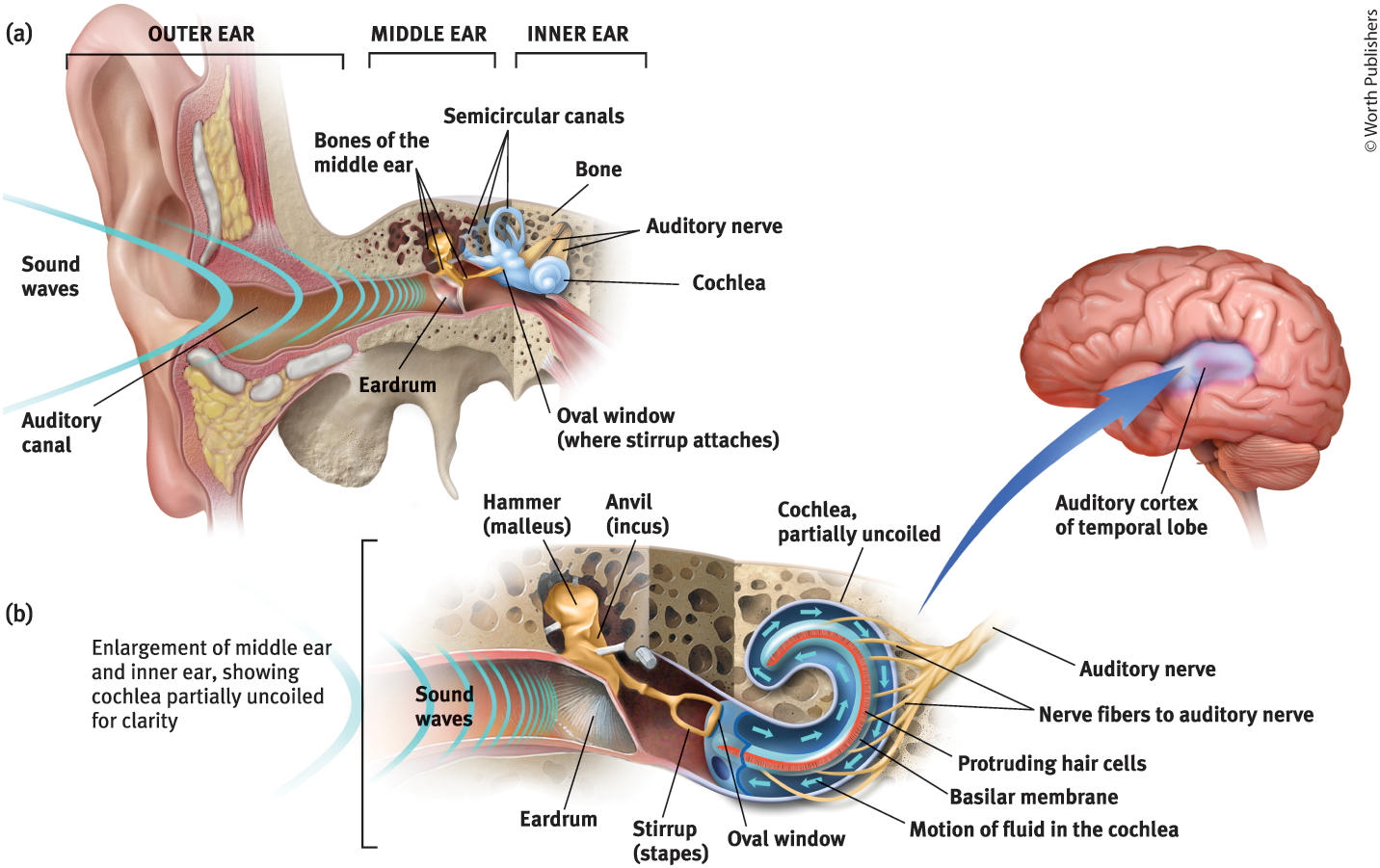
Inner Ear
The innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs
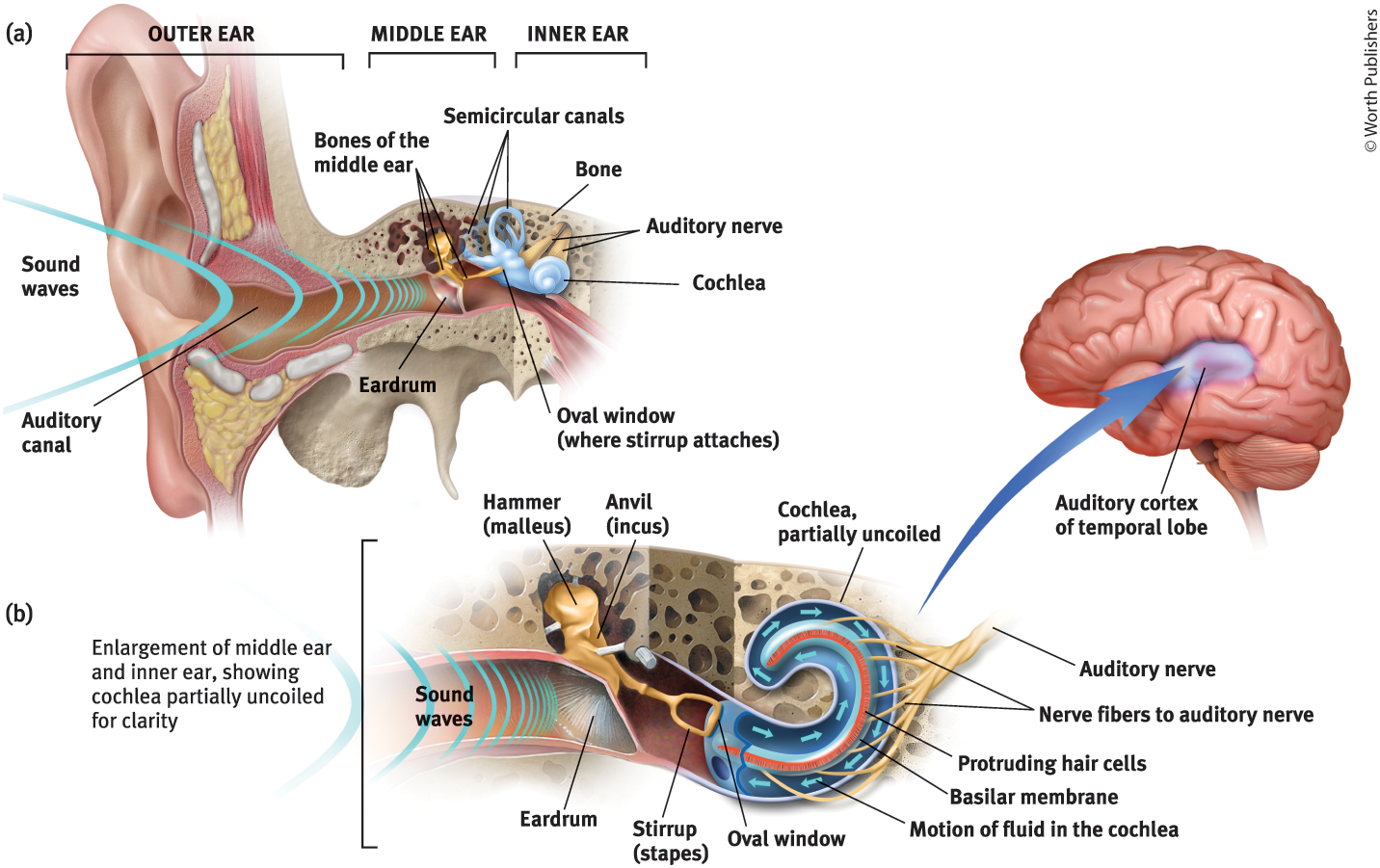
Oval Window
Cochlea’s membrane-covered opening

Purpose of the Oval Window
Vibrates, moving the fluid inside the cochlea
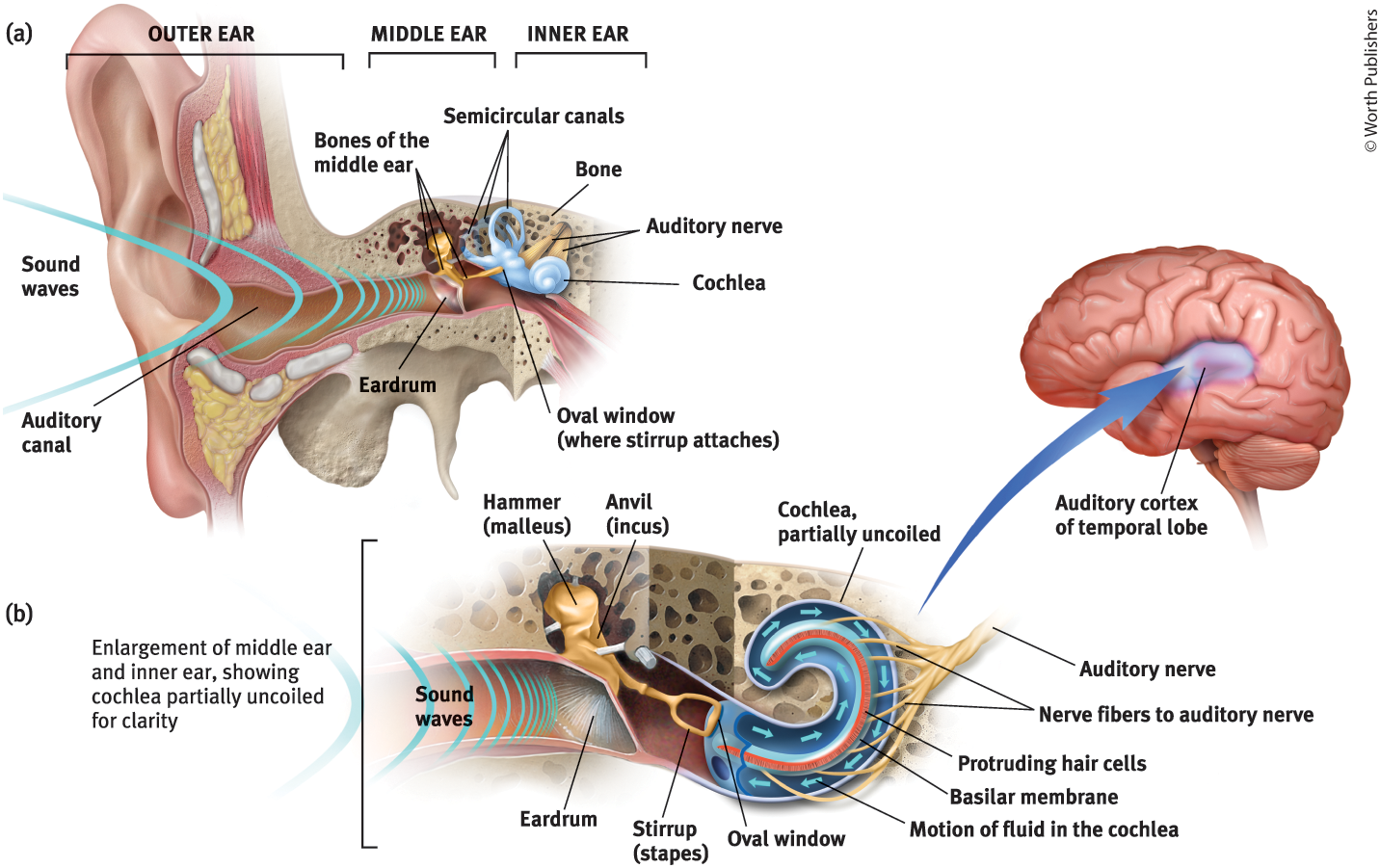
The motion of the fluid in the cochlea causes…
Ripples in the basilar membrane

The ripples in the basilar membrane leads to…
bending of the hair cells lining its surface, which triggers impulses in adjacent nerve cells
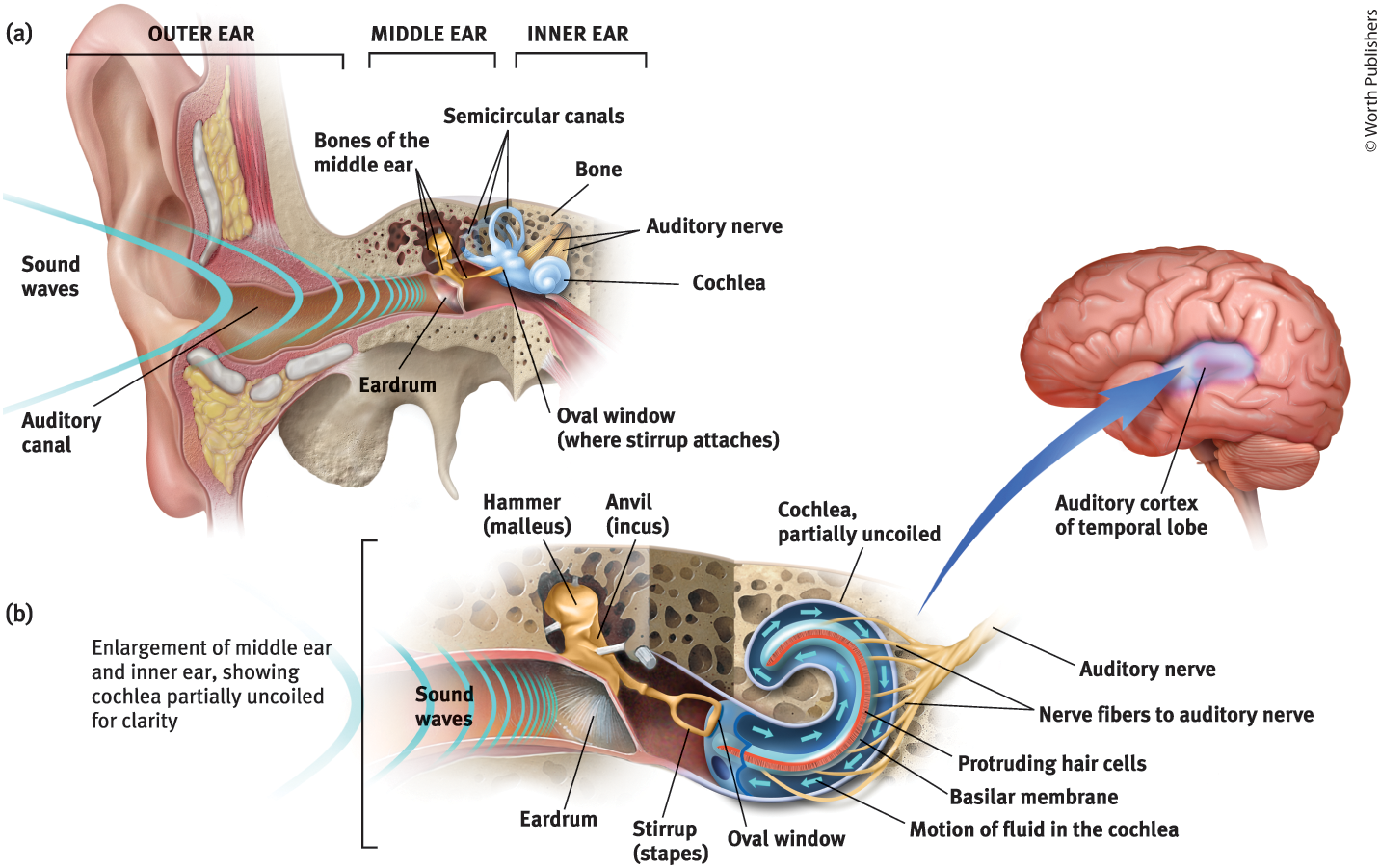
When impulses in adjacent nerve cells are triggered in the ear…
axons connect those nerve cells to form the auditory nerve
Auditory Nerve
Carries neural messages to the thalamus and then to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Most common form of hearing loss, caused by damage in the cochlea’s receptor cells or to the auditory nerve (also called nerve deafness)
Conduction Hearing Loss
Less common form of hearing loss, caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea
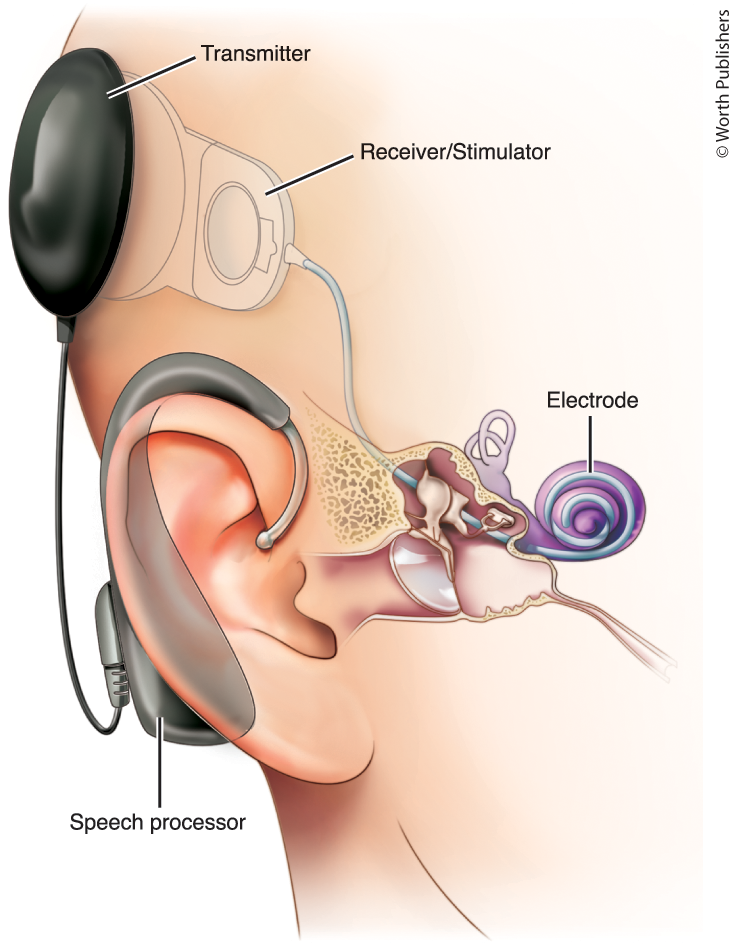
Cochlear Implant
Device for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve through electrodes threaded into the cochlea
Place Theory
The theory that different sound frequencies activate different locations along the cochlea’s basilar membrane, allowing the brain to determine pitch depending on where the membrane vibrates (also called place coding)
Frequency Theory
The theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of the tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch (also called temporal coding)
Nociceptors
Sensory receptors that detect hurtful temperatures, pressure, or chemicals - brain processes these sensations and then produce perceptions of pain (mostly located in skin, but also on other organs)
Gate-Control Theory
Theory that the spinal cord contains a neurological ‘gate’ that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain
How does the gate-control theory work?
The ‘gate’ is opened by the activity of pain signals traveling up small nerve fibers and is enclosed by activity in larger fibers or by information coming from the brain
Endorphins
Natural painkillers that are released in response to strong pain or vigorous exercise
Phantom Limb Sensations
Brain may misinterpret and amplify spontaneous but irrelevant central nervous system activity without normal sensory imput from a missing limb
Tinnitus
The phantom sound of ringing in the ears
Who experiences phantom sights/hallucinations?
It occurs in those who lose vision
The 2 factors of memory snapshots that are recorded
Pain’s peak (worst moment)
Amount of pain at the end
Longer duration of pain=…
less painful over time
What can help reduce pain (other than having it for a longer duration of time)?
Placebos, distractions, and hypnosis
Hypnosis
Social interaction where one person (hypnotist) suggests to another (the subject) that certain perceptions, feelings, thoughts, or behaviors will spontaneously occur
Social Influence Theory
States that hypnosis is a by-product (results from) normal social and mental processes
Dissosiation Therapy
States that hypnosis is a special dual-processing state of dissociation, this theory seeks to explain why, when no one is watching, previously hypnotized people may carry out post-hypnotic suggestions
Dissociation
A split in different levels of consciousness, allows some thoughts and behaviors to occur simultaneously with others
Posthypnotic Suggestions
A suggestion, made during a hypnosis session, to be carried out after the subject is no longer hypnotized
Why are posthypnotic suggestions used by some clinicians?
To help control undesired symptoms and behaviors
Selective Attention
Attention is redirected to a particular stimuli, plays a role in hypnotic pain relief
Gustation
Our sense of taste
How does gustation work?
Each taste bud contains a pore that catches food chemicals and releases neurotransmitters
Olfaction
Our sense of smell
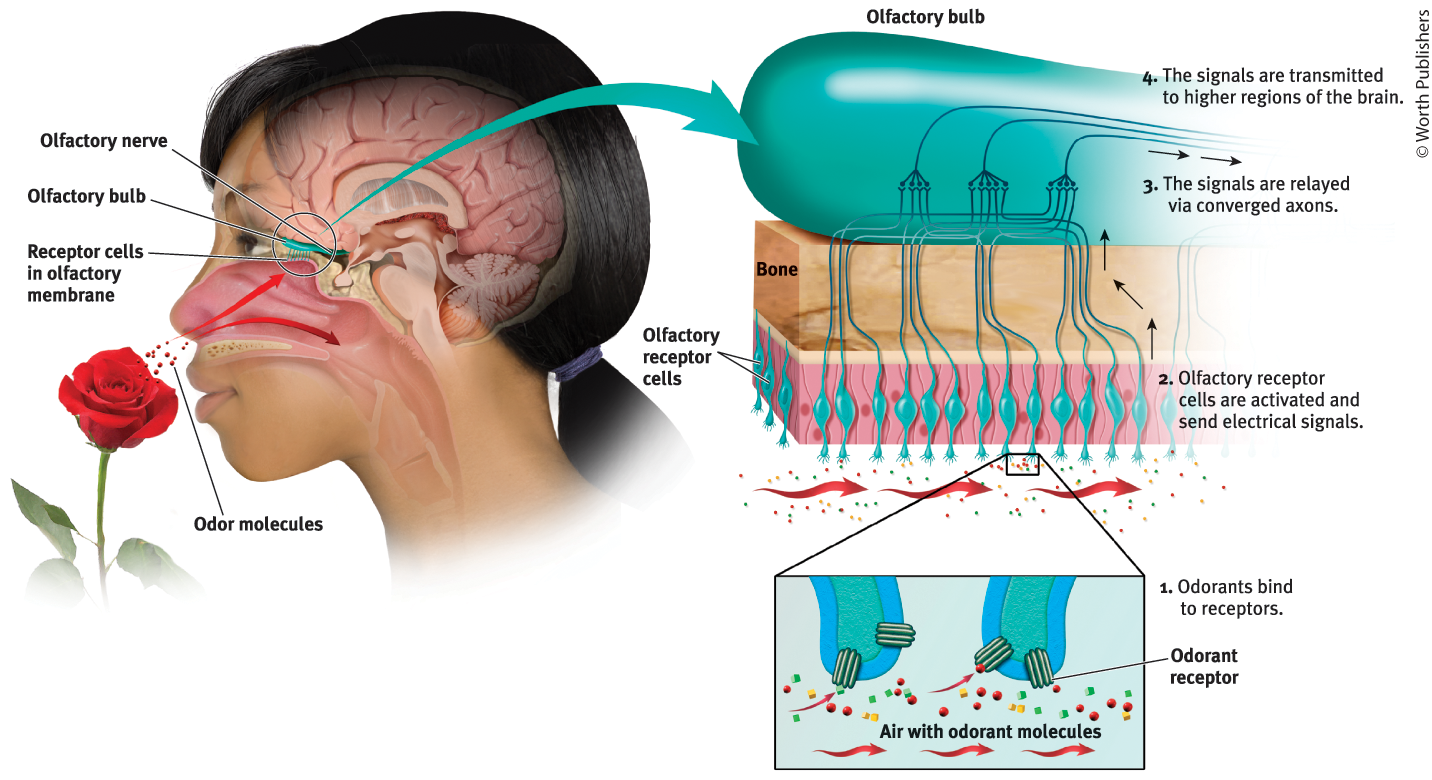
How does olfaction work?
Molecules of a substance carried in the air reach a tiny cluster of receptor cells at the top of each nasal cavity. Olfactory receptors then respond selectively
Pheromones
Chemical substance that can be smelled that affect the behavior or physiology of the person
How do pheromones work?
Hotline runs between brain area receiving info from nose and brain’s limbic centers associated with memory and emotion
Propioceptors
Position and motion sensors all over the body that provide constant feedback to the brain
Kinesthesia
Our movement sense, our system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
Vestibular Sense
Our balance sense, our sense of body movement and position that enables our sense of balance
We can be fooled by mechanisms that…
normally give us an accurate experience of the world
Sensory Interaction
The principle that one sense can influence another
The smell of food influences taste. This is an example of…
Sensory interaction
Embodied Cognition
The influence of bodily sensations, gestures, and other states on cognitive preferences and judgements
Synesthesia
The simulation of one sense triggers the experience of another
Some people who hear certain numbers think of it as a specific color in their head. This is an example of…
synesthesia
Extrasensory Perception (ESP)
The controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input. Includes telepathy, clairvoyance, and precognition
Telepathy
Mind-to-mind communication
Clairvoyance
Perceiving remote events (ex. knowing there is a house on fire across the country)
Precognition
Perceiving future events (ex. predicting unexpected events in the next month)
Parapsychology
The study of paranormal phenomena, includes ESP and telekinesis/psychokinesis (mind reading)
Auditory Canal
Tube in the outer ear that collects sound waves and sends them to the eardrum