Understanding the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Cell Division
Process for growth, repair, and reproduction.
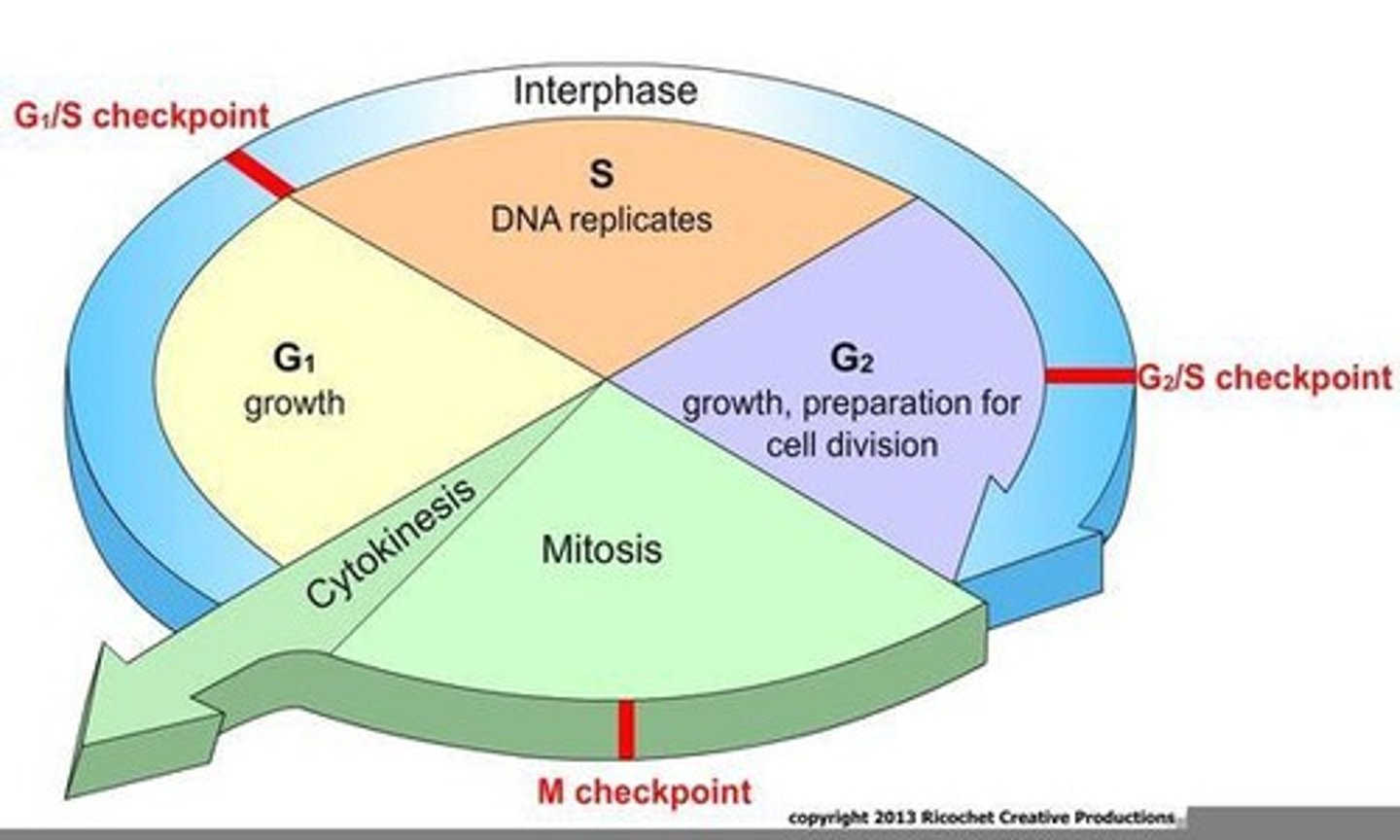
Mitosis
Asexual reproduction creating identical offspring.
Meiosis
Process producing gametes for sexual reproduction.
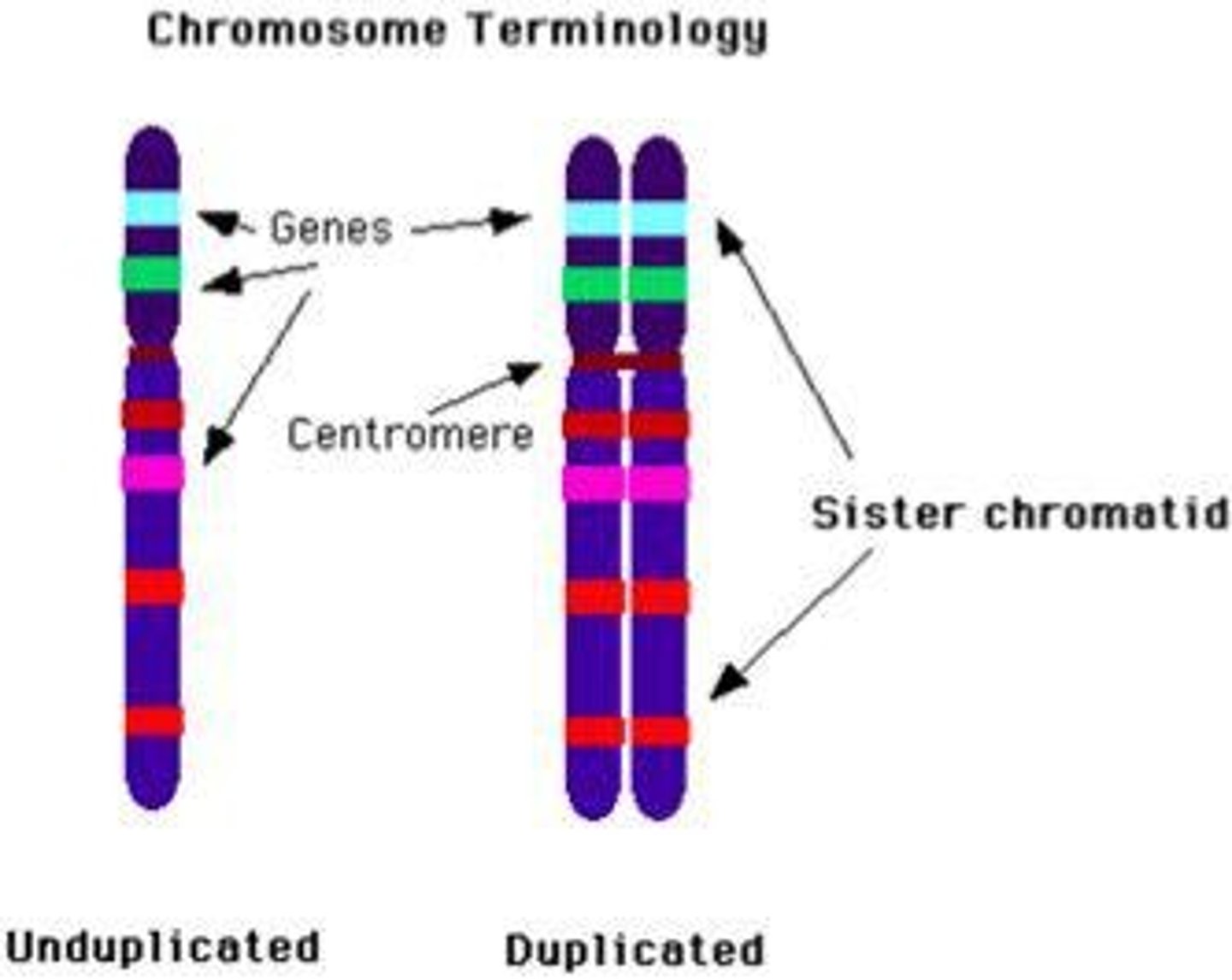
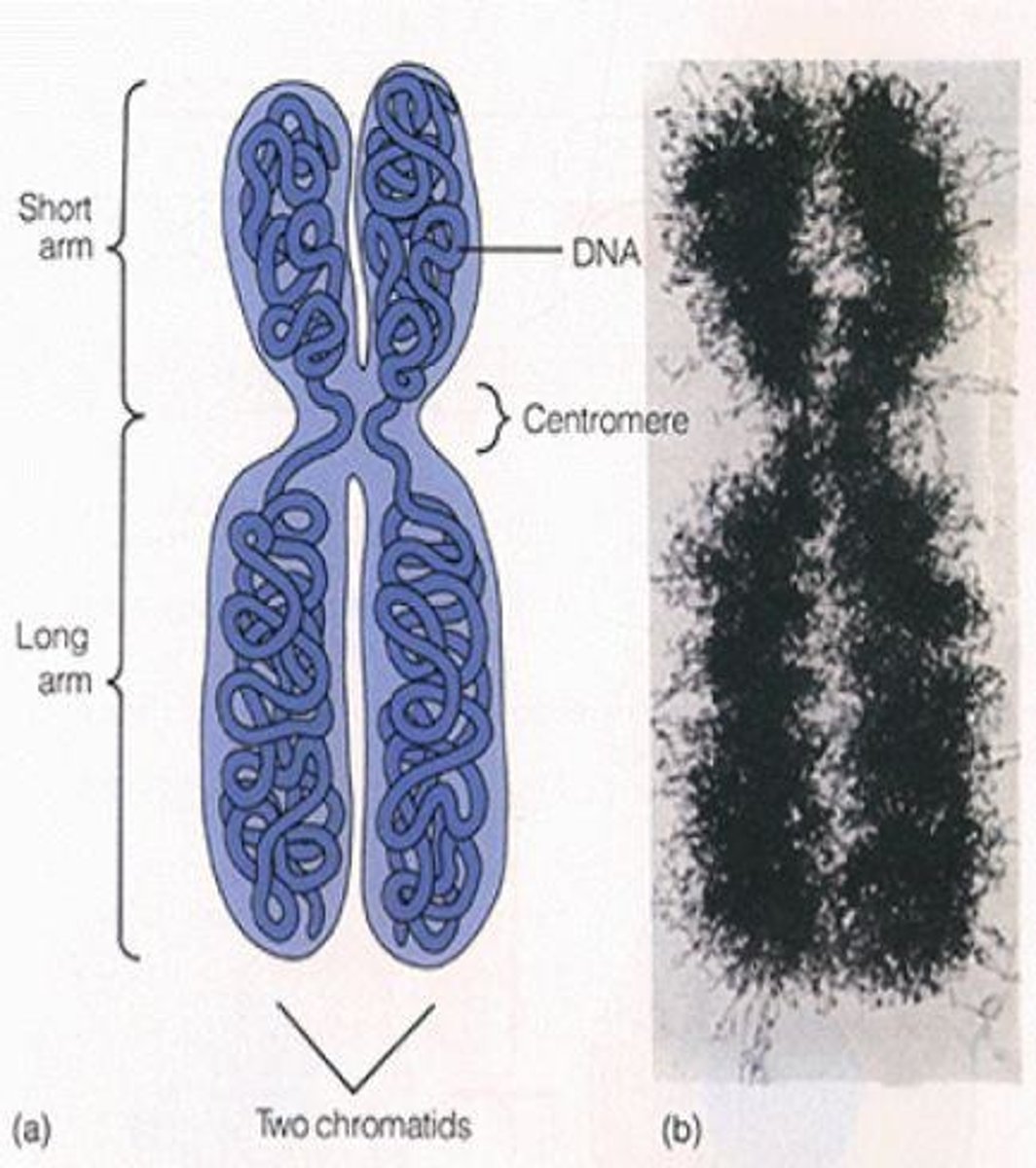
Chromosome
DNA structure containing genetic information.
Chromatid
Identical halves of a duplicated chromosome.

Centromere
Region connecting sister chromatids.
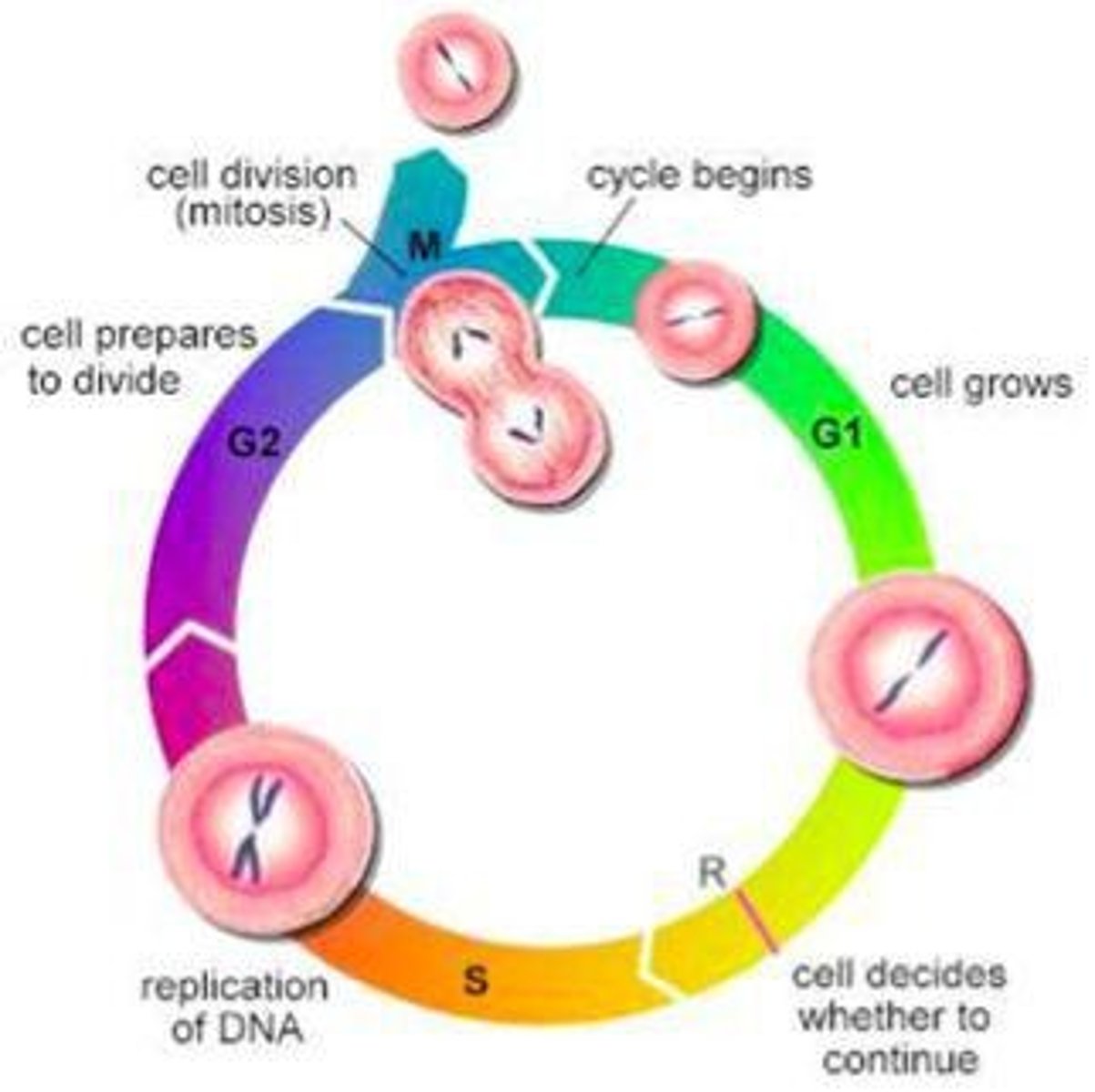
Interphase
Phase where the cell grows and performs functions.
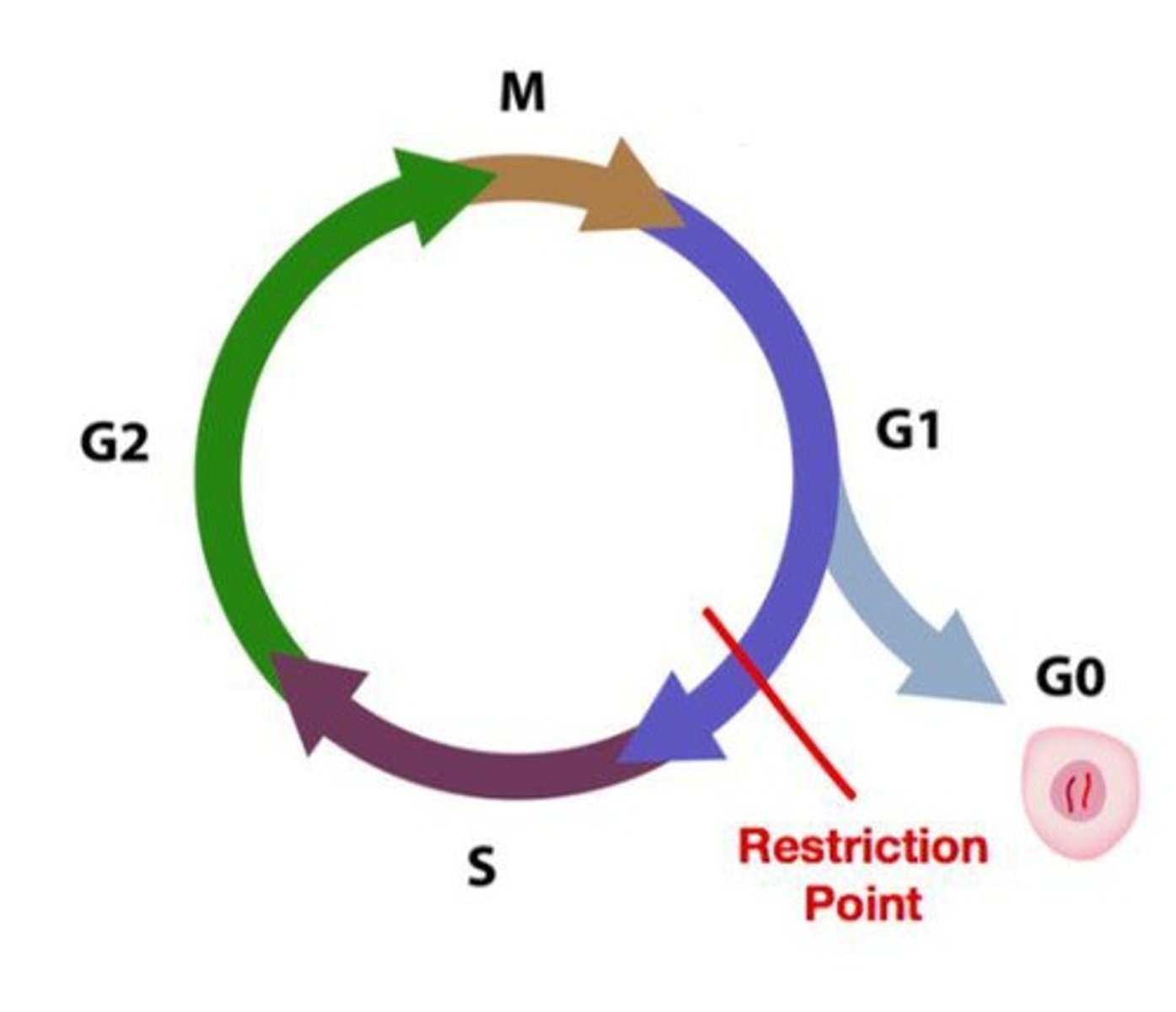
G1 Phase
First growth phase of the cell cycle.
S Phase
Phase where DNA is replicated.
G2 Phase
Second growth phase before mitosis.
Prophase
First stage of mitosis; chromosomes condense.
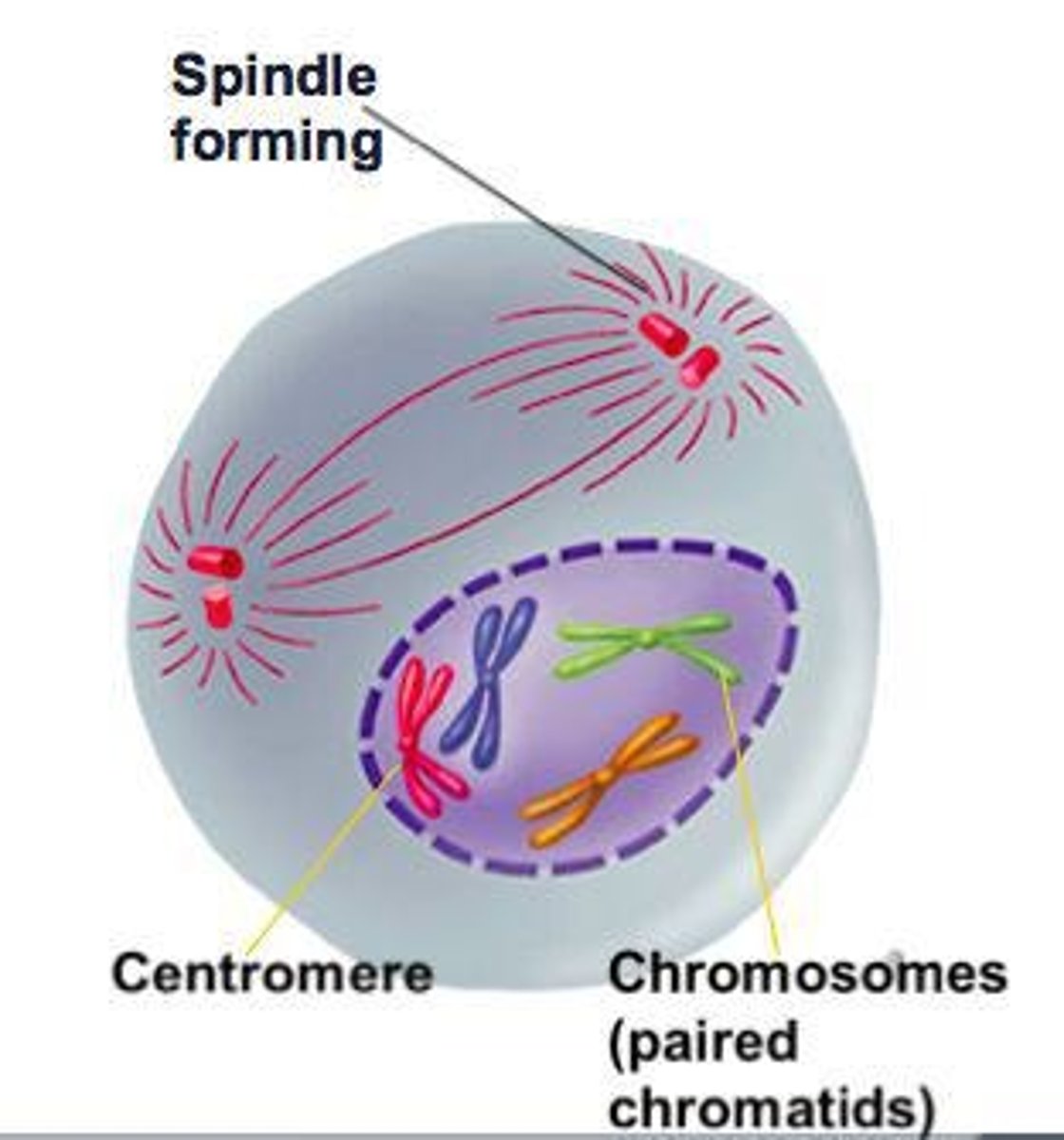
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equator.
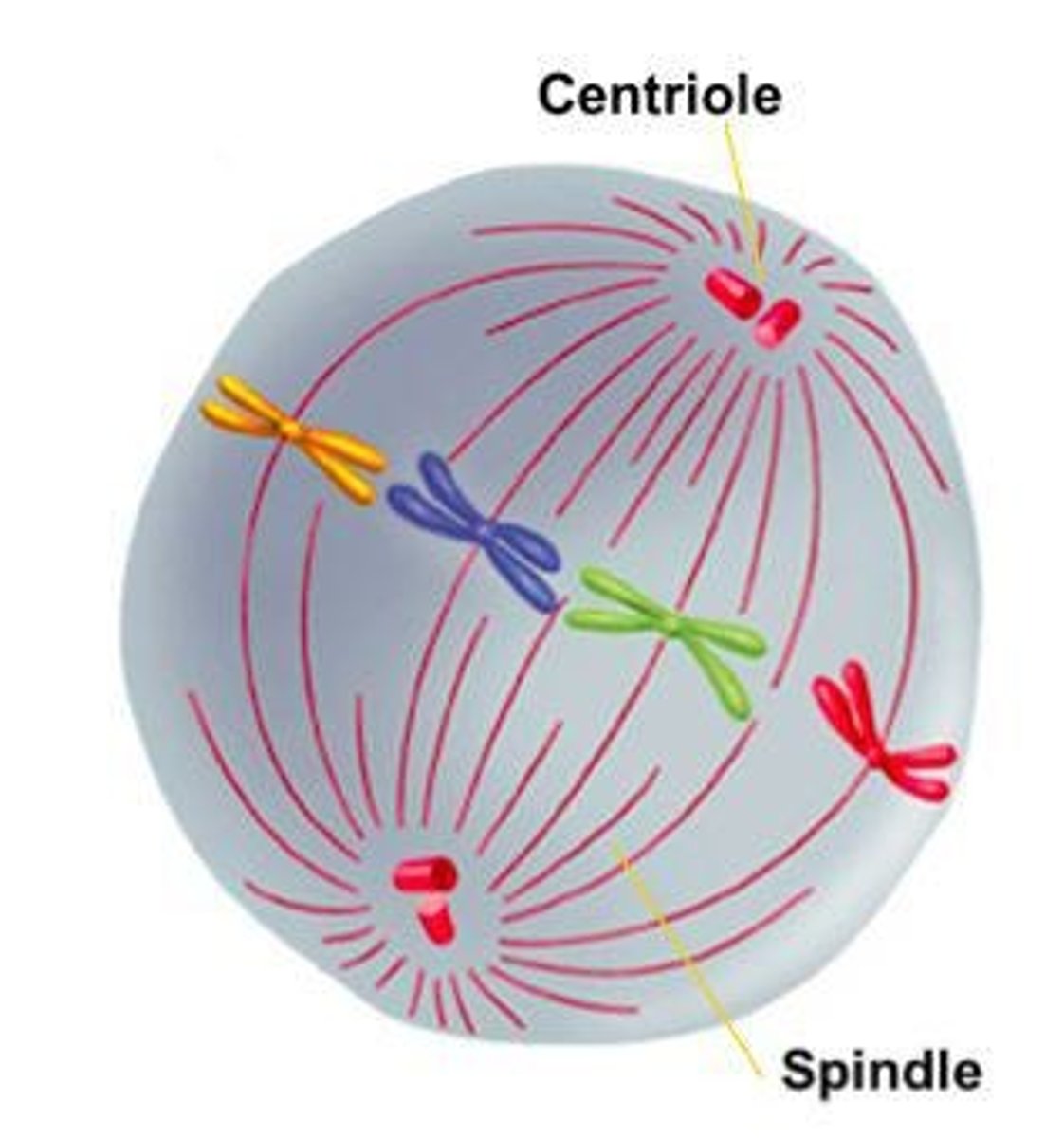
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move apart.
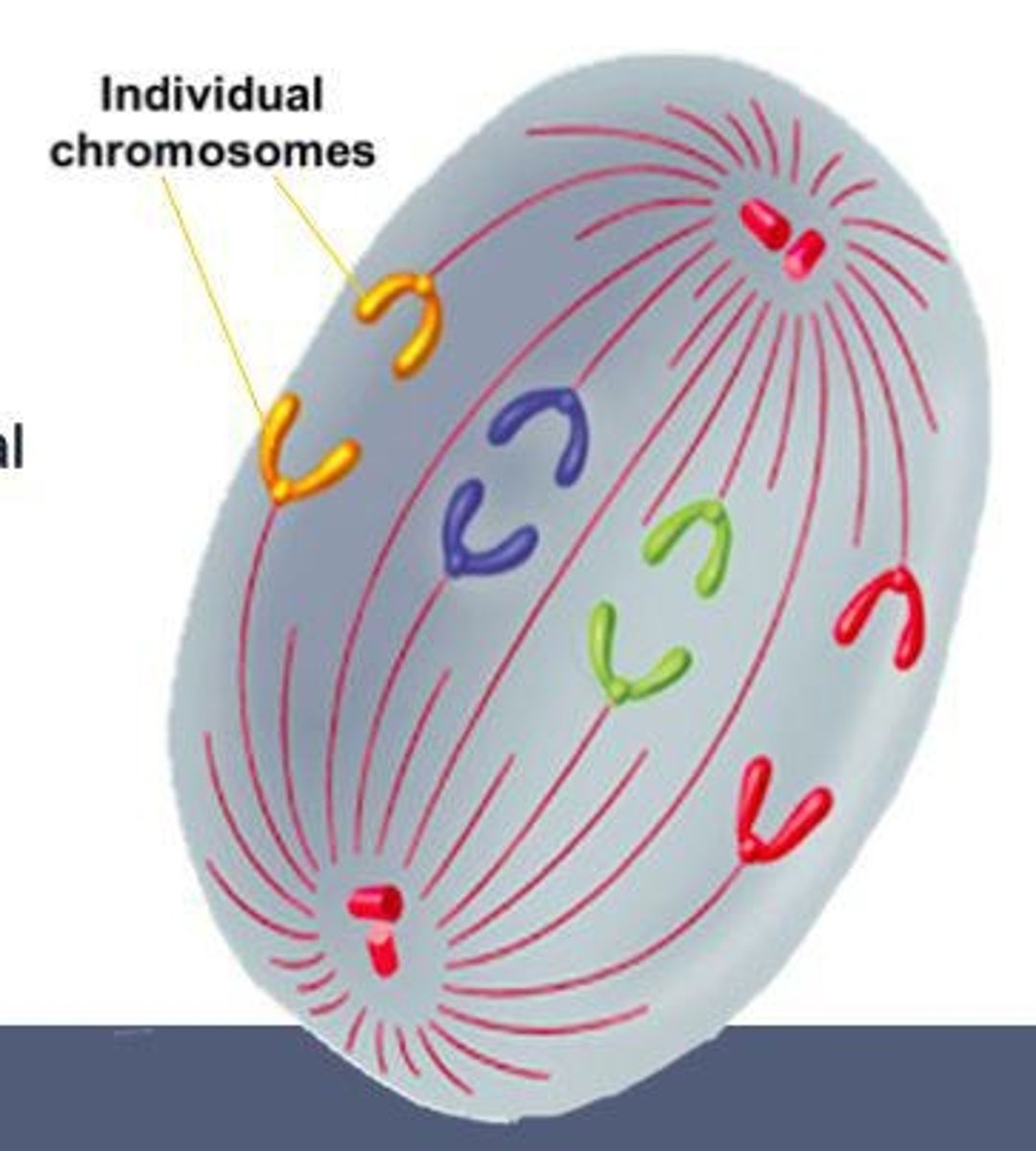
Telophase
Final stage of mitosis; nuclear membranes reform.

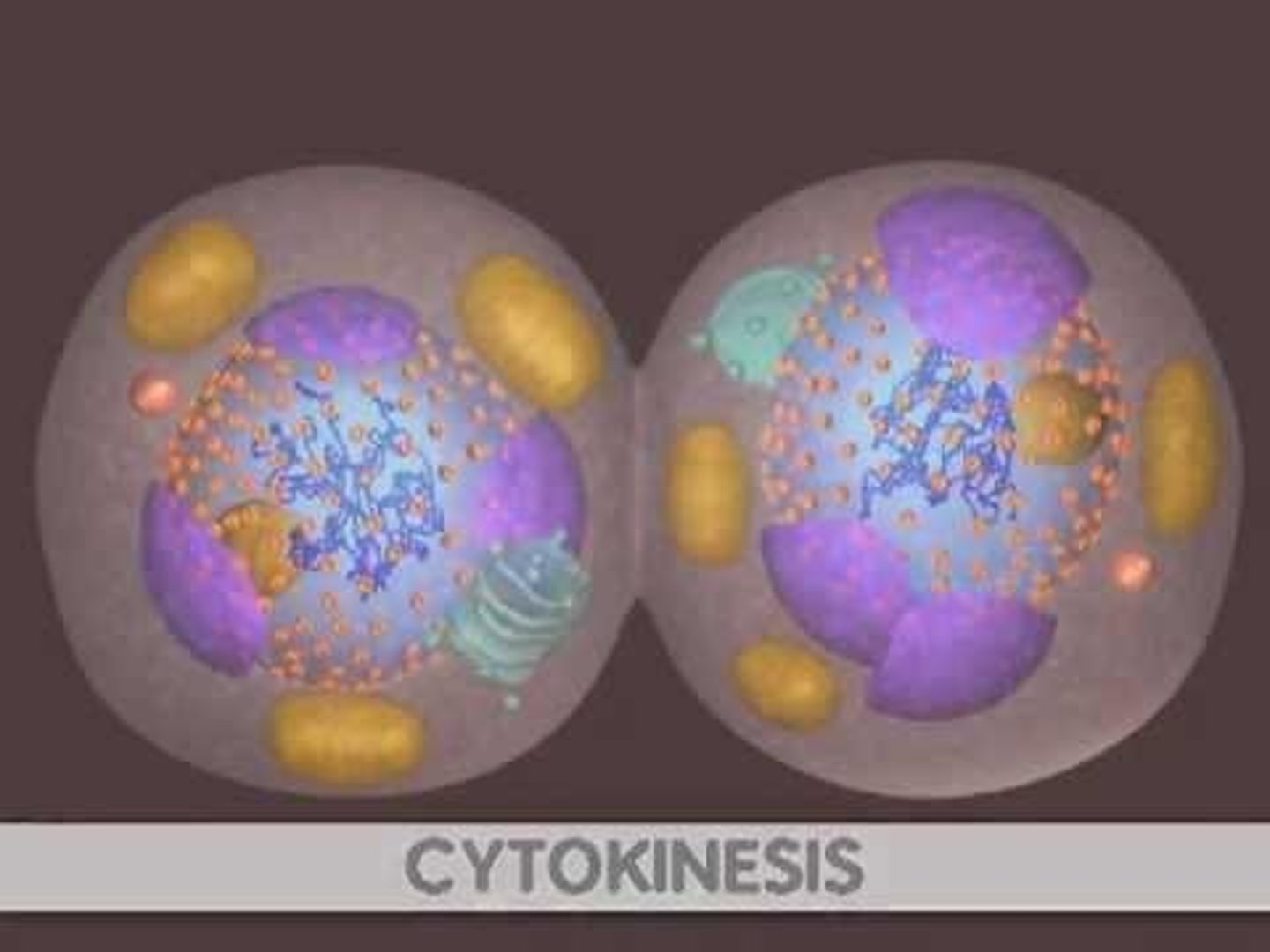
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells.
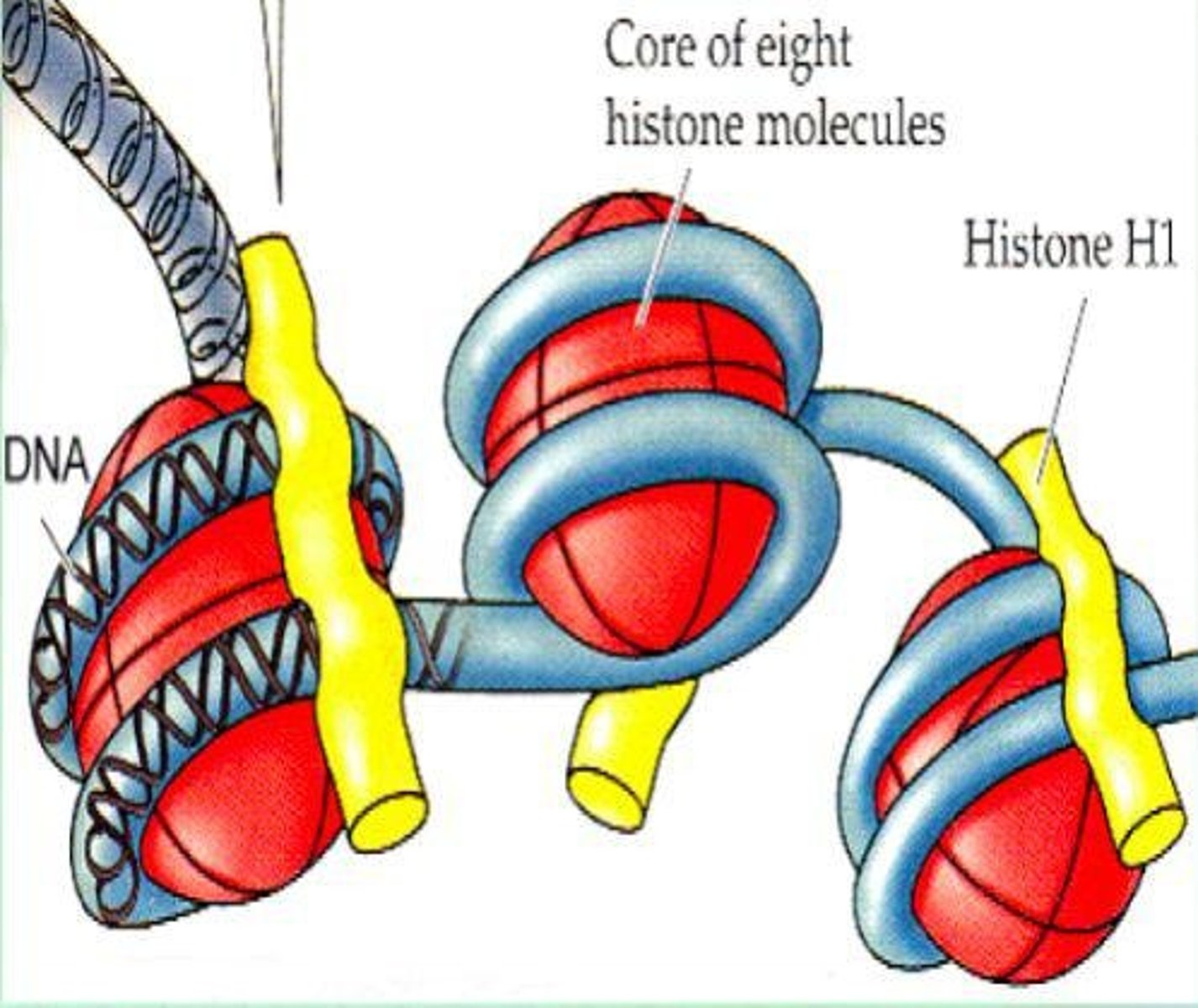
Histones
Proteins around which DNA is coiled.
Chromatin
Uncondensed form of DNA in non-dividing cells.
Checkpoint
Control mechanism ensuring proper cell cycle progression.
Asexual Reproduction
Single organism replicates itself via mitosis.
Sexual Reproduction
Fusion of gametes to form offspring.
Eukaryotic Chromosome
Linear DNA structure found in eukaryotic cells.
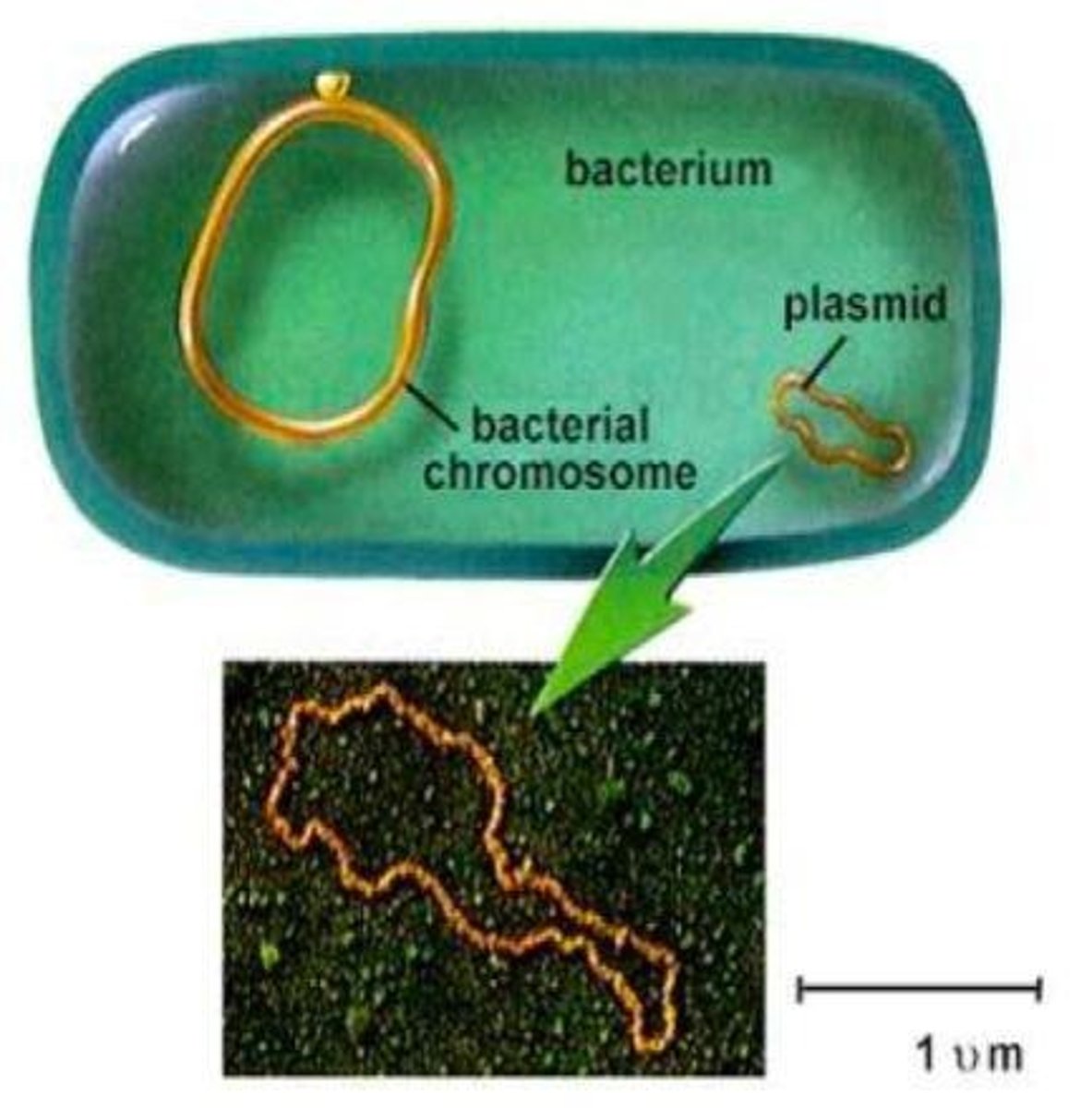
Prokaryotic Chromosome
Circular DNA structure in prokaryotic cells.
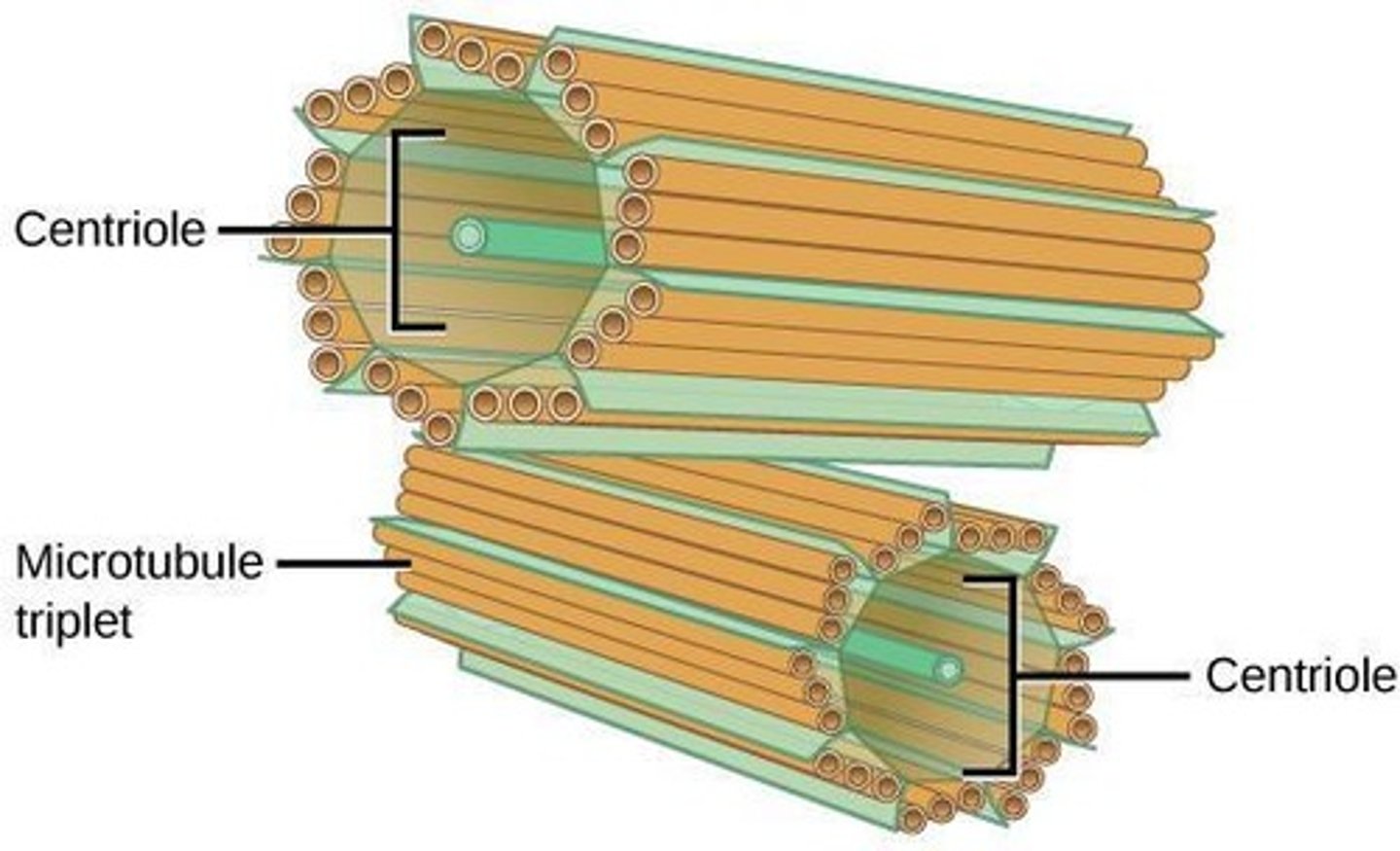
Centriole
Organelle involved in cell division.
Interphase
Phase where cell prepares for division.
S phase
Synthesis phase; DNA is replicated.
G2 phase
Gap 2; cell grows and prepares for mitosis.
G2 checkpoint
Checks DNA replication for integrity and completeness.
Integrity
Ensures DNA is correct and free of errors.
Completeness
Confirms DNA replication is fully done.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death for damaged cells.
G0 state
Nondividing state where cells perform functions.
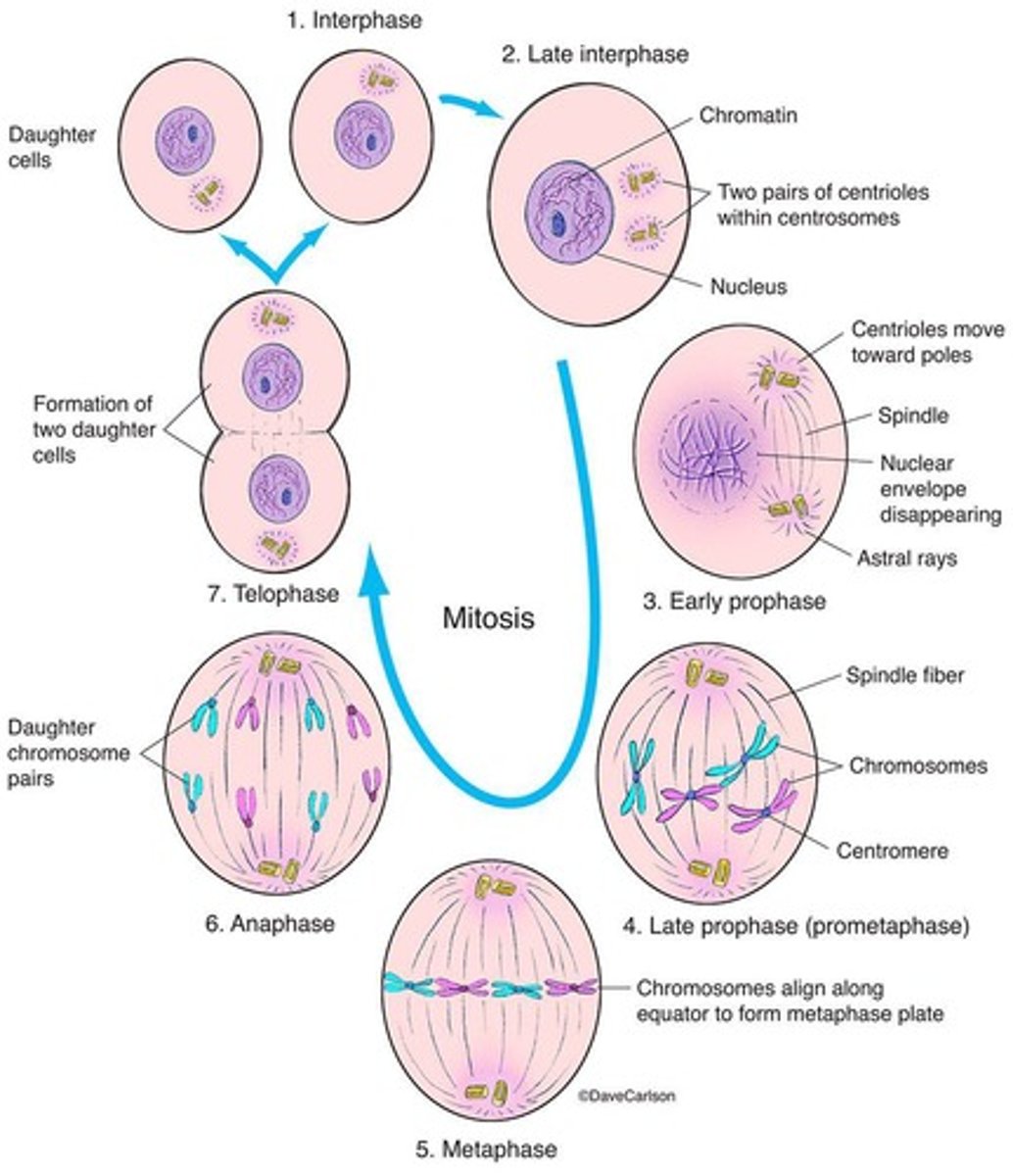
Mitosis
Process of cell division forming two identical cells.
PMAT
Phases of mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
Prophase
First mitosis phase; chromosomes condense and centrioles separate.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Spindle checkpoint
Ensures chromosomes are properly aligned before separation.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
Telophase
Chromosomes gather, nuclear membrane reforms, and decondense.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm forming two daughter cells.
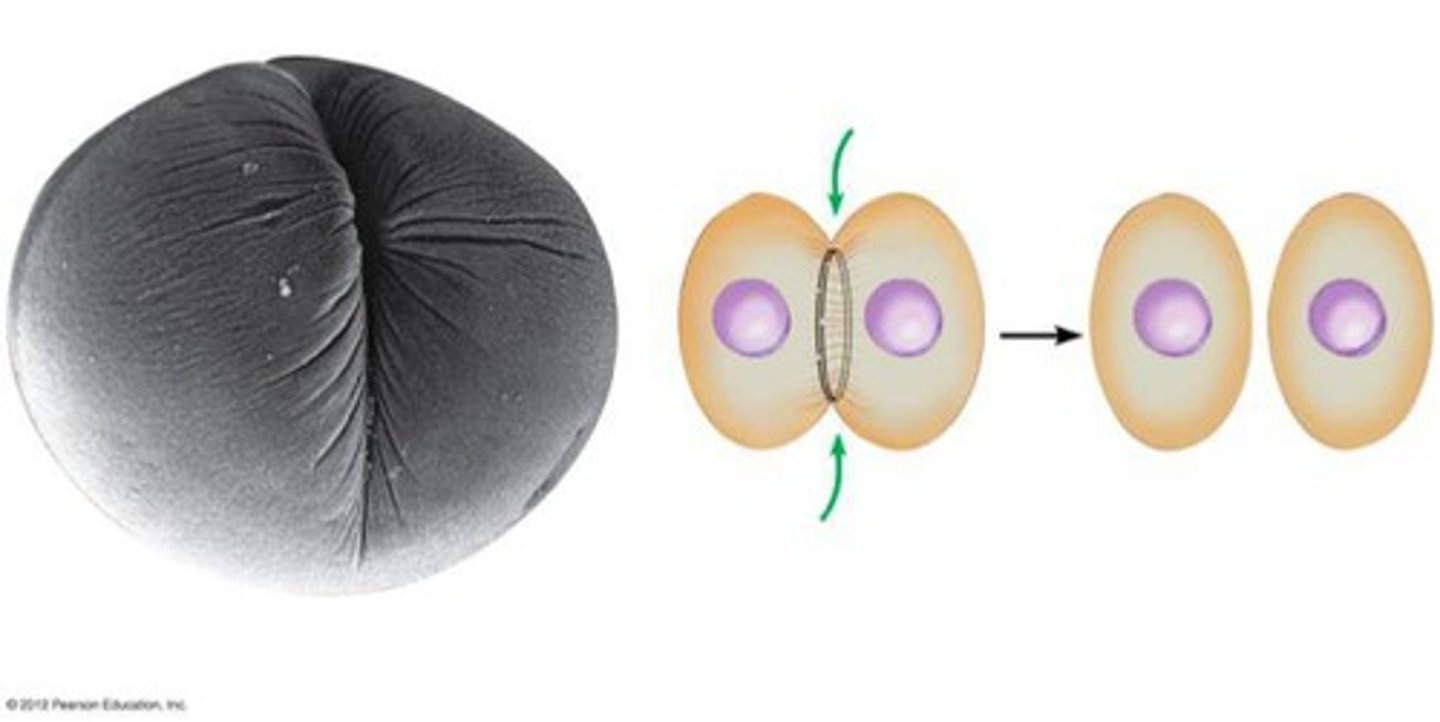
Cleavage furrow
Pinching of cell membrane in animal cell cytokinesis.
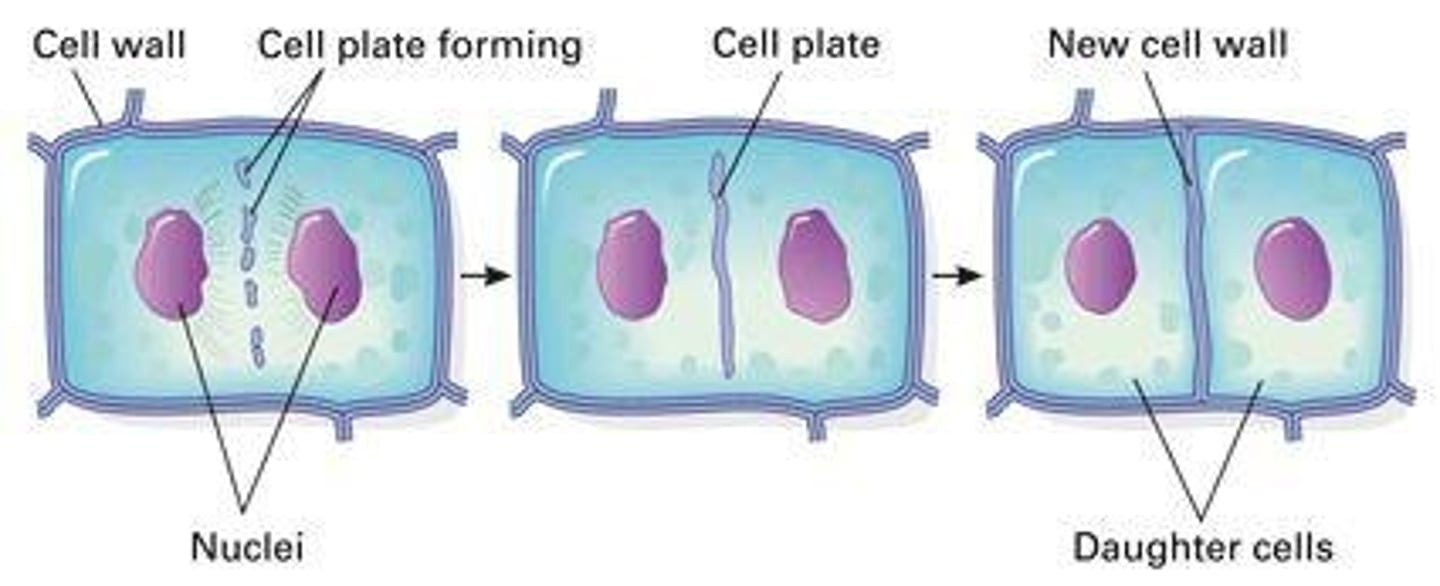
Cell plate
Formation in plant cells during cytokinesis.
Asexual reproduction
Single parent produces genetically identical offspring.
Binary fission
Prokaryotic reproduction; parent splits into two identical cells.
Microtubules
Structures that help separate chromosomes during mitosis.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction without the fusion of gametes.
Fragmentation
Parent breaks into fragments, forming new organisms.
Budding
Parent forms a bubble-like bud that detaches.
Cell Differentiation
Process where cells develop distinct functions and structures.
Zygote
Cell formed from the fusion of two gametes.
Blastocyst
Hollow ball of cells in early embryonic development.
Embryo
Initial stage of multicellular organism development.
Potency
Stem cells' ability to become different cell types.
Totipotent
Stem cells that can develop into any cell type.
Pluripotent
Stem cells that can develop into most cell types.
Multipotent
Stem cells with limited ability to differentiate.
Stem Cells
Unspecialized cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation.
Epigenetics
Mechanisms that regulate gene expression above DNA level.
Telomeres
DNA caps protecting chromosomes during replication.
Mitosis
Cell division process that produces two identical cells.
Differentiation triggers
Factors influencing cell specialization during development.
Stem cell locations
Found in bone marrow, fat, and tissue linings.
Cellular division timeline
Differentiation starts after the first few divisions.
Extracellular conditions
External factors affecting cell differentiation and development.
Signal proteins
Internal signals that influence gene expression and differentiation.
Immortal cells
Cells that can replicate indefinitely without aging.
Cellular characteristics
Distinct features of cells despite identical genomes.
Telomere
Protective end of chromosomes, limits cell division.
Cellular Senescence
Point where a cell stops dividing.
Immortal Cells
Cells that can divide indefinitely under conditions.
Telomerase
Enzyme that extends telomeres, preventing cell death.
Embryonic Stem Cells
Cells capable of becoming any cell type.
Cancer Cells
Cells that divide uncontrollably, ignoring growth signals.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSC)
Reprogrammed skin cells to behave like stem cells.
Hayflick Limit
Maximum number of divisions for typical cells.
HeLa Cells
First immortal cell line from Henrietta Lacks' tumor.
Stem Cell Differentiation
Process of stem cells becoming specialized cell types.
Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF)
Cell collection from fat tissue, includes stem cells.
Uncontrolled Mitosis
Unlimited cell division leading to cancerous tumors.
Oncogenes
Proteins that promote tumor cell development.
Replicative Immortality
Ability of cancer cells to divide indefinitely.
Metastasis
Spread of cancer cells to other body parts.
Hematogenous Metastasis
Cancer spread through the circulatory system.
Lymphatic Metastasis
Cancer spread through lymphatic system.
Potency
Ability of stem cells to differentiate into various types.
Pluripotent
Ability to differentiate into nearly any cell type.
Regenerative Cells
Cells that can heal and repair tissues.
Cell Culture
Growing cells in a controlled environment outside the body.
Growth Factors
Signals that promote cell division and growth.
Cancer Mutations
Genetic changes that accelerate cell division.