Edexcel A Level Biological Psychology
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
Monozygotic twins
Identical, share 100% of their genes as they come from one fertilised egg.
What should be considered about MZ twins?
- Do not share the same environment
- There are some physical differences, such as fingerprints
- Can become less identical over time
- Some characteristics, such as IQ and personality might become more alike as twins age
Dizygotic twins
Not identical, come from two separate eggs fertilised at the same time. Share 50% of genes.
Why are twin studies useful?
If a characteristic comes from genes, MZ twins should be more likely to share it. Psychologists can compare behaviour between a group of identical twins and fraternal twins to see which group shared the most similarity.
Concordance rate
The extent to which the same behaviour is the same between twins. An agreement rate when both twins have got a characteristic.
Strengths of using twin studies
- Twin studies are the main way of finding out if genes have any influence on behaviour.
- Both twins share their environment, so there should not be many environmental differences between the twins.
Weaknesses of using twin studies
- MZ twins will be treated more like twins than DZ twins, so environments are not the same.
- Epigenetic modification, there are differences between twins. Difficult to say if a characteristic is caused by genes conclusively
Twin Study - Gottesman and Shields (1966) procedure
- Case histories were collected for twins born between 1893 and 1945 from the Maudsley and Bethlem Royal Joint Hospital.
- Zygosity was determined by a combination of blood tests, finger-print analysis and resemblance in appearance.
- Tape-recorded 30 minute samples from semi-structured interviews were conducted to assess signs of schizophrenia, attitudes toward self,
parents and twin, and ego strength.
- Concordance rates were assessed for MZ and DZ twins of Grade 1 (both twins schizophrenic), or Grade 2 or 3 where only one twin had schizophrenia.
Twin Study - Gottesman and Shields (1966) conclusion
Genes do play a role in the development of schizophrenia, but can't conclusively say it is solely due to genes - only 42% in MZ
Twin Study - Gottesman and Shields (1996) - Twins were assessed for their ......While..... (W)
Zygosity (e.g. blood grouping). While twins share genetic information it is difficult to separate environmental factors so studies cannot establish
genetics as a causal factor for behavior.
Twin Study - Gottesman and Shields (1996) - There was a higher concondance rate for...... The.....(W)
MZ twins for schizophrenia compared to DZ twins. The predisposition of schizophrenia was not 100% twin studies are not able provide conclusive evidence of genetic influences on human behaviour.
Twin Study - Gottesman and Shields (1996) - To determine the presense of a ..........If the
Mental disorder qualitative and quantitative methods were used (e.g. case histories). • If the same measures of schizophrenia (e.g. MMPI) are used then a twin study could be easily replicated.
Twin Study - Gottesman and Shields (1996) - Twins were sampled using .......Yet,
Opportunity sampling from twins seen by the Maudsley and Bethlem Royal Joint hospital. Yet, twin studies have small sample sizes as twins are not common, so findings may not be representative of a wider population.
Why are adoption studies useful?
It is the only direct way to isolate the influence of genes and the environment.
In what circumstances in adoption studies suggest the roles of genes?
Similarities between child and their biological parents
In what circumstances in adoption studies suggest the roles of environment?
Similarities between child and their adoptive parents
Heston (1966)
- American Study
- Sample of 97
- 47 with schizophrenic mothers
- 50 without schizophrenic mothers
Strengths of adoption studies
- Developmental trends (patterns) can be studied because studies are longitudinal. Same children can be studied at different times during development.
- Control for environment, separates genes from environment.
Weakness of adoption studies
- Adopted children are often placed into families very similar to their biological families
- They are matched, so the environments might not be as different as thought
What are the 3 main brain scanning techniques?
PET scans, CAT scans and fMRI scans
Brain scanning lacks ecological validity as ..........
it takes place in an artificial setting
Brain scanning could be unethical because ....
Frequent exposure to radiation could cause high dangers E.G Cancer
Brain scans can be repeated easily to.....
Test for reliability in findings about human behavior.
What are PET scans useful for?
Investigating areas of the brain that are not functioning normally, indicate damage or tumours.
How do PET scans work?
PET scans investigate brain activity when a human is doing a task. It involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the participant
in an artificial setting
• Frequent exposure to radiation could mean brain
scanning could be unethical
• Raine et al. (1997) found differences in murderer brain
activity using PET scans showing their contribution
• Brain scans can be repeated easily to test for reliability in
findings about human behaviour
Strengths of PET scans
- Less dangerous than surgery
- Valid measure
- Reliable because it can be repeated and same results found again
Weaknesses of PET scans
- Invasive
- Ethical implications, need informed consent and a good reason to carry it out
- Can cause panic if claustrophobic
- Difficult to isolate different brain functioning precisely, as they will be using other parts of the brain as well.
How do fMRI scans work?
Uses blood flow of brain to indicate level of activity - head placed in large electromagnet
Strengths of fMRI scans
- No danger from radiation
- Detection of blood flow is very precise so slight changes can be detected
- Medical use, looking at brain structure and functioning
Weaknesses of fMRI scans
- Cannot look at receptors of neurotransmitters unlike PET scans
- Too much head movement can distort imaging
- The brain is never at rest, so it is not easy to gather a baseline measure
- Risks, such as those with pacemakers and those who are claustrophobic.
How do CAT scans work?
- Multiple X-ray beams passed around the head at different angles - Produces a detailed 3D image
What are CAT scans useful for?
Detecting areas of brain damage after an accident or position of tumours
Strengths of CAT scans
- Less harmful than PET scans
- Can detect changes in physical structures, so good for detecting tumours or haemorrhages
- Not painful, non-invasive
Weaknesses of CAT scans
- MRI gives a clearer picture
- Involves X-raying which can cause damage, notably cancers.
Research using PET scans
Raine (1997)- investigate whether people charged with murder and pleading NGRI have brain differences that might link to their aggression.
Correlations
A way of looking at relationships between two variables, not causes. If two variables are correlated, you can predict one from the other.
In a correlation, the SAME person produces the two scores. True or false?
True
What are the three important features of correlation design?
1. There is no IV or DV, only two variables of equal importance
2. Hypothesis will be about a relationship between two variables (not a difference)
3. Hypothesis could be directional as it could predict a positive or negative correlation.
Name an example of co-variables in biological psychology
Measuring the number of genes a person shares (closeness of family relationship) and a behavioural charactersitic such as the amount of aggression they show.
What type of graph do you use to show correlations?
Scatter diagrams
Types of correlations
- Positive correlation
- Negative correlation
- Uncorrelated
Negative correlation
When one variable increases and the other variable decreases.
What are the two main parts in the nervous system?
Central nervous system and Peripheral nervous system
What does the CNS consist of?
Brain and spinal cord
What is the role of the CNS?
Central processing and control point for all human behaviour. Processes all information from the senses and is responsible for controlling behaviour.
What is the role of the spinal cord in the CNS?
Connects the brain to the rest of the body, and allows messages to be passed from body to brain and from brain to other parts of the body.
Neurones
Nerves in the CNS that communicate with other cells at the same time
Neurotransmitter
A chemical involved in passing information from one neurone to another in synaptic transmission
Structure of a neurone
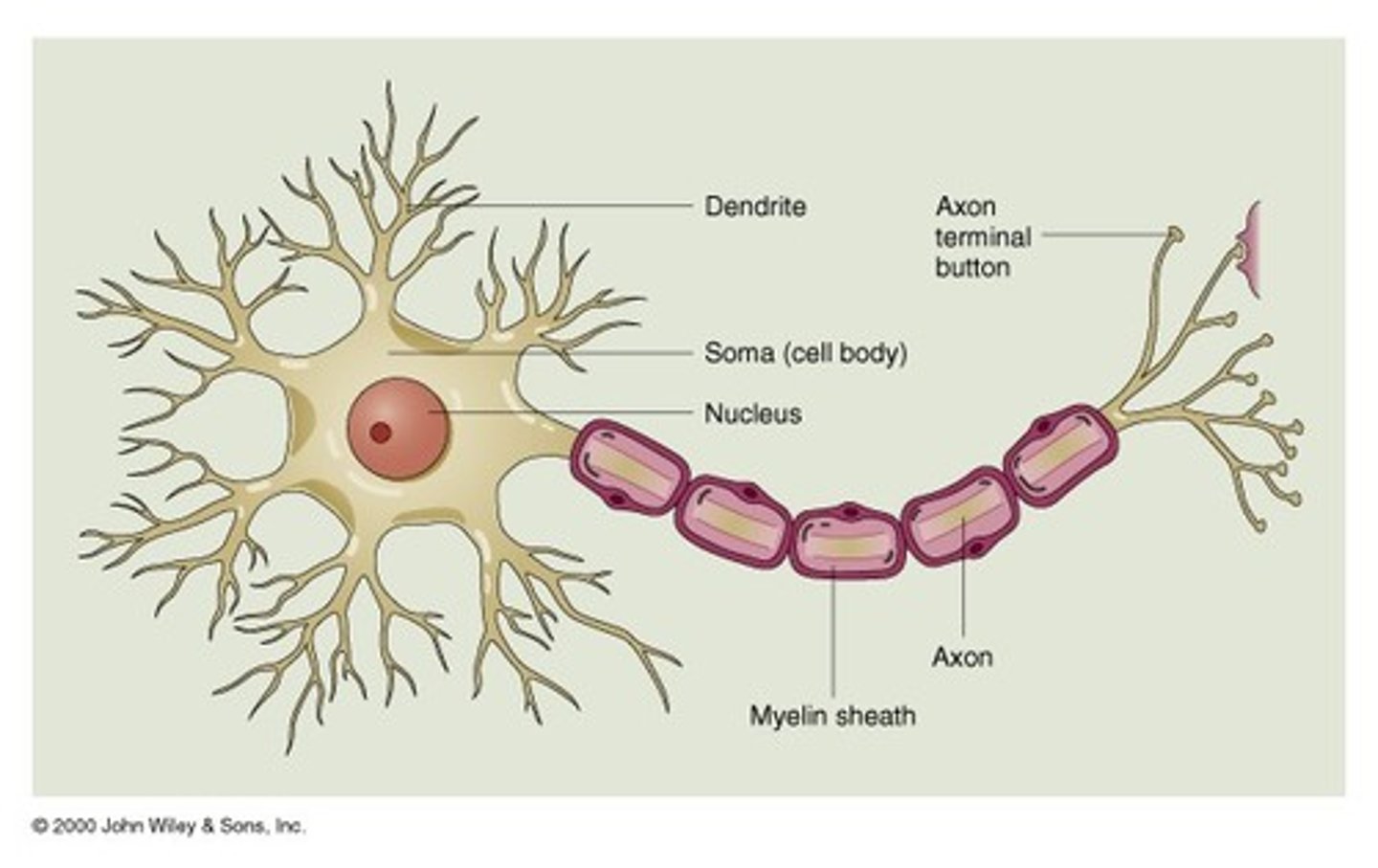
What are the parts of the neurone?
1. Cell body
2. Nucleus
3. Myelin sheath
4. Nodes of Ranvier
5. Axon terminal
6. Terminal buttons
7. Dendrites
8. Axon
9. Schwann's cells
Synaptic transmission
An electrical impulse travels along the pre-synaptic neuron (1). The impulse reaches the synaptic vesicles to release a neurotransmitter (1).
These diffuse across the synaptic gap and attach receptors (1).
How is a synaptic transmission generated?
1. Electrical impulse down the axon triggers release of neurotransmitters from axon terminals.
2. Released into synaptic gap to be picked up by the receptors on dendrites or to be taken up again for re-use
Pre-synaptic neurone
Neurone sending the message
Post-synaptic neurone
Receiving neurone
Neurotransmitters in synaptic transmission
- When AP reaches axon terminal, calcium channels open, flooding terminal button with calcium ions
- Vesicles release neurotransmitter
- Vesicles fuse with the membrane
Receptors in synaptic transmission
- Designed to bind to a specific neurotransmitter
- When detecting the neurotransmitter, it will be absorbed by the post-synaptic neurone
- Any not absorbed will be destroyed or reabsorbed by pre-synaptic neurone
Function of neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that act between neurones in the brain. Allows the brain to process thoughts and memories.
4 common neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine
- Noradrenaline
- Dopamine
- Serotonin
Noradrenaline
Mood control, sleeping, dreaming and learning.
Dopamine
Posture and control of movement. Reinforcement in learning, and dependency such as addictions. Hormonal regulation, such as menstrual cycle.
Serotonin
Mood control, particularly limbic system. Feeling pain, sleep, regulating body temperature and hunger.
The brain is in two halves, called...
Hemispheres
Corpus callosum
Section that joins the two hemispheres
Cortex
Outer layer of the brain
Pre-frontal cortex
- Has connections with parts of the brain relating to neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin
- Regulating emotions, so aggression comes from LACK of regulation or control over behaviour
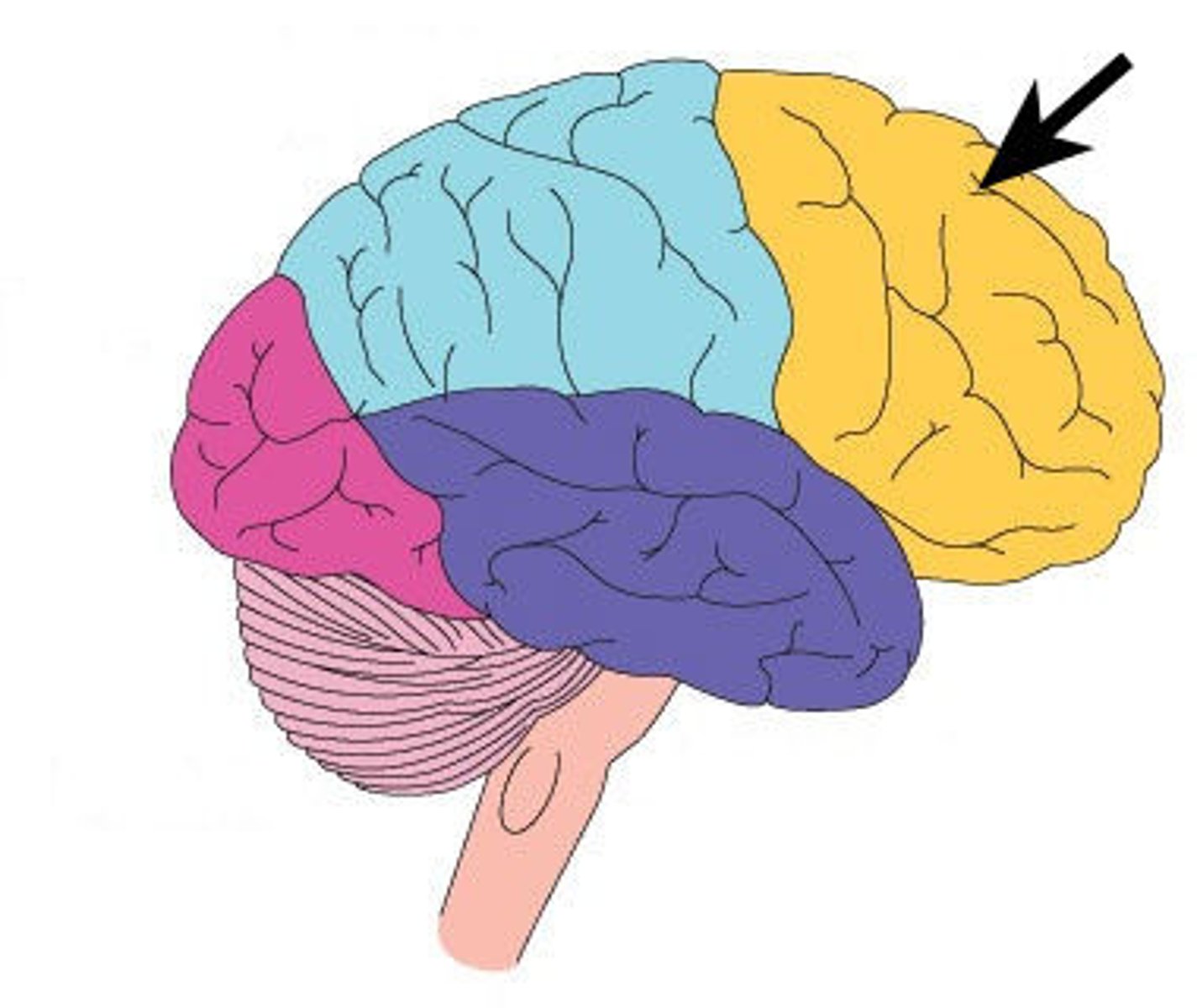
Orbitofrontal cortex
Accepting delayed gratification and deferring rewards
Ventromedial cortex
Experience of emotions.
What are the differences between the left and right hemisphere pre frontal cortex?
Left hemisphere involved in positive emotions and right hemisphere with negative emotions.
Prefrontal cortex role in aggression
Damage to prefrontal cortex:
- Focus on the present
- Not be able to plan long term
- Wanting immediate rewards
- Unable to control aggressive reactions
- Raine et al (1998) emotional impulsive aggression had low prefrontal cortex functioning
Amygdala
- Limbic system
- Self-preservation, flight/fight response
- Centre for emotions and motivation
- Combines all sensory modality to give an instinctive feeling or reaction
- Identifying threat
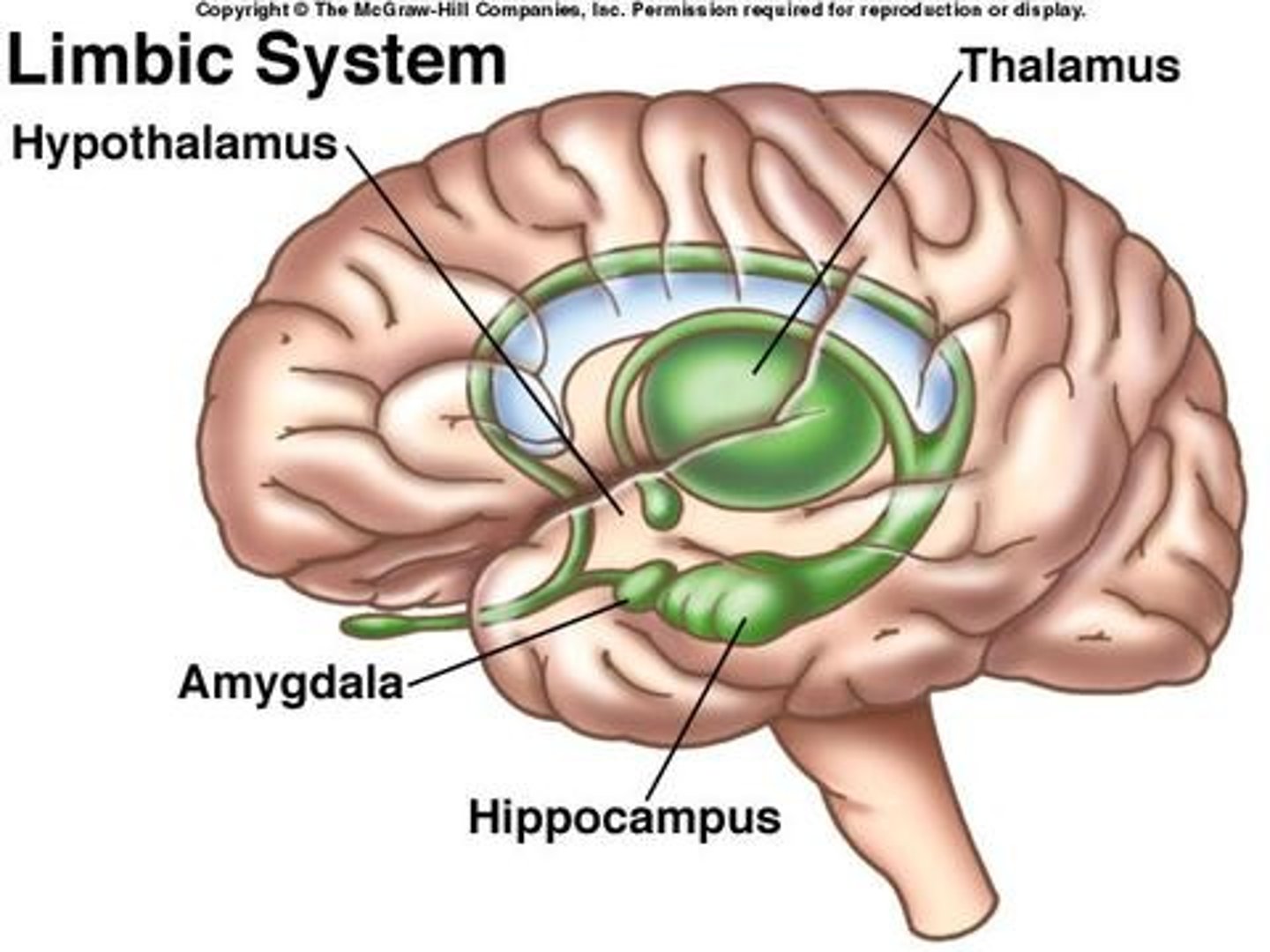
Animal studies involving amygdala
If amygdala is stimulated using electrical current, the animal shows aggression. If amygdala is removed, animal becomes passive and unresponsive and doesn't respond to fear.
Hypothalamus
- Limbic system
- Maintain homeostasis - regulating hunger, thirst and response to anger, agression
- Regulating hormones used to signal between organs and tissue
- Hormones regulating sexual function, testosterone production
Recreational drug
Drugs taken for pleasure
Examples of recreational drugs
Cocaine, heroin, cannabis and ecstasy
Psychoactive drug
Drugs that have an effect on the CNS
Specific mode of action
Act in a specific way in the synapse
Reward pathway in the brain
Pleasure centre, where pleasure seems to be so desired that the animal will continue to behave in such a manner that the pleasure received. The desire for pleasure over-rides other drives
Effects of nicotine in the synapse
- Release more neurotransmitter in response to an impulse
- Increases number of impulses
- More dopamine in the reward system
What is the long term effect of nicotine in the synapse?
- Binding over time affects receptors, decreases dopamine receptors
- Change in the shape of the cell
- Without nicotine, more dopamine is required to stimulate the post-synaptic neurone to a 'normal' level
Desensitisation
When more of a substance is required to achieve the same response, leading to addiction.
Effects of cocaine in the synapse
- Blocks reuptake
- More neurotransmitter (dopamine) in the synapse
- Over-stimulation at the post-synaptic receptors
What are the long-term effects of cocaine in the synapse?
- Dopamine receptors become damaged
- Become fewer
- Desensitisation
- Addiction
How can cannabis affect memory function?
- Binds to cannabinoid receptors, blocking them
- Less activity in neurones in the hippocampus
- Making memories can be affected
Recreational Drugs on Synaptic Gap
Recreational drugs work by increasing or decreasing neurotransmitters at the synaptic gap. (1) If a drug increases the level of dopamine, the user experiences an intense feeling of pleasure or euphoria (1).
Consuming drugs can....
Affect synaptic functioning by increasing or decreasing neurotransmitters which will impact on her level of stress.
Alcohol can increase .......However, ....
Serotonin making people feel happier about situations. However, alcohol would also increase GABA which would make memory less efficient.
What is a hormone?
A chemical produced by the body that sends messaged to organs of the body via the bloodstream.
How is testosterone production controlled?
Hypothalamus and pituitary gland control how much testosterone the testes produce and secrete. Hypothalamus sends a signal to pituitary gland to release gonadotrophic substances.
How does testosterone lead to aggression?
Anti-natal exposure to testosterone has an effect on the developing brain, leading to increased spatial ability and (possibly) competitive aggression
Wagner et Al (1979)
Castrated male mice had reduced aggression. Later, injected the mice with testosterone which re-established aggression.
Dabbs and Hargrove (1987)
- Measured levels of testosterone in the saliva of 87 female prisoners in a maximum-security prison
- Degree of violence used by these women was positively correlated with testosterone levels and with their aggression
Pompa et al (2007)
found an association between cortisol and direct physical aggression amongst male adolescents.
Evolution
How inherited characteristics in organisms evolve from generation to generation.
Survival of the fittest
Those who are more adapted to the environment survive, and they pass on those genes to their offspring to aid survival
Natural selection
The way some characteristics may aid survival over other characterisitcs
Examples of aggressive behaviour in social living
- Gain territory and resources
- Defending against attacks
- Inflicting cost on same-sex rivals (fighting for mates)
- Negotiating status and power hierarchies
- Deterring rivals from future aggression
- Deterring mates from infidelity
How might aggression lead to survival?
If a male is aggressive to protect a female or their child, which would aid survival of genes
How can infidelity lead to aggression?
- Male needs to reproduce to pass on their genes
- Another male competing for the female is a threat
- Male would result in aggression to protect or defend the female.
Dobash and Dobash (1984)
Violence against women often came from partner jealousy. Sexual jealousy lead to aggression.
Why do males express jealousy?
- Need to compete with other males for access to choosy females
- Lower status men take greater risks using aggression
- If female is unfaithful, man faces paternity uncertainty
- Males cannot risk wasting investment on offspring who are not their own, so show more jealous, violent aggression relating to female infidelity