Lec 21_Allergies and Histamine
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
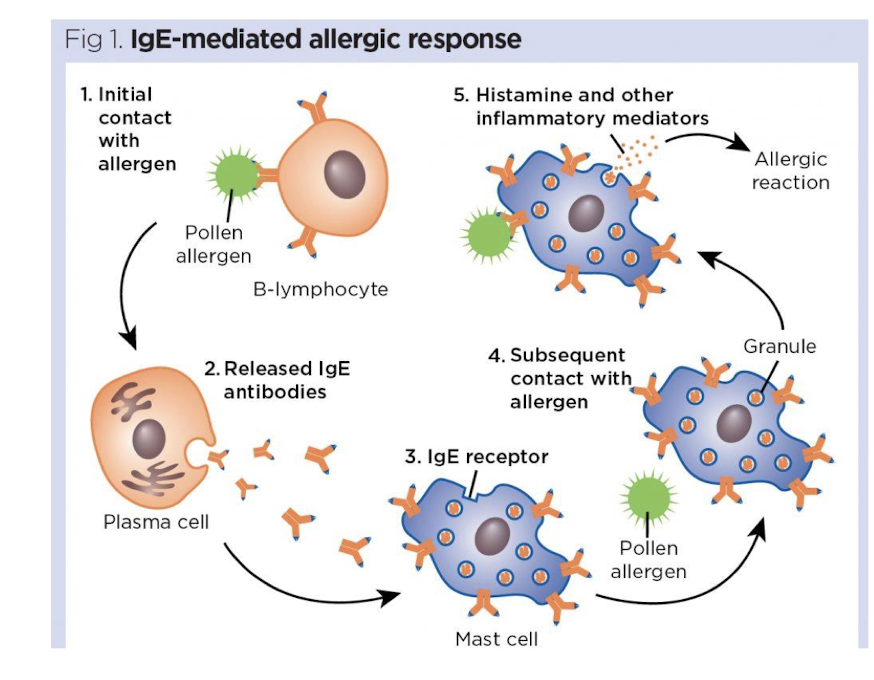
Describe the IgE-mediated allergic response
Initial contact with allergen
released IgE antibodies from the plasma cell
antibodies bind to the mast cell
pollen allergen then binds to the IgE on the mast cell
This binding triggers the mast cell to release histamine and other inflammatory mediators, leading to allergy symptoms.
What are the 2 main storage sites of histamine?
mast cells in tissues
basophils in the blood
Where is the receptor H1 located and its actions?
Smooth muscle
pain and itching of skin
bronchoconstriction
vasodilation (histamine causes NO release)
local edema
Where is the receptor H2 located and its actions?
Stomach, heart, mast cells
gastic acid secretion from parietal cells
cardiac stimulant effect
(-) feedback to reduce histamine release
Where is the receptor H3 located and its actions?
Nerve endings, CNS
decrease transmitter release from histaminergic and other neurons
Where is the receptor H4 located and its actions?
Leukocytes
chemotactic effects on eosinophils and mast cells
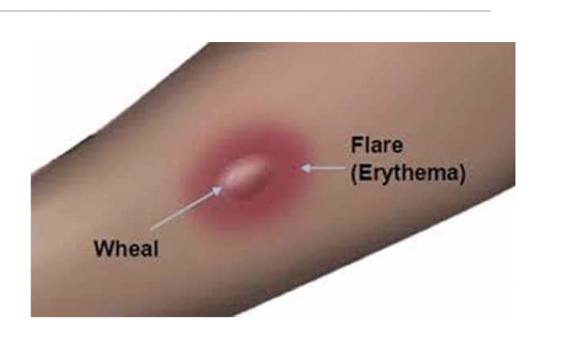
What is the Triple response (Intradermal Lewis reaction)?
Histamine effects
Flush/red spot - vasodilation of local caps
Flare - vasodilation of arterioles = wider reddened area
Wheal - localized edema results from increased cap permeability
What effects does histamine have on the nervous system?
powerful stimulant of pain and itching (bug bites)
HA - dilate brain arterioles
What effects does histamine have on the skin?
vasodilation leads to reddening of the skin
What effects does histamine have on the CV system?
Decrease BP
balance between vasodilation effect (NO), baroreceptor reflex, and histamine induced catecholamine release (H1 and H2 effect)
Increase HR
direct histamine stimulation of the heart - positive inotropic and chronotropic
reflex tachycardia
Edema
stimulation causes a separation of the endothelial cells allowing fluid to leak
Overall which receptors do we note lie in the heart?
a. B1, M1, H1
b. B1, M3, H1
c. B2, M2, H2
d. B1, M2, H2
d. B1, M2, H2
Vasodilation effects of histamine stem from _____ receptors on peripheral vasculature
H1
List some of the body’s responses to histamine
increase HR
blood clots
gastric acid secretion
blood vessel dilation
bronchoconstriction
increase permeability of caps
adrenaline release
runny nose
swelling and inflammation
teary eyes
In allergic rhinitis, what can be expected from
Exposure to antigen
Subsequent exposure to antigen
Exposure to antigen
stimulates IgE production
sensitization of mast cells
Subsequent exposure to antigen
produces an allergic reaction
“explosive” release of histamine
What is the stepwise management of allergic rhinitis?
Step 1: oral H1 antihistamine PRN and/or intranasal saline
Step 2: add intranasal corticosteroids (fluticasone furoate, fluticasone propionate, mometasone furoate)
Step 3: Intranasal saline + INCS + intranasal antihistamine
Step 4: step 3+ consider additional adjuncts (oral corticosteroids, nasal/oral decongestant)
Step 5: refer to specialist, ENT surgery and/or allergy specialist for allergen immunotherapy
T/F: prevention of sx is more effective than after sx appear
true
What is the primary pharmacotherapy?
oral antihistamines
What is the difference between first generation H1R antagonists vs Second generation H1R antagonists?
First gen
sedating
passes BBB
Second gen
non-sedating
poor passing into BBB
longer duration of action
List the 1st generation H1R antihistamines
diphenydramine (Benadryl)
chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton)
doxylamine (Unisom)
meclizine (Antivert, Bonine, Dramamine)
hydroxyzine (Atarax, Vistaril)
promethazine (Phenergan)
olapatadine (Patanol, Pataday)
Which of the first gen H1R are used for N/V?
meclizine (Antivert, Bonine, Dramamine)
promethazine (Phenergan)
What are the 2nd gen H1R antagonists?
Fexofenadine (allegra)
Loratadine (Claritin, Alavert)
Desloratadine (Clarinex)
Cetirizine (Zyretec)
Levocetirizine (xyzal)
Azelastine (Asteline)
Because of their lower potential to induce drowsiness, _____ and _____ may be recommended for individuals working in jobs where wakefuless is critical
Loratadine and fexofendadine
Which anti-histamine generation is recommended for patients 1st line with uncontrollable sneezing and coughing?
2nd generation H1 antagonists
Which generation of antihistamines is ideal for acute care? long term care?
acute care - 1st
long term care - 2nd
What are the options for intranasal antihistamines?
Olopatadine (Patanase)
Azelastine (Astelin)
Azelastine (Astepro)
Azelastine/fluticasone (Dymista)
Olopatadine/Mometasone (Ryaltris)
Which of the intranasal antihistamines is OTC only?
Azelastine (Astepro)
What are the side effects typically experienced with intranasal antihistamines?
bitter taste
epitaxis
somnolence (drowsy,sleepy)
HA
What is the mechanism of nasal steroids?
reduce inflammation by reducing mediator release
suppress neutrophil chemotaxis
reduce intracellular edema
mild vasoconstriction (help with nasal stuffiness)
Do nasal steroids undergo first pass effect?
no
List the OTC and Rx intranasal steroids
Fluticasone (flonase)
Mometasone (Nasonex)
Triamcinolone (Nasacot)
Budesonide (Rhinocort)
Beclomethasone (Qnasl) - Rx
What are the ADE of intranasal steroids?
Minor
sneezing, stinging, HA, epitaxis, taste
very little systemic absorption
What are the therapeutic receptor antagonists (LTRA) options?
montelukast (singulair)
Zafirlukast (Accolate)
What are common and serious ADE for LTRAs
Common
HA
flu-like syndrome
elevated liver enzymes
N/V/D
neuropsychiatric events - agitation, aggression, anxious, irritability, restlessness, insomnia, tremors, dream abnormalities, hallucinations, depression and suicidality including suidice
Serious
hypersensitivity - Churg-strauss syndrome
Hepatitis (zafirlukast)
allergic granulomatosis, asthma, fever, eosinophilia and other signs of vasculitis
Churg-strauss syndrome
Besides allergies, what other condition includes recs for use of LTRAs?
asthma
What are the mechanism of mast cell stabilizers?
Indication of use?
MOA: inhibit mediator (histamine) release from mast cells
Use: prophylaxis (for prevention, not tx because onset takes 2 weeks)
What are the therapeutic options for mast cell stabilizers?
Cromolyn
Nedocromil
What are the PK of mast cell stabilizers?
inhalation of eye drop delivery
poor absorption because of low solubility (local effect)
long onset of action (weeks)
How do decongestants work?
alpha stimulation vasoconstricts the nasal mucosa vessels, shrink swollen mucosa and improve breathing
T/F: decongestants are only found as nasal sprays
false - oral tablets too
What are the routes and meds of decongestants?
Nasal spray
phenylephrine (neo-synephrine)
oxymetazoline (afrin)
Oral
pseudoephedrine (sudafed)
phenylephrine (sudafed PE)
What are the common and serious side effects of decongestants?
Common
hypertension and cardiac acceleration (vasoconstriction)
asthma exacerbation
Serious
hypertension and cardiac acceleration (vasoconstriction)
dryness of nasal mucosa
define rhinits medicanentosa
nasal congestion that occurs after 5 days of topical use (rebound)
from over use of nasal spray
Which decongestant is considered the safest systemic decongestant?
Pseudoephedrine
Describe Pseudoephedrine
safest systemic decongestant
oral delivery
slow onset with long duration of action
minimal effects on BP and HR - pt with HTN should be controlled before use
What is the general contraindication of pseudophedrine?
It is a MOI (monoamine oxidase inhibitor) and may result in extreme hypertension
Are decongestants alpha agonists or antagonists?
Decongestants are primarily alpha agonists that stimulate alpha-adrenergic receptors to cause vasoconstriction and reduce nasal congestion.
What are the therapeutic options for cough suppressants?
Benzonatate (Tessalon)
Opiates
Guaifenesin
local anesthetic on stretch receptors that trigger cough in respiratory passages
is known as cough reflex suppressants and can help alleviate coughing by numbing these receptors - Benzonate (Tessalon)
prevents muscle contraction > > cough reflex is stopped
Describe opiates used as cough suppressants
Codeine
Dextromethorphan (Delsym)
OTC
crosses BBB and activates opioid receptors
Which cough suppressant works as an expectorant where mucus is loosened ONLY
Guaifenesin (mucinex)
What is the goal of immunotherapy for allergies?
desensitization
slow and gradual process
increasing doses of specific antigen
What is the MOA of immunotherapy?
diminished IgE production
Increased IgG production
reduced inflammatory mediator release
reduced tissue response
Who is immunotherapy for allergies NOT recommended for?
pre-existing immunological conditions (immunocompromised)
history of non-compliance
Besides allergies, what are alternate uses for H1R antagonists?
Motion sickness (1st gen)
meclizine (antivert)
promethazine (phenergran)
Sleep aids (1st gen)
diphenhydramine (benadryl)
Doxylamine (unisom)