Paints & Polymers, Pt 1
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Trace Evidence class w/ Dr. Elizabeth Chesna
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Long-chain like chemical structures formed by the linking together of smaller units (monomers).
Polymers
One of two synthesis methods, where the reaction of the monomer functional groups to form a covalent bond.
Step Growth
One of two synthesis methods, where monomers are linked to an active site on the growing polymer chain
Chain Growth
Includes paints and other liquids that convert to a solid following application to form a protective and/or decorative film.
Coating
Generic term for polymer that occasionally indicates a thermoset polymer, and most often can be used interchangeably with the term “binder”.
Resin
Pigmented coating
Paint
What are paints made out of?
A mix of binders, pigments, additives, and volatile components
Responsible for binding the pigment particles together and providing adhesion to the surface. Form the paint film backbone
Binders
Insoluble solid particles used to impart color and/or provide anti-corrosion protection.
Pigments
What is the most significant pigment and why?
Titanium Dioxide, refractive index
Used in metallic finished and can be used in combination with other colored pigments. Generally irregular corn-flake or silver-dollar shaped.
Aluminum flakes
Provide color by means of interference
Effect pigments
Substances added to paints in small quantities with the purpose of improving specific properties. Since they come in small quantities, they are not forensically dependable.
Additives
Commonly referred to as the solvent, and is responsible for dissolving the binder and providing proper consistency. They evaporate as the coating is applied, meaning not often involved in forensic application.
Volatile substances
Why would it be important to find lead from the paint chip of a suspect’s vehicle?
Lead was banned from automotive coatings in the early 2000s
A type of paint application where droplets of paint in a fine spray are directed towards the surface. Only a fraction of the droplets reach the intended surface, leaving an overspray which may be valuable in forensics.
Spraying
A type of paint application involving the submersion of an item into a tank. Used for tools, agricultural parts, and even automotive primers. Common defects include gradient thickness and formation of drips/tear drops.
Dipping
A type of paint application where the metallic body is submerged in an aqueous bath and, with the help of an electric current, the coating or primer layer is deposited. Used in over 98% of automotive bodies.
Electrodeposition
What is the formal name for the paint layers applied by the manufacturer?
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM)

This type of analysis involves holding the paint chip by forceps with one hand, and using the other to cut across the surface. Can document number, sequence, relative thickness, and colors. Requires patience and practice.
Cross-sections
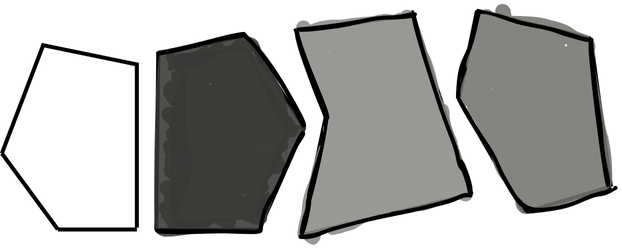
This type of analysis refers to a thin cut of a single layer, generally horizontally, across the layer surface.
Thin peels
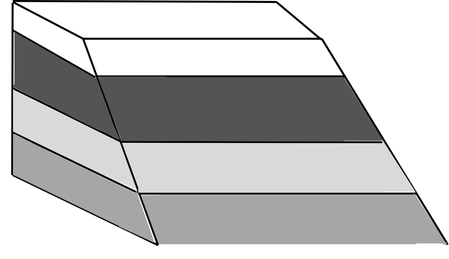
This type of analysis involved cutting the layer system at an oblique angle using a scalpel. The result is an angled surface. Most useful when the interior layer is very thin and difficult to observe.
Wedge cut
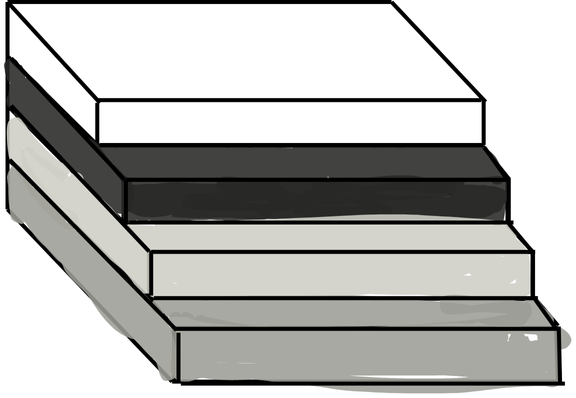
This type of analysis involves removing a layer with a scalpel to expose the layer underneath. Hold sample on a glass microscope slide with the larger surface face down.
Stair step
Fill in the blank: The more paint layers that transfer, the _____ the number of paint systems that could share this common source.
Lower
What are these?…
- weathering characteristics
- dirt/debris
- sag
- overspray
- solvent popping/trapping
- sanding marks
Defects in paint