DENT Fun. I - Amino Acids/Proteins
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Functions of Proteins
- Enzymes
- Regulation of gene expression
- Transport
- Storage
- Structure
Peptide
Short polymer of amino acids
Protein is read from the ____ terminus to the ____ terminus.
amino/carboxyl
Amino Acid Structure
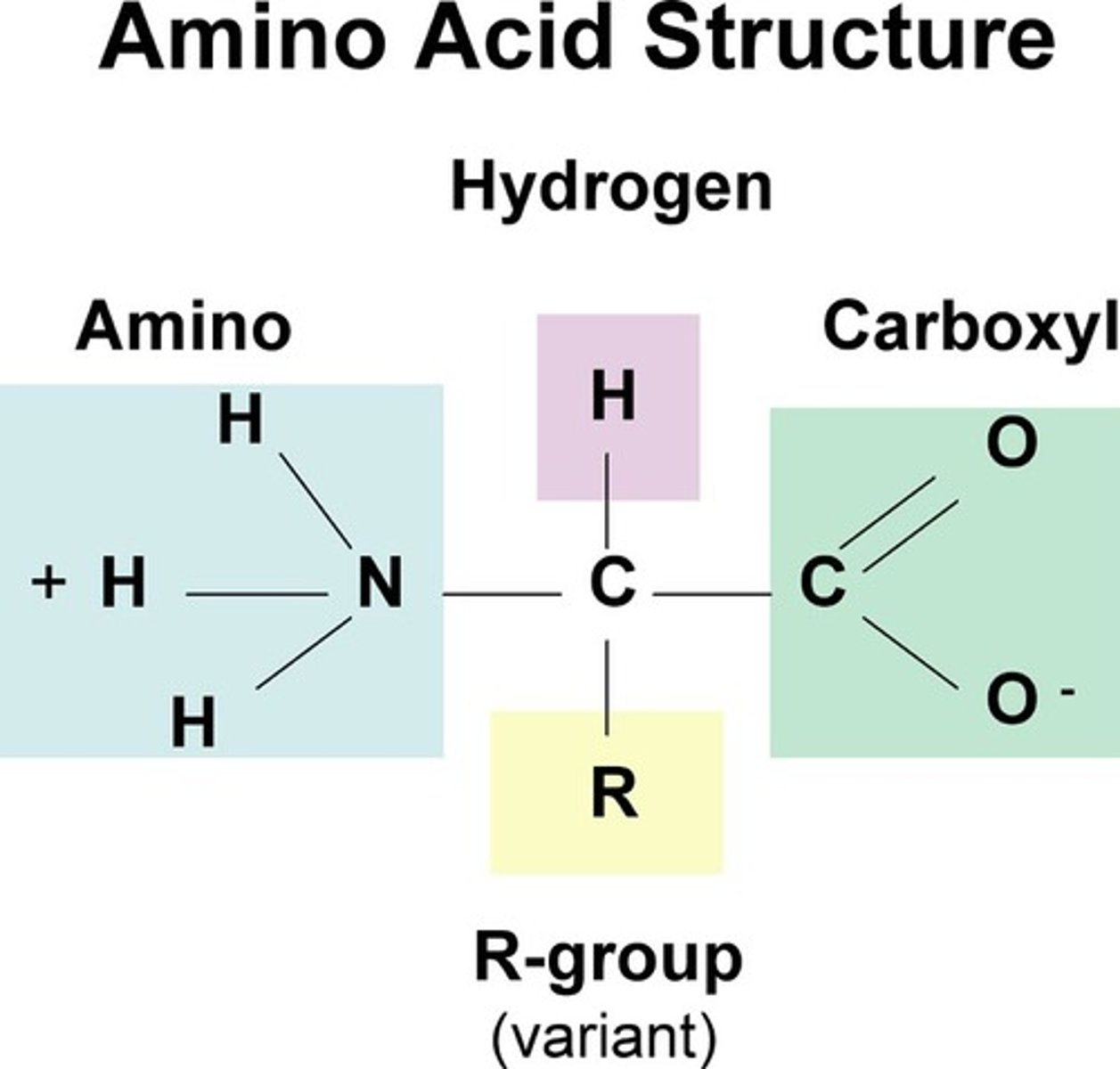
Amino Acids are ____.
weak polyprotic acids
L
Leucine (Leu)
I
Isoleucine (Ile)
P
Proline (Pro)
A
Alanine (Ala)
V
Valine (Val)
M
Methionine (Met)
W
Tryptophan (Trp)
F
Phenylalanine (F)
G
Glycine (Gly)
S
Serine (Ser)
N
Asparagine (Asn)
Q
Glutamine (Gln)
T
Threonine (Thr)
C
Cysteine (Cys)
Y
Tyrosine (Tyr)
D
Aspartic Acid (Asp)
E
Glutamic Acid (Glu)
K
Lysine (Lys)
R
Arginine (Arg)
H
Histidine (H)
Ka = ____
[H+][A-]/[HA]
Nonpolar Amino Acids
8
- L
- I
- P
- A
- V
- M
- W
- F
Polar Amino Acids
7
- G
- S
- N
- Q
- T
- C
- Y
Acidic Amino Acids
2
- D
- E
Basic Amino Acids
3
- K
- R
- H
What are the 6 rare amino acids that occur in proteins?
- Selenocysteine (U)
- Pyrrolysine (O)
- Hydroxylysine
- Hydroxyproline
- Carboxyglutamic Acid
- Pyroglutamic Acid
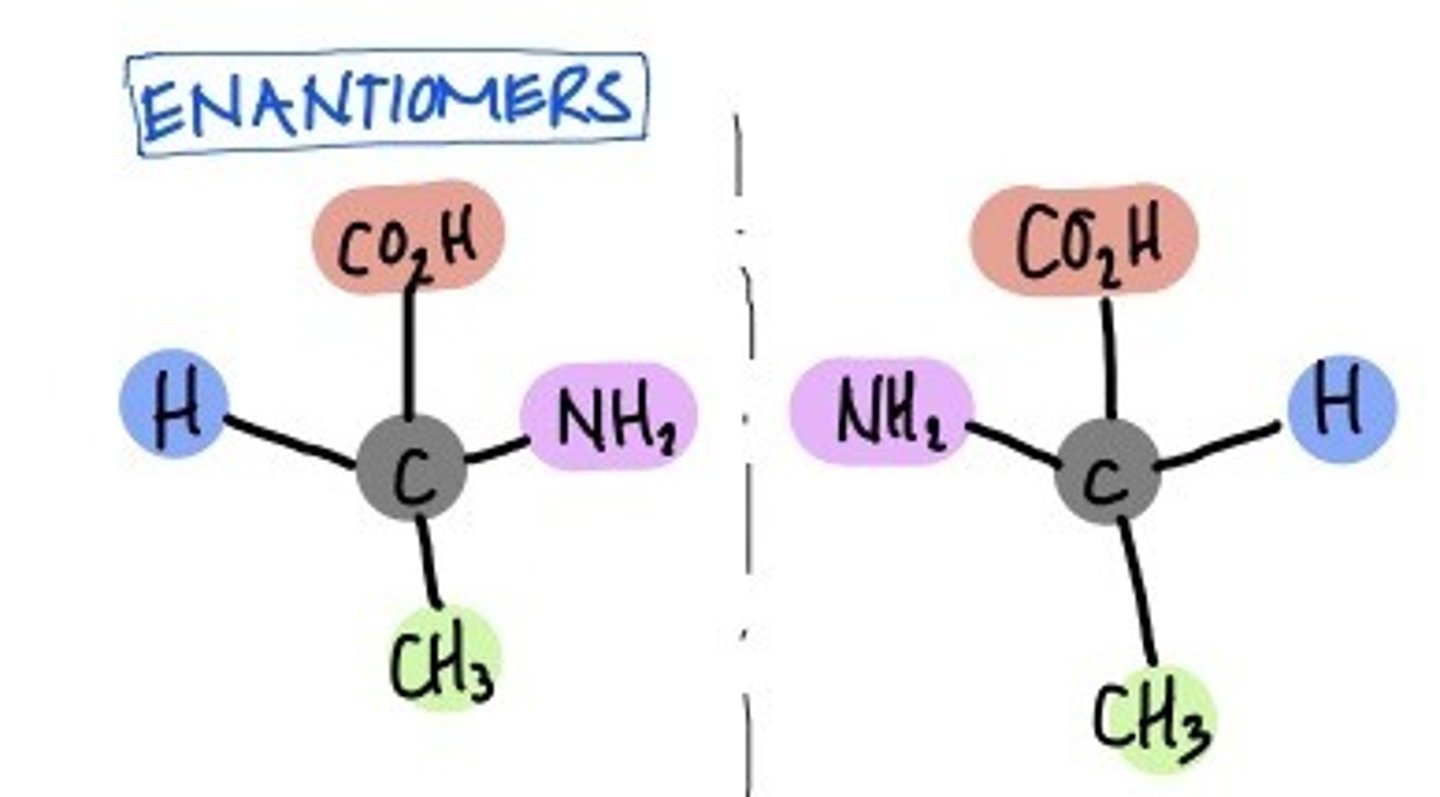
Chiral Center
Carbon with four different substituents and lack a plane of symmetry
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other
L-Amino Acid
Amino group on the left
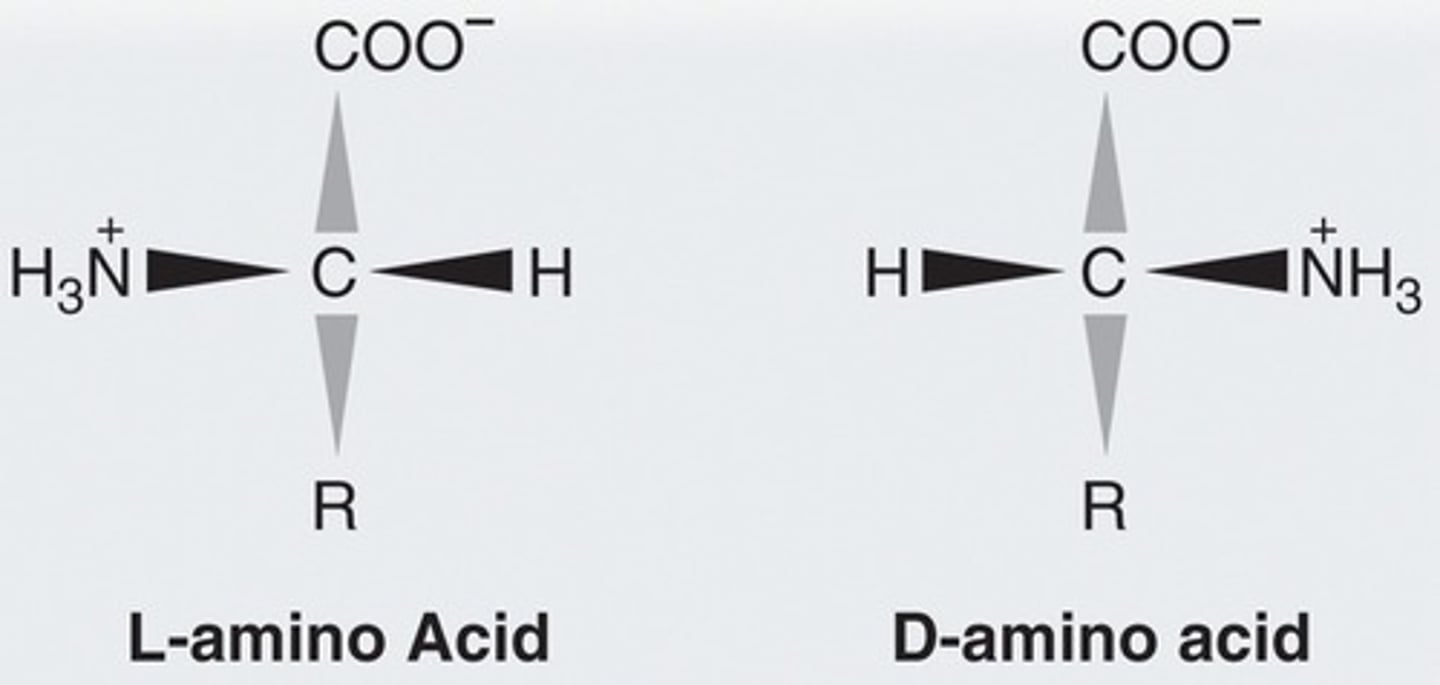
D-Amino Acid
Amino group on the right
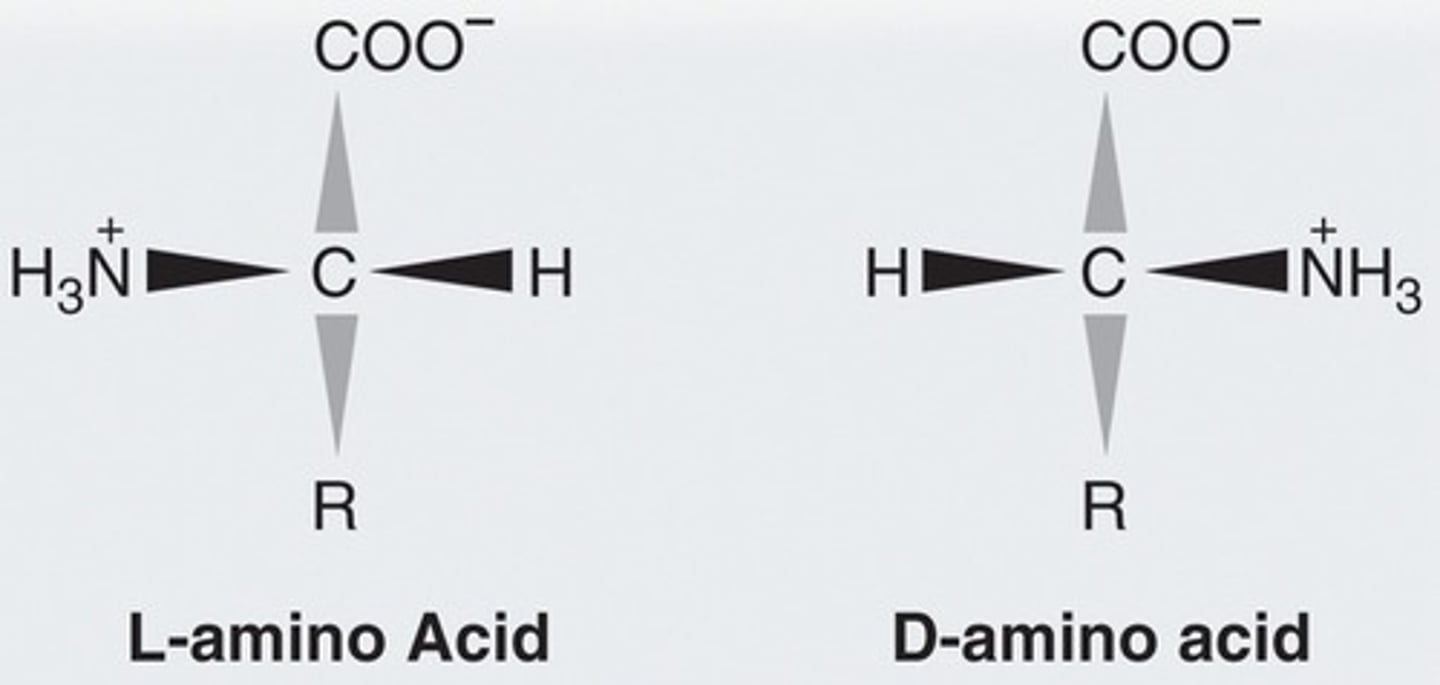
____-Amino Acids predominate in nature.
L
R, S System
R: clockwise
S: counterclockwise
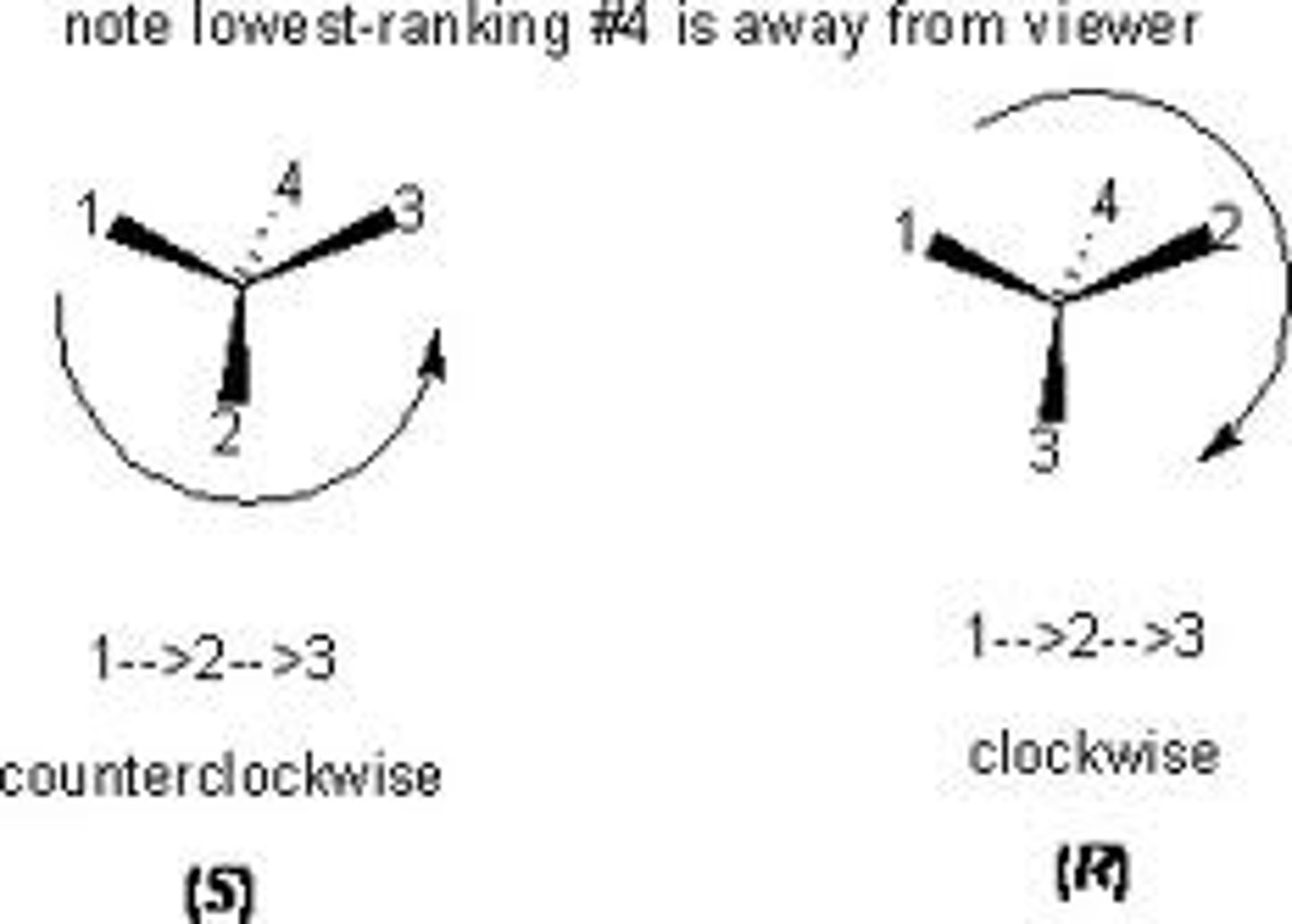
Functional Group Priorities
(1) SH
(2) OH
(3) NH2
(4) COOH
(5) CHO
(6) CH2OH
(7) CH3
Peptide Backbone
N-C-C
Alpha Carbon
Central carbon atom of each amino acid
Peptide Bonds
- Covalent bonds between amino acids that release water when formed
- COO- (carboxyl) + NH3+ (amino)
- Has double-bond character due to Carboxyl
Trans-Conformation
Largest groups are opposite; Most stable
Syn-Conformation
Largest groups are eclipsed
Primary Structure
Amino acid sequence
What is the difference between conformation and configuration?
Conformation can be changed by rotating a bond while configuration requires breaking a bond to change
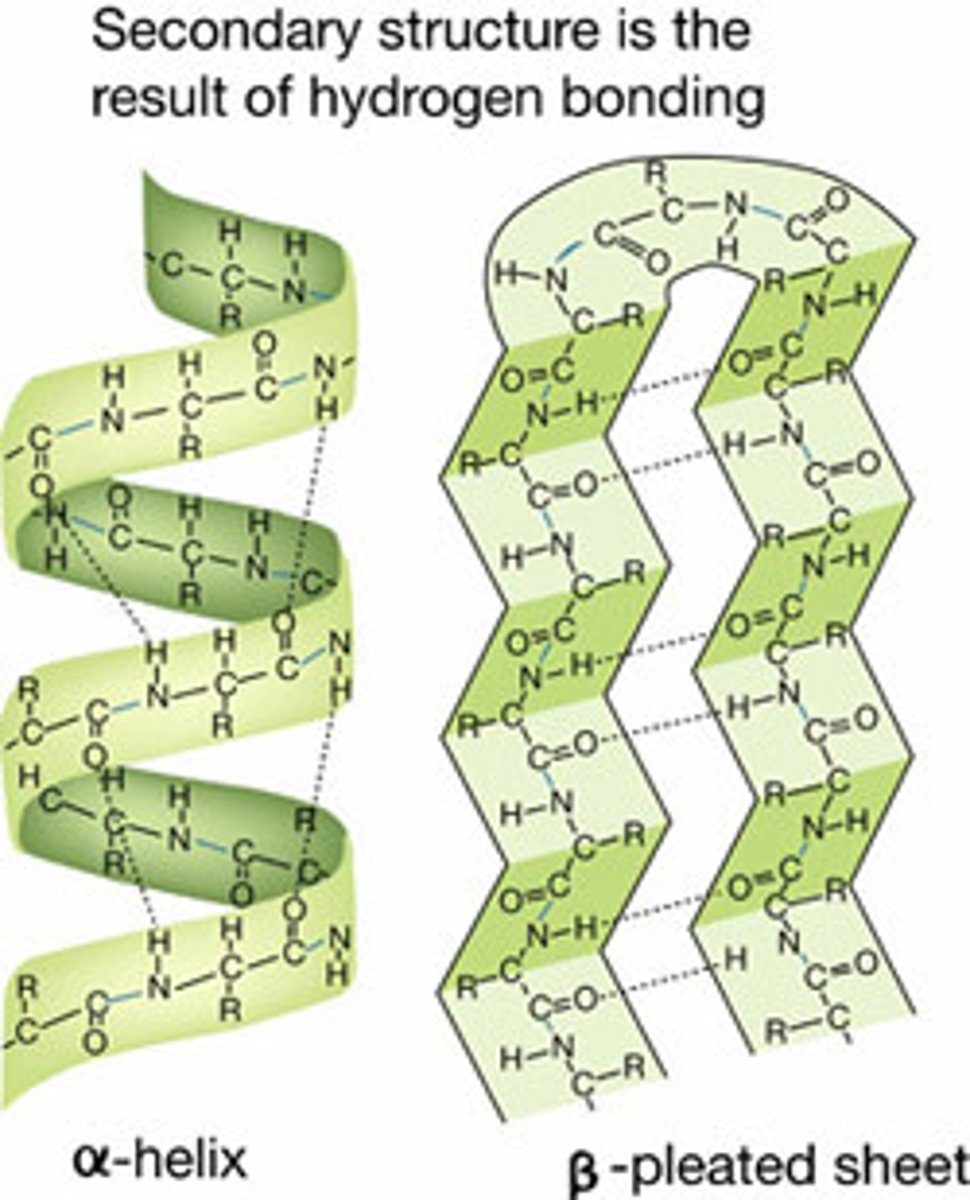
Secondary Structure
Noncovalent interactions of amino acids cause formation of sheets or helices
Tertiary Structure
3-D Shape of a polypeptide
Quaternary Structure
Association of 2 or more polypeptides, forming a functional protein
Proteins can be separated by ____ and ____.
size/charge
Proteins are least soluble at their ____.
isoelectric point
Isoelectric Point
The pH value at which the amino acid exists as a zwitterion (neutral)
Spectroscopy (NMR)
Use of infrared wavelengths to identify an amino acid
What is the best wavelength for absorbance?
280 nm
What amino acids can absorb UV light?
- Phe
- Tyr
- Trp
Determination of Protein Concentration via UV absorption depends on ____.
the presence of aromatic rings
What 2 methods can help sequence a Protein?
- Real Amino Acid Sequencing
- Sequencing the corresponding DNA
What are the 2 methods of "Real Amino Acid Sequencing"?
- Sanger Method
- Mass Spectrometry
Protein Sequencing Process
(1) Separate polypeptide
(2) Remove disulfide bonds
(3) Use proteolytic enzymes to make shorter polypeptides
(4) Determine sequence
(5) Use overlapping fragments to reconstruct the protein
a-Helix
Spiral
B-Sheet
The primary chain "zig-zags" back and forth forming a "pleated" sheet. Adjacent strands are held together by hydrogen bonds.
____ drive protein folding.
Hydrophobic interactions
Ionic interactions typically occur on the ____.
protein surface
phi angle (ϕ)
Angle around the alpha carbon-amide nitrogen bond
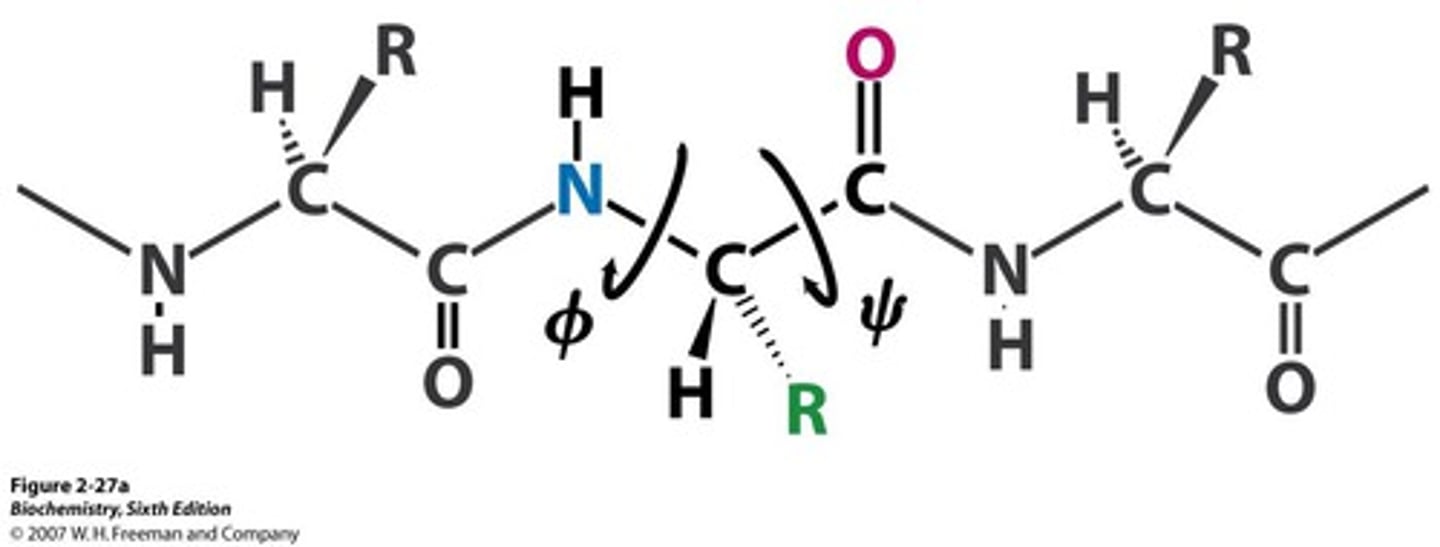
psi angle (Ψ)
Angle around the alpha carbon-carbonyl carbon bond
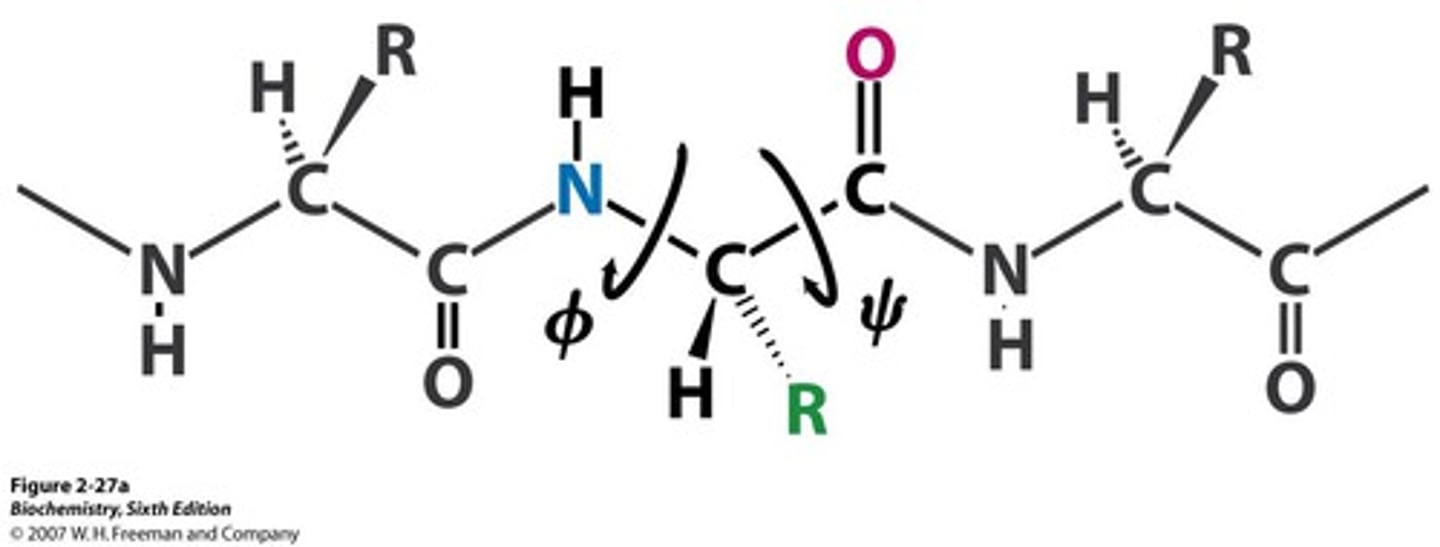
What combination of phi and psi angles are unfavorable?
(1) ϕ = 0*
Ψ = 180*
(2) ϕ = 180*
Ψ = 0*
(3) ϕ = 0*
Ψ = 0*
Cause orbital overlap and strain on the peptide bond
Ramachandran Map
List plotting the most favorable combinations of phi (ϕ) and psi (Ψ) angles for different structures
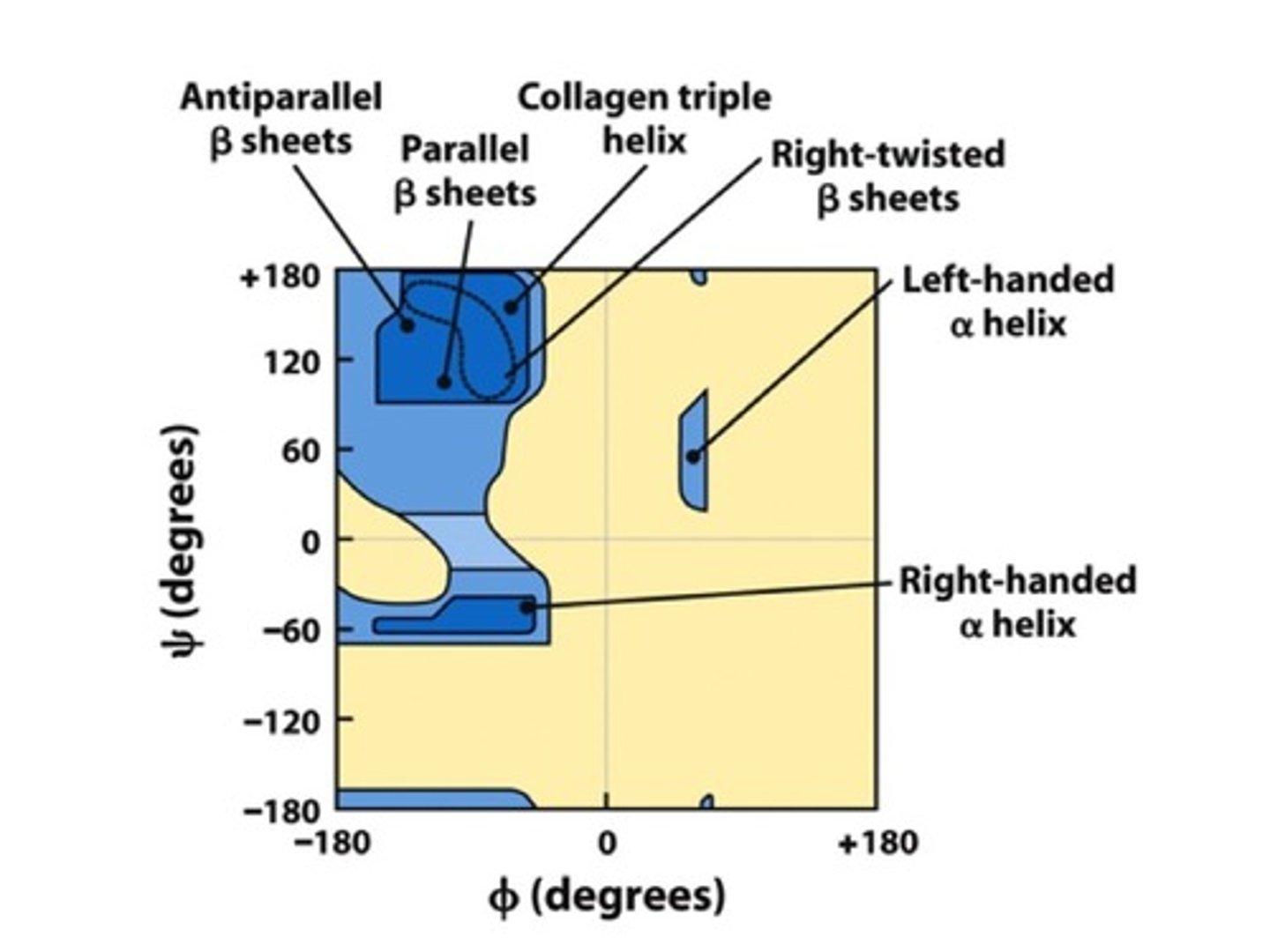
Secondary structures are stabilized by ____.
Hydrogen Bonds
What are the 4 Secondary Structures?
- Alpha-Helices
- Other Helices
- Beta-Sheet
- Tight Turns
Alpha-Helix
- Residues/Turn: 3.6
- Rise/Residue: 1.5
- Rise/Turn: 5.4
- ϕ = -60*
- Ψ = -45*
The arrangement of N-H and C=O groups along an Alpha-Helix creates a large net ____.
dipole moment
Helix Capping
- The formation of H-bonds with other nearby donor and acceptor groups
- Aids in the formation of the Alpha-Helix
Beta-Pleated Sheet
- A type of protein secondary structure; results from hydrogen bonding between polypeptide regions running antiparallel to each other
- Strands may be parallel or anti-parallel
Rise/Residue of Parallel Strands (B-Sheet)
3.25 Angstroms
Rise/Residue of Antiparallel Strands (B-Sheet)
3.47 Angstroms
Beta-Turn
- A type of protein secondary structure consisting of four amino acid residues arranged in a tight turn so that the polypeptide turns back on itself
- Carbonyl C is H-Bonded to an Amide 3 residues away
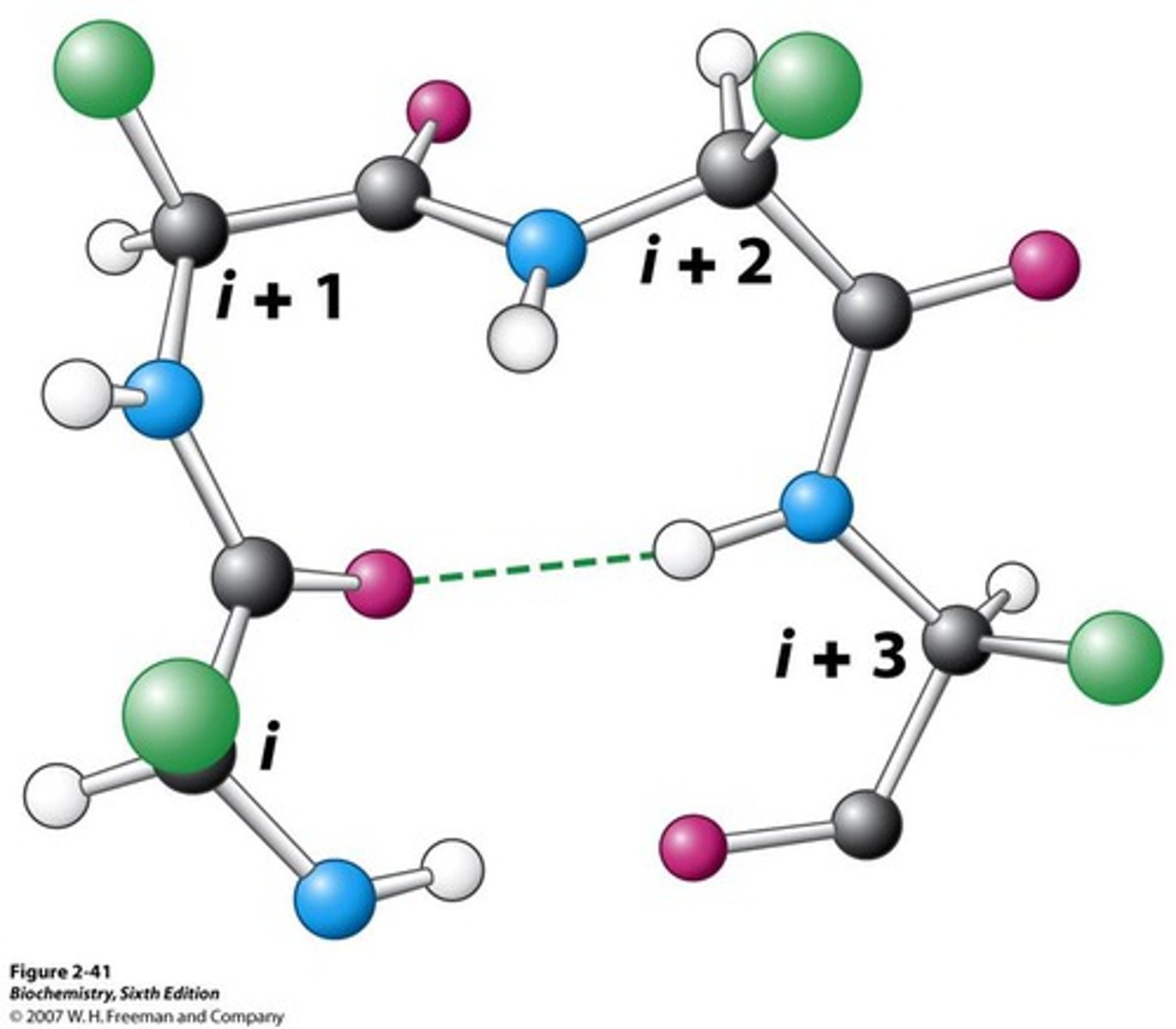
What 2 amino acids are prevalent in Beta-Turns?
- Proline
- Glycine
What are the 2 forms of Beta-Turns?
- Type 1: Proline in Pos.3
- Type 2: Proline in Pos.2, Glycine in Pos.3
X-Ray Crystallography
Technique used to study the three-dimensional structure of molecules. Utilizes the diffraction of X-Rays off of a crystal to create a protein model.
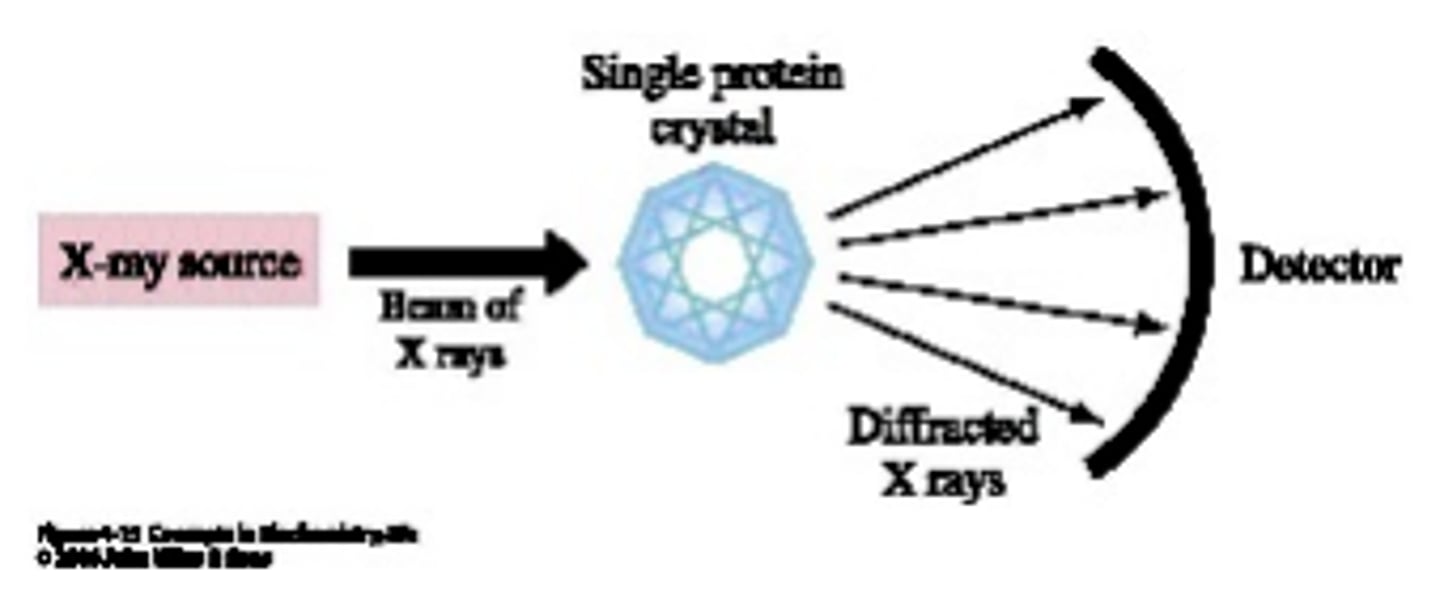
Proteins form into the most ____ structures possible.
stable
What 2 factors drive Protein Stability?
- Formation of many intramolecular H-Bonds
- The Hydrophobic amino acids cluster on the interior
What are the 2 Protein Tertiary Structures?
- Globular
- Fibrous
Globular Proteins
Spherical, water-soluble proteins that maximize internal bonds and minimize solvent contact
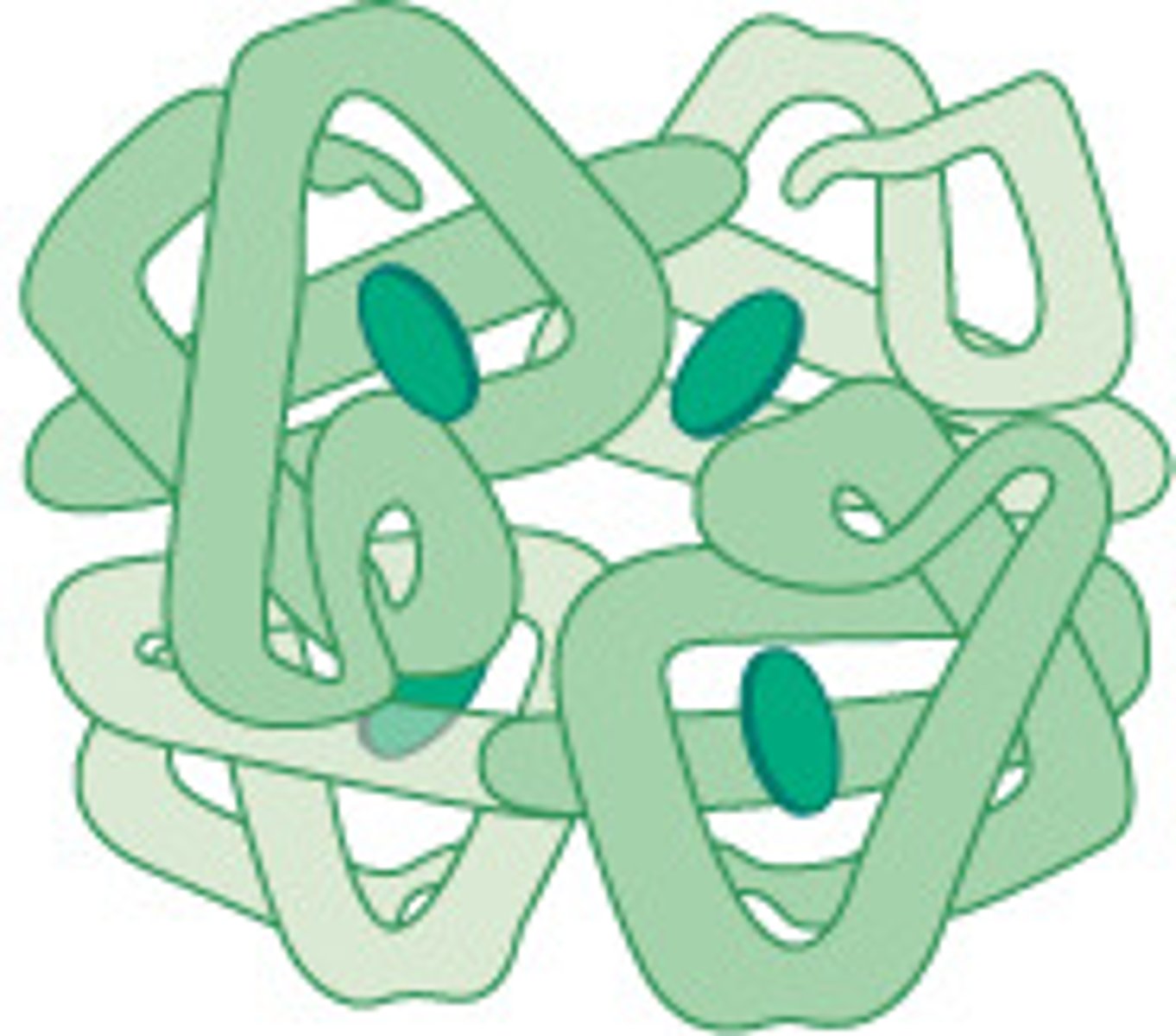
Fibrous Proteins
- Long, insoluble, structural proteins that maximize intermolecular bonds and molecule-molecule contact
- Mechanically strong

What are the 3 Fibrous Proteins?
- a-Keratin
- B-Keratin
- Collagen
a-Keratin
- Hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails
- Protein composed of a coiled-coil motif
Coiled-Coil Motif
Protein motif in which two alpha-helices twist around each other in a left-handed supercoil, interacting through hydrophobic contacts
B-Keratin
- Protein that composes the feathers of birds
- Forms extensive B-Sheets instead of fibers
Collagen
- Structural protein found in the skin and connective tissue
- Composed of a Triple Helix
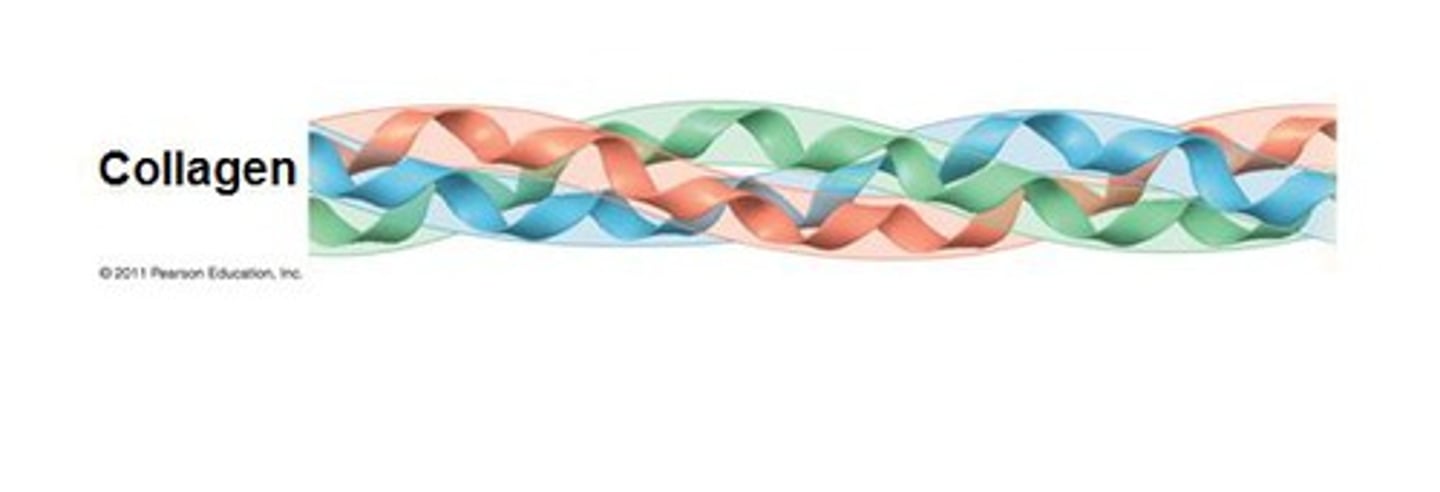
What is the typical amino acid composition of Collagen?
Gly-Pro-Hydroxyproline
What are the 2 types of Collagen?
Right-Handed Helix
- 3.6 residues/turn
- 5.4 rise/turn
Left-Handed Helix
- 3.3 residues/turn
- 9.9 rise/turn
Globular Proteins mediate ____.
cellular function; more numerous than fibrous proteins
What are the 4 classes of Globular Proteins?
- Alpha: Alpha-Helices dominate
- Beta: Beta-Sheets dominate
- a/B: Helices and Sheets are intermingled
- a + B: Contain separate Helical and Sheet domains in one protein
What are the 5 advantages of Quaternary Structure?
- Stability: Surface/Volume Ratio
- Efficiency
- Assembly
- Cooperativity
- Regulation: Based on protein-protein interaction
There is a large amount of ____ in quaternary structure of Proteins.
symmetry
Proteins are purified by ____.
chromatography
The native structure of proteins are flexible under ____ conditions.
physiological