Teeth, pharynx and esophagus, stomach, digestive system
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
mastication
chewing food into smaller pieces
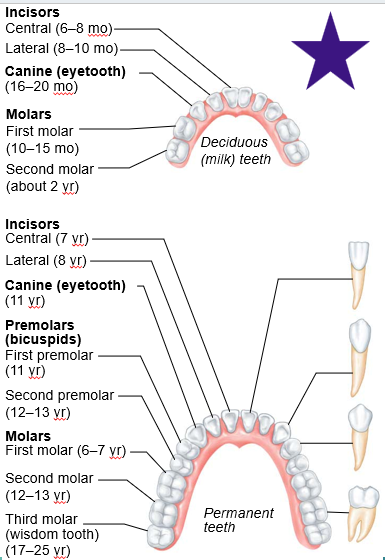
how many teeth are dentition (baby teeth)
20 during 6 and 24 months of age
how many adult permanenet teeth do you develope
32
all molars except the 3rd one is
wisdom teeth
teeth classification:
incisors?
canines?
premolars?
molars?
incisors: cutting
canines: tear or puncture
premolars: grinding or crushing food
molars: best grinders
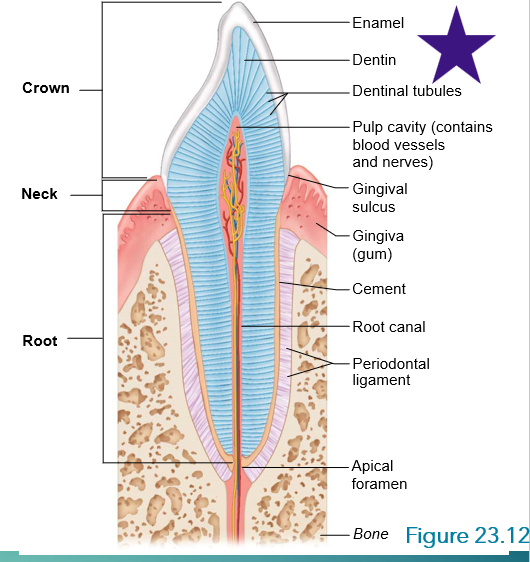
canine tooth interior anatonmy:
crown?
root?
dentin?
pulp?
crown: hardest enamel
root: bone in your jaw connected to the crown
dentin: under enamel
pulp: nerves, blood vessel, connective tissure
what is an impacted tooth?
treatment?
tooth remained trapped in the jawbone
treament: surgical removal
Dental caries (cavities)
Dental plaque
prevention?
dental cavities: demineralization of enamel and dentin from bacterical action
Dental plaque: sugar, bacteria, and dedbris adheres to teeth
prevention: daily flossing and brushing
Gingivitis
plaque calcifies to form calculus (tartar)
Perioddontitis (periodontal disease)
neglected gingivitis can escalate to disease
immunce cells attack not only baterical intruders but your body tissues in tooth.
The pharynx
type of epithelium?
food passes from mouth into oropharynx and then into laryngopharynx.
allows passage food, fluids, and air
stratified dsquamous epithelium
esophagus has 4 what?
esophageal muscosa contains what epithelium? it changes to what epithelium at stomach
4 alimentary canal layers
stratified squamuos epithelium then to simple columnar at stomach
esophagus:
pierces diaphragm at?
joins stomach at?
what surrounds cardial orifice?
pierces diaphragm at: esophageal hiatus
joins stomach at: cardinal orifice
what surrounds cardial orifice: gastroesophageal (cardiac) sphincter
clinical:
Heartburn
causes?
first symptom?
can also be caused by?
heartburn: caused by stomach acid regurgitating into esophagus
first symptom: gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
also caused by: hiatal hernia
the stomach:
what is the name of converting bolus of food to paste?
when the stomach is empty it forms folds called?
a termporary storage tank that starts chemical breakdown of protein digestion.
converts bolus of food to paste like chyme
when empty, stomach mucosa forms many folds called rugae
what nervous system supplies stomach?
parasympathetic fibers are supplied by?
autonomic nervous system
supplied by vagus nerve
muscularis externa are smooth muscles that allow stomach to?
churn, mix, move, and pummel chyme. then rams it into small intestine
the stomach’s modified mucosa:
consist of what epithelium?
secretes two layer coat of?
simple columnar epithelium
two layer coat of: alkaline mucus
gastric glands produce what?
gastric juice
the stomach’s secretory glands:
4 types of gland cells that produce gastric juice
muscous neck cells
parietal cells
chief cells
enteronendocrine cells
cells of gastric glands:
parietal cells secretion?
chief cells secretion?
parietal cells secretion: hydrochloric acid (HCL)
chief cells secretion: pepsin
cells of gastric glands:
enteroendocrine cells secretion?
serotonin?
histamine?
hormones:
somatostain?
gastrin?
serotonin: stimulates muscle cell contractions
histamine: stimulates parietal cells to releaces HCI
hormones:
somatostatin: inihibts all gastric gland secretions
Gastrin: stimulates HCI secretion
the stomach’s protective mucosal barrier:
3 factors of stomachs muscosal barrier protection?
bicarbonate-rich mucus
tight junctions - prevent juice seeping underneath tissue
damaged epithelial cells are quickly replaced
clinical:
gastritis
peptic or gastric ulcers?
most ulcers caused by bacterum __?
inflmmation caused by a breach in stomach’s mucosal barrier
peptic or gastric ulcers: causes erosions in stomach wall
ulcers caused mostly by helicobacter pylori
digestive processes in stomach:
milk protein (casein) broken down by ___ in infanats?
stomach function secretion of ____ for vitamin b12 absoprtion
rennin
intrinsic factor
regulation of gastric secretion:
neural mechanism:
vagus nerve stimulates?
sympathetic stimulaties?
hormonal mechanisms:
gastrin stimulates?
vagus nerve stimulates: increase secretion
sympathetic stimulaties: decreases secretion
gastrin: stimulates HCI secretion