A Level Topic 4 - Production Costs and Revenues
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Decreasing returns to scale
When output increases by a smaller proportion than the increase in inputs
Diseconomies of scale
When long run average costs rise as output increases.
Increasing returns to scale
When output increases by a larger proportion than the increase in inputs
Internal Economies of Scale
Firms taking action to reduce unit costs, Purchasing, Financial, Managerial, Marketing and Risk Bearing Economies
External Economies of Scale
Cost savings that are outside of the control of the firm e.g. Location of suppliers, infrastructure, skills of the workforce in the area
Labour Productivity
Measure of effectiveness of workers calculated as Total Output / Avg No of Workers
Law of diminishing returns
When variable factors are added to fixed factors eventually the return per variable factor increase with fall
Long run
Time period in which none of the factors of production are fixed so any can be increased
Long Run Average Cost
Total cost per unit of output over a long period of time
Mechanisation
When a firm changes from being more labour intensive to more capital intensive
Minimum efficient scale MES
The lowest level of output at which average costs are minimised. Creates a barrier of entry for other firms entering the market.
Normal profit
Total revenue is equal to total costs, the minimum amount needed to keep a firm operating in an industry
Production
Turning raw materials into finished or semi finished output
Productivity
Measure of effectiveness, how well does the firm use its resources to turn inputs into outputs Total Output/Total Inputs
Short run
Time period in which at least one of the factors of production are fixed and cannot be increased or decreased
Specialisation
When an individual/firm or country focuses on performing one task or producing a specific product
Sunk Cost
Unrecoverable expenditure associated with entering a market
Supernormal/Abnormal Profit
Any level of profit over and above normal profit
Technical Economy of Scale
Increasing capacity through the introduction or better technology or more efficient machinery
X Inefficiency
When a firm does not have the incentive to control costs and therefore the average costs of production are higher than necessary
Benefits of Specialisation

Drawbacks of Specilisation

Diagram - Diminishing marginal returns
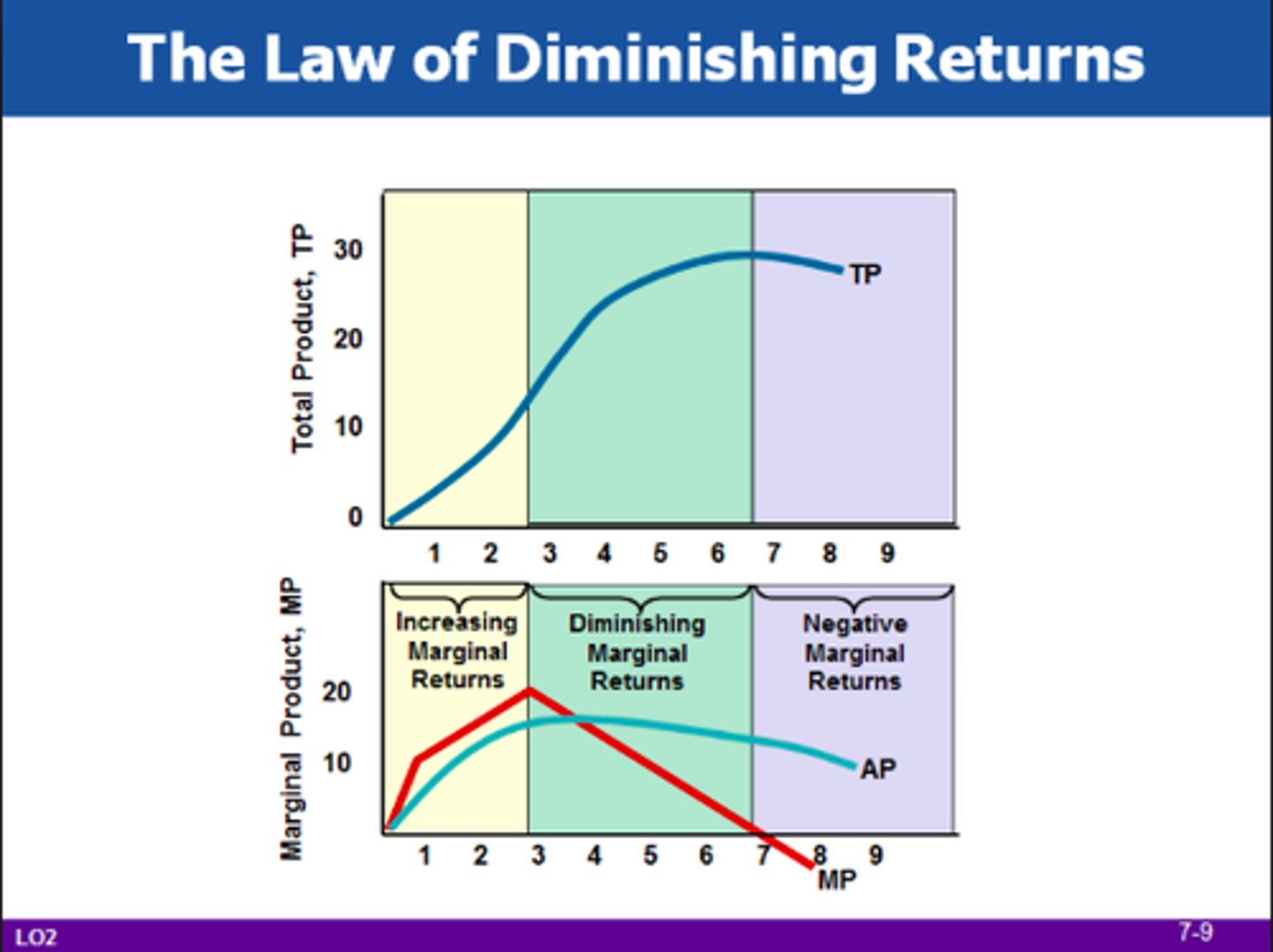
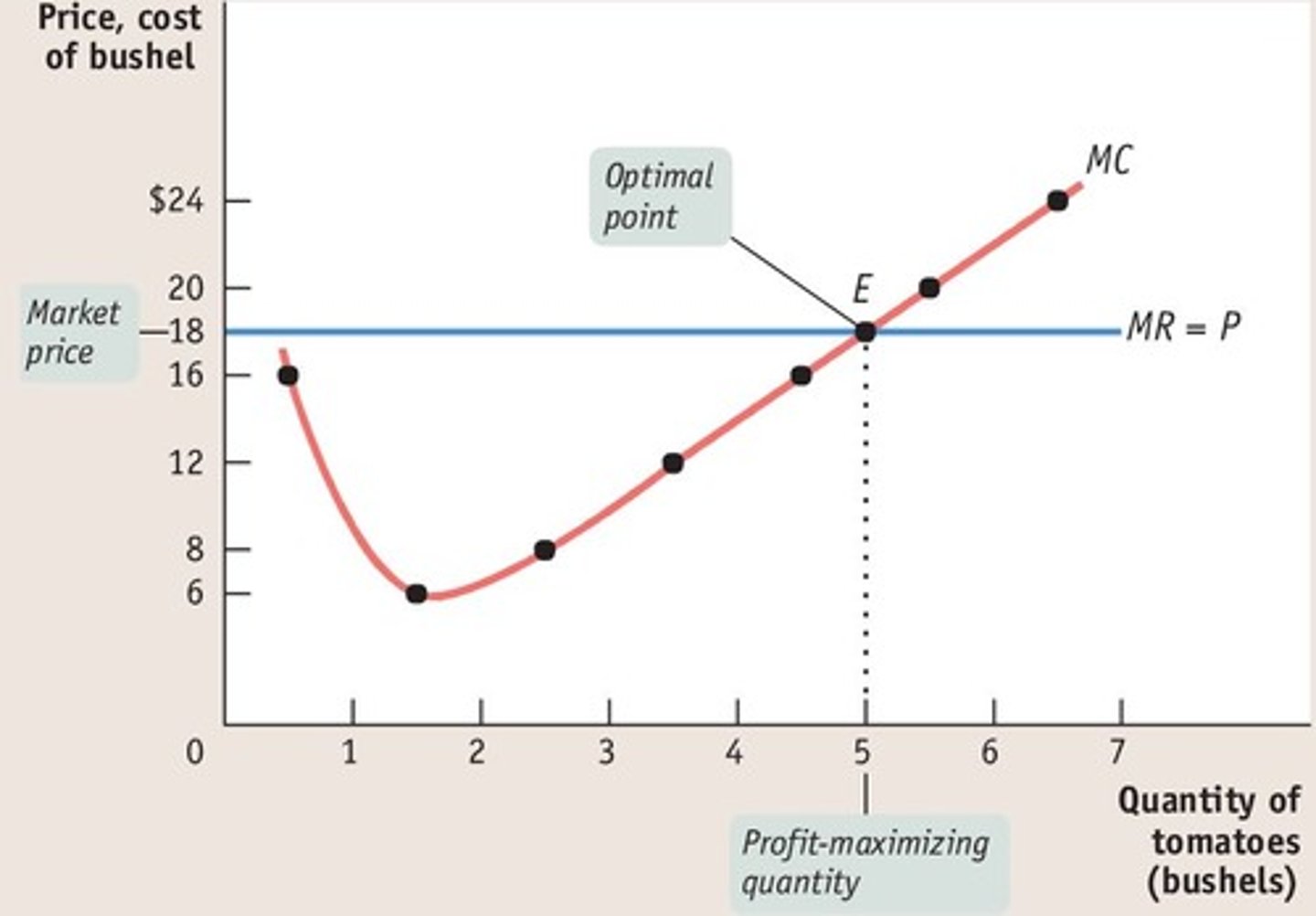
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing ONE additional unit of output
Draw the marginal cost curve
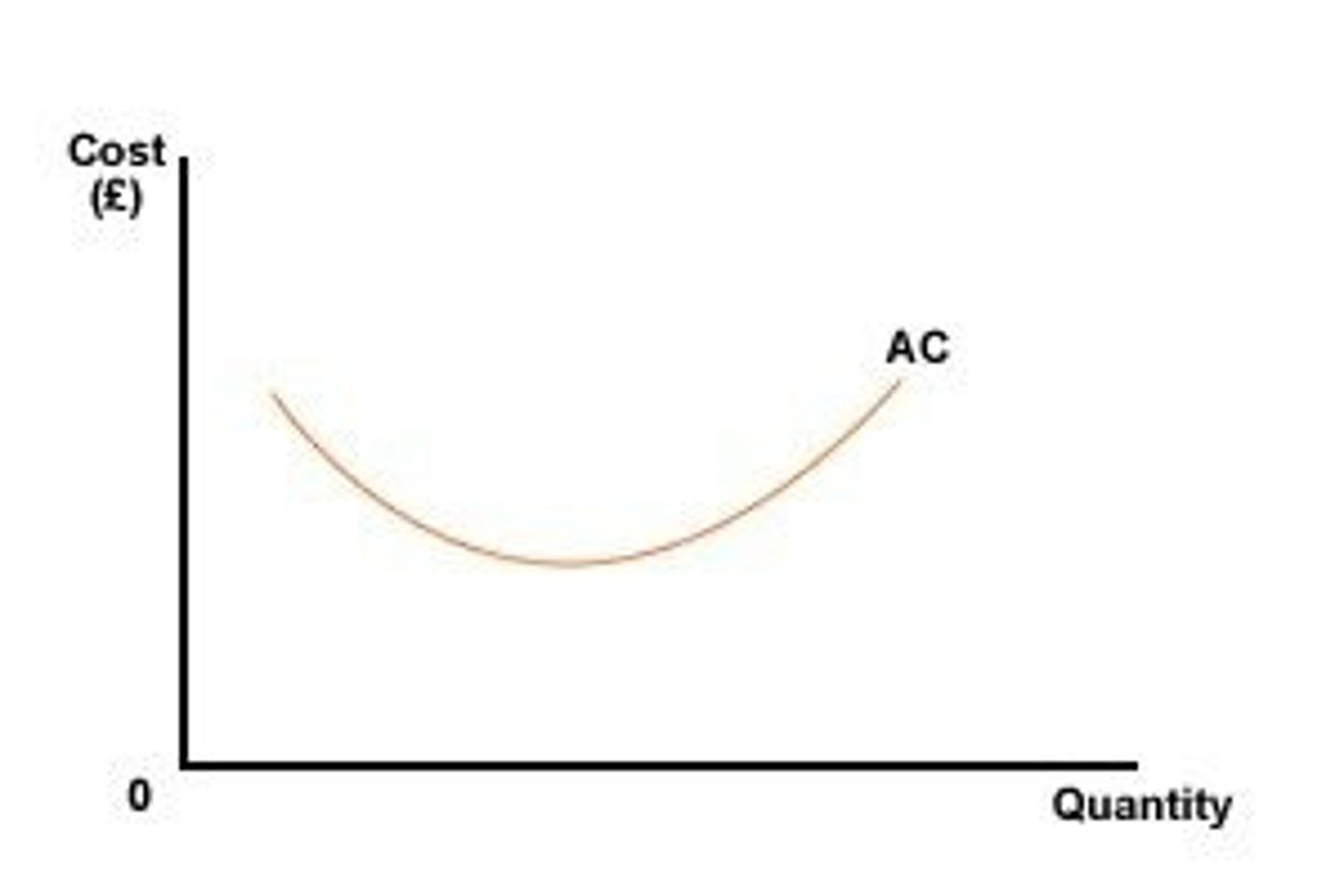
Draw the average cost curve
Marginal Revenue
Revenue recieved by the firm from selling the last unit of output.
Why is AR also the Demand Curve?
AR is average revenue, and the calculation for average revenue is Total Revenue / Quantity. Total Revenue = Price Quantity. Therefore AR = Price Quantity / Quantity => Price (as the Quantity is cancelled out). Hence AR = P, and D = P so we can say that D = AR.
What is the role of profit - why is it important?
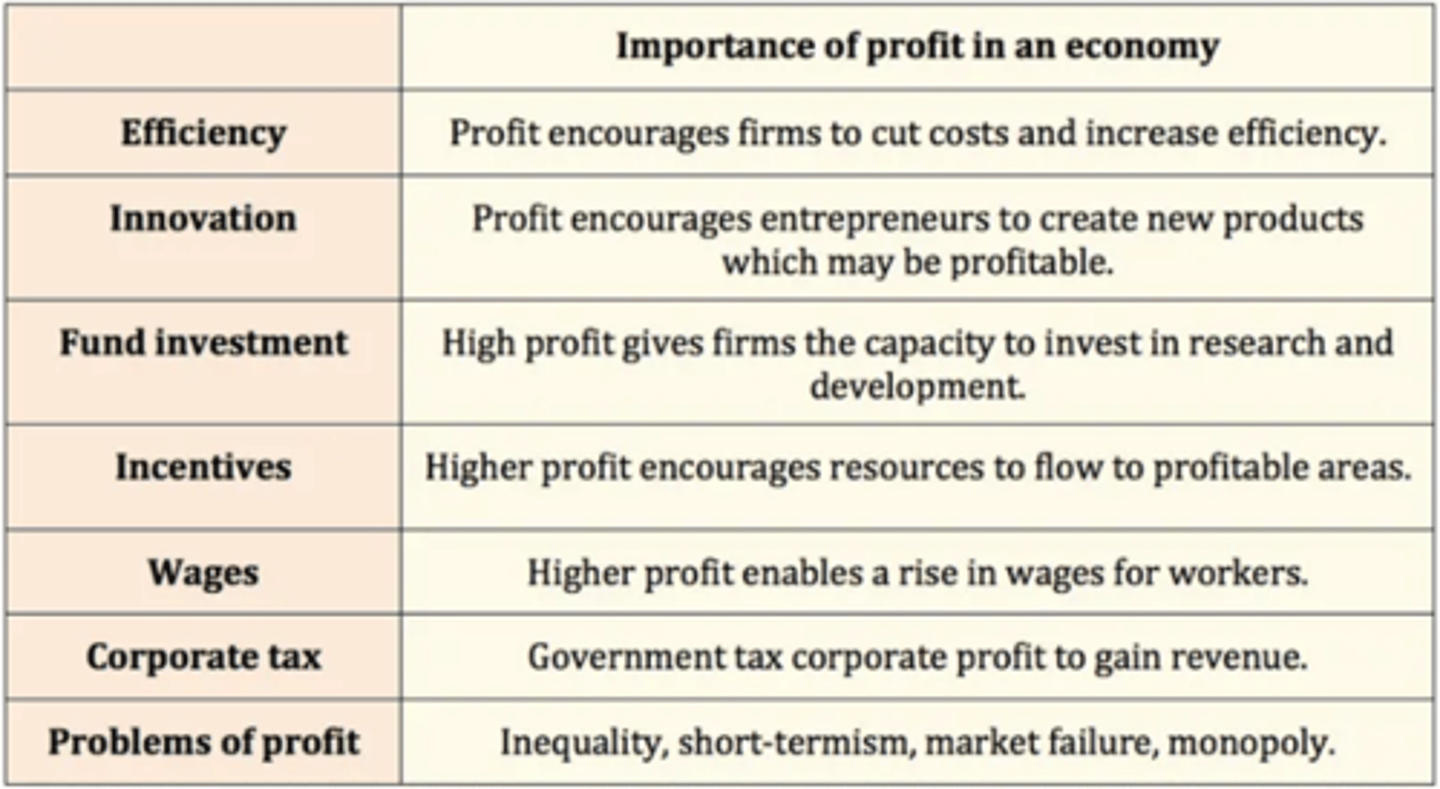
Invention
Invention is the discovery or development of a product or process by applying previous knowledge in new ways.
Innovation
Innovation is applying basic discoveries or inventions to produce a useful product or process and bringing it to the market
Technological Change
Technology lowers the cost of production and provides new products, it increases both productive and allocative efficiency for all firms. Technological change is the rate of developments in technology
Creative Destruction
the process of how capitalism leads to a constantly changing structure of the economy. Old industries and firms, which are no longer profitable, close down enabling the resources (capital and labour) to move into more productive processes
Economies of scope
When it is cheaper to make a range of products
Average Cost
The total production cost divided by the total output (cost per unit of output)
Average Revenue
Total revneue divided by total output (revenue per unit of output)
Division of labour
When production is split into smaller tasks and a worker performs one task
Economies of Scale
When long run average costs fall as output increases
Fixed Cost
Costs of production that do not vary with output produced e.g. rent, insurance,
Profit
Total revenue - total costs
Total Costs
Total Fixed Costs + Total Variable Costs
Total Revenue
Price of each good x the quantity sold. Total income recieved by the firm from its trading activities
Variable cost
Cost that increase or decrease as production levels increase or decrease. Directly related to output
Automation
Where parts of the production process are controlled by machines/robotics
Constant returns to scale
When output increases by an equal proportion to the increase in inputs
Types of disecnomies of scale
Communication Coordination Control