S437 Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach Vocabulary Flores
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

83 Terms
Alimentary canal
Tube through which food passes in the digestive system. Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus
Ingestion
Taking in a substance through the mouth

Propulsion
Action of pushing forward
Mechanical digestion
Physically breaking food up into smaller pieces

Chemical digestion
Breaking food up into smaller pieces through the use of enzymes and other digestive juices
Absorption
uptake of a substance by a tissue (like the uptake of nutrients by the small intestine)
Defecation
to void excrement from the intestines through the anus
Cephalic phase
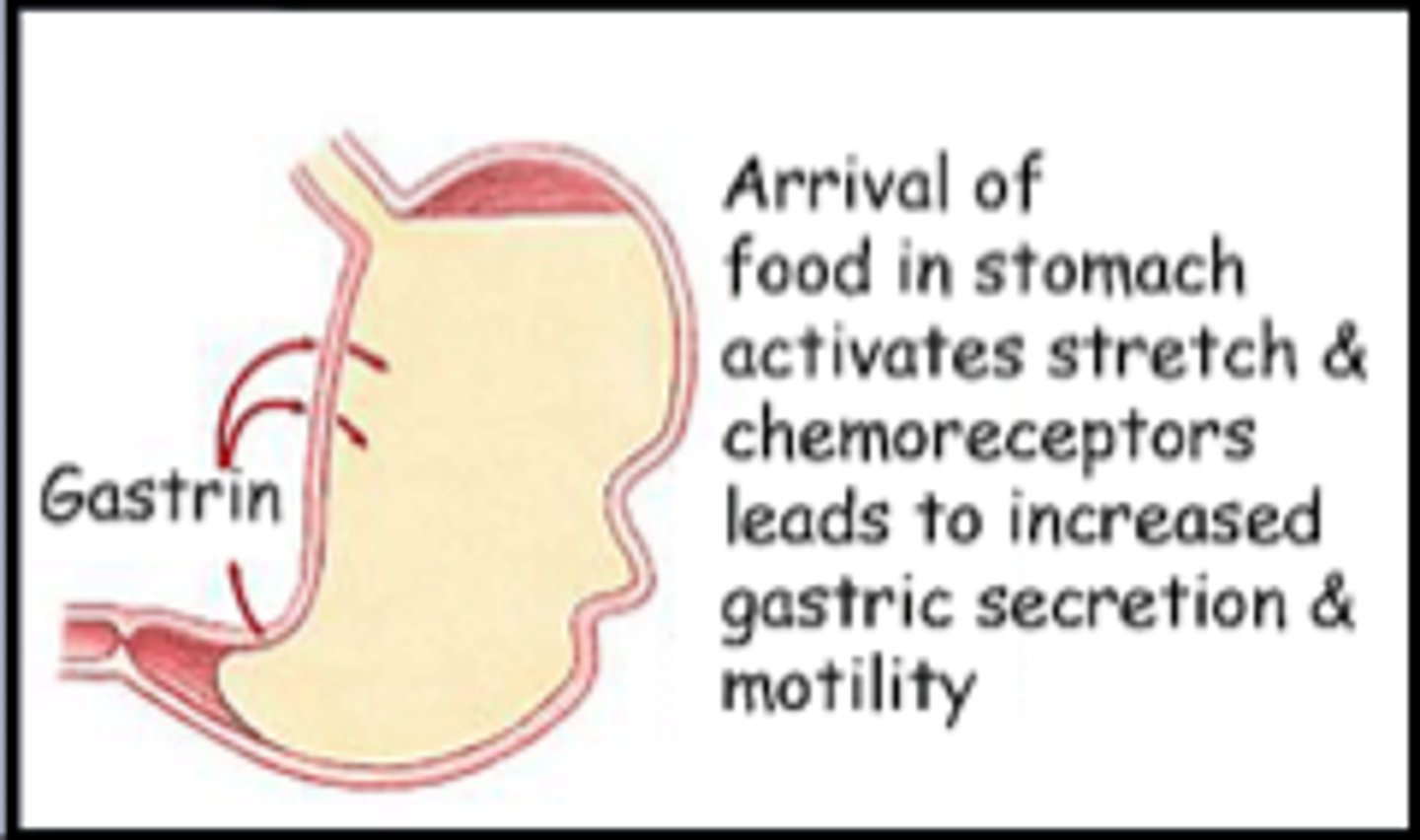
thinking about, smelling, or seeing food which has not entered the alimentary canal; when food is in the mouth

Gastric phase
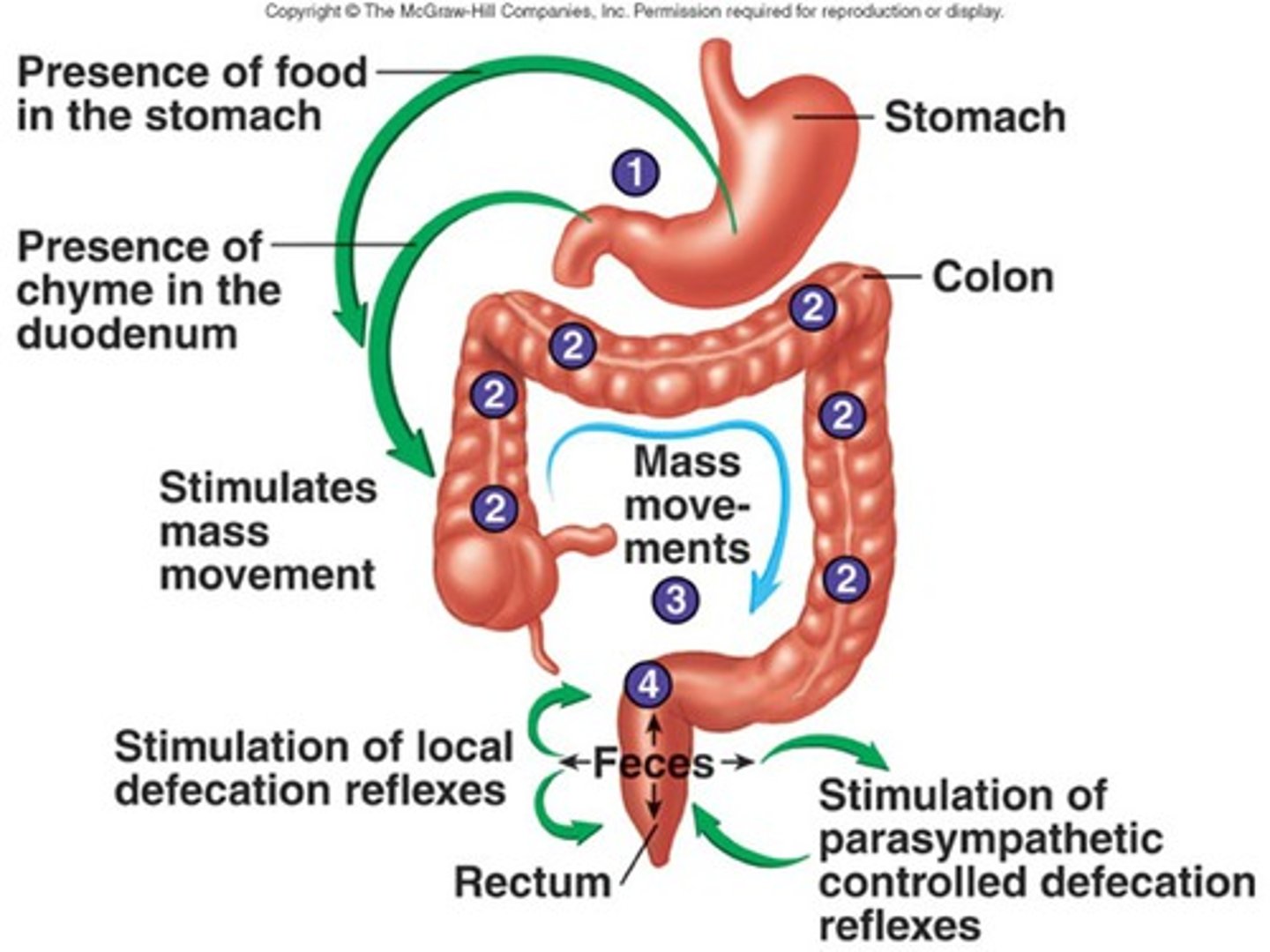
Period in digestion when food is in the stomach
Intestinal phase
Period in digestion when food is in the small intestine
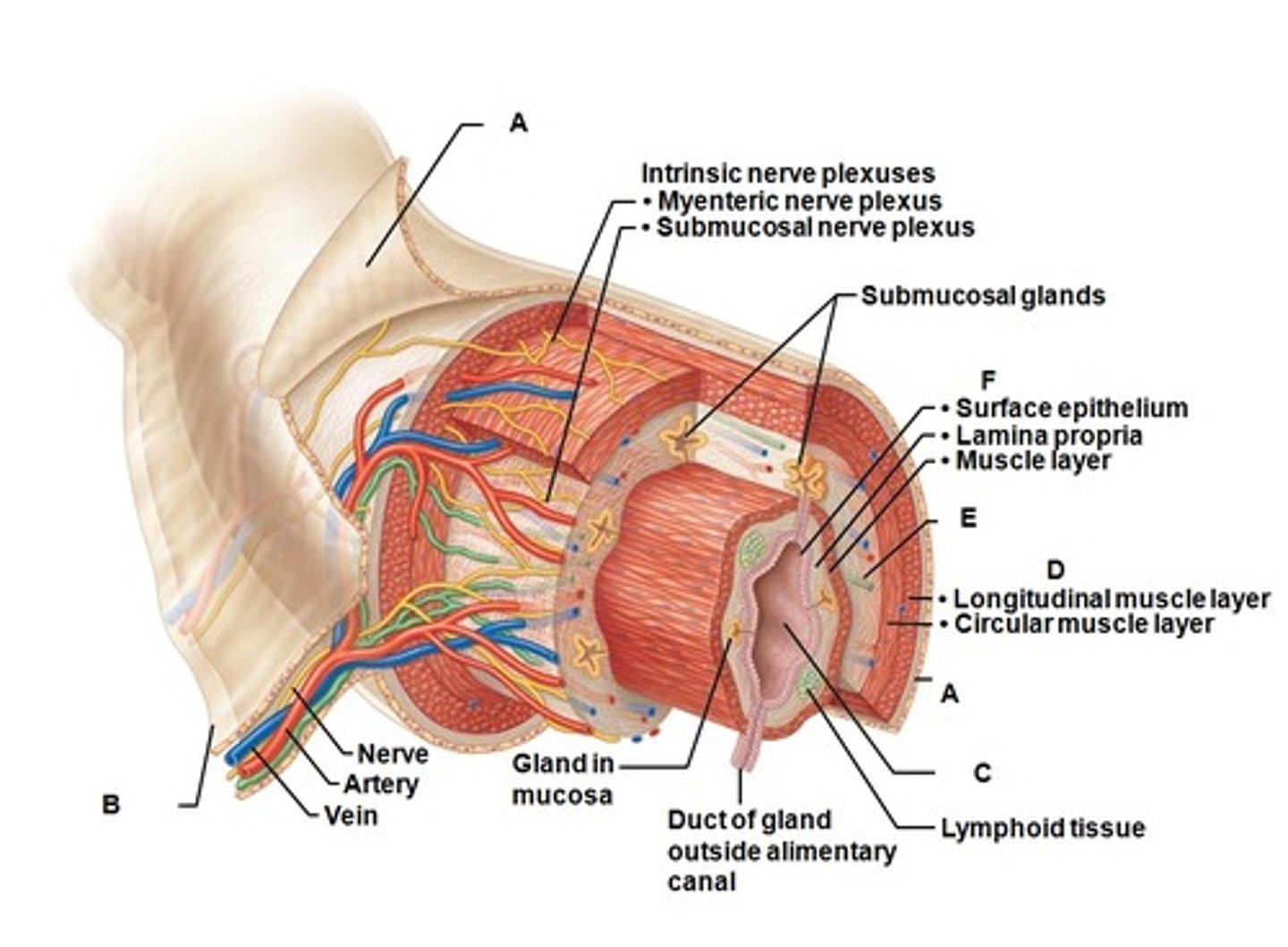
Mucosa
most deep of the 4 layers of the alimentary canal
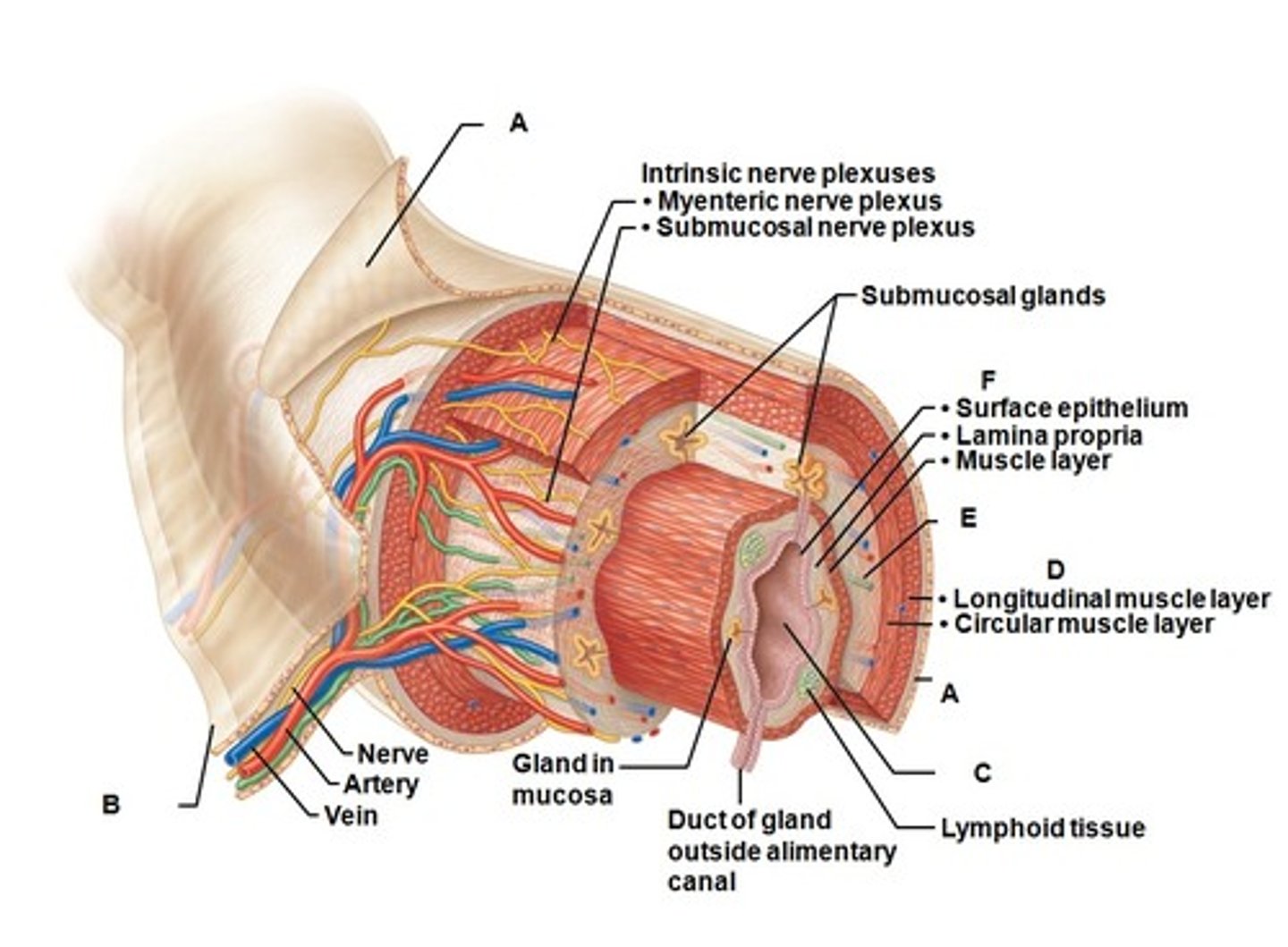
Epithelium (mucous membrane)
Most deep of the 3 layers of the mucosa.
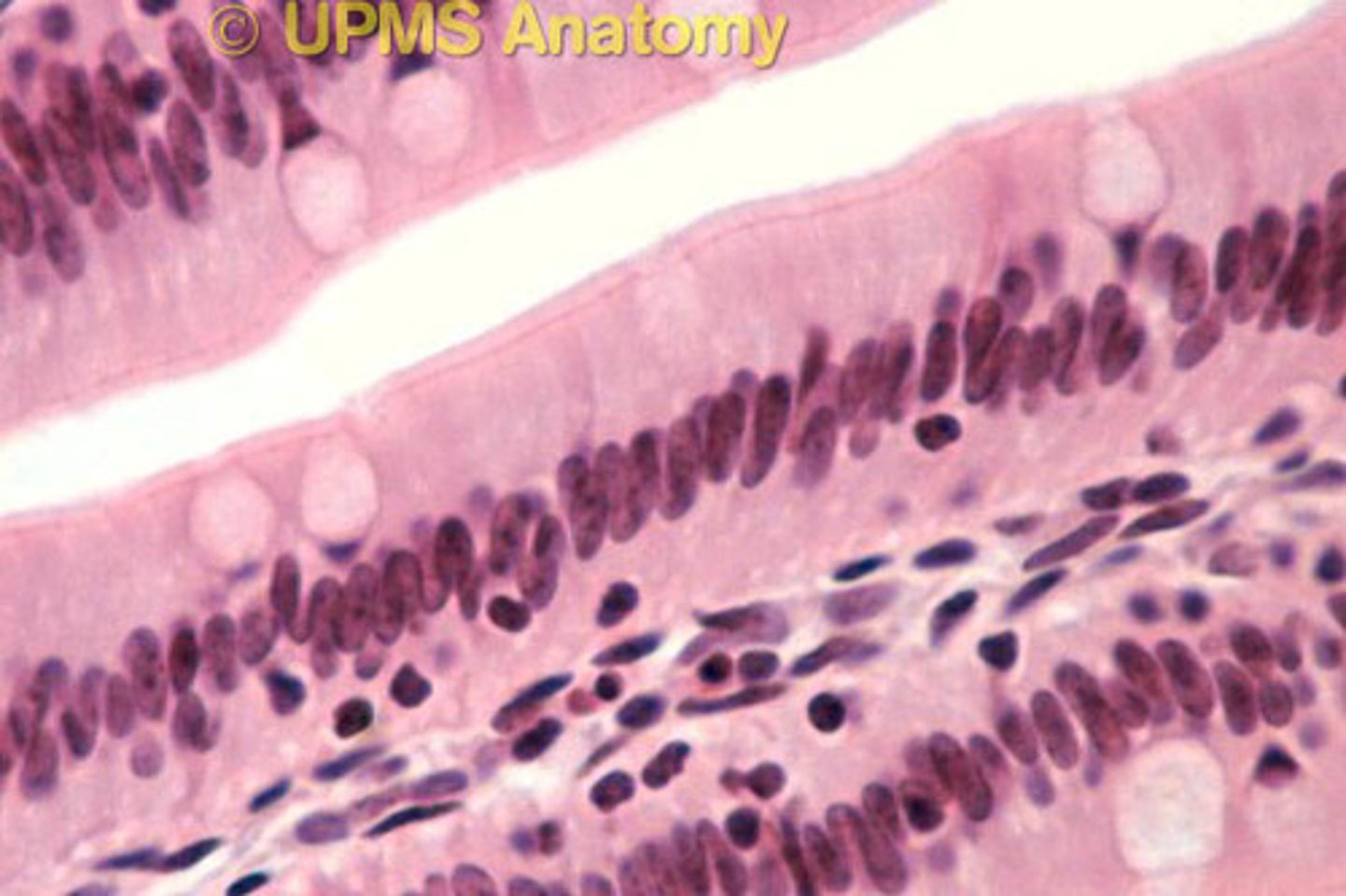
Lamina propria
middle layer of mucosa; made of connective tissue, contains blood vessels & lymph vessels
Muscularis mucosa
most superficial layer of mucosa; thin muscular layer
Submucosa
made of dense connective tissue, blood vessels, and lymph vessels; contains glands that release digestive secretions & submucosal plexus
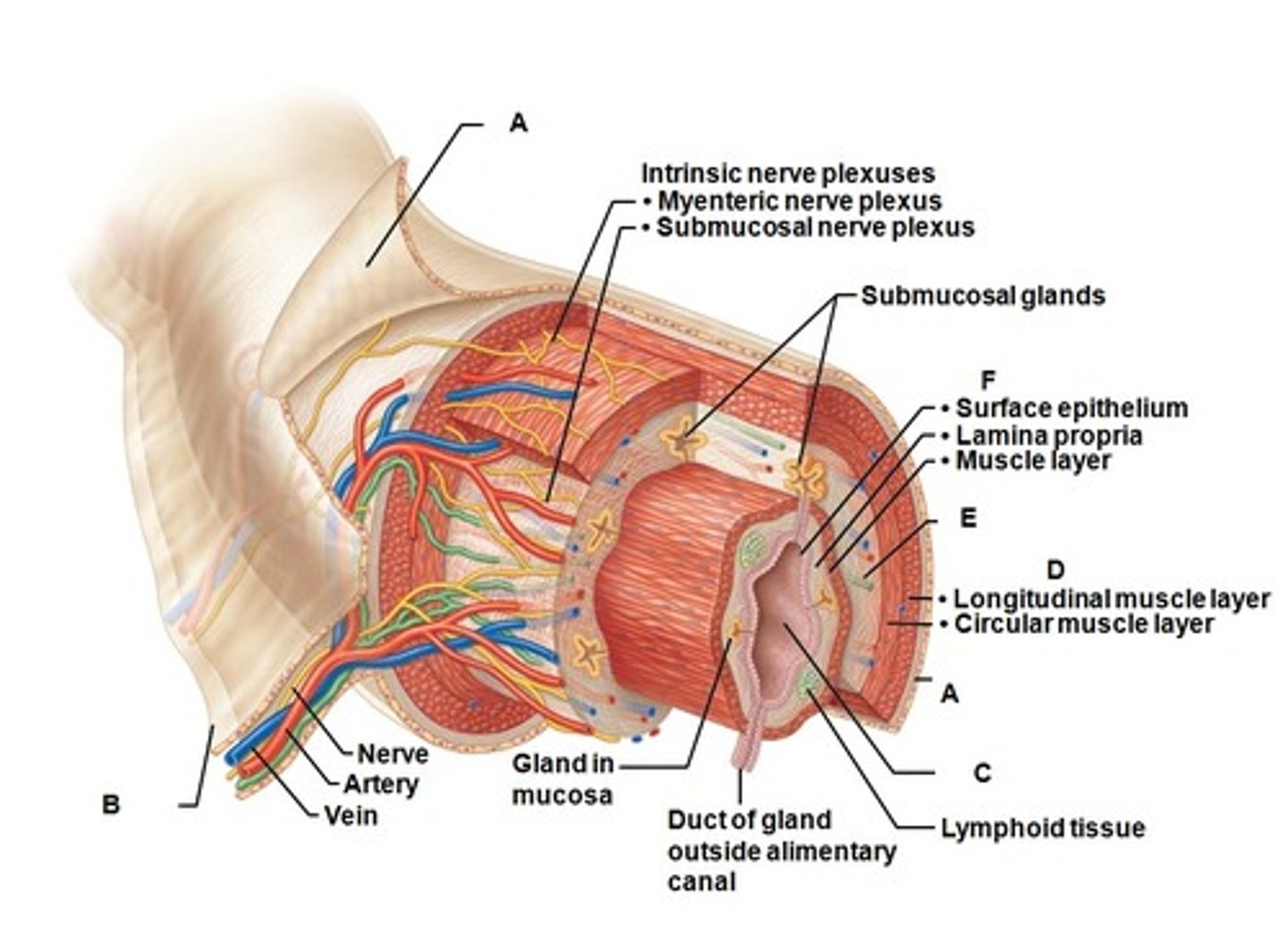
Muscularis
made of 2 layers of muscle, the circular and longitudinal layers; innervated my myenteric plexus
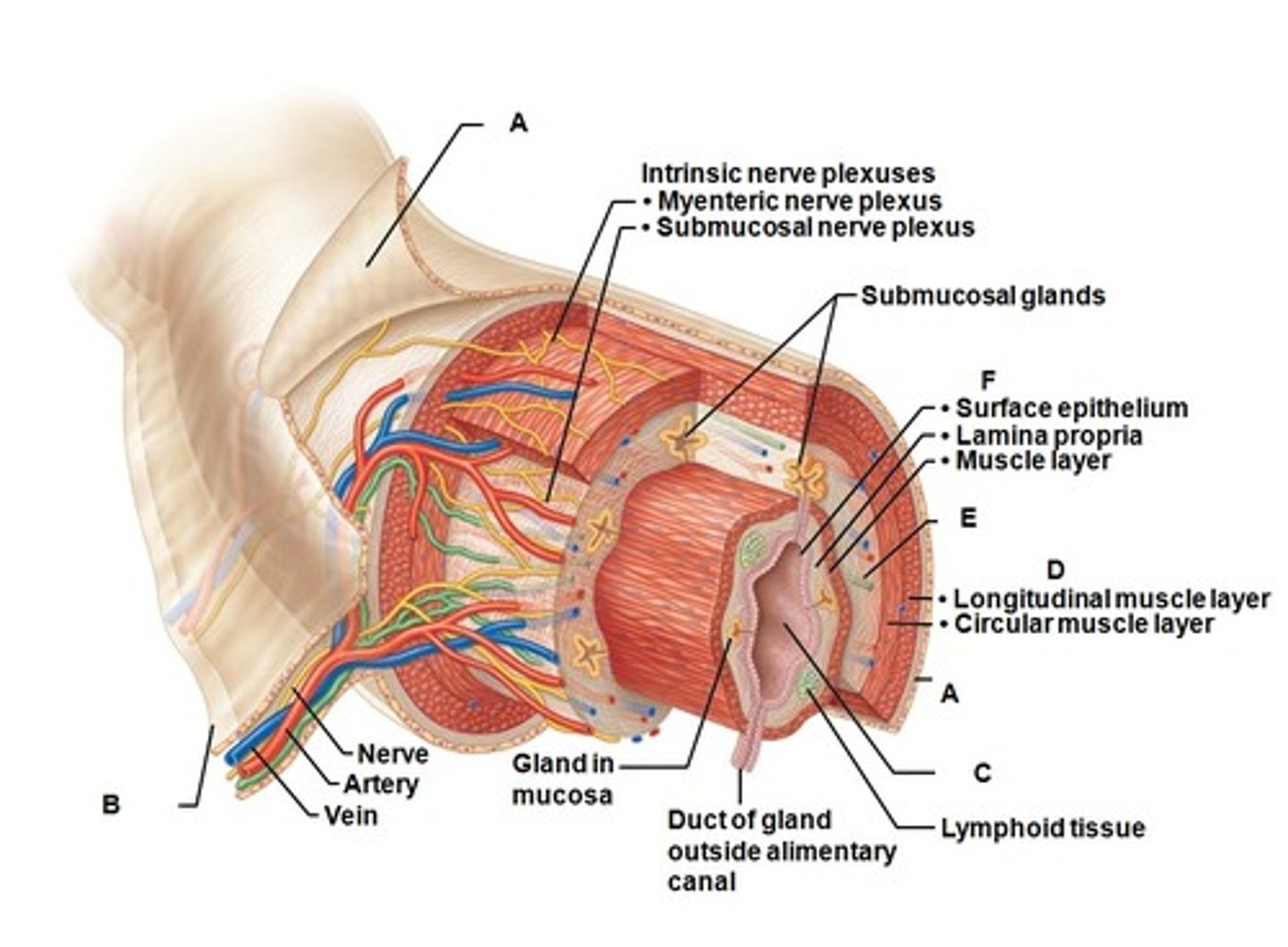
Serosa
Most superficial layer; made of areolar connective tissue and epithelium; called the adventitia in the esophagus
Mouth
oral (buccal) cavity
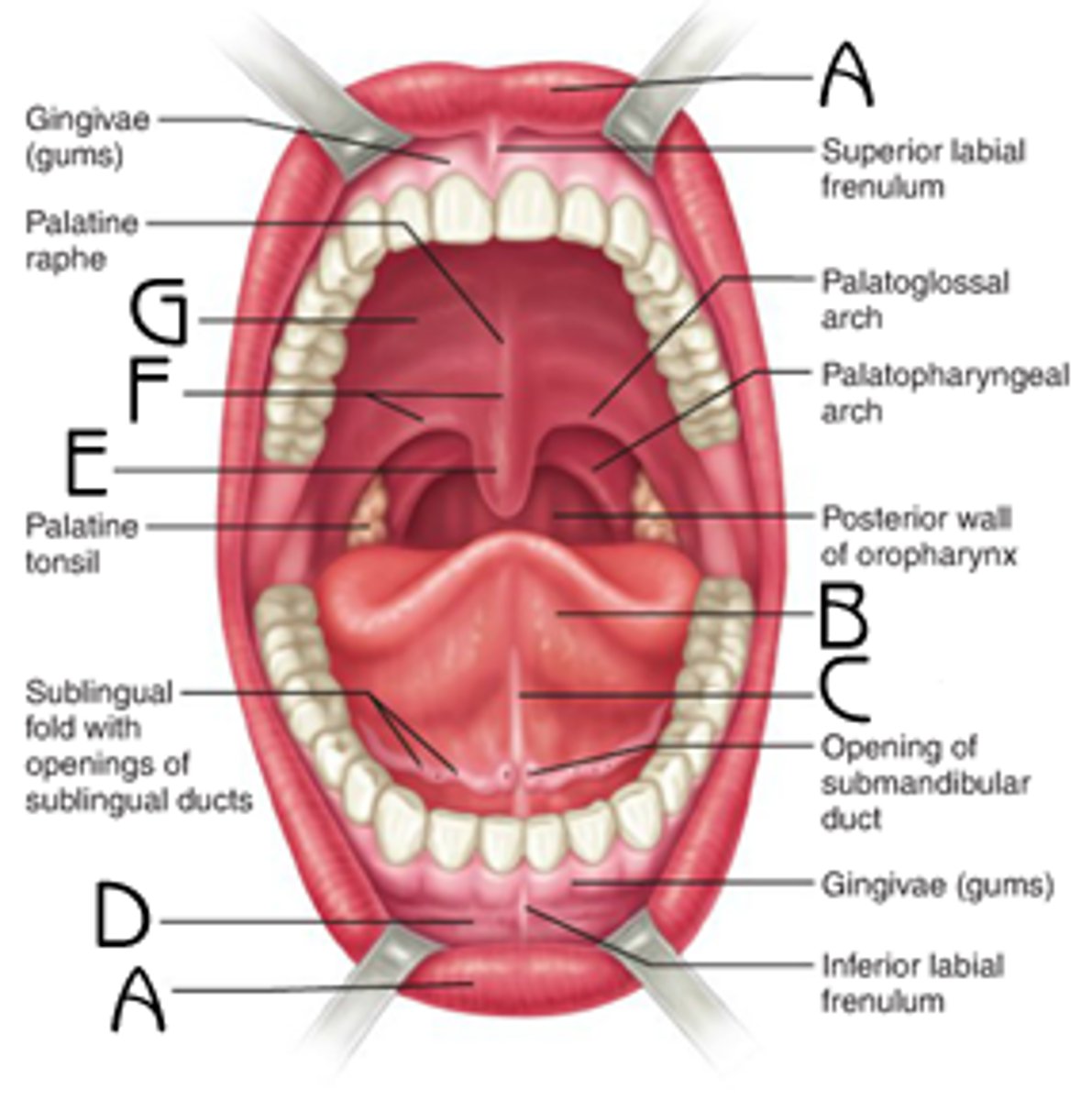
Lips
labia; highly vascularized, thin layer of keratin
Superior & inferior labial frenulum
connect lips to gums
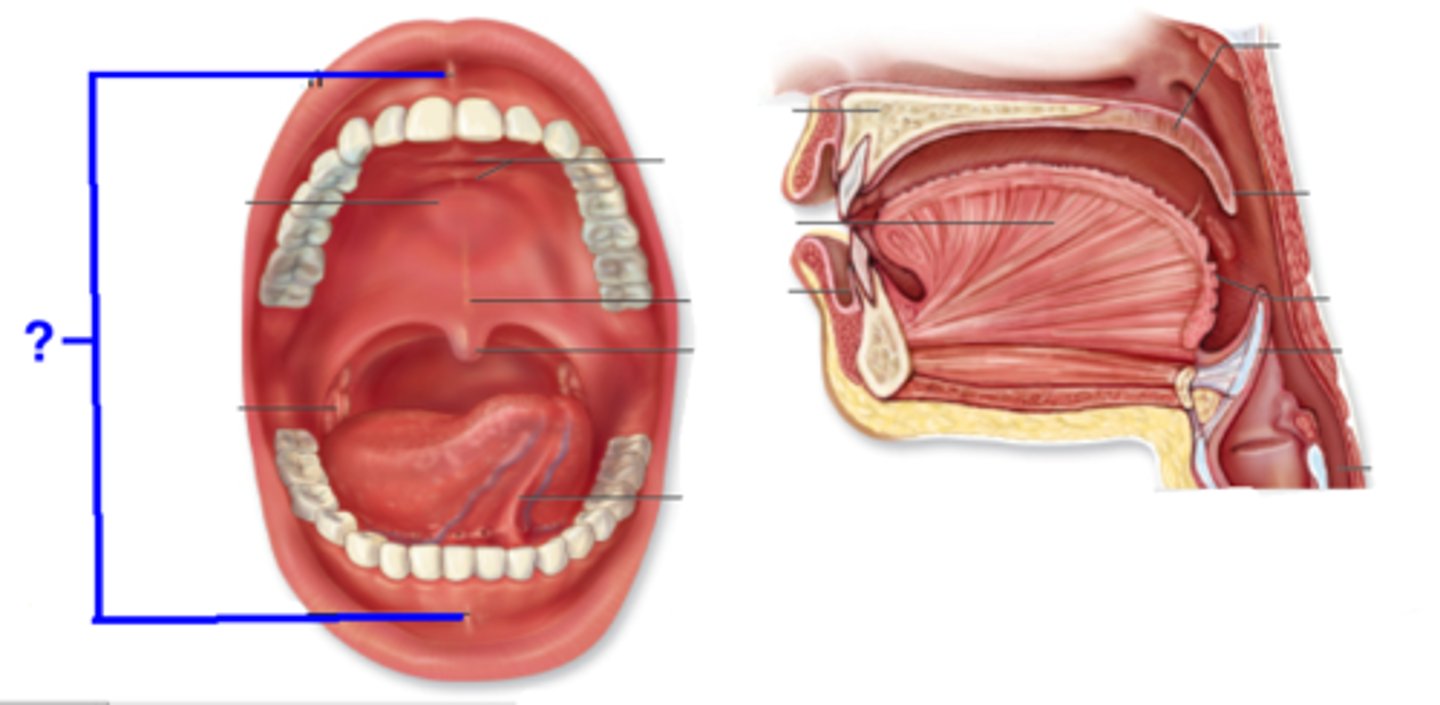
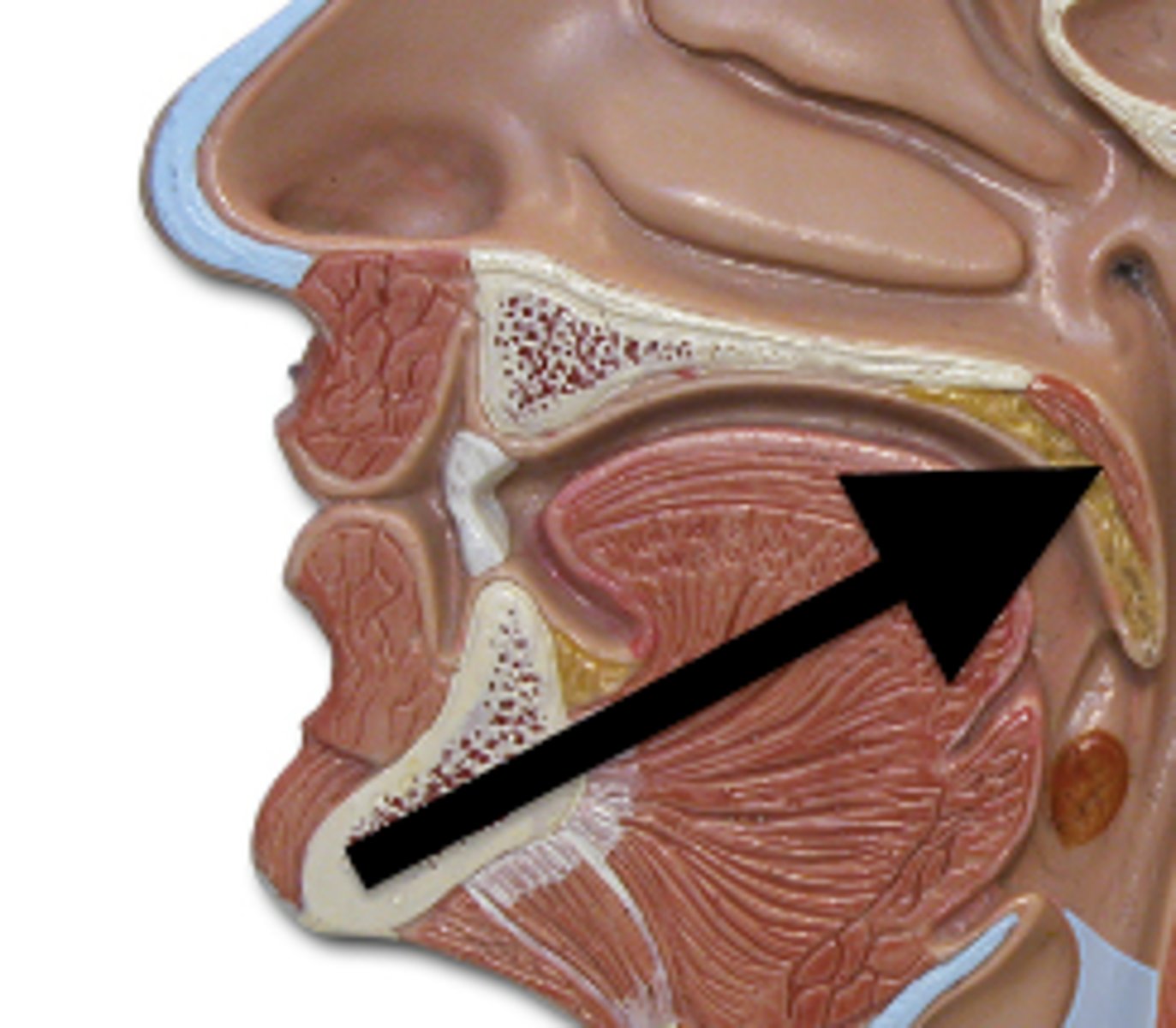
Hard palate
Anterior region of the roof of the mouth; separates mouth and nasal cavity; rigid shelf to push food against w/tongue
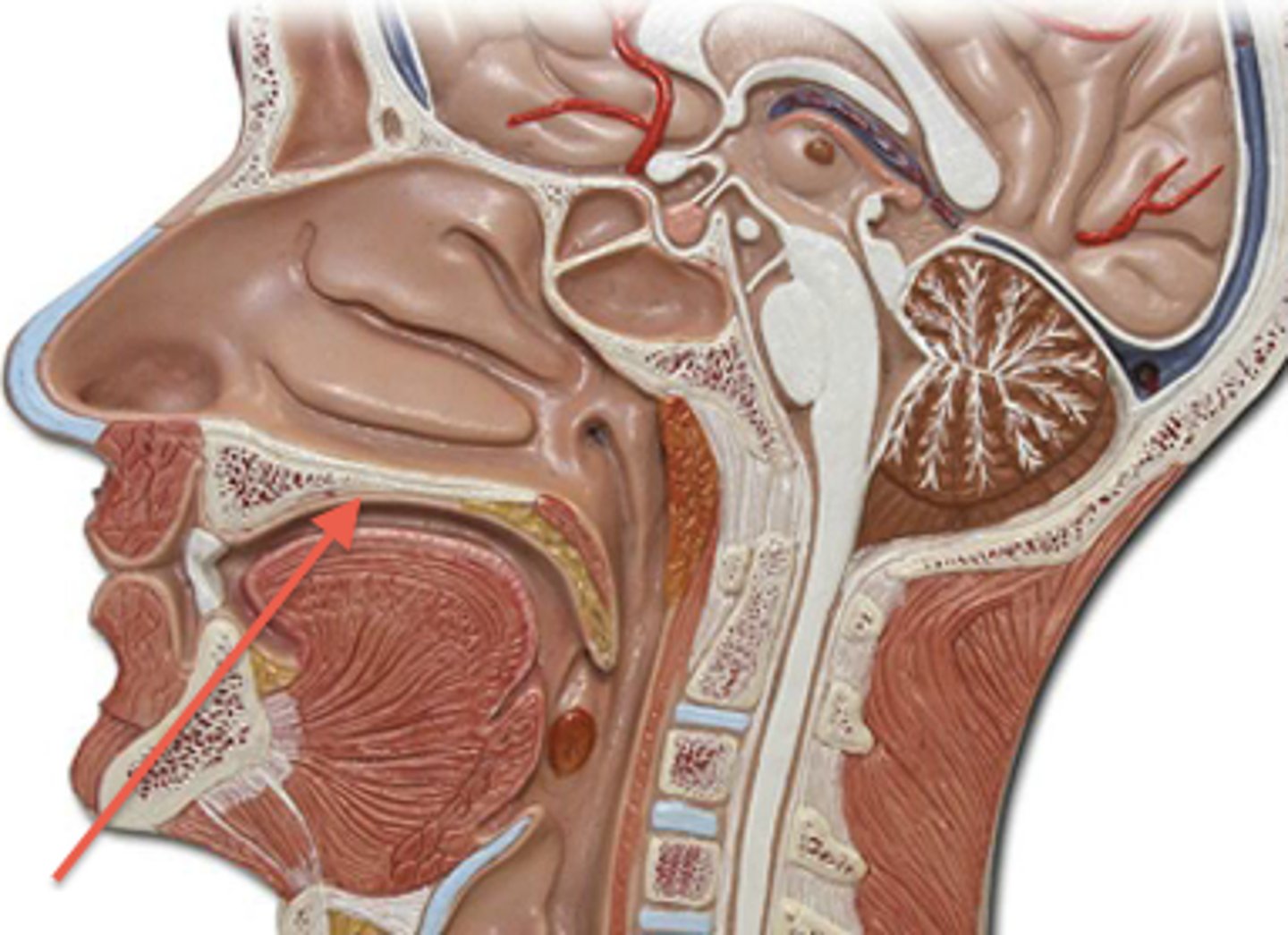
Soft palate
made of skeletal muscle; manipulated when we yawn, swallow, sing; moves up w/uvula to keep food out of nasal cavity when we swallow
Bolus
Ball of food, saliva, and mucus that is swallowed
Tongue
Strong muscle; helps mechanically and chemically digest food; involved in taste and touch reception as well; positions bolus for swallowing
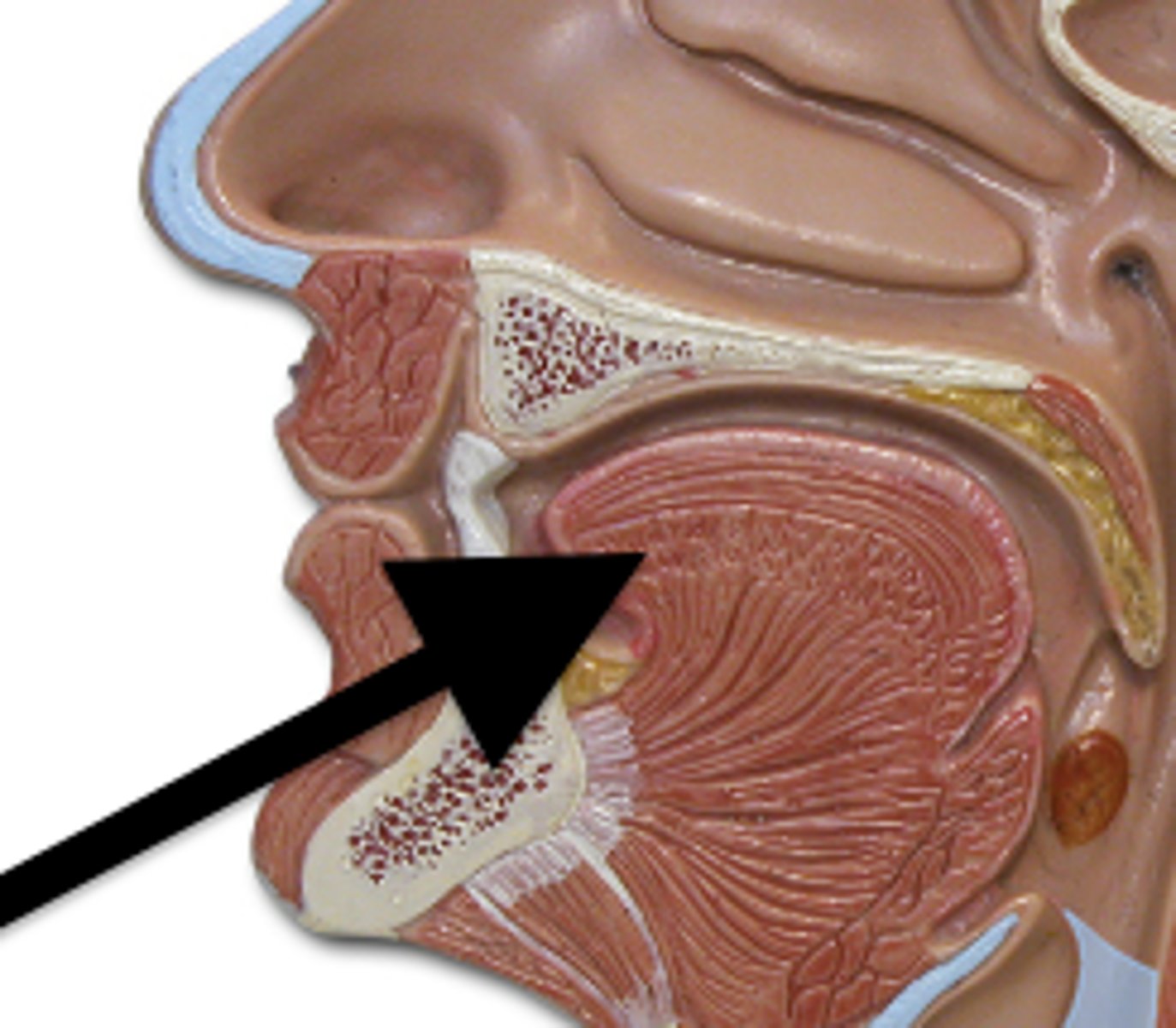
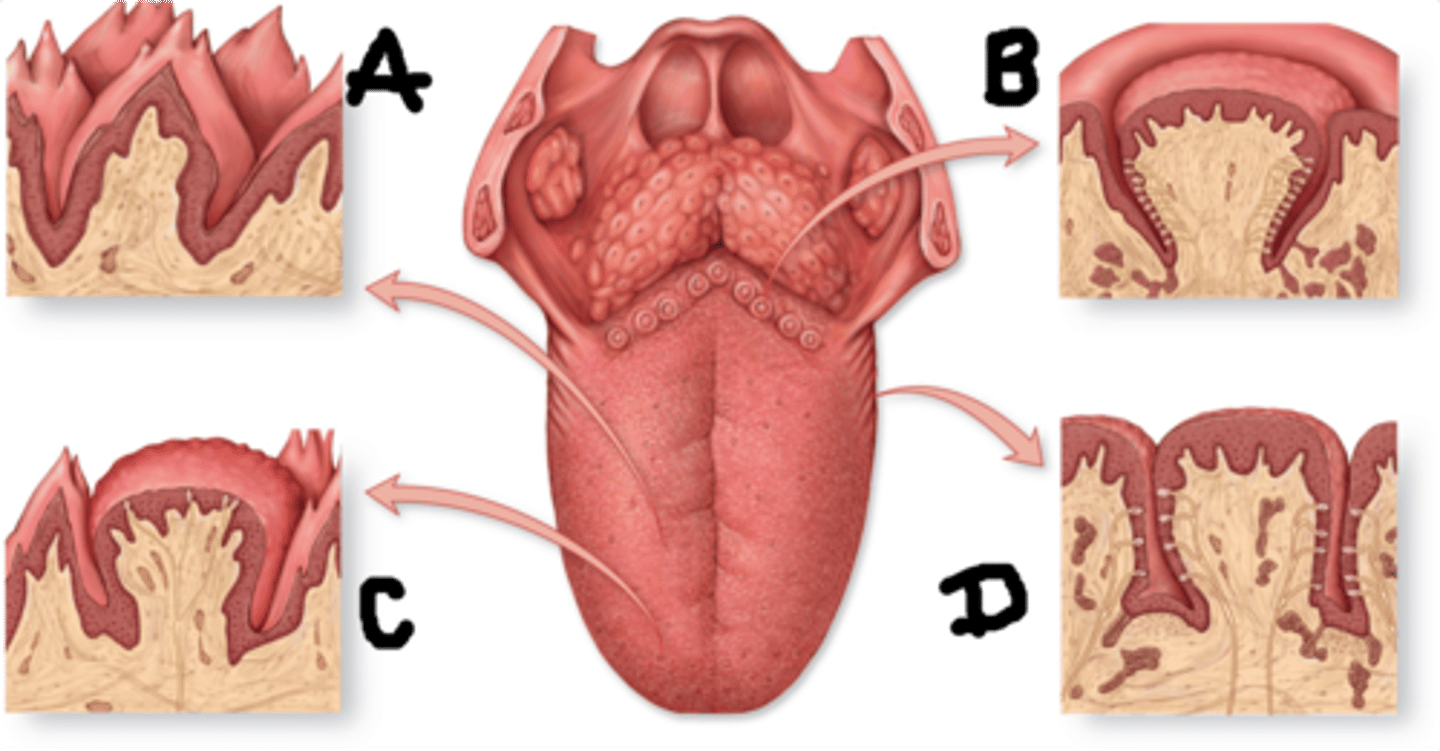
Papillae
extensions of lamina propria on surface of tongue; contain taste buds or touch receptors
Lingual glands
produce lingual lipase
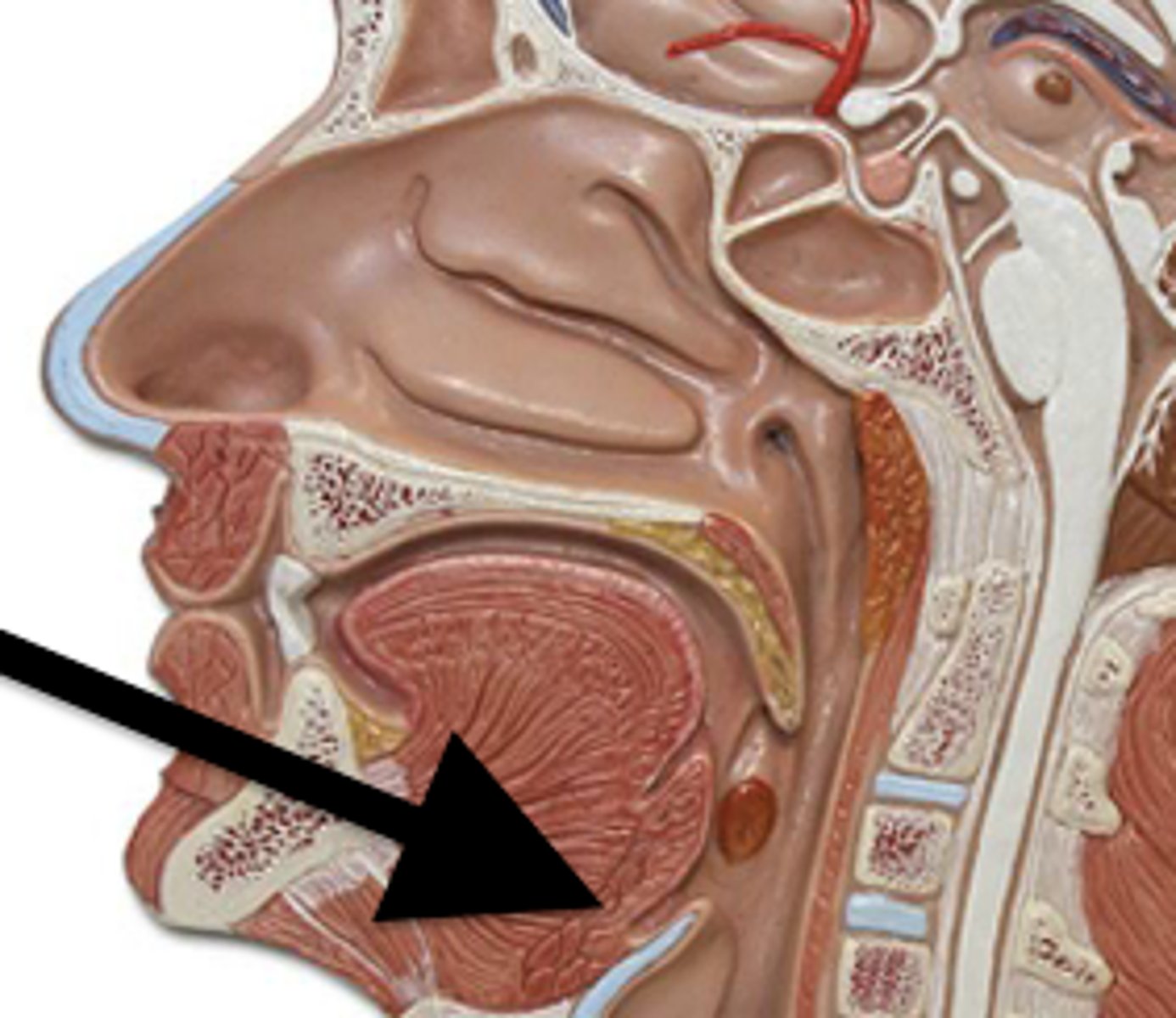
Lingual lipase
Helps digest fats; activated in stomach
Lingual frenulum
attacks tongue to floor of mouth
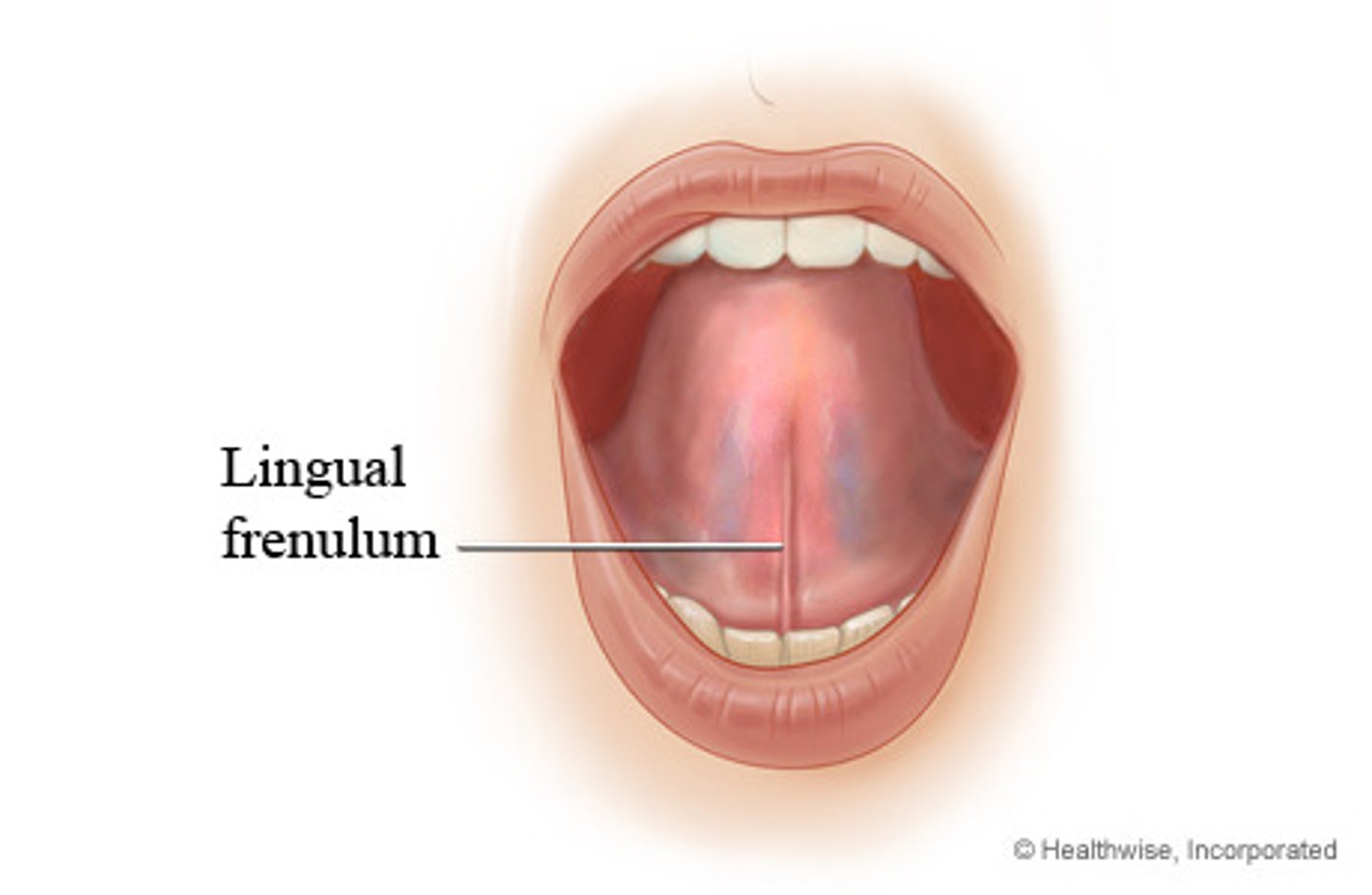
Ankyloglossia
Tongue tied; lingual frenulum is short or malformed
Saliva
95.5% water, 4.5% mucus, ions, enzymes, waste; moistens food & begins chemical digestion of carbs
Salivary amylase
enzyme in saliva that begins chemical digestion of carbohydrates; deactivated by acid in stomach when it is swallowed
Lysozyme
antibacterial enzyme in saliva
Parotid glands
salivary glands between masseter & ear; makes watery saliva w/salivary amylase & little to no mucus
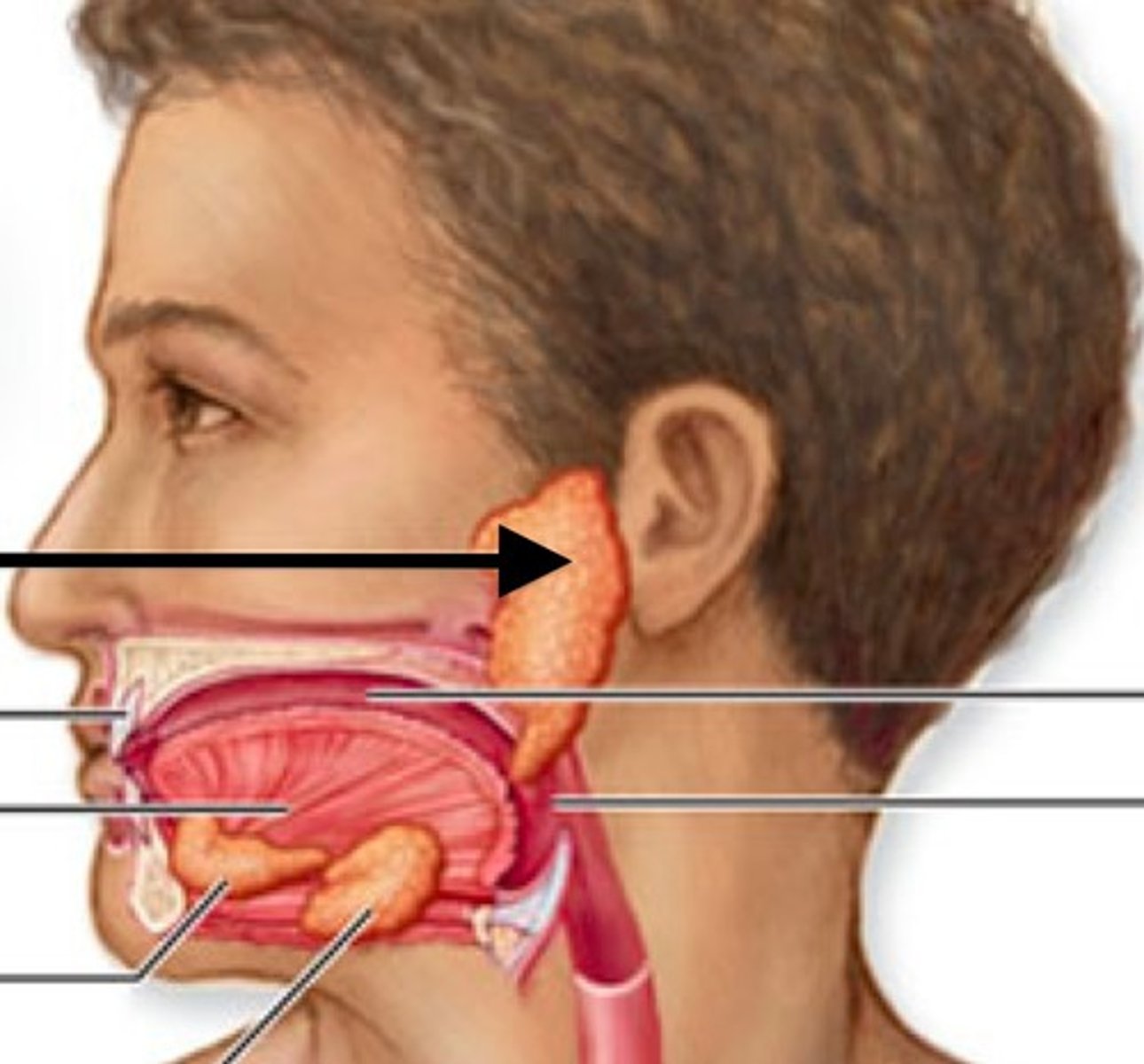
Submandibular glands
salivary glands below the jaw; produce saliva w/more mucus than parotid glands do & makes salivary amylase
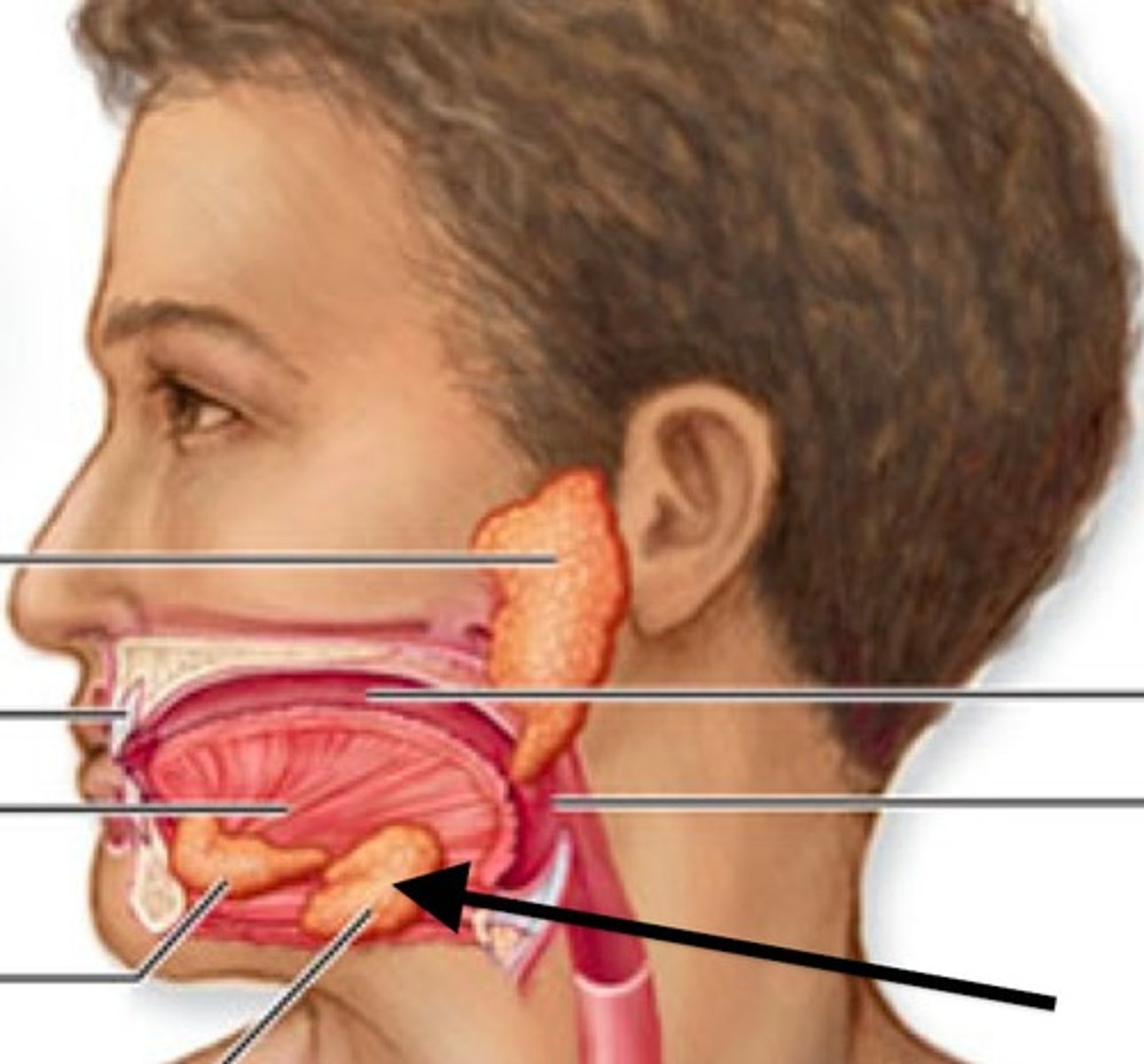
Sublingual glands
salivary glands below the tongue; produce saliva w/lots of mucus and very little salivary amylase
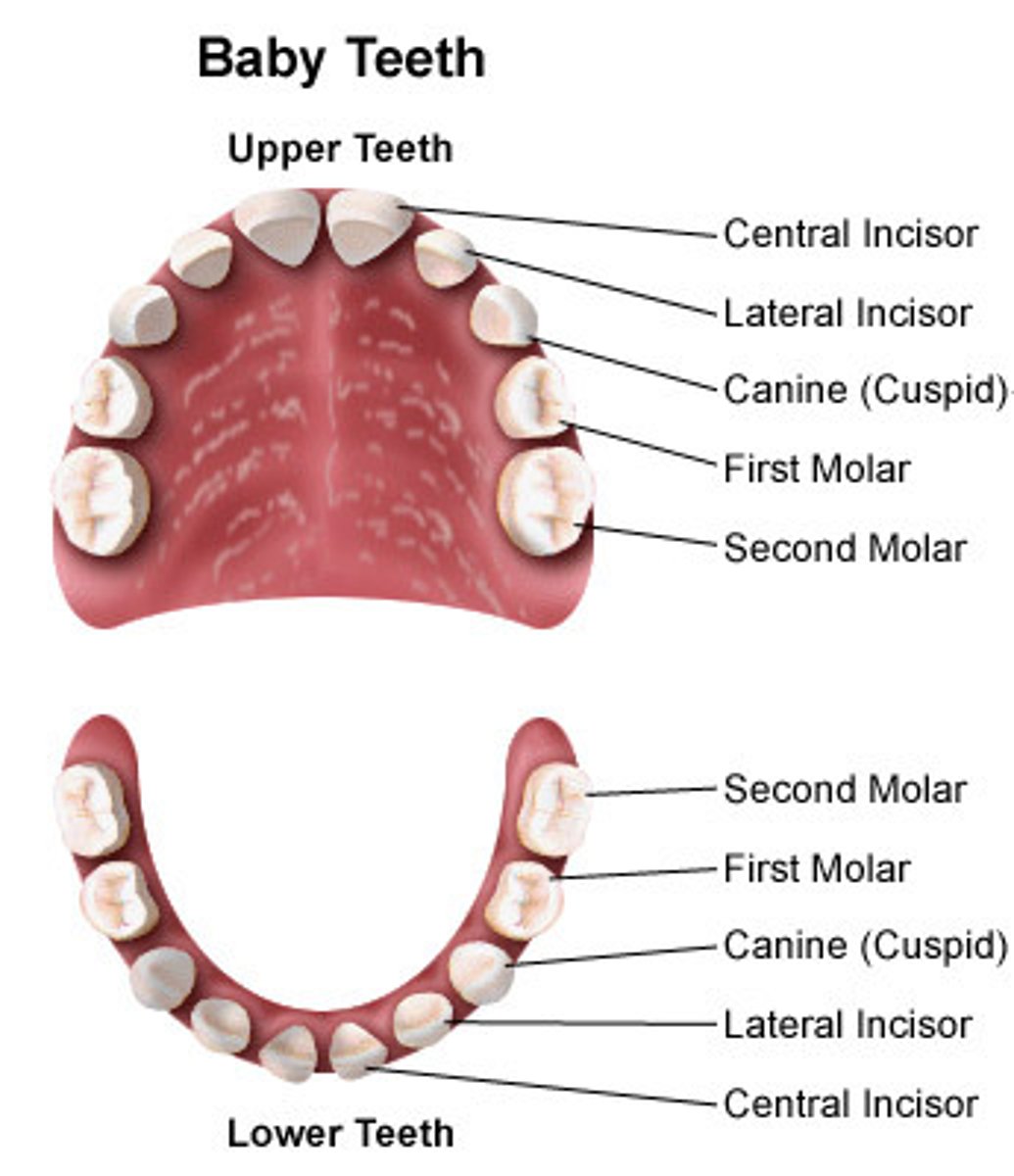
Deciduous teeth
Teeth that fall out; 20 of them
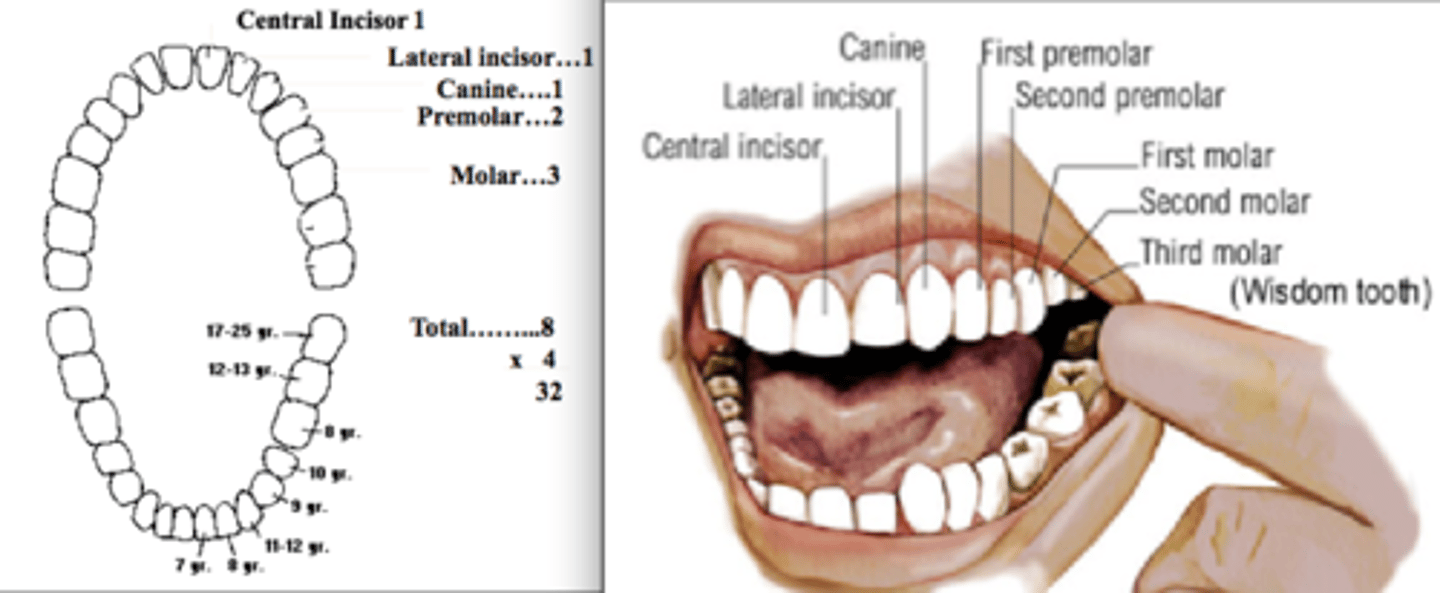
Permanent teeth
32; 8 incisors, 4 cuspids (canines), 8 premolars, 12 molars (3rd pair are wisdom teeth)
Gingivae (gums)
soft tissue surrounding teeth sockets & necks of teeth
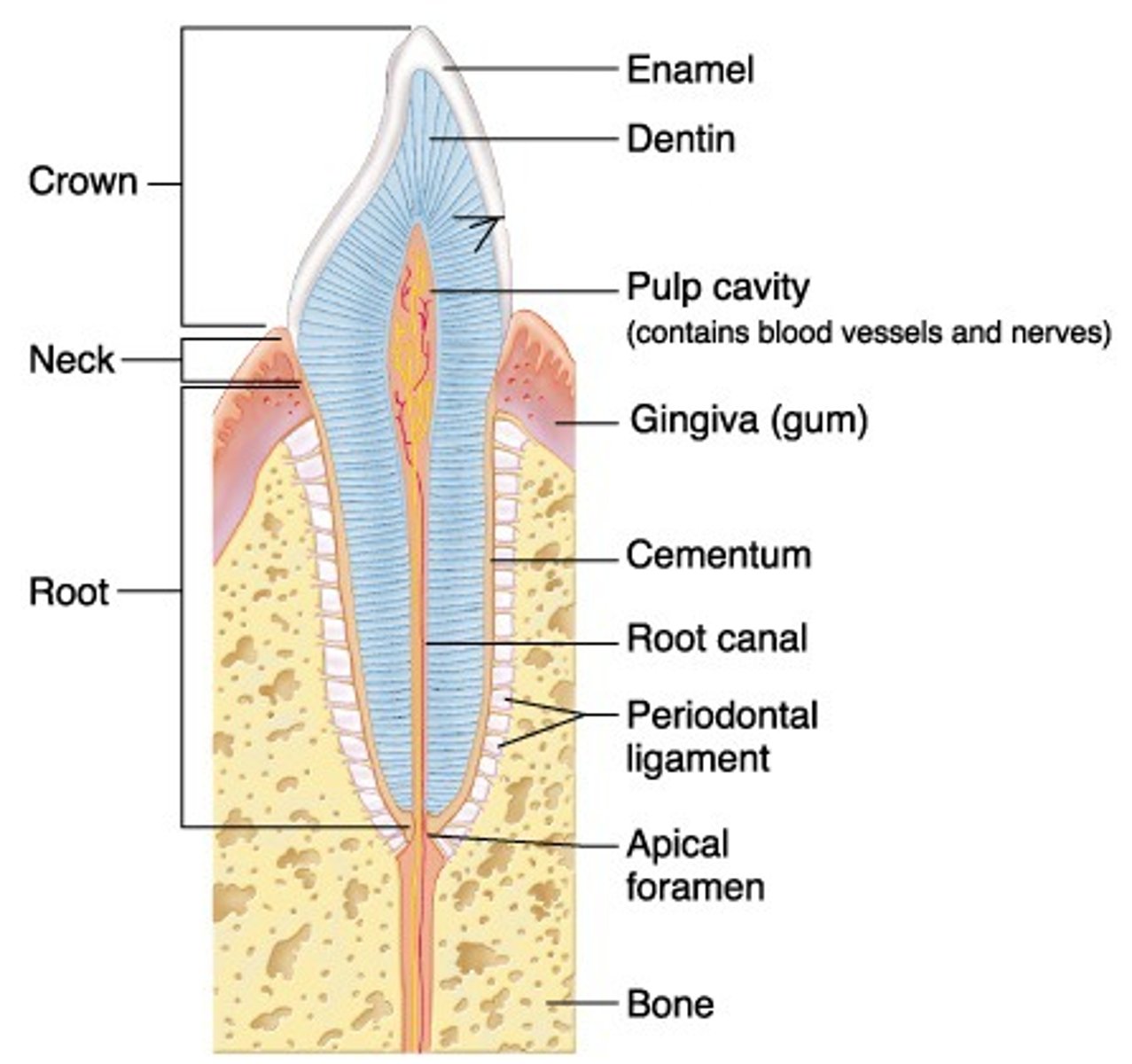
Crown
Part of tooth above the gumline
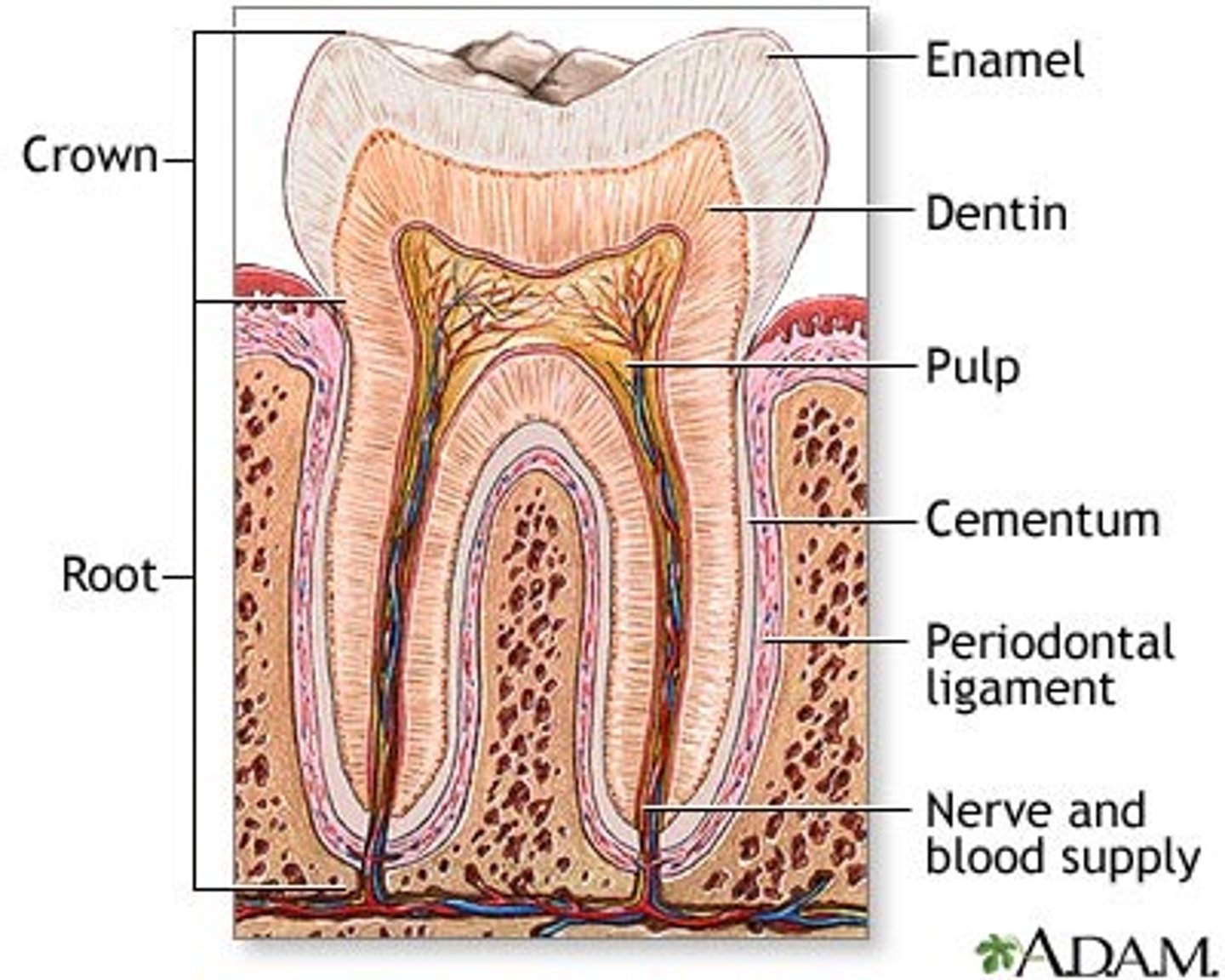
Root
Part of tooth below the gumline
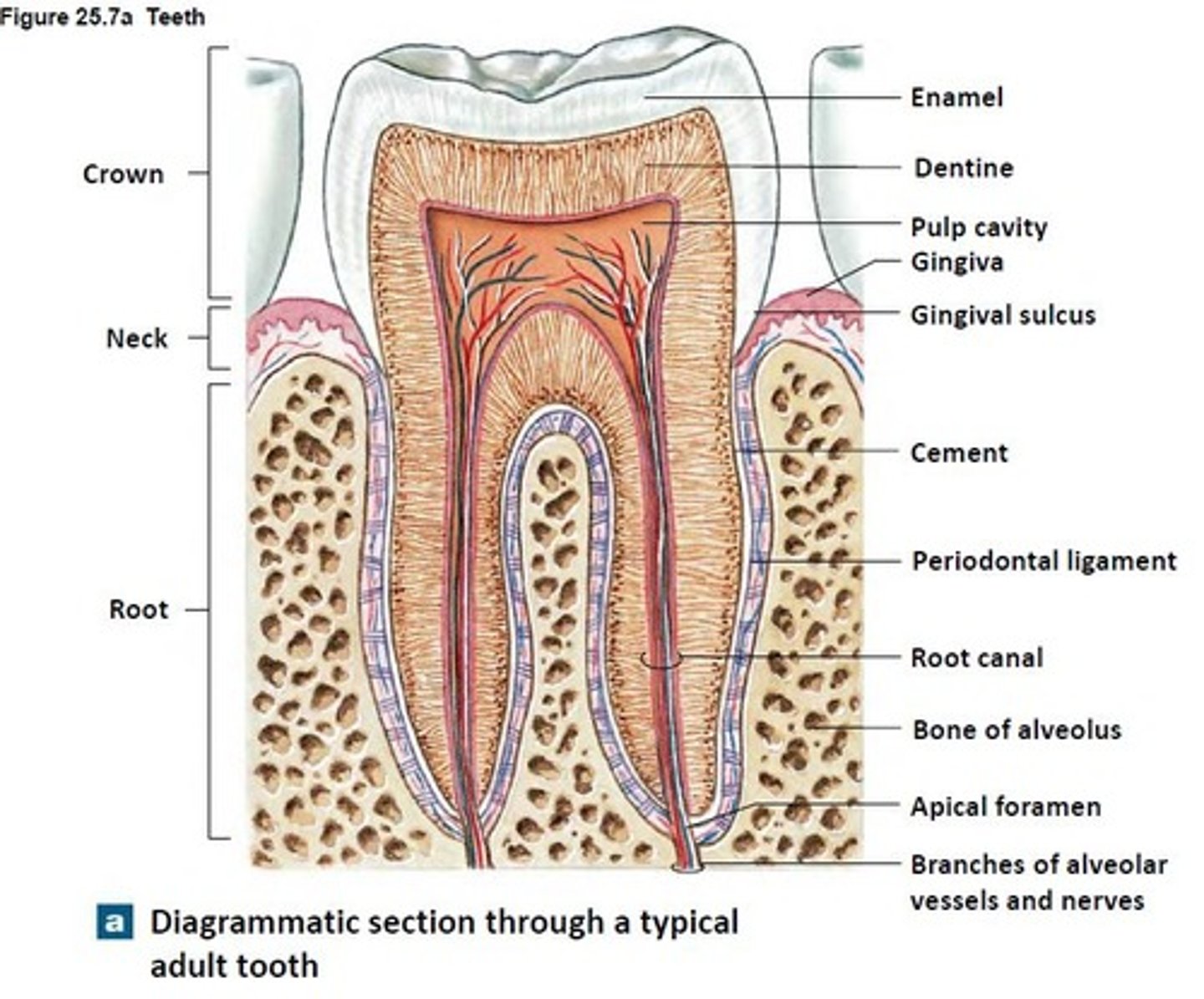
Pulp cavity
found in crown & root, contains nerves and blood vessels
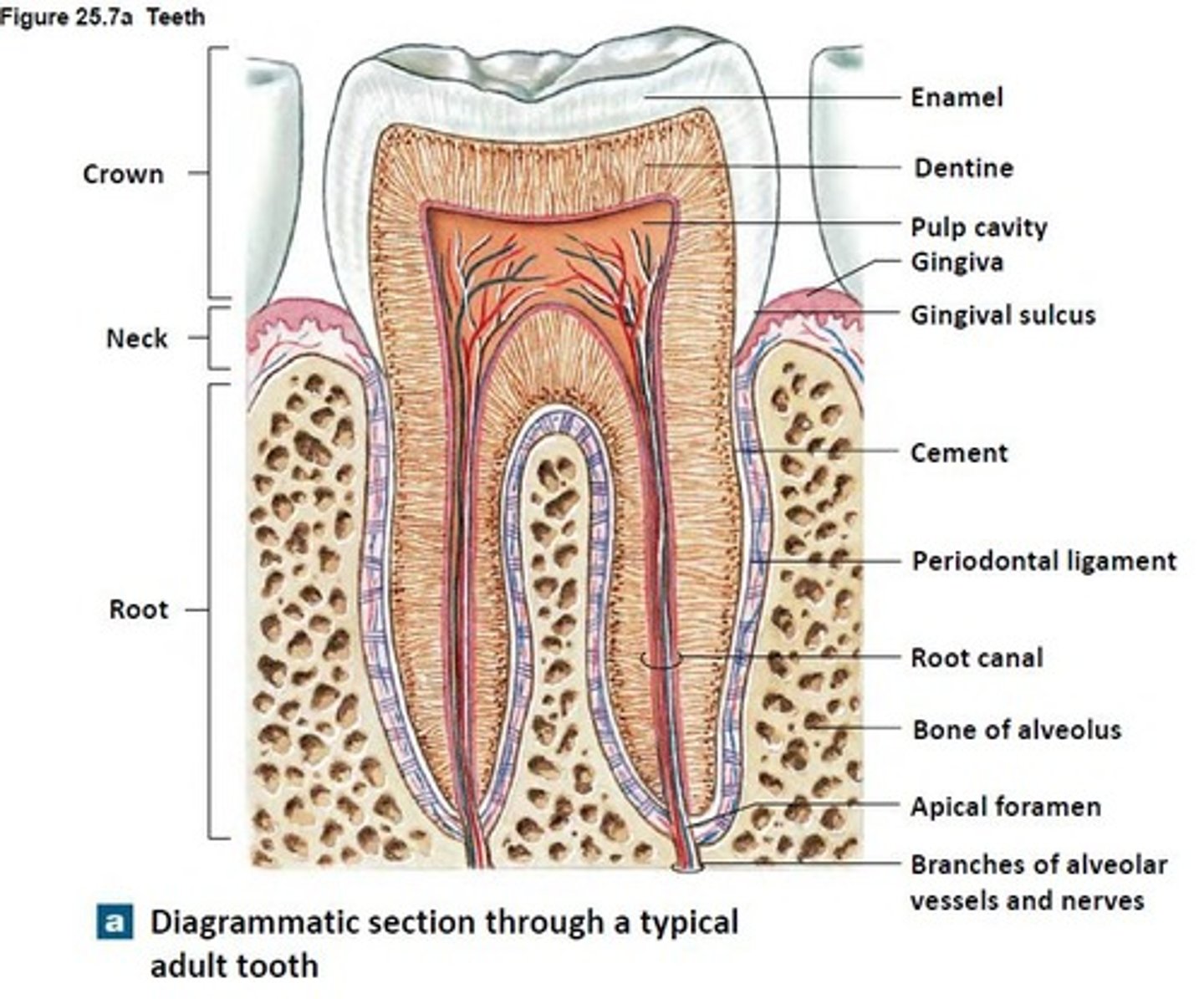
Dentin
bone-like tissue covering pulp cavity
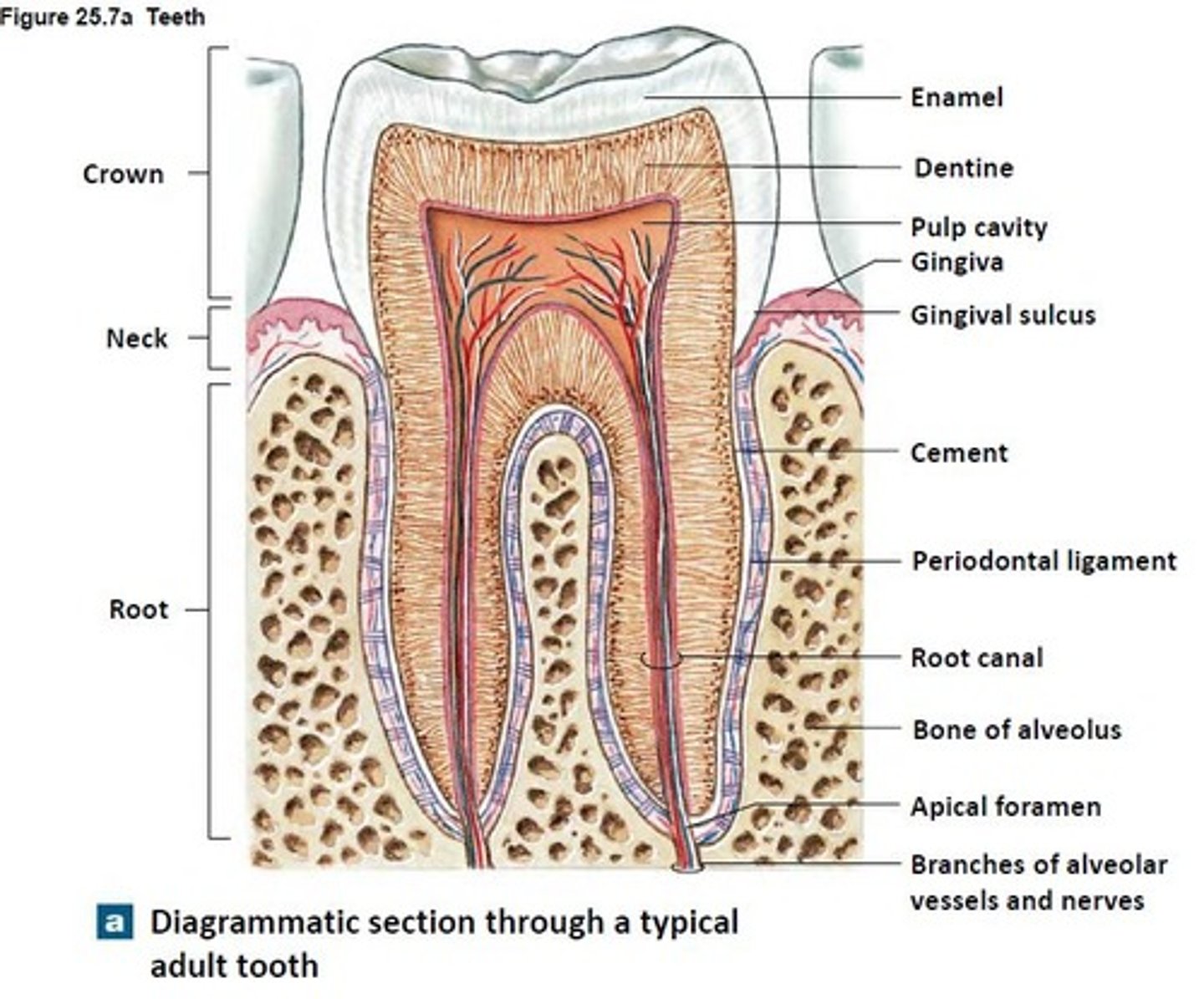
Cementum
harder bone-like layer covering dentin below the gumline; connects tooth to jaw bone
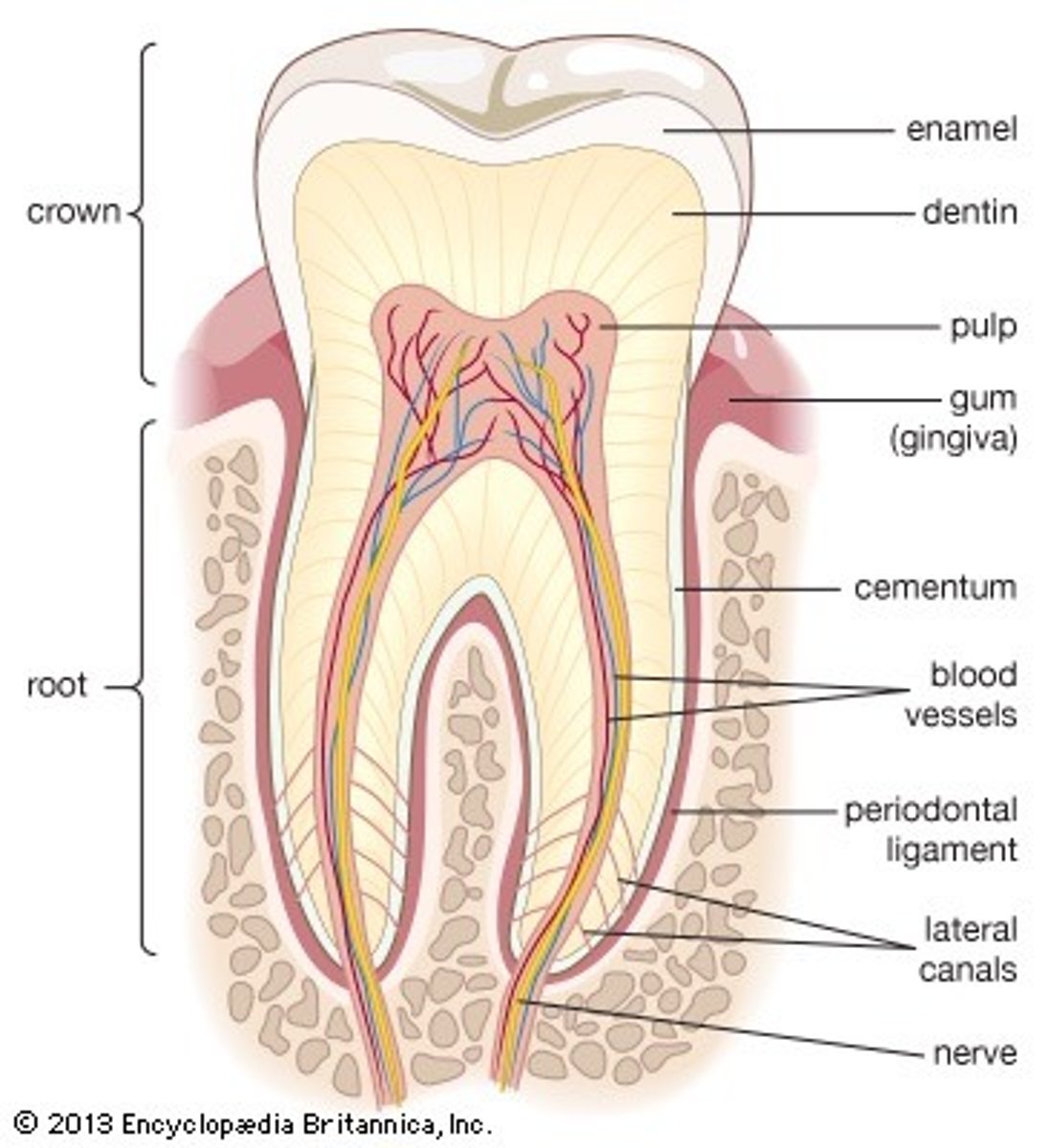
Enamel
outer layer covering dentin in the crown; hardest substance in the body
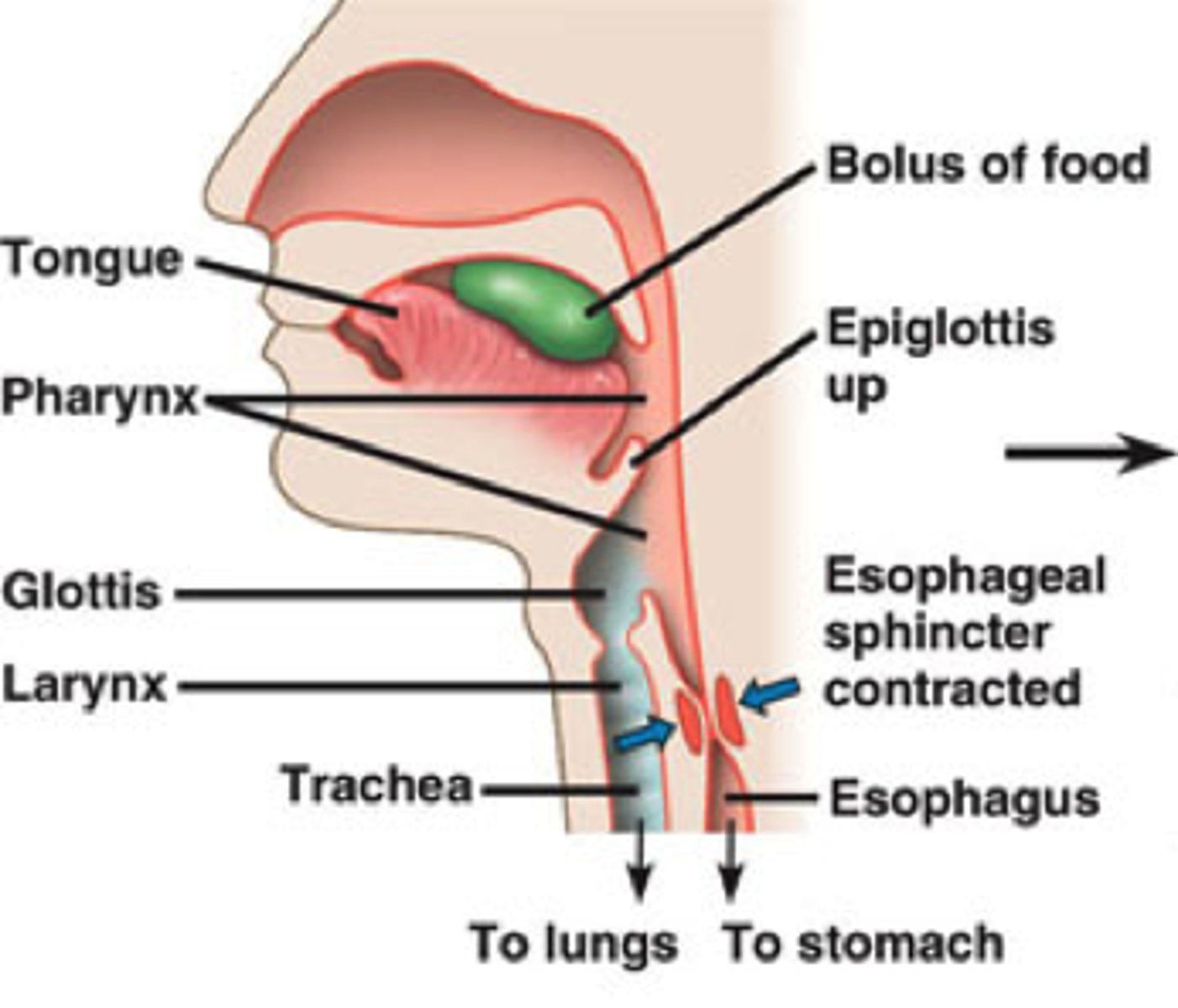
Pharynx (throat)
receives food and air from mouth; receives air from nasal cavity
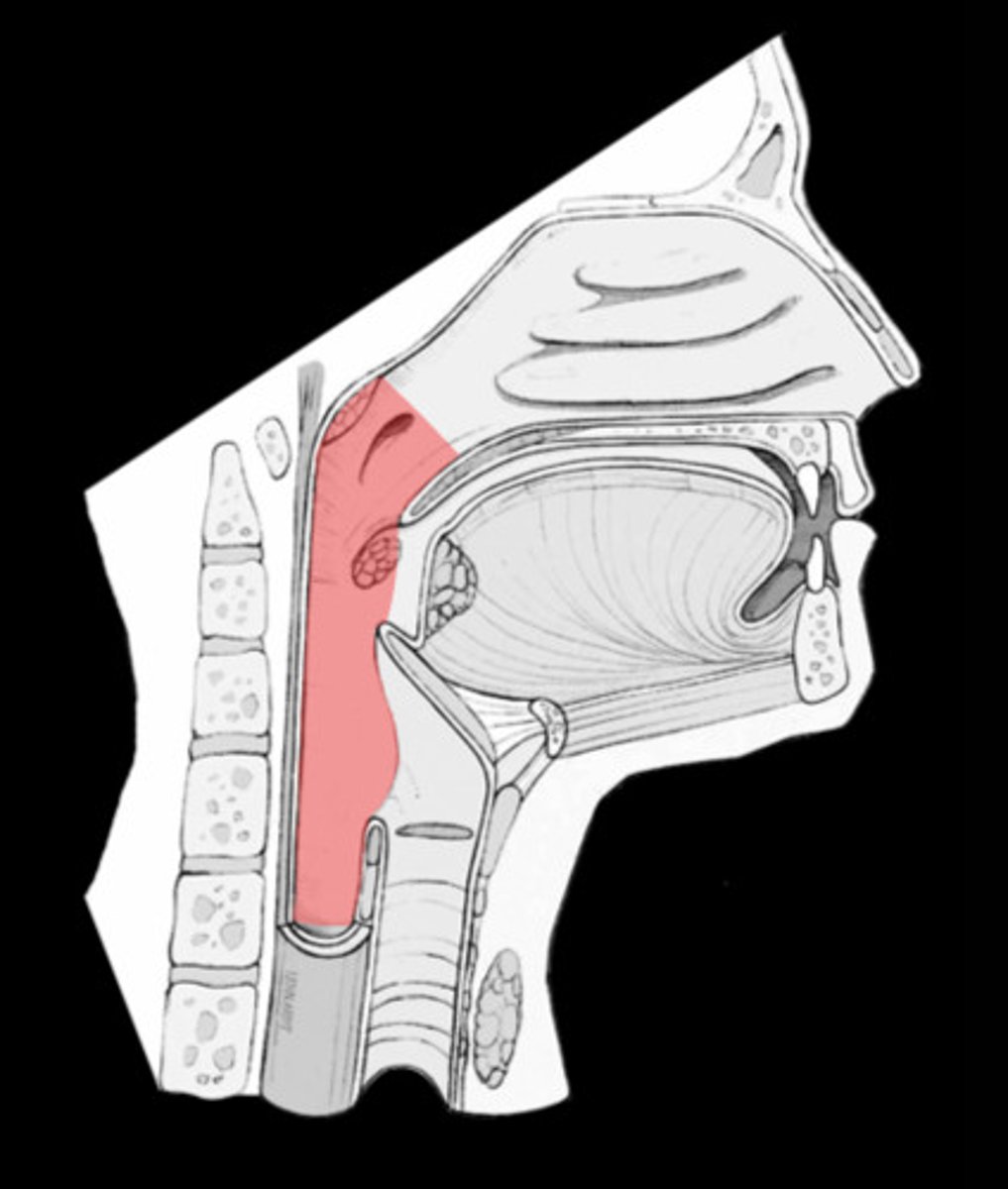
Nasopharynx
involved in breathing only; opening from nasal cavity into back of oral cavity
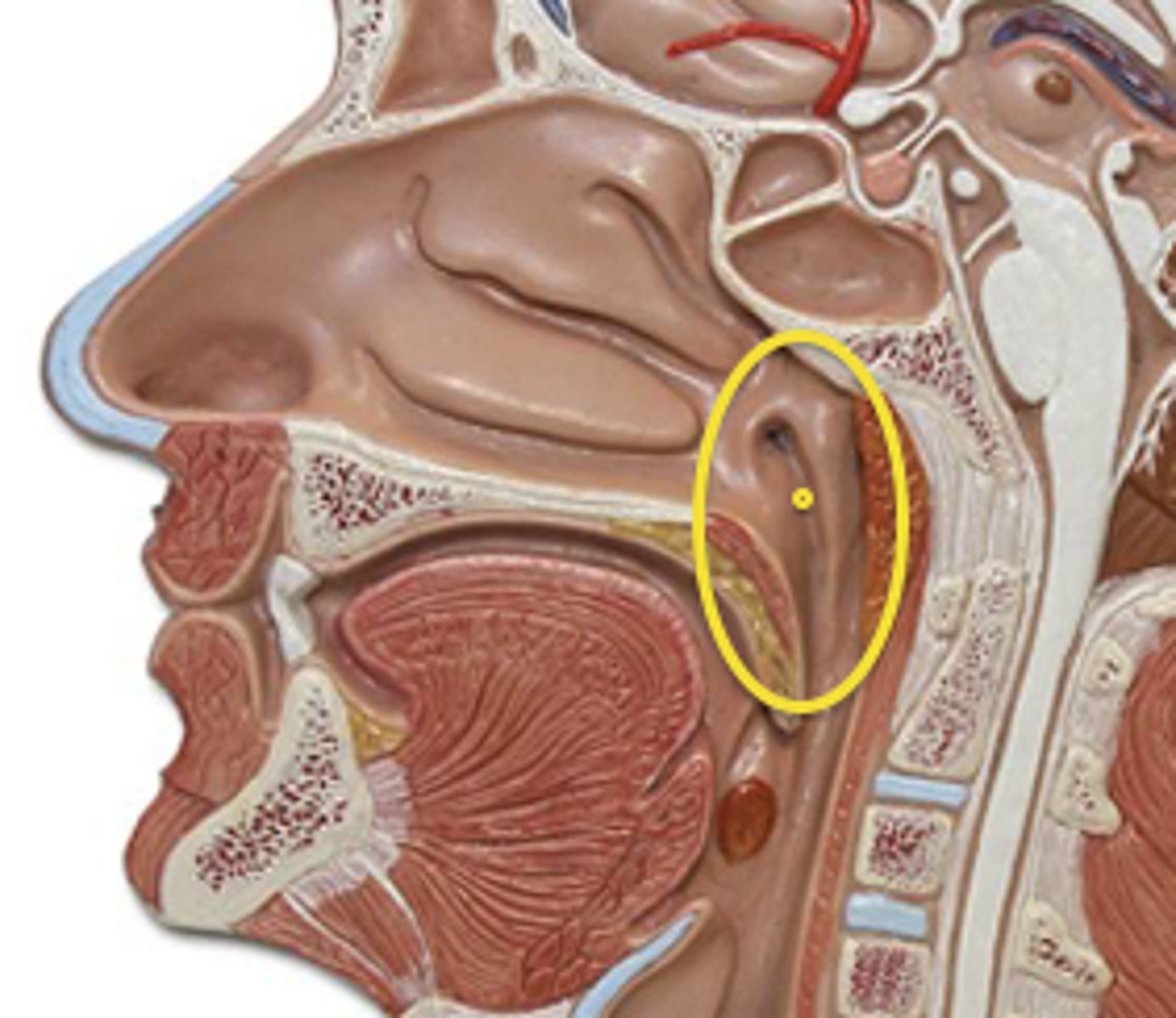
Oropharynx
Part of pharynx at posterior end of the oral cavity; involved in breathing & swallowing
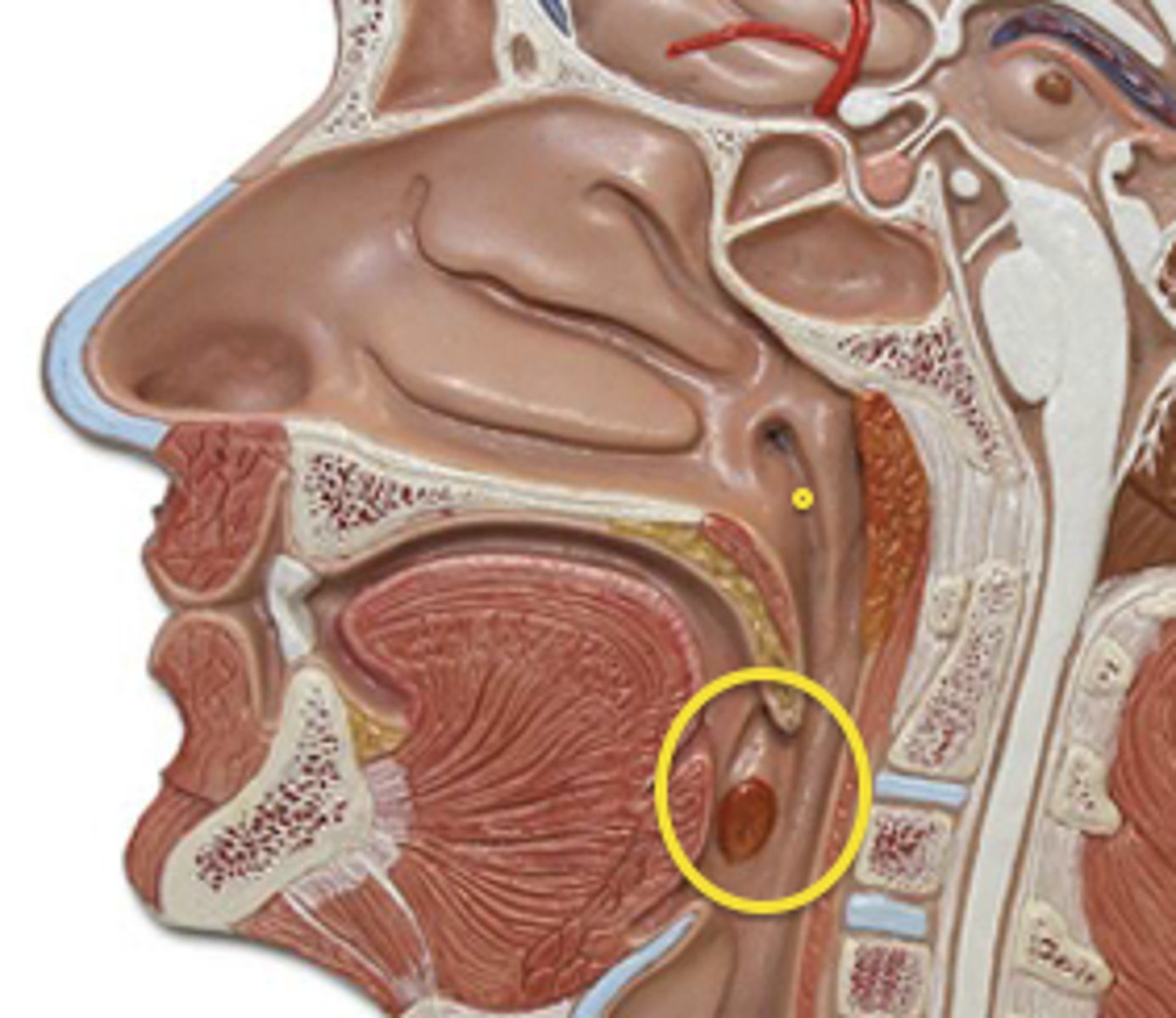
Laryngopharynx
Most inferior portion of pharynx; involved in breathing & swallowing
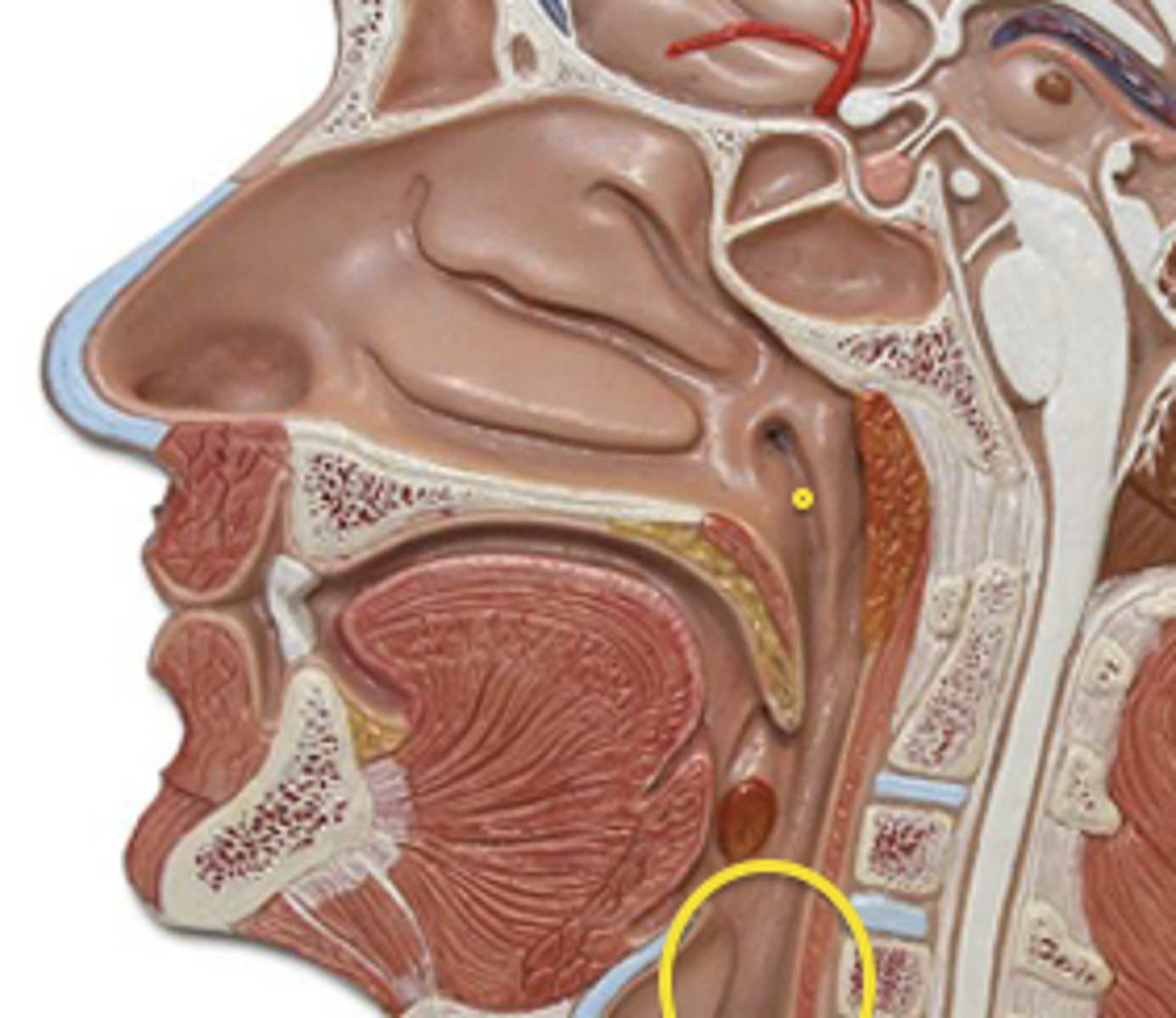
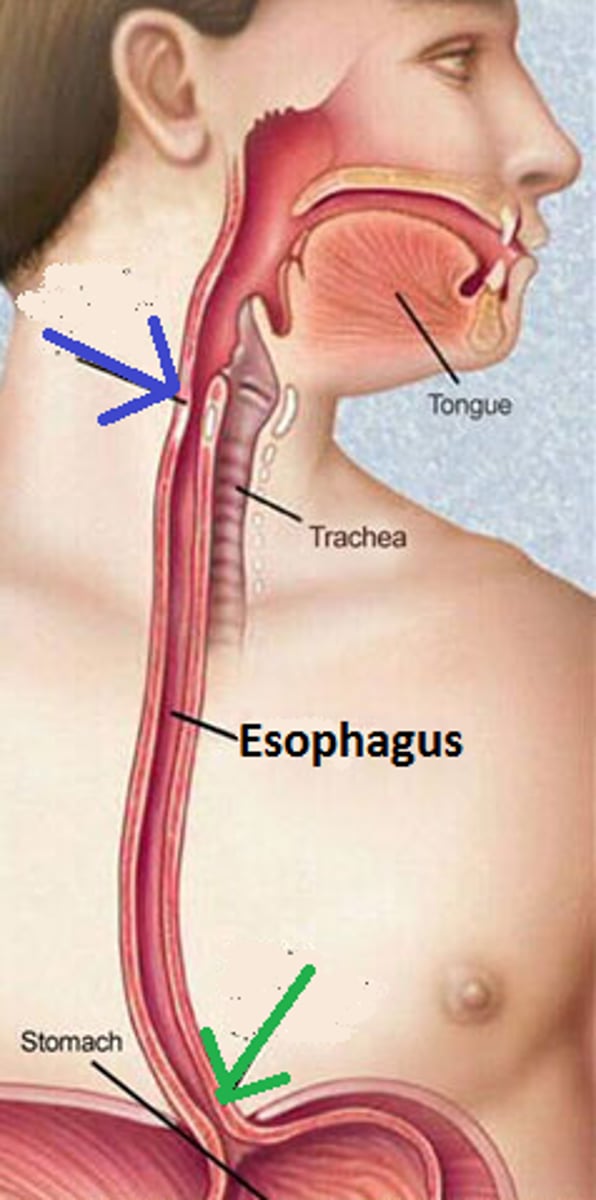
Esophagus
Muscular, 10 inch tube that passes through the mediastinum and connects pharynx to stomach
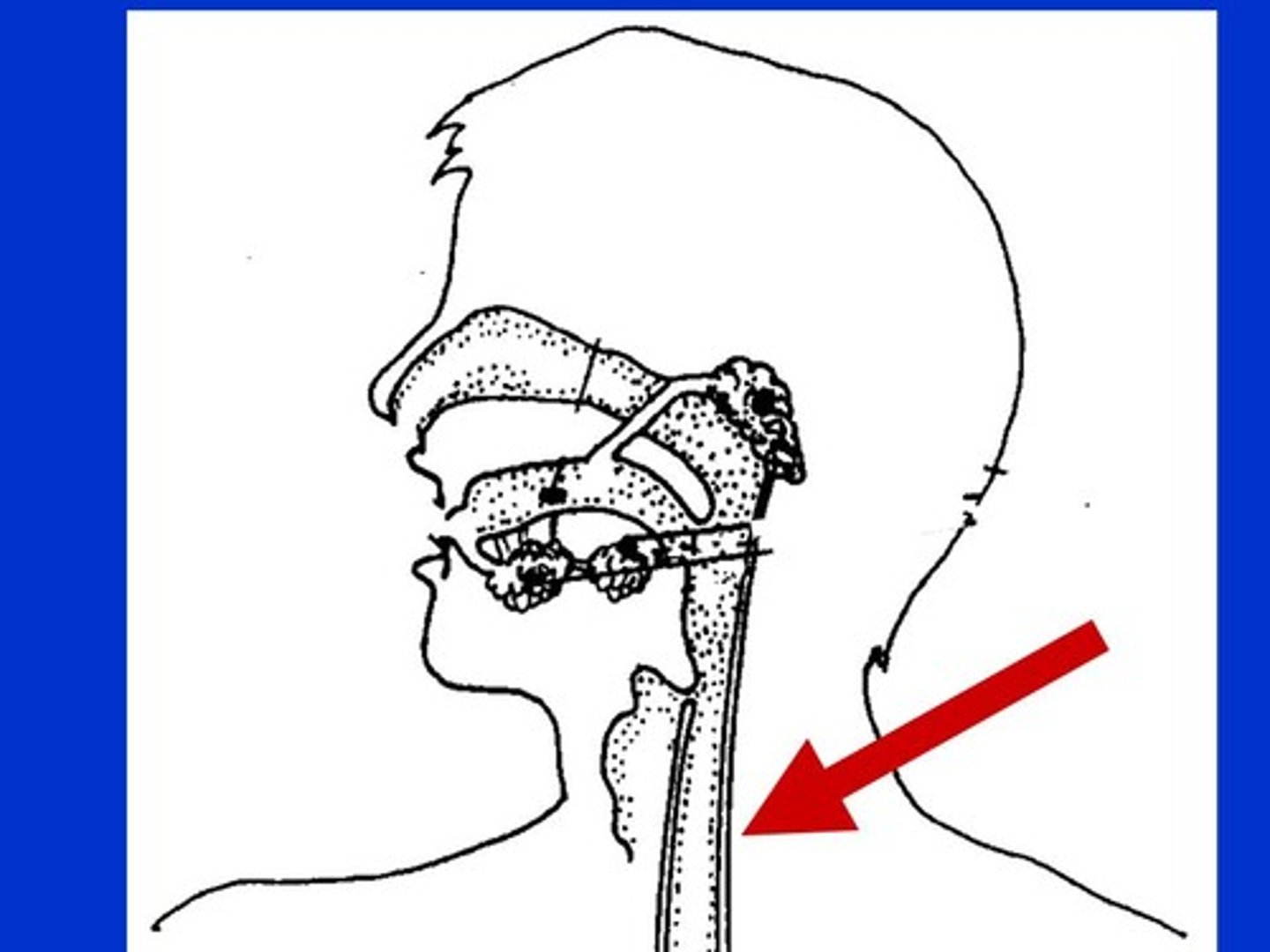
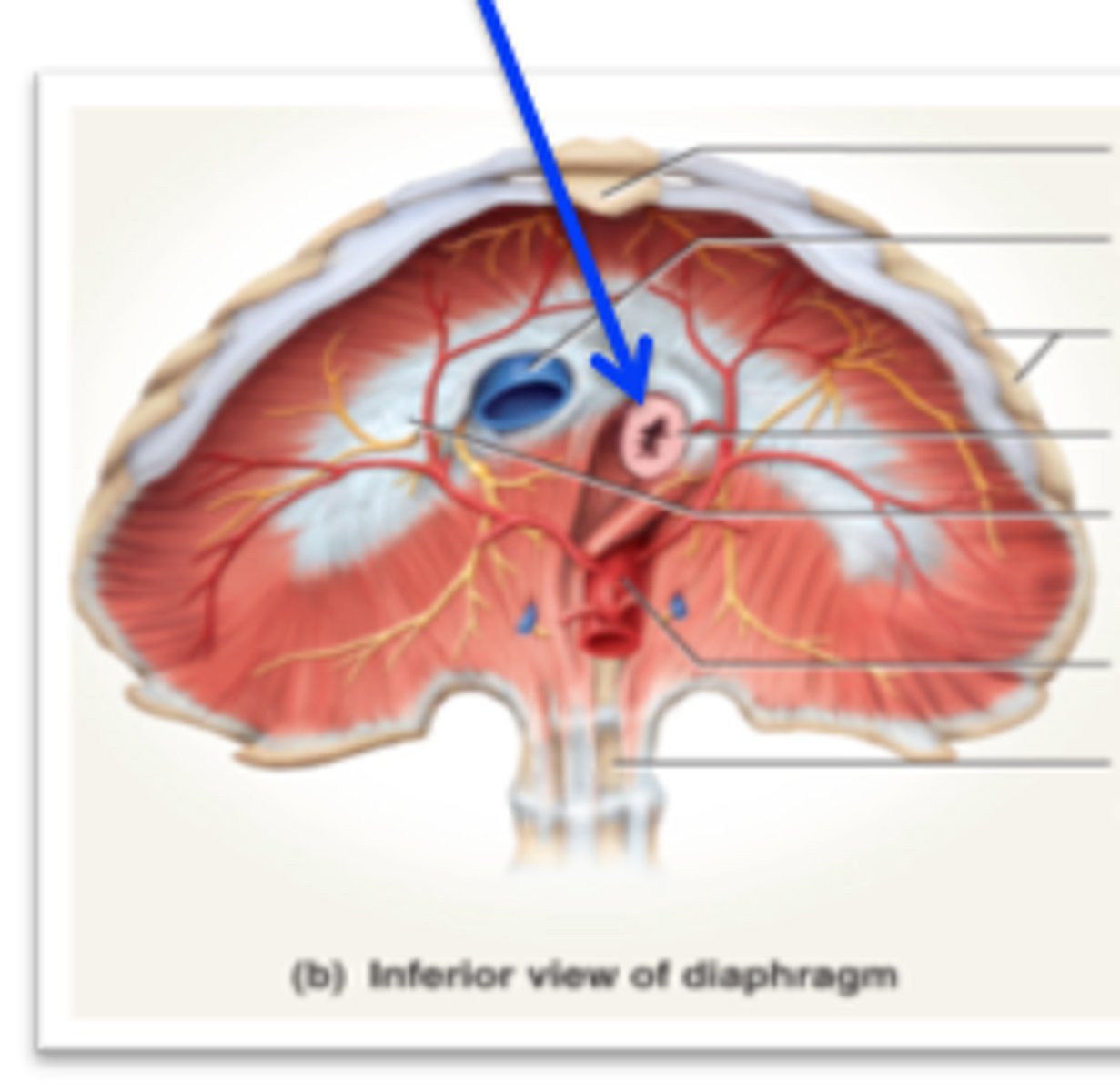
Esophageal hiatus
Opening in diaphragm through which esophagus enters the abdominal cavity
Upper esophageal sphincter
ring of muscle at superior end of esophagus - relaxes to allow food to enter esophagus
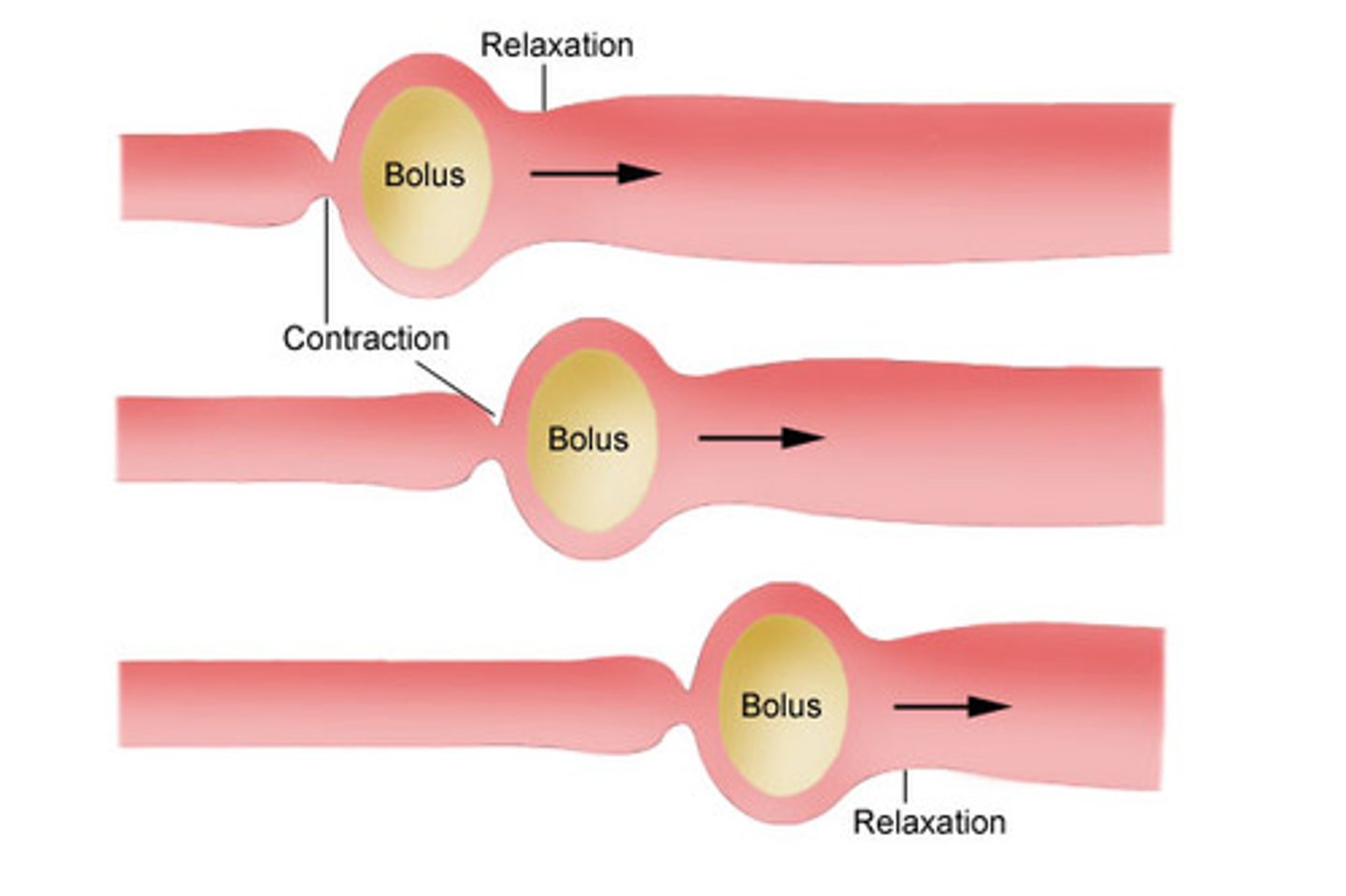
Peristalsis
Wavelike contractions of muscle that push bolus toward stomach
Lower esophageal sphincter (cardiac sphincter, gastroesophageal sphincter)
opens to allow food into stomach; when it doesn't close completely the stomach contents reflux = heartburn
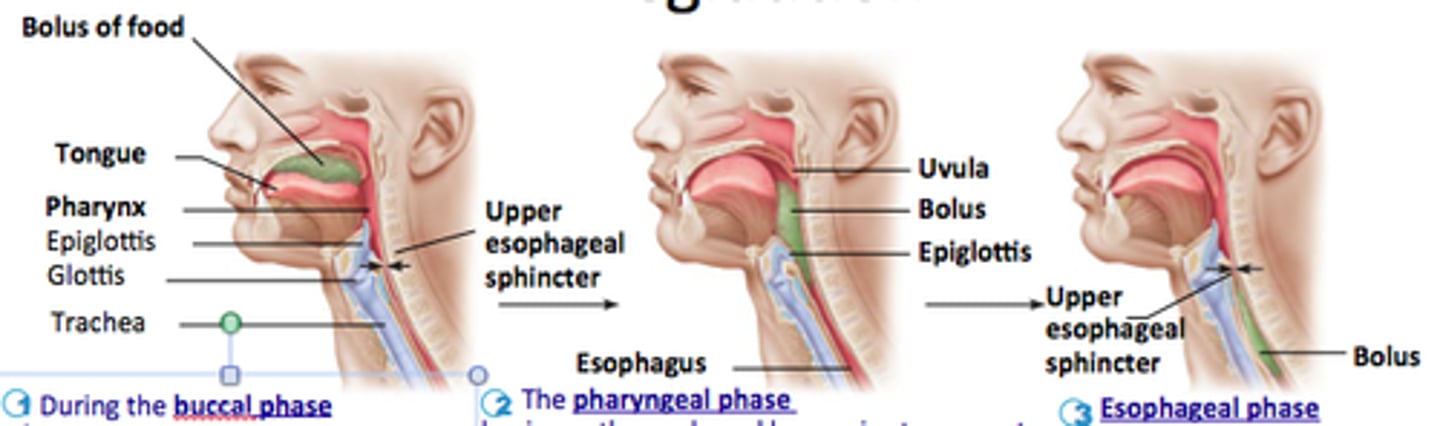
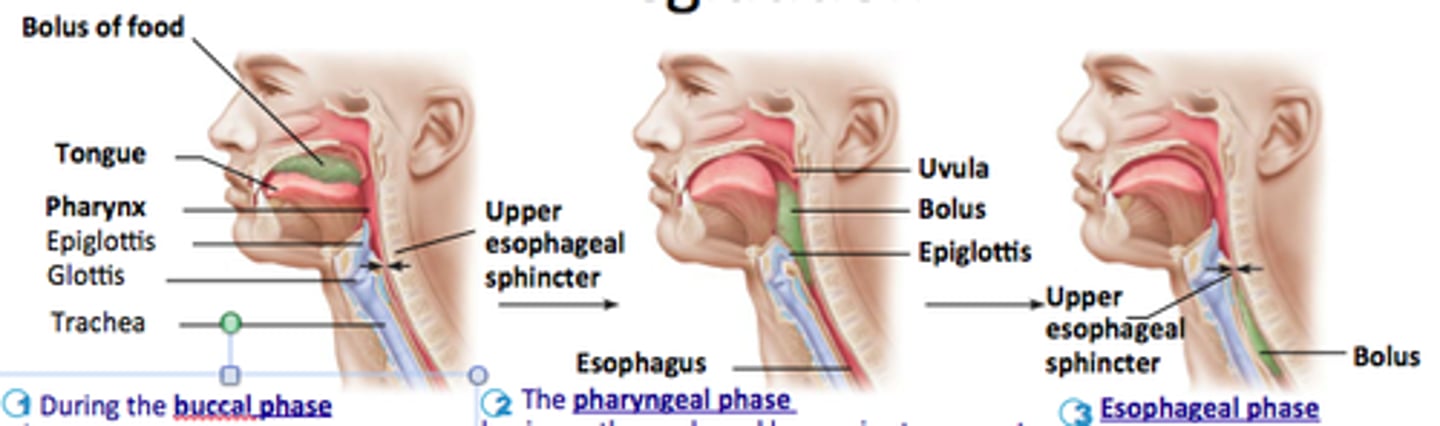
Deglutition
Swallowing; 3 phases (voluntary/oral, pharyngeal, esophageal)
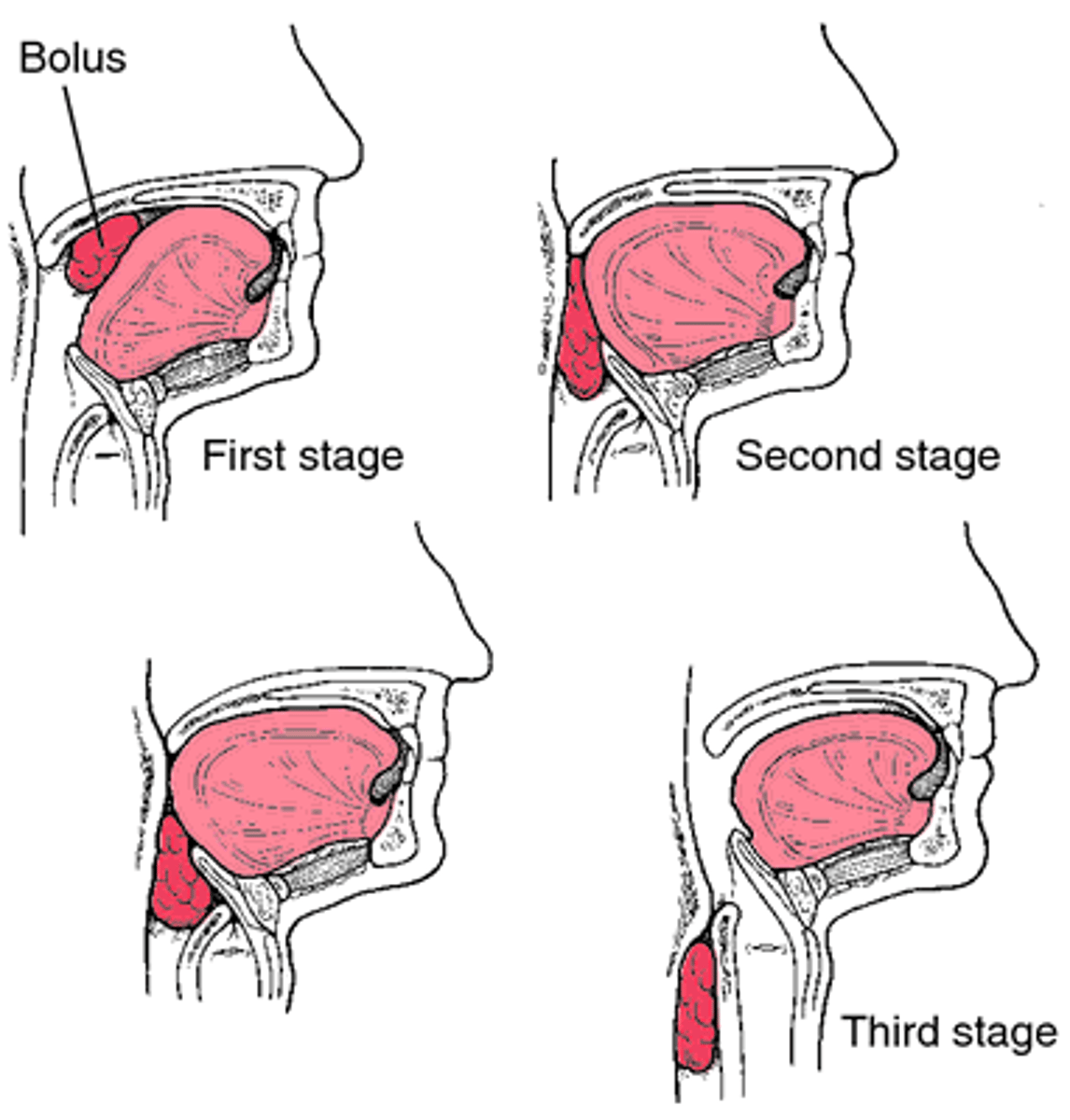
Voluntary phase (of deglutition)
tongue pushes bolus to back of oral cavity
Pharyngeal phase (of deglutition)
uvula and soft palate move up to close off nasopharynx; laryngeal muscles close opening into respiratory system; pharyngeal muscles constrict & push food into oropharynx & laryngopharynx; Upper esophageal sphincter relaxes
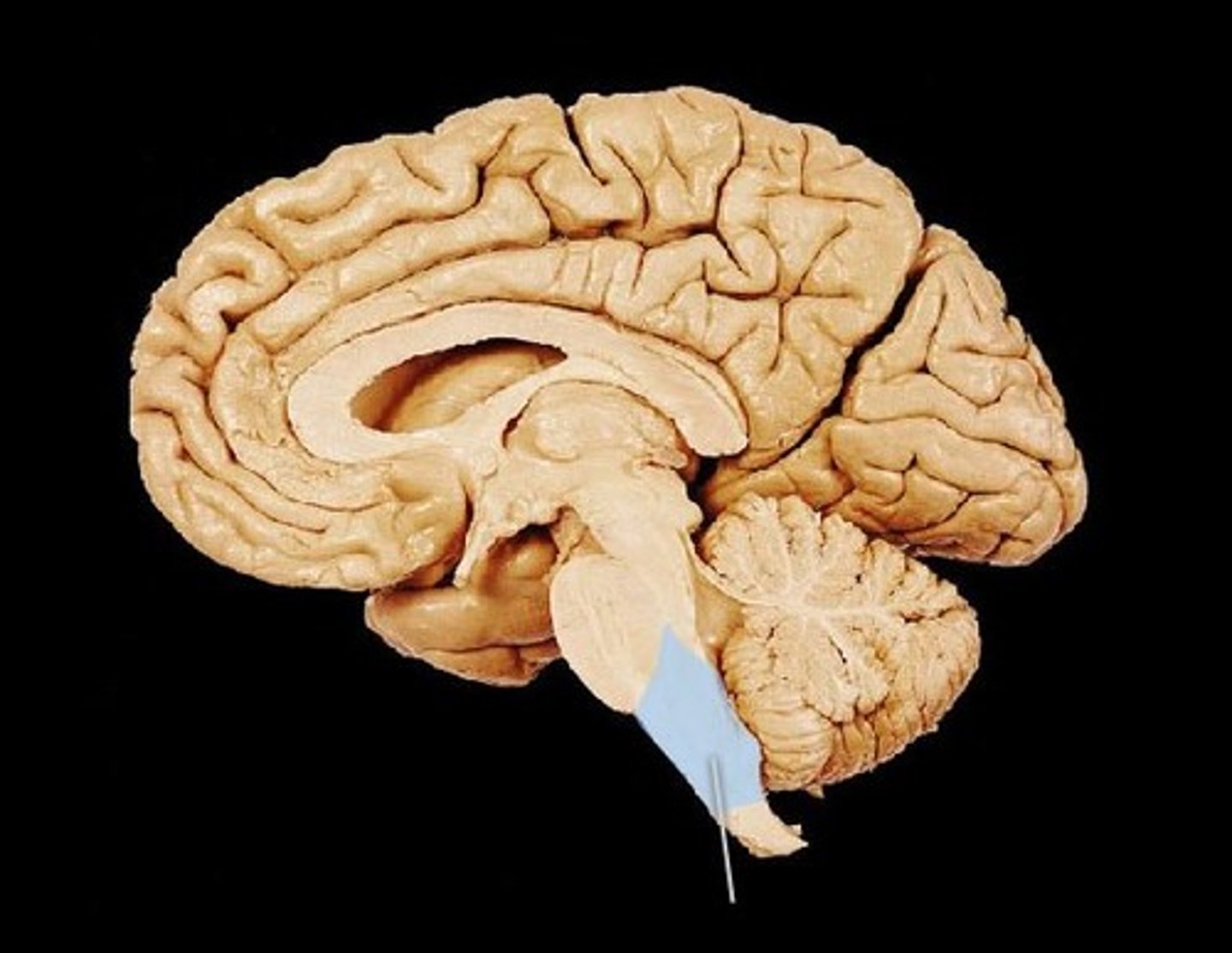
Medulla oblongata
swallowing center of brainstem
Esophageal phase
peristalsis begins; distention of esophagus near stomach opens cardiac sphincter; food enters stomach
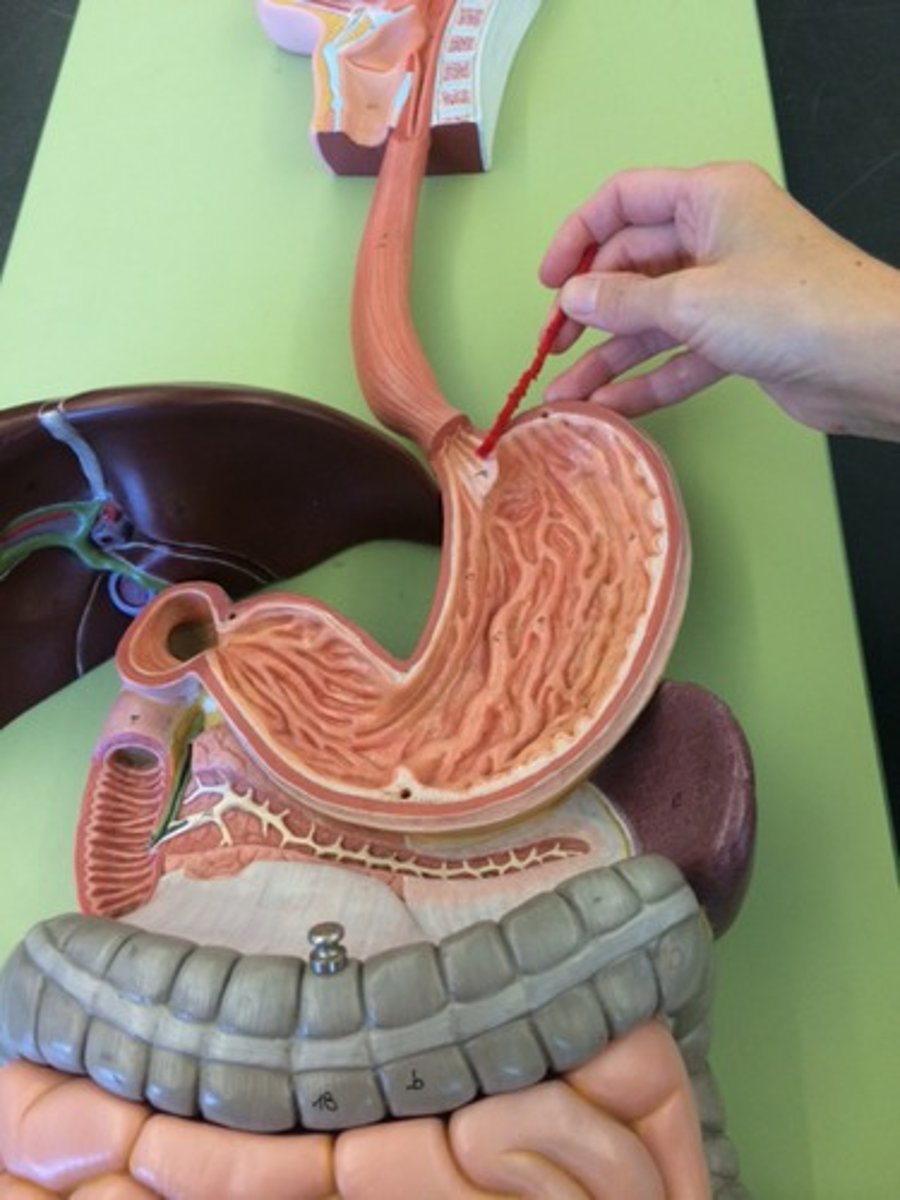
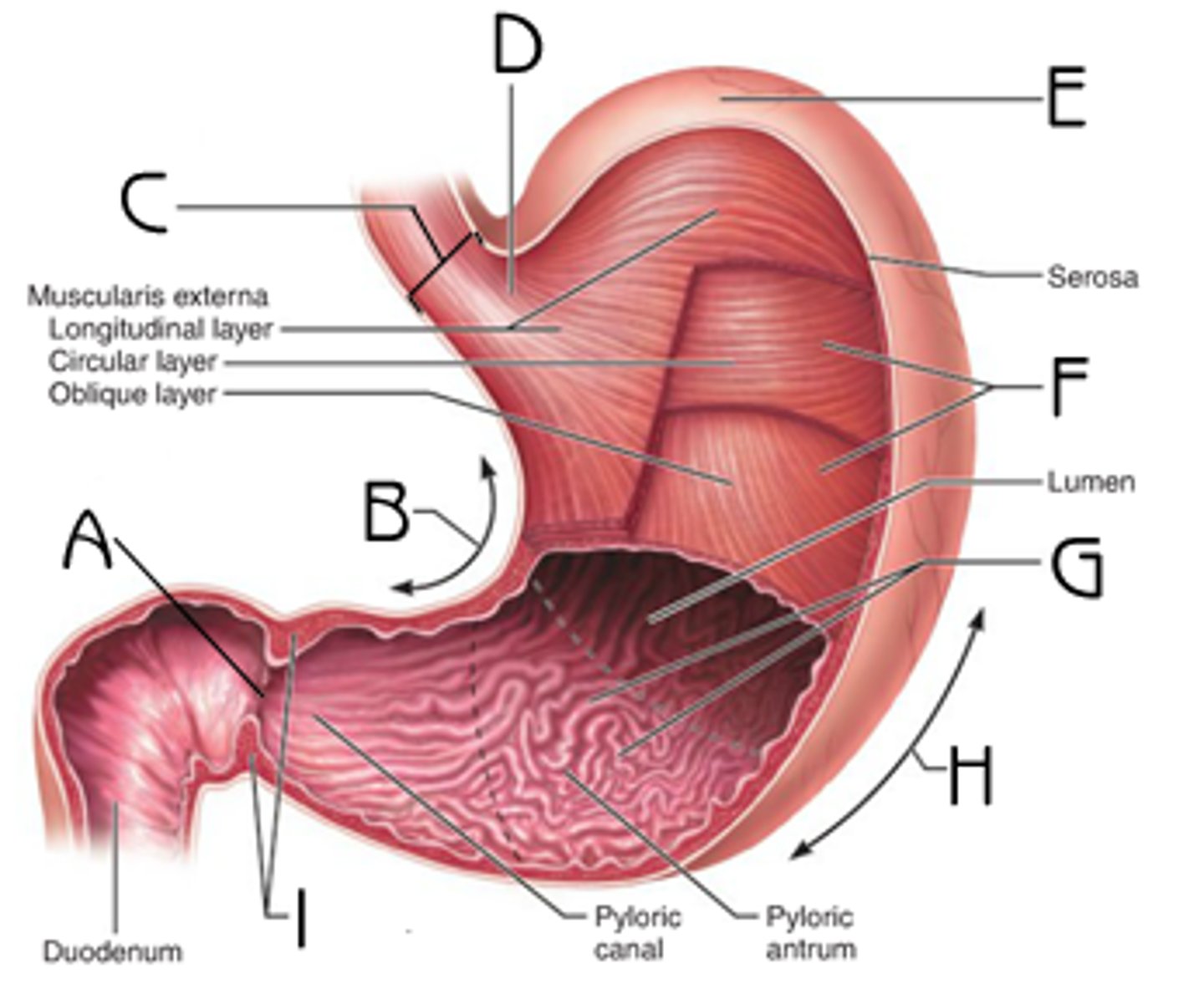
Stomach
J-shaped sac; chemically digests proteins and fats (mainly proteins); mechanically digests all food; Stores food we eat until small intestine is ready to digest it; absorbs alcohol, water, and aspirin
Chyme
Acidic, soupy mixture of partially digested food and digestive juices in the stomach
Cardia
Point where esophagus connects to the stomach
Fundus
Inferior to diaphragm and superior and to the left of the cardia; contains cells that produce Ghrelin
Ghrelin
Hormone that targets the hypothalamus and triggers feeling of hunger
Body
Main part of stomach
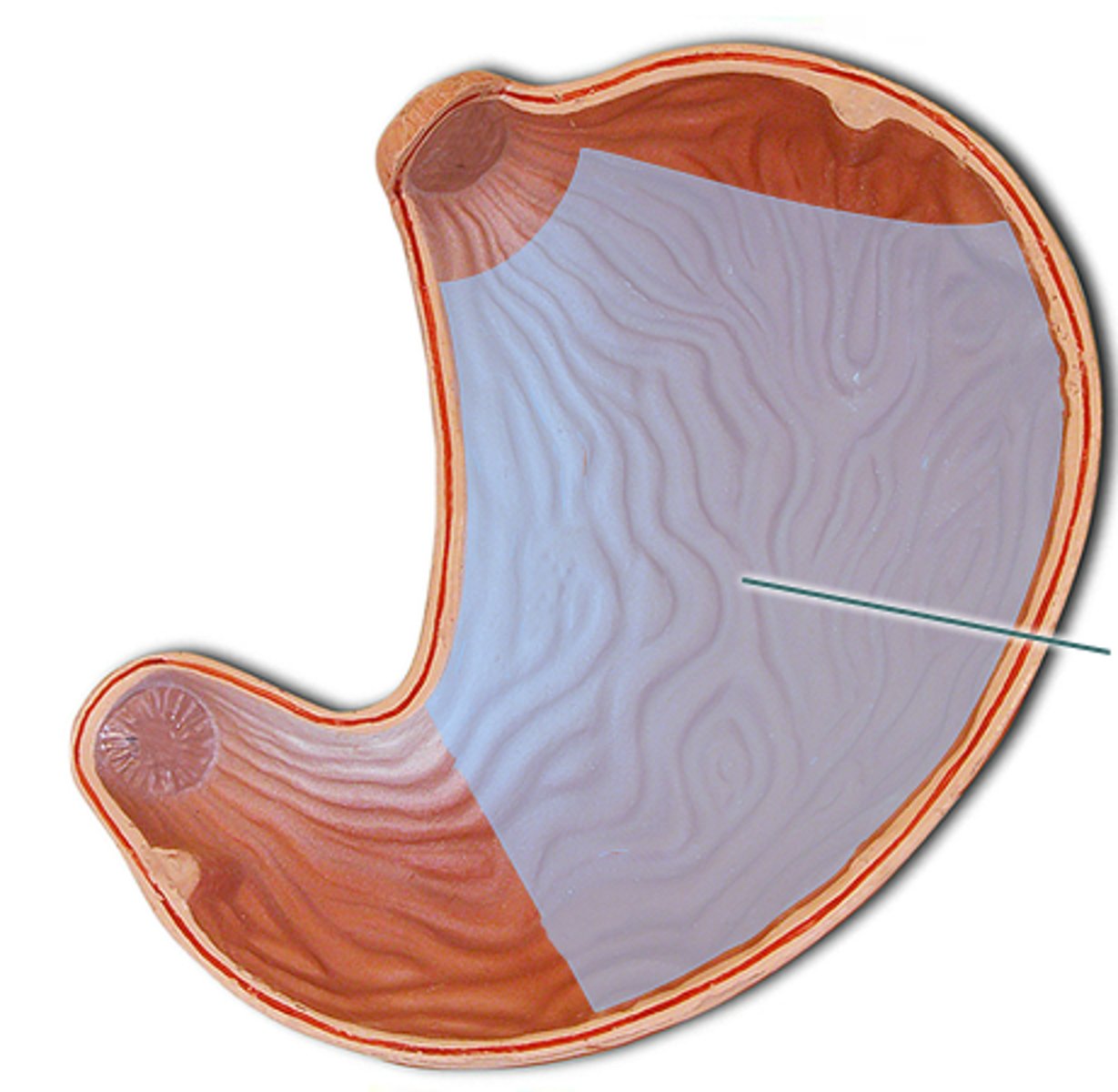
Pylorus
Funnel shaped portion of the stomach; connects the stomach to the duodenum
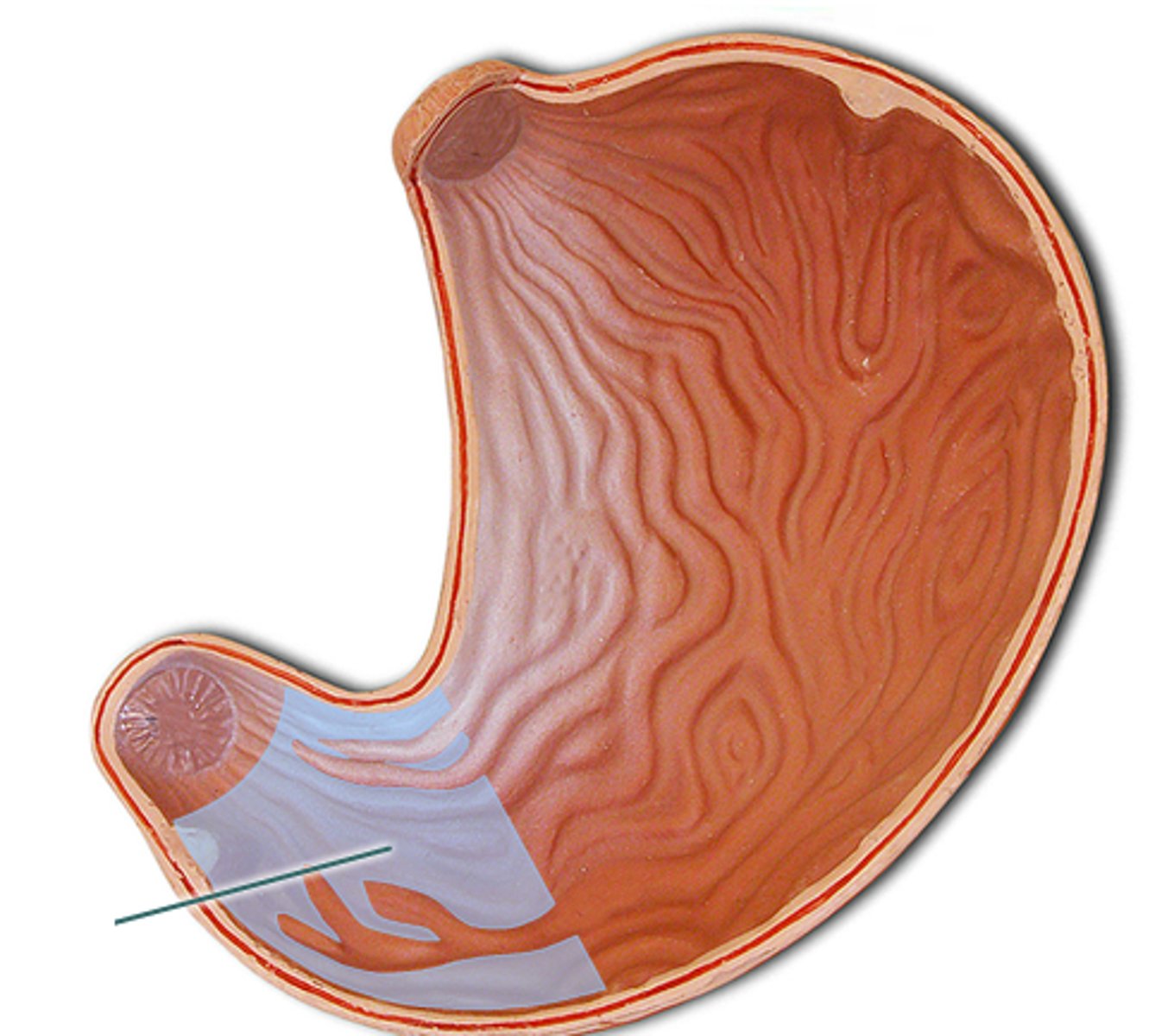
Pyloric antrum
wide end of the pylorus connects to the body of the stomach
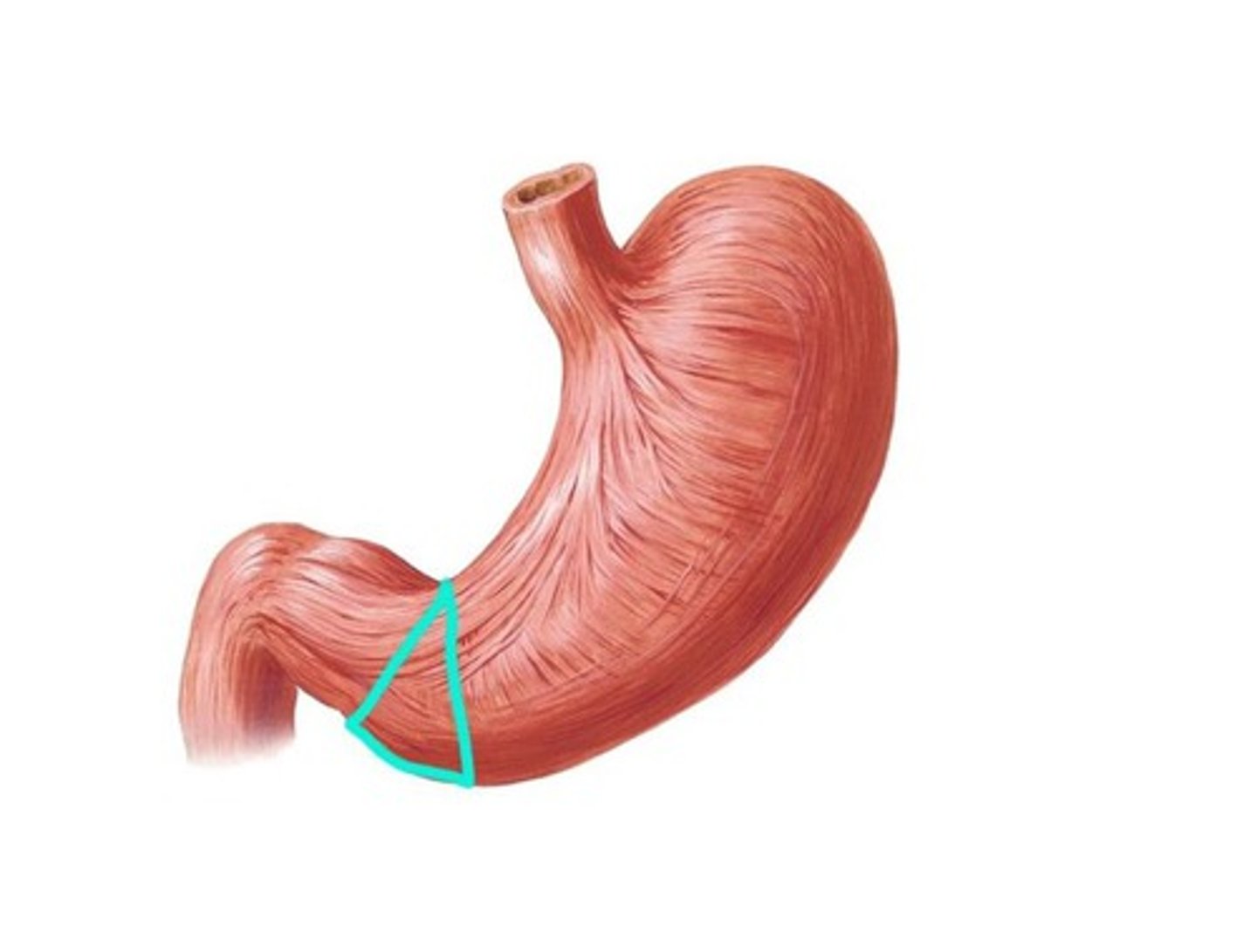
Pyloric canal
narrow end of pylorus that connects pylorus to duodenum
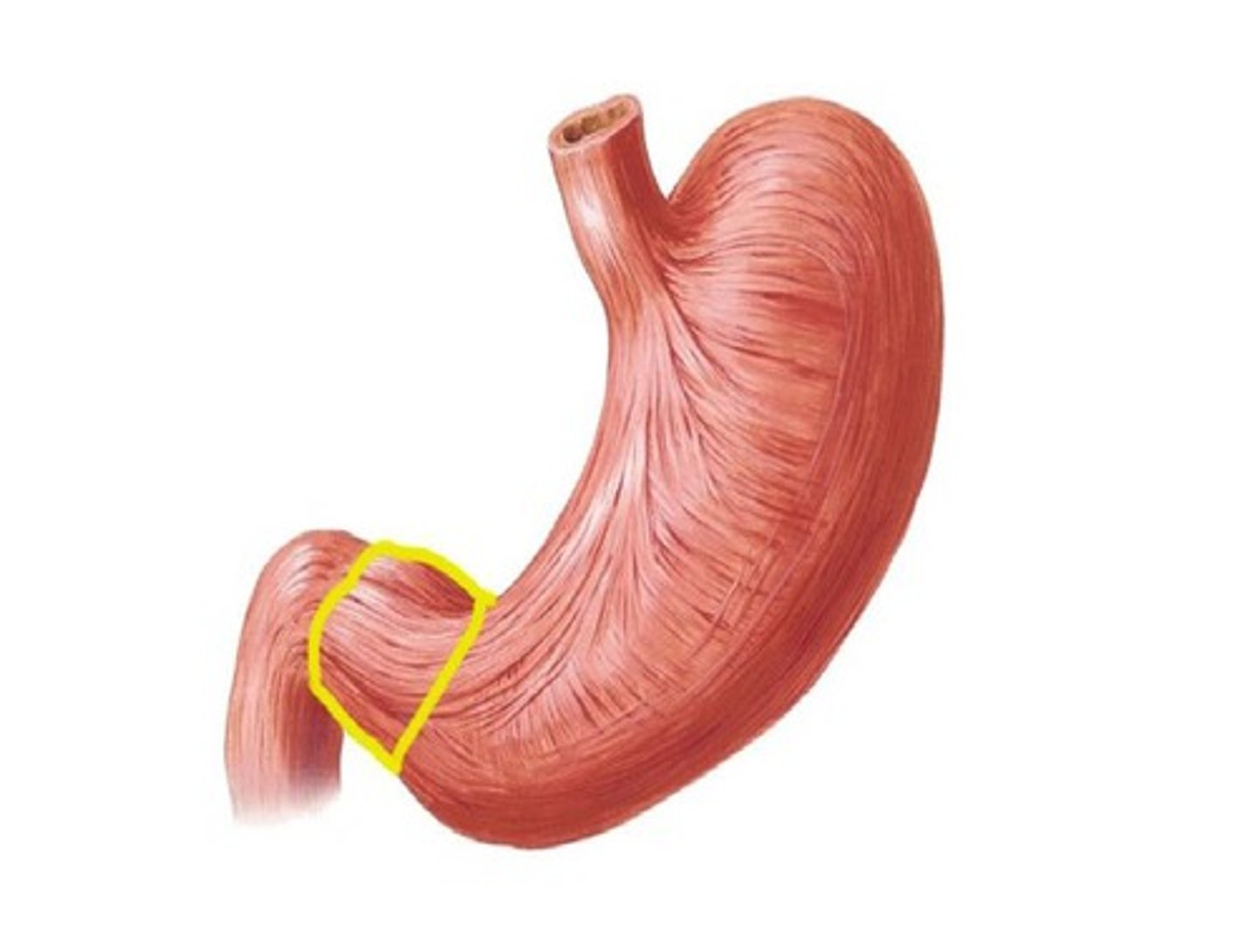
Pyloric sphincter
ring of muscle that controls gastric emptying
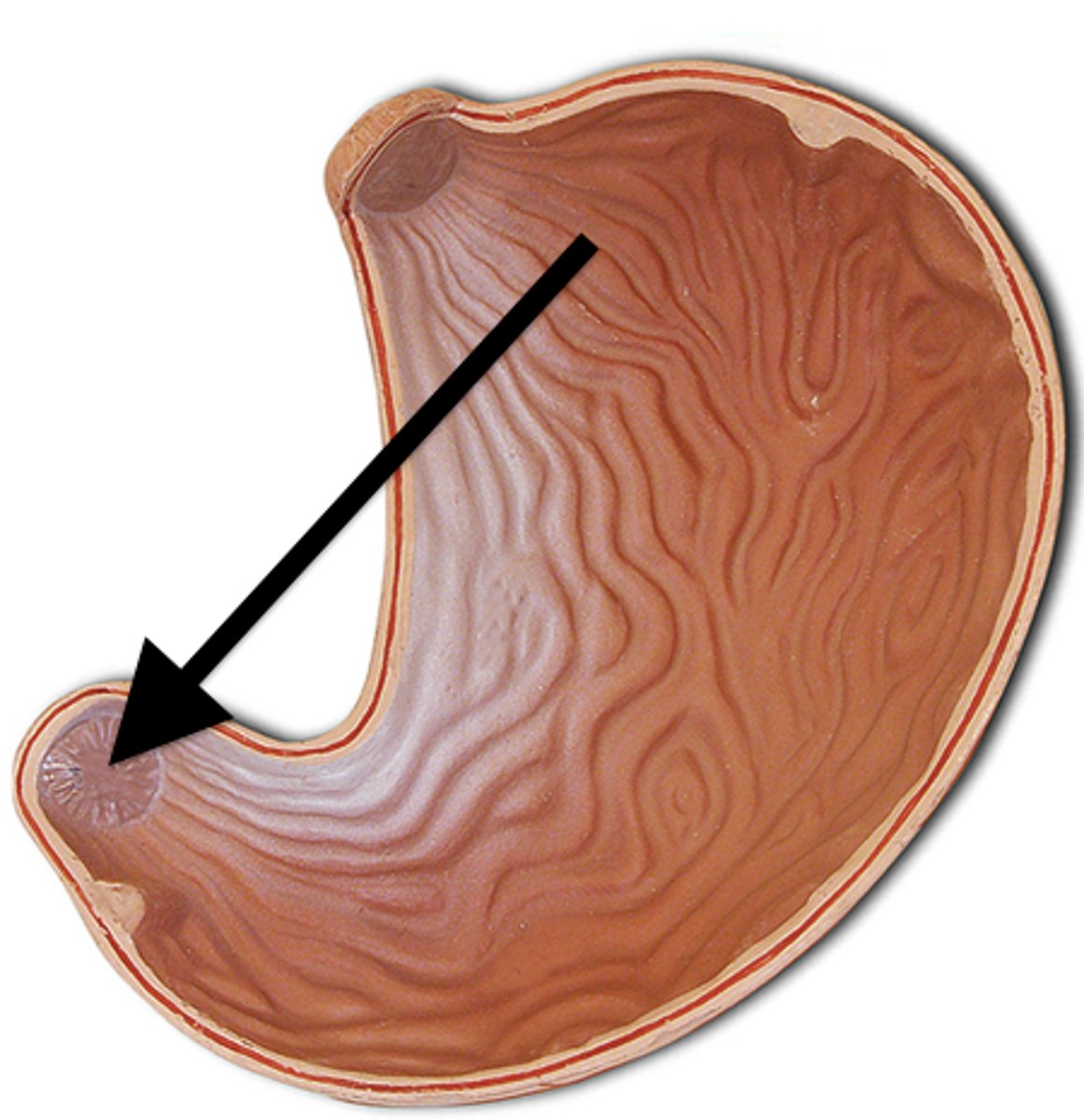
Greater curvature
convex lateral surface of the stomach
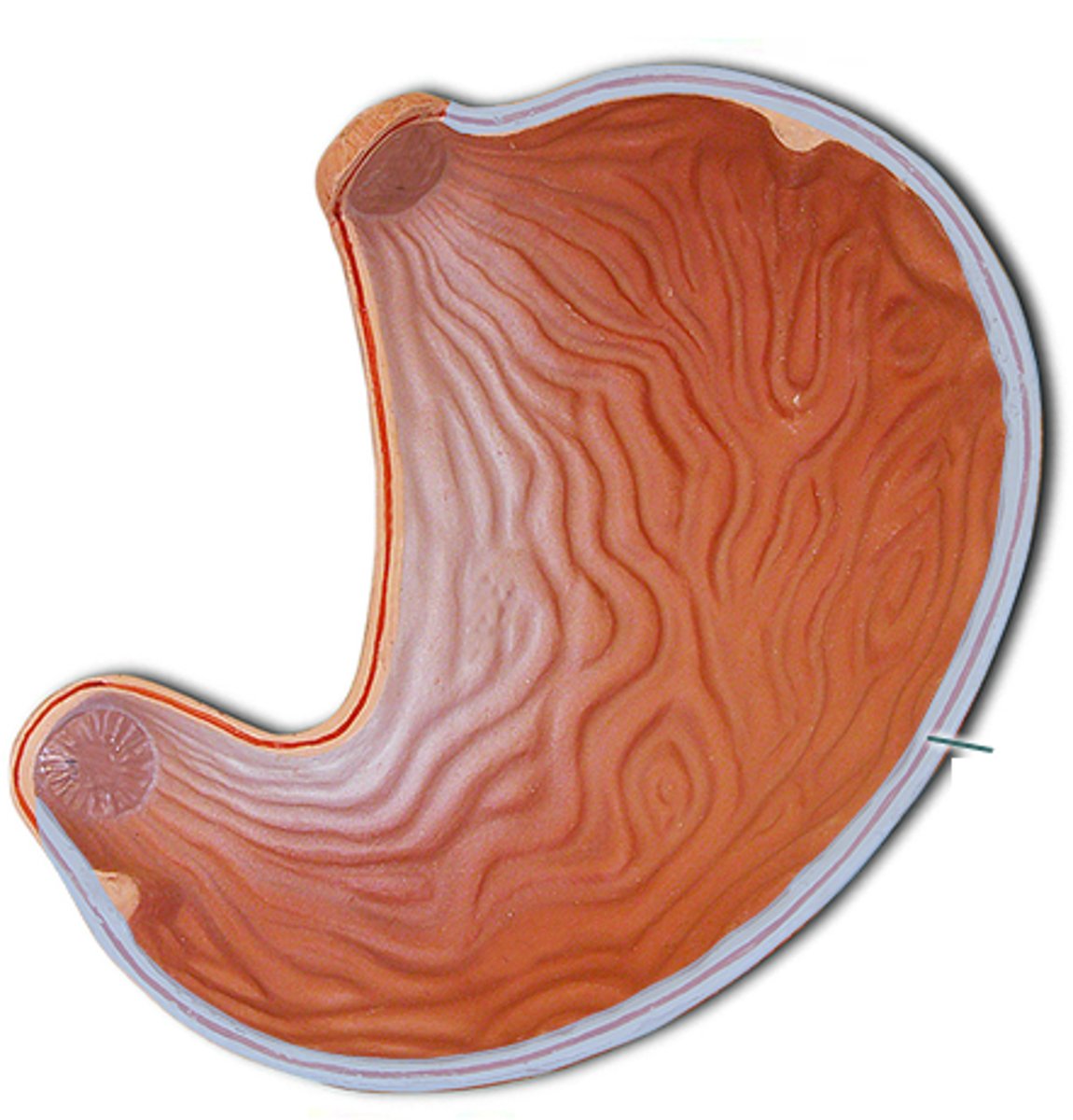
Lesser curvature
concave medial surface of the stomach
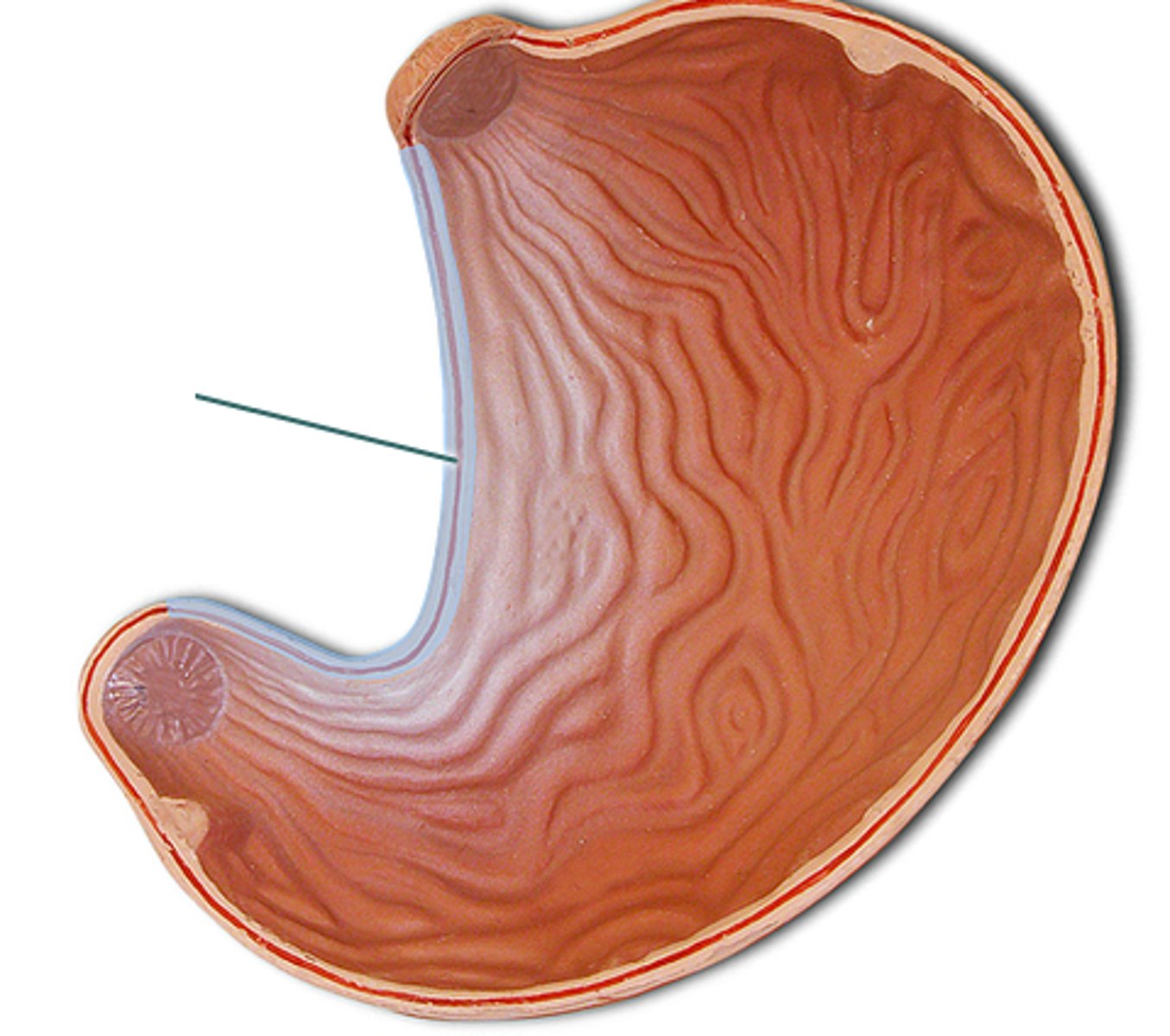
Oblique layer
Extra inner layer of muscle in the stomach that allows for more churning of food
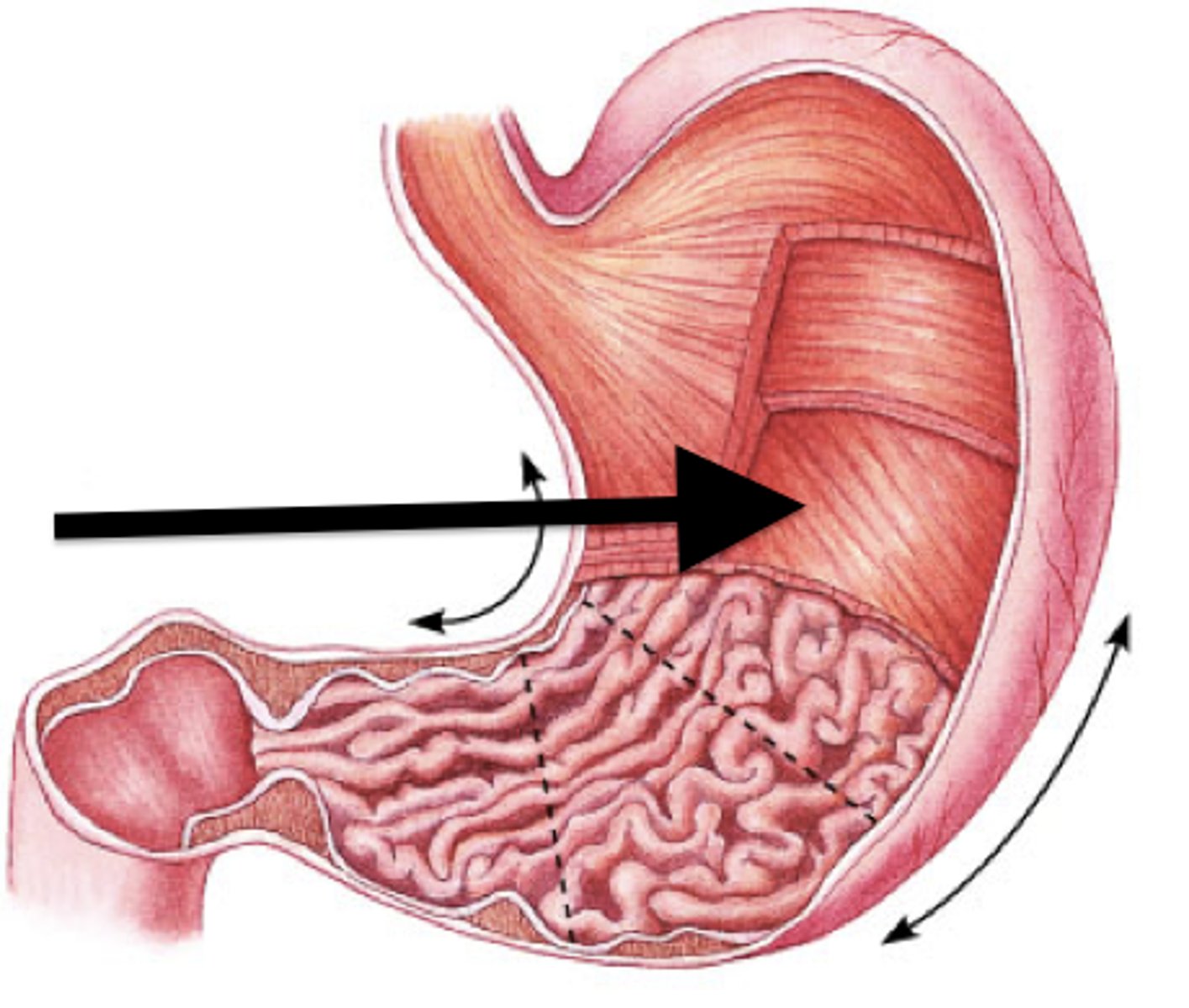
Gastric pits
Pits of epithelial lining that open up into gastric glands
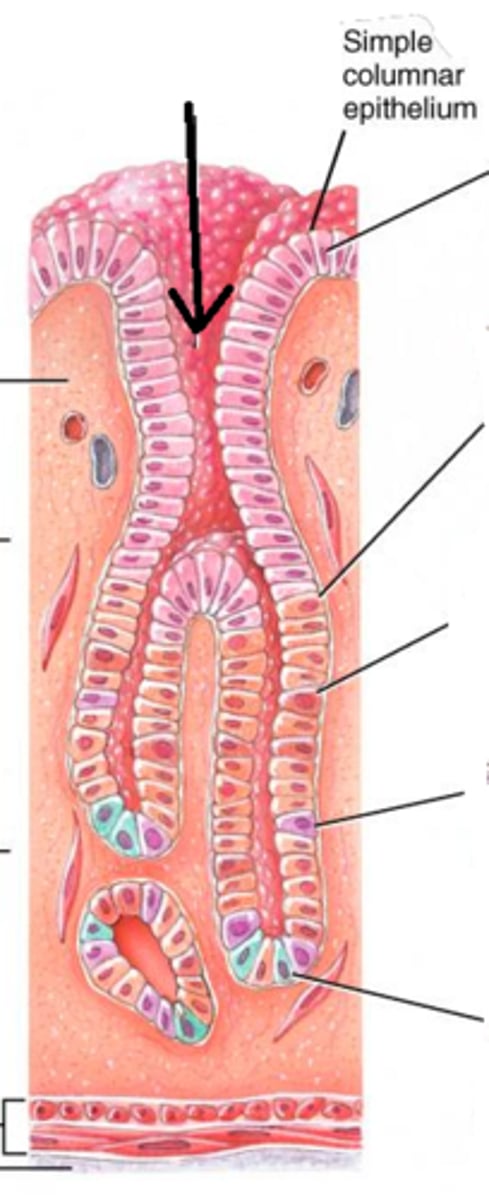
Gastric glands
contain cells that secrete digestive juices, enzymes, and hormones
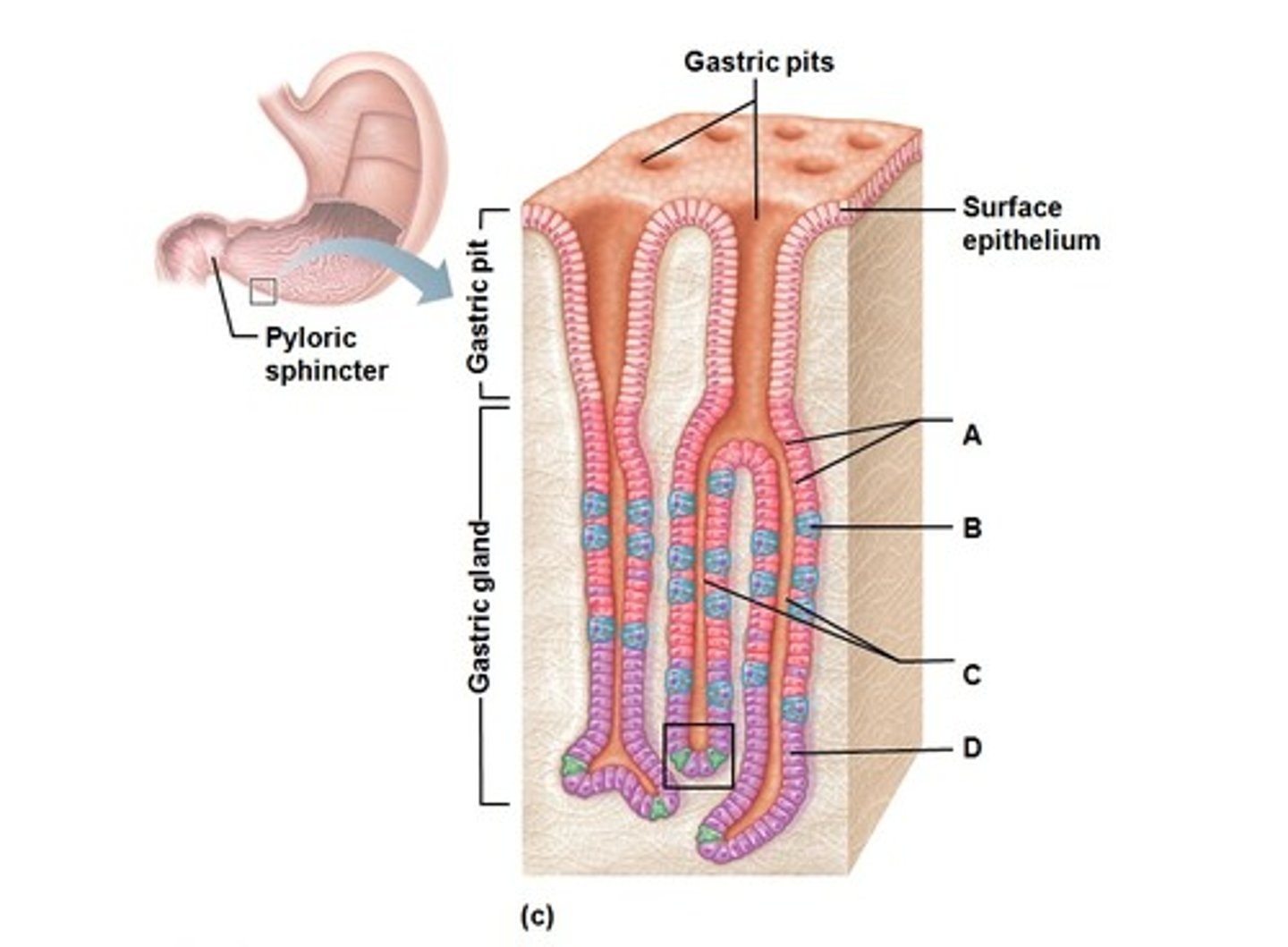
Chief cells
cells in the gastric glands that secrete pepsinogen and gastric lipase
Parietal cells
Secrete HCl and intrinsic factor
G cells
Secrete gastrin
Mucus cells
Secrete mucus
pepsinogen
inactive form of enzyme pepsin; activated into pepsin when it comes into contact with Hal
pepsin
protein digesting enzyme
gastric lipase
helps digest fats
intrinsic factor
stimulates the small intestine to absorb vitamin B12
gastrin
hormone that stimulates gastric glands to secrete and promotes emptying of stomach; produced when we see, smell, or taste food
Mucosal barrier
physical barrier that protects mucosa of stomach from protein digesting enzymes & HCl; also contains bicarbonate ions to neutralize stomach acid