RBCs (erythrocytes)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Red blood cells (RBC’s)
are highly specialized for O2 transport function
RBC (1)
biconcave disk
RBC (2)
production=destruction with at least 2 million new RBC’s per second
Cell membrane (strong & flexible)
inner surface; cytoskeletons( spectrin and actin) allow RBC’s to squeeze through smaller capillaries
Cell membrane (strong & flexible) (2)
outer surface: glyco;lipids (antigens) determine the blood types (A/B/O and RH+/RH-, etc)
cytoplasm (no nucleus or organelles)
no mitochondria (not consume o2; use anaerobic fermentation to produce atp
cytoplasm (no nucleus or organelles) (2)
contain carbonic anhydrase that catalyzes CO2+H20 ↔ H2CO3
RBC (3)
contains hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (HB)
the oxygen-carrying protein that gives blood its red color
Hemoglobin (2)
mainly carries O2 from lungs to tissue( by heme-fe2+ portion)
hemoglobin (3)
280 million HB molecules per RBC (about 33% of cytoplasm is HB)
hemoglobin (4)
carries small percentage of CO2 from tissue from tissue to lungs (by globin)
hemoglobin (5)
binds to carbon monoxide (CO) much stronger than O2 (230 times). and decreases its own O2- carrying capacity , results in “carbon monoxide poisoning”
hemoglobin (6)
can also carry nitrogen monoxide (NO, vasodilator) that will enhance blood flow and local O2 delivery
Hemoglobin makeup
4 heme + globin
Globin
protein; 4 polypeptide chains
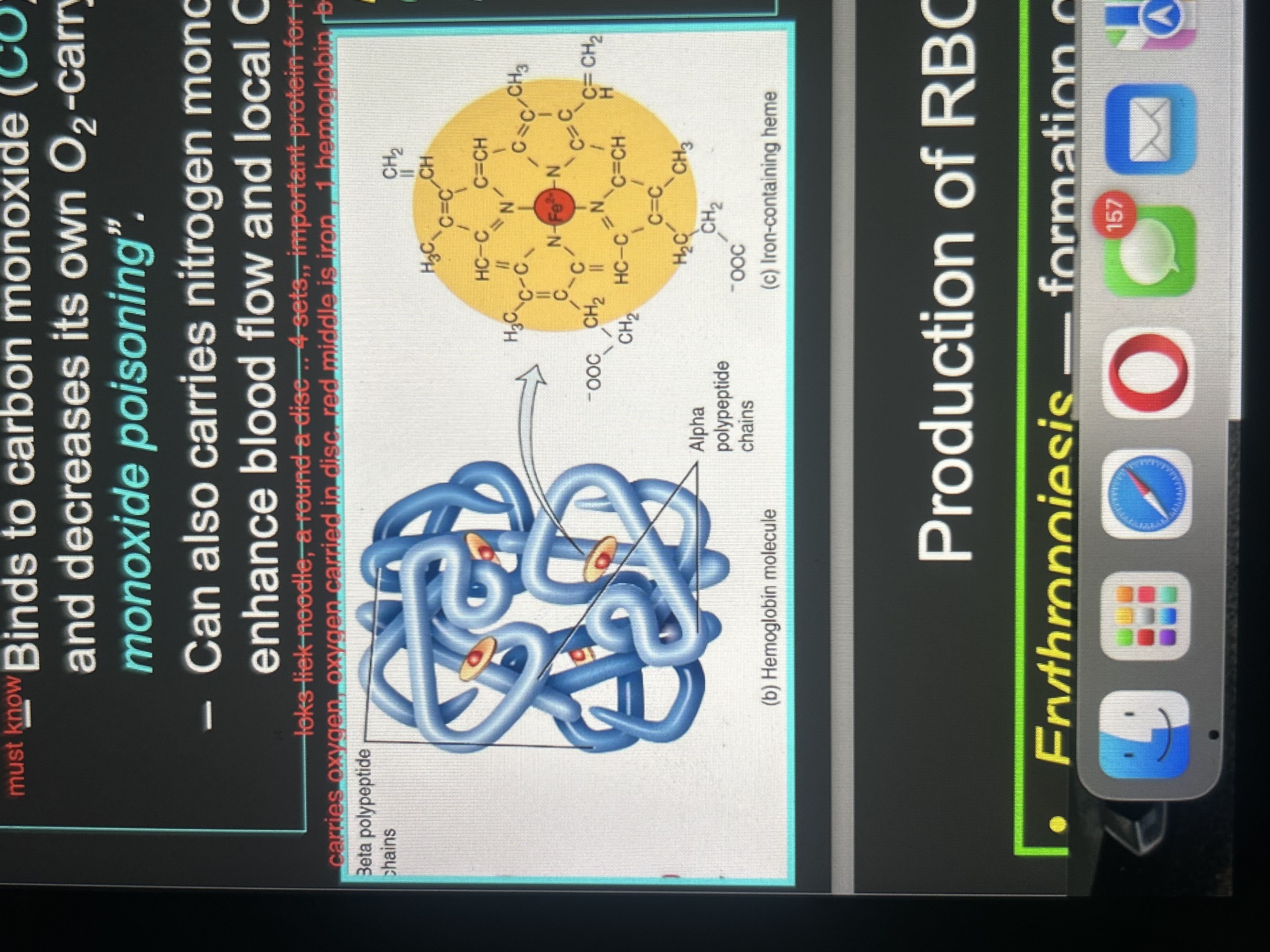
Heme
pigment, each contains an iron ion (Fe2+) that can combine reversibly with one O2 molecule
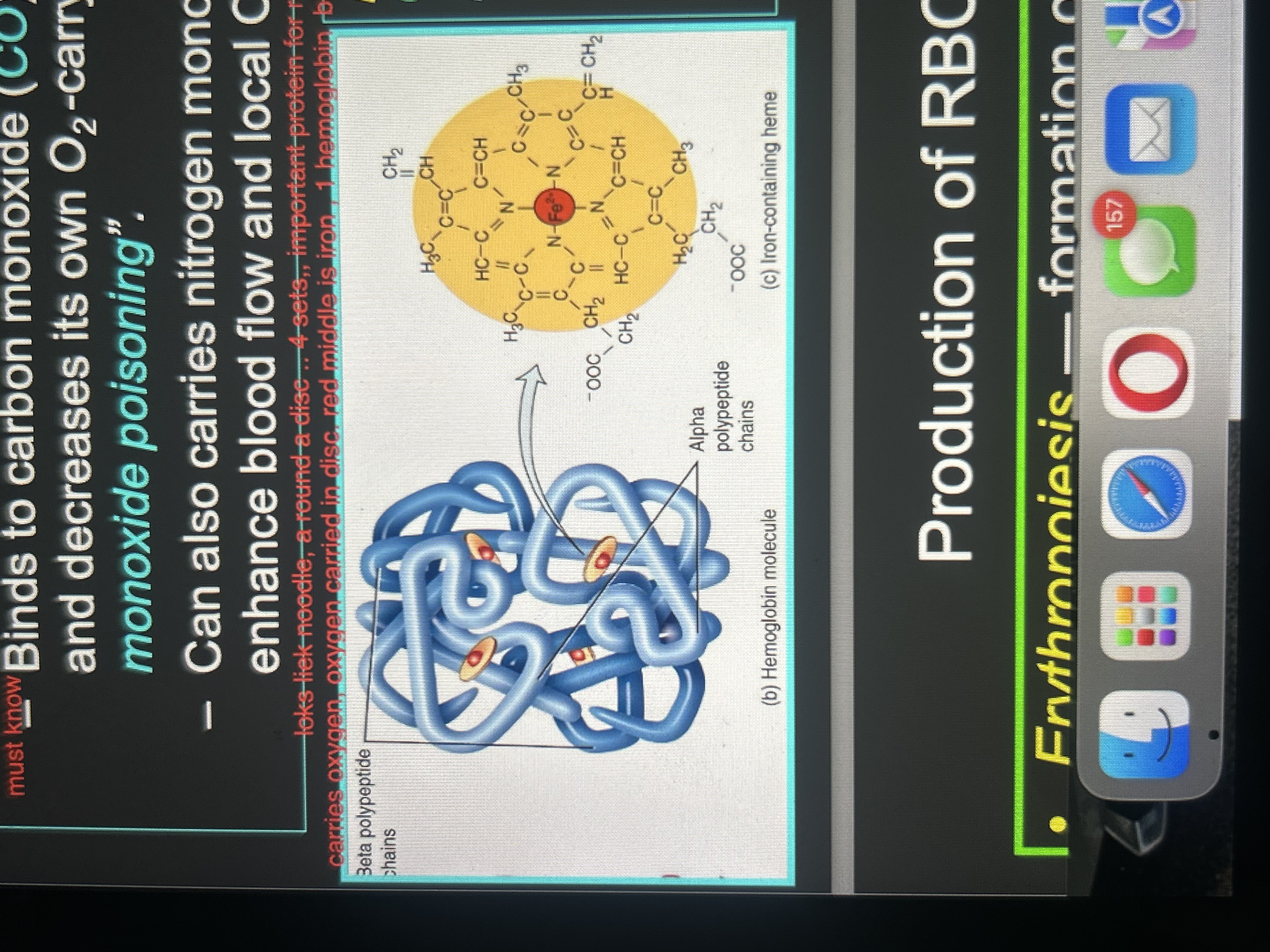
heme (2)
4 heme attached to a polypeptide chain
production of RBS
Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (1)
formation of erythrocyte (RBC), which occurs in adult. red bone marrow (RBM).the main stimulus for erythropoiesis is hypoxia (O2 deficiency at the tissue level)
Erythropoiesis(2)
(in RBM) pluripotent stem cell then goes to myeloid stem cell; pro erythroblast (produces the hemoglobin) ; nucleus is ejected; reticulocyte; leaves bone marrow and enter bloodstream
Erythropoiesis(3)
(in blood) reticulocyte then ejects the remaining organelles (1-2day after being in the blood stream) and turn into mature RBC
Normal reticulocyte count
0.5 ~ 1.5% of blood RBC
Low reticulocyte count
in an anemic person might indicate bone marrow problem (leukemia, nutritional deficiency, etc)
high reticulocyte count
might indicate recent blood loss or successful iron therapy
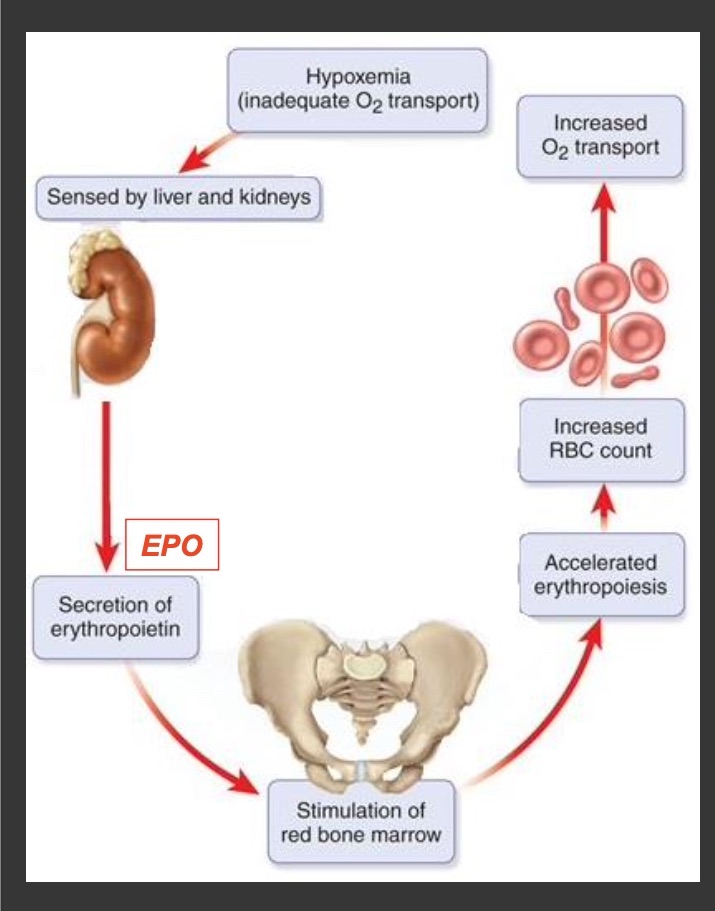
Hypoxemia
(Negative Feedback Control of RBC Production)
oxygen(O2) levels in the blood go down
Hypoxia
(Negative Feedback Control of RBC Production)
oxygen(O2) delivery to tissue and organs go down
Hypoxemia example (1)
can cause hypoxia , EX: on a mountain the altitude is high so the O2 is less.
Hypoxemia example (2)
RBC production goes down so the O2 transport is down
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 1)
it detects oxygen levels are low
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 2)
it releases erythropoietin (EPO)
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 3)
The EPO stimulates red bone marrow
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 4)
erythropoiesis increases then increases the reticulocyte production, reitculocyte mature into RBC
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 5)
the RBC count increases (oxygen carrying capacity of blood)
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 6)
blood O2 level rises
kidney response to Hypoxia/hypoxemia (step 7)
Negative feedback happens when the O2 level are sufficient again, EPO secretion decreases
fetal and newborn liver also produce EPO