Exercise 33 nitrate reduction test KTTK (MB. LAB)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Know what type of respiration nitrate reduction is responsible for
anaerobic respiration
dissimilatory nitrate reduction (denitrification)
assimilatory nitrification
denitrification
the process by which nitrate is reduced to nitrogen gas by soil microbes when oxygen is not present.
what denitrification produced during this process
Denitrification converts nitrate to nitrite and then nitrite to nitric oxide, nitrous
oxide, or nitrogen gas
how you know denitrification process occurs in the nitrate broth
occurs by presence of gas in the Durham tube
Know why the color reactions in nitrate broth occur
Is a result of reactions between metabolic products and reagents added after the incubation.
Know what a Durham tube is
Is a small, inverted test tube placed inside a larger test tube containing a liquid medium, used to trap any gas produced by microorganisms during growth
Why is the Durham tube added to nitrate broth?
for indication of gas production from conversion on nitrate to nitrogen gas.
Know what is added to the inoculated and incubated tubes if
evidence of denitrification is not present
Reagents A and B are added to each tube where if nitrate has been reduced to nitrite
After addition of zinc dust to reduce any remaining nitrate in tube to nitrite
reagent A
sulfanilic acid
reagent B
a-Naphthylamine
Tubes turn red after reagent A and B
test is positive nitrate reduction and presence of nitrate reductase
If tube does not turn red after reagent A and B
zinc dust is added to determine if nitrate is still present or has been reduced past nitrite
Know what it means if the tubes turn red after zinc dust is added
and what it means if they don’t turn red
• Tubes that weren’t red after addition of reagents A and B, but are red after addition of zinc dust are considered negative
• Tubes that still aren’t red are considered positive for presence of nitrate reductase because the nitrate is gone and was reduced to
nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, nitrogen gas, or ammonium
Know why (application) the nitrate reduction test is used
• Used to identify organisms that reduce nitrate to nitrite
• Nitrate reduction test is especially used to differentiate Enterobacteriaceae from Gram-negative rods that either do not reduce nitrate to nitrite or reduce it past nitrite to N2 or other compounds
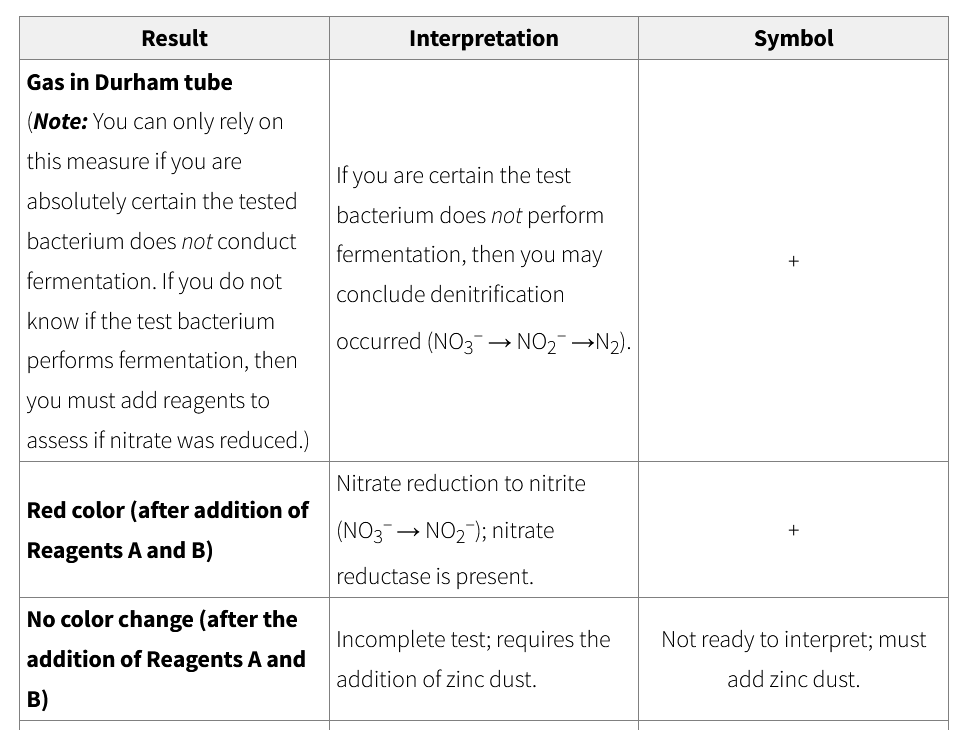
nitrate reduction test results and interpretations

look of tubes before incubation
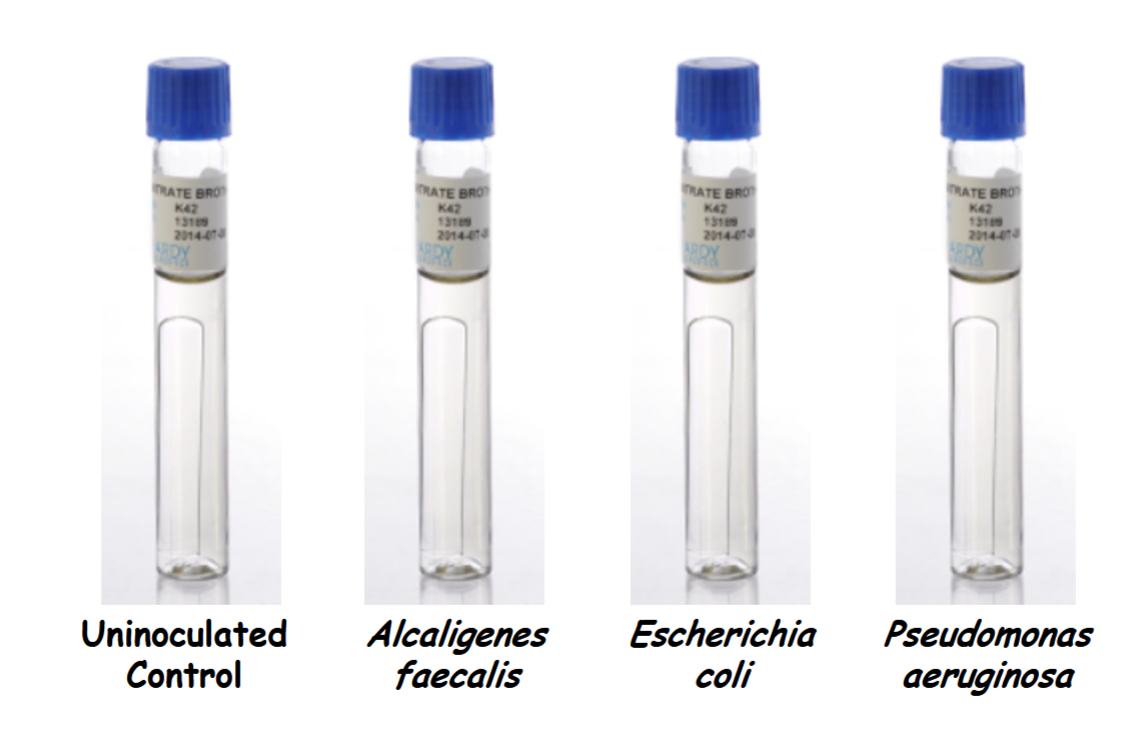
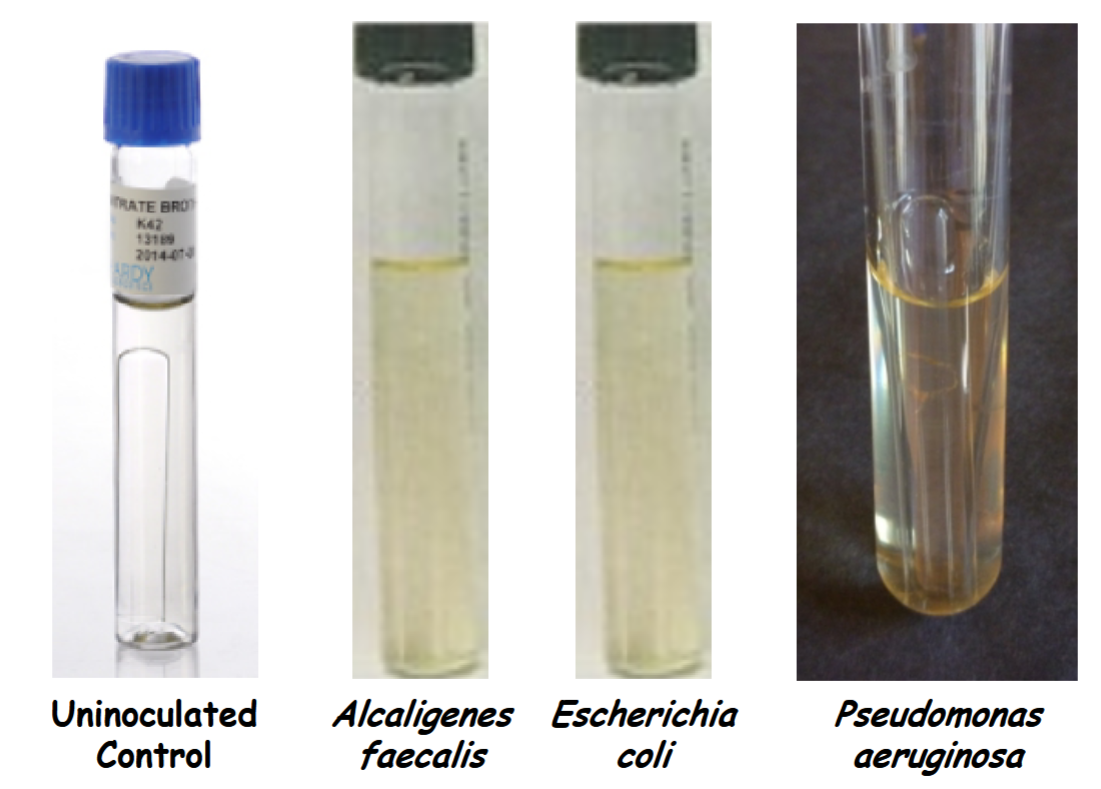
look of tubes after incubation and before reagents added
pseudomonas aeruginosa has gas in Durham tube +
If test bacterium does not perform fermentation, then you may conclude denitrification occurred (NO3– → NO2– →N2).

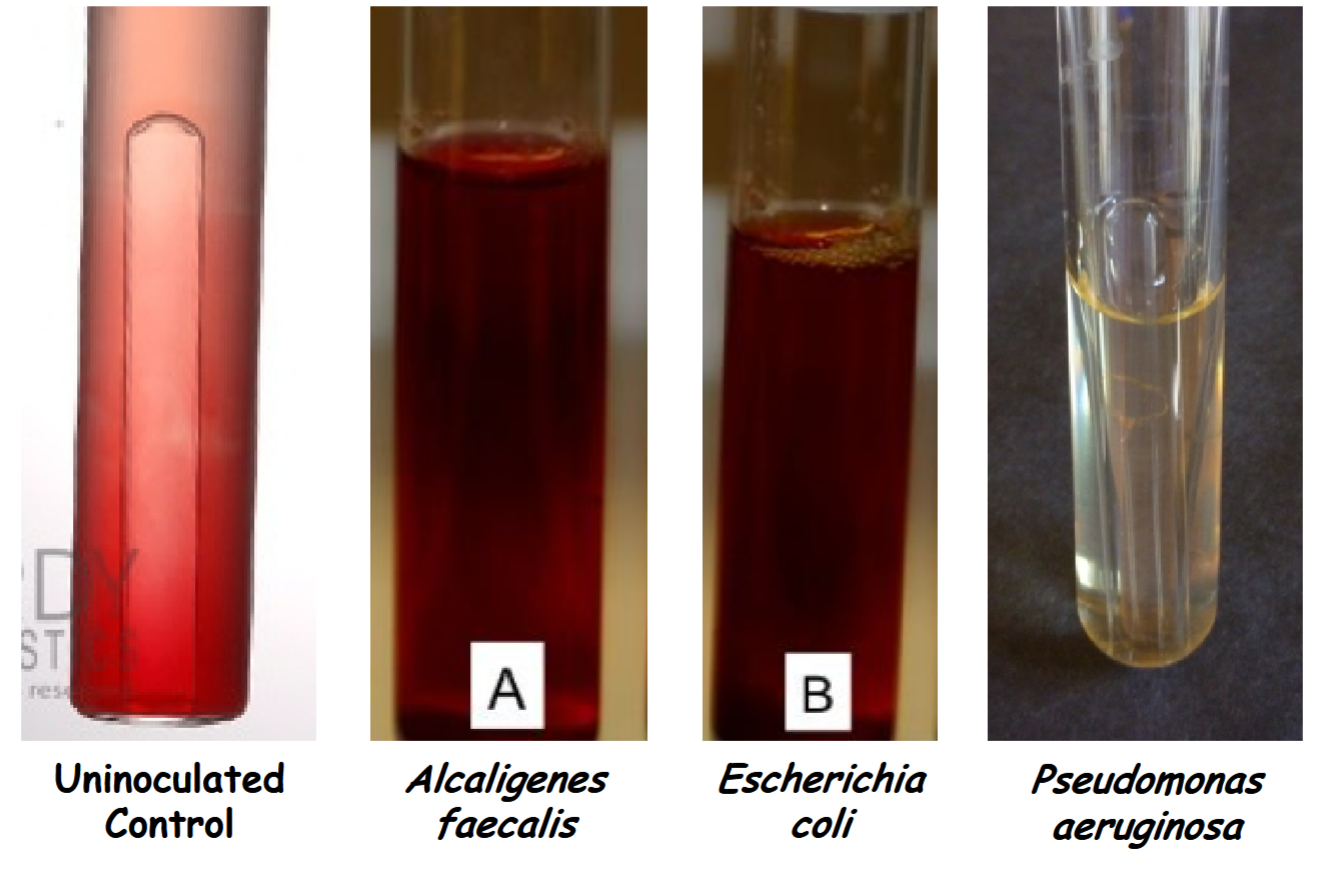
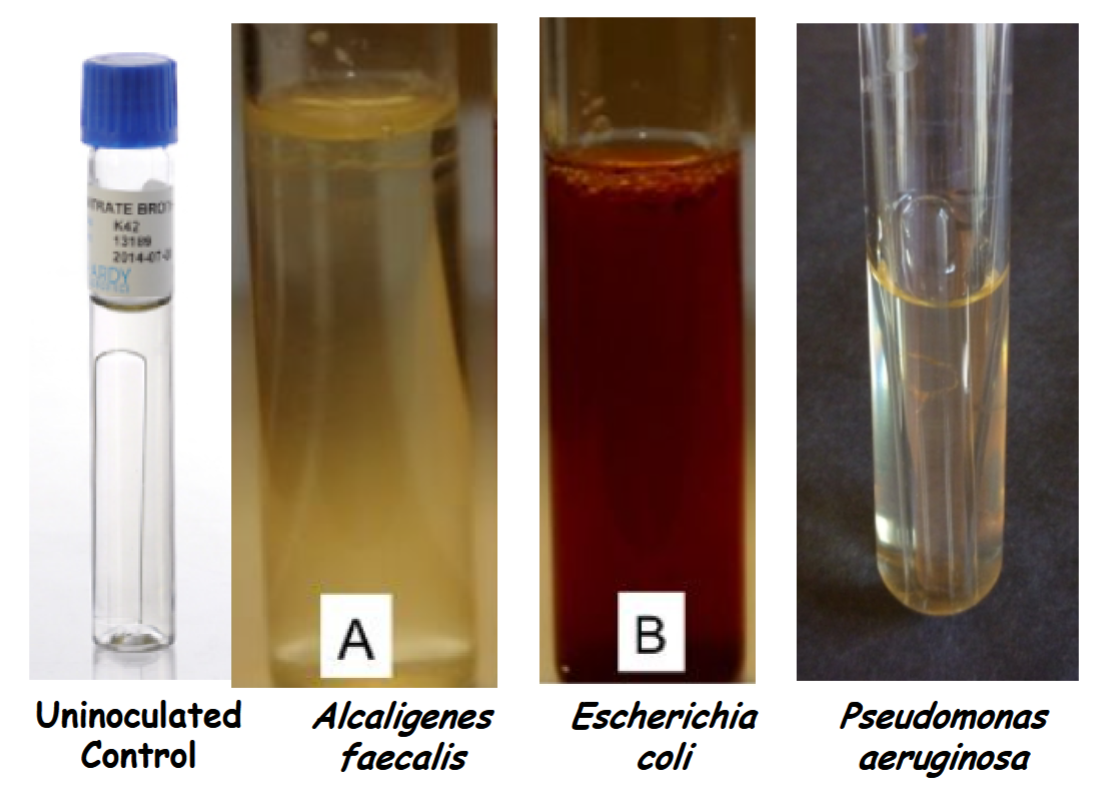
look of tubes after reagents A and B are added
Escherichia coli Nitrate reduction to nitrite (NO3– → NO2–); nitrate reductase is present. +
uninoculated control, Alcaligenes faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa Incomplete test; requires the addition of zinc dust. Not ready to interpret.
look of tubes after Zinc has been added
uninoculated control :no nitrate reduction -
Alcaligenes faecalis: no nitrate reduction -
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Nitrate reduction to gaseous (NO, ½N2O, or ½N2) or reduction to nongaseous nitrogen compounds such as ammonium (NH4+) +
