ib econ- 4.2: types of trade protection
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/global-economy/4-2-types-of-trade-protection
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is a tariff?
a specific tax on imported goods and services
draw the diagram for a tariff
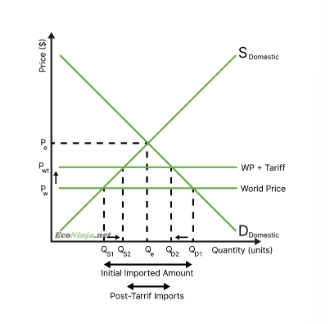
how do tariffs work?
when the world price is much lower than the domestic equilibrium, domestic producers lose out as they have to compete with international firms. to support domestic firms, the government might put a tariff in place - raising the cost of foreign products by taxing them. this makes foreign goods more expensive than before, meaning that more people consume domestic products.
what are the impacts of tariffs on imports, price, quantity supplied by domestic firms, quantity demanded, and on government revenue?
imports decrease
price increases
quantity supplied by domestic firms increases
quantity demanded by consumers decreases
the government earns extra tax revenue
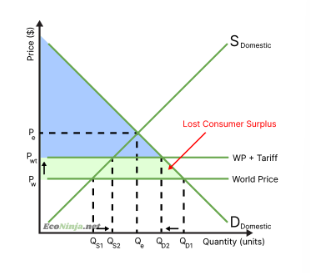
what is the effect of tariffs on consumers?
surplus lost as prices increase
in the long run, foreign companies may choose to stop selling as the price is too high, which decreases competition, decreasing consumer choice
the effects depend on the price elasticity of the product
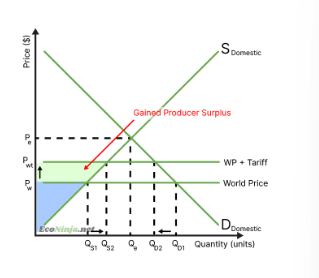
what is the effect of tariffs on producers?
surplus is gained by domestic producers as prices increase
foreign companies lose out as their goods are marked up and look less attractive
in the long run, other governments may retaliate, which negatively affects domestic producers
these effects depend on the price elasticity of the product
what is the effect of tariffs on the market?
the gained surplus for producers is smaller than the lost surplus for consumers
hence, tariffs make markets less efficient, as they reduce the social/community surplus.
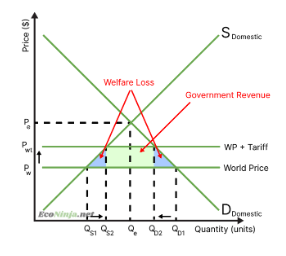
what are the effects of tariffs on the government?
they receive increase tax revenue
they will be protecting domestic producers, strengthening a national industry
however, it will have to spend money administrating and regulating the tariff
other countries might say it is unfair and complain
the world trade organisation may step in and fine the country
what is a quota?
a quantitative limit on imports of a good or service into a country
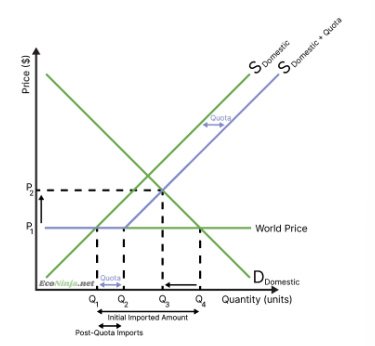
draw the diagram for a quota and explain how they work
before the quota domestic producers were willing and able to supply Q1, but consumers were demanding Q4, so imports were Q1→Q4, and the price was P1
after the quota, imports are restricted to a certain amount (Q1→Q2), and domestic producers have to produce the rest of the demand, so they can ask for equilibrium prices.
this equilibrium meets at (q3, p2)
domestic producers now produce q3, and consumers also demand this
foreign producers are only allowed to export q1→q2
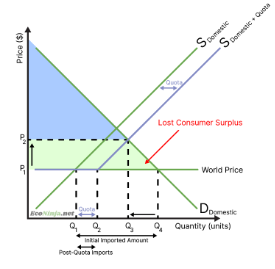
what is the effect of a quota on consumers?
surplus is lost as prices increase
since the amount of imports decrease, there is less choice for consumers
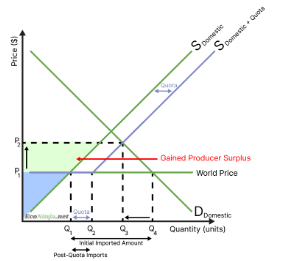
what is the effect of a quota on producers?
surplus is gained for domestic producers as prices and quantity demanded increases
in the long run, other governments may retaliate, negatively affecting domestic producers
foreign producers will be able to sell less products, but at a higher price, hence, the change in revenue will depend on the ped of the product
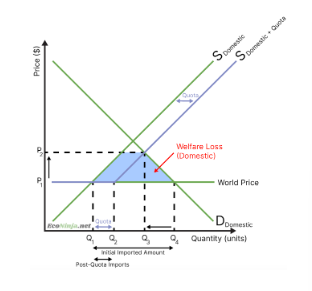
what is the effect of a quota on the market?
gained producer surplus is smaller than lost consumer surplus
hence, quotas make markets less efficient, as they reduce the social surplus
what is the effect of a quota on the government?
no visible effect in revenue
in many cases, govs. sell import licences in markets with quotas, earning itself some revenue
the gov. also has to spend extra money as it has to administrate this quota (prevent smuggling etc.)
what is a subsidy?
a form of financial assistance to producers by lowering their costs of production and encouraging higher output
what are the two types of subsidy and what is the difference between them?
production subsidies: general subsidies meant to lower the cost of production of goods for domestic producers (reducing imports)
export subsidies: targeted subsidies meant to protect certain exporting domestic producers
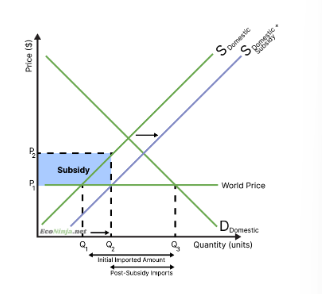
draw the diagram for a production subsidy
Before subsidy:
Domestic producers produce at Q1, because price is at P1
Consumers consume at Q3, because price is at P1
Hence, the rest is imported (Q1 <-> Q3)
After subsidy:
Domestic producers get a subsidy of P1 <-> P2, so they produce as if the price is P2, so at Q2
Domestic consumers still get the price of P1, so they still consume at Q3
Hence, the new imported amount is Q2 <-> Q3
what is the effect of a subsidy on consumers?
no change for consumers, other than the fact that they now buy more domestic product. if domestically produced goods are worse quality then consumers will be worse off, but international trade diagrams assume homogeneous products
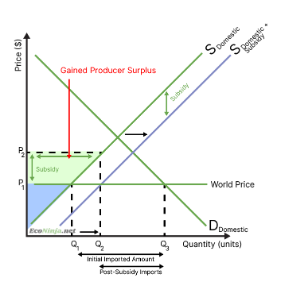
what is the effect of a subsidy on producers?
domestic producer surplus increases
foreign producers lose out as they now export less
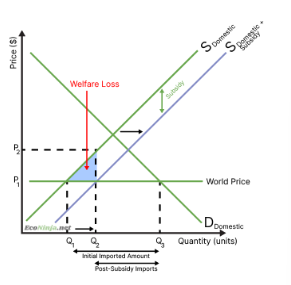
what is the effect of a subsidy on the market, and on the government?
because producer gain is larger than consumer loss, the market experiences a positive surplus change
however, the government has to dish out a subsidy, which is taxpayer money it could have spent on other things (opportunity cost)
a welfare loss is still created, as some of the subsidy does not translate to surplus for producers. this is because, due to the subsidy, producers are not incentivised to produce as efficiently as before
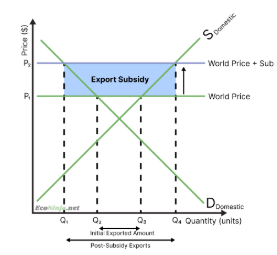
draw the diagram for an export subsidy and explain how it works
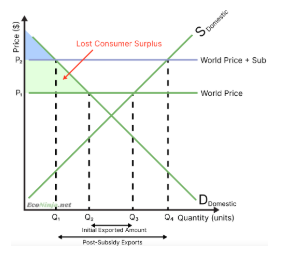
Before export subsidy:
Domestic producers produce at Q3, because price is at P1
Consumers consume at Q2, because price is at P1
Hence, the rest is exported (Q2 <-> Q3)
After export subsidy:
Domestic producers get a subsidy of P1 <-> P2, so they produce as if the price is P2, so at Q4
Since producers get a higher price exporting, they are only willing to sell domestically if they get the same price P2
This means domestic consumers now have to pay P2 instead of P1, reducing their demand from Q2 to Q1
Hence, the new exported amount is Q1 <-> Q4
what is the effect of export subsidies on consumers?
because firms can now earn more money by exporting, they are only willing to sell domestically if they can sell at the same price as abroad, meaning that consumers have to pay more money and decreasing their surplus
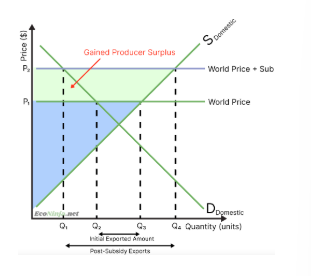
what is the effect of export subsidies on producers?
firms get to sell more of their products while also earning more per product, in the form of payments from the government
this means domestic producers significantly increase their surplus
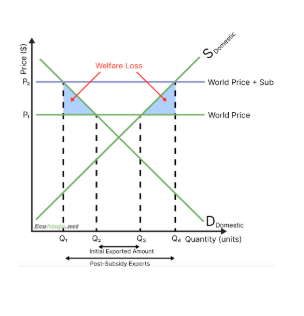
what is the effect of export subsidies on markets and governments?
because the producer gain is larger than the consumer loss, the market experiences a positive surplus change
however, the government has to dish out a subsidy, which is taxpayer money they could’ve spent on other things (opportunity cost)
a welfare loss is still created, as some of the subsidy does not translate to surplus for producers, as producers are not incentivised to produce as efficiently as before
what are administrative barriers?
rules, regulations and standards applied to imports of goods and services from foreign firms in an effort to reduce the imports
what are the impacts of administrative barriers on domestic producers, consumers, foreign firms and market efficiency?
favours domestic producers as it complicates and raises costs of imports
negatively affects consumers as they will have less choice and experience higher prices
may upset other countries who retaliate with their own barriers
hampers market efficiency, but protects domestic industry
what are some examples of administrative barriers?
stricter or more frequent inspection of an imported good or service, making the process more tedious
implementing a complex application process for foreign firms who want to start selling abroad, disincentivising them from doing so
an outright ban on imports of a certain good or service