W3 Cornea II
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What does a reduction in pH lead to?
Hypoxia and hypercapnia
What is hypoxia?
Oxygen deprivation, leading to increased anaerobic respiration and more lactic acid produced
What is hypercapnia?
Slow down of carbon dioxide efflux, abusing carbon dioxide combining with water to form carbonic acid
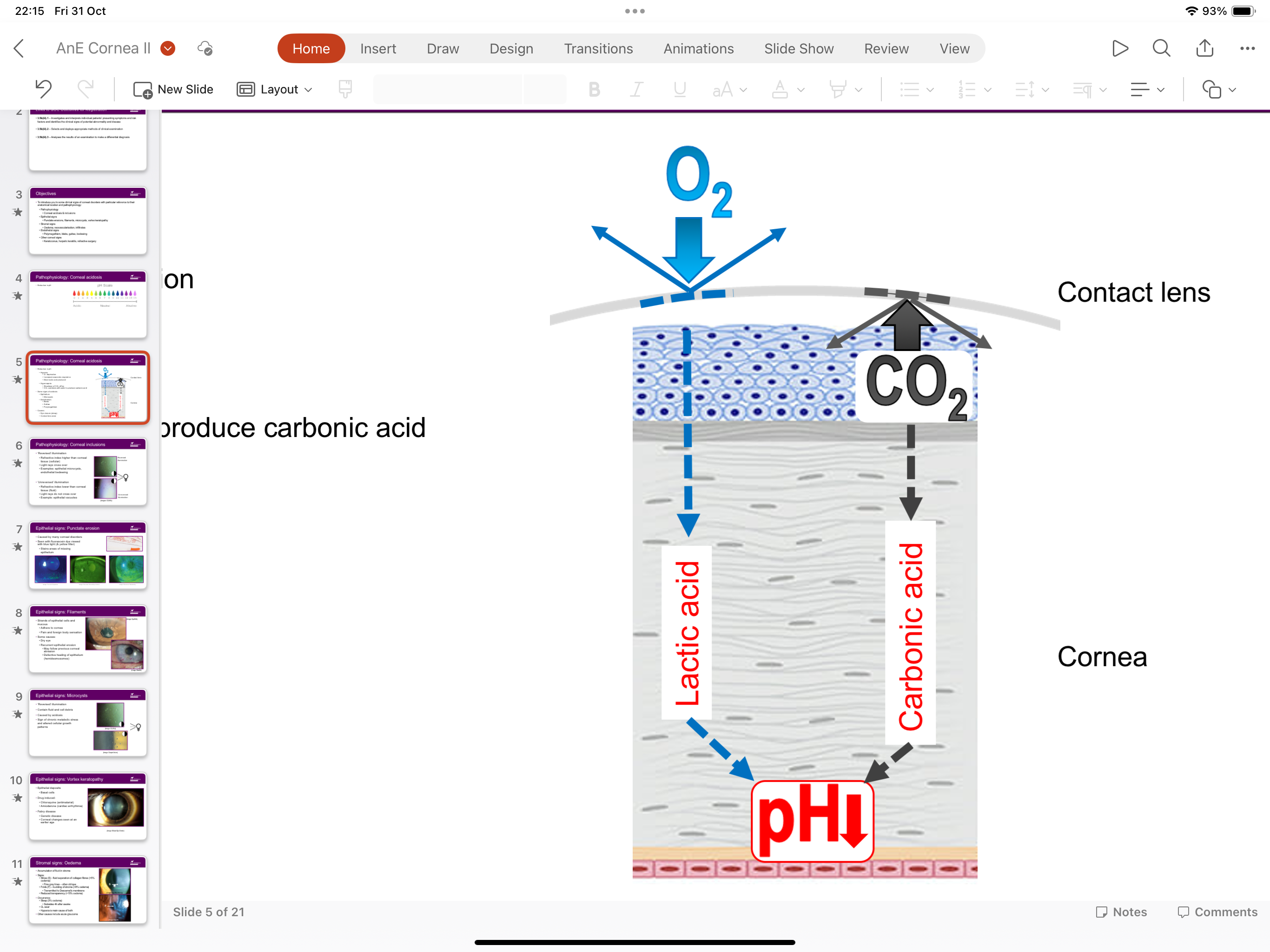
What are signs of corneal acidosis?
In the epithelium- micro cysts
In the endothelium- blebs, guttae and polymegathism
What are causes of acidosis?
Wearing contact lenses, partial eye closure during sleep
What causes reversed illumination?
Refractive index being higher than corneal tissue, causing light rays to cross over in cases like epithelial microcysts or endothelial bedewing
What causes unreversed illumination?
Refractive index lower than corneal tissue so light rays do not cross over in cases like epithelial vacuoles
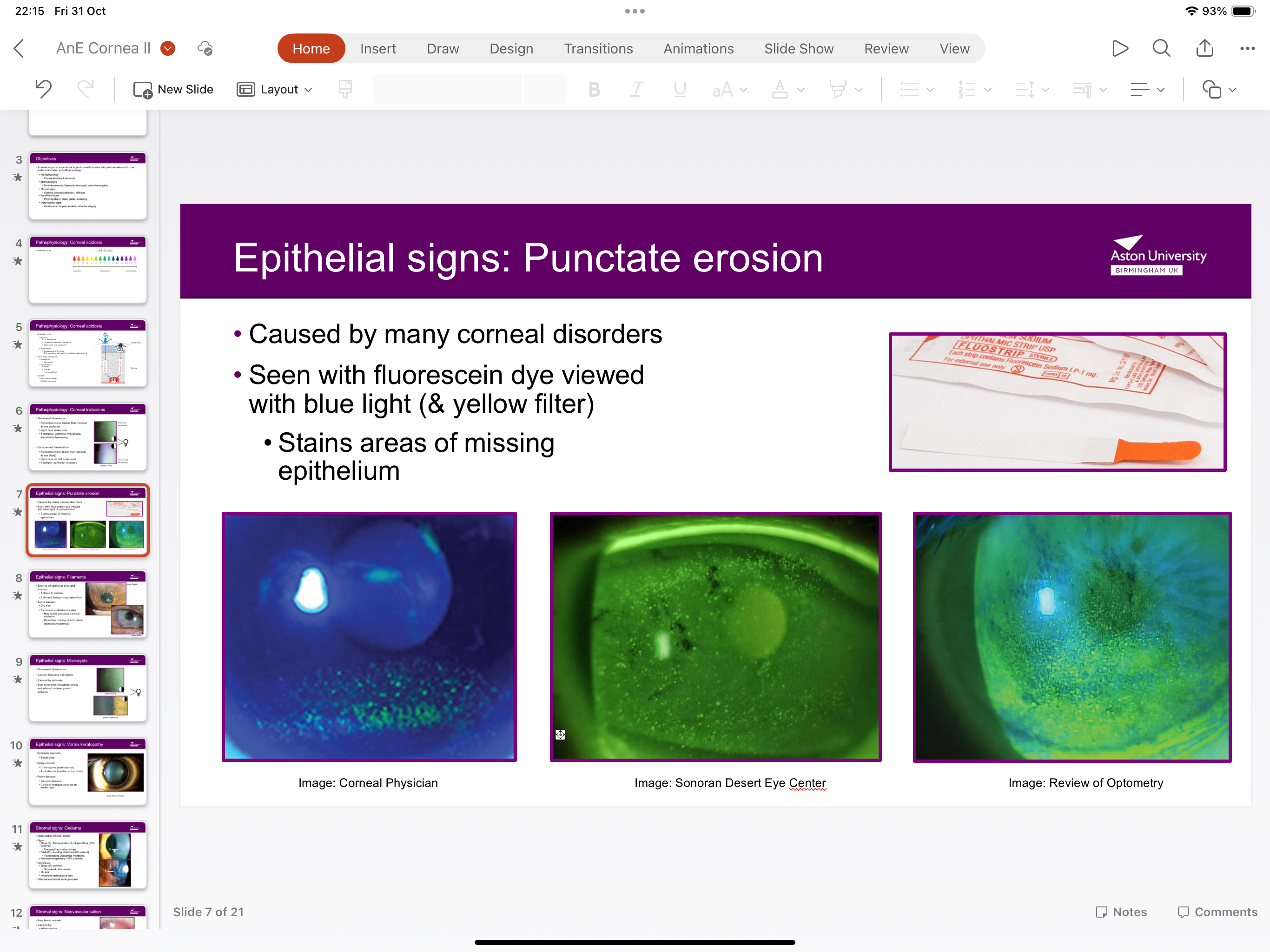
What is punctuate erosion?
Caused by corneal disorders and is seen with flueorescin dye viewed with blue light and yellow filter and it stains areas of missing epithelium
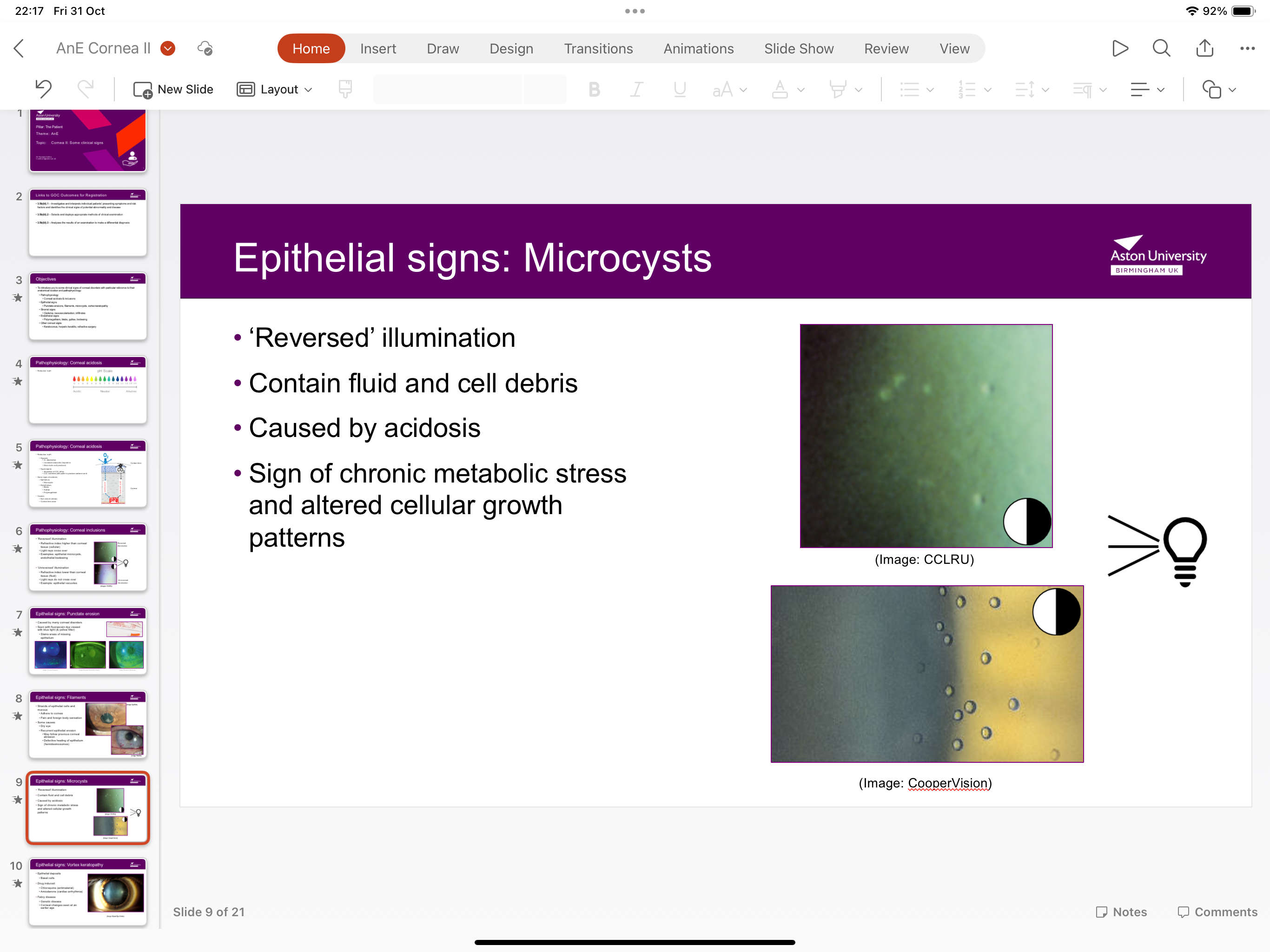
What are microcysts?
Contains fluid and cell debris and is caused by acidosis and is a sign of chronic metabolic stress and altered cellular growth patterns
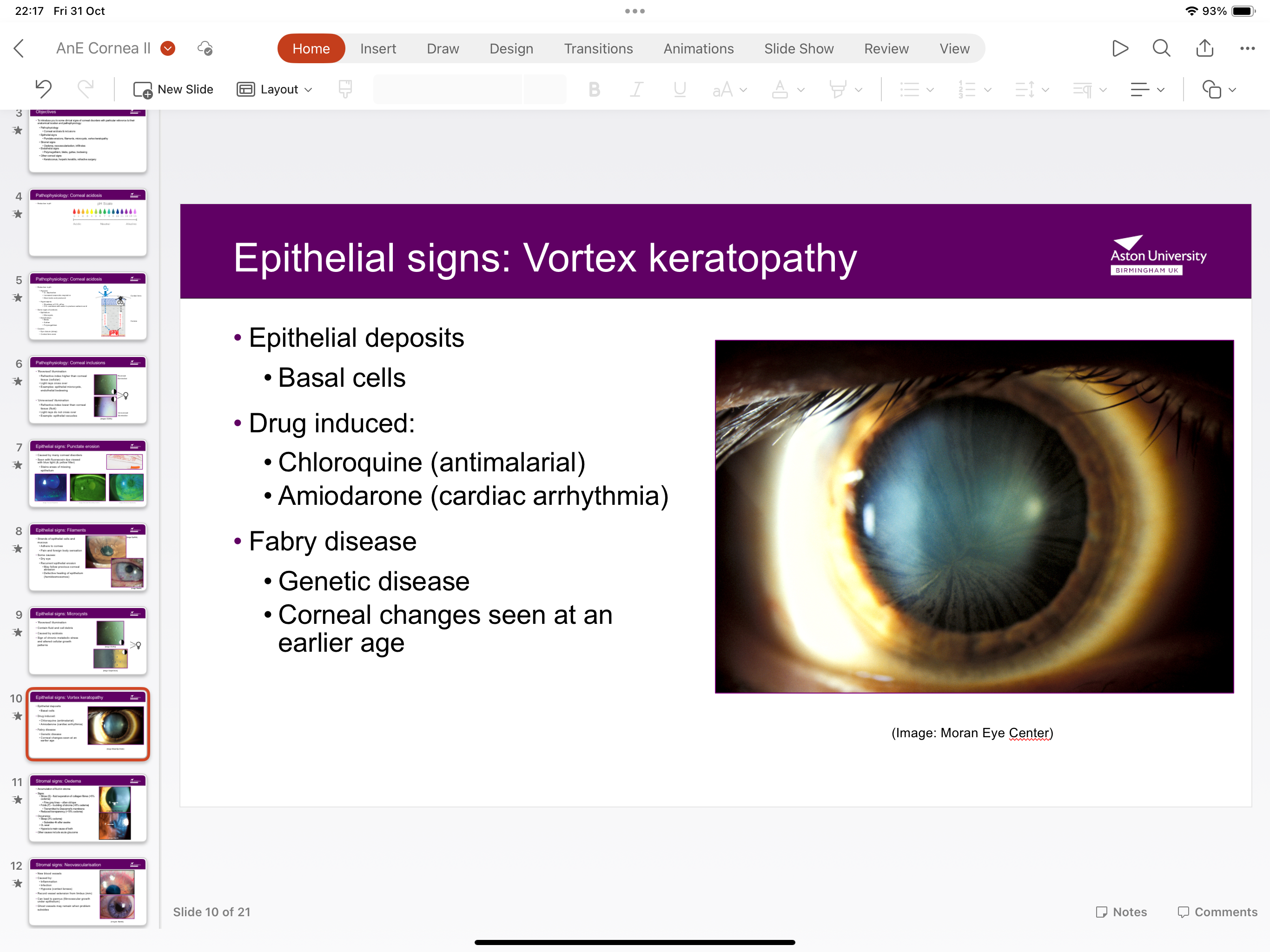
What is vortex keratopathy?
Epithelial deposits in basal cells which can be caused by drugs
What is oedema?
Accumulation of fluid in the stroma
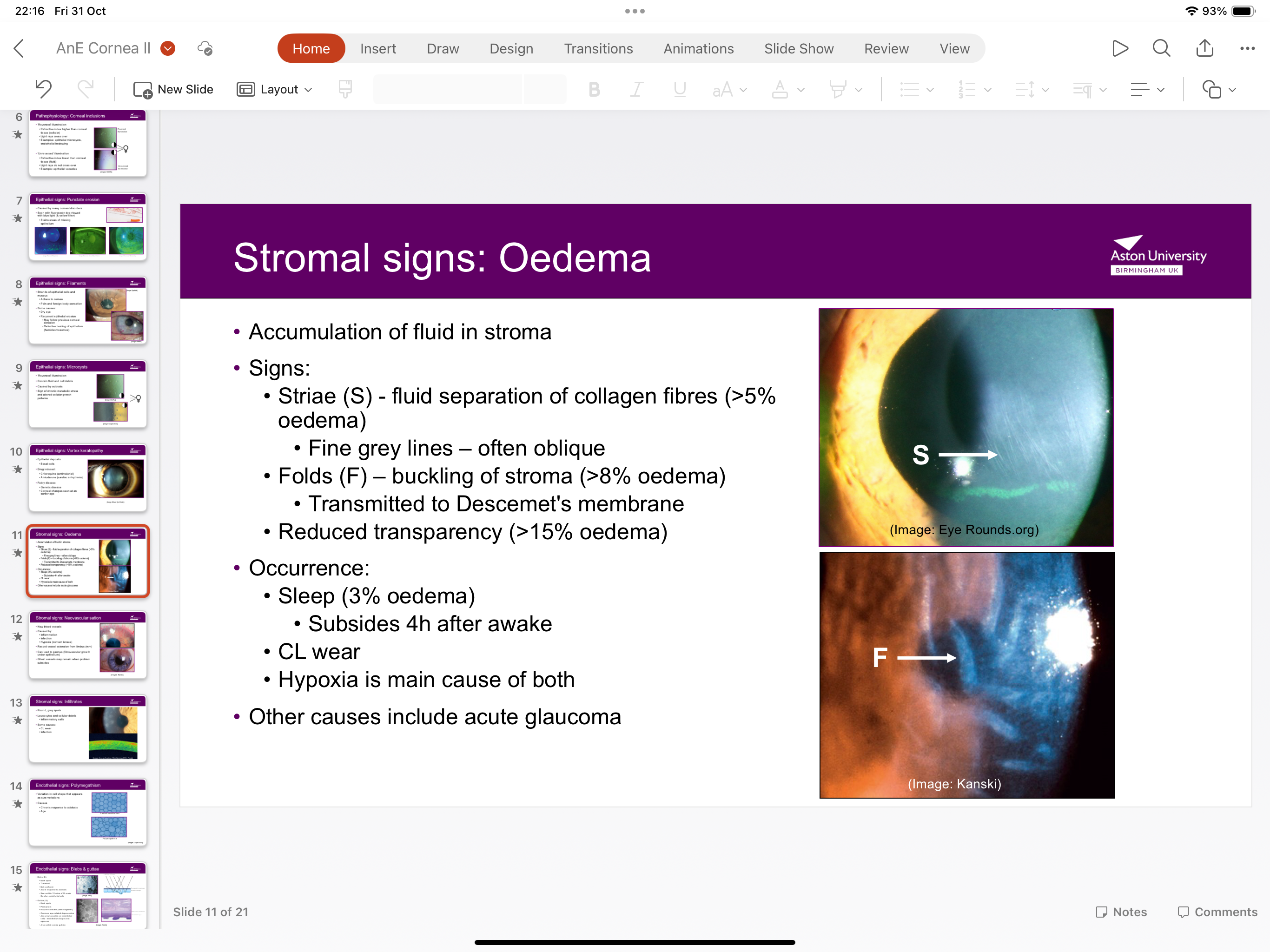
What are signs of oedema?
Fluid separation of collagen fibres >5%
Buckling of stroma/folds >8%
Reduced transparency from spread to descements membrane >15%
What are causes of oedema?
Sleep (subsides after a few hours), wearing contact lenses, acute glaucoma
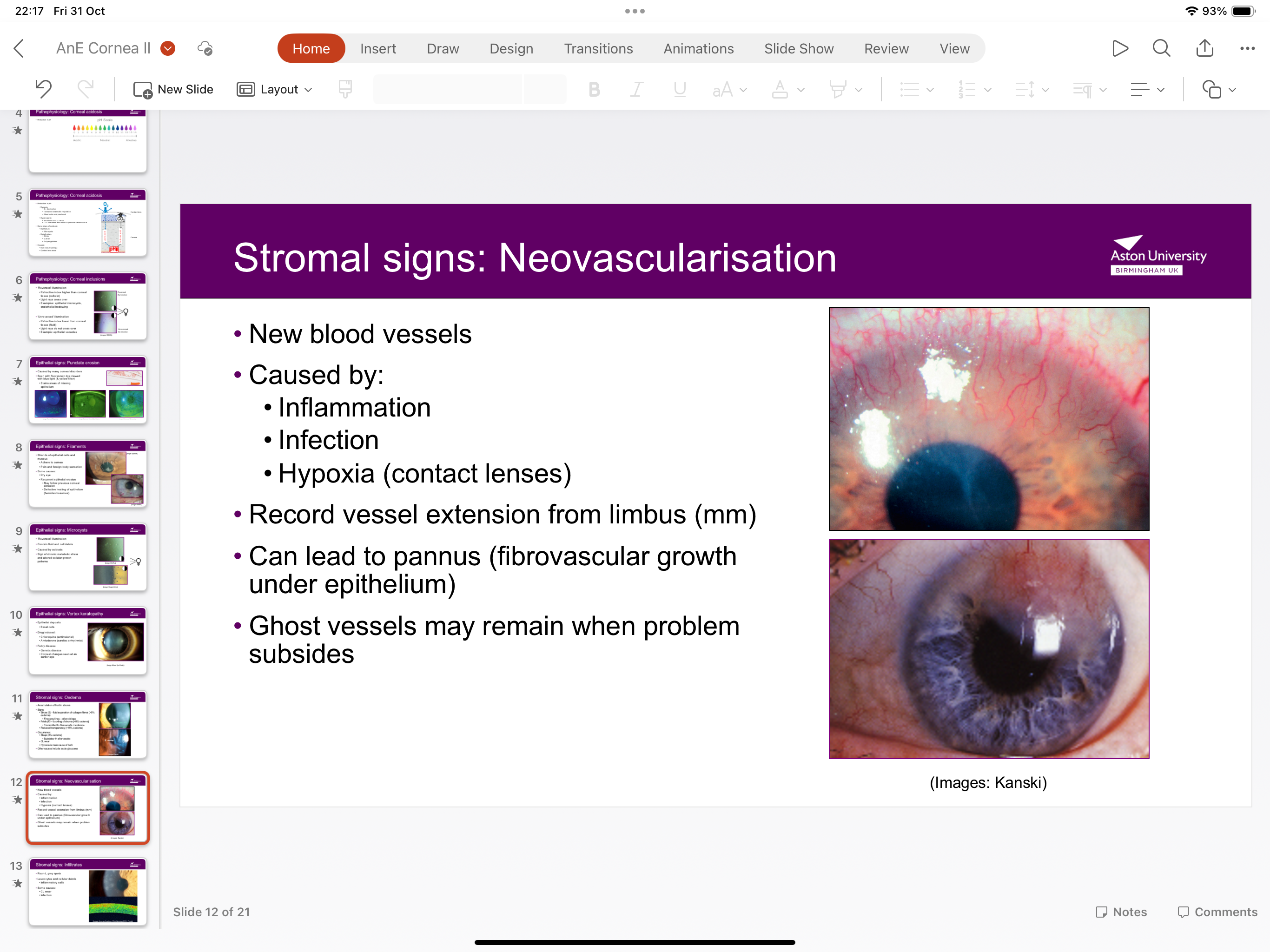
What is neovascularisation?
New blood vessels caused by hypoxia from CL, inflammation, infection
Vessels extend from limbus nd can lead to pannus fibrovascular growth under endothelium)
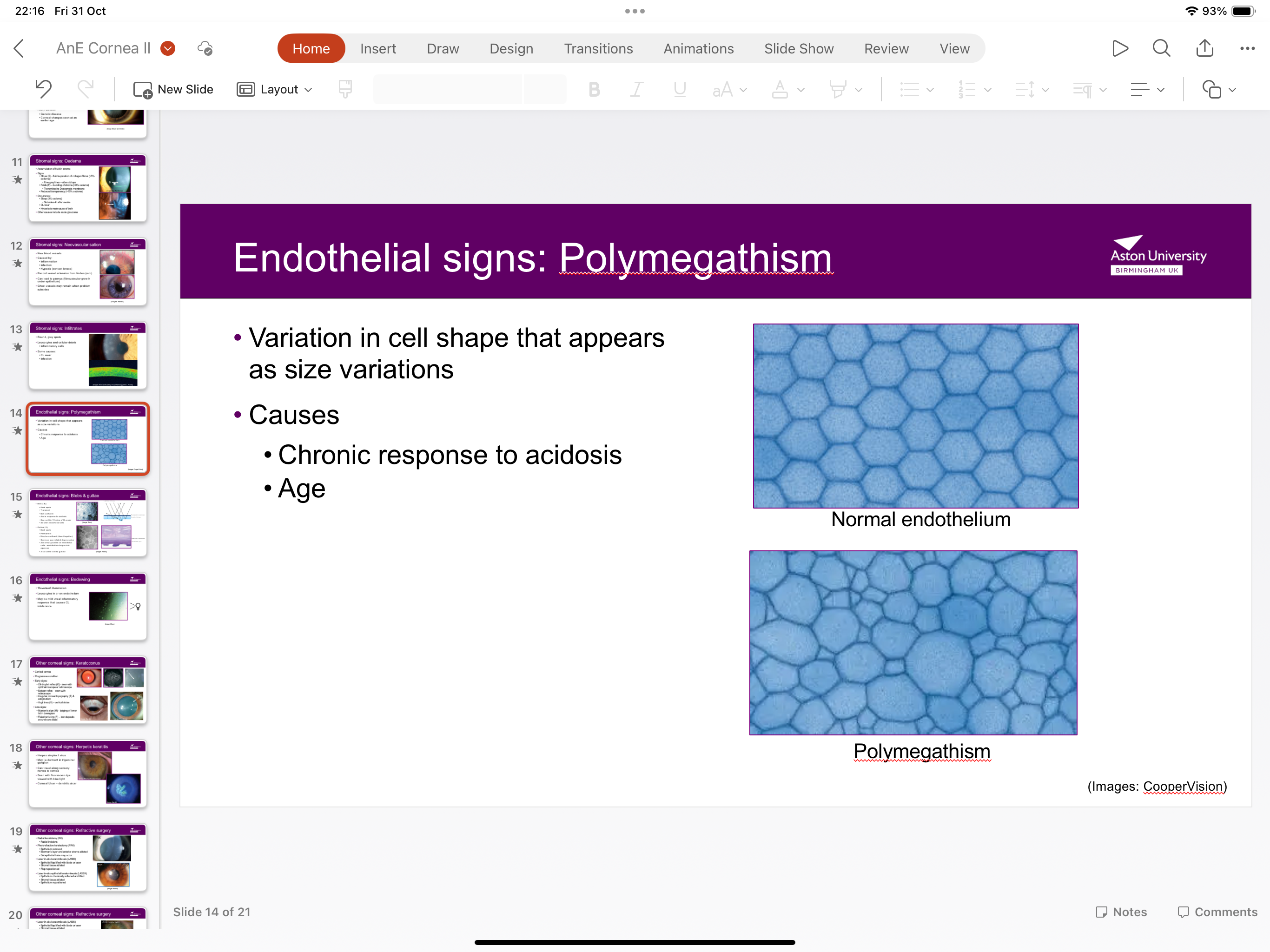
What is polymegathism?
Variation in cell shape caused by chronic response to acidosis or age
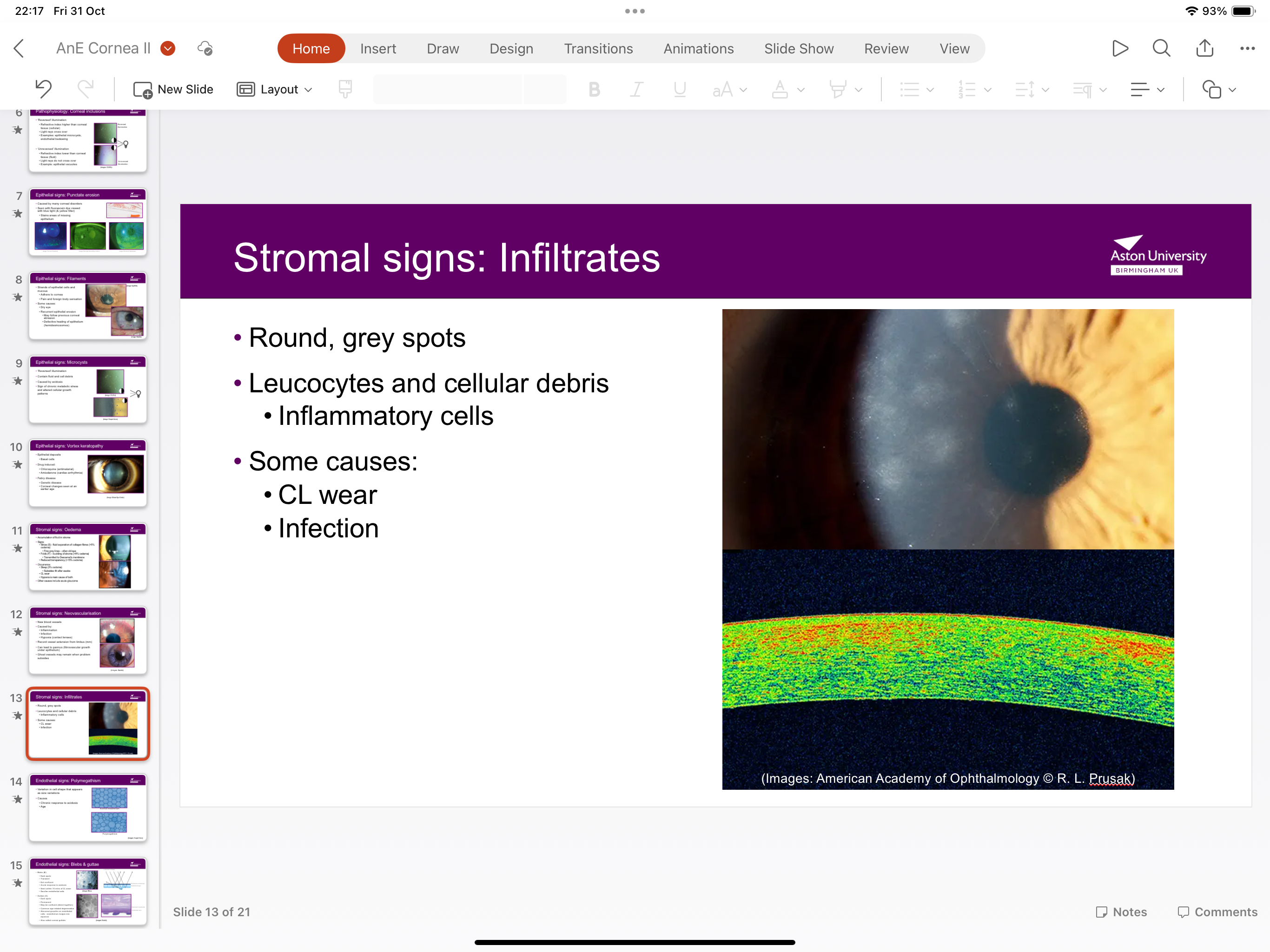
What are infiltrates?
Round grey spots caused by leukocytes and cellular debris- caused by contact lenses wear and infection
What are blebs?
Dark spots which are an acutely response to acidosis used by swollen endothelial cells and can be seen 10 mins after contact lens wear
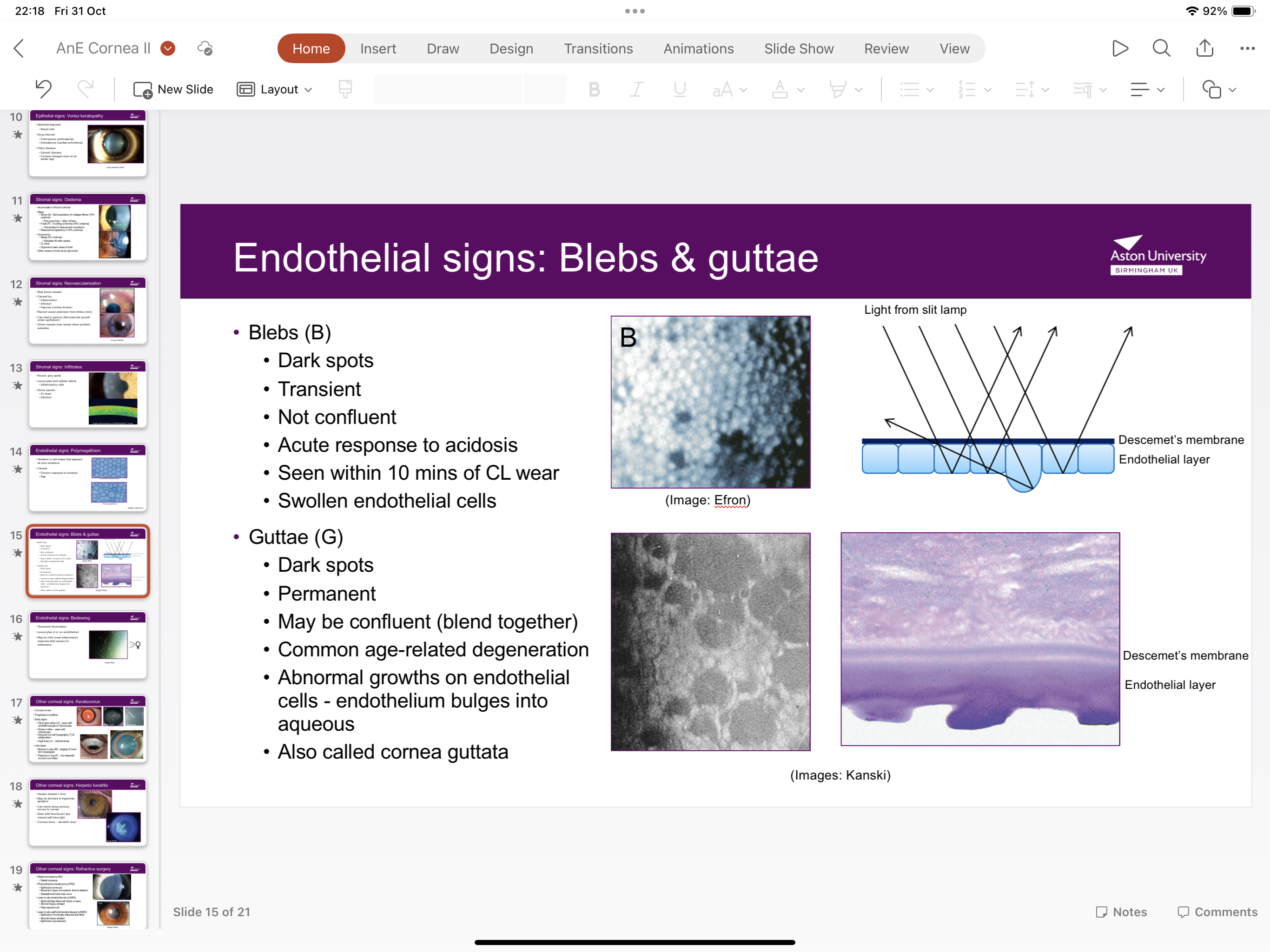
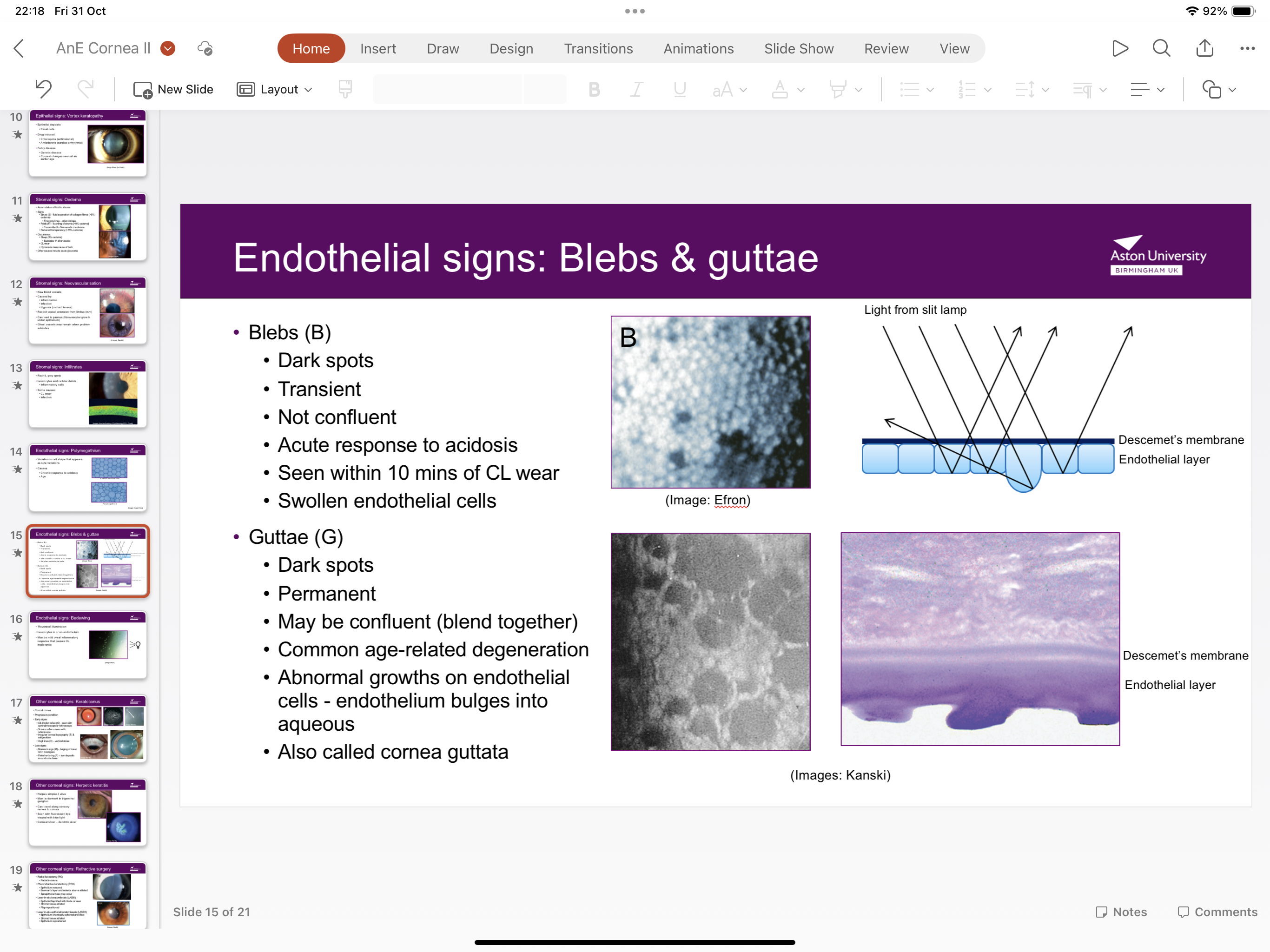
What is guttae?
Permanent dark spots which may be confluent (blend together) caused by abnormal growths on endothelial cells endothelium bulges into aqueous- age related
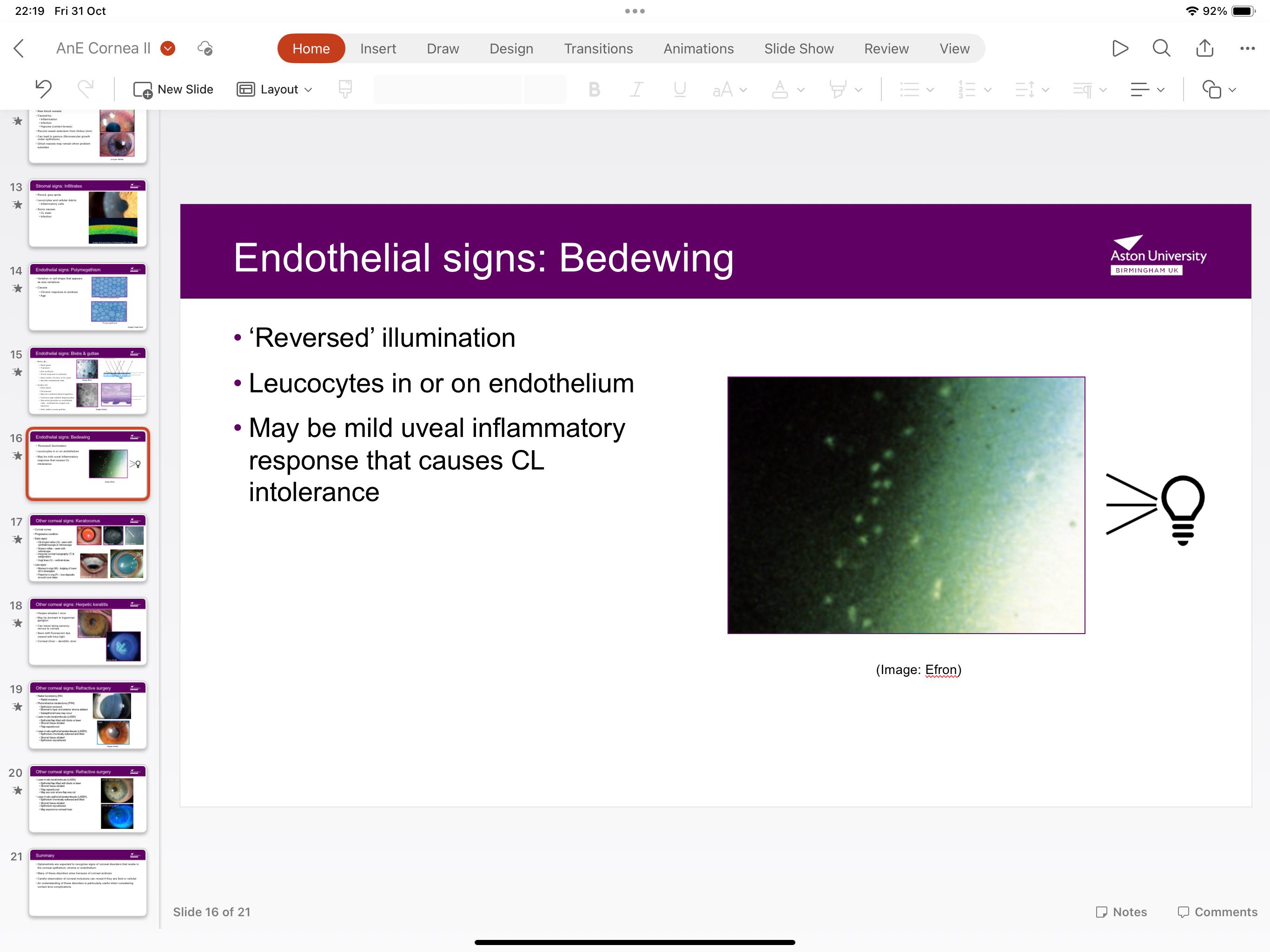
What is bedewing?
Leucocytes in or on endothelium due to mild uveal inflammatory response causing contact lens intolerance
What are epithelial signs of disease?
Punctuate erosion, microcysts, filaments, vortex keratopathy
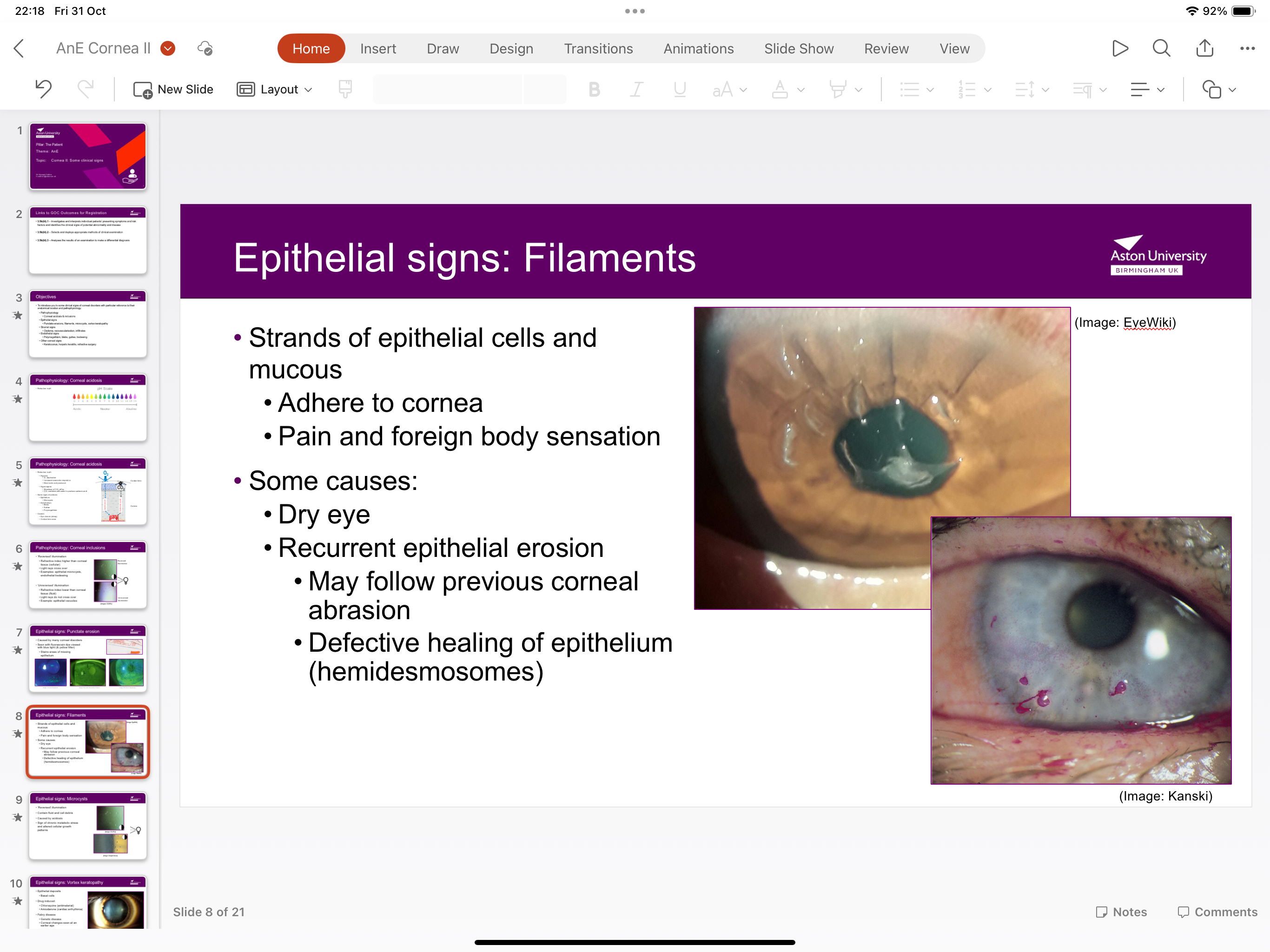
What are filaments?
Strands of epithelial cells and mucus high adhere to cornea causing pain caused by dry eye, recurrent epithelial erosion
What are stromal signs of disease?
Oedema, neovascularisation, infiltrates
What are endothelial signs of disease?
Polymegathism, blebs, guttae and bedewing
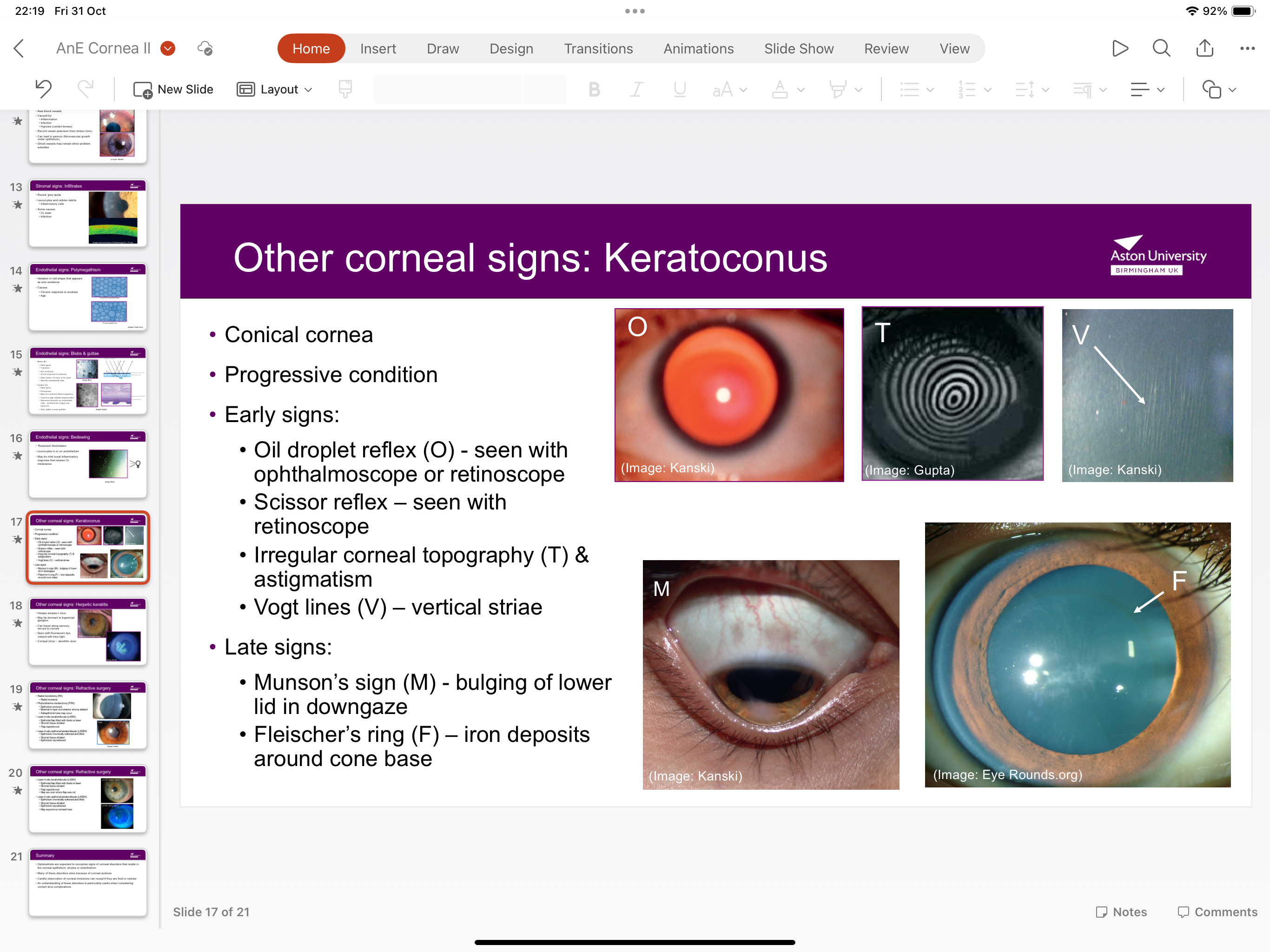
What is keratoconus?
Conical cornea- early signs include irregular astigmatism, scissor reflex and Vogt lines
Late signs involve bulging of lower lid iron deposits around cone base
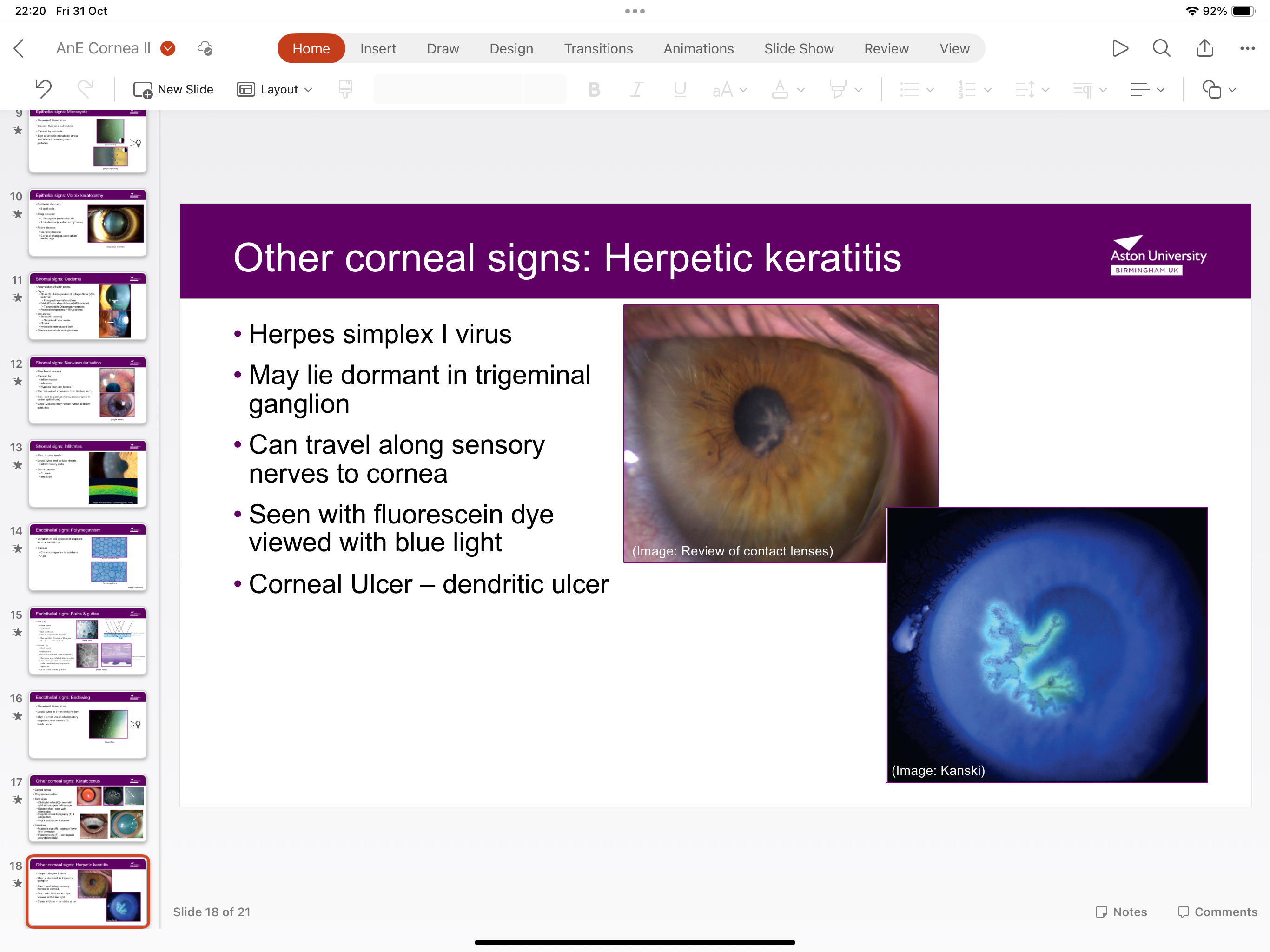
What is herpetic keratitis?
Herpes simplex I virus, seen with fleurescin dye under blue light can travel along sensor nerve to cornea and lies dormant in trigeminal ganglion
What are examples of refractive surgery?
RK, PRK, LASIK and LASEK
What is RK
Radical incisions
What is PRK?
Epithelium removed, bowman’s layer and anterior stroma ablated (removed surgically)
What is LASIK?
Epithelial flap lifted with laser, stromal tissue ablated and flap repositioned
What is LASEK?
Epithelium chemically lifted and softened, stromal tissue ablated and epithelium repositioned
What are drawbacks to LASIK and LASEK?
LASIK- may see scar where flap was cut
LASEK- may experience corneal haze