Chapter 15: special senses vision
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
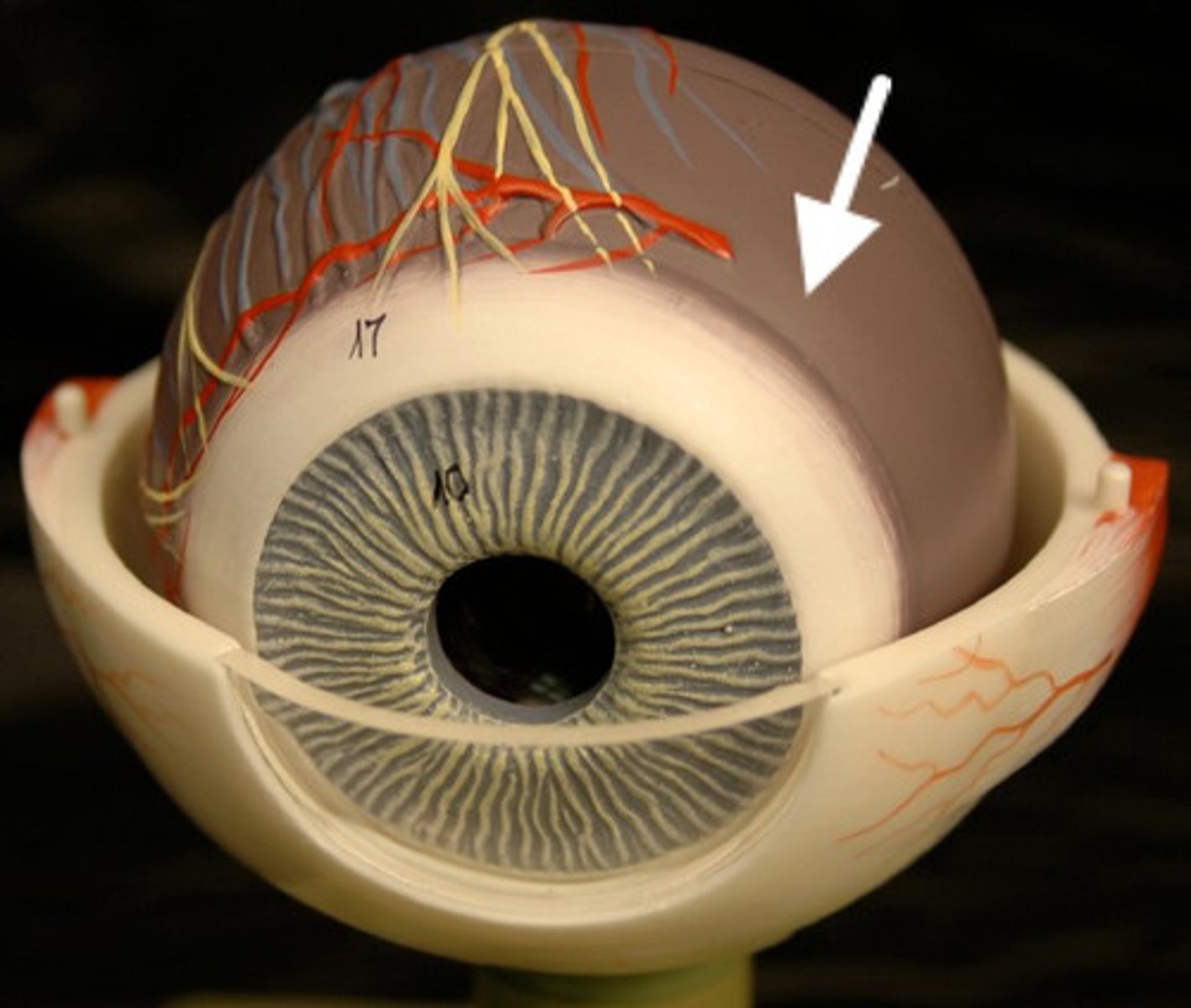
sclera
- white of eye
- F: muscle attachment, maintains shape of eyeball
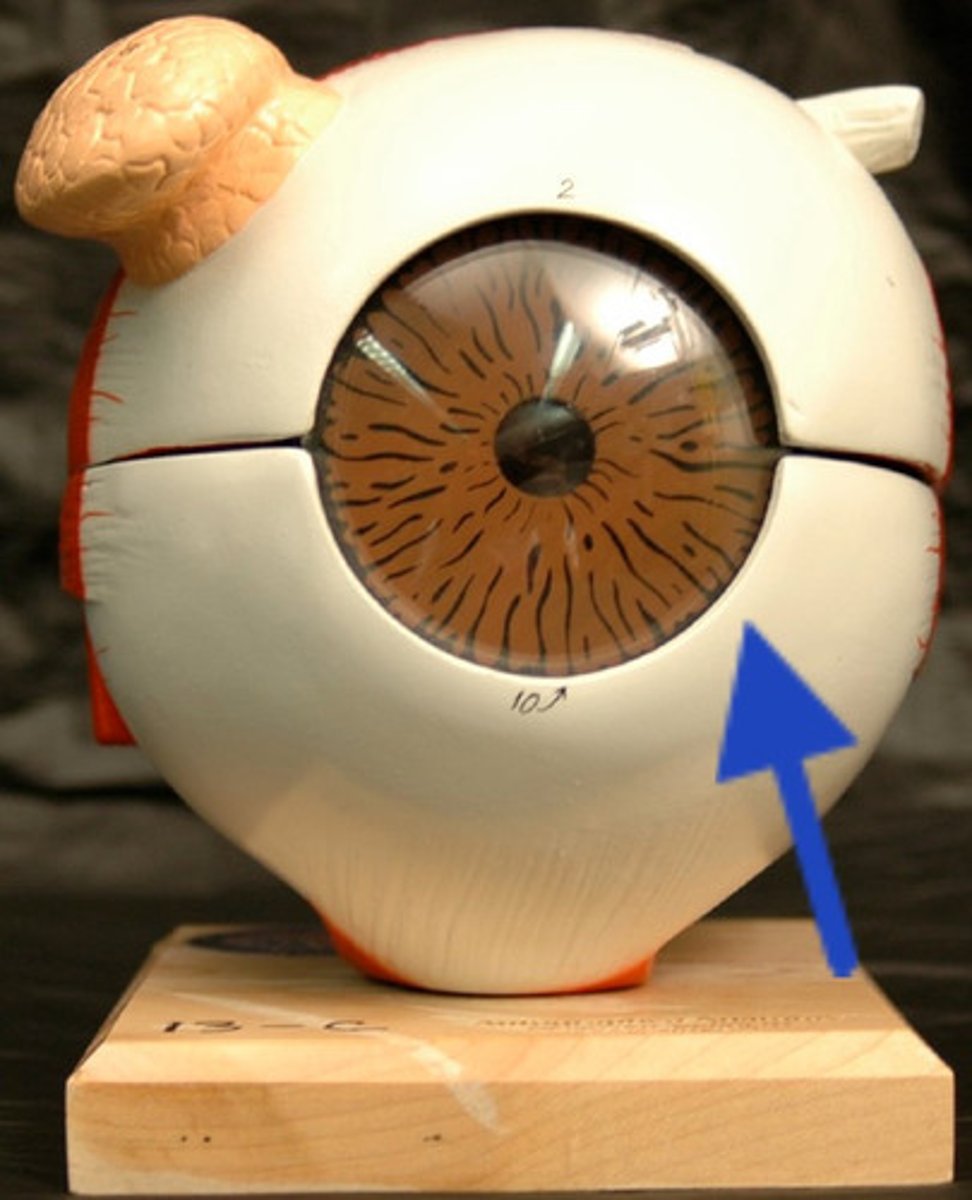
cornea
- transparent layer, bulges avascular
-F: refracts light
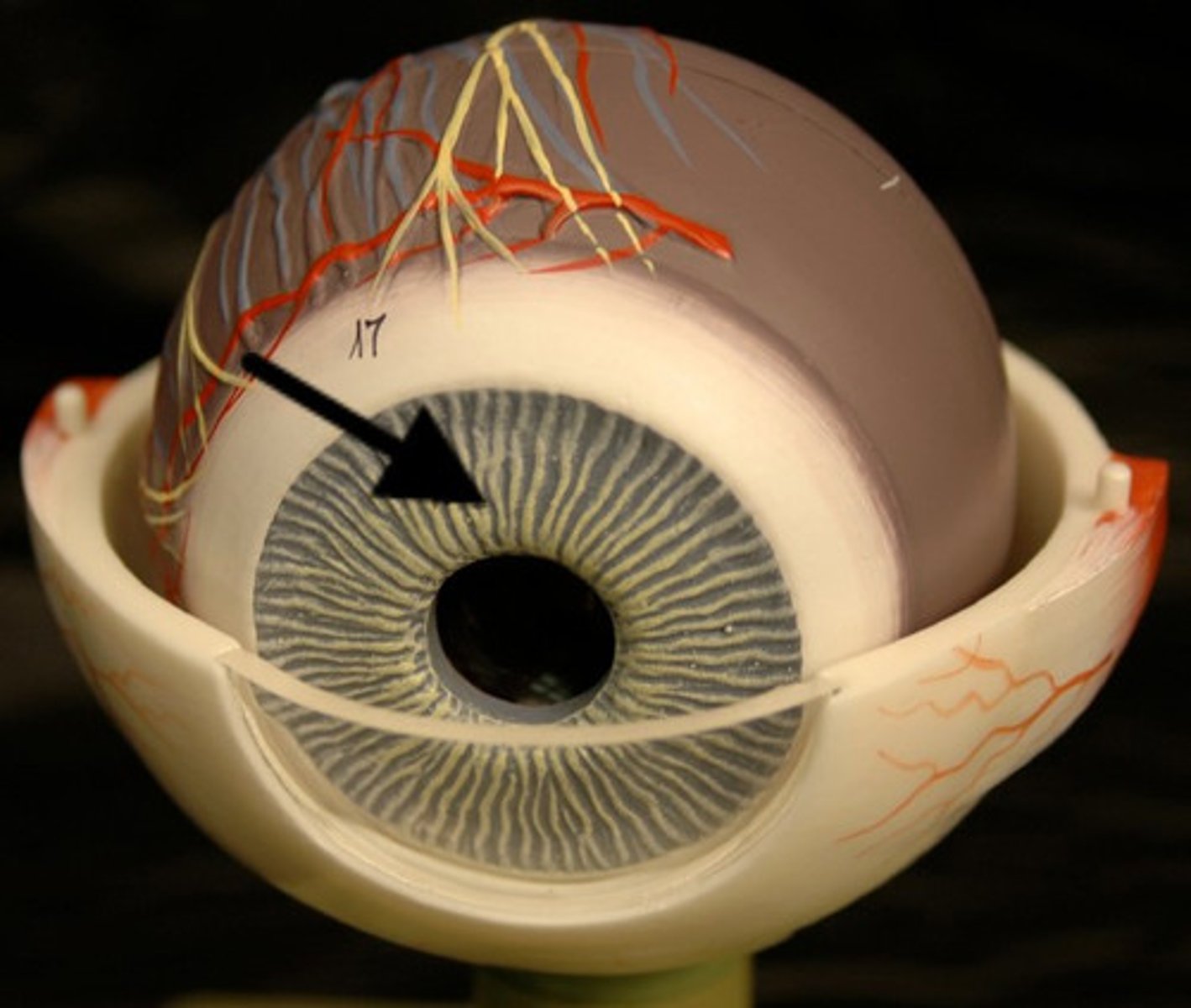
Iris
- pigmented
-F: contains muscle that control amount of light enter eye by changing pupil diameter
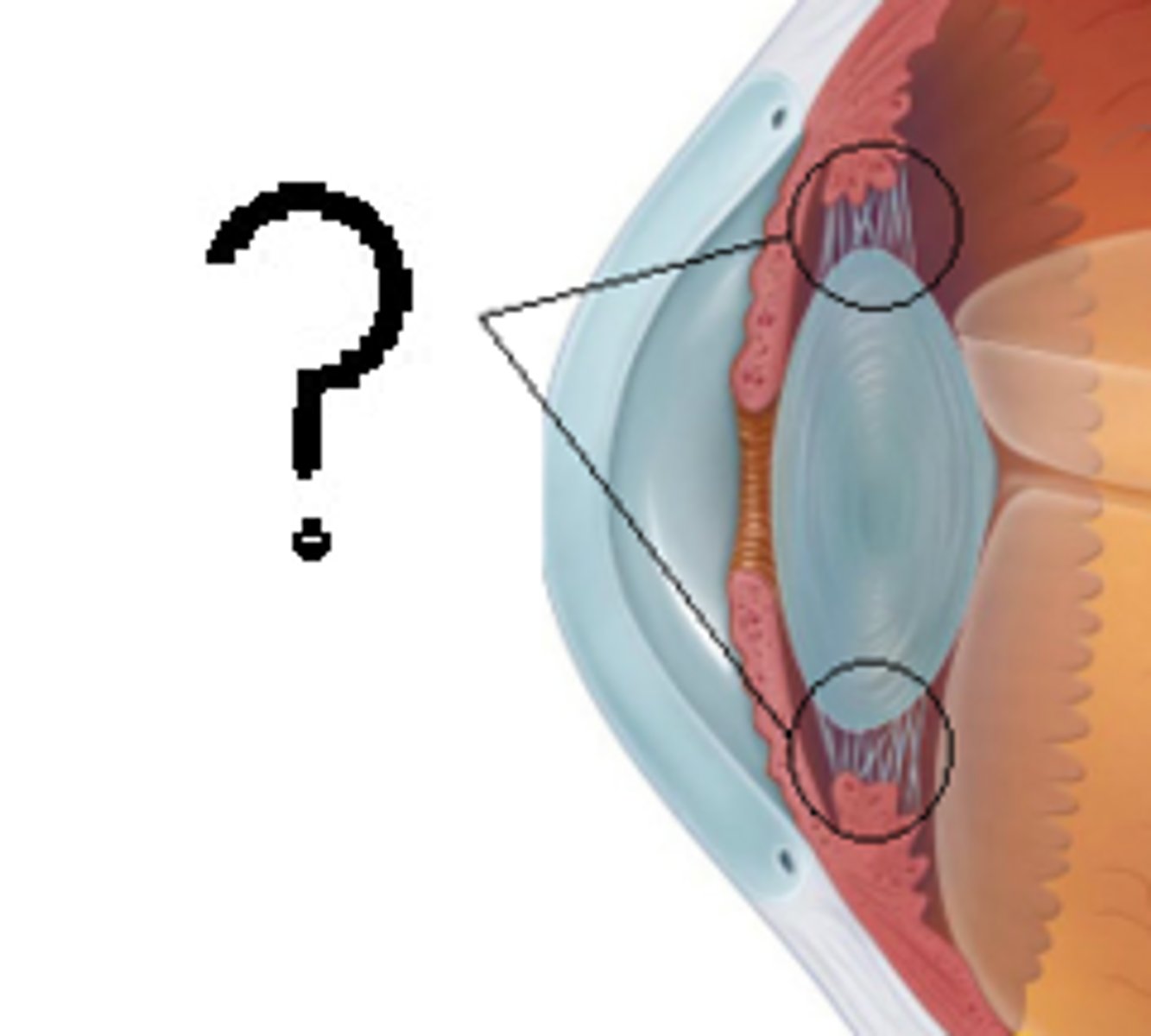
Ciliary body
- contains ciliary muscle and process
-F: change shape of lens
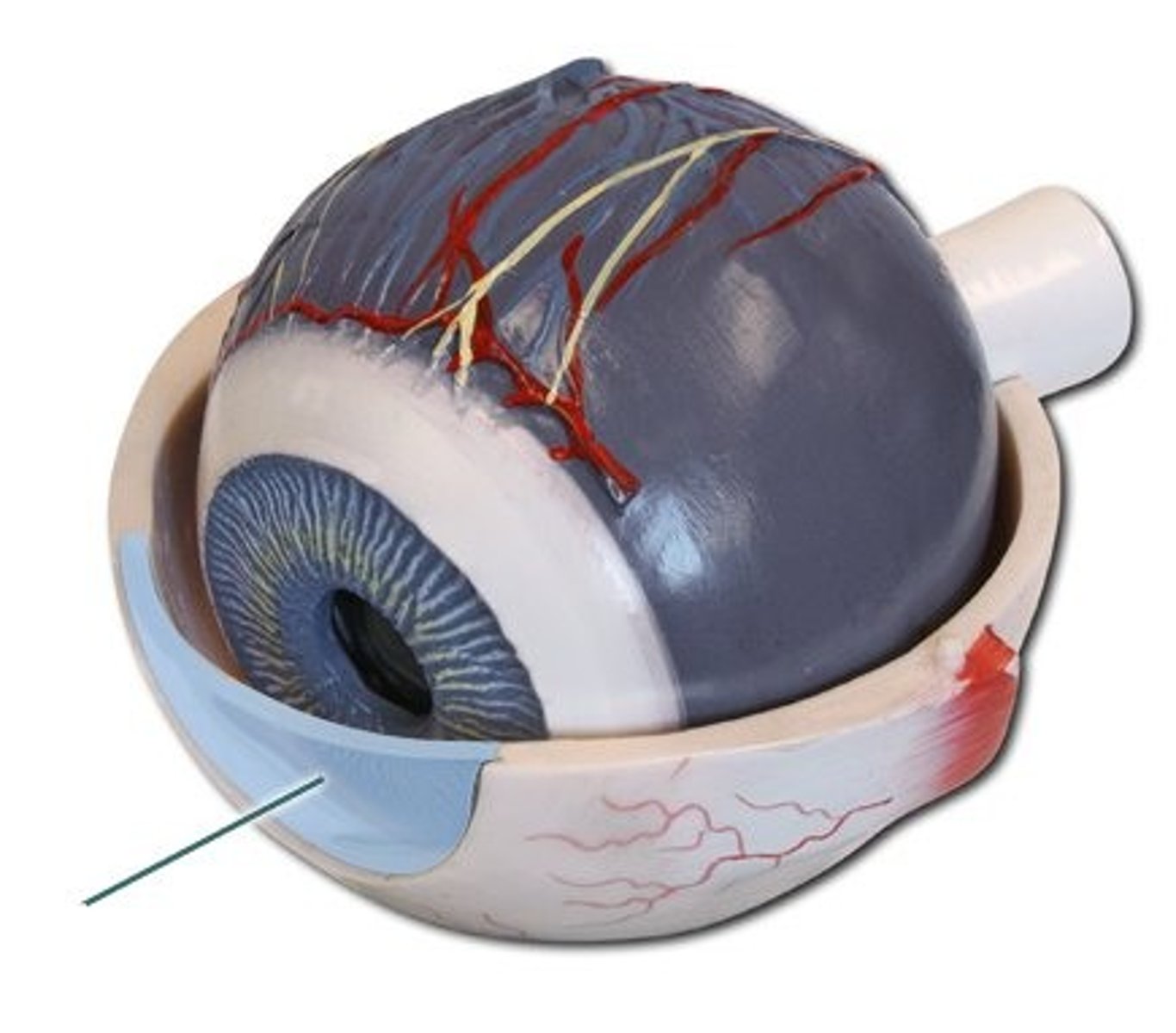
Choroid
- dark membrane with blood vessels
- F: nourishes eye, absorbs excess light
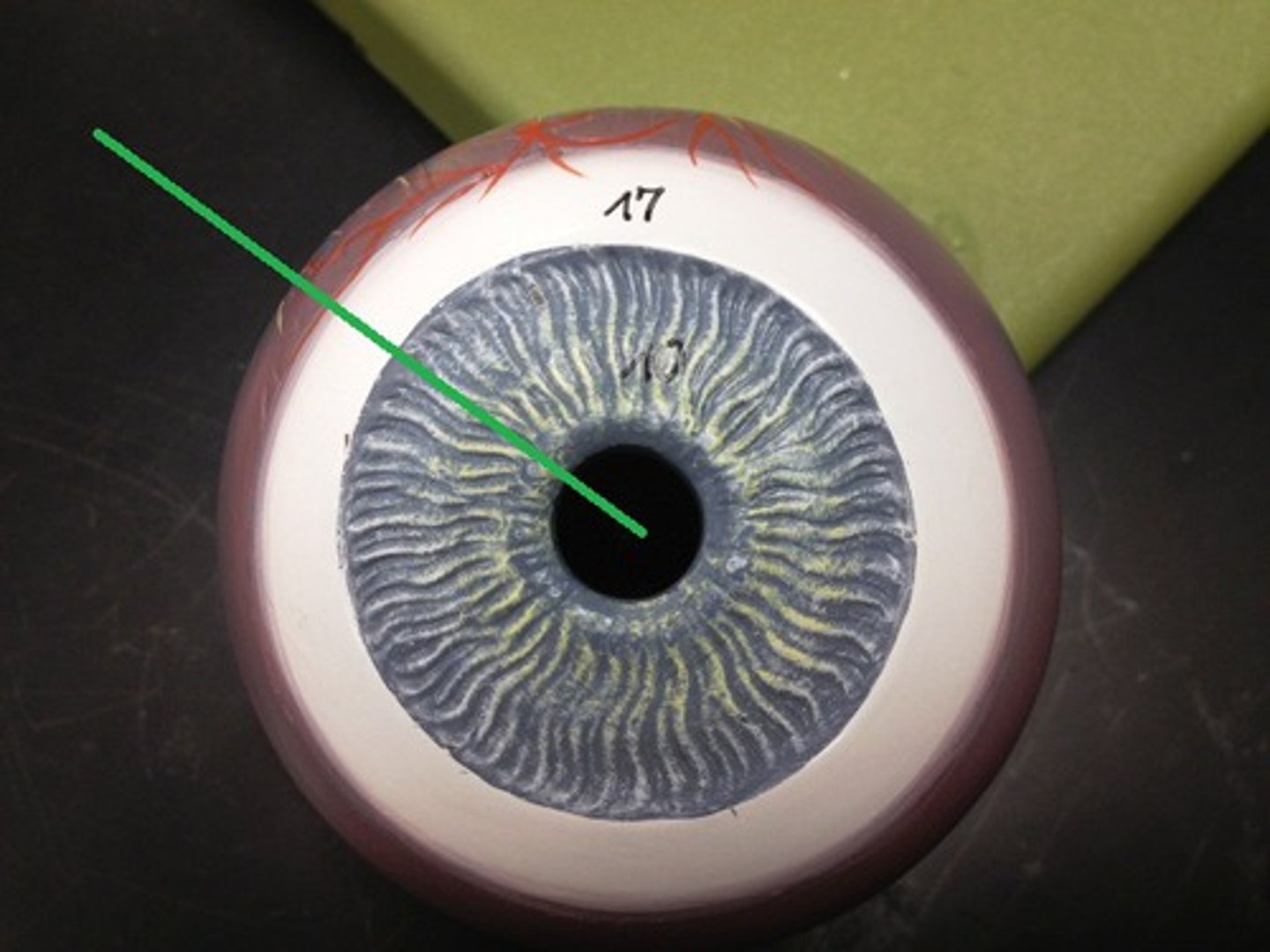
pupil
- opening of iris
- F: allows light to enter eye
superficial layer of retina
- pigmented
-F: absorbs light (reduces scattering)
deep layer of retina
- contains photoreceptors
-F: detects light
lens
-F: refracts light rays to focus them onto retina
vitreous body( Humor)
- gelatinous material fills posterior cavity
- F: maintains shape of eye, does some refracting of light
pupillary constriction
- less light in
- pupillary sphincter muscle contracts
- occurs in parasympathetic system
pupillary dilation
- more light in
- pupillary dilator muscle contracts
- occurs in sympathetic system
rods
F: respond to low light, night vision, peripheral vision
cones
f: function best in bright light, perceive color
macula lutea
area if high photoreceptor density
fovea centrails
- center of macula lutea, has many cones
- F: produces highest visual acuity
optic disc
region with no photoreceptors because the optic nerve exits the eye here
blind spot
no image seen when light enters your eye and lands on optic disc
phototrandsduction
changing light into electrical signal (AP)
photopigment
- chemical that absorbs light
rods- one type
cones- 3 type: blue, green, red
what is the structure of the retinal layers
1. rods/cones
2. bipolar cells- synapse with rods/cones and ganglion cells
3. retinal ganglion cells- axons gather to for optic nerve
Step 1: sensation of light
1: light breaks down photopigment in rods/cones
Step 2: sensation of light
2. alters membrane potential ( rod or cone) and NT released/decreased
step 3: sensation of light
3. alters membrane potential of bipolar cell and NT released/decreased
step 4: sensation of light
4. bipolar cell influence ganglion cell, may generate AP
step 5: sensation of light
5. ganglion cell Ap tranmits to brain via optic nerve ( axons of ganglions)
step 6: sensation of light
AP to brain and cortex
refraction
bending of light rays
focal point
point where rays converge
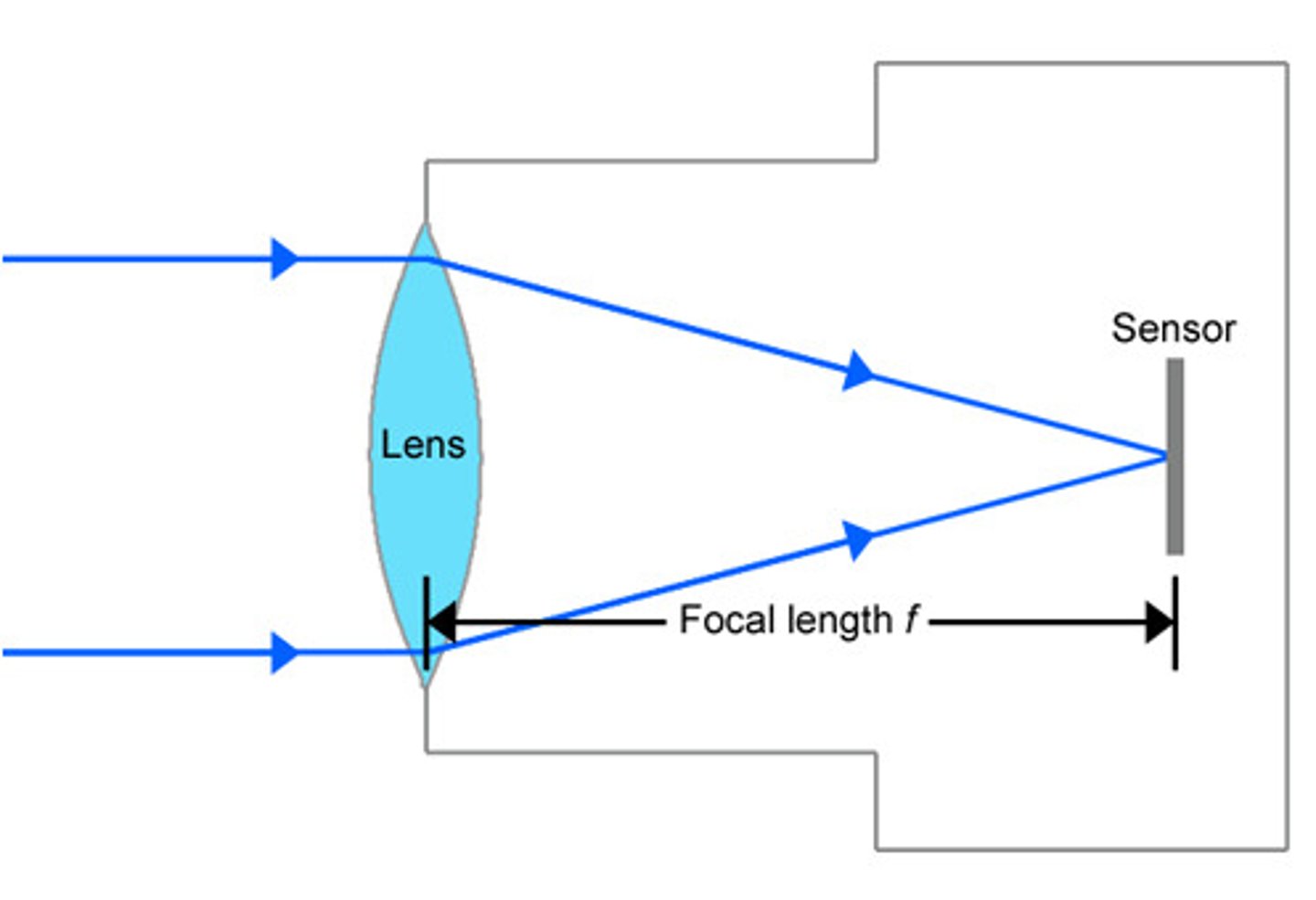
focal length
distance from lens or surface to focal point
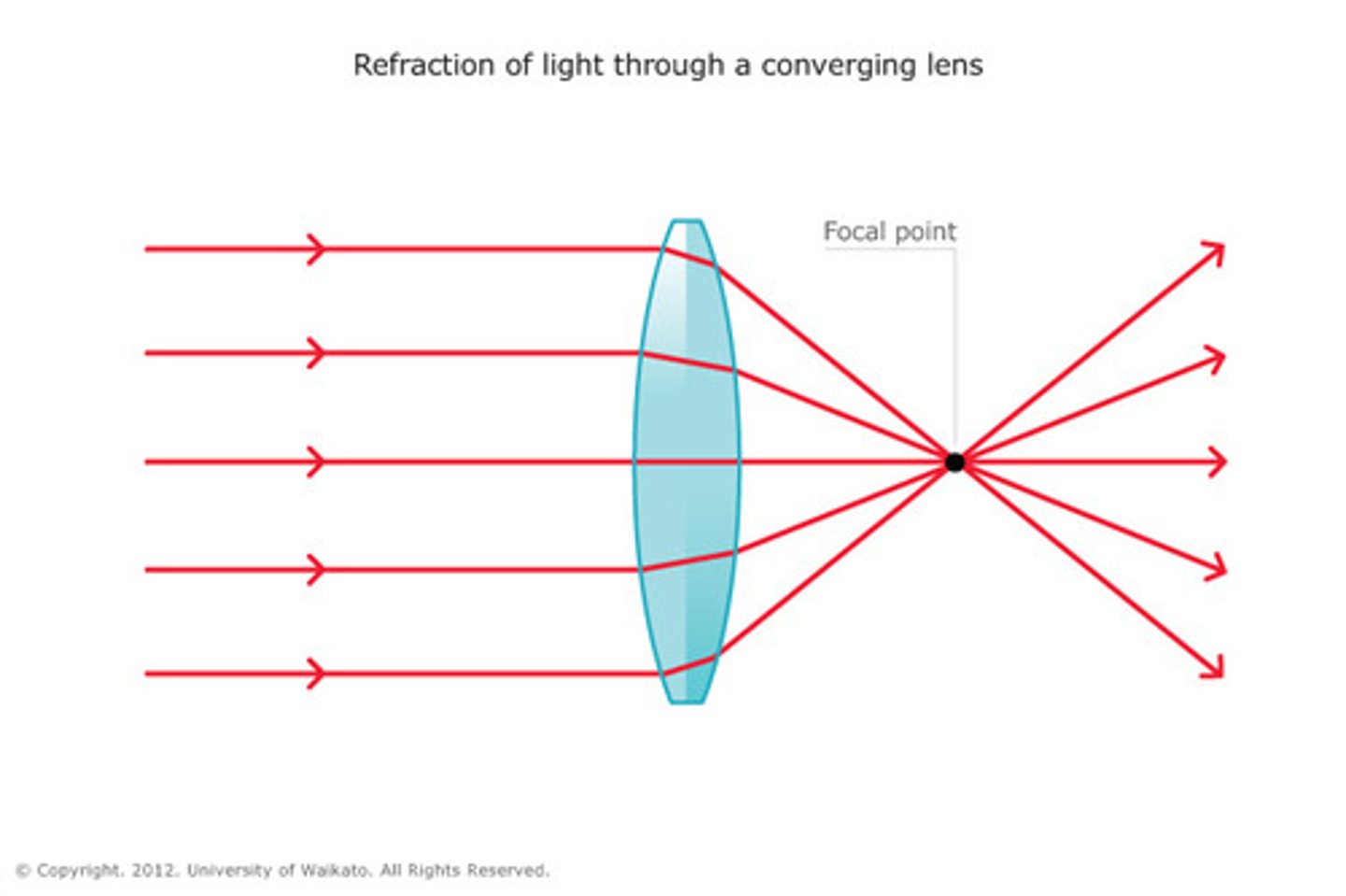
convex surface
light rays converge and focus on the focal point
concave surface
light rays diverge and do not focus

accommodation
- adjust lens thickness
- changes refraction
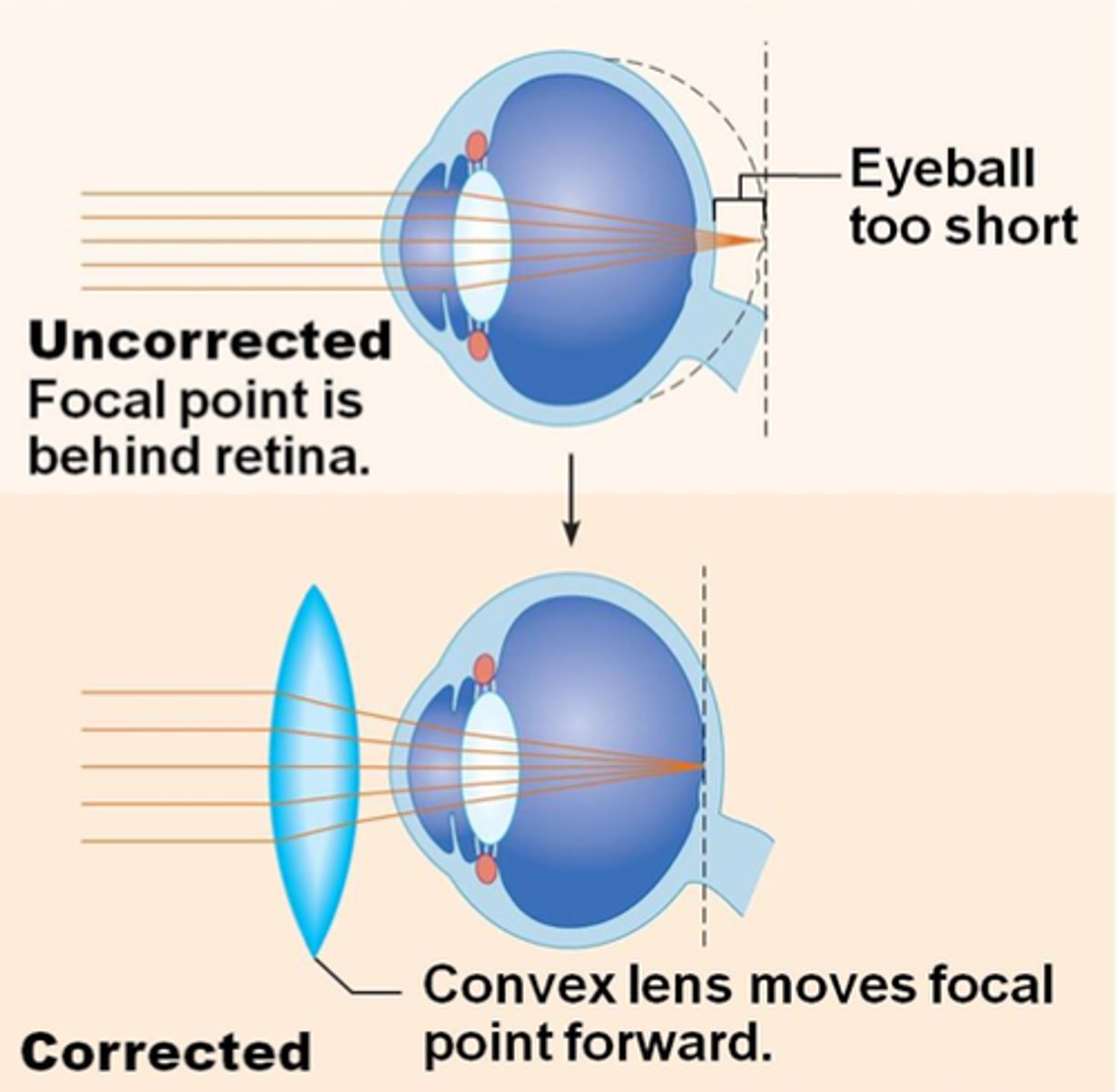
Hyperopia
- farsightedness
- focal point behind retina
-eyeball to short or cornea to flat
-correction: add convex lens
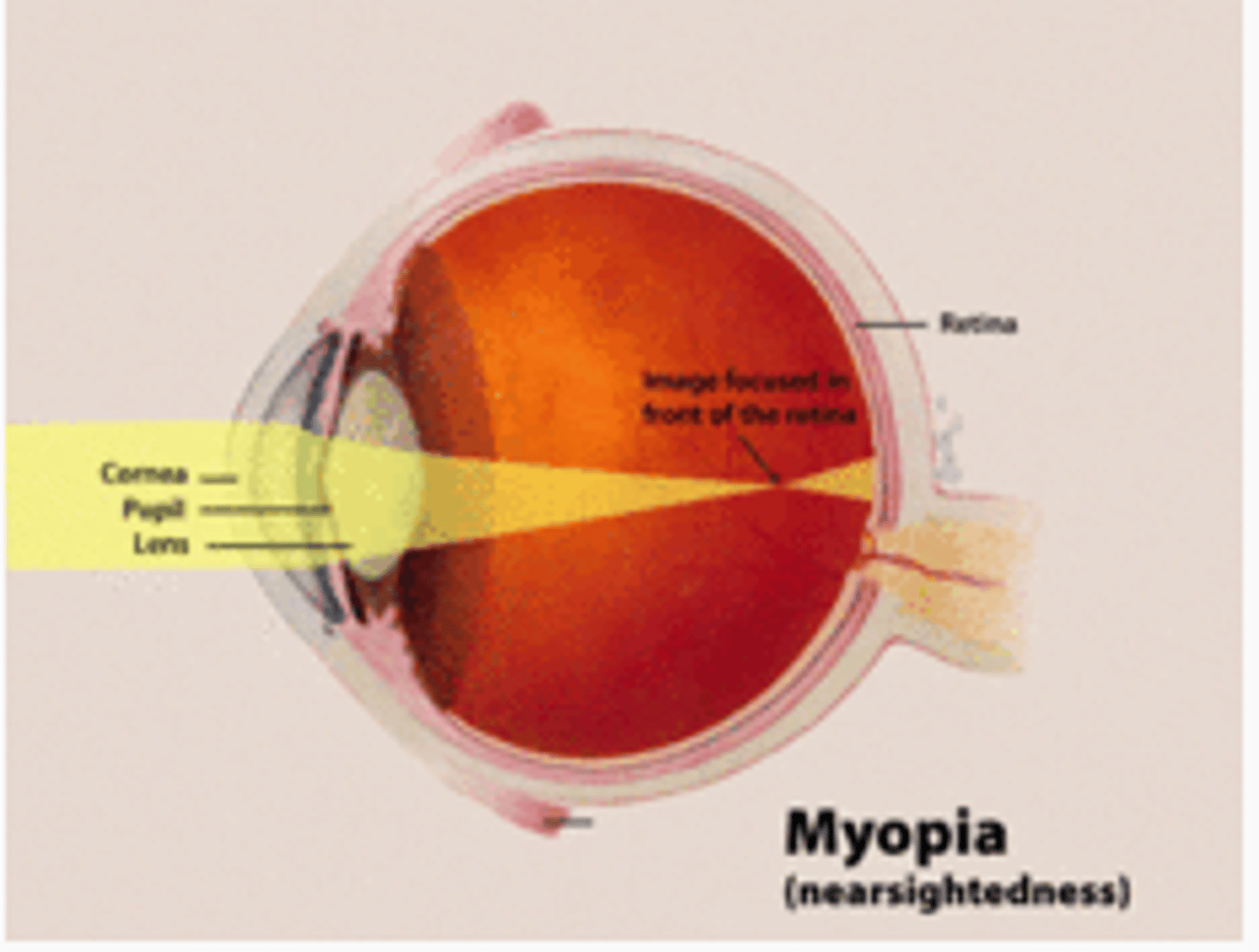
Myopia
-nearsightedness
- eyeball to long or cornea curves to much
-focal point in front of retina
- correction : add concave lens
emmetropia
-20/20 vision
-lights rays converge right on retina
Presbyopia
- lens stiffens, doesn't bulge poor accommodation
- near object focal point behind retina
Astigmatism
-irregular curvature of the cornea or lens
- light rays unevenly refracted, blurry vision