Work and Energy
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Work Done
Energy transfer when a force moves an object.
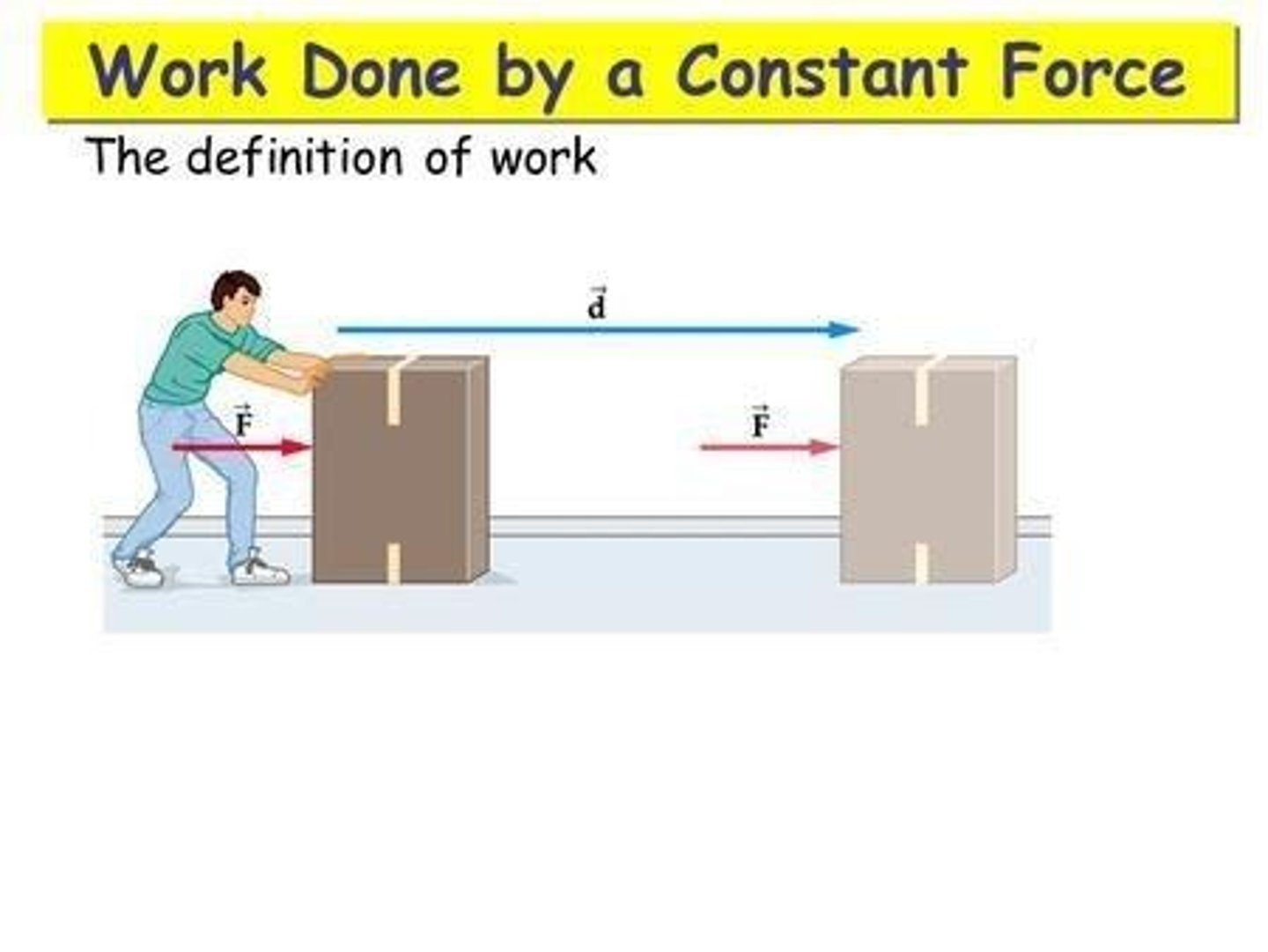
Work Equation
W = Fd, where W is work done.
Conservation of Energy
Total energy remains constant during transfer.
Gravitational Potential Energy
Energy stored due to an object's height.
GPE Formula
GPE = mg∆h, where m is mass.
Kinetic Energy
Energy an object possesses due to motion.
KE Formula
KE = ½(mv²), where v is velocity.
Elastic Potential Energy
Energy stored in deformed elastic objects.
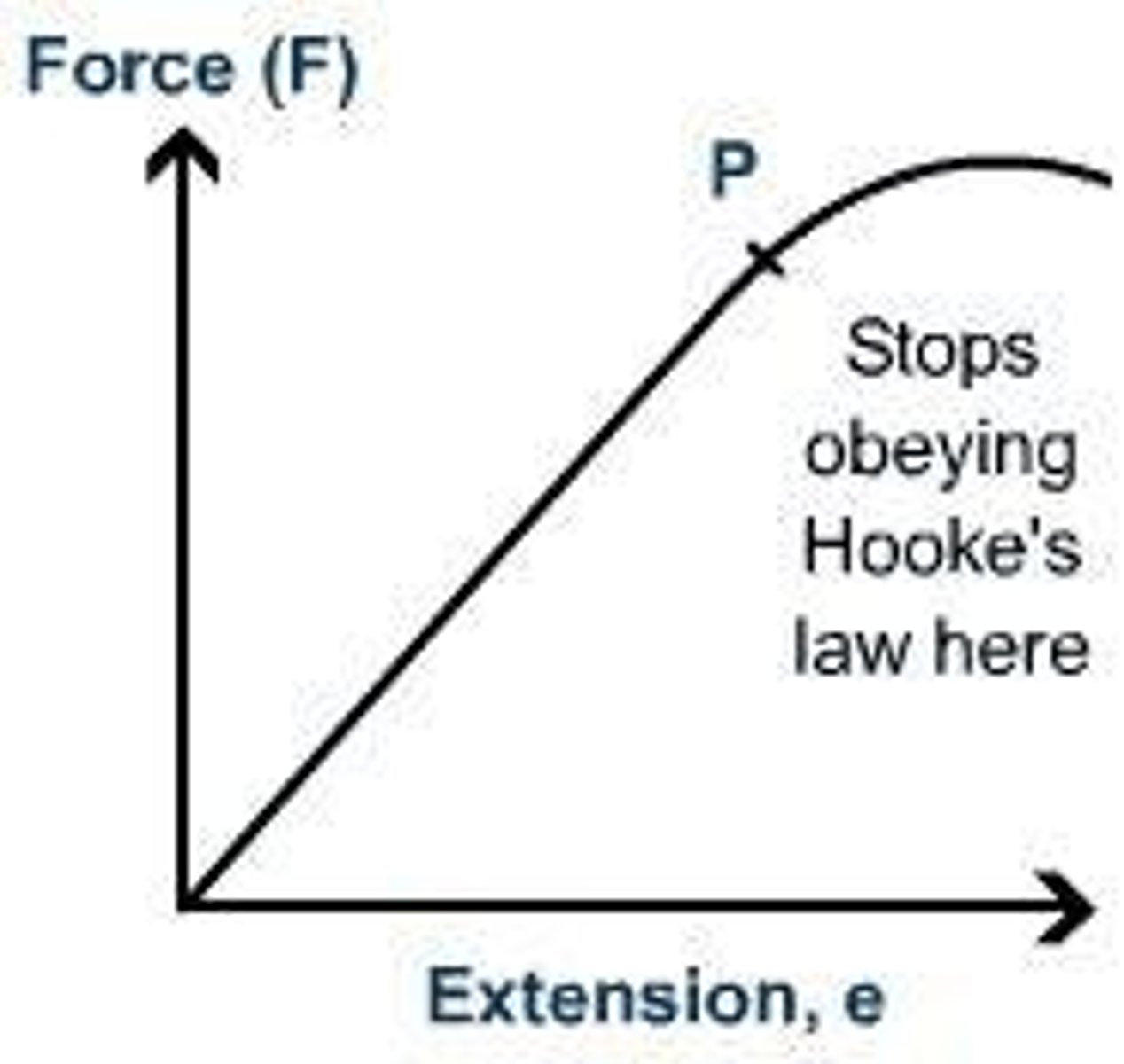
Hooke's Law
F = kx, relates force and extension.
Spring Constant
Measure of a spring's stiffness (k).
Force-Extension Graph
Graph showing relationship between force and extension.
Elastic Deformation
Reversible change in shape of a spring.
Plastic Deformation
Permanent change in shape beyond elastic limit.
Work on Spring
Work done equals area under force-extension graph.
Energy Efficiency
Ratio of useful energy output to input.
Vehicle Efficiency
Percentage of energy converted to useful work.
Frictional Forces
Opposing forces that reduce energy efficiency.
Drag Forces
Resistance forces acting against vehicle motion.
Engine Power
Rate of doing work, varies by engine size.
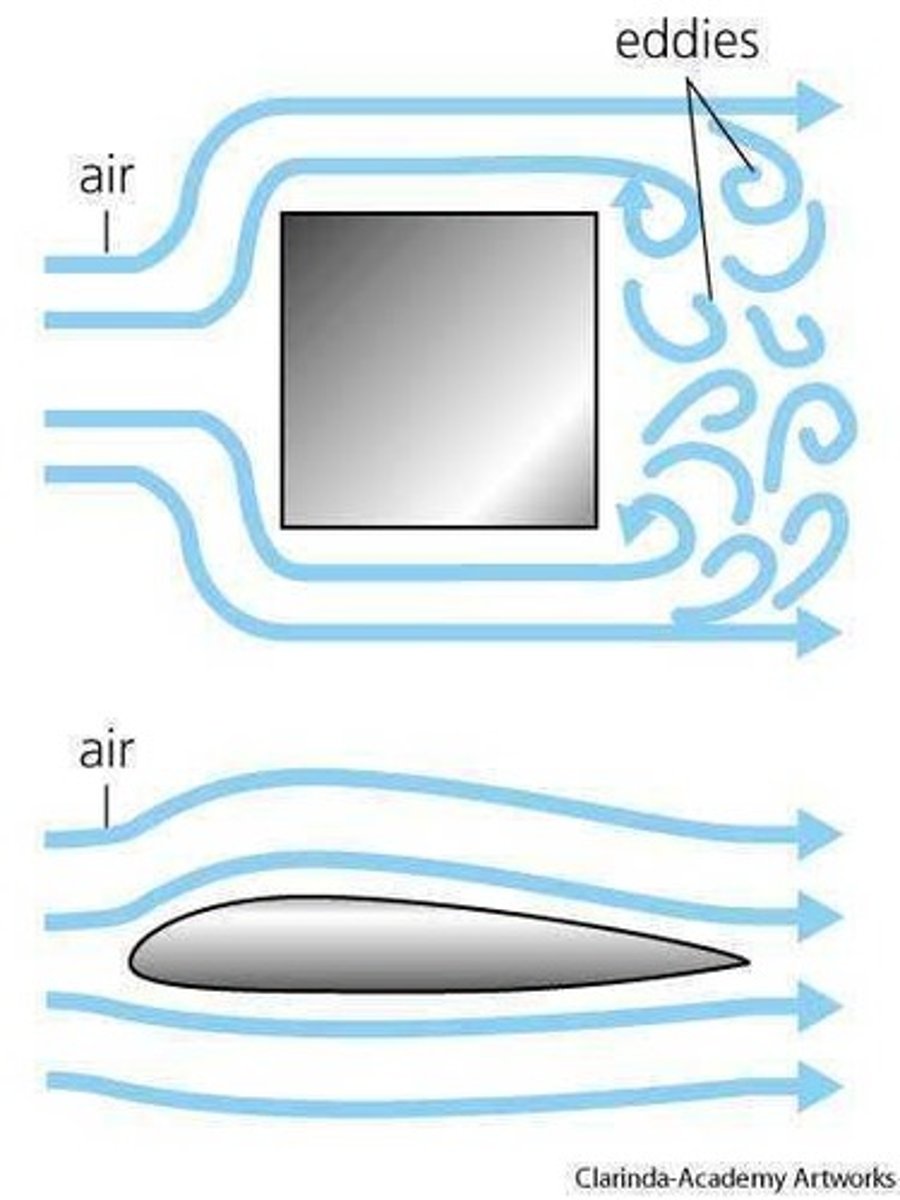
Aerodynamics
Design to reduce air resistance on vehicles.
Rolling Resistance
Force needed to move a vehicle's tyres.
Idling Losses
Energy wasted when a vehicle is stationary.
Inertial Losses
Energy lost during acceleration and deceleration.
Chemical Energy
Energy stored in fuel, converted to mechanical.
Mechanical Energy
Energy associated with the motion of objects.
Heat Energy
Non-useful energy lost during work processes.
Energy Conversion Rate
Efficiency of converting one energy form to another.