Lab - 3B
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6 CO2 + 36 ATP + 6H2O
Glycolysis is anaerobic and occurs in cytoplasm
Kreb’s cycle and ETC are aerobic
Each step is reaction that requires specific enzyme
As glucose is broken down, energy is released
Released energy is used to make ATP
Energy-requiring processes are fueled by splitting molecules of ATP
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Monosaccharides
Simple sugar
Glucose and fructose
Glucose is preferred molecule for fuel
Disaccharides
Simple sugars
2 monosaccharides linked together
Sucrose (glucose and fructose) and maltose (glucose and glucose)
Polysaccharides
Complex carbohydrates
Long chains of monosaccharide monomers
Starch (stored glucose)
Glycogen (stored glucose in animals)
Fermentation
Occurs after glycolysis if oxygen is not available; products of glycolysis remain in cytoplasm
Anaerobic
Fewer steps than aerobic respiration pathway that occurs in mitochondria
Fewer ATP are produced per glucose molecule
ETC
Cristae of mitochondria
Carrier molecules transfer electrons through redox reactions
Produces majority of ATP (32-34 ATP molecules)
NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers
Membrane protein pumps pump hydrogen ions across membrane creating concentration gradient outside membrane
Oxygen is final electron acceptor, which generates water
ATP synthase
Generates ATP
Hydrogen ions move down concentration gradient
ADP is converted to ATP
ATP cycle
Used for growth, homeostasis, manufacturing compounds and cell structures, transporting vesicles, contracting fibers, and pumping materials in and out of cell
When energy is needed, ATP is split to ADP and phosphate group, which releases energy; energy that remains after cellular processes is released as heat
ADP and P can rejoin to make ATP during catabolism
Structure of ATP
Nitrogen base (adenine), ribose sugar, 3 phosphate groups
Phosphates extend from molecule like a tail
Bond that holds 3rd phosphate in place is high-energy phosphate bond; takes energy to form bond and breaking it releases energy
Cells use energy from cellular respiration to attach 3rd phosphate group to form ATP from ADP
3rd phosphate is cleaved off to release energy when its needed
Lactic acid fermentation (animal and bacterial cells)
Main product is lactic acid along with pyruvate and NAD+ (2 of everything)
Difficult to measure in animals, so yeast is often used
Alcoholic fermentation (plant and yeast cells)
Produces ethanol and carbon dioxide and NAD+ (2 of everything)
Makes wine and beer
Gluconeogenesis
Reverse of glycolysis
Pyruvate to glucose to metabolic intermediates
Respirometer
Compares fermentation of different carbs by yeasts
Small and large test tubes
Small tube is filled with yeast solution to be tested
Large test tube is place over small one, and they are inverted together (turn upside down) introducing as little air as possible. The solution in the small tube is now contained in a closed system.
The size of the gas bubble on top of the small tube will change depending on the gas produced by the yeast.
A drop of red marker fluid is placed inside graduated sidearms to aid in reading volume
Gas bubble should be read by leading edge
Microbial growth
Affected by atmospheric gases, temperature, pH, radiation, osmotic pressure, and availability of nutrients
Psychrophiles (low temperatures), psychotrophs (between psychrophiles and mesophiles) mesophiles (middle temperatures), and thermophiles (high temperatures)
Obligate aerobe: oxygen is required for metabolism; can detoxify oxygen products
Microaerophile: small amount of oxygen required for metabolism; cannot detoxify oxygen products at reduced levels
Facultative anaerobe: can use oxygen for metabolism but not required; can detoxify oxygen products
Aerotolerant anaerobe: use of oxygen in metabolism not required; can detoxify oxygen products
Obligate anaerobe: oxygen not required for metabolism; can’t detoxify oxygen products
Toxic by-products of oxygen are superoxide ion, peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals; need catalase, superoxide dismutase, or peroxidase to degrade them
Anaerobe jar
Inoculated plates are placed in jar and chemical envelope is activated and added; chemical catalyze reactions to remove oxygen from jar; indicator strip is used to verify conditions inside jar; indicator strip will change colors in presence of oxygen, indicating chemical reaction did not take place
Fluid thioglycollate medium (FTM)
Liquid medium used to support growth of aerobes and anaerobes
Contains indicator that turns pink where oxygen is present
Contains agar to localize organisms into area of tube where oxygen conditions are most favorable for their growth
Oxygen levels are highest at top (pink) and lowest at bottom (yellow)
Obligate aerobes will only grow on surface of tube
Obligate anaerobes will only grow on bottom of tube
Facultative anaerobes will grow throughout tube
Microaerophiles will appear as small thin band of growth near but not at top of tube
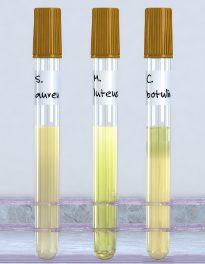
Identify type of microorganism
S. aureus: facultative anaerobe
M. luteus: obligate aerobe
C. botulinum: obligate anaerobe

Identify type of microbe
Facultative anaerobe