Equine D&M Final Exam
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Horse resp disease clinical signs
tachypnea, dyspnea, cough (with or without a cough), unilateral or bilateral nasal discharge, decreased performance, fever, and lymphadenopathy
This occurs when bacteria that is normally inhabits the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity is aspirated
Bacterial pneumonia
This occurs when the bacterial pneumonia infection spreads from the lung tissue to the pleural space
Pleuropneumonia
This refers to chronic airway inflammation caused by sensitivity to the environment irritants like dust, molds, and other inhaled allergens
Equine asthma
How do we diagnose equine asthma?
-rebreathing examinations and BAL are important diagnostic tools.
-Make sure to do a cytological examination to rule out infection versus inflammatory
Treatment for equine asthma
-Mixture of environmental changes and medications to control inflammation and bronchoconstriction.
-Corticosteroids and bronchodilators are often administered via nebulization or inhaler for direct airway administration
This Is a common highly contagious respiratory disease of horses caused by the bacterial pathogen Streptococcus equi equi.
Strangles
Strangles treatment
antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, and heat therapy to draw out abscesses
How do we diagnose strangles?
culture of nasal discharge or samples obtained by nasopharyngeal wash or guttural pouch flush
Guttural pouches
two large systemic dilatations of the Eustachian tubes that are located just above the pharynx and larynx
This Is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by equine herpesvirus type 1 and type 4. Clinical signs include fever, lethargy, and nasal discharge.
Equine Rhinopneumonitis
Equine Rhinopneumonitis diagnosis
PCR analysis of blood and nasal secretions
This is a contagious viral disease that produces limb swelling, conjunctivitis, abortion, and respiratory disease in horses.
Viral Arteritis
How do we diagnose viral arteritis?
serology
This is a persistent viral disease of horses that cause anemia, fever, and weight loss. It is diagnosed by the Coggins test.
Equine infectious anemia
This is known as equine granulocytic and is caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilium. Clinical signs are fever, anemia, icterus, lethargy, stiffness, and limb edema.
Anaplasmosis
How do we treat Anaplasmosis?
consists of IV antimicrobials, such as oxytetracycline and steroids, if necessary, for edema
This is a tick born illness caused by the bacteria spirochete bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi. Clinical signs include low-grade fever, joint swelling, lameness, laminitis, muscle tenderness, skin rash, chronic weight loss, uveitis, and hypersensitivity to touch.
Lyme disease
How do we diagnose Lyme disease?
Western blot, ELISA, multiplex assay, and the C-6 ELISA SNAP test
How do we treat Lyme disease?
IV oxytetracycline or oral doxycycline for at least one month is typically required
This is a bloodborne disease caused by the parasite Babesia caballi or Theileria equi. Clinical signs include fever, anemia, jaundice, weight loss, ventral edema, increased respiration, possible enlarged spleen
Piroplasmosis
This is a common arrhythmia in horses, especially fit, athletic animals. It occurs as the result of altered conduction through the Av node, resulting in contracture of the atria without the ventricles.
Second degree AV block
This is the most common clinically relevant arrhythmia in horses. Clinical signs include exercise intolerance or poor performance.
A-Fib
How do we treat A-fib in horses?
• Quinidine through an NG tube or oral tablets
• Electrical conversion under anesthesia can be accomplished by placing electrodes into the heart with ultrasound guidance
Skin is the barrier against...
Chemicals
Heat
Cold
Microbial pathogens
UV light
What are the main functions of the skin?
-Prevents loss of water and electrolytes
-Regulates body temp
-Regulates blood pressure by peripheral vascular changes
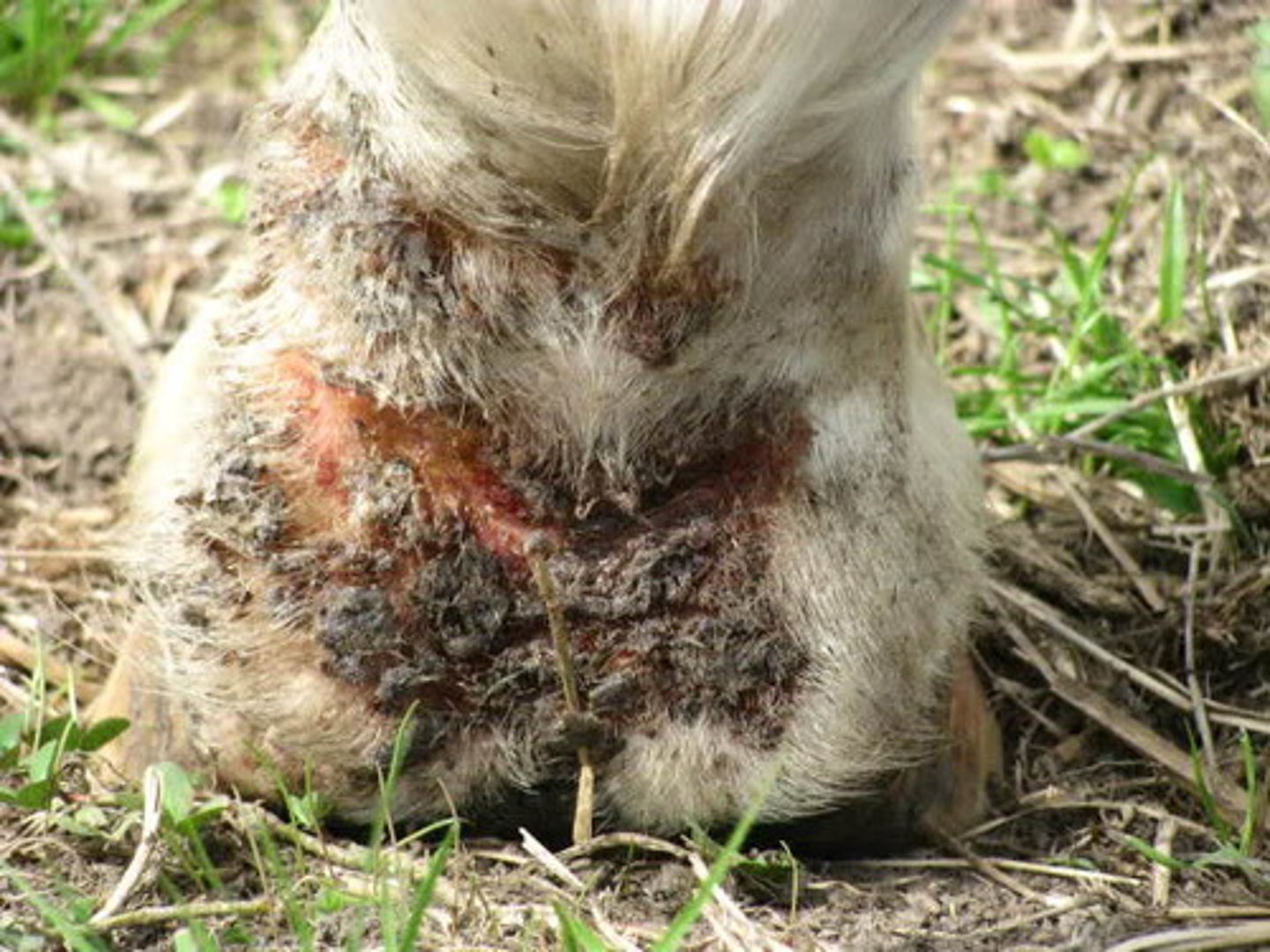
Pastern dermatitis
Horse allergies
-Insect Hypersensitivity
- Food Allergy
- Contact Allergies
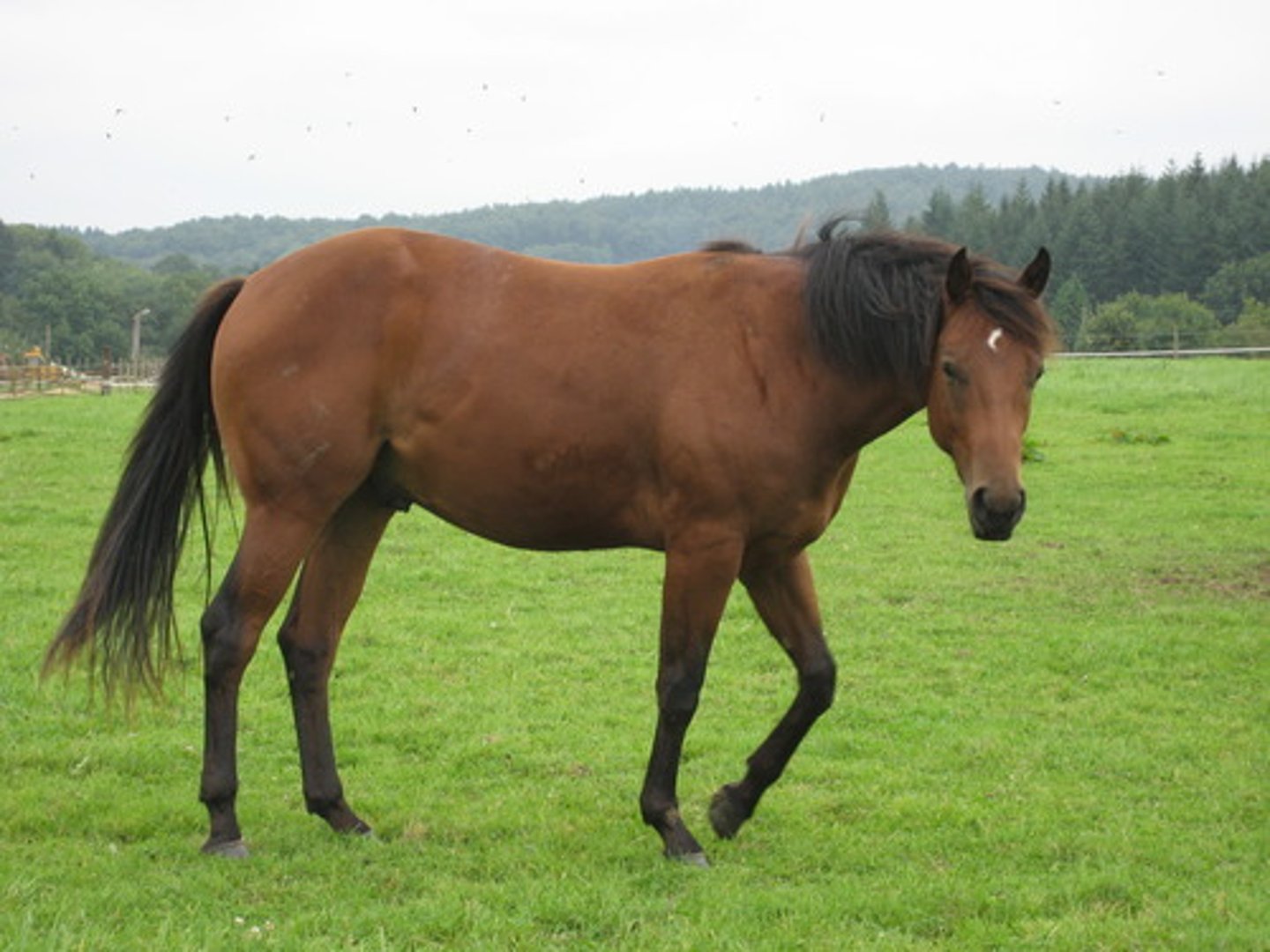

Dermatophilosis (Rain Scald/Rain Rot)
- Dermatophilis congolensis (a bacteria)
- Chronic moisture and skin damage predispose
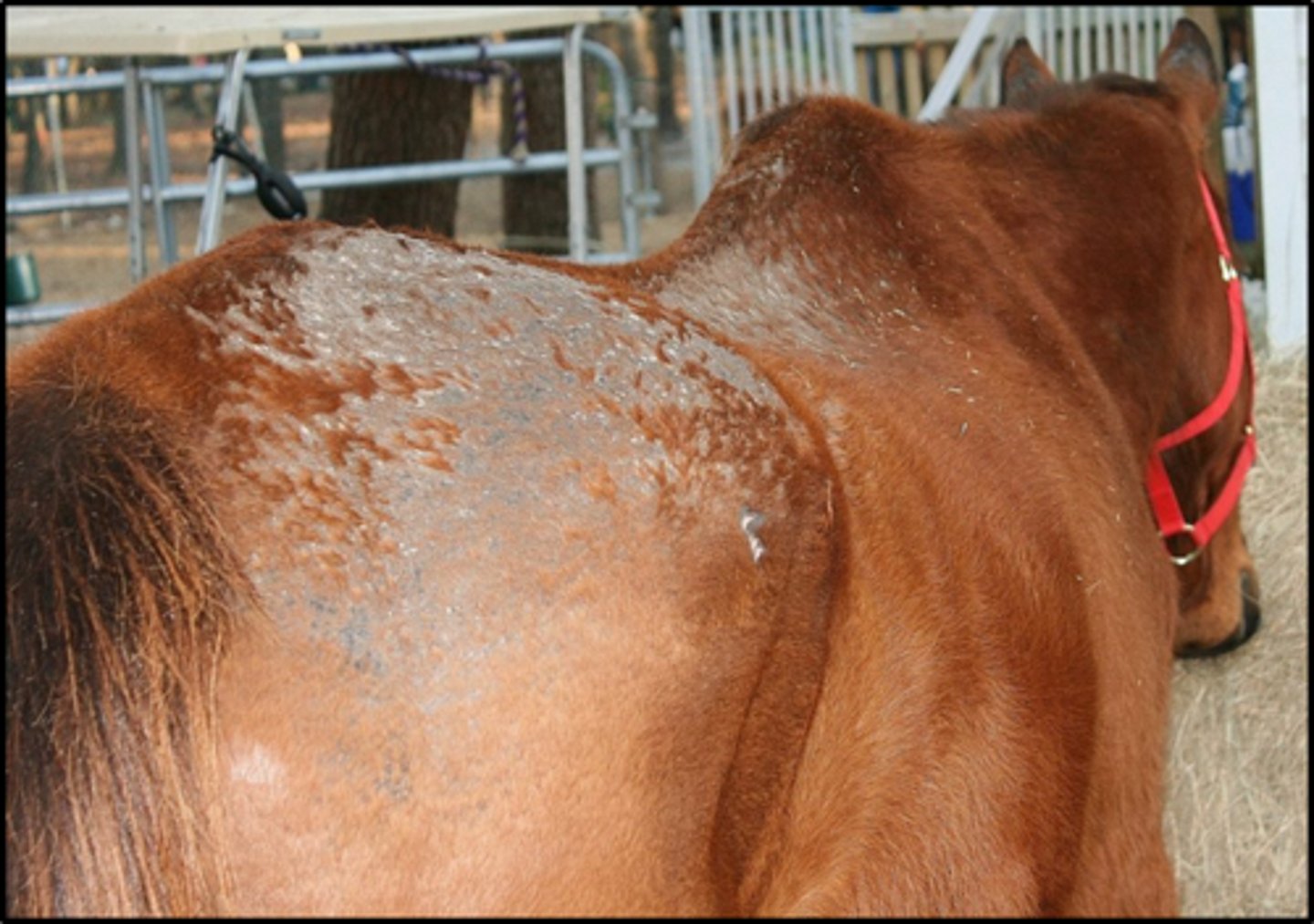
Dermatophytosis (Ringworm)
-Various fungal species
- Contagious to many species
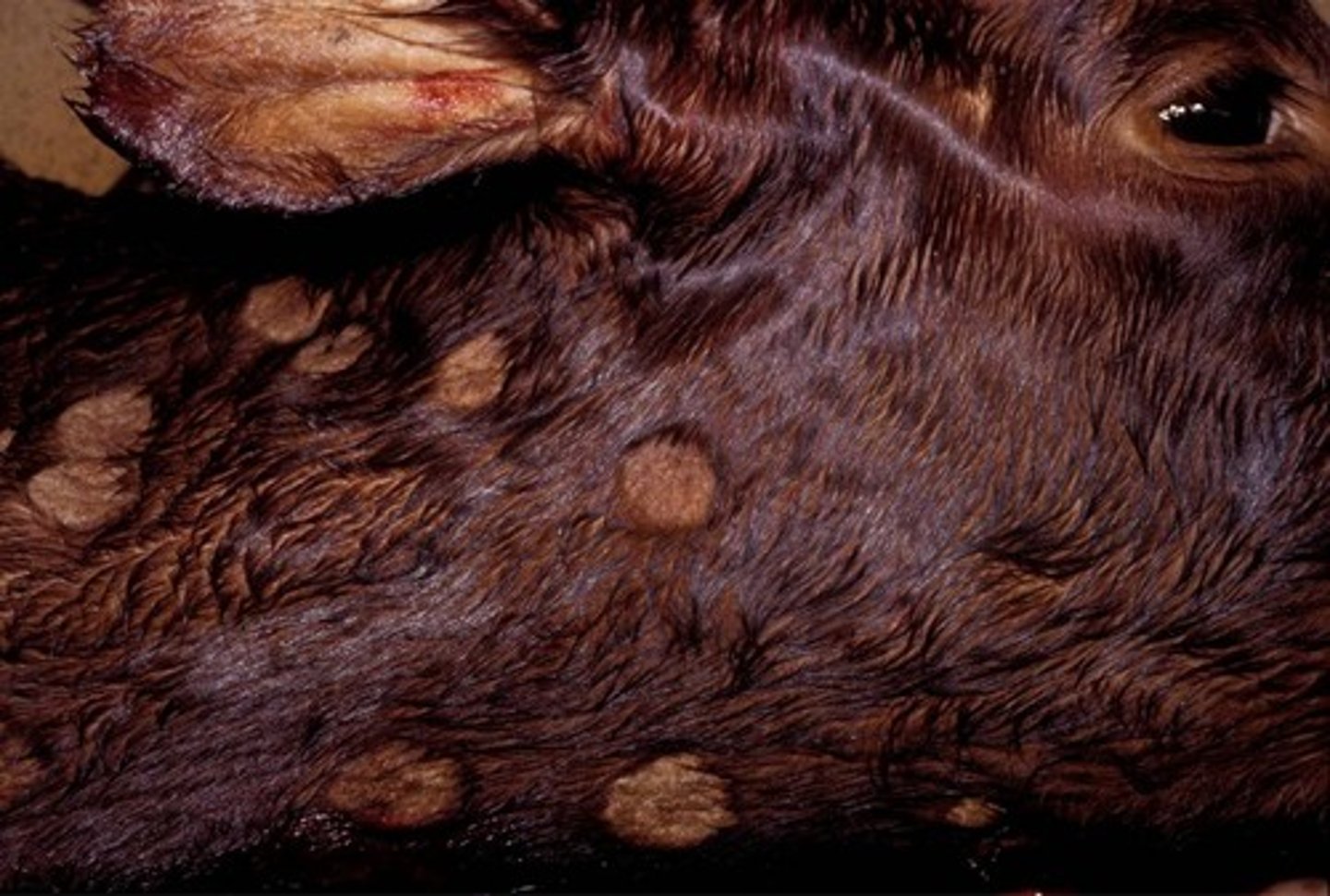
Bacterial folliculitis
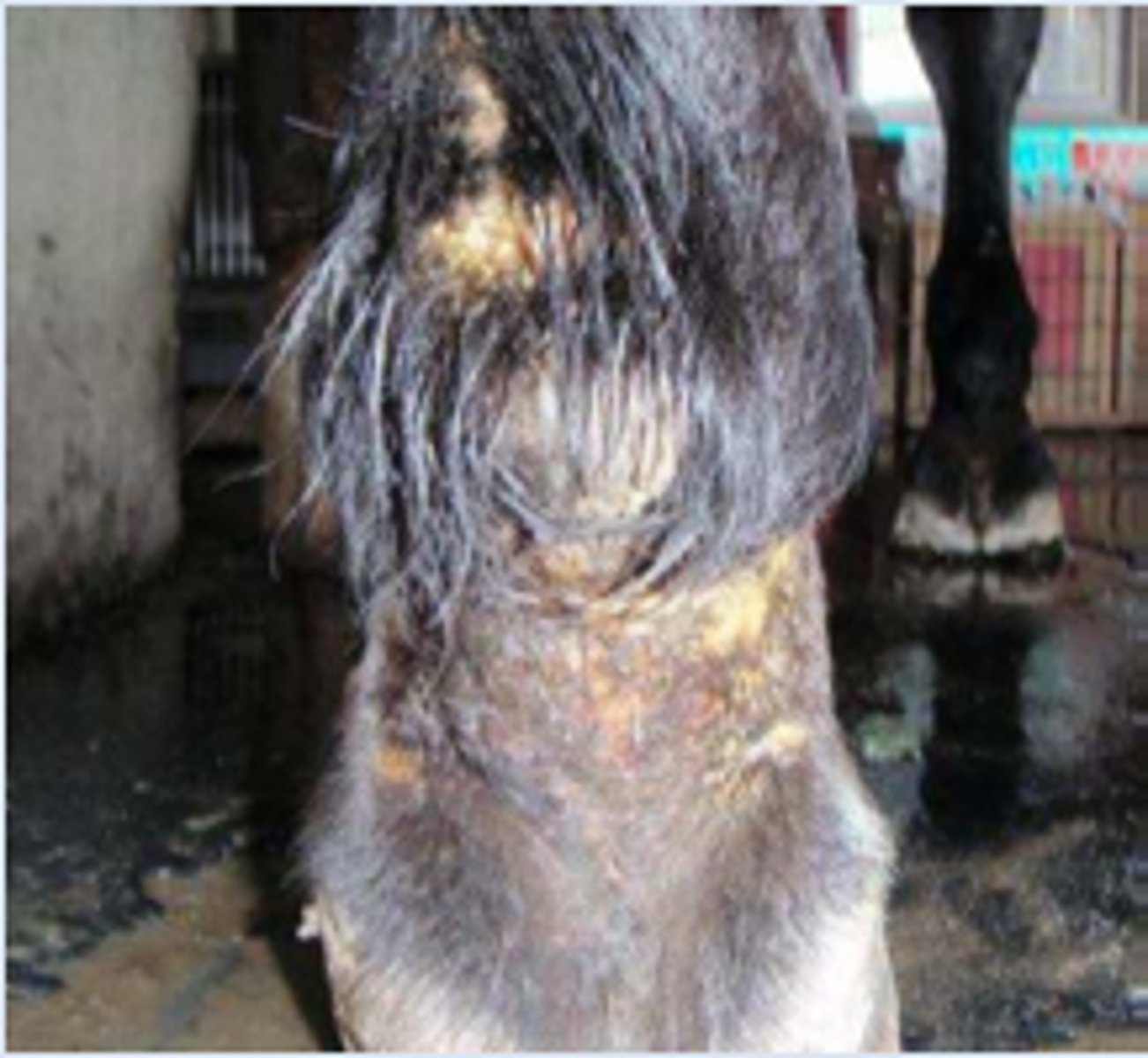
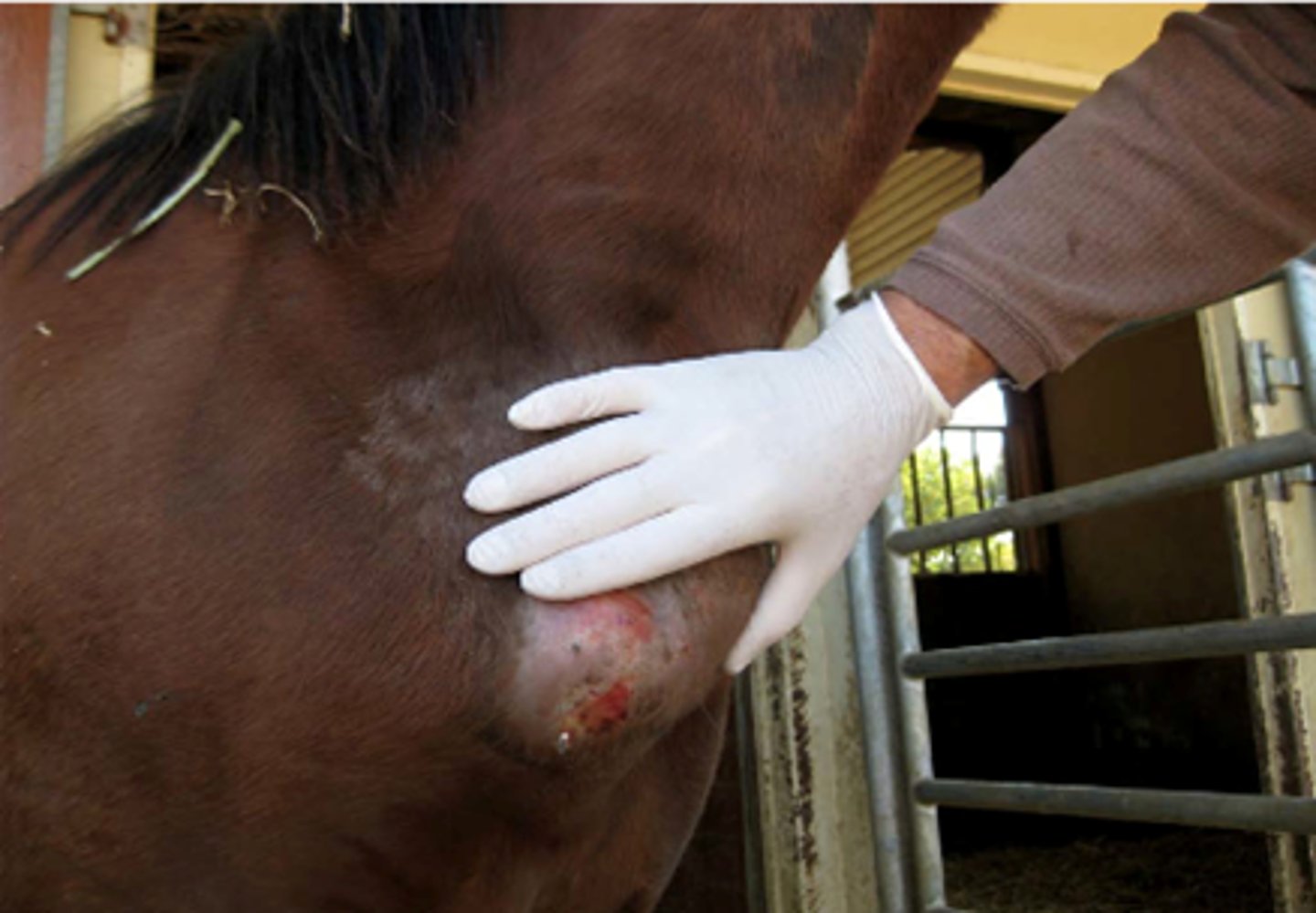
Corynebacterium Infection (Pigeon Fever)
-Caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
- Generally forms external abscesses
- Rarely forms internal abscesses
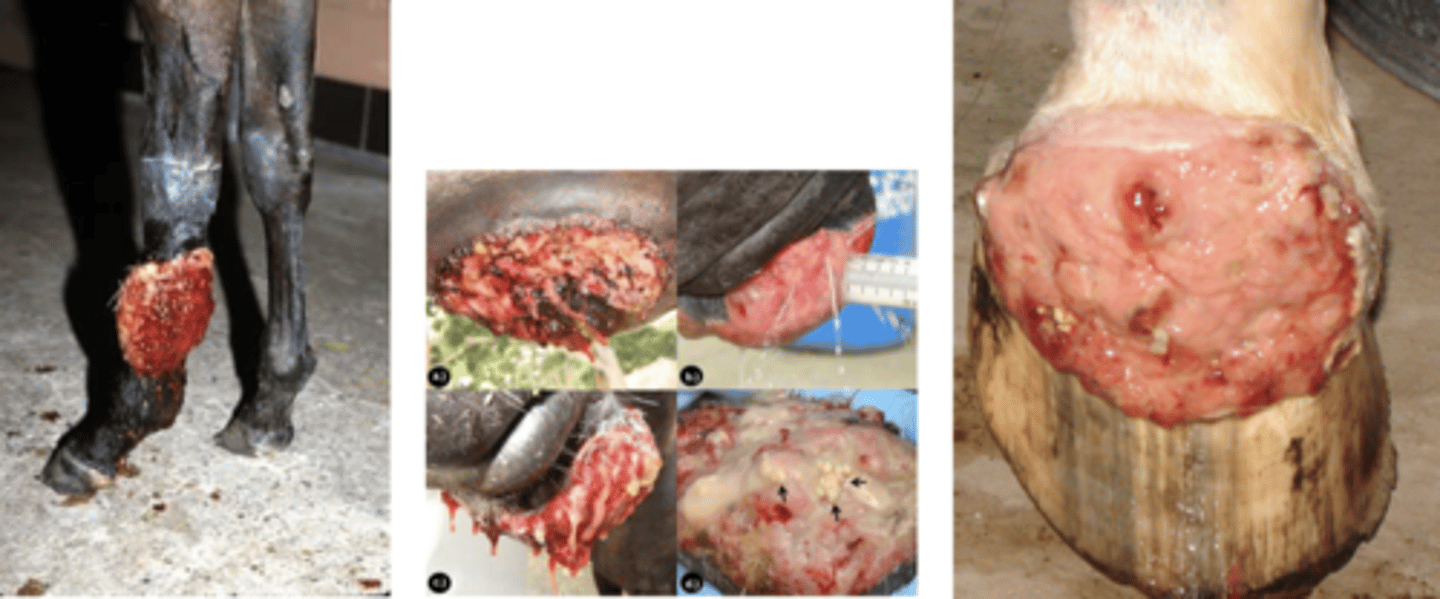
Pythiosis
-Caused by Pythium insidiosum, a fungus-like organism that lives in standing water
- Very aggressive
- Hard to treat
Which disease is caused by fungus?
ringworm
What purpose does piloerection serve in horses?
traps air between hairs to keep horse warm
What is the most common skin tumor in horses?
sarcoids
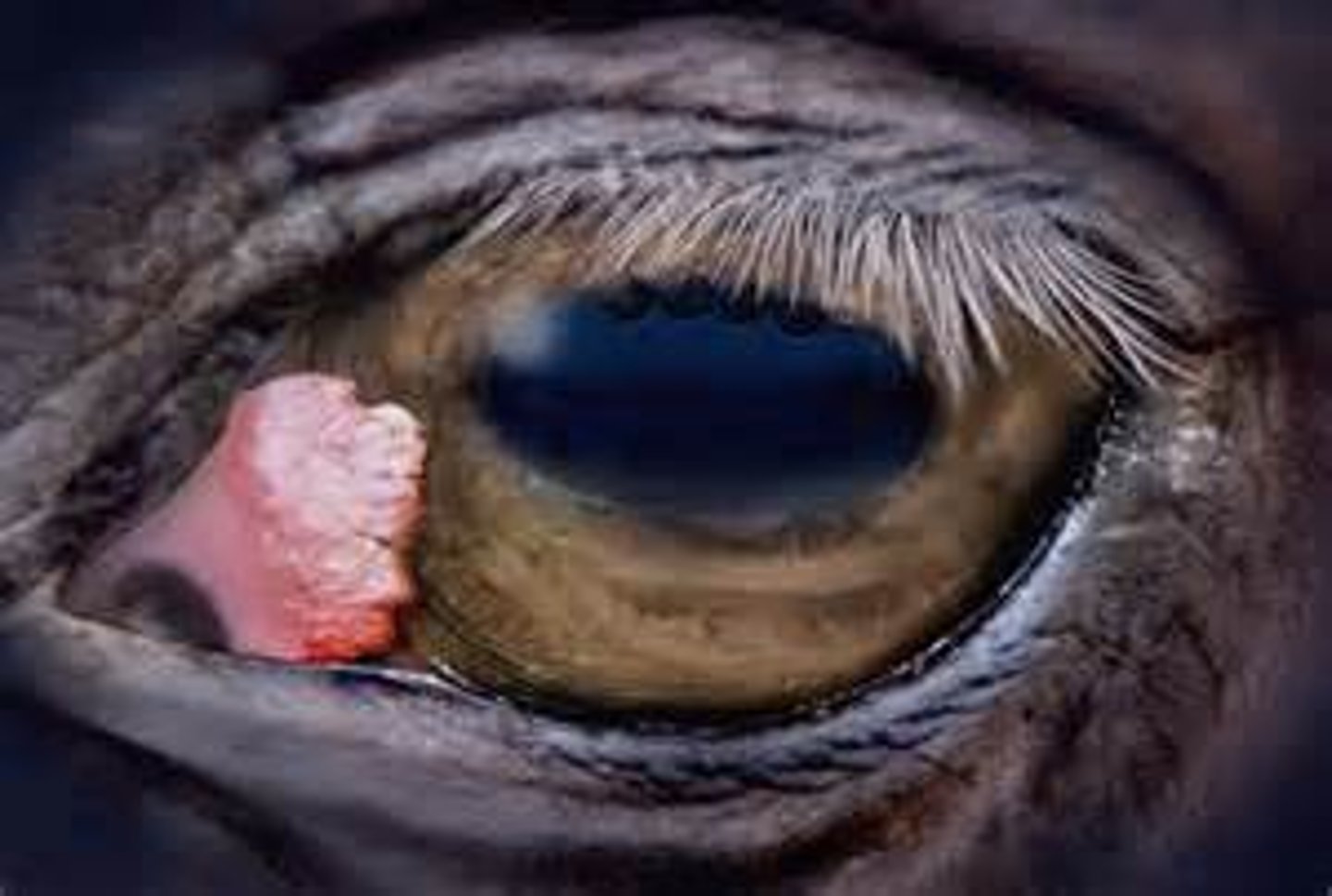
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-Eyes, genitalia, nose
- Pale skinned horses
Melonoma
-Gray horses
- Usually dark gray or black
- Perenium, parotid, commissure of lips, prepuce/penis

Hair sampling is useful for......
suspected Ringworm and Rainrot
What are we looking for with the adhesive tape prep?
pinworms
Topical tumor treatment
-5-Fluorouracil Ointment
-Useful for pre-cancerous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-Kills rapidly dividing cells
Cisplatin Beads
-Implant in and around skin tumors
-more likely to cause renal tumors than carboplatin
Pyelonephritis
infection of the kidneys
Cystitis
infection of the bladder
Horse urine normally contains.......
calcium crystals
Horse urinary stones will/will not be dissolved with diet?
WILL NOT
Sabulous Cystitis
-Accumulation of crystals and mucus in bladder
-Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis (EPM), Cauda Equina Syndrome, Equine Herpes Myeloencephalitis (neurologic EHV-1)

What are the most common types of urogenital tumors?
Squamous cell carcinomas and Melanoma
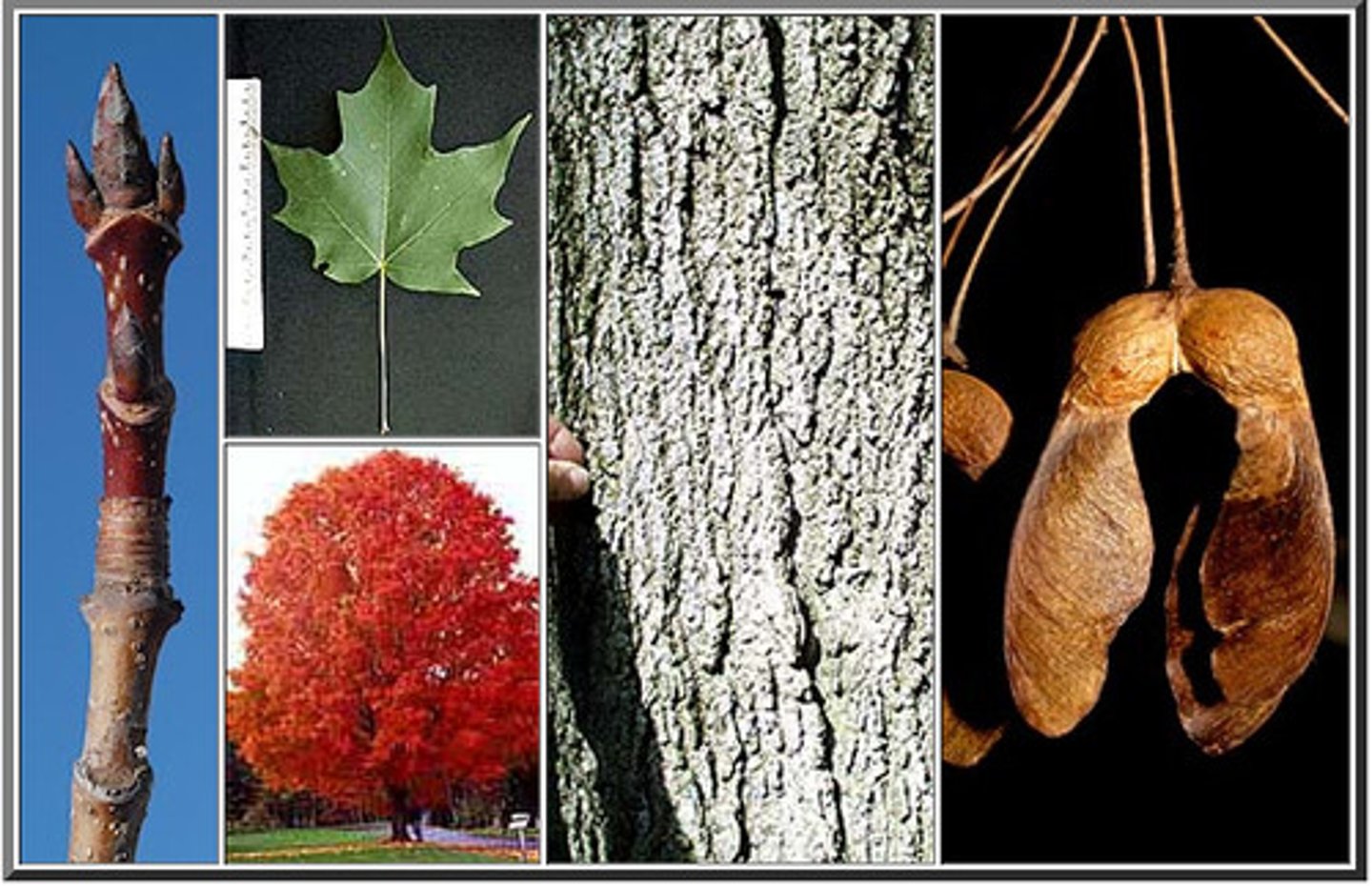
What kind of plant toxicity will cause kidney disease in horses?
wilted Red maple

Pre-renal azotemia is caused by.....
dehydration
Renal azotemia is caused by....
injury to the kidneys
Post-renal azotemia is caused by.......
Obstruction of urine flow due to urinary tract calculi
Azotemia
Elevated BUN (>22 mg/dl) and/or Creatine (>2.0mg/dl)
Free catch urine collection method is used for what?
to evaluate urine for unsanctioned drugs in competition horses
Percutaneous ultrasound
-images kidneys
-Ultrasound probe: 3-5 MHz curvilinear probe
Kidney biopsy risks:
hemorrhage and infection
What does a kidney biopsy do?
Detects microstructural abnormalities
Endoscopy size in males:
2 meter scope
Endoscopy size in females:
1 meter scope
What is the composition of most urinary stones in horses?
Calcium carbonate
Upper body wounds
Heal predominantly by contraction
Do not get exuberant granulation tissue
Heal quickly, even if large
Epithelialization is minimal
Lower limb wounds
Wound Expansion
Limited Contraction
Exuberant Granulation
Prolonged Healing
Extensive Epithelialization
Primary closure of wounds
Closure with suture or staples
Acute wounds
Rapid healing
Delayed Primary Closure
After "Golden Period" (>6 hours)
Before granulation tissue (4-5 days)
Time permits: Reduced inflammation, Decontamination, Debridement
Second Intention Healing
Natural process
Wound contraction and epithelialization
Contraction more desirable than epithelialization
Most appropriate for many equine wounds
What is Initial Wound Management used for?
to assess and control blood loss
Horse blood volume
8% of body weight
Aseptic prep of skin _________ wound
around
Lavage solutions
-0.1% Povidone iodine solution (1 ml stock/liter saline)
-0.05% Chlorhexidine solution (25 ml of 2%stock/liter saline)
What is the purpose of bell boots?
protects the coronary bands and heels
Which wounds heal predominantly by contraction, do not get exuberant granulation tissue ("proud flesh"), and heal quickly, even if large?
Upper body wounds
True or False: Larger wounds are always more significant than smaller wounds
False
Primary layer of wound bandaging
rolled gauze and elastic adhesive tape
Secondary layer of wound bandaging
-cotton roll and vet wrap
-reduces swelling
Emergency goals for extremity fractures
-Prevent damage to nerves and blood vessels of limb
- Keep the fractured bone from penetrating skin and becoming an open fracture
- Stabilize limb to relieve anxiety
- Minimize further damage to fractured bone ends and surrounding soft tissue
Vertebral fractures
-Immediate treatment is needed to reduce spinal Cord inflammation
-Diuretics (Furosamide)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS, DMSO)
- Analgesics
- Corticosteroids (peracute): Dexamethasone 0.2-0.3mg/kg
Cranium fractures are often accompanied by......
serious neurologic deficits
Fractures involving temperomandibular joint:
guarded to poor
In case of cranium fractures, what task is typically most urgent?
assessing and treating the neurologic injury
True or False: Adult horses with limb fractures should be transported with their bodies as free as possible and their heads tied.
FALSE
What is the normal rectal temperature for a horse at rest?
99-101.5 degrees F
What is the normal pulse rate for an adult horse at rest?
24-48 bpm
What is the normal respiratory rate for an adult horse?
6-16 bpm
True or False: Bluish tented gums in horses are often referred to as cyanotic. These colored gums indicate that there is low oxygen content in the tissue.
True
True or False: Isoquinoline - pyrozines (Parziquantel) targets tapeworms only.
TRUE
When a lame horse is trotted on pavement, which foot will sound louder when it strikes the ground?
the foot on the sound limb
A horse is being evaluated for lameness on a straight line on a hard surface. The horse is sound (no lameness) at the walk. She has a consistent lameness in the right forelimb at the trot. What grade is this on the AAEP lameness scale?
Grade 3
TRUE or FALSE: Horses are hind gut fermenters that rely on the bacteria in the large intestine to digest cellulose.
TRUE
Horses need to have large amounts of excess tooth removed gradually over time to avoid killing the tooth. What is the maximum amount of tooth that should be removed at one time?
3-5 mm
True or False: Exploratory celiotomy rarely reveals the specific cause of colic.
FALSE, it always reveals the specific cause
What is the most common problem of the equine esophagus?
obstruction
Which of the following procedures does not require a sterile surgical-type prep, for at least 5 minutes?
nerve block
True or False: Horses are more sensitive (more likely to have toxic side effects) from local anesthetics than ruminants.
False
True or False: Acepromazine is a useful drug to reduce anxiety in horses undergoing lameness exam. It will not produce profound sedation.
TRUE
When prepping a site for a joint block, the skin should be scrubbed from:
middle then outward
True or False: Horses are considered long day breeders
TRUE
True or False: The three main sites for bacteria are the GI tract, respiratory tract, and the umbilicus
True
True or False: Premature foals are delivered before 320 days.
True
Horse vision
285° Monocular
65° Binocular
Depth perception depends on _____________vision
binocular