Horseshoe bats
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Regarding harmonics, what can be seen in the calls of both species?
More energy is exerted into the second harmonic, sometimes the fundamental is absent.
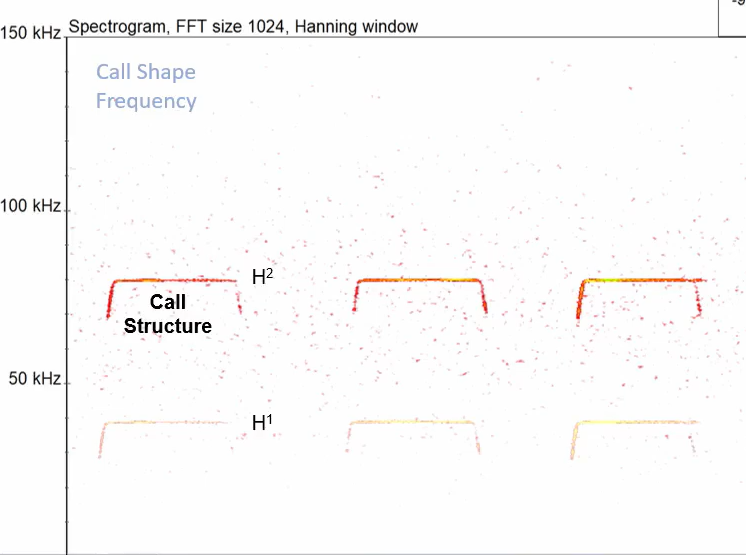
What FMaxE would be expected of LHS?
106-110kHz (H2)
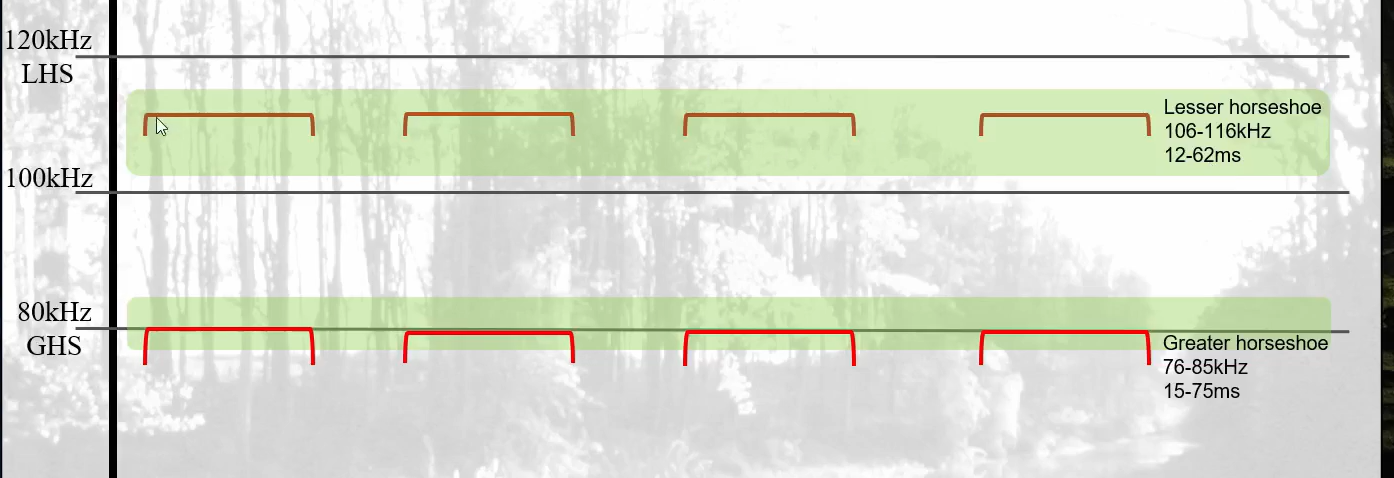
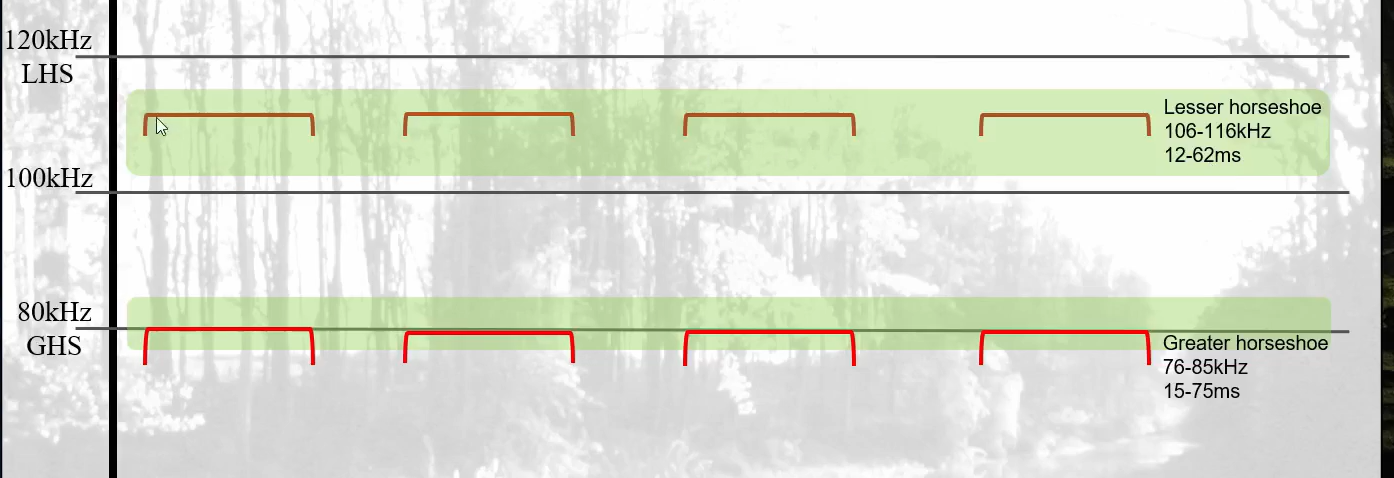
What FMaxE would be expected of GHS?
76-85kHz (H2)
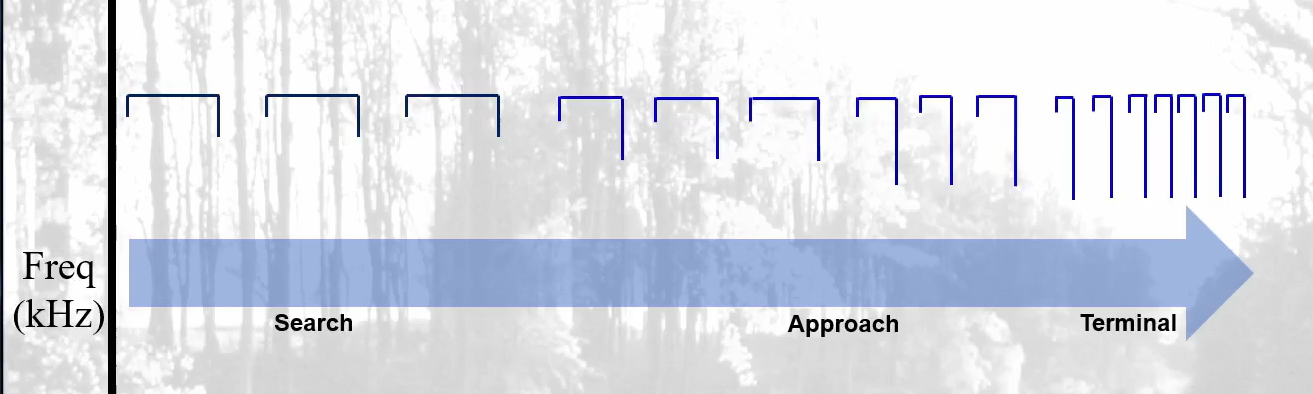
How do calls change during approach and terminal phases?
The end frequency will decrease as the bat nears the target
What should calls sound like in heterodyne?
Some sort of bubbling or babbling
What should calls sound like in time expansion?
Whistling
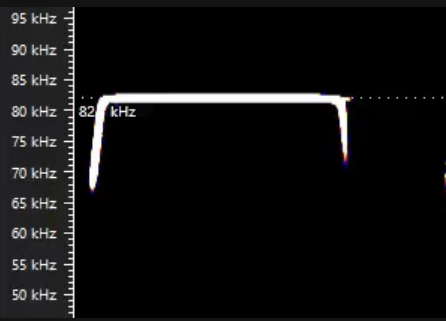
What species is most likely here and why?
GHS. FMax <100kHz
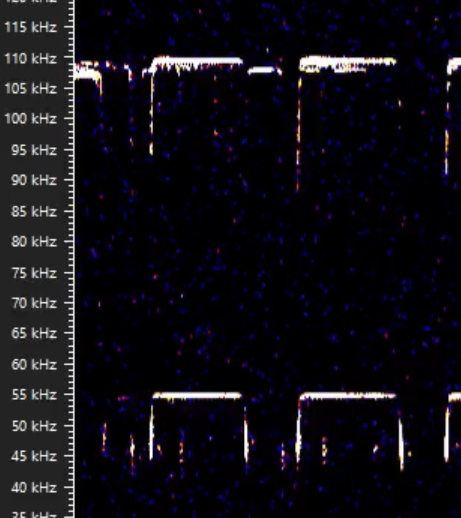
What species is likely here and why?
LHS. FMax >100kHz
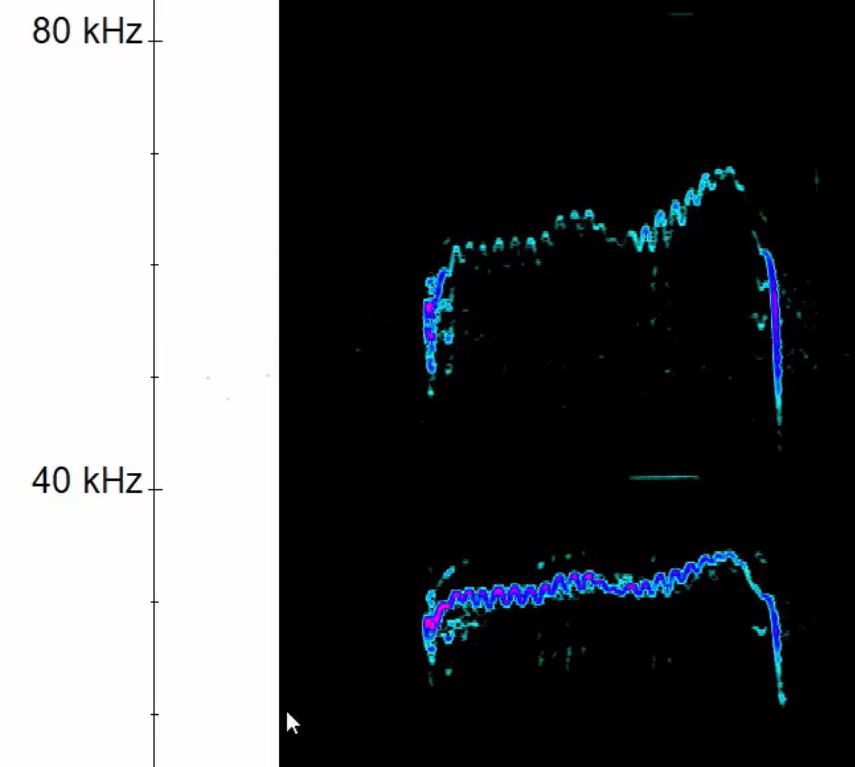
What is this social call referred to as and how can it be distinguished from Nyctalus?
A long trill. The frequency is too high for Nyctalus.
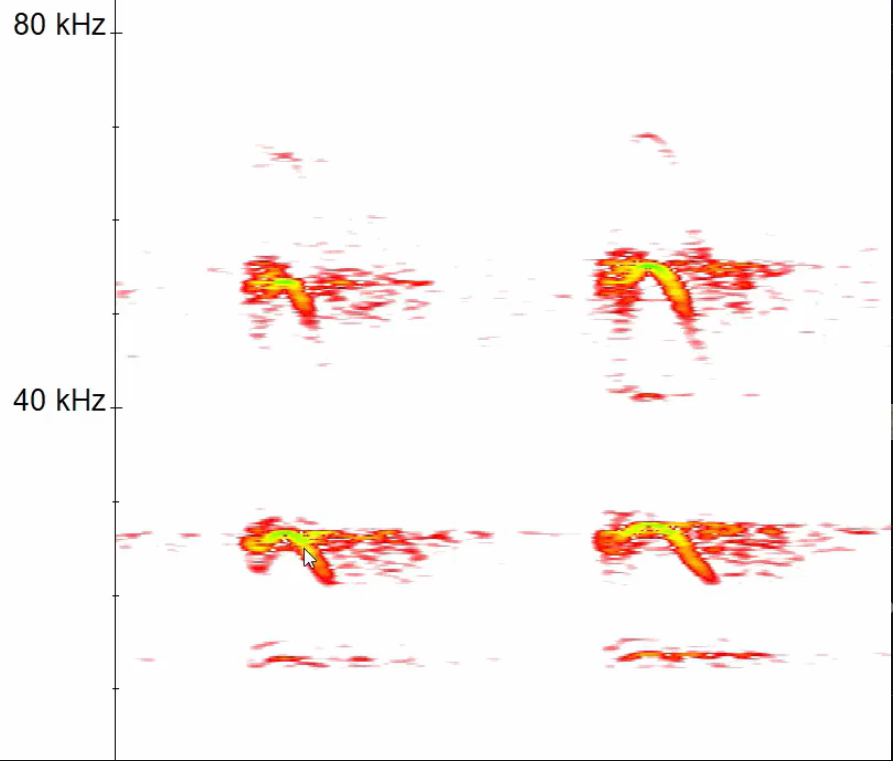
What is this social call referred to as and how can it be distinguished from Daubenton’s?
FM arched call. Frequency is too low for Daubenton’s and it sounds completely different.