Functional Groups
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
hydrophilic substances
Form hydrogen bonds with water (ions, sugars, cellulose, some proteins)
Polar & charged (IONIC)
hydrophobic substances
Does not form hydrogen bonds with water
Nonpolar & uncharged (NONIONIC)

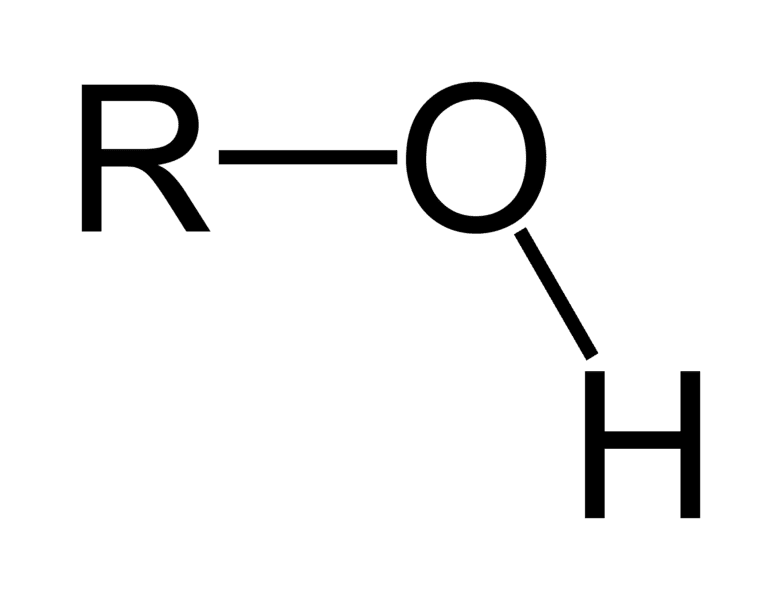
Hydroxyl
-OH
Polar = Hydrophilic
Acidic
Alcohol
Ex: Ethanol
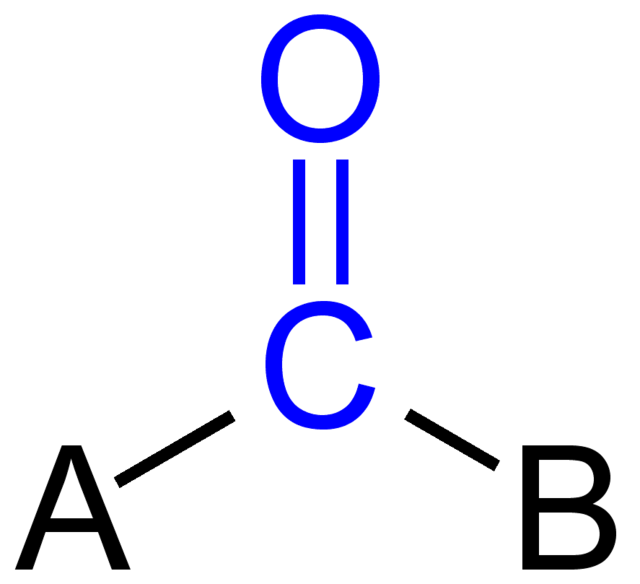
Carbonyl
C=O
Polar = Hydrophilic
"Aldehyde" = Terminal
"Ketone" = Internal
Ex: Acetone
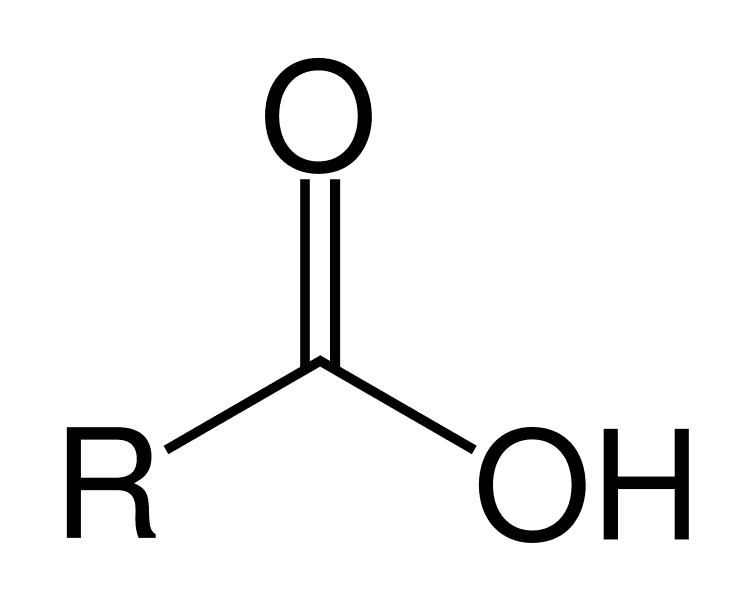
Carboxyl
-COOH
Charged
Polar = Hydrophilic
Acidic
Component in amino & fatty acids
Ex: Glycine
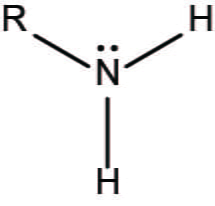
Amino
-NH2
Charged
Polar = Hydrophilic
Basic
Amines
Ex: Glycine
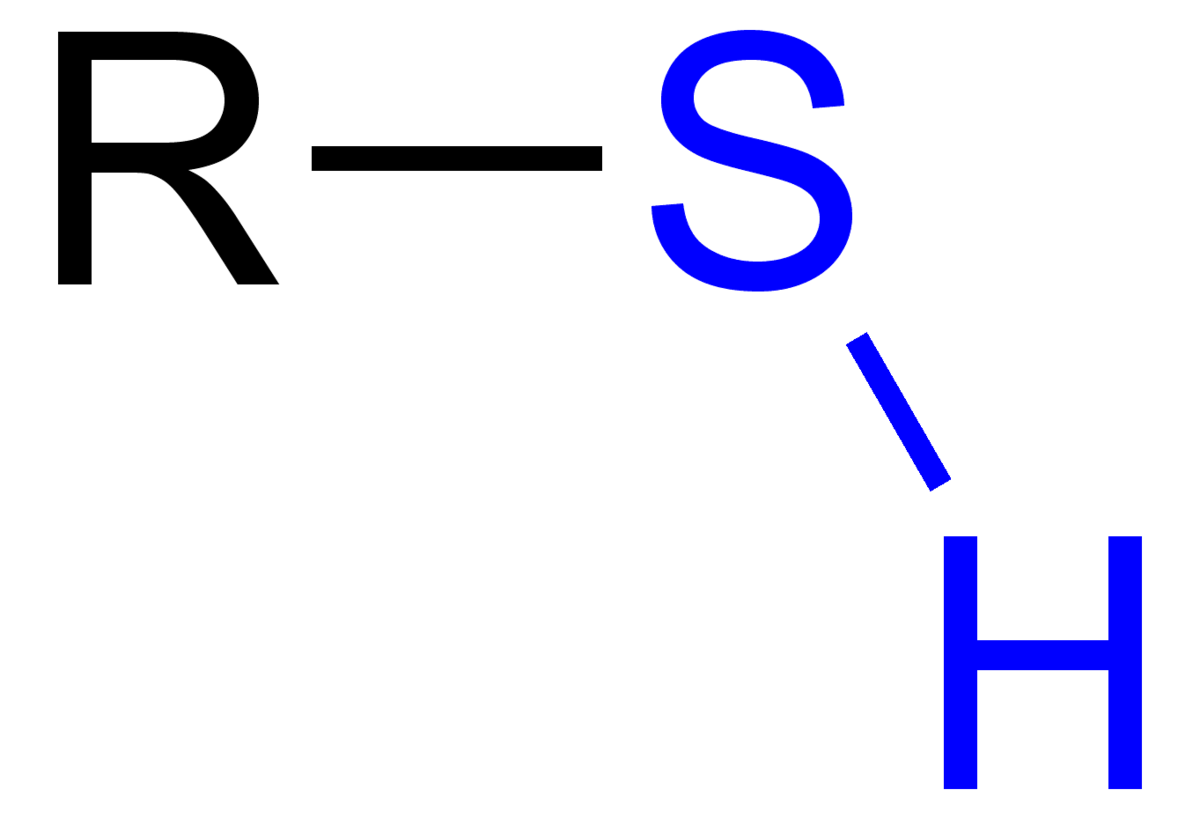
Sulfhydryl
-SH
Weakly Polar = Weakly Hydrophilic
Neutral
Used in: Protein structures
Ex: Cysetine
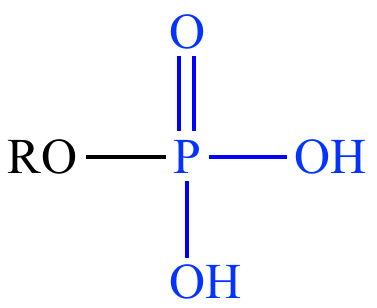
Phosphate
-PO4H2
Charged
Acidic
Polar = Hydrophilic
Phospholipids & Nucleic Acids
Ex: Ethanol
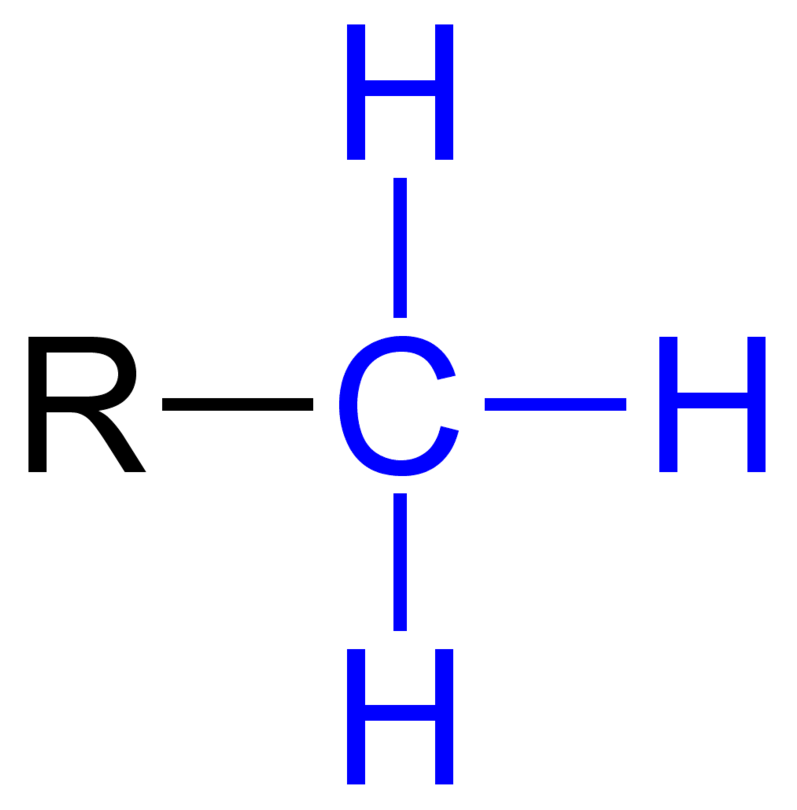
Methyl
-CH3
Nonpolar = Hydrophobic
Neutral
Used in: gene expression
Ex: 3-Methyl cytosine
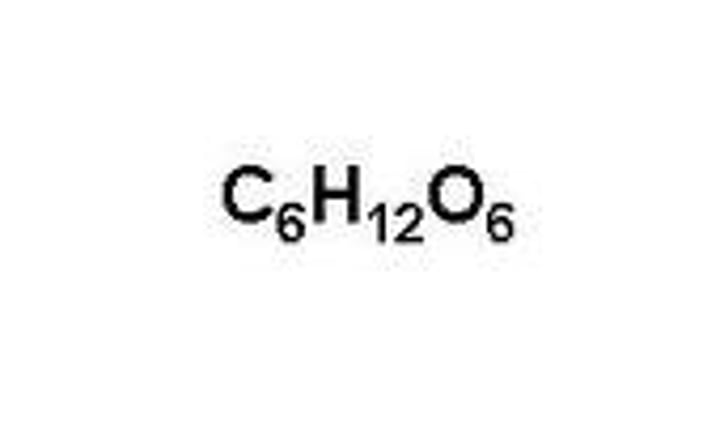
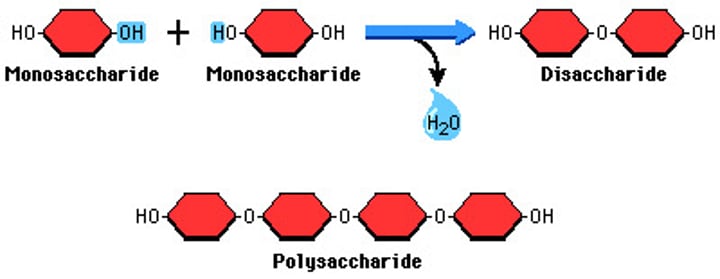
Carbohydrates
• CH2O
• Monomers end in “-ose”
• Very Polar = Very Hydrophilic
• Carbonyl Group
• Monosacc + Monosacc = Glysodic Linkage
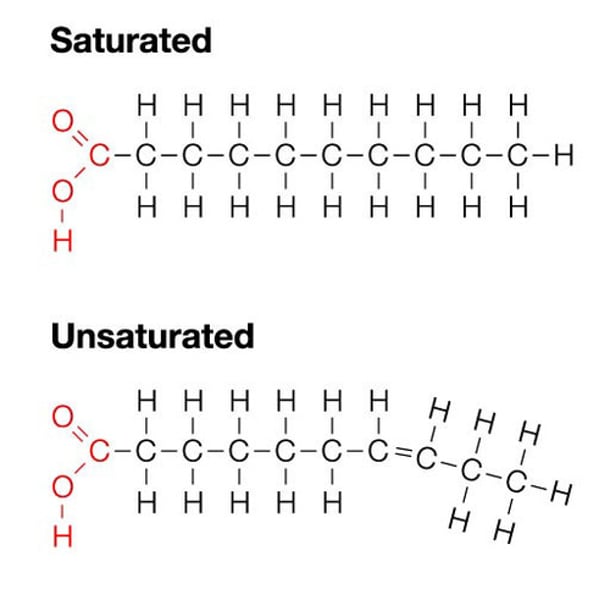
Lipids
• Glycerol
• Nonpolar = Hydrophobic
• Saturated & Unsaturated
• Lipid + Lipid = Ester Linkage
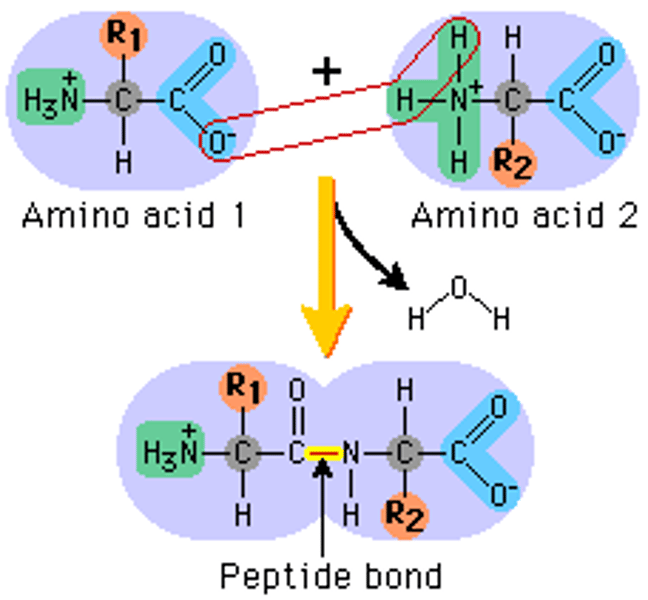
Proteins
• Primary
Linear
• Secondary
Hydrogen bonds btw close amino acids
• Tertiary
Complex, 3D
• Quarternary
Several polypeptide chains
Nucleic Acids
• DNA & RNA
•Transmits hereditary info
• Linked by covalent bonds (Phosphodiesters)
•Nucleotides = Monomer
Big → Small
Hydrolysis
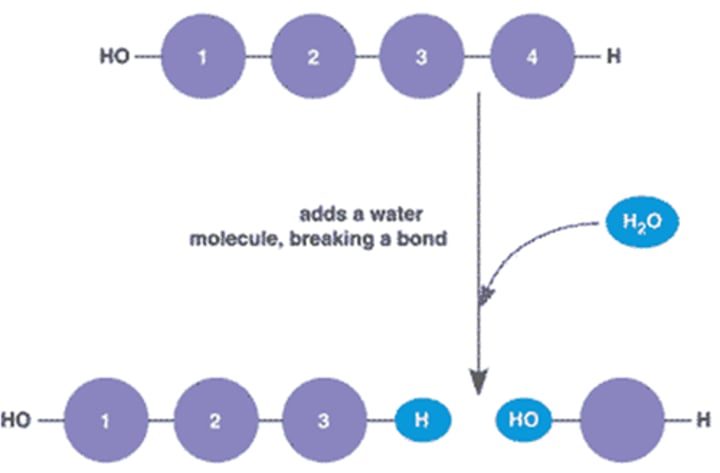
Small → Big
Dehydration
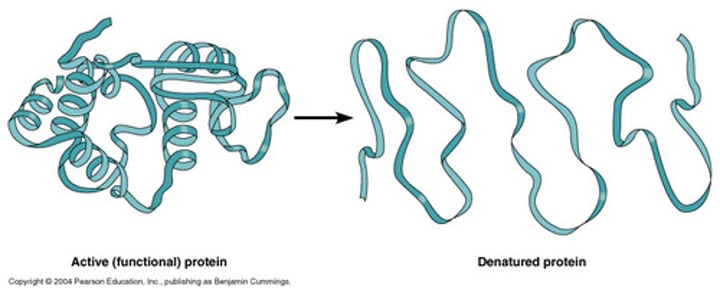
Denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or other factor