Exam 2 PHS study guide
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
English
Based off of body parts, units, not systematically related
Metric system
Based off of seven base units, all other units derived from these (nature)
Four fundamental properties
Length, time, mass, charge
Metric prefixes
Represent small and large amounts by factors of 10
Density
How much matters packed into a given volume
Mass
The fundamental quantity matter that makes up an object
Volume
How much space something takes up
General scientific activity
Collect observations, develop, explanations, and test, explanations
Atomic number
number of protons
Atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
Isotopes
Many variations of the same elements same number of protons but different numbers neutrons
SI base units
meter (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), mole (mol), candela (cd)
Quantum mechanics
Explains about wave, particle, duality, quantize, energy, explains what classical physics cannot, i.e. black body radiation
Mole
Avogadro's number 6.02x10^23
Quantitative use of equations
Molecular use of reactants and products. Mole ratios of reactants and products. Mass ratios of reactants and products.
Nomenclature rules ionic
1) Write symbol for positive ion first followed by negative ion symbol
2) assign subscripts to assure compound is electrically neutral
Nomenclature rules covalent
1) First element in formula named first with number indicated by Greek prefix
2) stem name of second element next Greek prefix for number ending in ied
How to read the periodic table
Each row is a period. Each vertical line is a family. The left side of the table is metals where the right side is not metals.
Chemistry
The study of matter and the changes undergoes
States of matter
Solid liquid gas aqueous
(s)
Solid
(l)
Liquid
like dissolves like
polar dissolves polar, nonpolar dissolves nonpolar
(g)
Gas
(aq)
aqueous
Monoatomic
One
Diatomic
Two
Triatomic
Three
Valance electrons
Outer electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom
Ionic bond
Electrons are given up to foreign either plus or minus ionic bond electrons are transferred
Covalent bond
Electrons are sharing, typically between nonmetals the right side of the periodic table
Empirical
Ionic in the simplest whole number
Molecular
Covalent, actual number in a compound
Formula weight
Number of atomic weight of atoms in a chemical formula
Percent composition of compounds
Finding the mass percent of an individual element from the weight
Balance equations
Change coefficients
Combustion reaction
A hydrocarbon in the presence of oxygen reacts to carbon dioxide and water
Combination reaction
A + B --> AB synthesis reaction in which two or more substance combined to form a single compound
Decomposition reaction
AB --> A + B a compound is broken down into simpler functions
Replacement reaction
An atom or polyatomic ion is replaced in a compound by a different atom or a polyatomic ion X+AB —-> XB+A
Ion exchange reaction
AX + BY --> AY + BX a reaction that takes place when the ions are one compounds interact with ions of another compound
Properties of water
1) universal solvent
2) solid phase less than than liquid
3) high specific heat
4)high latent heat of vaporization
5) all results from waters chemical structure
Water structure
Polar covalent bonding, oxygen negative center hydrogen two ends positive
Solution
Components of a solution solvent and solute
Solvent
Present in larger amounts
Solute
Components is often in solvent
Solubility
Concentration of saturated solution
Saturation
Solute dissolving limit
Miscible
Can mix an any proportions without separating
Immiscible
Do not mix
Soap
Has properties of both polar and nonpolar
Concentration ratios
Relative amounts of solute and solvent
Ppm
parts per million
ppb
parts per billion
percent by volume
V solute/ m solvent times 100% = % solute
Molarity
Moles of solute in 1 L of solution
Molarity equation
moles of solute/1L of solution
Concentrated
large amount of solute
Dilute
small amount of solute
Electrolytes
Solutions of bionic substances, conduct electricity
Non-electrolytes
Non-conductors sugar and alcohol solution
Ionization
Forming ions from molecules may occur as polar molecules
Normal Boiling point
Temperature where vapor pressure equals average sea level atmospheric pressure
Freezing point
Kinetic energy molecules reduce enough to allow crystallization
Properties of acids
Proton donor, change in color, neutralize bases
Properties of basis
Proton acceptor, reverse color, slippery on skin
PH scale
Pure water weekly ionized seven heaven, neutral, acid below seven, alkine above seven
Percent by weight
m solute / m solvent times 100% = solute
Hydroxide
OH-
Nitrite
NO2 charge -1
Nitrate
NO3 charge -1
Carbonate
CO3 charge -2
Sulfate
SO4 charge -2
Phosphate
PO4 charge -3
law of conservation of mass
atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions
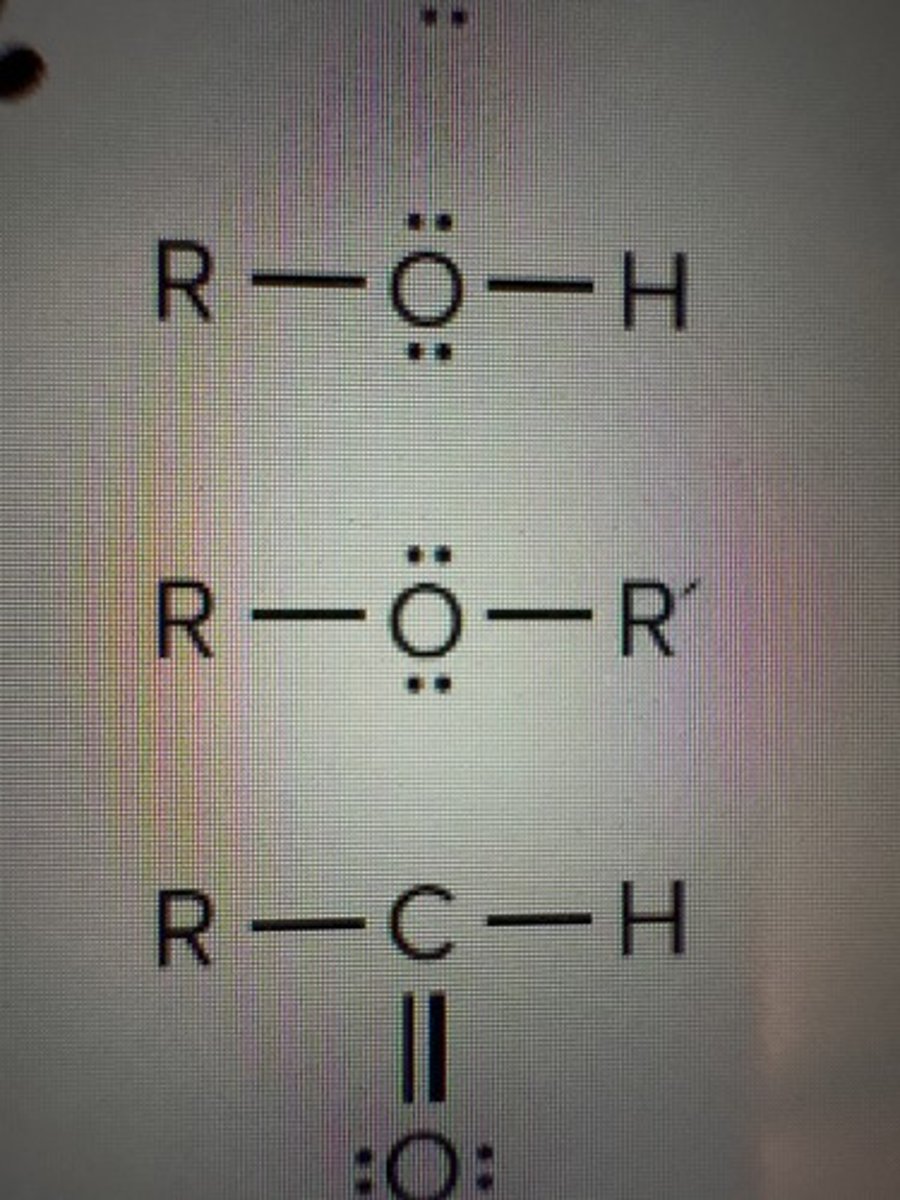
Functional groups
Responsible for chemical properties of organic compounds
Ketone
RCOR
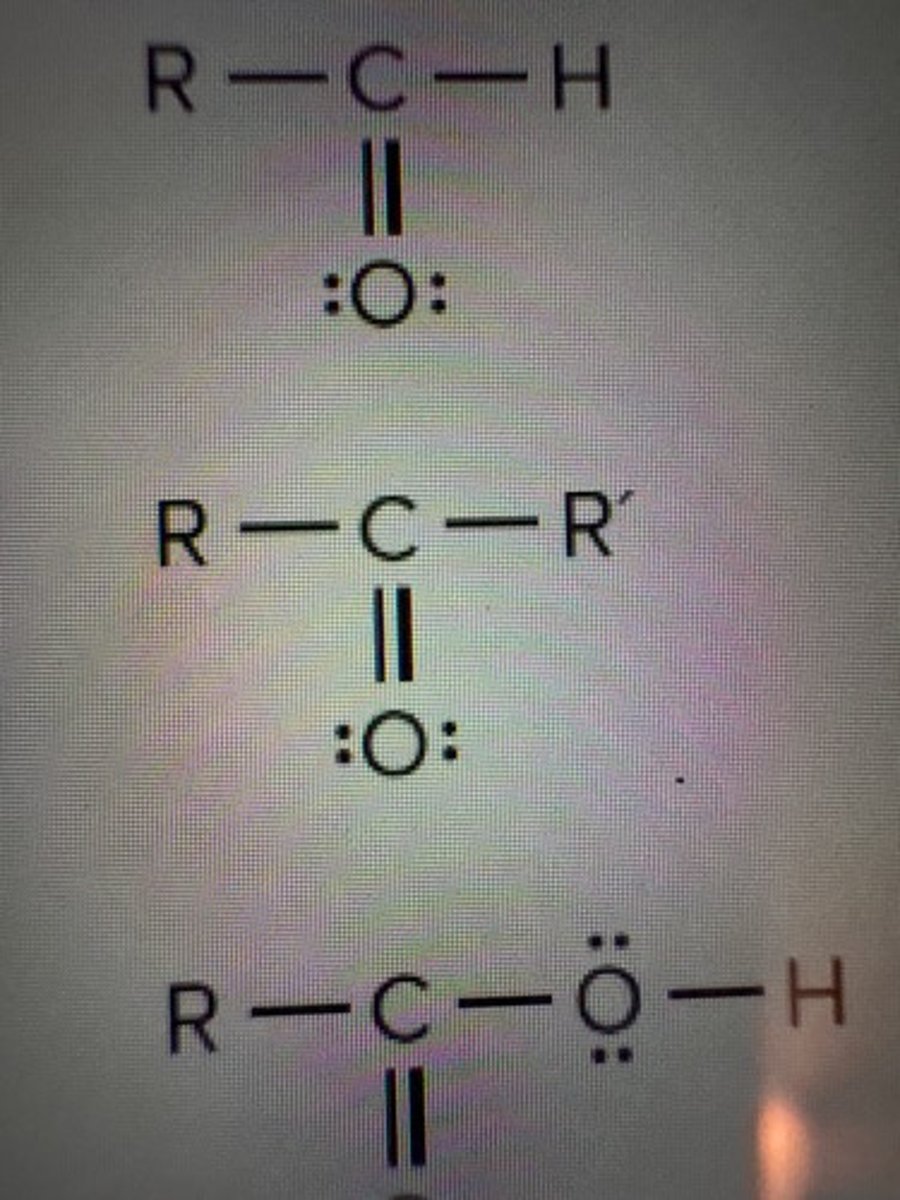
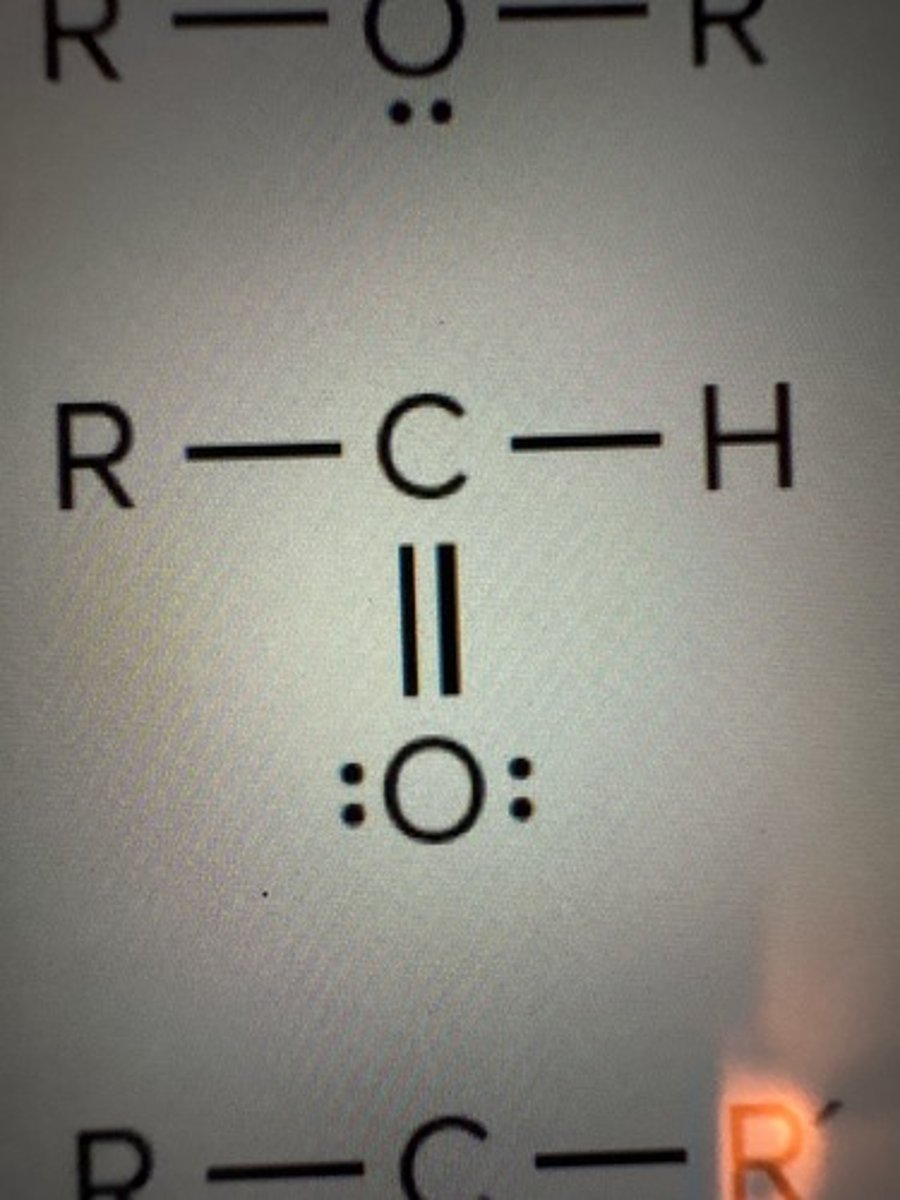
Aldehydes
RCHO
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
Saturated
All carbons are bonded to max of four atoms
Unsaturated
All carbons are bonded to two or three atoms
Alkanes
a hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds (CnH2n+2)
Alkenes
Hydrocarbons with a double carbon carbon bond (CnH2n)
Alkynes
Hydrocarbons with a triple carbon carbon bond (CnH2n-2)
Ethers
ROR