RBC and WBC abnormalities
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
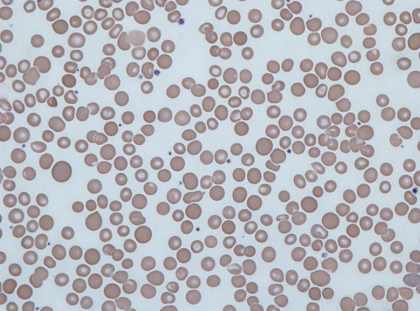
Anisocytosis - Variation in size (smaller / larger)
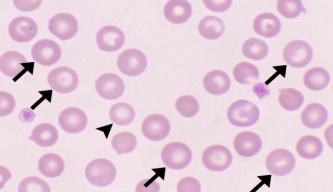
Macrocyte - Large red cell
Microcyte - Small red cell
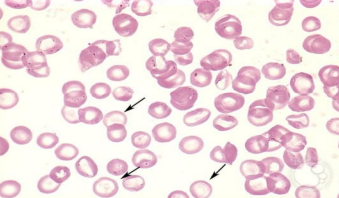
Hypochromic - Extremely pale looking central pallor RBCs (less Hb)
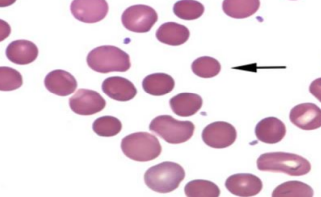
Hyperchromic - Very dark looking RBC (rarely found)
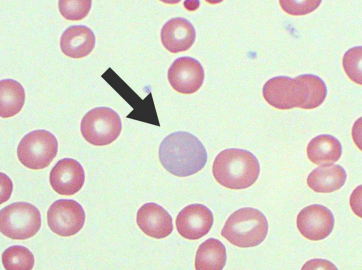
Polychromasia - Grayish blue reticulocytes. This happens when red blood cells are immature because they were released too early from the bone marrow.• Can be found in:
▫ Acute and Chronic Haemorrhage
▫ Haemolysis
▫ Effective treatment for anaemia
▫ High altitude
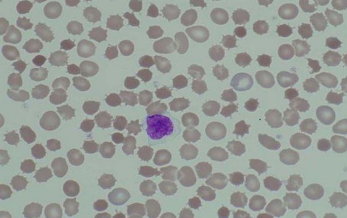
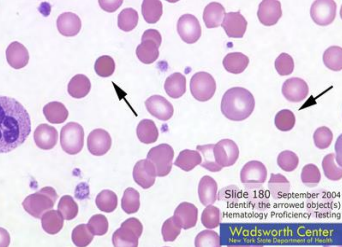
• Poikilocytosis - Variations in the shape of cells
Spherocytes - Spheres (not biconcave) under a blood film with no central pallor, increased haemoglobin content.
Can be found in hereditary spherocytosis, haemolytic anaemia
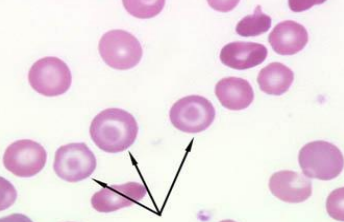
Codocytes (Target Cells) - Present with hyperchromic bull eyes surrounded by a halo of pallor.
Can be found in haemoglobinopathies, thalassemia
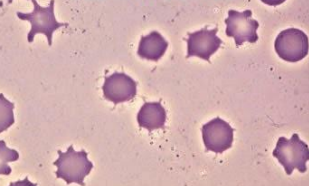
Acanthocytes (Spur Cells) - spiked cell membrane, with irregular thorny projections that vary in width, length and number.
Can be found in liver disease, reaction to a splenectomy, etc.
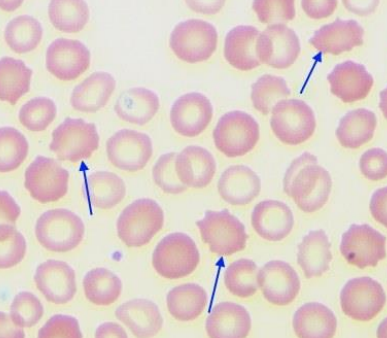
Echinocytes (Burr Cells) - short, blunt, evenly spaced projections. abnormal membrane, that has thorny projections.
Can be found in renal and liver disease; and may be caused by poor fixation and high humidity in the laboratory ambience.
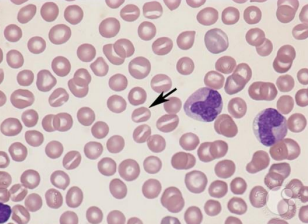
Stomatocytes (Mouth Cells) - Instead of having a central pallor, cells possess a central “slit” of pallor. Their appearance are mostly due to increased red cell permeability, resulting in increased volume.
Can be found in acute alcoholism, liver & gallbladder diseases, etc.
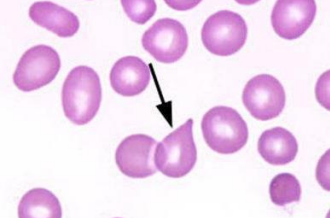
Dacrocytes (Teardrop Cells) - Shaped like teardrops. Occurs when the red cells stretch out in order to navigate its way into the periphery or as a result of stretching from the pitting action of the spleen.
Can be found in myelofibrosis, etc
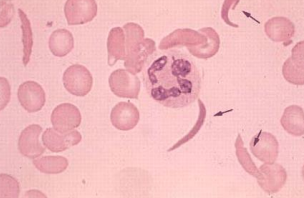
Drepanocytes (Sickle Cells) - The red blood cell folds in on itself, producing its unique shape - the blade of a sickle, or a crescent.
Can be found in sickle cell disease.
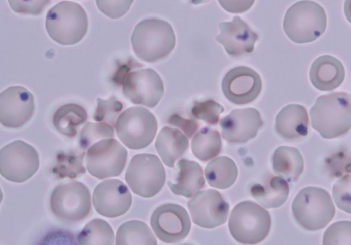
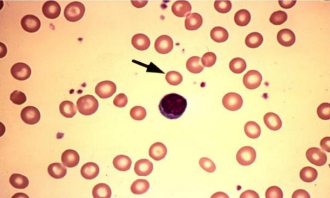
Heinz bodies - Presence of purple-blue inclusions which are composed of denatured precipitated haemoglobin.
Can be found in thalassemia, G6PD deficiency, haemolytic anaemia, etc.
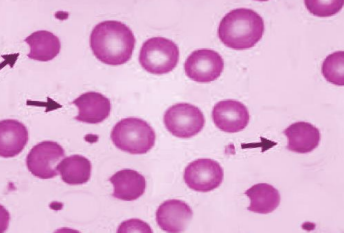
Degmacytes (Bite Cells) - One or more semi-circular portions removed from the cell margin. These “bites” result from the removal of denatured haemoglobin by macrophages in the spleen.
Can be found in G6PD deficiency.
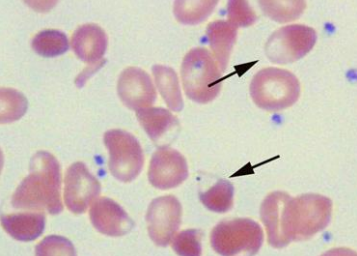
Blister Cells - Red blood cells originally containing inclusions are “pitted” or removed by macrophages in the spleen. Blister cells have a similar appearance to bite cells, except that there is a residual rim of RBC cytoplasm. Can be found in G6PD deficiency
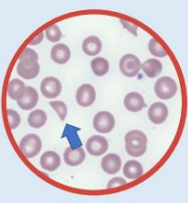
Helmet cells schistocytes - One single amputated zone with a straight border and sharp angulated edges.
Can occur due to mechanical damage in the circulation / mechanical heart valves / receiving dialysis / RBC abnormalities such as acquired and inherited RBC disorders.
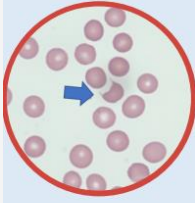
Keratocyte (Horn cell) schistocytes - Pair of spicules separated by a semicircular concave segment of membrane. (morphologically identical to bite cells, consisting of a curved bite-shaped peripheral defect in their surface)
Can occur due to mechanical damage in the circulation / mechanical heart valves / receiving dialysis / RBC abnormalities such as acquired and inherited RBC disorders.
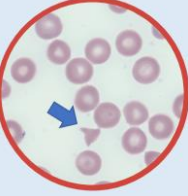
Triangle cell schistocytes - Small fragments with sharp angles or spines.
Can occur due to mechanical damage in the circulation / mechanical heart valves / receiving dialysis / RBC abnormalities such as acquired and inherited RBC disorders.
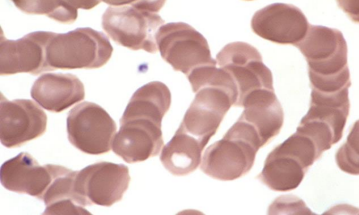
Rouleaux (Stacked Coin) ▫ Rouleaux is when RBC's are arranged in rows like "stacked coins" due to an increase in proteins.
Can be found in multiple myeloma.
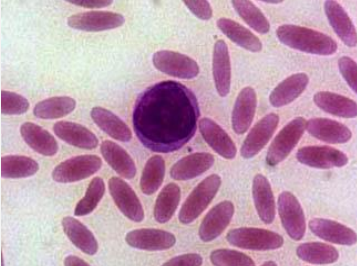
Elliptocytes/Ovalocytes ▫ Cigar-shaped erythrocytes.
Found in hereditary elliptocytosis, etc.
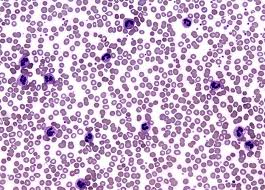
Neutrophilia ▫ Increased amount of neutrophils. Can be found in infections, inflammation, etc.
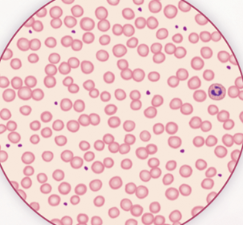
Neutropenia ▫ Lower levels of neutrophils. Can be found after chemotherapy, infections, autoimmune conditions, etc.
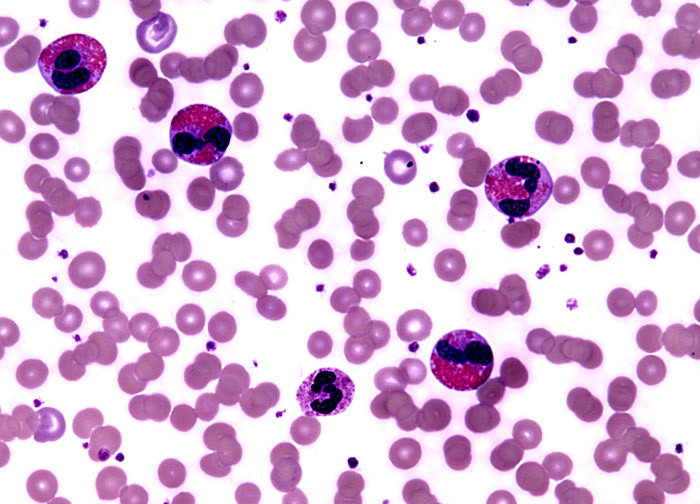
Eosinophilia ▫ Increased amounts of eosinophils. Can be found in presence of parasites, allergies or cancer.
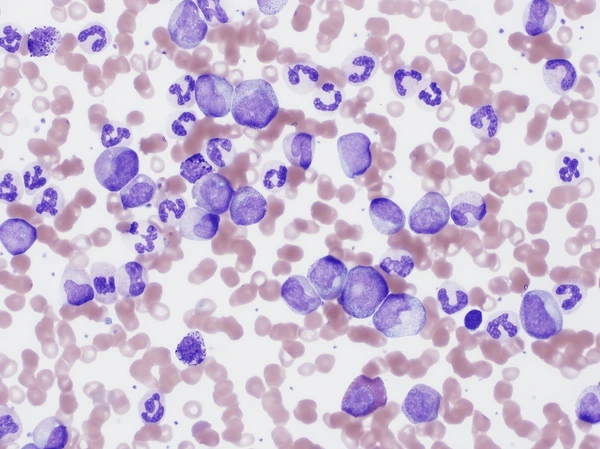
Basophilia - Increased amounts of basophils. Can be found in chronic myeloid leukaemia, hypersensitivity, etc.
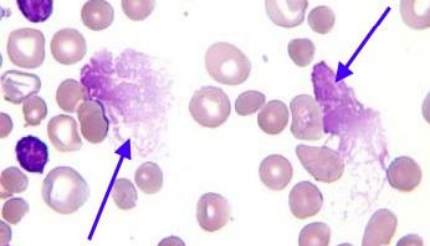
Basket Cell or Smudge Cell: ▫ Basket cells, or smudge cells, are formed due to fragile cells, typically lymphocytes, that are easily damaged during the slide preparation. Can be found in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL).
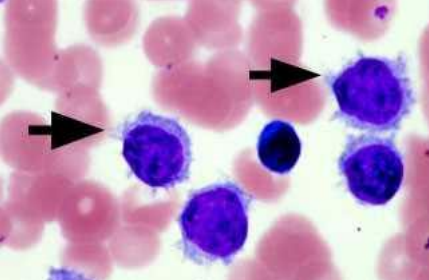
Hairy cell ▫ These excess B cells are abnormal and look "hairy" under a microscope. Can be found in Hairy Cell Leukaemia
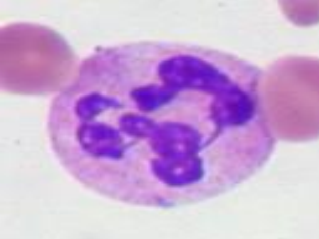
Hypersegmented neutrophils: > 5 lobed neutrophil ▫ These are neutrophils with 6+ nuclear lobes. Can be found in megaloblastic anaemia
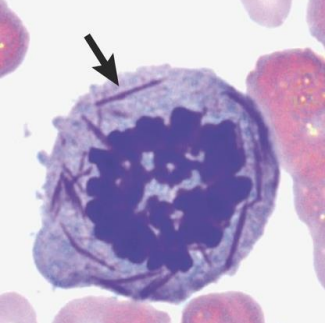
Auer rods ▫ Auer rods are red staining, needle-like bodies seen in the cytoplasm of myeloblasts. They are cytoplasmic inclusions which result from an abnormal fusion of the granules. Can be found in acute myeloid leukaemia's.
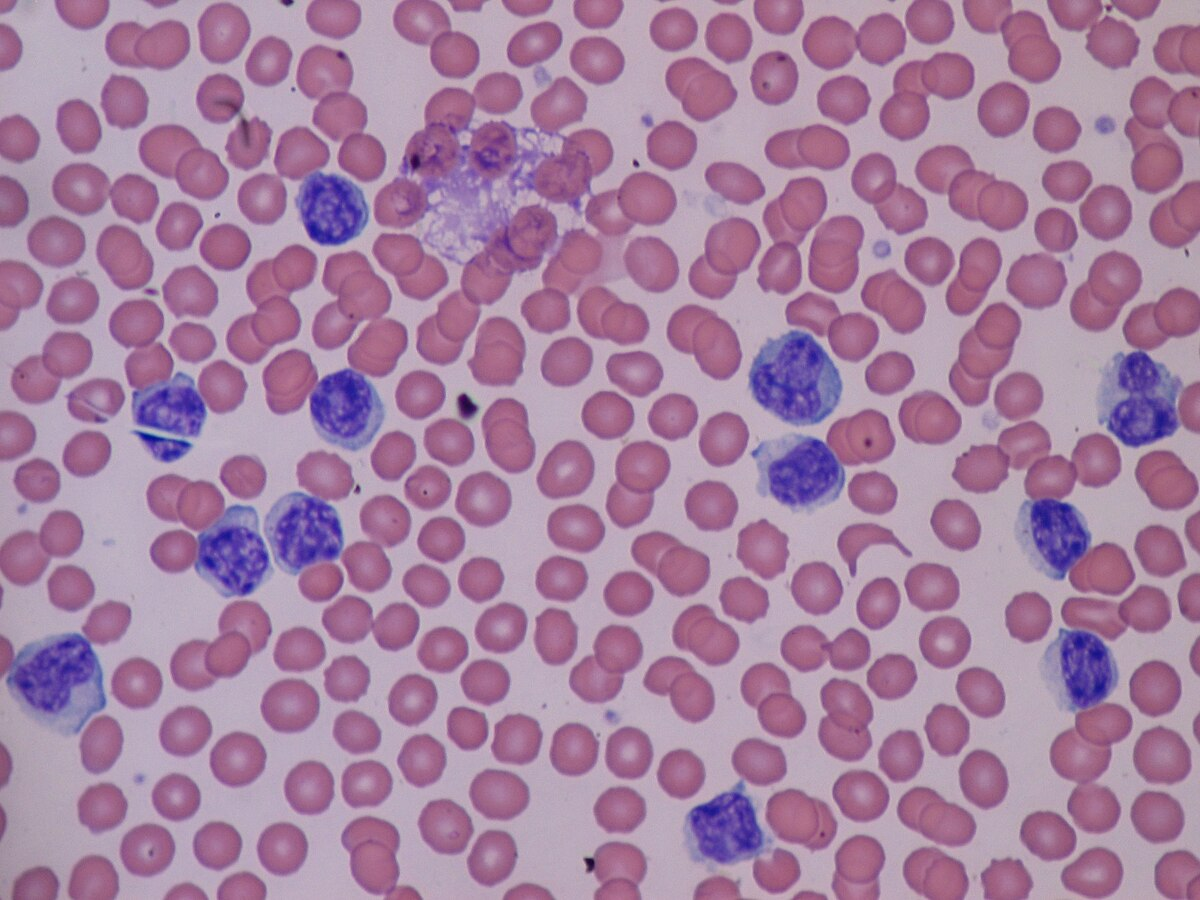
Lymphocytosis ▫ Increased amount of lymphocytes. Can be found in infections, chronic inflammation, etc.
phiia
increase in that type of cell/blood levels
osis
increase in that type of cell/blood levels or used to refer to a disease process
penia
decrease in blood levels or that type of cell