Human Resource Management Lecture #3 Managing Organizational Change
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Internal Drivers
Performance
Innovation
Human resources
Participation
Leadership
Conflict
Safety
External Drivers
Social
Technological
Economic
Political
Legal
Ecological
Sources of individual resistance to change
Economics
Security
Habit
Selective perception
Loss of freedom or inconvenience
Fear of the unknown
Sources of organizational resistance to change
Organizational culture
Structural inertia
Existing contracts or agreements
Established resource allocations
Loss of expertise
Threats to power relationships
Lewin’s theory of planned change
Change is a social process:
Equilibrium
Resistance to change
Managing change involves:
Forcefield analysis
Creating a critical mass
What is Lewin’s theory of Forcefield analysis
A decision-making tool used to analyze and understand the forces that influence a situation or change process.
How to conduct a force field analysis
Define the current situation and the desired situation
Identify all restraining forces
Identify all driving forces
Evaluate forces and assign a score
Design a plan of action
Driving forces
Positive forces for change
Restraining forces
Obstacles for change
What is Lewin’s theory of Planned Change
Focuses on the process of change itself, outlining how organizations or individuals can transition from a current state to a desired future state.
Three stages of Lewin’s theory of Planned Change
Unfreezing: thaw “ways of doing”
Increase driving forces, reduce resisting forces or combination of both
Movement: modify behaviors by seeing “organization as a system of learning”
Refreezing: embed changes to avoid regression by positive reinforcement, by coaching, by revising rules governing behavior
Critical mass
The point at which enough people within an organization or group have adopted or supported a change
Consultants’s Standard
Same as Lewin’s Theory of Planned Change, but broken down in 8 steps instead of 3.
Unfreeze
Establish a sense of urgency
Move
Guiding coalition
Change vision
Communicate the change vision
Empower others to take action
Generate short time wins
Freeze
Consolidate gains, promote change
Institutionalise new approaches
What are Dynamic Capabilities
Resources that allow organizations to seize opportunities when they come along.
Dynamic Capabilities: Adaptive Capability
Flexible adjust of business priorities, management and organization structures
Dynamic Capabilities: Absorptive Capability
Bring in and use new information and knowledge
Dynamic Capabilities: Innovative Capability
Develop and create new products and markets
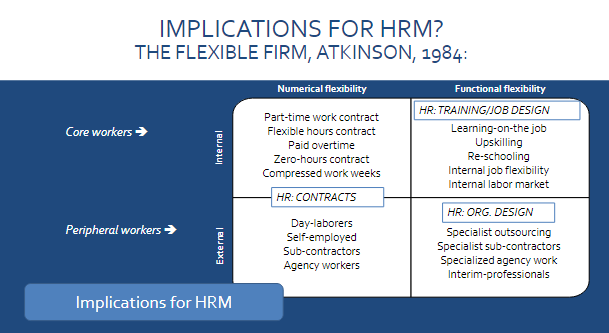
Adaptive capability: The Flexible Firm Model
The flexible firm: The speed with which an organization can adjust its workforce
Numerical flexibility: Ability of a firm to adjust the number of employees based on demand
Functional flexibility: Ability of a firm to shift employees into different roles or tasks
Absorptive capability: Absorptive Capacity
Absorptive Capacity = The capacity of the organization to access information from outside the organization, bring it in the organization, learn from it and convert that learning into new knowledge.
Aims at knowledge transfer and strong social ties within and outside the organization
Innovative Capability: Exploitation and Exploration
Innovation Capability = Management systems that encourage knowledge creation and proactive behavior at all levels of the organization, and a strategy oriented towards innovation.
Exploitation = Optimizing existing capabilities and existing expertise
Exploration = Learning new things, taking risks
Succesful innovation is not about radical shifts and doing something completely different, but about the balance between exploration and exploitation.
How do you build dynamic capabilities?
Dynamic capabilities can be developed by human resource maangement, by investing in workforce scalability, in a learning organization, and by balancing exploration/exploitation for innovation.
What is a career
Work experiences a person has throughout their life, which can include changes in jobs or breaks between jobs, from the time they start working until they retire
Career succes
Succesful careers are important to individuals, organizations and society because they comprise wealth, good performance and low unemployment costs.
Two ways to define career success
Objective measures
Salary, promotions, job titles
Subjective measures
Personal satisfaction, purpose, work-life balance
Contested vs Sponsored Careers: Contested
The most qualified and skilled people win the best careers
Level of education
Networking skills
Contested vs Sponsored Careers: Sponsored
Those with the right connections and who receive help from influential others win the best careers
Access to career sponsorship
Opportunities for training and development
Protean careers
Objective career success replace by subjective career success
Personal sense of fulfillment is more valued than money
More equal relationship between employers and employees
Autonomy and flexibility
The freedom to choose my own career path is one of my most important values
People make their careers more self-directed and flexible (for example: freelancer)
Employability
Employability = Being employable: being able to find a job, being able to keep it, and being able to obtain new employment if needed
Employability Radius
The range of jobs and tasks that one is able to perform
Employability competences
A set of resources that helps individuals broaden their employability radius
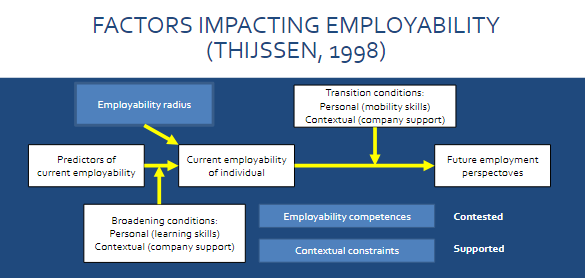
Factors impacting employability
Employability radius
Employability Competencies
Contextual Constraints
External factors that may limit employability (economic downturns, industry-specific changes)
Predictors of current employability
Current employability of individual
Broadening conditions: Personal, contextual
enhancing skills and providing growth opportunities
Transition conditions: Personal, contextual
how easily an individual can shift between roles or adapt to new job markets
Dealing with change
Organizations need dynamic capabilities
Employees need to maintain their employability
Flexicurity theory
Concept that aims to strike a balance between flexibility for employers and security for employees.
Employment Transition Support Policies:
Employment law allows easy hiring and firing
Guarantee of income in transition periods (social welfare/unemployment)
Support for career transitions (job training, networking, funds)
Educational policies, stimulate lifelong learning
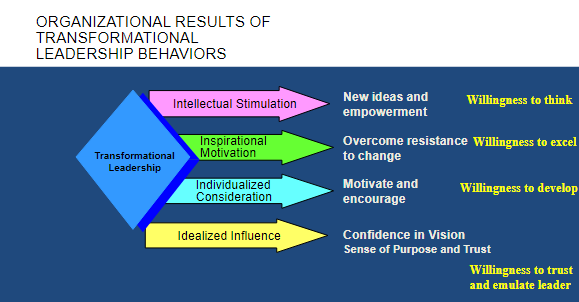
Organizational results of transformational leadership behaviors