Bio 2 Check In
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all check ins expect 6
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a general transfer?
\
a. transcription b. translation c. reverse transcription d. DNA replication
\
a. transcription b. translation c. reverse transcription d. DNA replication
c. reverse transcription
2
New cards
Imagine the gene that encodes primase acquires a mutation that makes it produce non-functional proteins. What problem could this cause for the cell?
a. this will not cause a problem for the cell
b. translation cannot occur
c. DNA replication cannot occur
d. transcription cannot occur
a. this will not cause a problem for the cell
b. translation cannot occur
c. DNA replication cannot occur
d. transcription cannot occur
c. DNA replication cant occur
3
New cards
At the start of translation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the
a. operator
b. terminator.
c. recognition site.
d. promoter.
e. consensus sequence.
a. operator
b. terminator.
c. recognition site.
d. promoter.
e. consensus sequence.
c. recognition site
4
New cards
mRNA splicing...
a. occurs during transcription, and enables RNA polymerase to jump over intronic gene regions
b. is the name for the transcript elongation process as it occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryote.
c. occurs in the cytoplasm.
d. serves to excise introns and attach exons together.
e. serves to excise exons and attach introns together.
a. occurs during transcription, and enables RNA polymerase to jump over intronic gene regions
b. is the name for the transcript elongation process as it occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryote.
c. occurs in the cytoplasm.
d. serves to excise introns and attach exons together.
e. serves to excise exons and attach introns together.
d. serves to excise introns and attach exons together.
5
New cards
Imagine a gene that has a large deletion near the end of one of its introns. Which of the following is a likely result of this mutation?
\
a. The mature mRNA is the right length because snRNPs bind to consensus sequences in the exons.
b. The resulting polypeptide is unaffected because introns are not part of the coding region.
c. Translation does not occur because the small ribosomal subunit could not bind to the right place on the mRNA.
d. The mature mRNA is too long because a consensus sequence is missing or partially missing, leading to incorrect splicing.
e. Transcription does not occur because the RNA polymerase could not bind to the promoter.
\
a. The mature mRNA is the right length because snRNPs bind to consensus sequences in the exons.
b. The resulting polypeptide is unaffected because introns are not part of the coding region.
c. Translation does not occur because the small ribosomal subunit could not bind to the right place on the mRNA.
d. The mature mRNA is too long because a consensus sequence is missing or partially missing, leading to incorrect splicing.
e. Transcription does not occur because the RNA polymerase could not bind to the promoter.
d. the mature mRNA is too long bc a consensus sequence is missing or partially missing, leading to incorrect splicing
6
New cards
Imagine a gene has a single transversion in the binding region of its promoter. Which of the following is a likely result of this mutation?
a. The mRNA cannot be translated because the start codon is missing.
b. The gene product is unchanged, but is produced at lower than normal levels.
c. The mRNA cannot be translated because the ribosome cannot recognize where to bind.
d. The gene product has a different amino acid sequence than the product of the wild type (non-mutant) gene.
a. The mRNA cannot be translated because the start codon is missing.
b. The gene product is unchanged, but is produced at lower than normal levels.
c. The mRNA cannot be translated because the ribosome cannot recognize where to bind.
d. The gene product has a different amino acid sequence than the product of the wild type (non-mutant) gene.
b. the gene product is unchanged, but is produced at lower than normal levels
7
New cards
Transcription and translation occur at the same time in ______
a. the ribosome
b. eukaryotes
c. prokaryotes
d. the nucleus
a. the ribosome
b. eukaryotes
c. prokaryotes
d. the nucleus
c. prokaryotes
8
New cards
After binding charged tRNA to an empty A-site of a ribosome that has its P-site occupied, the next step in the cycle of translation events is
a. nucleotide ligation
b. binding of polymerase to the promoter.
c. release of the tRNA occupying the P-site.
d. peptide bond formation.
a. nucleotide ligation
b. binding of polymerase to the promoter.
c. release of the tRNA occupying the P-site.
d. peptide bond formation.
d. peptide bond formation
9
New cards
An anticodon is part of...
a. aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
b. mRNA.
c. DNA.
d. a ribosome.
e. tRNA.
a. aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
b. mRNA.
c. DNA.
d. a ribosome.
e. tRNA.
e. tRNA
10
New cards
At the end of translation, termination is caused
\n a. by the mRNA detaching from the ribosome.
b. by a release factor entering the P site.
c. by the addition of a final amino acid.
d. by the large and small ribosomal subunits separating.
e. by a release factor binding to the A site.
\n a. by the mRNA detaching from the ribosome.
b. by a release factor entering the P site.
c. by the addition of a final amino acid.
d. by the large and small ribosomal subunits separating.
e. by a release factor binding to the A site.
e. by a release factor binding to the A site.
11
New cards
In the context of the genetic code, the term "redundancy" refers to the concept that
a. there are many, many codons.
b. there is only one codon for methionine.
c. there are several codons for most amino acids.
d. there is only one codon for most amino acids.
a. there are many, many codons.
b. there is only one codon for methionine.
c. there are several codons for most amino acids.
d. there is only one codon for most amino acids.
c. there are several codons for most amino acids.
12
New cards
Peptide bond formation is catalyzed by
a. RNA polymerase.
b. aminoacyl-tRNA.
c. ribosomal RNA.
d. aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
a. RNA polymerase.
b. aminoacyl-tRNA.
c. ribosomal RNA.
d. aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
c. ribosomal RNA
13
New cards
Which statement is FALSE?
a. Prokaryotes, in general, lack intervening sequences such as introns which appear in eukaryotic genomes.
b. Eukaryotic mRNA is modified at both ends, while prokaryotic mRNA is not.
c. Transcription and translation are separated in time and space in prokaryotes.
d. Eukaryotes carry out mRNA processing while prokaryotes do not.
a. Prokaryotes, in general, lack intervening sequences such as introns which appear in eukaryotic genomes.
b. Eukaryotic mRNA is modified at both ends, while prokaryotic mRNA is not.
c. Transcription and translation are separated in time and space in prokaryotes.
d. Eukaryotes carry out mRNA processing while prokaryotes do not.
c. Transcription and translation are separated in time and space in prokaryotes.
14
New cards
In the image above, what does the label "1" correspond to?
\n a. 5' end of rRNA
b. 3' end of mRNA
c. 3' end of rRNA
d. 5' end of DNA
e. 5' end of mRNA
\n a. 5' end of rRNA
b. 3' end of mRNA
c. 3' end of rRNA
d. 5' end of DNA
e. 5' end of mRNA
e. 5' end of mRNA
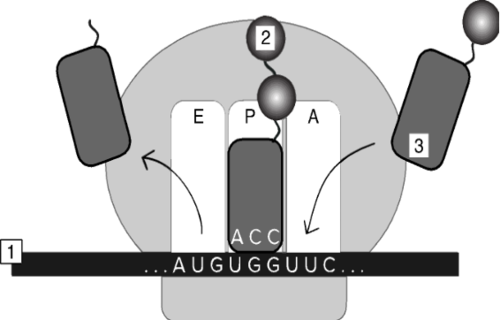
15
New cards
In the image above, what does the label "2" correspond to?
a. proline
b. phenylalanine
c. tryptophan
d. methionine
e. lysine
a. proline
b. phenylalanine
c. tryptophan
d. methionine
e. lysine
d. methionine
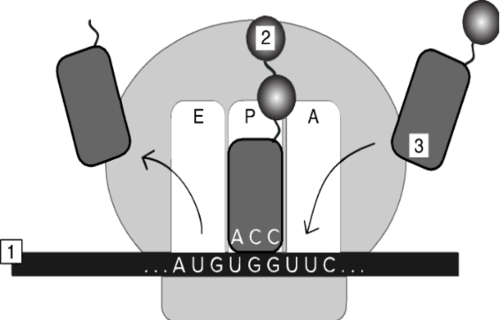
16
New cards
In the image above, what does the label "3" correspond to?
a. UAC
b. AAC
c. TTG
d. UUC
e. AAG
a. UAC
b. AAC
c. TTG
d. UUC
e. AAG
e. AAG
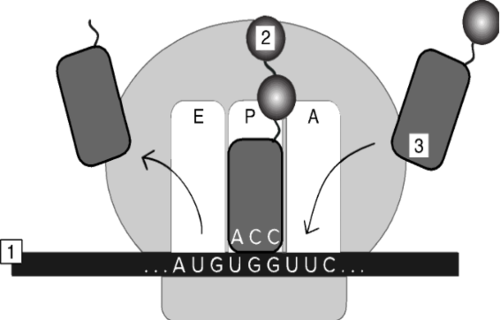
17
New cards
E coli were grown in a 14N (light) medium, and then transferred into a 15N (heavy) medium. After two generations of cell replication in the heavy medium, DNA was extracted and centrifuged to separate strands out by weight. Which of the tubes shown in this image would you expect to see as a result?
a.
b.
c.
a.
b.
c.
C
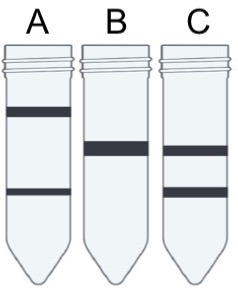
18
New cards
In the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which observation ruled out the conservative model of DNA replication?
a. No completely “heavy” DNA was observed after the first round of replication.
b. Three different DNA densities were observed after a single round of replication.
c. Completely “heavy” DNA was observed throughout the experiment.
d. The product that accumulated after two rounds of replication was all “heavy.”
a. No completely “heavy” DNA was observed after the first round of replication.
b. Three different DNA densities were observed after a single round of replication.
c. Completely “heavy” DNA was observed throughout the experiment.
d. The product that accumulated after two rounds of replication was all “heavy.”
a. No completely "heavy" DNA was observed after the first round of replication.
19
New cards
If I start with 9 copies of my target DNA, how many PCR cycles are required to produce at least 4 billion copies? (Round your answer up to the next whole cycle.)
a. 28
b. 10
c. 29
d. 31
a. 28
b. 10
c. 29
d. 31
c. 29
20
New cards
If I start with 73 copies of my target sequence and run 31 PCR cycles, how many copies will result?
\n a. 1.65 \* 10^5 \n b. 7.01 \* 10^4
c. 1.57 \* 10^11
d. 2.93 \* 10^23
\n a. 1.65 \* 10^5 \n b. 7.01 \* 10^4
c. 1.57 \* 10^11
d. 2.93 \* 10^23
c. 1.57 \* 10^11
21
New cards
During DNA replication, the daughter strand that is synthesized in many small sections interspersed by RNA primers is called the ________ strand.
a. parent
b. lagging
c. leading
d. template
a. parent
b. lagging
c. leading
d. template
b. lagging
22
New cards
Which of the following molecules is NOT present during replication inside of a cell?
a. DNA polymerase III
b. DNA primer
c. RNA primer
d. primase
e. DNA polymerase I
a. DNA polymerase III
b. DNA primer
c. RNA primer
d. primase
e. DNA polymerase I
b. DNA primer
23
New cards
Which of the following mechanisms is/are able to correct mistakes made by DNA polymerase? (select ALL correct answers)
a. proofreading
b. excision repair
c. mismatch repair
d. reverse transcription
a. proofreading
b. excision repair
c. mismatch repair
d. reverse transcription
a, b, c. proofreading, excision repair, mismatch repair
24
New cards
During DNA replication, new bases are added to the ____ end of the new strand.
a. 3’
b. 5’
a. 3’
b. 5’
a. 3'
25
New cards
The replication complex moves along the parent strand in the _____ direction.
a. 3’
b. 5’
a. 3’
b. 5’
b. 5'
26
New cards
What molecule is responsible for removing the RNA primers and replacing them with DNA bases?
\n a. DNA polymerase III
b. exonuclease
c. RNA polymerase
d. primase
e. DNA polymerase I
\n a. DNA polymerase III
b. exonuclease
c. RNA polymerase
d. primase
e. DNA polymerase I
e. DNA polymerase I
27
New cards
Okazaki fragments are parts of the
a. leading strand
b. parent strand
c. RNA primer
d. lagging strand
a. leading strand
b. parent strand
c. RNA primer
d. lagging strand
d. lagging strand
28
New cards
Telomeres... (select ALL correct answers)
a. can be extended by telomerase in stem cells b. protect the ends of the chromosomes c. become shorter every time the genome is replicated
a. can be extended by telomerase in stem cells b. protect the ends of the chromosomes c. become shorter every time the genome is replicated
a,b,c
29
New cards
In a cell, DNA replication begins at the
a. end of a chromosome.
b. origin of replication.
c. middle of a DNA sequence.
d. end of each strand of DNA.
a. end of a chromosome.
b. origin of replication.
c. middle of a DNA sequence.
d. end of each strand of DNA.
b. origin of replication
30
New cards
RNA primers are built by
a. RNA polymerase
b. DNA polymerase I
c. primase
d. DNA polymerase III
a. RNA polymerase
b. DNA polymerase I
c. primase
d. DNA polymerase III
c. primase
31
New cards
Adding dideoxycytidine to the growing strand prevents it from lengthening further because
a. it has no phosphate groups on the 5’ carbon.
b. it has no hydroxyl group on the 5’ carbon.
c. it has no hydroxyl group on the 3’ carbon.
a. it has no phosphate groups on the 5’ carbon.
b. it has no hydroxyl group on the 5’ carbon.
c. it has no hydroxyl group on the 3’ carbon.
c. it has no hydroxyl group on the 3' carbon.
32
New cards
A prokaryotic gene with a large deletion mutation in its -10 element
a. will be missing some of the amino acids from the protein it encodes.
b. is likely to be transcribed all the time.
c. is unlikely to be transcribed because sigma factors will prevent RNA polymerase from binding the promoter.
d. is unlikely to be transcribed because RNA polymerase needs to recognize the -10 site in order to bind the promoter.
a. will be missing some of the amino acids from the protein it encodes.
b. is likely to be transcribed all the time.
c. is unlikely to be transcribed because sigma factors will prevent RNA polymerase from binding the promoter.
d. is unlikely to be transcribed because RNA polymerase needs to recognize the -10 site in order to bind the promoter.
d. is unlikely to be transcribed because RNA polymerase needs to recognize the -10 site in order to bind the promoter.
33
New cards
Genes that share a conserved -10 and -35 element and are expressed all the time during normal cell growth are called
a. structural genes
b. operons
c. promoters
d. housekeeping genes
a. structural genes
b. operons
c. promoters
d. housekeeping genes
d. housekeeping genes
34
New cards
Polycistronic RNA \[select ALL correct answers\]
a. contains multiple start and stop codons.
b. contains only one promoter.
c. must be edited to remove introns.
d. encodes multiple proteins.
a. contains multiple start and stop codons.
b. contains only one promoter.
c. must be edited to remove introns.
d. encodes multiple proteins.
a. contains multiple start and stop codons, b. contains only one promoter, d. encodes multiple proteins.
35
New cards
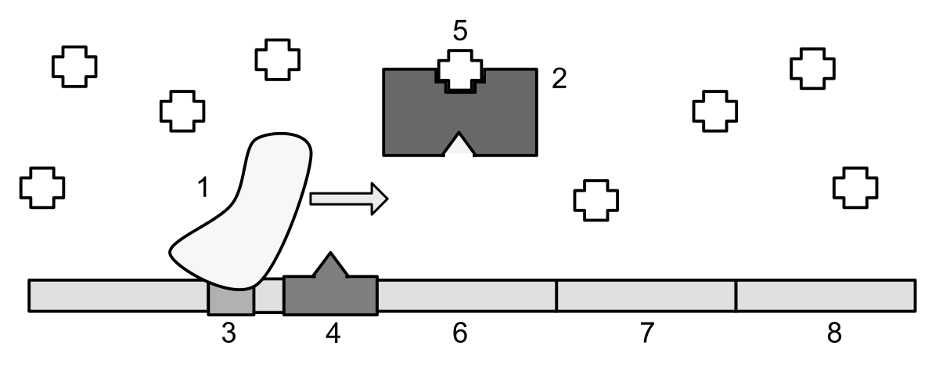
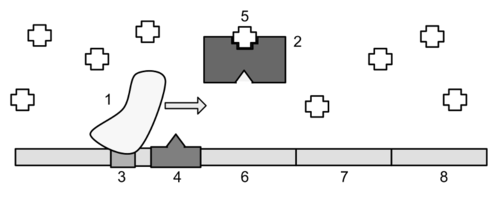
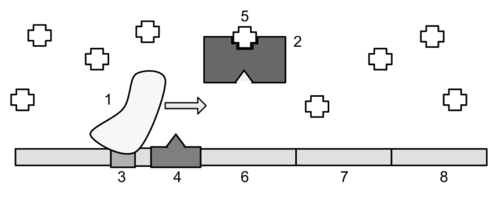
In the image above of the lac operon, the object labeled "1" is
a. the operator
b. allolactose
c. RNA polymerase
d. lac repressor protein
e. lactose
a. the operator
b. allolactose
c. RNA polymerase
d. lac repressor protein
e. lactose
c. RNA polymerase
36
New cards
In the image above of the lac operon, the big rectangle labeled "2" is
a. the promoter
b. the co-repressor
c. lac repressor protein
d. lactose
e. RNA polymerase
a. the promoter
b. the co-repressor
c. lac repressor protein
d. lactose
e. RNA polymerase
e. lac repressor protein
37
New cards
In the image above of the lac operon, lactose is present and therefore
a. RNA polymerase cannot bind to the promoter.
b. the lac repressor protein is bound to the operator.
c. glucose must be absent.
d. the lac repressor protein is not bound to the operator.
a. RNA polymerase cannot bind to the promoter.
b. the lac repressor protein is bound to the operator.
c. glucose must be absent.
d. the lac repressor protein is not bound to the operator.
d. the lac repressor protein is not bound to the operator.
38
New cards
When glucose and lactose are both present in the cell, the lac operon
a. is transcribed at high levels.
b. is blocked by the repressor.
c. is transcribed at low levels.
d. is not transcribed.
a. is transcribed at high levels.
b. is blocked by the repressor.
c. is transcribed at low levels.
d. is not transcribed.
c. is transcribed at low levels
39
New cards
co-inducer molecule (negative regulation of lac):
a. tryptophan
b. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
c. cAMP
d. allolactose
e. RNA polymerase
a. tryptophan
b. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
c. cAMP
d. allolactose
e. RNA polymerase
d. allolactose
40
New cards
activator (positive regulation of lac):
a. allolactose
b. cAMP
c. RNA polymerase
d. tryptophan
e. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
a. allolactose
b. cAMP
c. RNA polymerase
d. tryptophan
e. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
e. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
41
New cards
co-activator molecule (Positive regulation of lac):
\n a. allolactose
b. tryptophan
c. RNA polymerase
d. cAMP
e. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
\n a. allolactose
b. tryptophan
c. RNA polymerase
d. cAMP
e. cAMP receptor protein (CRP)
d. cAMP
42
New cards
If a bacterial genome contains a nonsense mutation in the coding region for the lac repressor protein, what will happen to lac expression in that cell?
a. The lac genes will always be transcribed at a high level, no matter how much glucose is present.
b. The lac genes will never be transcribed.
c. The lac genes will always be transcribed, but transcription levels will vary depending on how much glucose is present.
d. The lac genes will only be transcribed very low, no matter how much lactose is present.
a. The lac genes will always be transcribed at a high level, no matter how much glucose is present.
b. The lac genes will never be transcribed.
c. The lac genes will always be transcribed, but transcription levels will vary depending on how much glucose is present.
d. The lac genes will only be transcribed very low, no matter how much lactose is present.
c. The lac genes will always be transcribed, but transcription levels will vary depending on how much glucose is present.
43
New cards
If a bacterium has a mutation in its CRP such that CRP can never bind to the promoter, what will be true of lac expression in that cell?
a. The lac genes can only be transcribed at a low level, even if there is no glucose in the cell.
b. The lac genes will always be transcribed at the highest level.
c. The lac genes will never be transcribed.
d. The lac genes will be transcribed at varying levels depending on how much glucose is present.
a. The lac genes can only be transcribed at a low level, even if there is no glucose in the cell.
b. The lac genes will always be transcribed at the highest level.
c. The lac genes will never be transcribed.
d. The lac genes will be transcribed at varying levels depending on how much glucose is present.
a. The lac genes can only be transcribed at a low level, even if there is no glucose in the cell.
44
New cards
The ability of glucose to prevent lactose metabolism is an example of
a. catabolite repression
b. monophasic growth.
c. anabolic repression.
d. metabolic activation.
a. catabolite repression
b. monophasic growth.
c. anabolic repression.
d. metabolic activation.
a. catabolite repression
45
New cards
Deletion of the operator in the trp operon would result in
a. no synthesis of tryptophan.
b. decerased transcription of the *trp* genes.
c. continuous synthesis of tryptophan.
d. synthesis of the wrong amino acid.
a. no synthesis of tryptophan.
b. decerased transcription of the *trp* genes.
c. continuous synthesis of tryptophan.
d. synthesis of the wrong amino acid.
c. continuous synthesis of tryptophan
46
New cards
Which of the following statements is NOT true for the trp operon?
a. The presence of tryptophan activates gene expression
b. The operon has a promoter and an operator.
c. It is a repressible operon.
d. The absence of tryptophan activates gene expression.
a. The presence of tryptophan activates gene expression
b. The operon has a promoter and an operator.
c. It is a repressible operon.
d. The absence of tryptophan activates gene expression.
a. The presence of tryptophan activates gene expression
47
New cards
Epigenetic modifications
a. alter the probability of transcription initiation.
b. change the sequence of the DNA.
c. are only found in prokaryotes.
d. are never heritable.
a. alter the probability of transcription initiation.
b. change the sequence of the DNA.
c. are only found in prokaryotes.
d. are never heritable.
a. alter the probability of transcription initiation.
48
New cards
The packing of nuclear DNA is facilitated by the
a. availability of negatively-charged histones which attract DNA to wrap around them.
b. availability of positively-charged histones which attract DNA to wrap around them.
c. presence of the nuclear membrane, which acts as a barricade to the linear propagation of DNA and thereby folds the DNA back on itself.
d. methylation of guanine bases.
a. availability of negatively-charged histones which attract DNA to wrap around them.
b. availability of positively-charged histones which attract DNA to wrap around them.
c. presence of the nuclear membrane, which acts as a barricade to the linear propagation of DNA and thereby folds the DNA back on itself.
d. methylation of guanine bases.
b. availability of positively-charged histones which attract DNA to wrap around them.
49
New cards
DNA methylation appears to play a role in
a. inactivation of genes by preventing translation.
b. promoting DNA replication.
c. enhancing transcription in prokaryotes.
d. inactivation of genes by blocking transcription.
a. inactivation of genes by preventing translation.
b. promoting DNA replication.
c. enhancing transcription in prokaryotes.
d. inactivation of genes by blocking transcription.
d. inactivation of genes by blocking transcription
50
New cards
In which of the following would you expect to find the most methylation of the DNA?
a. Pseudogenes
b. Gene families
c. Coding regions
d. Barr bodies
a. Pseudogenes
b. Gene families
c. Coding regions
d. Barr bodies
d. Barr bodies
51
New cards
Which of the following epigenetic events does NOT contribute to X-chromosome inactivation?
\
a. Repressors binding to a silencer
b. Histone acetylation
c. Interfering RNA
d. DNA methylation
\
a. Repressors binding to a silencer
b. Histone acetylation
c. Interfering RNA
d. DNA methylation
b. histone acetylation
52
New cards
What could happen to a cell that has a missense mutation in the coding region of its histone deacetylase gene?
a. It would be harder for the cell to condense its DNA into heterochromatin.
b. It would not be able to transcribe the histone deacetylase gene.
c. It would be easier for the cell to add acetyl groups to its histones.
d. It would not be able to regulate gene expression using DNA methylation.
a. It would be harder for the cell to condense its DNA into heterochromatin.
b. It would not be able to transcribe the histone deacetylase gene.
c. It would be easier for the cell to add acetyl groups to its histones.
d. It would not be able to regulate gene expression using DNA methylation.
a. It would be harder for the cell to condense its DNA into heterochromatin.
53
New cards
Interfering RNA is
a. only found in prokaryotic cells.
b. transcribed but not translated.
c. never transcribed.
d. mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation.
a. only found in prokaryotic cells.
b. transcribed but not translated.
c. never transcribed.
d. mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation.
b. transcribed but not translated.
54
New cards
What could happen if an interfering RNA contains a mutation that prevents the RNA from binding to its target gene?
a. The polypeptide produced by translating the interfering RNA would be incorrectly folded.
b. The target gene would not be transcribed.
c. The target gene would be overexpressed.
d. The target gene would acquire mutations.
a. The polypeptide produced by translating the interfering RNA would be incorrectly folded.
b. The target gene would not be transcribed.
c. The target gene would be overexpressed.
d. The target gene would acquire mutations.
c. the target gene would be overexpressed
55
New cards
An unknown protein has a helix-turn-helix structural motif in one of its subunits. From this we could guess that the protein is
a. a mediator that does not bind directly to DNA.
b. the product of a mutated gene.
c. unable to bind to RNA polymerase.
d. a transcription factor that can recognize a specific sequence of DNA bases.
a. a mediator that does not bind directly to DNA.
b. the product of a mutated gene.
c. unable to bind to RNA polymerase.
d. a transcription factor that can recognize a specific sequence of DNA bases.
d. a transcription factor that can recognize a specific sequence of DNA bases.
56
New cards
If the genes for several different enzymes are regulated by the same transcription factor, we can guess that
these enzymes are all part of one pathway and act during successive steps in that pathway.
57
New cards
Eukaryotic organisms coordinate the expression of functionally related genes by
a. having general transcription enhancers/silencers for multiple genes.
b. having specific enhancers/silencers for each individual gene.
c. clustering related genes on the same chromosome.
d. transcribing the genes as a single polycistronic mRNA from a shared promoter.
a. having general transcription enhancers/silencers for multiple genes.
b. having specific enhancers/silencers for each individual gene.
c. clustering related genes on the same chromosome.
d. transcribing the genes as a single polycistronic mRNA from a shared promoter.
a. having general transcription enhancers/ silencers for multiple genes
58
New cards
Regulatory DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors include
\
a. inducers and repressors.
b. start and stop codons.
c. promoters and terminators.
d. enhancers and silencers.
\
a. inducers and repressors.
b. start and stop codons.
c. promoters and terminators.
d. enhancers and silencers.
d. enhancers and silencers
59
New cards
What mechanism could be used to make sure a particular gene is only expressed in a certain tissue of the body?
a. Chromatin remodeling to make sure this region of the genome is euchromatin in the correct tissue. b. Methylation of that gene's promoter in all other tissues except where it should be expressed. c. Specific transcription factors that are only present in that tissue. d. All of the above could work.
a. Chromatin remodeling to make sure this region of the genome is euchromatin in the correct tissue. b. Methylation of that gene's promoter in all other tissues except where it should be expressed. c. Specific transcription factors that are only present in that tissue. d. All of the above could work.
d. All of the above could work.
60
New cards
If an organism has a sequence-level mutation in an enhancer for gene A, then
a. gene A will be underexpressed.
b. the transcription factor protein will be mutated.
c. the sequence-level mutation will only be observed in the tissue that gene A would normally be expressed in.
d. gene A will be expressed normally.
e. gene A will produce a mutated protein.
a. gene A will be underexpressed.
b. the transcription factor protein will be mutated.
c. the sequence-level mutation will only be observed in the tissue that gene A would normally be expressed in.
d. gene A will be expressed normally.
e. gene A will produce a mutated protein.
a. gene A will be underexpressed.
61
New cards
We observe that a gene has five TATA boxes in its promoter. What can we guess about the product of this gene?
\
a. This gene product is probably only needed in certain tissues or at certain times.
b. This gene product is probably extremely important to the organism because its promoter has been replicated multiple times.
c. This gene product is probably a misformed protein because the TATA boxes are getting in the way of the coding region.
d. This gene product is probably useless to the organism because its promoter is long.
\
a. This gene product is probably only needed in certain tissues or at certain times.
b. This gene product is probably extremely important to the organism because its promoter has been replicated multiple times.
c. This gene product is probably a misformed protein because the TATA boxes are getting in the way of the coding region.
d. This gene product is probably useless to the organism because its promoter is long.
b. This gene product is probably extremely important to the organism because its promoter has been replicated multiple times.
62
New cards
Which of these is a quantitative trait? \n a. Flower color in irises can be either purple or yellow. \n b. Pea plants produce anywhere between 15 and 100 seeds per season. \n c. Adult giraffes' necks have a maximum length of 6 feet and a minimum of 4 feet. \n d. Sparrow beaks are different lengths depending on their food sources; we measure beak length in millimeters.
d. Sparrow beaks are different lengths depending on their food sources; we measure beak length in millimeters.
63
New cards
A sparrow population currently eats seeds that are mostly of medium size. Larger birds prefer somewhat larger seeds and smaller birds prefer somewhat smaller seeds. The population currently is experiencing stabilizing selection for body size. Which condition will most likely lead to directional selection for smaller size?
\n a. more seeds that are somewhat larger than average and fewer that are smaller than average \n b. a decrease in population size of the sparrows \n c. more seeds that are smaller in size \n d. A reduction in the overall number of seeds, with no change in the distribution.
c. more seeds that are smaller in size
\n a. more seeds that are somewhat larger than average and fewer that are smaller than average \n b. a decrease in population size of the sparrows \n c. more seeds that are smaller in size \n d. A reduction in the overall number of seeds, with no change in the distribution.
c. more seeds that are smaller in size
c. more seeds that are smaller in size
64
New cards
An evolutionary trade-off is observed when \n a. several different species have the same type of trait \n b. a beneficial trait is linked to a harmful trait \n c. there are more individuals with a heterozygous genotype than homozygous. \n d. selection favors extremes of a trait
\
\
b. a beneficial trait is linked to a harmful trait
65
New cards
Selection can \n a. choose between different genotypes that have the same phenotype associated with them. \n b. allow less-fit individuals to survive and reproduce just in case their traits are useful to future generations. \n c. cause new alleles to be created via mutation. \n d. act on existing variation in a population.
d. act on existing variation in a population
66
New cards
Which of these is an example of an evolutionary trade-off? \n a. Cyanide-producing clover is more common in warmer regions than colder regions. \n b. Skates and rays have a flattened body shape, and so do flounders. \n c. Left-mouthed and right-mouthed scale-eating fish exist in equal proportions in a population. \n d. TTX-resistant garter snakes can eat toxic newts, but are also unable to move as quickly as non-resistant snakes.
d. TTX-resistant garter snakes can eat toxic newts, but are also unable to move as quickly as non-resistant snakes.
67
New cards
If a population of mice experiences a drought during which only the smallest individuals are able to find enough food to survive, then the population has undergone
a. stabilizing selection
b. directional selection
c. disruptive selection
a. stabilizing selection
b. directional selection
c. disruptive selection
directional
68
New cards
Genetic drift is most likely to affect allele frequencies when
a. populations are large
b. populations are small
a. populations are large
b. populations are small
b. populations are small
69
New cards
Which of these is NOT a requirement for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium to be present in a population? \n a. natural selection does not occur \n b. mutation does not occur \n c. individuals can move freely between one population and another \n d. the population is very infinitely large \n e. sexual selection does not occur
c. individuals can move freely between one population and another
70
New cards
Metamorphosis can be a useful live history trait because…\[ select ALL correct answers\]
a. having a non-sessile life stage enables dispersal to new areas
b. juveniles and adults occupy the same niche
c. it is required in order to be a heterotroph
d. it prevents competition between juveniles and adults for food and habitat spaces
a. having a non-sessile life stage enables dispersal to new areas
b. juveniles and adults occupy the same niche
c. it is required in order to be a heterotroph
d. it prevents competition between juveniles and adults for food and habitat spaces
a. having a non-sessile life stage enables dispersal to new areas and d. it prevents competition between juveniles and adults for food and habitat spaces
71
New cards
Which of these traits is unique to cnidarians?
a. radial symmetry
b. having stinging tentacles to capture prey
c. have a nerve net
d. have a swimming larval stage
a. radial symmetry
b. having stinging tentacles to capture prey
c. have a nerve net
d. have a swimming larval stage
b. having stinging tentacles to capture prey
72
New cards
pseudocoelomate animals can be expected to have ________ __muscular systems and__ __________ internal compartmentalization of the body than coelomates
less complex, less
73
New cards
select ALL of the following character states that are synapomorphies of Bilateria
a. bilateral symmetry
b. radial symmetry
c. central nervous system
d. blastopore develops into mouth
a. bilateral symmetry
b. radial symmetry
c. central nervous system
d. blastopore develops into mouth
a. bilateral symmetry and c. central nervous system
74
New cards
the protein product of a hox gene acts as a
a. repressor
b. transcription factor
c. ribosomal protein
d. blueprint for building a body segment
a. repressor
b. transcription factor
c. ribosomal protein
d. blueprint for building a body segment
b. transcription factor
75
New cards
select ALL of the following animals that belong to the clade Lophotrochozoa
a.lobsters
b. clams
c. snails
d. ctenophores
a.lobsters
b. clams
c. snails
d. ctenophores
b. clams and c. snails
76
New cards
Having a hard exoskeleton that must be shed regularly in order for the animal to grow is a synapomorphy of
a. chordata
b. ecdysozoa
c. arthropoda
d. placozoa
a. chordata
b. ecdysozoa
c. arthropoda
d. placozoa
b. ecdysozoa
77
New cards
Here is part of an mRNA transcribed from the hox gene Antp in a fruit fly. The first start codon is where translation begins. We are just looking at the first little part of the sequence here: the full mRNA is several hundred bases long.
aca aaa aug acg aug aca aau aac ug**g**
gaa agc aug acg uca uau
\
Imagine that during replication early in embryonic development, a transition occurs at the underlined base position. What type of mutation is this?
a. missense
b. nonsense
c. silent
d. gain of function
aca aaa aug acg aug aca aau aac ug**g**
gaa agc aug acg uca uau
\
Imagine that during replication early in embryonic development, a transition occurs at the underlined base position. What type of mutation is this?
a. missense
b. nonsense
c. silent
d. gain of function
b. nonsense
78
New cards
in the area of the body with the mutated Antp, what will occur?
a. a leg will grow in the wrong place
b. an antenna will develop instead of a leg
c. all of the leg genes will be overexpressed
d. all of the genes will be underexpressed
a. a leg will grow in the wrong place
b. an antenna will develop instead of a leg
c. all of the leg genes will be overexpressed
d. all of the genes will be underexpressed
d. all of the genes will be underexpressed
79
New cards
which clade of bilaterians has secondarily evolved radial symmetry?
a. hemichordata
b. echinodermata
c. arrow worms
d. mollusca
a. hemichordata
b. echinodermata
c. arrow worms
d. mollusca
b. echinodermata
80
New cards
How many separate times did a nervous system (CNS or nerve net) probably evolve with animalia?
a. once
b. twice
c. three times
d. four times
a. once
b. twice
c. three times
d. four times
c. three times
81
New cards
Which of these is not a type of heterotrophy?
a. parasitism
b. predation
c. herbivory
d. photosynthesis
a. parasitism
b. predation
c. herbivory
d. photosynthesis
d. photosynthesis
82
New cards
A three- way split on a phylogenetic tree indicates that
a. the common ancestor was split into 3 different species at the same time
b. we are uncertain about which clade diverged first
c. there is no known outgroup for this tree
d. there are no synapomorphies supporting this split
a. the common ancestor was split into 3 different species at the same time
b. we are uncertain about which clade diverged first
c. there is no known outgroup for this tree
d. there are no synapomorphies supporting this split
b. we are uncertain about which clade diverged first
83
New cards
The coelom is
a. a fluid-filled body cavity that contains organs and muscles
b. a type of sessile animal
c. a developmental stage
d. a component of the CNS
a. a fluid-filled body cavity that contains organs and muscles
b. a type of sessile animal
c. a developmental stage
d. a component of the CNS
a. a fluid-filled body cavity that contains organs and muscles
84
New cards
An animal has bilateral symmetry, a CNS, and an internal skeleton made of bone. It probably belongs to the clade
a. protostomata
b. echinodermata
c. chordata
d. cnidaria
a. protostomata
b. echinodermata
c. chordata
d. cnidaria
**c. chordata**
85
New cards
Foxes often save excess food by burying it in the ground. Suppose a researcher rears in isolation a fox cub from birth; the cub has no access to dirt for digging. Once the fox is an adult, the researcher moves the fox to an outdoor enclosure. The researcher presents the fox with excess food to see if it will bury the food. This type of study is called a(n) _______ experiment, and it was used to study the _______.
a. deprivation; genetic determination of a behavior
b. isolation; cost and benefits of a behavior
c. knockout; role of learning in behavior
d. deprivation; development of a behavior
a. deprivation; genetic determination of a behavior
b. isolation; cost and benefits of a behavior
c. knockout; role of learning in behavior
d. deprivation; development of a behavior
a. deprivation; genetic determination of a behavior
86
New cards
Which research question does NOT refer to proximate causes of a behavior?
\n a. How do experimentally displaced pigeons find their way back to their home loft?
b. How does dispersal affect the evolutionary fitness of Belding's ground squirrels?
c. How do rhesus macaques find their food?
d. Do mother goats learn the odor of their offspring?
\n a. How do experimentally displaced pigeons find their way back to their home loft?
b. How does dispersal affect the evolutionary fitness of Belding's ground squirrels?
c. How do rhesus macaques find their food?
d. Do mother goats learn the odor of their offspring?
b. How does dispersal affect the evolutionary fitness of Belding's ground squirrels?
87
New cards
You are investigating the function of a pheromone receptor found in the vomeronasal organ (VNO) of mice. You hypothesize that when pheromones produced by a female mouse bind to the VNO receptors of a male mouse, the binding stimulates mating behavior. You test your hypothesis by doing a knockout experiment, silencing a gene needed for the VNO receptor to work. When you expose the knockout male mouse to a female mouse, the knockout mouse mates with the female. When you expose the same knockout male mouse to a male mouse, the knockout mouse tries to mate with the male. When you test a normal male mouse under the same situations, the male mates with the female, but reacts aggressively toward the male. What conclusion can you draw from these
a. The VNO receptors are necessary for mating behavior.
b. Male mice cannot distinguish between male and female mice.
c. There is a single gene that controls mating behavior in male mice.
d. The VNO receptors are necessary for sex identification.
a. The VNO receptors are necessary for mating behavior.
b. Male mice cannot distinguish between male and female mice.
c. There is a single gene that controls mating behavior in male mice.
d. The VNO receptors are necessary for sex identification.
d. The VNO receptors are necessary for sex identification.
88
New cards
The umwelt of an animal
\n a. easier to study if we remove the animal from its natural habitat.
b. the same for every animal that lives in a certain habitat.
c. only relevant to understanding genetically programmed behaviors.
d. is how it senses and understands its environment.
\n a. easier to study if we remove the animal from its natural habitat.
b. the same for every animal that lives in a certain habitat.
c. only relevant to understanding genetically programmed behaviors.
d. is how it senses and understands its environment.
d. is how it senses and understands its environment.
89
New cards
Avoiding being eaten is typically a compromise for animals. If a male frog remains silent, then he can’t attract mates. Inability to attract mates is a(n) _______ cost of remaining silent for the male frog.
a. risk
b. energetic
c. genetic
d. opportunity
a. risk
b. energetic
c. genetic
d. opportunity
d. opportunity
90
New cards
Most prairie vole young remain at their natal burrow even after they have reached adulthood and help their parents rear subsequent litters of younger siblings. Breeding pairs with helpers have higher reproductive success than those without helpers. Young that leave the natal burrow have low survival and reproductive success. Prairie vole helpers have no _______ fitness but do have _______ fitness.
\
\n a. indirect; direct
b. inclusive; direct
c. direct; indirect
d. indirect; inclusive
\
\n a. indirect; direct
b. inclusive; direct
c. direct; indirect
d. indirect; inclusive
**c. direct; indirect**
91
New cards
A scientist rings a bell every time she feeds a dog. Soon, the dog starts salivating whenever he hears the bell, even if there is no food available. In this scenario, the sound of a bell is
a. the conditoned stimulus
b. the unconditioned stimulus
c. a releaser for instinctive behavior
d. a stimulus that the dog is becoming habituated to
a. the conditoned stimulus
b. the unconditioned stimulus
c. a releaser for instinctive behavior
d. a stimulus that the dog is becoming habituated to
a. the conditoned stimulus
92
New cards
When a male stickleback sees another fish with a red belly, he will attack it to defend his territory. The red belly in this situation is
a. a releaser for a learned behavior
b. a releaser for a fixed action pattern
c. the ultimate reason for the behavior
d. a chemical signal
a. a releaser for a learned behavior
b. a releaser for a fixed action pattern
c. the ultimate reason for the behavior
d. a chemical signal
b. a releaser for a fixed action pattern
93
New cards
A sea hare that has never been part of a behavioral study is injected with mRNA extracted from a sea hare that has become habituated to a noxious stimulus. Which of the following statements characterizes the change we might expect in the behavior of the sea hare that receives the mRNA injection?
a. The recipient will associate the noxious stimulus with another, harmless stimulus.
b. The recipient will now react more strongly to the noxious stimulus.
c. The recipient will not change its behavior in response to the stimulus.
d. The recipient will now react less strongly to the noxious stimulus.
a. The recipient will associate the noxious stimulus with another, harmless stimulus.
b. The recipient will now react more strongly to the noxious stimulus.
c. The recipient will not change its behavior in response to the stimulus.
d. The recipient will now react less strongly to the noxious stimulus.
d. The recipient will now react less strongly to the noxious stimulus.
94
New cards
Increasing the strength of a response to a stimulus is associated with the sensory nerves involved
\n a. getting less electrically excited in response to the stimulus.
b. releasing more neurotransmitters in response to the stimulus.
c. connecting to new motor nerves that allow its response to change.
d. releasing fewer neurotransmitters in response to the stimulus.
\n a. getting less electrically excited in response to the stimulus.
b. releasing more neurotransmitters in response to the stimulus.
c. connecting to new motor nerves that allow its response to change.
d. releasing fewer neurotransmitters in response to the stimulus.
b. releasing more neurotransmitters in response to the stimulus.
95
New cards
A behavior that is a fixed action pattern
a. has no genetic basis.
b. can be interrupted and changed while it is happening.
c. is a type of learned behavior.
d. is performed the same exact way every time.
a. has no genetic basis.
b. can be interrupted and changed while it is happening.
c. is a type of learned behavior.
d. is performed the same exact way every time.
d. is performed the same exact way every time.
96
New cards
Which statement about the cost–benefit approach to animal behavior is false?
a. The approach includes opportunity costs of performing the behavior.
b. The approach assumes that animals have limited time and energy.
c. The approach assumes that animals don’t engage in behaviors whose benefits exceed their costs.
d. The approach includes energetic costs of performing the behavior.
e. Benefits are measured in terms of fitness gained by performing the behavior.
a. The approach includes opportunity costs of performing the behavior.
b. The approach assumes that animals have limited time and energy.
c. The approach assumes that animals don’t engage in behaviors whose benefits exceed their costs.
d. The approach includes energetic costs of performing the behavior.
e. Benefits are measured in terms of fitness gained by performing the behavior.
c. The approach assumes that animals don’t engage in behaviors whose benefits exceed their costs.
97
New cards
Which of these stimulus types is NOT sensed by mechanoreceptors?
a. sound
b. touch
c. electricity
d. light
a. sound
b. touch
c. electricity
d. light
d. light
98
New cards
agonistic behaviors involves
a. finding food
b. caring for offspring
c. fighting
d. mating
a. finding food
b. caring for offspring
c. fighting
d. mating
c. fighting
99
New cards
Some birds need to hear other individuals singing in order to be able to sing their own song properly. This is evidence that
a. birdsong is a consummate behavior.
b. birdsong is a learned behavior.
c. birdsong is an instinctive behavior.
d. birdsong is an evolutionary adaptation.
a. birdsong is a consummate behavior.
b. birdsong is a learned behavior.
c. birdsong is an instinctive behavior.
d. birdsong is an evolutionary adaptation.
b. birdsong is a learned behavior.
100
New cards
\
\