HSC 101: Cancer
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Furman University
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Cancer
Abnormal, uncontrolled multiplication of cells caused by damage to DNA
Carcinogen
Any substance that causes cancer
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells from one part of the body to another
Chromosomes
the threadlike bodies in a cell nucleus that contain molecules of DNA; most human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes
Gene
the threadlike bodies in a cell nucleus that contain molecules of DNA; most human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, a chemical substance that carries genetic information
Oncogenes
deoxyribonucleic acid, a chemical substance that carries genetic information
Second Most Common Cause of Death
Cancer after heart disease
What Causes Cancer
Cancer can be caused by various factors, including genetic mutations, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices that damage DNA.
DNA Damage
occurs when you either lose a tumor suppressor gene '“brakes” or activate growth regulating gene “accelerator”
DNA Mutations
are changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to cancer if they occur in genes that control cell growth and division.
Estrogen
is a hormone that can promote the growth of certain types of breast cancer cells and is linked to an increased risk of hormone-responsive cancers.
External factors that damage DNA
include radiation, certain chemicals (EX. Tabacco smoke), and viruses that can lead to mutations and increased cancer risk.
Internal factors that damage DNA
Free radicals: highly reactive atom or molecule with an unpaired electron
Hormones: estrogen (breast), insulin, insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1)
Inherited mutations: mutated breast cancer gene 1 or 2 (BRCA 1, BRCA 2)
Immune conditions: that can affect the body's ability to repair DNA damage, increasing cancer susceptibility.
Tabacco is responsible for ___ of all Cancer Death
30%
Diet and exercise account for ___ of cancer death
30%
What is the current rate of cancer in men and women?
Nearly 1:2 men and more than 1:3 women
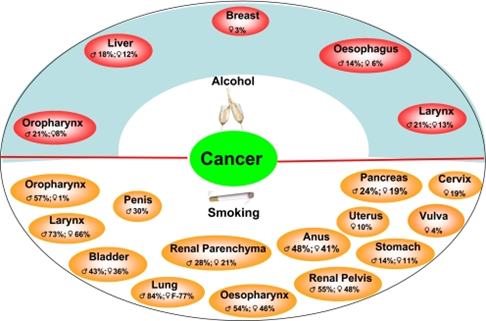
What types of Cancers are linked to Obesity

What types of cancer are linked to alcohol and smoking?
The percentage contribution of genetic and environmental factor to cancer
.The contribution of genetic factors and environmental factors towards cancer risk is 5–10% and 90–95% respectively.
Benign Tumor
A benign tumor is a non-cancerous growth that does not invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body.
Malignant Tumor
A malignant tumor is a cancerous growth that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, often leading to serious health complications.
Angiogenesis
the process through which new blood vessels form from existing ones, often essential for tumor growth and metastasis.
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells from the original tumor to distant sites in the body, often leading to the formation of new tumors.
Oxidation
is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion, often associated with the release of energy.
Oxidation can create
reactive oxygen species that can damage cells and DNA. (Free Radical)
Free Radical can destabilize other molecules
by stealing their electrons, leading to chain reactions that cause cellular damage.
Free Radical and the immune system
play a complex role, where they can help in fighting infections but also contribute to inflammation and tissue damage.
Free radical can damage
protein, lipids, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA),
How do our bodies fight free radicals and repair the damage they cause?
Using antioxidants which are vitamins, minerals, and other compounds that can either
work independently by donating their electrons or hydrogen molecules to free radicals to stabilize them and reduce the damage caused by oxidation or
Antioxidant minerals function within complex antioxidant enzyme systems that convert free radicals to less damaging substances that are excreted by our bodies.
What else can help stabilize free radicals
beta-carotene and phytochemicals help stabilize free radicals and prevent damage to cells and tissues.
Ascorbic Acid
is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals and regenerate other antioxidants in the body. Vitamin C is a well known antioxidant that may prevent cataracts and cancers of the stomach, throat, mouth, and pancreas.
High consumption of ____ and ___ reduce the risk of many cancers
Fruits and vegetables
How Food can Block cancer Progression
Carcinogens (Destroy and excrete carcinogens)
Damages DNA (Enhance DNA repair capacity)
Uncontrolled Cell Division (Slow tumor growth)
Cancer Invades Nearby Tissues (Induce Apoptosis)
Cancer Spreads Throughout Body (Slow cancer progression)
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death in the United States
primarily caused by smoking (80%) and then radon exposure
Risk factors for Lung Cancer
include smoking, radon exposure, and asbestos.
E-cigarettes cause
Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Endothelial Damage, Impaired Immunity, DNA Damage, and Impaired Brain Development of the Prefrontal Cortex
Estrogen Exposure occurs more frequently if?
the women have never had children, had 1st child after age 30, has long menstrual history, obesity, alcohol, use, inactivity.
Screening for breast Cancer
Age 20-40: self-breast exam monthly and clinical breast exam every 3 yrs
Age > 40: self-breast exam monthly, clinical breast exam annually, annual mammogram
How does obesity increase cancer risk?
Obesity increases cancer risk through chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances. These factors can promote the development and progression of various cancers.
Colorectal Cancer screening
is recommended starting at age 45 for average-risk individuals. It involves tests like colonoscopy and fecal occult blood tests and a flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Testing for melanoma
involves full skin examinations, biopsy of suspicious moles, and may include dermoscopy and imaging tests to assess the extent of the disease. ABCDE test