SW2 Midterm 2 BST
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
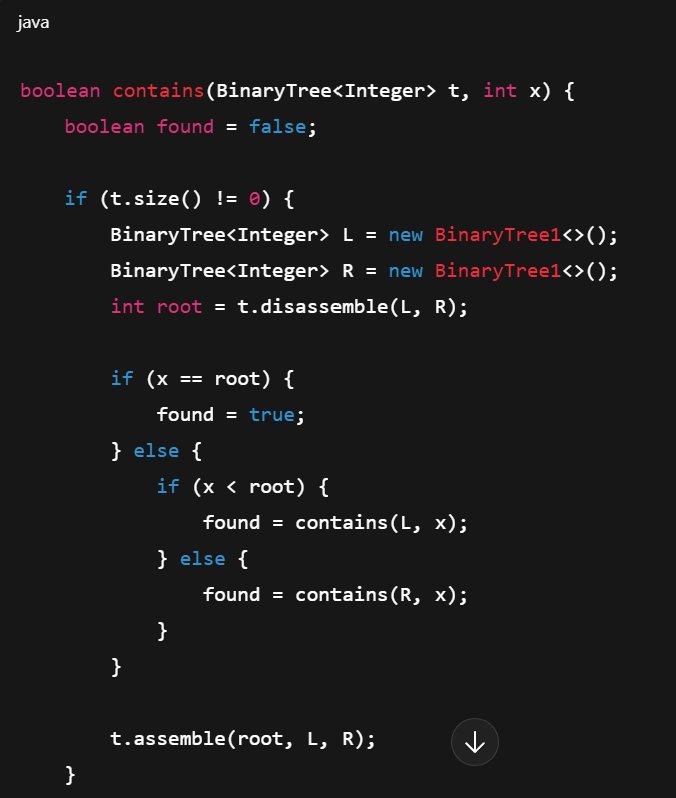
contains Algorithm (searching in BST)
returns a binary tree t
if t is empty x is not found
r is the root, of t then found
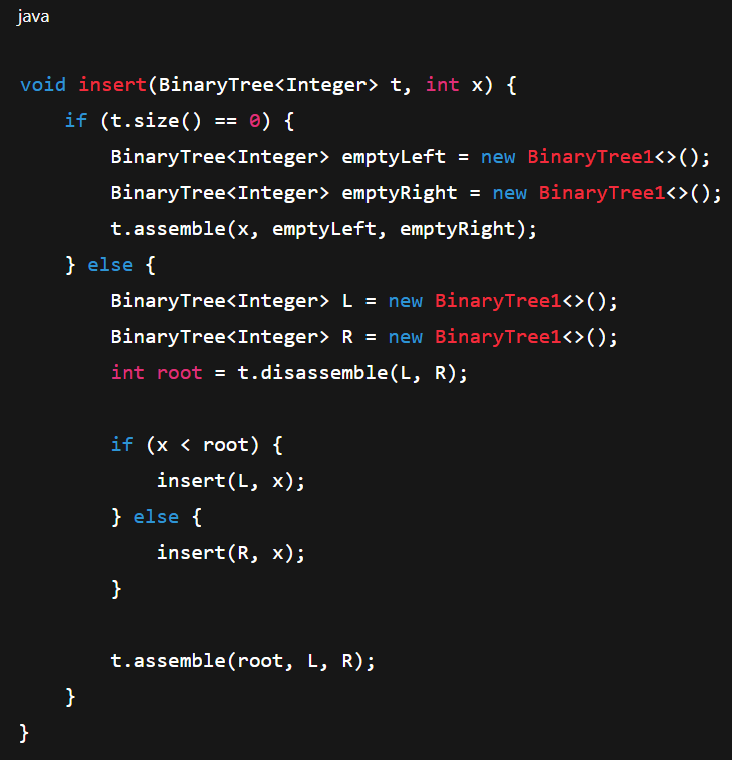
Insert Element in BST
if tree is empty, assemble single node tree with x
otherwise compares x with r and resemble recursively
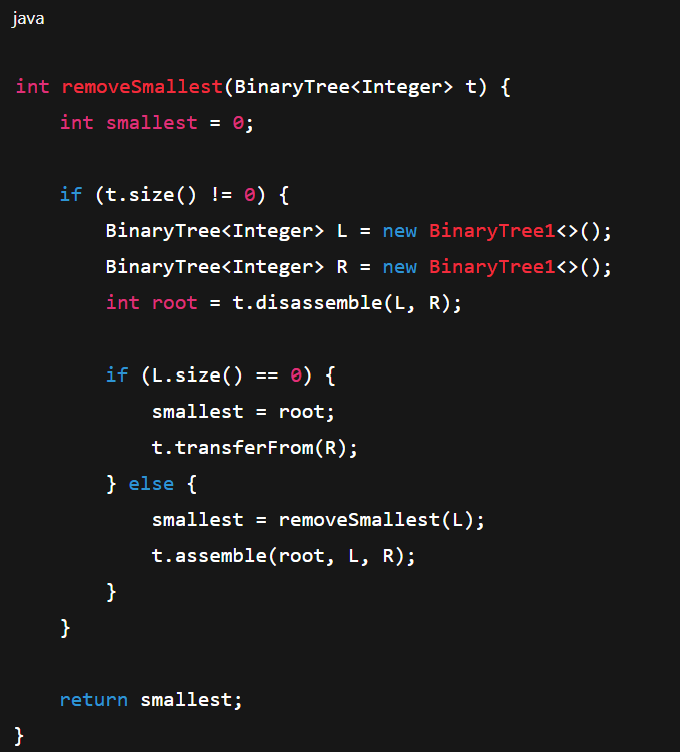
removeSmallest(HelperFunction)
located in the left most side of the tree
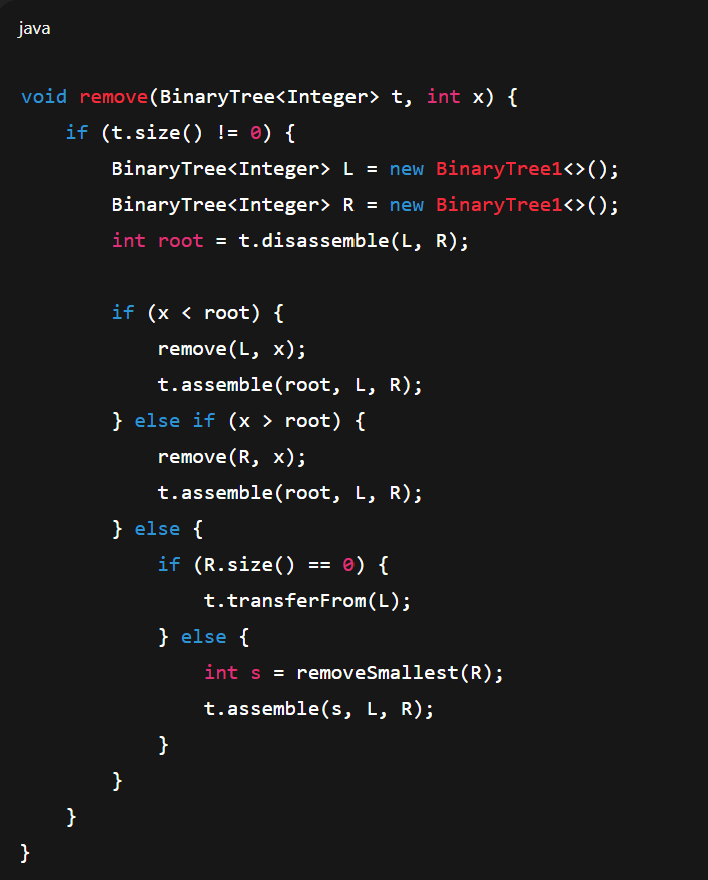
remove (Delete specific element from BST)
3 cases: deleting leaf, deleting a single child, deleting from a node with two children
O(h) complexity worst case
Height (Tree Height)
Mathematical:
-empty tree: 0
-non empty Tree = 1+Math.max(height(L), height(R))

size (counting all nodes)
empty: 0
nonempty: 1 + size(leftTree) + size(rightTree)
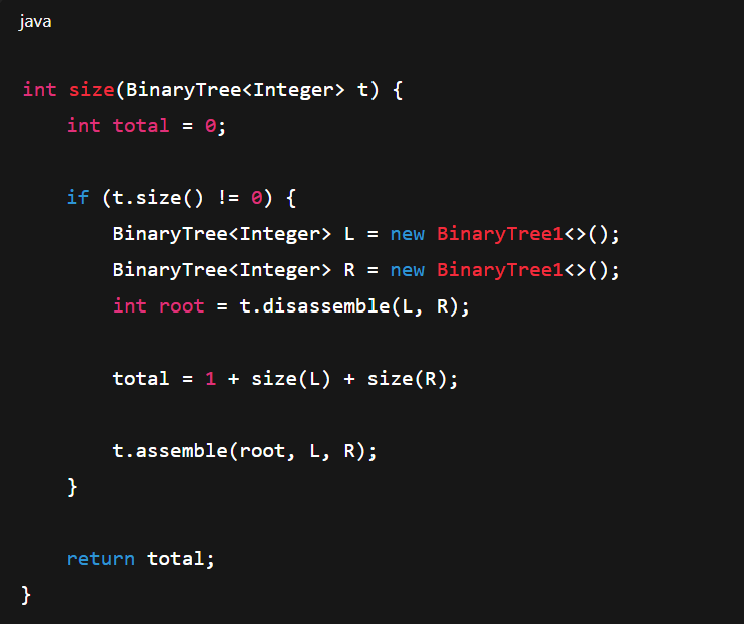
PreOrder
root>left>right
Traversal for copying or printing the tree structure
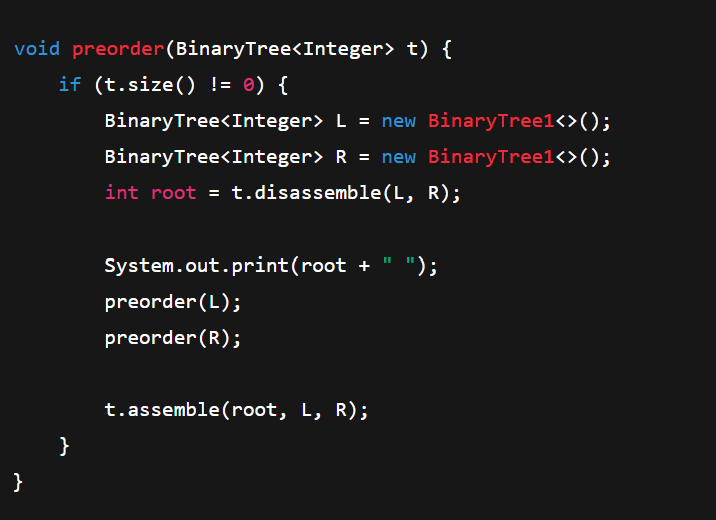
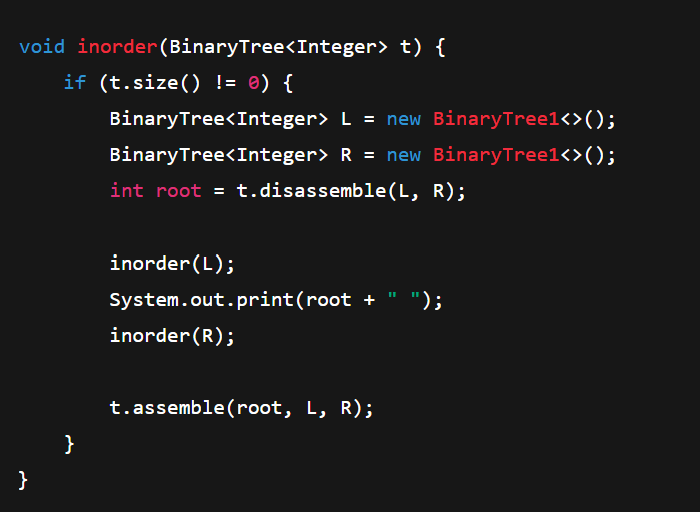
In Order Traversal
Left>Root>Right
getting keys from BST in sorted order
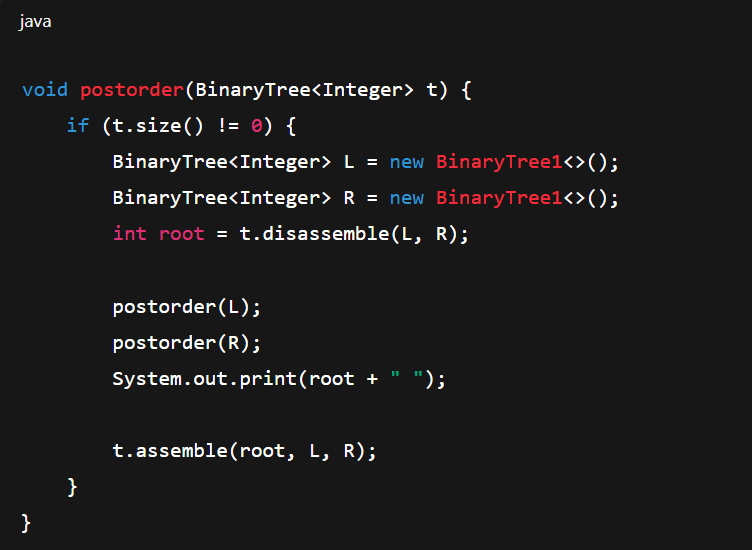
Post-order
Order: left>right>Root
Traversal for deleting a subtrees/tree, children first (need to delete the children first before deleting the root)
BST order
root k > left subtree
root k < right subtree
Math.max(a,b)
-Returns greater of two numbers
-Used for height
Mathematical size of non empty Tree
b.size = 0
Characteristics of Binary Trees
size, labels, height, follow recursive structure, do not have to be balanced
Assemble (T root, Binary Tree<T> left, Binary Tree<T> left, )
Kernal method: combines root, and the 2 subtrees
T disassemble (BinaryTree <T> left, BinaryTree<T>right)
returns the root value and breaks apart the left and right subtrees, and clears the original tree
T root()
returns the root (so long as its nonempty)
T replaceRoot (T x)
replaces the root with x (and returns old root) such that it is a nonempty Tree
Iterator<T> iterator()
return an iterator that visits labels in-order by contract