IB BIO TOPIC 7
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is cell respiration?
It’s a process where the body turns sugar into energy using oxygen.
What are the 4 steps involved?
The steps include breaking down sugar, preparing molecules, a cycle that creates more energy, and a final chain that produces the most energy.
Where does the first step happen and what does it do?
It takes place in the cell fluid and breaks sugar into smaller pieces, producing a little energy.
What is the second step?
It connects the first and third steps, setting up molecules for more energy production.
What happens in the cycle step?
This step produces more energy by breaking down the molecules from the first process.
What happens in the final step?
This part creates a large amount of energy using oxygen to help break down products from the cycle.
What happens if there’s no oxygen?
Without oxygen, only a small amount of energy is produced, and it can cause a buildup of acid in muscles.
What is the system responsible for breathing?
It helps take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body.
Why is exchanging gases important?
It allows the body to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide, which is essential for energy production.
How do plants exchange gases?
They do this through small openings in their leaves that allow gases to enter and exit.
How do humans exchange gases?
Oxygen moves from the air to the blood, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the air.
Why is surface area important?
Having more space allows for faster movement of gases in and out of the body.
How are lungs designed to help with gas exchange?
The air sacs in the lungs have thin walls and lots of space, which makes it easier for gases to move quickly.
What is the fluid that helps keep air sacs from collapsing?
This fluid helps the air sacs stay open when breathing out.
What are the tiny blood vessels around air sacs?
These vessels help move oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the air sacs.
What is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs?
It’s how the body gets rid of carbon dioxide and takes in oxygen through breathing.
What is tidal volume?
It’s the amount of air taken in or pushed out with each normal breath.
What is vital capacity?
It’s the most air a person can breathe out after taking a deep breath.
How does the heart help circulate blood?
It pumps blood through the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
What is a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart?
This vessel has thick walls to handle the pressure.
What is a blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart?
These vessels have valves that prevent blood from flowing backward.
What are tiny vessels that connect arteries and veins?
They allow the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between the blood and body cells.
What happens when the heart beats?
The heart contracts and relaxes to pump blood through the body.
What happens when there’s a blockage in a blood vessel?
This can lead to a condition where the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen, which can cause serious damage.
What is homeostasis?
It’s how the body keeps things balanced, like temperature and sugar levels, even when things outside change.
What is negative feedback?
It works to bring things back to normal when they get too high or low.
What is positive feedback?
It keeps pushing a process forward, like when contractions become stronger during childbirth.
What is diabetes?
It’s a condition where the body can’t manage blood sugar properly.
What causes Type 1 diabetes?
It happens when the body doesn’t produce enough of a hormone to regulate sugar levels.
What causes Type 2 diabetes?
It’s caused by the body not using that hormone properly, often due to being overweight.
What is thermoregulation?
It’s how the body keeps its temperature steady, no matter how warm or cold it is outside.
What structure makes veins?
They are made of thin walls with less muscle.
What structure makes arteries?
They are made of thick, strong walls with more muscle.
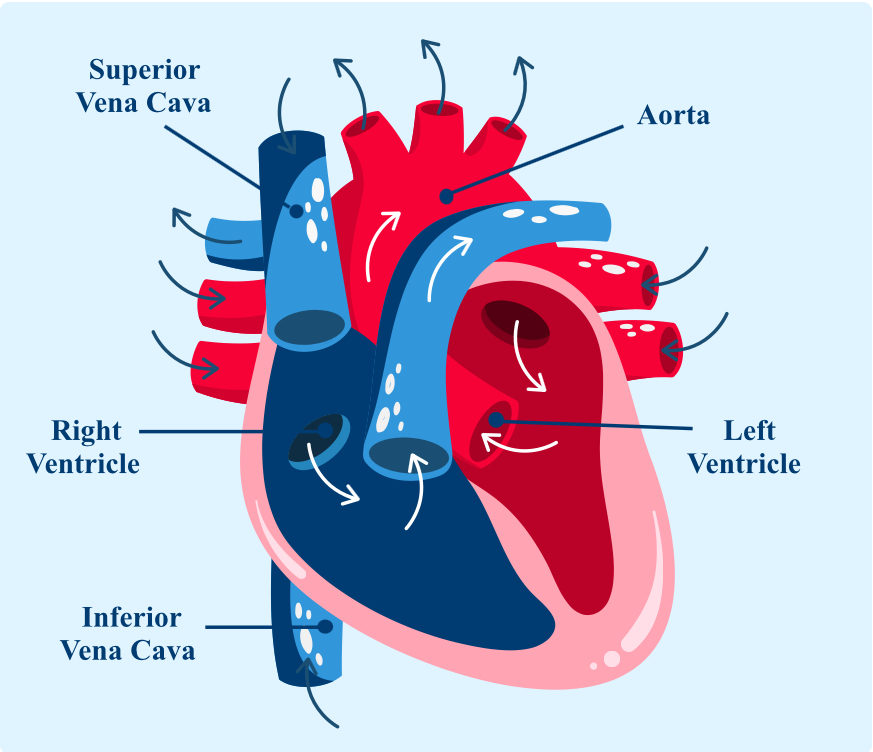
What is this?
A heart.