APUSH Period 3 Review
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War in North America (1754-1763) mirrored the Seven Years War in Europe (1756-1763). English colonists and soldiers fought the French and their Native American allies for dominance in North America. England's eventual victory brought England control of much disputed territory and eliminated the French as a threat to English dominance in the Americas.
Pontiacs Rebellion
1763 - Indian rebellion led by chief Pontiac shortly after the end of the seven years war. Attacked British forts in the west
Proclamation of 1763
forbade British colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains, and which required any settlers already living west of the mountains to move back east.
Sugar Act
(1764) British deeply in debt partl to French & Indian War. English Parliament placed a tariff on sugar, coffee, wines, and molasses. colonists avoided the tax by smuggling and by bribing tax collectors.
Quartering Act
(1765) Required colonies to provide food and quarters for British troops. Many colonists saw it as an encroachment on their rights.
Stamp Act
(1765) Part of Grenville's plan to defray the cost of maintaining the British army along the American frontier. Revenue stamps were attached to printed matter and legal documents, newspapers, and insurance papers etc. For the colonists the main issue was "no taxation without representation." Public protests increased until it was repealed in 1766.
Declaratory Act
In 1766, the English Parliament repealed the Stamp Act and at the same time signed the Declaratory Act. This document stated that Parliament had the right "to bind" the colonies "in all cases whatsoever." It is important because it stopped the violence and rebellions against the tax on stamps. Also, it restarted trade with England, which had temporarily stopped as a defiant reaction to the Stamp Act.
Townshend Act
passed by Parliament in 1767, placed taxes on imported materials such as glass, lead, paint, paper, and tea. Led to outrage and tons of people boycotted British goods.
Patrick Henry
founding father, served as the first and sixth post-colonial Governor of Virgina. (famous "Give me liberty, or give me death!" speech)
Sons of Liberty
A radical political organization for colonial independence which formed in 1765 after the passage of the Stamp Act. They incited riots and burned the customs houses where the stamped British paper was kept. After the repeal of the Stamp Act, many of the local chapters formed the Committees of Correspondence which continued to promote opposition to British policies towards the colonies. The Sons leaders included Samuel Adams and Paul Revere.
Samuel Adams
American Revolutionary leader and patriot, Founder of the Sons of Liberty and one of the most vocal patriots for independence; signed the Declaration of Independence
Paul Revere
American silversmith remembered for his midnight ride (celebrated in a poem by Longfellow) to warn the colonists in Lexington and Concord that British troops were coming (1735-1818)
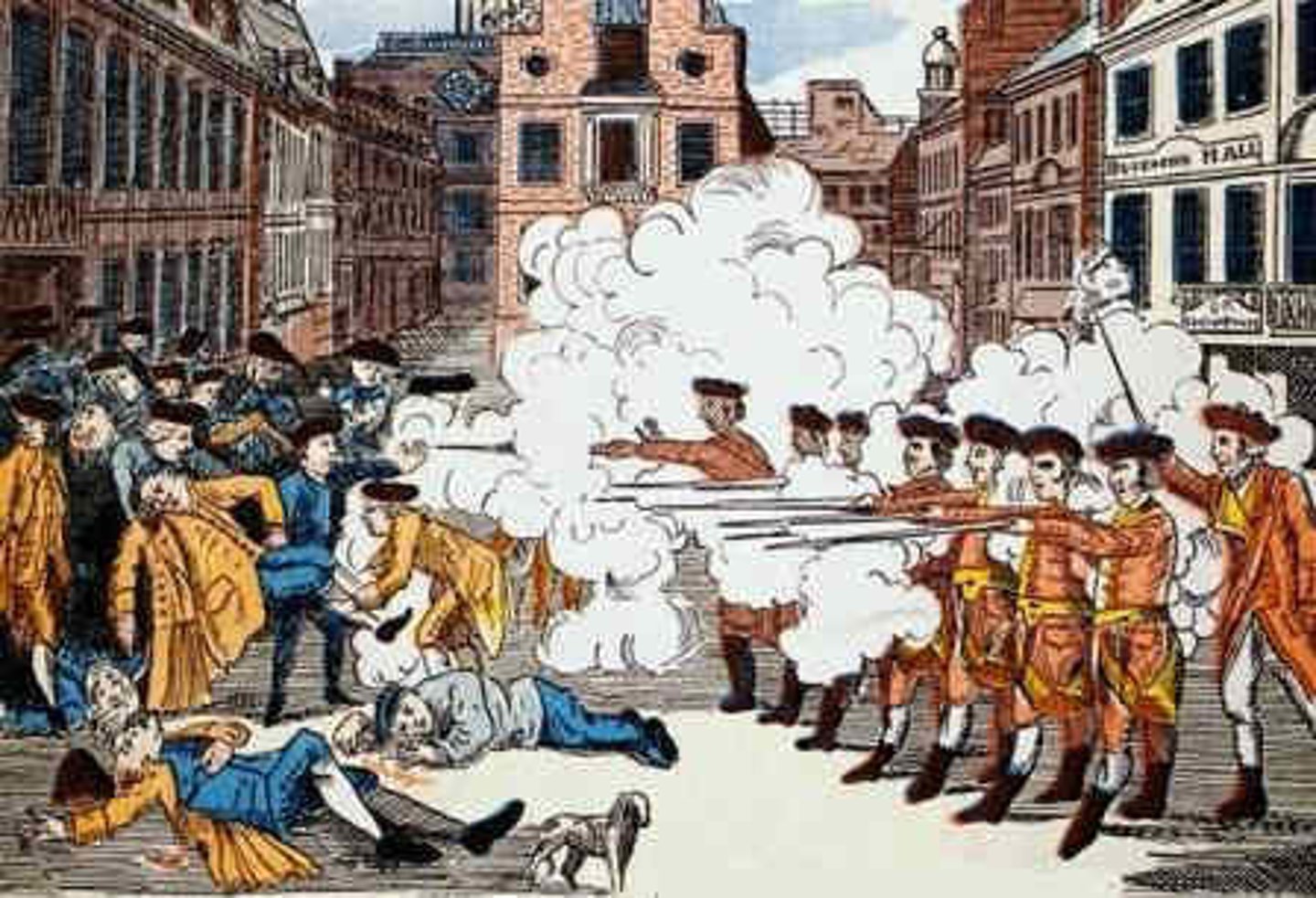
Boston Massacre
British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists who were teasing and taunting them. Five colonists were killed. The colonists blamed the British and the Sons of Liberty and used this incident as an excuse to promote the Revolution.

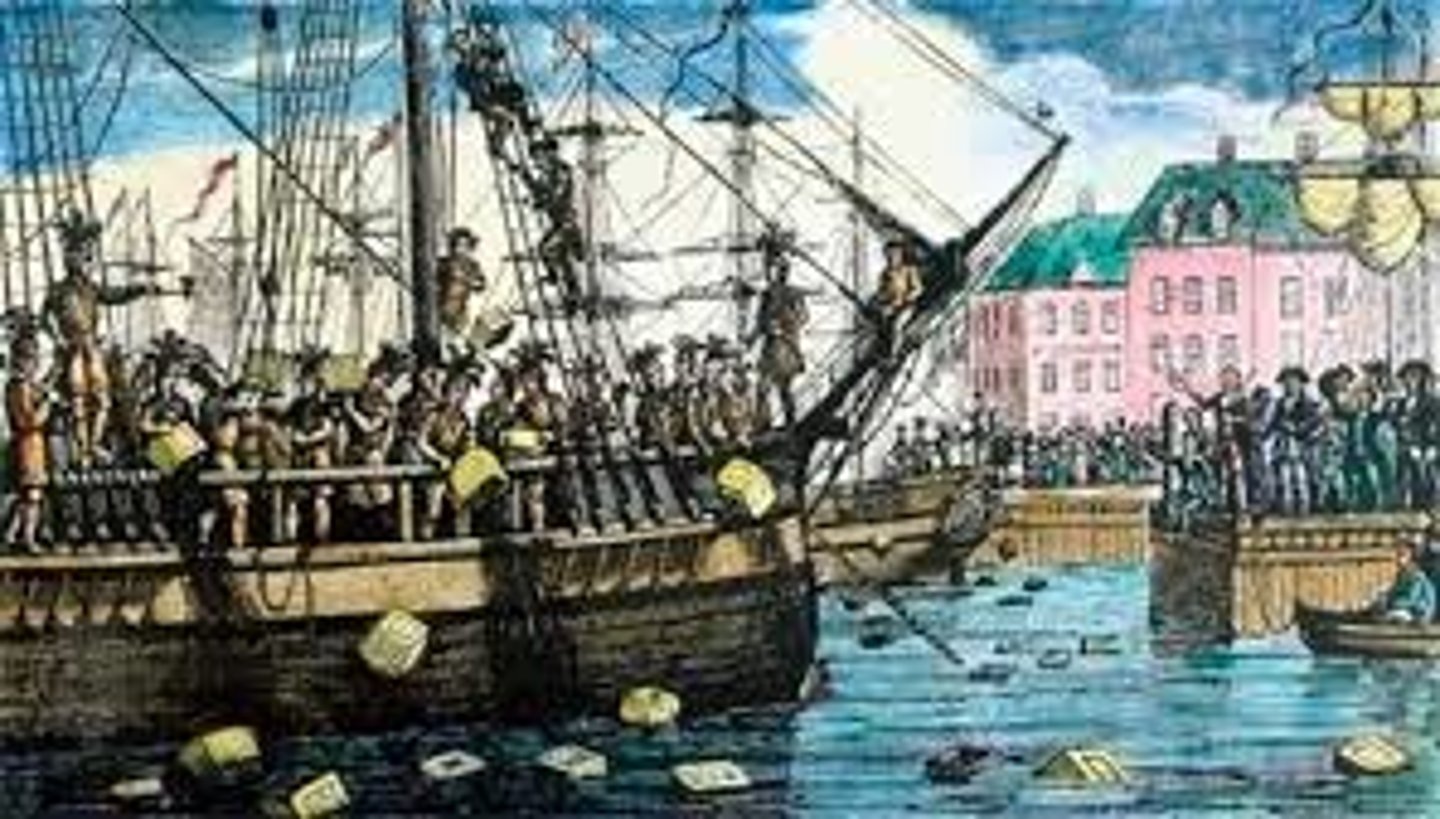
Boston Tea Party
Demonstration (1773) by citizens of Boston who (disguised as Indians) raided three British ships in Boston harbor and dumped hundreds of chests of tea into the harbor as a protest to taxes on tea

Intolerable Acts
in response to Boston Tea Party, 4 acts passed in 1774, Port of Boston closed, reduced power of assemblies in colonies, permitted royal officers to be tried elsewhere, provided for quartering of troop's in barns and empty houses
Coercive Acts
1. port act closed the port of Boston until the tea was paid for.
2. MA Gov't act reduced the power of the MA legislature while increasing the power of the royal governor.
3. Allowed royal officials accused of crimes to be tried in England instead of the colonies.
4. expanded the quartering act to enable British troops to be quartered in private homes--applied to all colonies.
Quebec Act
1744, law passed by Parliament in response to the Boston Tea Party, Expanded the borders of Canada, took land away from the colonies and gave it to Quebec, tried to take away colonies local self-rights
Salutary Neglect
an English policy of relaxing the enforcement of regulations in its colonies in return for the colonies' continued economic loyalty
Albany Plan of Union
plan proposed by Benjamin Franklin in 1754 that aimed to unite the 13 colonies for trade, military, and other purposes; the plan was turned down by the colonies and the Crown
1st Continental Congress
On September 1774, delegates from 12 colonies gathered in Philadelphia. After debating, the delegates passed a resolution backing Mass. in its struggle. Decided to boycott all British goods and to stop exporting goods to Britain until the Intolerance Act was canceled.
John Adams
A Massachusetts attorney and politician who was a strong believer in colonial independence. He argued against the Stamp Act and was involved in various patriot groups. As a delegate from Massachusetts, he urged the Second Continental Congress to declare independence. He helped draft and pass the Declaration of Independence. Adams later served as the first Vice President and the second President of the United States.
Thomas Jefferson
He was a delegate from Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and wrote the Declaration of Independence. He later served as the third President of the United States.
Benjamin Franklin
Printer, author, inventor, diplomat, statesman, and Founding Father. One of the few Americans who was highly respected in Europe, primarily due to his discoveries in the field of electricity. He was instrumental in negotiating French support for the Revolution.
Lexington and Concord
"The Shot Heard Round the World"- The first battle of the Revolution in which British general Thomas Gage went after the stockpiled weapons of the colonists in Concord, Massachusetts.
Bunker Hill
early battle of the Revolution which showed that the colonist could stand next to the British forces; the Americans inflicted large casualties on the British but in the end lost the battle due to a shortage of ammunition
2nd Continental Congress
1.Sent the "Olive Branch Petition"
2.Created a continental army with George Washington as the leader.
3. Agreed to write a formal letter declaring their independence from England.
Declaration of Independence
Drafted in 1776 by T. Jefferson declaring America's separation from Great Britain (3 parts-New theory of government, reasons for separation, formal declaration of war and independence)
Patriots
American colonists who were determined to fight the British until American independence was won
Tories
The Tories were colonists who disagreed with the move for independence and did not support the Revolution. (aka Loyalists)
Benedict Arnold
American General who was labeled a traitor when he assisted the British in a failed attempt to take the American fort at West Point.
Olive Branch Petition
before the revolution the 2nd Continental Congress sent a letter sent by the Second Continental Congress to King George III in 1775 in an attempt to avoid war (failed)
Thomas Paine
Revolutionary leader who wrote the pamphlet Common Sense (1776) arguing for American independence from Britain. In England he published The Rights of Man
Declaration of the Causes and Necessities of Taking Up Arms
A letter to the world explaining why the colonies were rebelling and that it was necessary
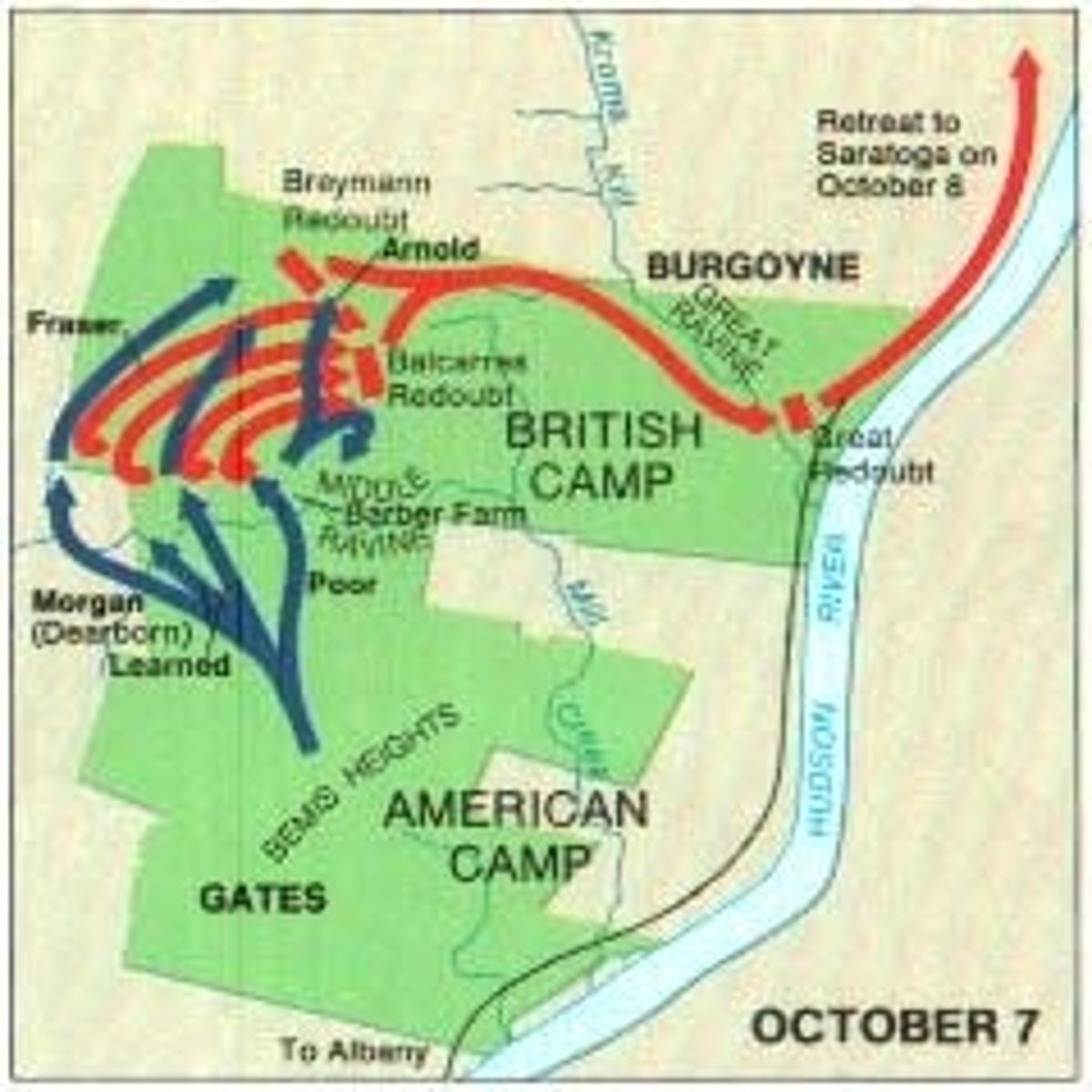
Saratoga
Battle won by the Americans in 1777 which helped convince the French to support the revolution.
French Alliance
The French entered the war in 1778, and assisted in the victory of the Americans seeking independence from Britain
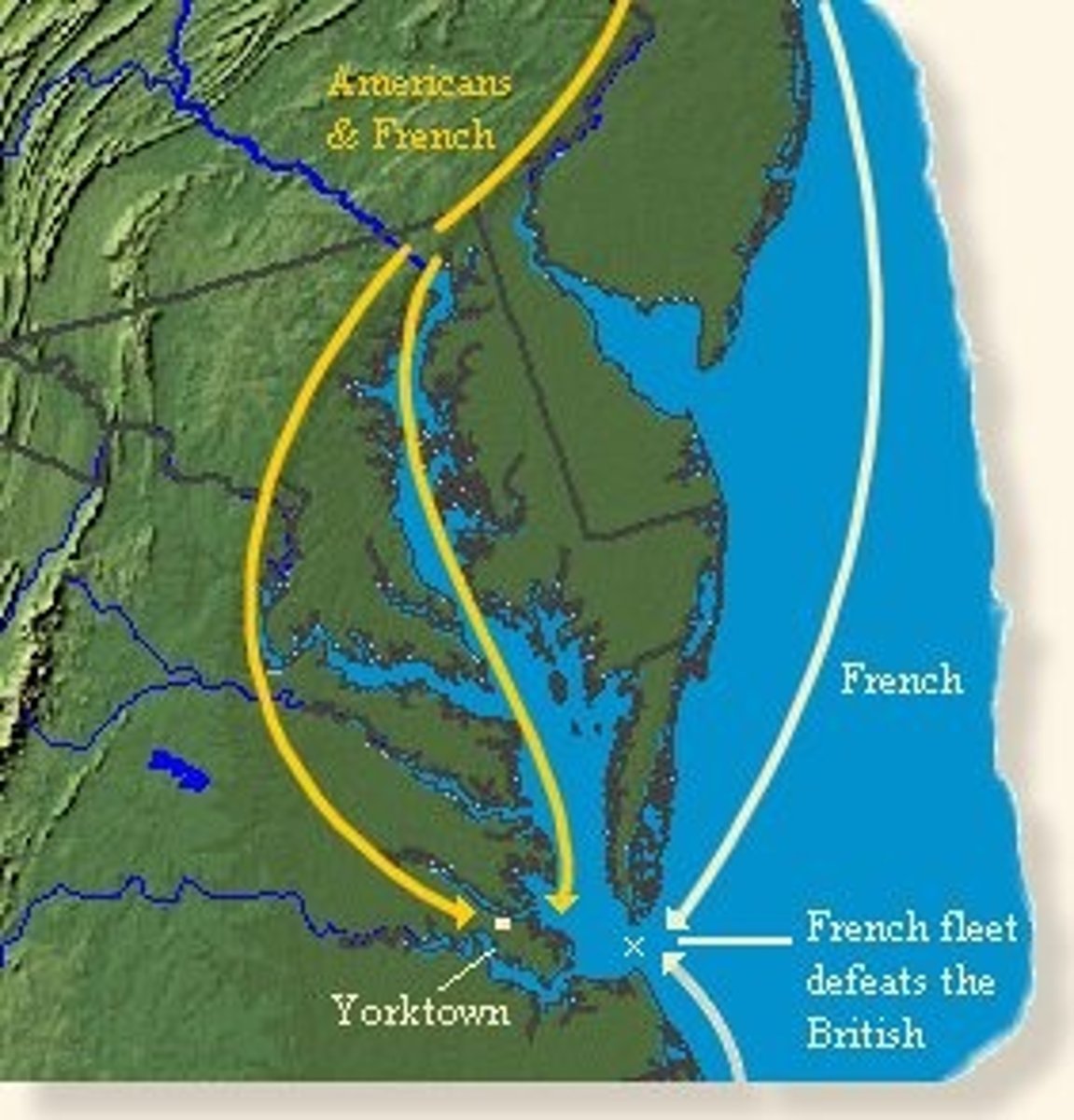
Yorktown
1781; last battle of the revolution; Benedict Arnold, Cornwallis and Washington; colonists won because British were surrounded and they surrended
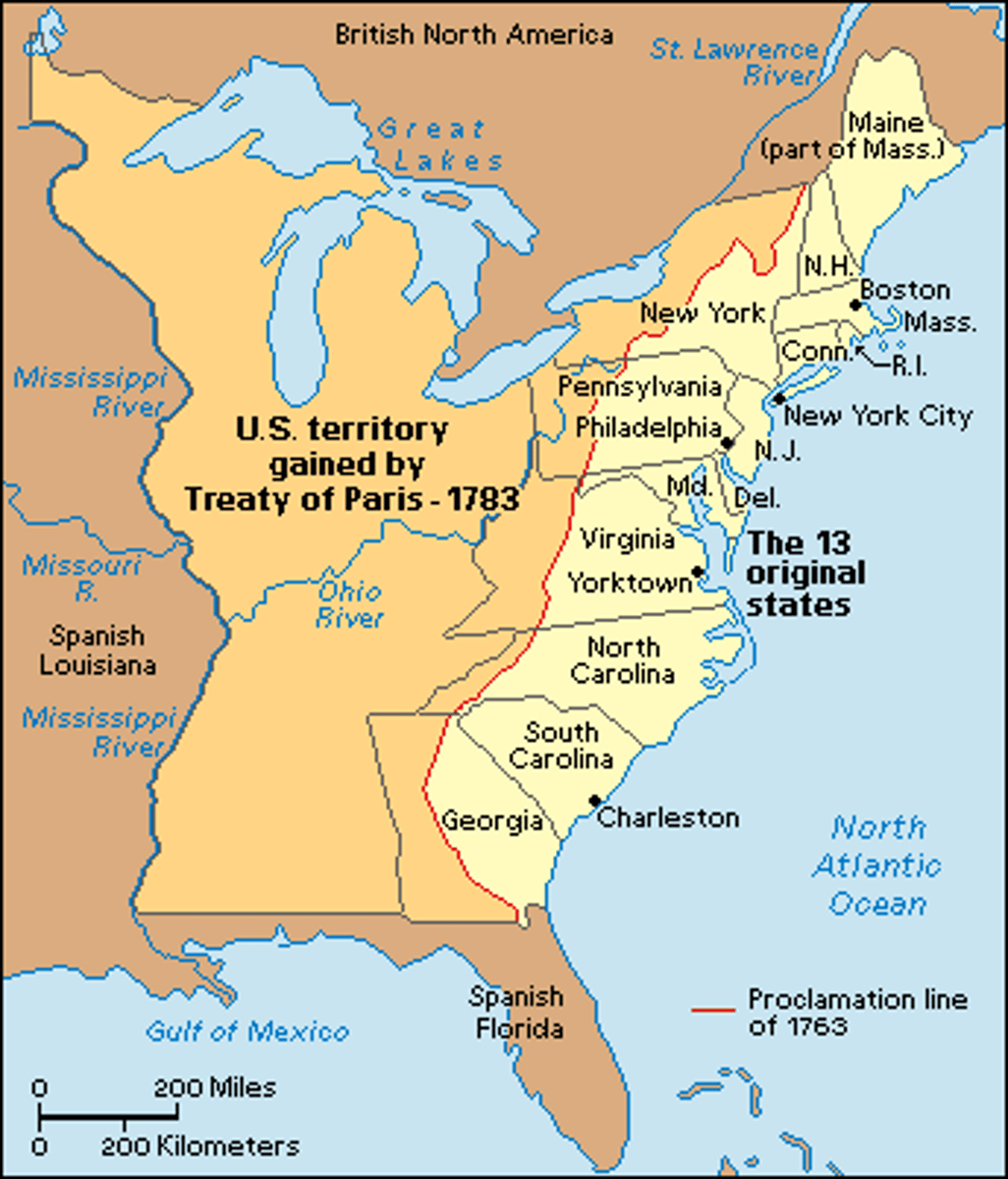
Treaty of Paris 1783
This treaty ended the Revolutionary War, recognized the independence of the American colonies, and granted the colonies the territory from the southern border of Canada to the northern border of Florida, and from the Atlantic coast to the Mississippi River
Separation of Power
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law
Articles of Confederation
Set up the 1st independent American government (1783-88). Nonbinding "league of friendship" among sovereign states with weak central government to help with common defense & cooperation (like the European Union). Replaced by our current constitution in 1788.
ratify
to approve, give formal approval to, confirm
land ordinance of 1785
A major success of the Articles of Confederation. Provided for the orderly surveying and distribution of land belonging to the U.S.
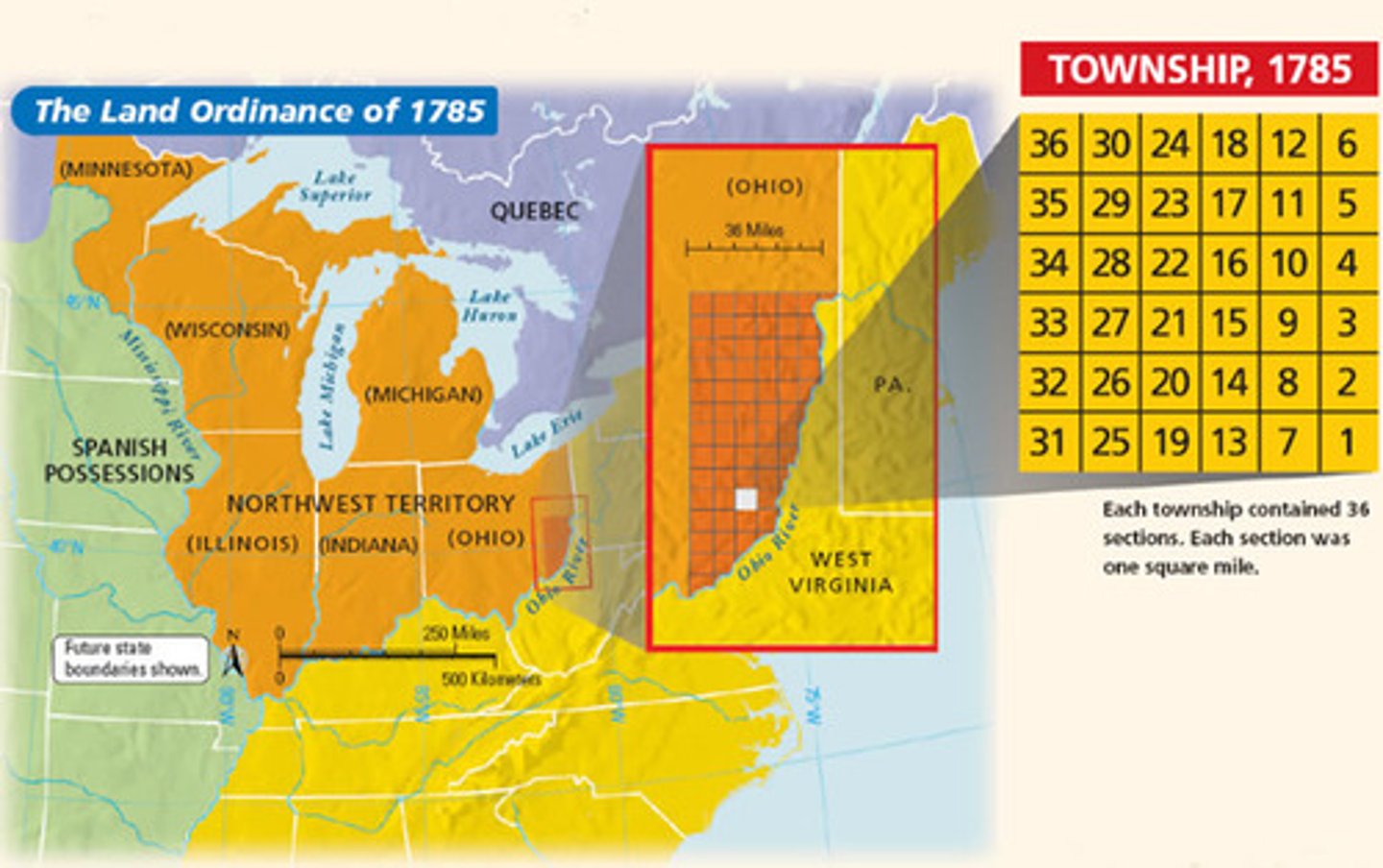
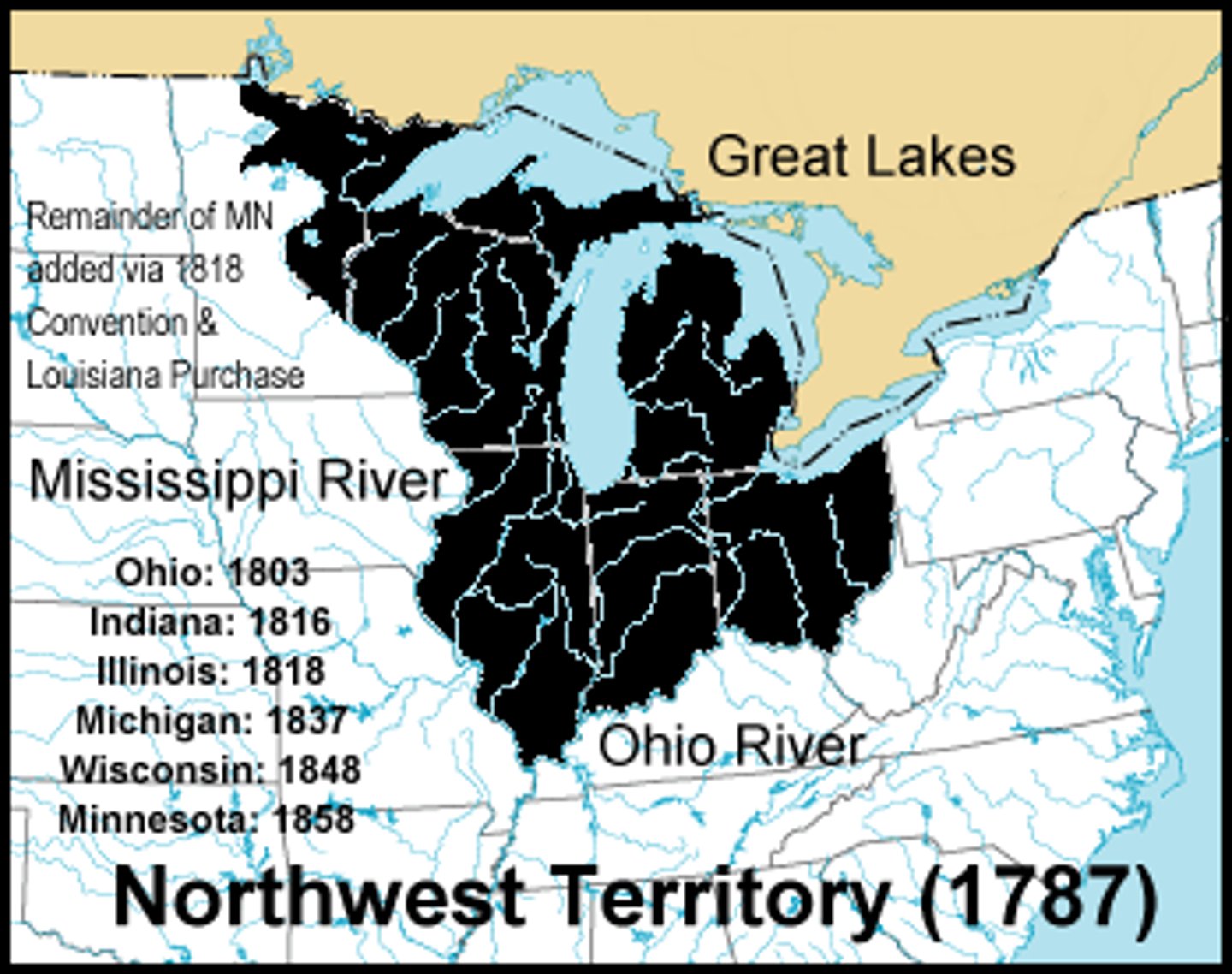
Northwest Ordinance 1787
Created the Northwest Territory (area north of the Ohio River and west of Pennsylvania), established conditions for self-government and statehood, included a Bill of Rights, and permanently prohibited slavery
Shay's Rebellion
Rebellion led by Daniel Shays of farmers in western Massachusetts in 1786-1787, protesting mortgage foreclosures. It highlighted the need for a strong national government just as the call for the Constitutional Convention went out.
Valley Forge
Place where George Washington and the Continental Army set up camp during the winter of 1777-1778; Washington lost almost half of his army to disease and starvation

Constitutional Convention
Meeting in 1787 of the elected representatives of the thirteen original states to write the Constitution of the United States.
James Madison
"Father of the Constitution," Federalist leader, and fourth President of the United States.
Alexander Hamilton
1789-1795; First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt.
John Jay
1st Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, negotiated with British for Washington
Federalists
Supporters of the Constitution that were led by Alexander Hamilton and John Adams. They firmly believed the national government should be strong. They didn't want the Bill of Rights because they felt citizens' rights were already well protected by the Constitution.
Anti-Federalists
Anti-Federalists rose up as the opponents of the Constitution during the period of ratification. They opposed the Constitution's powerful centralized government, arguing that the Constitution gave too much political, economic, and military control. They instead advocated a decentralized governmental structure that granted most power to the states
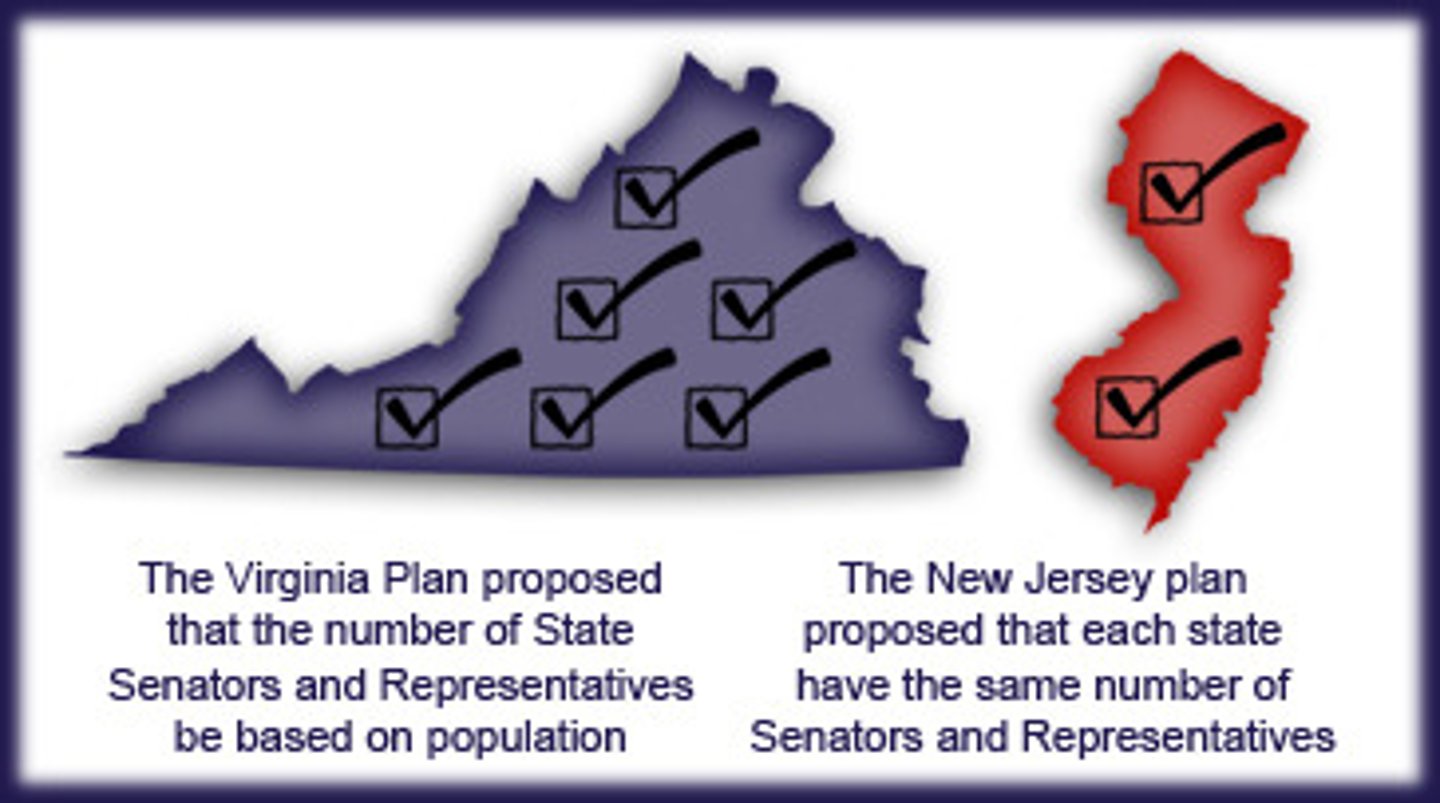
Virginia Plan
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for representation of each state in Congress in proportion to that state's share of the U.S. population.
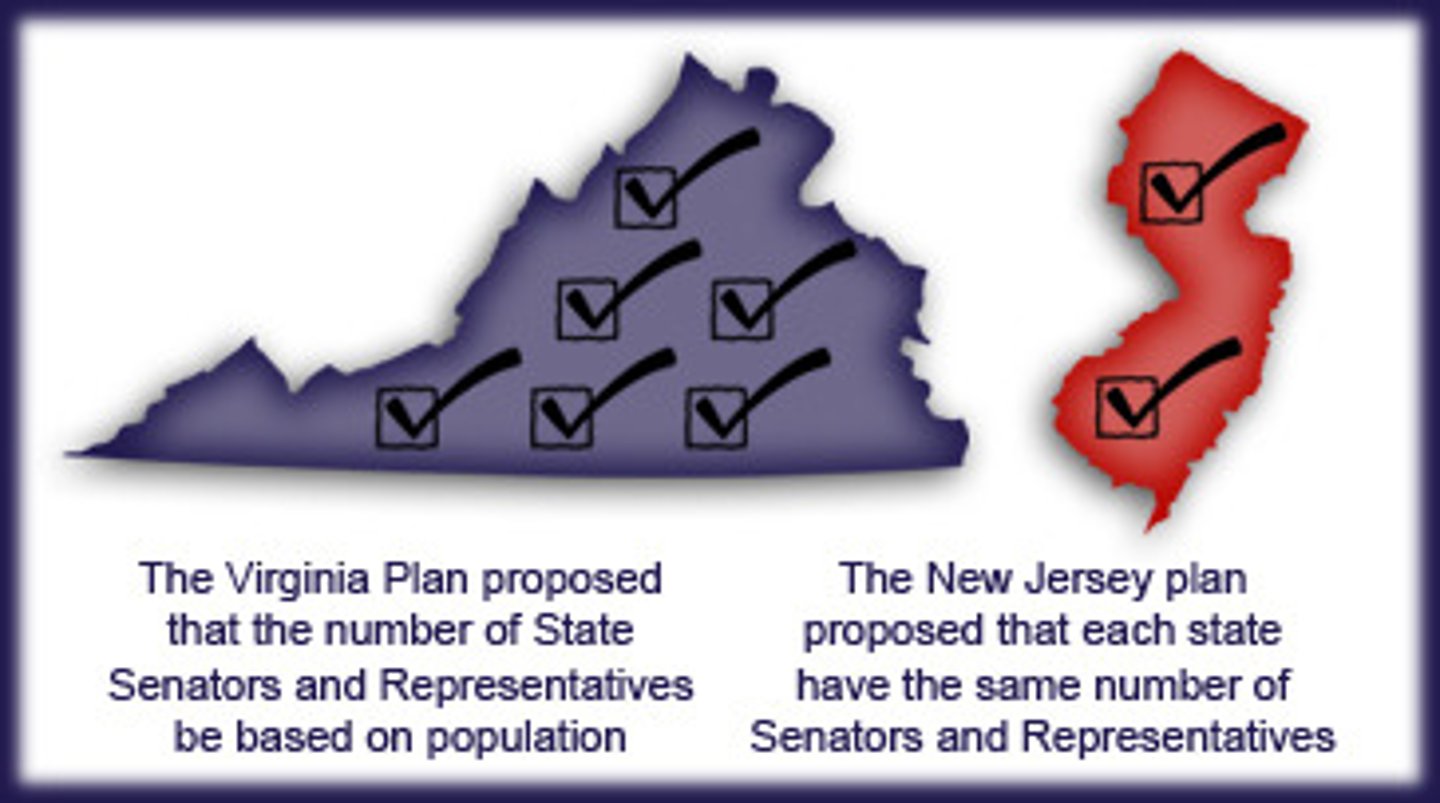
New Jersey Plan
Plan at Philadelphia Convention for equal representation in new Congress (1 state 1 vote). Also known as "small state plan." Opposite of the Virginia "big state" Plan. Becomes basis of representation in the Senate.
Bill of Rights
A formal statement of the fundamental rights of the people of the United States, incorporated in the Constitution as Amendments 1-10, and in all state constitutions.

George Washington
1st President of the United States; commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution (1732-1799)
Presidential Cabinet
Created by George Washington, a group of advisors that helped him run the government. Each is given a "department" and is referred to as the "secretary of..." (except for the Attorney General).
Proclamation of Neutrality
A formal announcement issued by President George Washington (1793), declaring the U.S. a neutral nation in the conflict between Great Britain and France.
Jay Treaty
(GW) 1795, Chief Justice John Jay was sent to Britain to stop the seizing of American's ships but Britain refused which lead to the closing of the western posts for the British
Pickney Treaty
1795 - Treaty between the U.S. and Spain which gave the U.S. the right to transport goods on the Mississippi river and to store goods in the Spanish port of New Orleans.
Whiskey Rebellion
A protest caused by tax on liquor; it tested the will of the government; Washington's quick response showed the government's strength and mercy (led an army to put down the rebellion)
Washington's Farewell Address
Warned Americans not to get involved in European affairs, not to make permanent alliances, not to form political parties and to avoid sectionalism.
XYZ Affair
Incident in which French agents demanded a bribe and loan from the U.S. diplomats in exchange for discussing an agreement that French privateers would no longer attack American ships; led to an undeclared war between U.S. and France
Alien and Sedition Acts
A series of laws that sought to restrict the activities of people who opposed Federalist policies (1798)
Election of 1800
Jefferson and Burr each received 73 votes in the Electoral College, so the House of Representatives had to decide the outcome. The House chose Jefferson as President and Burr as Vice President. (aka Revolution of 1800)
