Ornithology Midterm
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Feathers
Lack of teeth
Fusion and reduction of bones
Pneumatic bones (connected with respiratory system)
Bipedal
Digitigrade
Small size and mass
Forelimbs adapted for flight
Centralized body mass
High metabolic rate
Highly developed central nervous system and vision
What are the 11 things all modern birds share?
Feathers
Lack of teeth
Fusion and reduction of bones
Pneumatic bones
Centralized body mass
Name 5 things that define a bird.
Taxon
A recognized group in a classification
Nomenclature
A naming protocol developed by Carl von Linnae (Carolus Linnaeus) which consisted of latinized scientific bird names- two names for each species
Hairy woodpecker
Picoides villosus
Class Aves
What Class are all birds in?
Order Piciformes
What order are living birds in?
29
How many orders of living birds are there?
The American Ornithologist’s Union
The official list of accepted English common names is maintained by?
By morphological similarities and dissimilarities
How were birds initially classified?
Phylogenetic (groups defined by having a common ancestor)
How are birds classified now?
Comparative method
Studying evolution and adaptation by comparing morphology and behavior of species with different lifestyles. For example: Red Grouse of Great Britain remains dark coloured year-round while the similar Willow Ptarmigan of Newfoundland turns white in the winter.
The comparative method
A phylogenetic classification is necessary for the use of which method?
Biogeography
The study of the distribution of plants and animals across the surface of the Earth
Nearctic
Neotropical
Palearctic
Ethiopian
Oriental
Australasian
Oceanic
What are the 7 major faunal regions?
Ethiopian: Ostriches
Neotropical: Toucan
Oriental: Fairy Bluebirds
Australasian: Emus
Oceanic: Kagu
List the birds that are endemic to each faunal region
Ostriches
Which birds are endemic to the Ethiopian faunal region?
Toucans
Which birds are endemic to the Neotropical faunal region?
Fairy Bluebirds
Which birds are endemic to the Oriental faunal region?
Emus
Which birds are endemic to the Australasian faunal region?
Kagu
Which birds are endemic to the Oceanic faunal region?
Single occipital condyle
Single middle ear bone, the stapes
5-6 mandibular bones on each side of the jaw
Sclerotic ring supporting the eye structure
Scales on legs
Ankle sighted in the tarsal bones
Females are the heterogametic sex (ZW sex chromosomes)
What are the shared characteristics of birds and reptiles?
In the Jurassic Period
When did birds likely evolve?
Common Loon
Which birds have a Holarctic biogeography?
Osprey
Which birds have a cosmopolitan biogeography?
Trogons
Which birds have a Pantropical biogeography?
Emperor Penguins
Which birds have an Antarctic biogeography?
Hermann von Meyer
Who founded Archaeopteryx lithographica near Solnhofen quarry?
Feathers
What are the bird-like characteristics of Archaeopteryx lithographica?
Clawed digits on the forelimbs (unfused) + feathers
Toothed reptile-like jaws
Tiny cartilaginous sternum
Ribs without uncinate processes
Unfused tail bones
What are the reptile-like characteristics of Archaeopteryx lithographica?
Sinosauropteryx
Sinornithosaurus
Caudipteryx
Microraptor
Anchiornis
Name the protobird discoveries found in Liaoning, China, from the Jurassic-Cretaceous period.
Coelurosaurian Theropods
The discoveries from Liaoning, China indicated that birds descended directly from?
Avialae
All dinosaurs with feathered wings used for flapping flight. Birds directly descended from these.
Fujanvenator
Give an example of a Therapod feathered dinosaur
The Miocene
Order Passeriformes radiated explosively during?
Feathers evolved:
For flight directly
For insulation (then subsequently adapted for flight)
For display via sexual selection (then subsequently adapted for flight)
For mechanosensation (then subsequently adapted for flight)
What are the 4 feather evolution hypotheses?
Speciation
The evolution of new bird species which proceeds by genetic divergence of isolated populations, such as the colonization of oceanic islands or isolation within continental landmasses by warming or cooling climates
Linneaus presented the first classification of birds based on superficial morphological similarity rather than by specific cirteria in Systema Naturae .
Describe the early species concept.
Lumping and splitting trends change as species concepts change
As species concepts change, what happens?
Biological Species Concept
Ernst Mayer stated that species are groups of interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups
Reproductive isolation with geographical separation (ex: osprey)
Hybridization (ex: Mallard + Black Duck)
Problems with extinct forms
What are some problems of the Biological Species Concept?
Phylogenetic Species Concept
Charles Darwin states that the arrangement of the groups within each class, in due subordination and relation to each other, must be genealogical in order to be natural. Each taxon is monophyletic.
Leads to Splitting (ex: fox sparrow + murrelets)
What is the problem with the Phylogenetic Species Concept?
Taxonomic characters
Homologous structures shared by at least two taxa traceable phylogenetically to the same feature in an immediate common ancestor.
Parsimony
The explanation with the fewest evolutionary changes is the most likely explanation
Grebe + Loon
Longclaw + Meadowlark
Dovekie + Diving Petrel
Turkey Vulture + Black Vulture
What are some examples of convergent evolution in birds?
Electrophoresis of allozymes
DNA-DNA hybridization and melting point analysis
Mitochondrial DNA restriction site analysis and sequencing
What are some molecular genetic techniques to solve the taxonomic character problem?
Mix of similar DNA melts at a higher temperature and mis of dissimilar DNA melts at a lower temperature
Explain Sibley and Ahlquist’s DNA-DNA hybridization and melting point analysis.
Keratin
Feathers are made of?
Aerodynamic lifting surface
Smooth aerodynamic coating to body
Insulation
Camouflage
Communication
Sensory
What are the 6 primary functions of feathers?
25,000
What is the maximum number of feathers on a swan?
2-4 thousand
What is the minimum number of feathers in a small passerine?
Calamus, rachis, barb, barbicel, barbule, and ramus
What are the parts of a feather?
Pennaceous
The hard, firm-vaned part of a feather
Plumulaceous
The soft afterfeather
Contour
Flight
Down
Filoplumes
Semiplumes
Bristles
What are the 6 feather types?
Down feathers
Feathers without a firm vein - interlocking fibers that trap air
Filoplumes
Feathers that are sensory in function (neither insulating or aerodynamic)
Semiplumes
Feathers that are space filling
Bristles
Feathers that are mostly protective in function. In raptors they are used as flycatchers
Ornamental Feathers
Feathers of contrasting plumes with highly modified adornments
Preening
The rearrangement and maintenance of feathers using the foot and bill. The barbicel-barbule system is reoriented, dirt is cleaned off, feathers are dried if wet, and parasites are removed.
Uropygial gland
Secretes an oily wax and fatty acid that maintains feather flexibility and waterproofing
Crested Auklets
Which birds use the uropygial gland for smell?
Pitahuis
Which birds use the uropygial gland for poision?
Analgesidae (feather mites)
Sarcoptidae (itch mites)
Mallophagidae (bird lice)
Name 3 parasites that affect feathers?
Molting
Feather growth and replacement occurs by this process.
Follicles
The growth of new feathers occurs within?
The inferior umbilicus
Remaining living material withdraws from the finished feather through?
Basic
Plumage that occurs after the breeding season
Alternate
Specialized adornments grown before the breeding season
Prebasic and Prealternate
The two molts are called?
Melanins (produces gray, black, and brown)
Carotenoids (produces yellow, orange and red)
Porphyrins (produce unusual colours such as magenta)
What are the 3 biochrome pigments?
Psittacofulvins
Produce the red colour in parrots
Spheniscins
Produce the yellow colour in penguins
Porphyrins
Produces the magenta colour in Turacos
Structural colours
Colour (blue, green, iridescence) is produced by diffraction off regular structures (plates or tubules) on the feather surface. Short wavelengths (blue and green) are reflected off the grating, while longer wavelengths are absorbed
Airfoil
Reduced air pressure on the upperwing surface creates lift proportional to the surface are of the airfoil
Gliding flight
Wing acts like an airplane’s wing
Flapping flight
Flying that increases airspeed flow over lifting surfaces allowing dynamic soaring
Wing loading
The number of grams of body mass per square cm of wing surface area
Aspect ratio
The ratio of wing span squared / wing area. How long and narrow the wings are determines gliding efficiency.
Short and wide wings. Common Murre
What does a Low aspect ratio mean? Give an example of a bird that has a low aspect ratio.
Long and thin wings. Laysan Albatross
What does a high aspect ratio mean? Give an example of a bird with a high aspect ratio.
Dihedral
The angle at which the wings are held relative to the body. An adaptation for low flight speed.
Curvature
Non-flat wings in woodland species and gallinaceous birds
Penguin (small hard flippers)
Auk (air and water)
Shearwater/albatross (long narrow wings for high speed gliding)
Swift (long narrow stiff wings, almost all long primary)
What are some examples of birds with specialized wings?
Normal tail
The most common, basic tail which is compact and not vulnerable to damage. Very efficient with some limitations
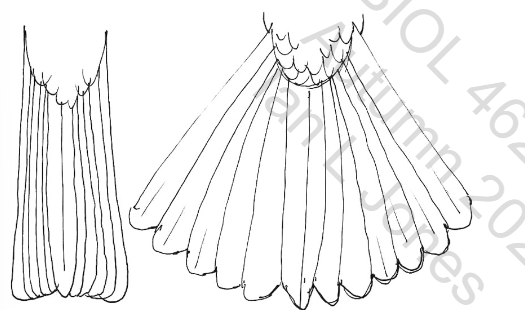
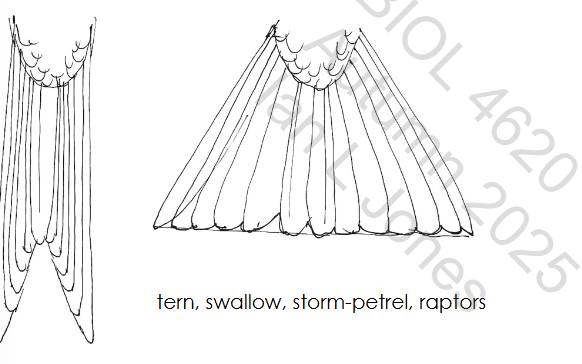
Forked tail
The most efficient tail found in raptors, aerial insectivores (swifts and swallows) and terns (plunge diving seabirds). Susceptible to damage
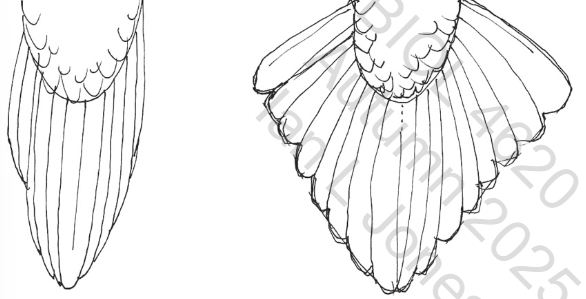
Graduated Tail
A tail not efficient for flight. Functions in balance, as a prop (in woodpeckers), or as an ornament (in pheasants). Very damage resistant
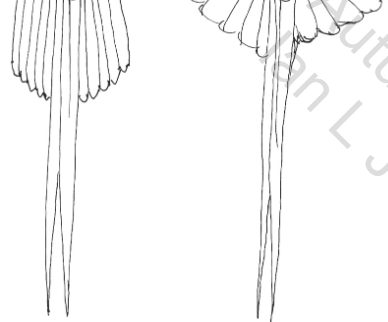
Streamer Tail
Long streamer tails that produce only drag, possibly for ornamental function. Northern pintail, long-tailed ducks, and others have these.
Normal
Forked
Graduated
Streamer
What are the four types of tails?
38-44 degrees
What is the body temperature of a bird?
6-12
How many air sacs do birds have?
9 (pair of cervical, pair of anterior thoracic, pair of posterior thoracic, pair of abdominal sacs, and one interclavicular air sac)
Most birds have how many air sacs?
Air sacs forcibly pump air through the lungs and aid in exhalation. 100% of gas is exchanged with each breath.
How do birds respirate?
Bird lungs consist of loops in which air passes
Why are bird lungs very different from other vertebrates?
Basal metabolic rate
The resting metabolic rate (inactive bird). Large birds have lower rates of this.
Active metabolism
Measured in relation to BMR; the energetic expense of flight
Insulation, pigmentation and behaviour
How do birds control their body temperature?