Quality Control (L23, 24)
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
See slides for additional
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Quality
1) Product conformance to design
2) Freedom from deficiencies
What does Freedom from deficiencies mean?
The product has everything that you do want and nothing that you do not want.
Causes of Random variation
Human variability
Raw material variability
Machine vibration, etc.
Assignable Variation
An exception from normal operating conditions
Not account for by random variations
Can be attributed to a cause (systematic error)
Operator mistakes
Defective raw materials
Tool failures
Machine malfunctions, etc.
Natural Tolerance Limits
Use of natural tolerance limits will yield 99.73% of parts within specification
PCI = 1
2700 defective parts per million

What is a preferred PCI value
PCI > 1.33
PCI = 2 is the goal
Control charts
track key process variables over time
What is depicted?
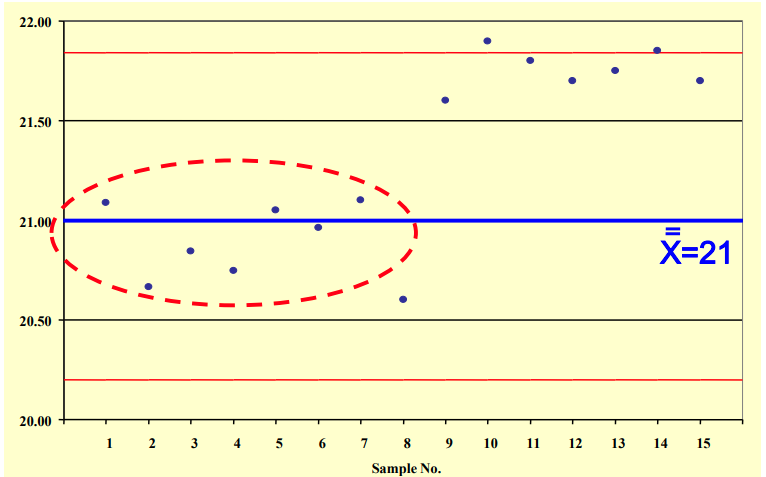
Process Shift
What is depicted?
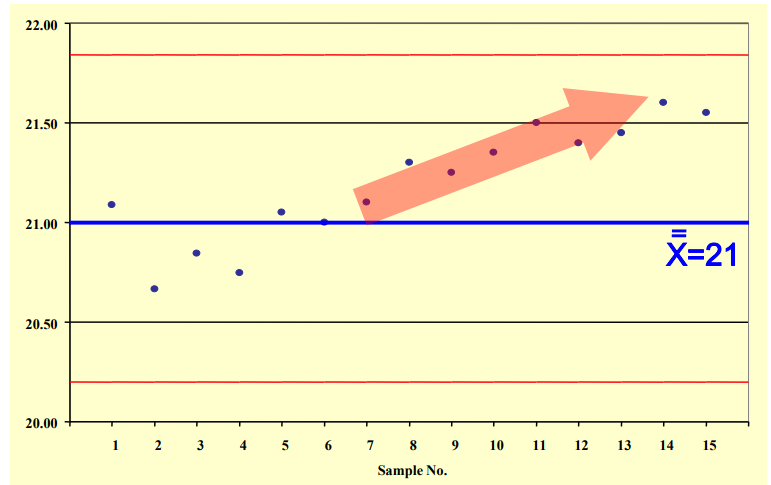
Process Drift
Control charts for attributes
Do not assess a specific quantitative variable
Focus on monitoring defect rate over time
Use of p and c chart
p Chart
fraction of defects per sample
c Chart
number of defects per sample
Inspection
Use of measurement and gaging to determine conformance to design specifications
Measurement
Comparison of an unknown quantity relative to a known standard
Two types of inspection
1) inspection by variables
2) inspection by attributes
inspection by variables
actual values of key dimensions are measured
Inspection by attributes
Gaged to determine if they are within tolerance (Pass/Fail)
(Not as good for SPC)
Quicker and cheaper
Manual Inspection
Inspection procedures are often performed manually
The work is boring and monotonous, yet the need for precision and accuracy is high
Because of the time and cost of manual inspection, statistical sampling procedures are often used to reduce the need to inspect every part
Risk can be reduced by using a larger sample size
Note: Many defective parts cannot be visually inspected
Functional inspection required or hidden features prevent contact inspection
100% Inspection
Theoretically, the only way to achieve 100% good quality is by 100% inspection
▪ All defects are screened and only good quality parts are passed
Problems with manual 100% inspection
1. The expense - the unit inspection cost is applied to every part in the batch
2. Human errors - in 100% manual inspection, there are almost always human errors
▪ Operator fatigue
▪ “Cherry-picking”/inspector bias
▪ Therefore, 100% inspection using manual methods is no guarantee of 100% good quality product
Parts sortation
separating parts into acceptable and unacceptable bins
Automated 100% inspection can accomplish what corrective actions
1) Parts sortation - separating parts into acceptable and unacceptable bins
▪ Three bins: acceptable, reworkable, & scrap
2) Feedback of inspection data can be used in upstream operation so compensating adjustments can be made in the process to reduce variability and improve quality
Methods of automated inspection
Coordinate measuring machines
2. Lasers
3. Machine vision
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)
Measuring machine consisting of a contact probe and mechanism to position the probe in three dimensions relative to surfaces and features of a work part
CMM Advantages
Higher productivity
Greater inherent accuracy and precision that conventional methods
Reduced human error
Reverse engineering
Scanning Laser Systems
laser beam deflected by a rotating mirror to sweep a beam of light past an object
Machine Vision
Acquisition, processing, and interpretation of image data by computer
Edge detection
determining locations of the boundaries of an object by identifying contrast in light intensity between adjacent pixels at borders
Feature extraction
determining feature values of an image
template matching
Compare one or more features of an image with corresponding features of a model
(template) stored in computer memory
Machine Vision Applications
Inspection
Part identification
Visual guidance and control
Safety monitoring