Introduction to Invertebrates in General Biology II
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Invertebrate
Animal lacking a backbone.
Choanoflagellates
Theorized to have given rise to animals.
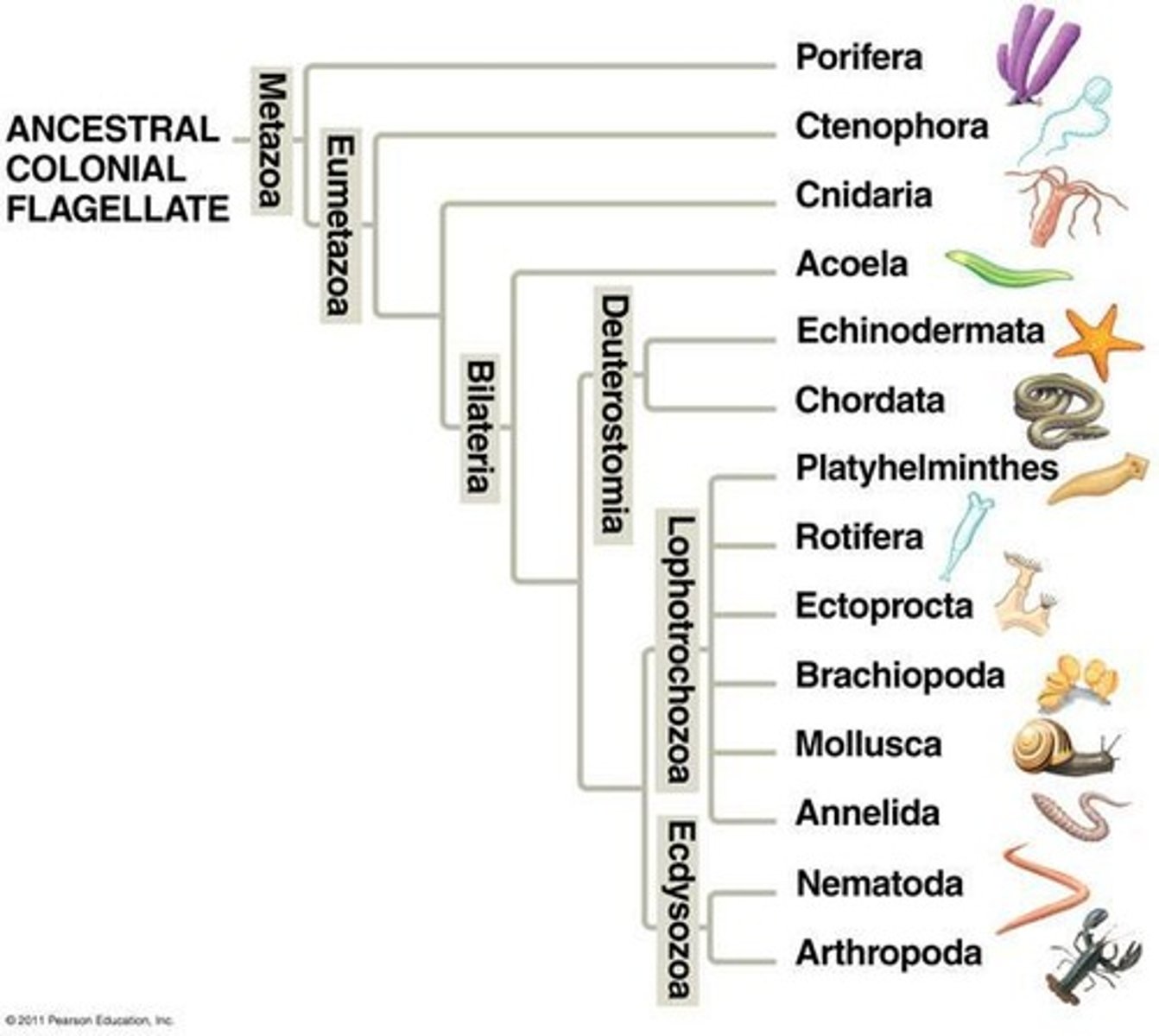
Porifera
One of the superphyla or phyla of invertebrates.
Cnidaria
One of the superphyla or phyla of invertebrates.
Lophotrochozoa
One of the superphyla or phyla of invertebrates.
Ecdysozoa
One of the superphyla or phyla of invertebrates.
Phylum Porifera
Known by its common name 'sponges', lack true tissues, mostly marine habitat, sedentary locomotion, and are filter feeders.
Hermaphrodites
Most sponges are hermaphrodites, with each individual functioning as both male and female, producing two types of gametes.
Sequential hermaphrodites
Exist first as one sex, later exist as the other.
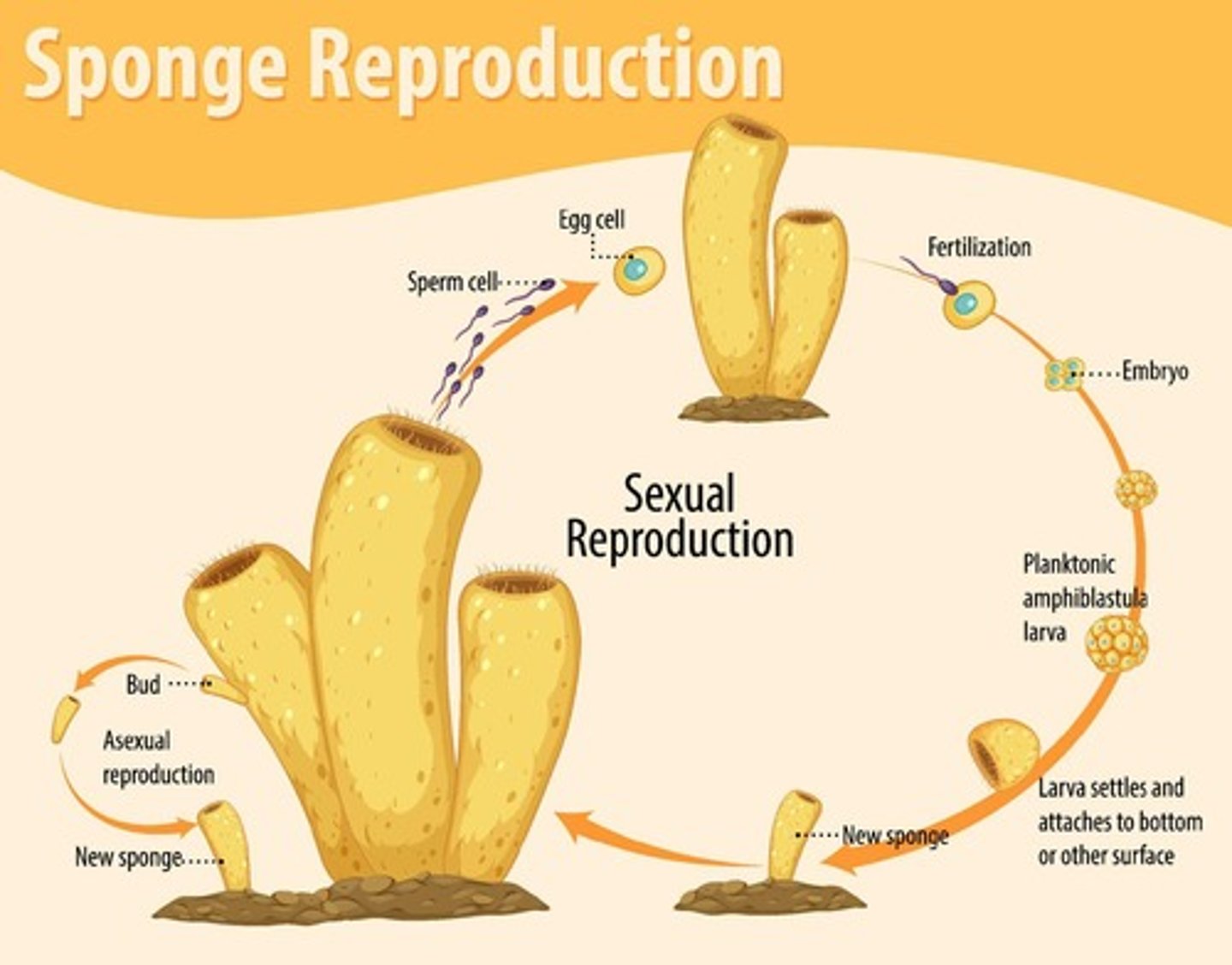
Sponge fertilization
Sperm from a 'male' sponge is released into the water current, drawn to a 'female' sponge to fertilize the egg.
Flow of Water in Sponges
Water flows through sponge's pores into spongocoel, then out of the osculum.
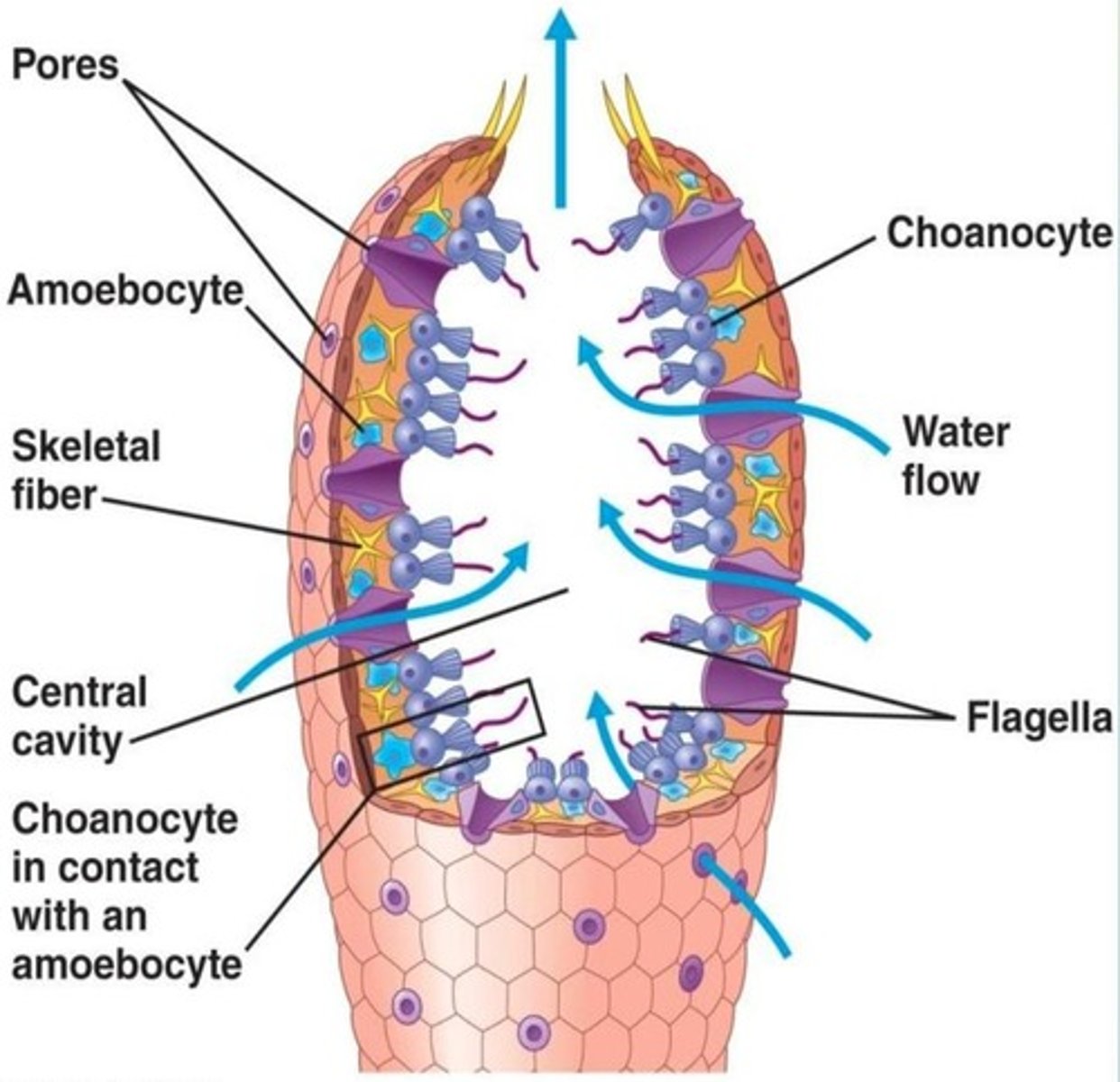
Choanocytes
Also known as 'collar cells', they engulf bacteria and food particles and resemble the choanoflagellate protist.
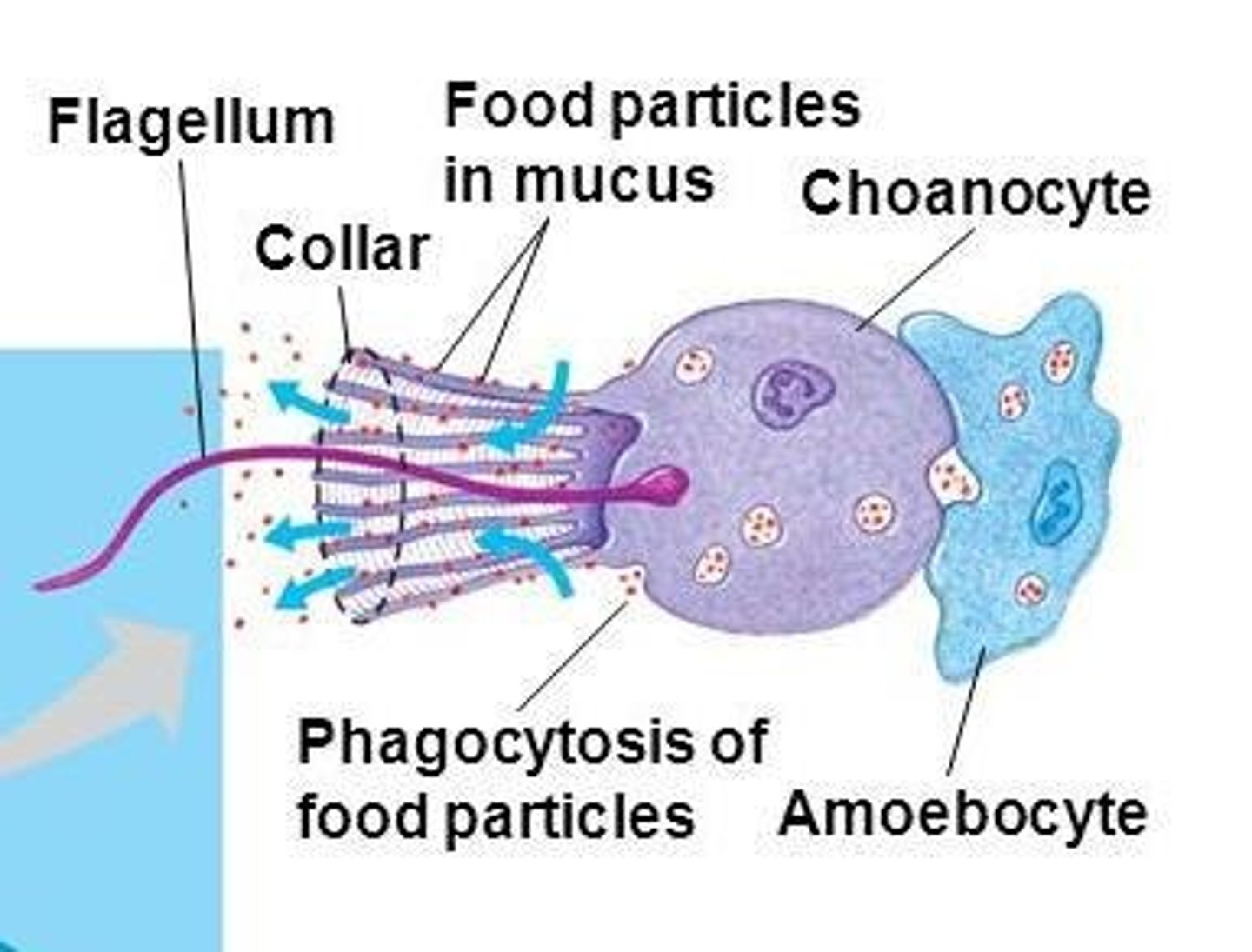
Amoebocytes
Totipotent cells found within the mesohyl that can develop into other types of cells, digest food engulfed by choanocytes, and manufacture tough skeletal fibers.
Commercial uses of sponges
Sponges are used for bath sponges and in the production of antibiotics/defense compounds, such as cribrostatin which kills cancer cells and penicillin-resistant bacteria.
Phylum Cnidaria
Part of the ancient clade eumetazoans, characterized by tissue-containing animals, aquatic habitat, motile and sessile locomotion, radial symmetry, and predatory nutrition.
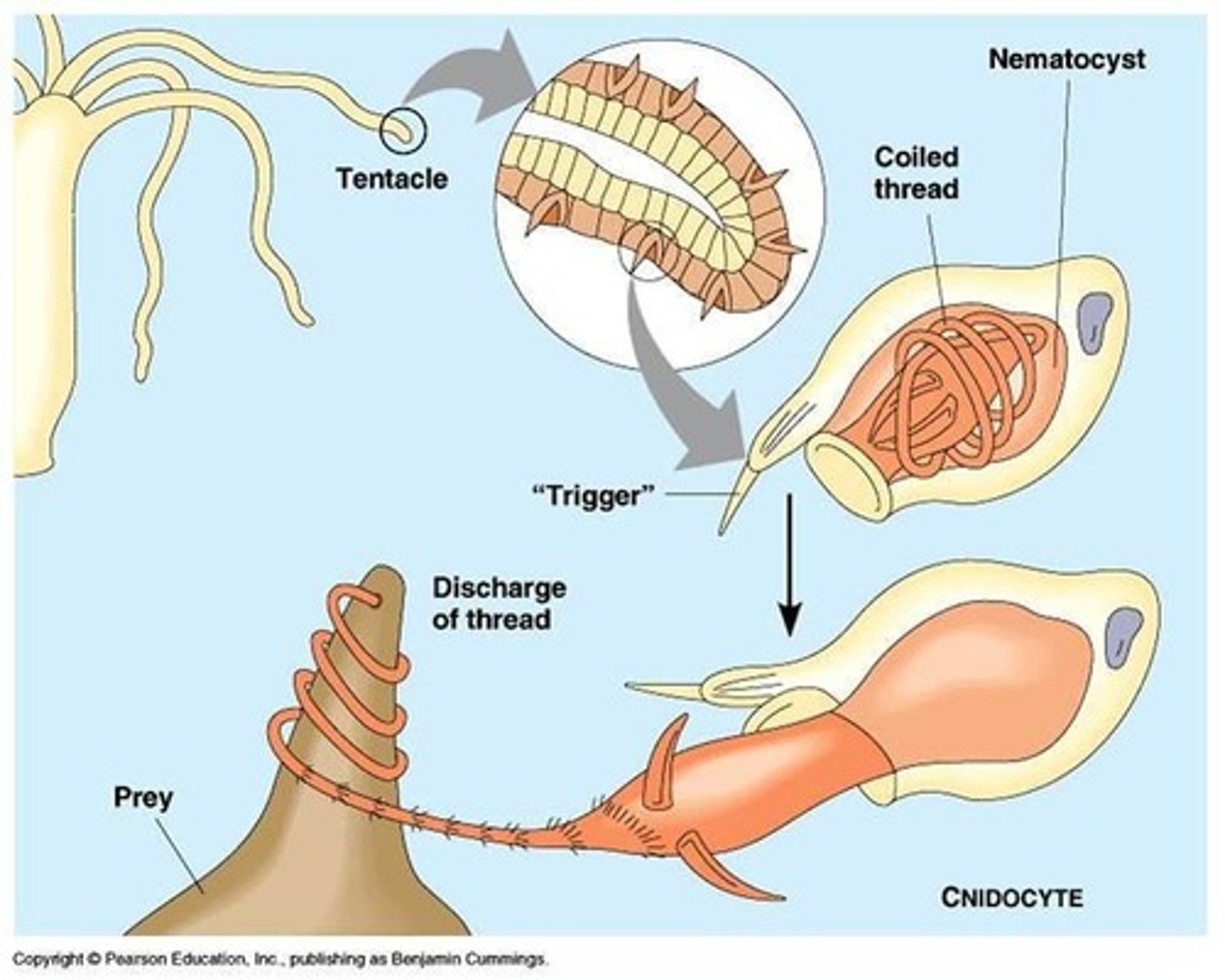
Cnidocytes
Cells aiding in prey capture, containing nematocysts.
Incomplete digestive system in Cnidarians
Single cavity with an opening as both mouth and anus.
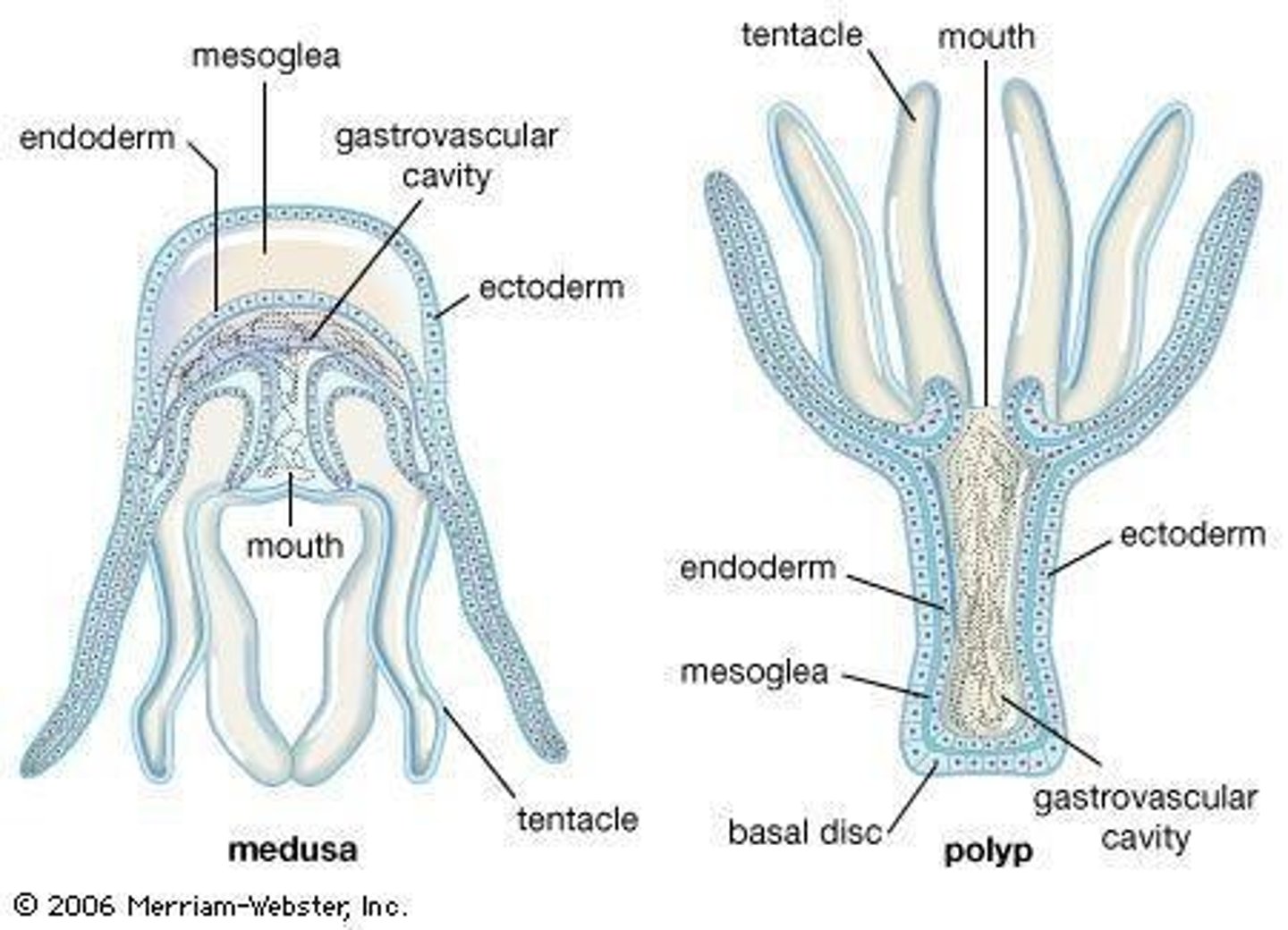
Body plans of Cnidarians
Two variations: Polyp, which adheres to surfaces on the opposite side of the mouth, and Medusa, which has a flattened shape with the mouth downwards.
Medusozoans
All members produce a medusa during their life cycle, most alternate between polyp form and medusa.
Anthozoans
All members only occur in polyp form, are sedentary, and form symbiotic relationships with algae.
Coral exoskeleton
Corals secrete a hard exoskeleton made of calcium carbonate, with polyp generations building upon earlier generations.
Coral Reef
Collections of thousands of individual coral colonies, providing habitat for many fish species.
Threats to coral reefs
Include pollution, ocean acidification, rising seawater temperature, and overharvesting.
SuperPhylum Lophotrochozoans
Part of the ancient clade Bilateria, characterized by bilateral organisms, aquatic or land habitat, motile locomotion, bilateral symmetry, and coelom or hemocoel body cavity.
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Known as flatworms, they have thin, flattened bodies, are triploblastic but acoelomates, and inhabit freshwater or damp terrestrial environments.
Excretory system of Platyhelminthes
Protonephridia maintains osmotic balance with surroundings through a network of tubules with flame bulbs.
Planarians
Genus Dugesia, found in freshwater ponds and streams, feeding on small dead animals.
Tapeworms
Parasitic flatworms found in the digestive tract of humans and farm animals, with a scolex and no digestive tract.
Rotifers
Known as 'Wheel-bearers', they inhabit freshwater, marine, and damp soil, with cilia around the mouth to draw water.
Phylum Mollusca
Soft-bodied organisms with a hard shell of calcium carbonate, found in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial habitats.
Chitons
Marine molluscs with a shell made of 8 unsegmented plates, using their radula to scrape algae off rocks.
Gastropods
Comprising ¾ of all molluscs, they have a single spiraled shell and are found in marine or freshwater habitats.
Bivalves
Aquatic molluscs like clams and oysters, characterized by no head or radula and adductor muscles that draw shell halves together.
Cephalopods
Marine predators with a beak-like jaw, modified foot into an excurrent siphon, and a reduced internal shell.
Phylum Annelida
Segmented worms known as 'little rings', including earthworms and leeches, found in sea, freshwater, and damp soil.
Earthworms
Terrestrial annelids that aerate soil and improve its texture through their fecal castings.
SuperPhylum Ecdysozoans
Organisms that undergo ecdysis or 'molting', including the phyla Nematodes and Arthropods.
Nematodes
Roundworms found in aquatic, damp soil, and moist tissues of plants and animals, covered by a tough cuticle.
Arthropods
Organisms with a cuticle exoskeleton made of chitin, an open circulatory system, and well-developed sensory structures.
Metamorphosis
A developmental process with two or more distinct stages, including incomplete and complete metamorphosis.
SuperPhylum Deuterostomia
Organisms with bilateral symmetry, radial cleavage, and formation of anus from blastopore, including Echinodermata and Chordata.
Phylum Echinodermata
Commonly known as echinoderms, examples include sea stars and brittle stars, with a hard endoskeleton and tube feet for locomotion.
Water Vascular System
A series of hydraulic canals and tube feet in echinoderms, aiding in locomotion and feeding.
Phylum Chordata
Commonly known as chordates, characterized by bilateral symmetry and includes groups like tunicates, lancelets, and vertebrates.