Acts / Compromises / Treaties / Amendments / Etc. (APUSH)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Treaty of Tordesillas
1494. Pope Alexander IV split the newly discovered lands. East to Spain (Latin America) and West to Portugal (some of Brazil and Africa)
Toleration Act
1649. Freedom of religion in Maryland.
Navigation Acts
1660s. Used to strengthen British mercantilist theory but poorly enforced.
Treaty of Paris of 1763
1763. Ended French and Indian War. France lost Canada and land East of the Mississippi to Britain, and New Orleans and West of Mississippi to Spain.
Proclamation Act
1763. Forbade colonists from moving West of the Appalachians.
Writ of Assistance
Enabled British officers to search homes and warehouses for goods that might be smuggled without search warrant.
Sugar Act
1764. Taxed colonists on sugar or molasses. First tax to raise revenue for the mother country.
Stamp Act
1765. Taxed printed goods. First internal tax since colonists could produce paper products (New England)
Townshend Act
1767. Taxed leader, paper, glass, tea, and paint. Repealed EXCEPT for tea.
Tea Act
1773. Made colonists buy tea from British East India Company only, monopolizing tea to raise prices later.
Intolerable Acts
1774. Punishment on Boston for Boston Tea Party.
1. Boston Port Act
2. Massachusetts Gov. Act
3. Administration of Justice Act
4. More quartering
Olive Branch Petition
1775. Last attempt at reconciliation. Letter to King George II, who did not respond.
Treaty of Paris of 1783
1783. Ended the American Revolution
Articles of Confederation
1781-1789. Created by 2nd Continental Congress. Gave too much power to state gov. Unicameral congress. No national guard. No executive leader.
Federalist Paper #10
Written by James Madison to promote a republic over a pure democracy so that minority groups could be heard.
Federalist Paper #51
Written by Madison to promote the ideas of checks and balances so that no one branch of government would overpower the other
Constituion
1787. Replaced Articles of Confederation
Connecticut Compromise
Created bicameral congress.
3/5 Compromise
Counted 3 people for every 5 slaves living for the purpose of both representation in Congress and property taxes.
Judiciary Act
1789. Created lower federal courts and court districts
Proclamation of Neutrality
1793. US would not get involved in French Revolution.
Jay Treaty
1794. Britain agreed to evacuate its posts on the US western frontier
Pinckney Treaty
1795. U.S given right by Spanish to navigate the Mississippi.
Alien and Sedition Acts
1798. John Adams (federalist). Made it more difficult for immigrants to come into the country.
1. Naturalization - 14 years to become citizens
2. Sedition - punishment for speaking against the U.S
3. Alien Act - president could deport any dangerous immigrant
Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions
1798. Found Alien and Sedition Acts null and void. t
Treaty of Ghent
1814. Ended War of 1812 in stalemate.
Rush-Bagot Treaty
1817. Signed between the U.S and Great Britain who agreed upon naval disarmament along the Great Lakes to ease tension at the northern border.
Adams-Onis Treaty
1819. U.S bought Florida from Spain.
Embargo Act
1807. Ended all of America's importation and exportation, hoping to pressure the French and British to recognize U.S. neutrality rights in exchange for U.S. goods but hurt the economy.
Non-Intercourse Act
1809. Jefferson. Stated that the US would trade with all foreign nations, except Great Britain and France. Replaced Embargo Act.
Treaty of 1818
1818. Treaty between Britain and America after the War of 1812, it allowed the Americans to share the Newfoundland fisheries with Canada, and gave both countries a joint occupation of the Oregon Territory for the next 10 years. 42 was U.S border, and 42-49th parallel was jointly owned.
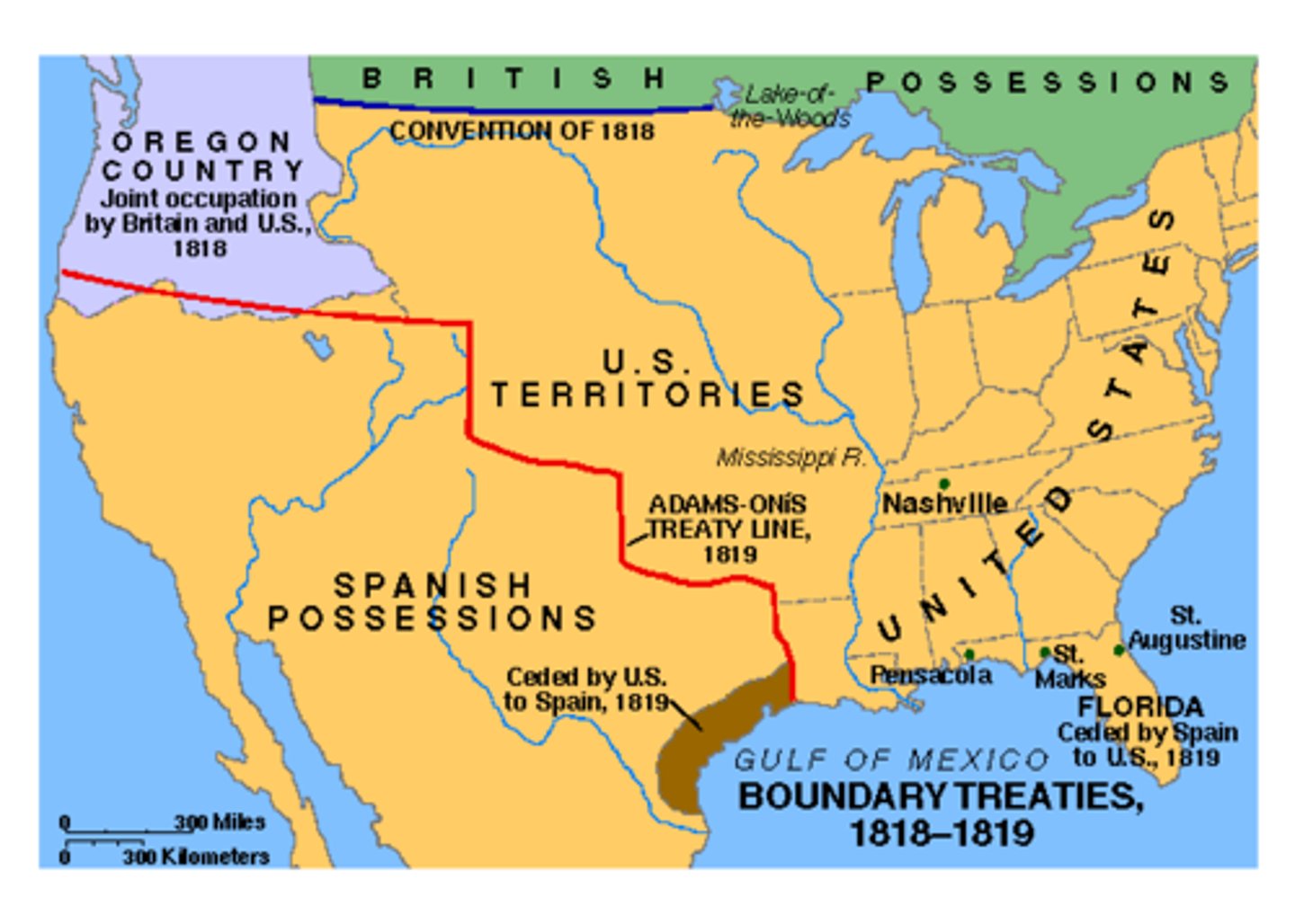
Missouri Compromise
1820. Created by Henry Clay, stating that Missouri would enter the union as a slave state. Maine broke away from Massachusetts and enter as a free state. Territory north of 36 degrees, 30 minutes would enter as a free state.
Tariff of 1828 (Tariff of Abominations)
1828. Highest tariff the nation had seen. Hated by John Calhoun (led to Exposition and Protest Act)
Exposition and Protest
1828. Written by John Calhoun in support of nullification, calling on compact theory, he argued the Tariff of 1828 was unconstitutional and that South Carolina could lawfully refuse to collect it (nullification)
Monroe Doctrine
1823. European powers could not colonize or interfere with the affairs of the U.S,
Indian Removal Act
1830. Andrew Jackson. Authorized the removal of Native Americans who lived east of the Mississippi River.
Compromise of 1833
1833. Proposed by Henry Clay. Tariff of Abominations would gradually decrease to the tax that had been set before 1828.
Webster-Ashburton Treaty
1842. Established Maine's northern border and the boundaries of the Great Lake states.
Oregon Treaty
1846. Settled dispute of Oregon boundary dispute, stemming from the Treaty of 1818 in which both U.S. and British settlers were granted free navigation of the territory. U.S expanded to the 49th parallel.

Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty that ended the Mexican War, granting the U.S. control of Texas, New Mexico, and California in exchange for $15 million. The U.S acquired the Mexican Cession.
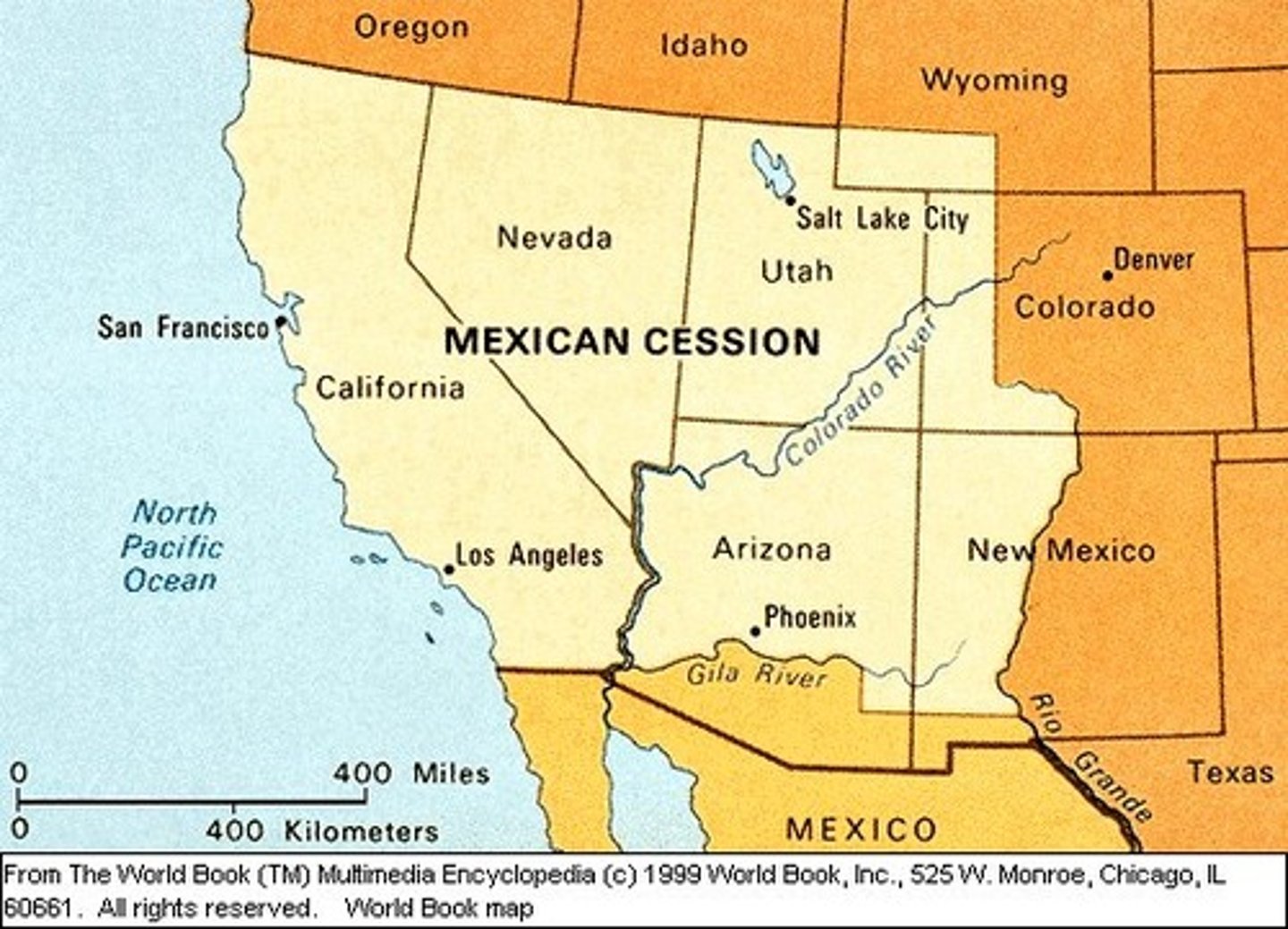
Wilmot Proviso
1846. Proposal to outlaw slavery in the land acquired by Mexican Cession.
Compromise of 1850 (Omnibus Bill)
1850. Proposed by Henry Clay when California had to decide whether to become a free or slave and had 5 provisions:
-California would be free
-Slave trade and auctions would be forbidden in D.C
-However, slavery would still be permitted in D.C
-Stricter fugitive slave laws would be enforced if caught using the underground railroad
-Rest of Mexican session would use theory of popular sovereignty
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854. Kansas and Nebraska (both north of 36 degrees, 30 minutes) had to enter as a free state according to the third provision of the Missouri Compromise, but this act gave them ability to exercise popular sovereignty. This resulted in the formation of the Republican party and Bleeding Kansas.
Crittenden Compromise
1860. Proposed by John Crittenden to avoid the Civil War. It would allow any state below 36 degrees, 30 minutes to enter the Union as a slave state. This was not passed by Lincoln, who opposed extension of slavery.
Emanicipation Proclamation
1863. Presidential order proclaimed by Lincoln. Any state still taking up arms against the US must free their slaves.
Conscription Act
1862. Drafted men between ages of 20 and 45 to serve in the Union Army.
13th Amdendment
1865. Lincoln. Officially abolished slavery after the war.
Morill Tariff Act
1861. James Buchanan. Increased tariff rates to help the Union get additional money and due to this new high tariff rate, new factories boomed in the North.
Morill Land Grant Act
1862. Federal government gave money to states in the West to improve education in their regions.
Homestead Act
1862. Lincoln. Encouraged Americans to continue to move to the West; government granted 160 acres of land in exchange for the land to be plowed and had 5 years of continued residence.
10% Plan
1863. Lincoln. A state could be reinstated into the union if 10% pledged allegiance.
Wade Davis Bill
1864. Proposed by Radical Republicans who wanted harsh punishments on the southerners so that they would never try to secede again. Required 51% of southerners to pledge allegiance.
Civil Rights Act of 1866
1866. Proposed by Radical Republicans and passed by over the veto of President Andrew Johnson. The act declared that all persons born in the United States were now citizens, without regard to race, color, or previous conditions, but was POORLY ENFORCED.
1st Reconstruction Act
1867. Congress required that the south be divided into 5 military districts and supposedly placed under martial laws so that the acts passed by congress were enforced. Vetoed by Johnson.
Black Codes
laws created by Southern states to overlook the new laws passed in attempts to restrict the newfound freedoms of African Americans
-could only work with letter of recommendation from their previous employers
-could not testify against whites in court
-some had curfews
Freedman's Bureau
1865. Wealth fare agency that gave good, housing, medical aid, schooling, and legal assistance to poor whites or former black slaves after the Civil War. Vetoed by Johnson.
Tenure Office Act
1867. Forbade the President to remove any cabinet member from office without permission of the senate. Viewed as unconstitutional by Johnson since cabinet is not even mentioned in Constitution.
14th Amendment
1868. Guaranteed citizenship and protection to all people of the U.S (entitled to "due process"). Also banned many ex-Confederates from holding public office and repealed 3/5 Compromise.
15th Amendment
1870. Granted male African Americans right to vote.
Compromise of 1877
1877. Ended Reconstruction by removing military troops from the South, appointing one southerner to serve in the cabinet, and allocating federal funds to recover the South.
Jim Crow Laws
Limited rights of blacks and enforced segregation. Literacy tests, grandfather clauses and poll taxes limited black voting rights
Amnesty Act of 1872
1872. Pardoned ex-Confederates by Ulysses S. Grant, except for highest leaders, such as Robert E. Lee
Chinese Exclusion Act
1882. Denied any additional Chinese laborers to enter the country while allowing students and merchants to immigrate.
Dawes Act
1887. Authorized the federal government to break up tribal lands by partitioning them into individual cheaper plots. Only those Indians who accepted the individual allotments were allowed to become US citizens.
Sherman Antitrust Act
1890. Banned any trust that restrained interstate trade or commerce
Interstate Commerce Comission
1887. Regulate railroads and other interstate trade.
Newlands Reclamation Act
1902. Roosevelt. Authorized the use of federal money to develop the west, it helped to protect national resources by building irrigation projects and dams in dry areas.
Hepburn Act
1906. Roosevelt. Used the Interstate Commerce Commission Act to regulate the maximum charge that railroads to place on shipping goods. Allowed ICC to regulate shipping prices of railroads [pro farmer, populist demand]
Meat Inspection Act
1906. Roosevelt. Set rules for sanitary meat packing and government inspection of meat products crossing state lines.
Mann-Elkins Act
1910. Taft. Allowed the federal government to regulate the telephone and telegraph companies.
16th Amendment
1913. Wilson. National income tax.
17th Amendment
1913. Wilson. Allowed. direct election of senators
Federal Trade Commission Act
1914. Woodrow. Made sure business remained fair by outlawing unfair methods of competition (Better Business Bureau)
Federal Reserve Act
1913. Woodrow. Put the nation's banking system under the supervision of the federal government for the first time.
Clayton Antitrust Act
1914. Woodrow. Enforced the Sherman Antitrust Act. Purpose was to restore competition in the business world.
Keating-Owen Act
1916. Woodrow. Tried to eliminate child labor in factories and sweatshops.
18th Amendment
1917. Woodrow. Prohibited the sale of alcohol. (Woody vetoed but congress passed it)
19th Amendment
1920. Woodrow. Women's suffrage.
Treaty of Paris of 1898
1898. Ended the Spanish-American War. US acquired Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. U.S now protectorate of Cuba (Truman granted Philippines their independence)
Teller Amendment
1898. Legislation that promised the US would not annex Cuba after winning the Spanish-American war
Open Door Policy
1899. Demanded open trade in China in order to protect US economic interests in that national. US wanted equal commercial access by all nations to the existing spheres of influence in China. Resulted in Boxer Rebellion in China in opposition.
Roosevelt Corollary
1904. Extension of Monroe Doctrine. Policed Latin America (protectorate) (big stick foreign policy of Roosevelt)
Gentlemen's Agreement
1907. Agreement between the United States and Japan that restricted Japanese immigration and segregated Japanese children from white students.
Proclamation of Neutrality 1914
1914. Wilson declared that the United States would remain "impartial in thought as well as in action." Aapproved of Wilson's policy.
Selective Service Act
1917. Required all men from ages 21 to 30 to register for the military draft
Sedition Act
1918. Made it illegal to speak against American war effort
Espionage Act
1917. Allowed postal authorities to ban treasonable newspapers, magazines, or novels.
Treaty of Versaille
1920. Imposed on Germany by the Allied powers after the end of World War I which demanded exorbitant reparations from the Germans
Wilson's 14 Points
1920. Plan for post-war peace: no secret treaties; freedom of the seas; removal of economic barriers; reduction of arms; adjust colonial claims. Rejected by Senate. US never joined League of Nations.
Volstead Act
1919. Enforced 18th amendment. Did not work.
Immigration Act of 1924
1924. Also known as the Johnson-Reed Act. Federal law limiting the number of immigrants that could be admitted from any country to 2% of the amount of people from that country who were already living in the U.S. as of the census of 1890.
McNary-Haugen Bill
1926. Designed to allow the federal government to purchase agricultural surpluses and sell them abroad at lowered prices.
Kellog-Briand Pact
1928. Nations denounced war.
Good Neighbor Policy
1933. Repealed Roosevelt Corollary, stating the US would intervene if Latin America asked.
Hawley-Smoot Tariff
1930. Raised tariff rates hoping Americans would buy American goods..
Reconstruction Finance Corporation
1932. Poured millions of dollars into big business but did not provide immediate relief to the destitute.
Agricultural Administration Act
Paid farmers to reduce supply so that it could exceed demand. Found unconstitutional since it exceeded how federal government could spend money and showed favortism towa