A&P - 3.5 Cell Growth & Division
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
cell cycle
life cycle of a single cell, from its birth until its division into two new daughter cells
the two major phases of the cell cycle include mitosis (cell division), and interphase, when the cell grows and performs all of its normal functions
mitosis and interphase are both further subdivided
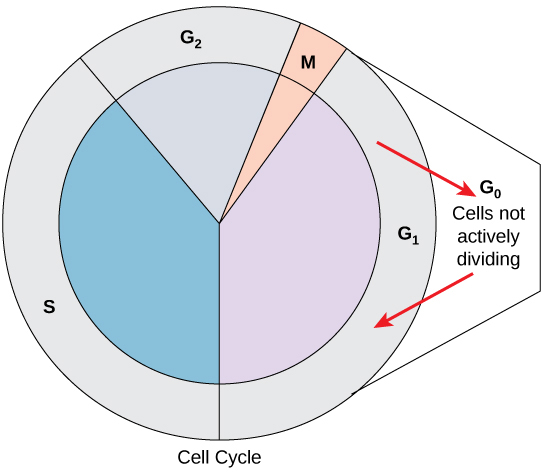
checkpoint
progress point in the cell cycle during which certain conditions must be met in order for the cell to proceed to a subsequence phase
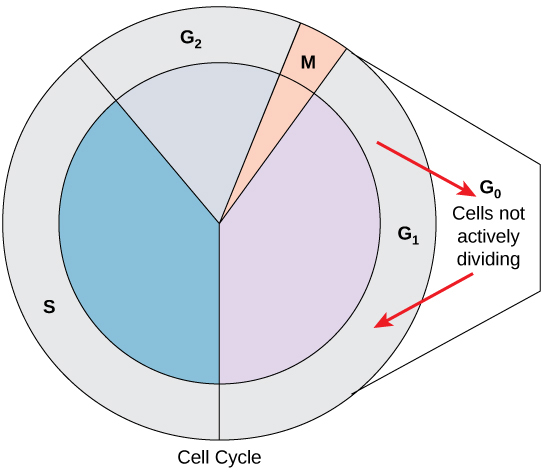
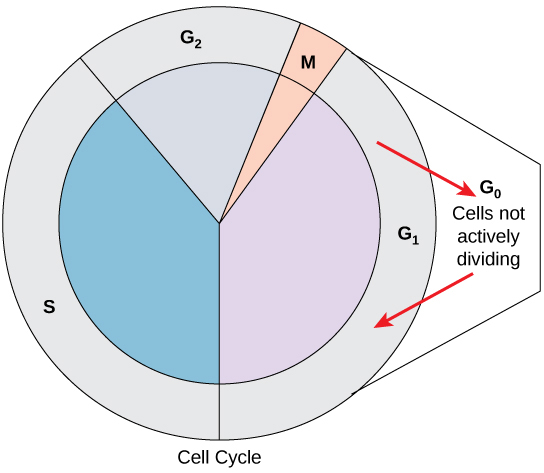
interphase
entire life cycle of a cell, excluding mitosis
phases:
G1
G0
S
G2
interphase: G0
phase of the cell cycle, usually entered from the G1 phase; characterized by long or permanent periods where the cell does not move forward into the DNA synthesis plate
cells not actively dividing
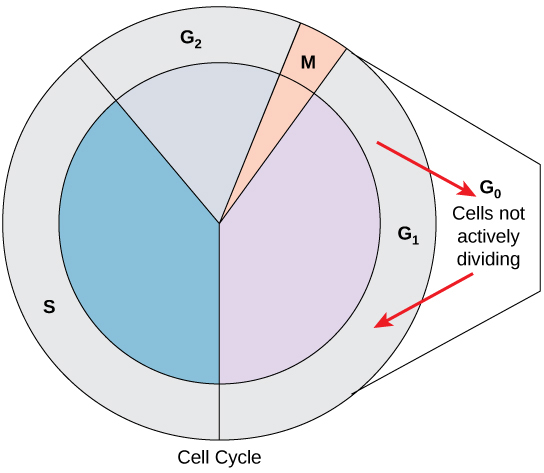
interphase: G1
first phase of the cell cycle, after a new cell is born
the cell grows in volume, performs its normal functions, undergoes protein synthesis, and duplicates its organelles
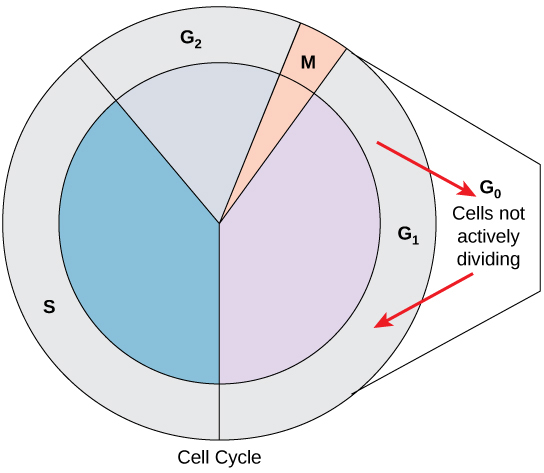
interphase: S
“DNA synthesis” - DNA replicates itself
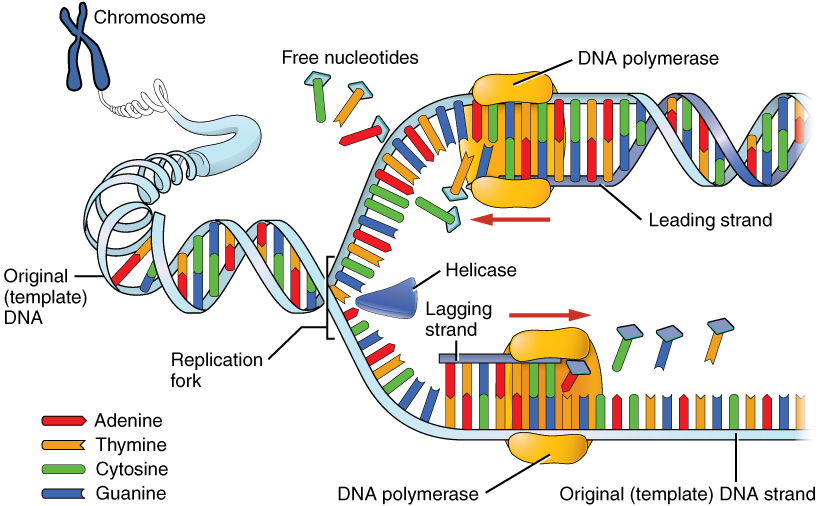
DNA replication
process of duplicating a molecule of DNA
single-stranded chromosomes form double-stranded chromosomes
helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA
DNA polymerase binds to the DNA and attaches complimentary nucleotides (A always binds to T while C always binds to G)
the daughter DNA is built continuously on the leading strand but discontinuously on the lagging strand
Okazaki fragments produced on the lagging strand are “glued” together by ligase
two daughter strands of DNA are produced with each having half of the original strand (semi-conservative replication)
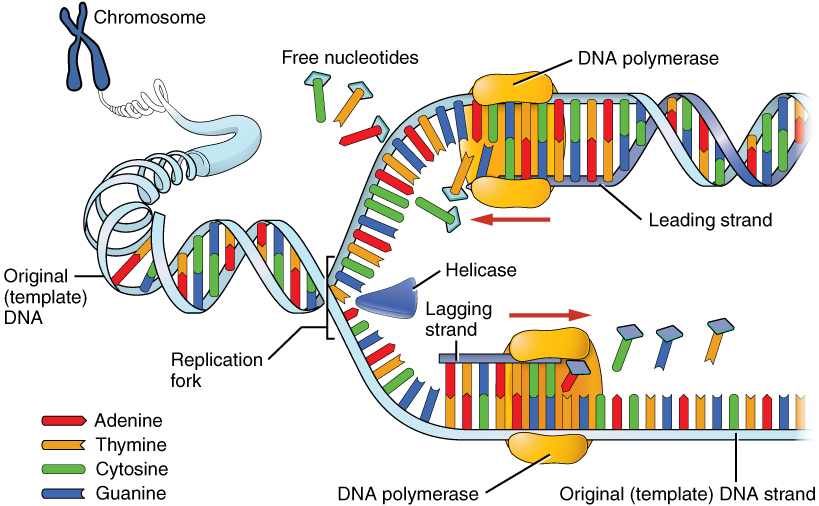
helicase
enzyme that functions to separate the two DNA strands of a double helix during DNA replication
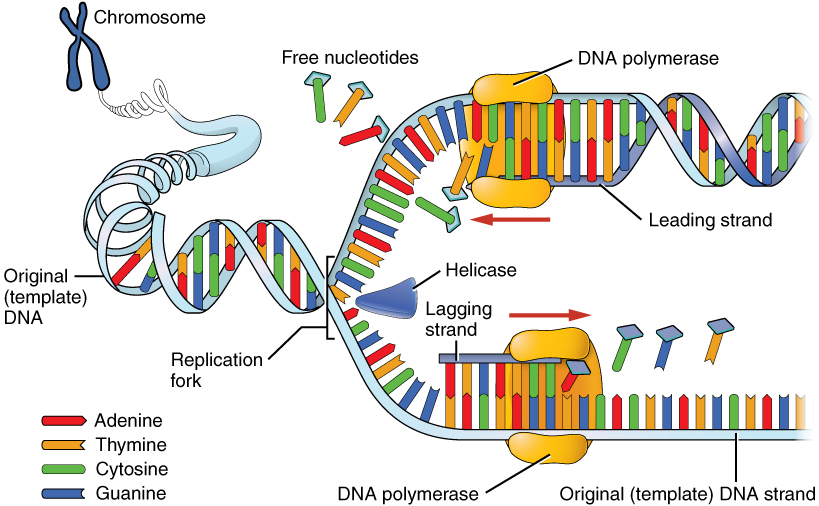
DNA polymerase
enzyme that functions in adding new nucleotides to a growing strand of DNA during DNA replication
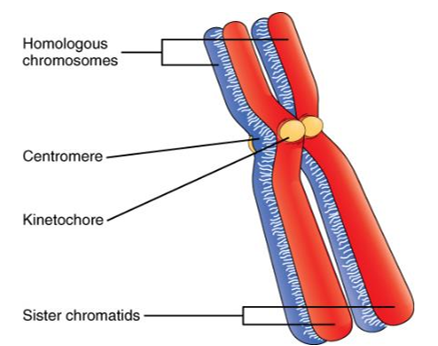
homologous chromosome
the chromosomes in a homologous pair each have the same genes in the same order, but there may be variation between them, resulting in different alleles
homologous: describes two copies of the same chromosome (not identical), one inherited from each parent
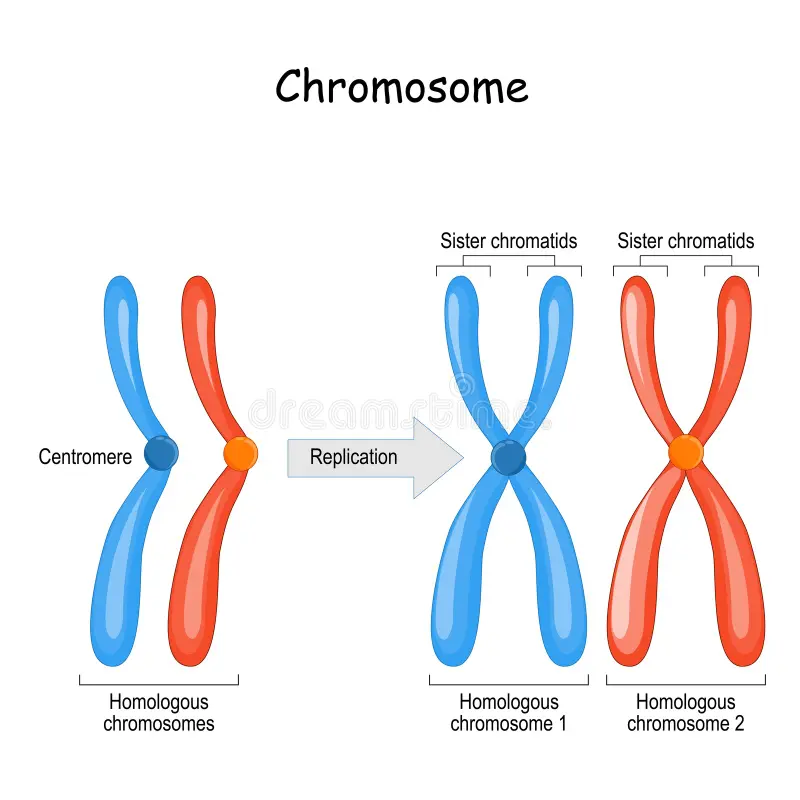
single-stranded vs. double-stranded chromosome
single-stranded: does not typically exist in living cells, the term refers to a single-stranded DNA, which is a DNA molecule consisting of one chain of nucleotides instead of the usual double helix
important for DNA REPLICATION
double-stranded chromosome: chromosomes composed of two identical sister chromatids joined at the centromere, which occurs after DNA replication in preparation for cell division
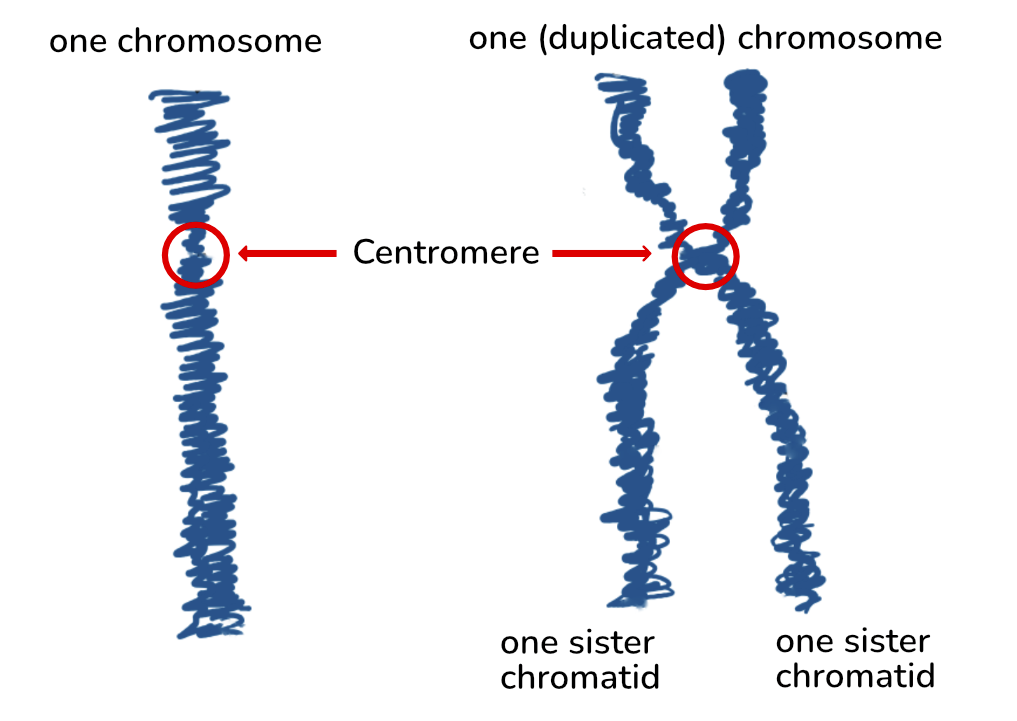
sister chromatid
each strand of the double-stranded chromosomes is called a sister chromatid
one of a pair of identical chromosomes, formed during DNA replication
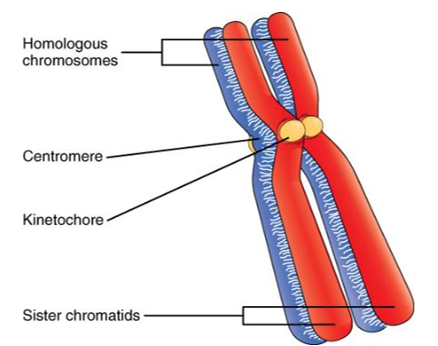
centromere
region of attachment for two sister chromatids (holds sister chromatids together)
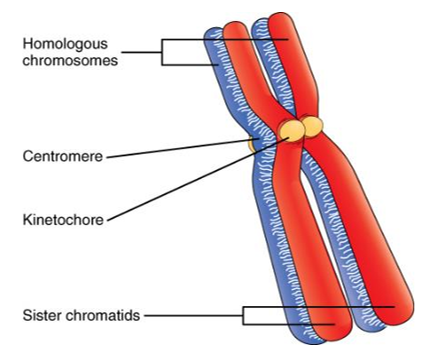
kinetochore
region of the centromere where microtubules attach to a pair of sister chromatids (forms on the centromere)
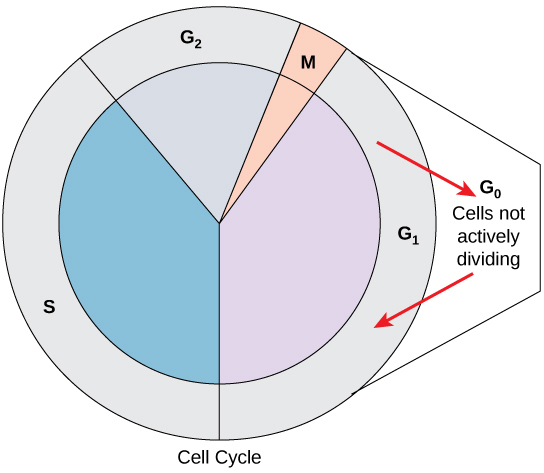
interphase: G2
third phase of the cell cycle, after the DNA synthesis phase
the cell prepares itself for division by making necessary protein
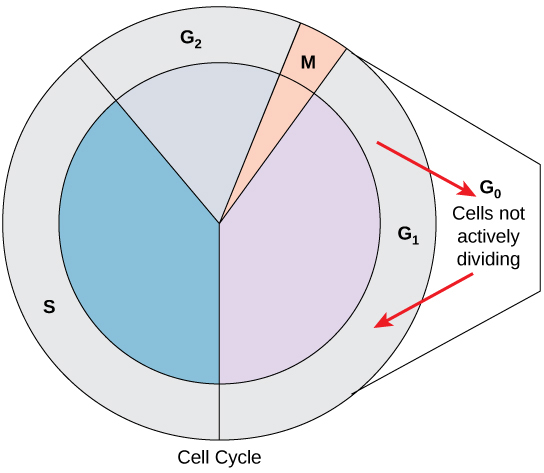
mitotic phase
phase of the cell cycle in which a cell undergoes mitosis
cell division
mitosis followed by cytokinesis
the stages of cell division oversee the separation of identical genetic material into two new nuclei (mitosis), followed by the division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis)
mitosis
division of the genetic material, during which the cell nucleus breaks down and two new, fully functional, nuclei are formed
occurs in all somatic cells (body cells) for the purpose of repair and replacement
somatic cell
all cells of the body excluding gamete cells (sex cells)
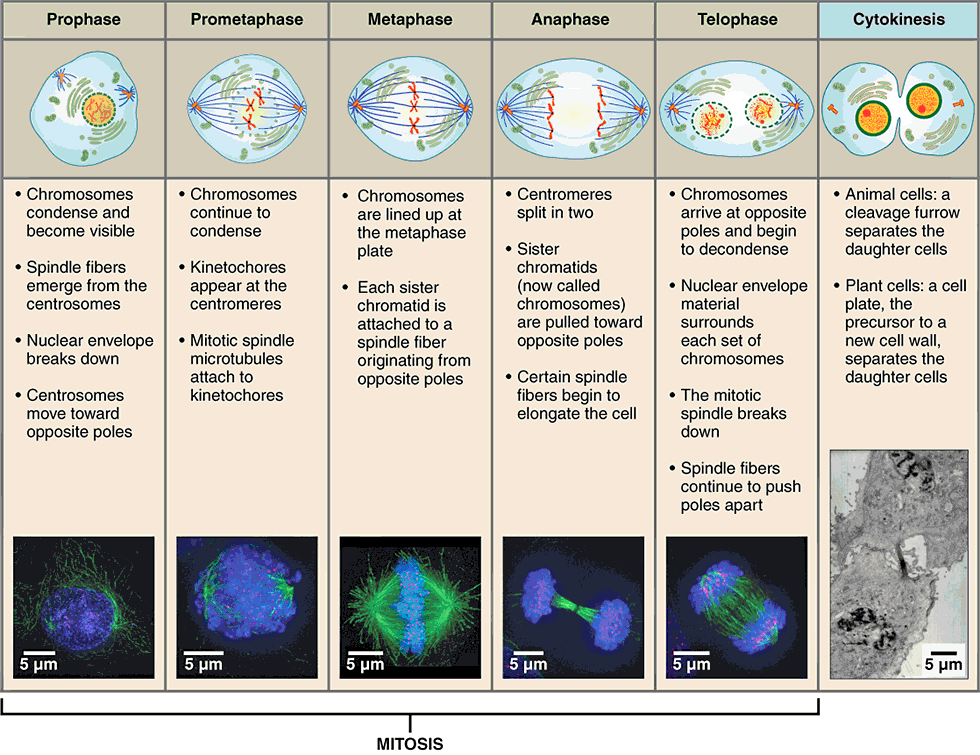
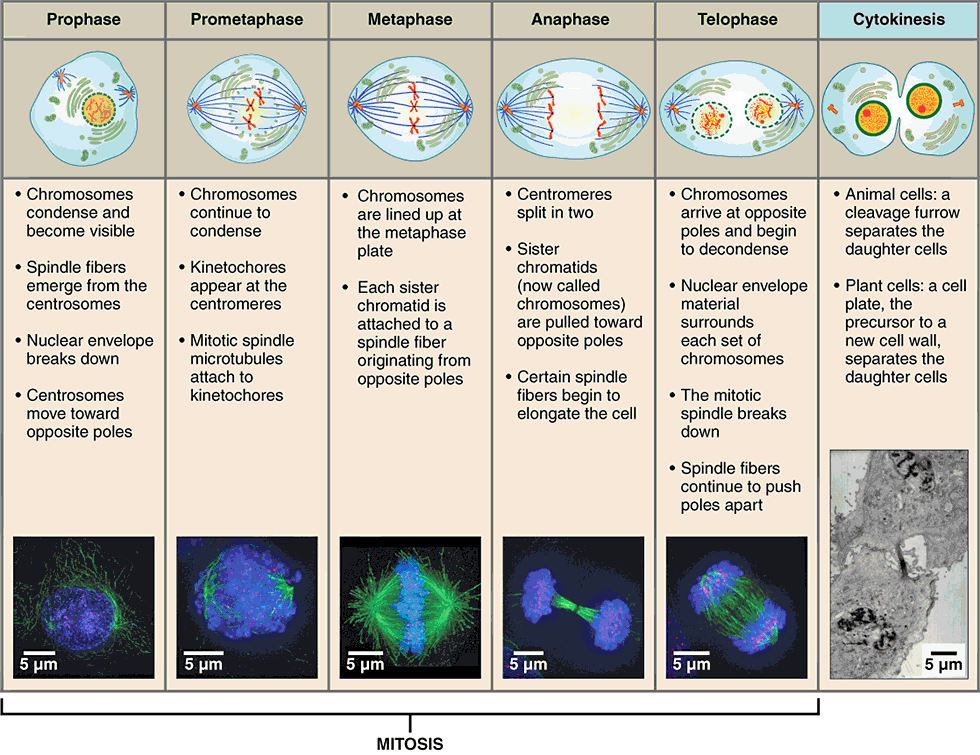
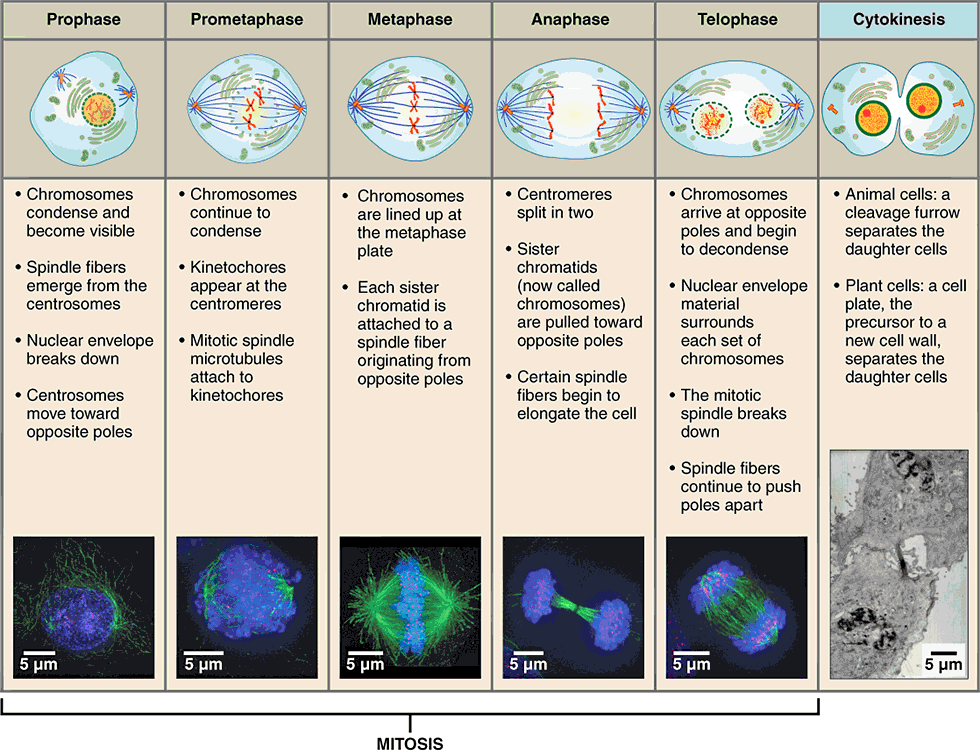
stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
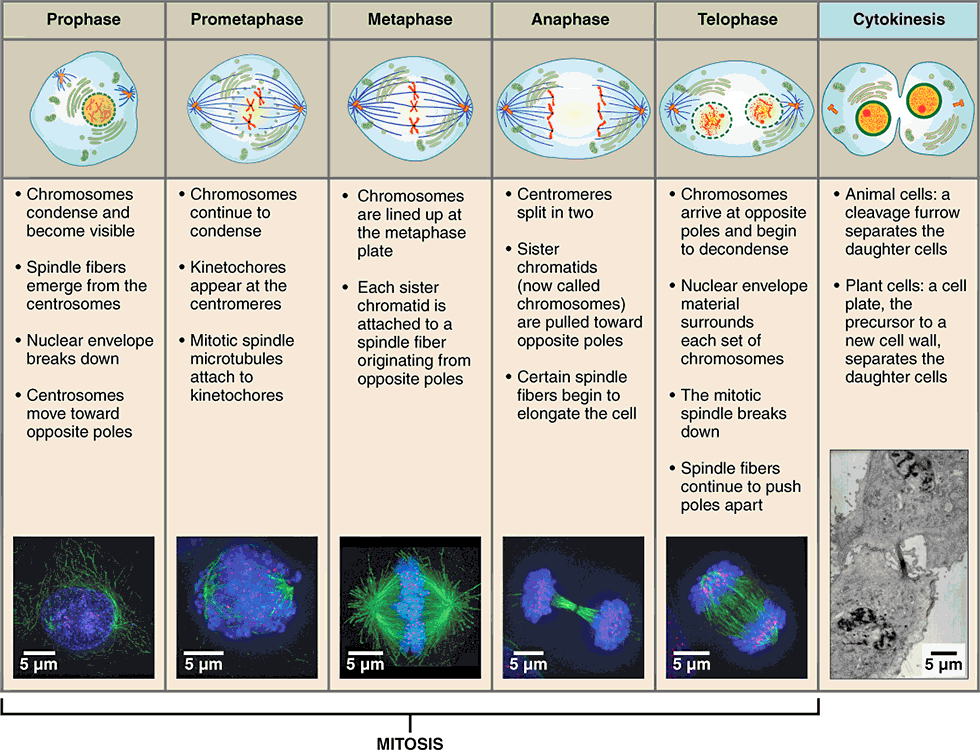
prophase
first stage of mitosis, characterized by breakdown of the nuclear envelope and condensing of the chromatin to form chromosomes
three changes characterize this phase:
nuclear membrane breaks down
double-stranded chromosomes condense and become visible
spindle fibers form (mitotic spindle)
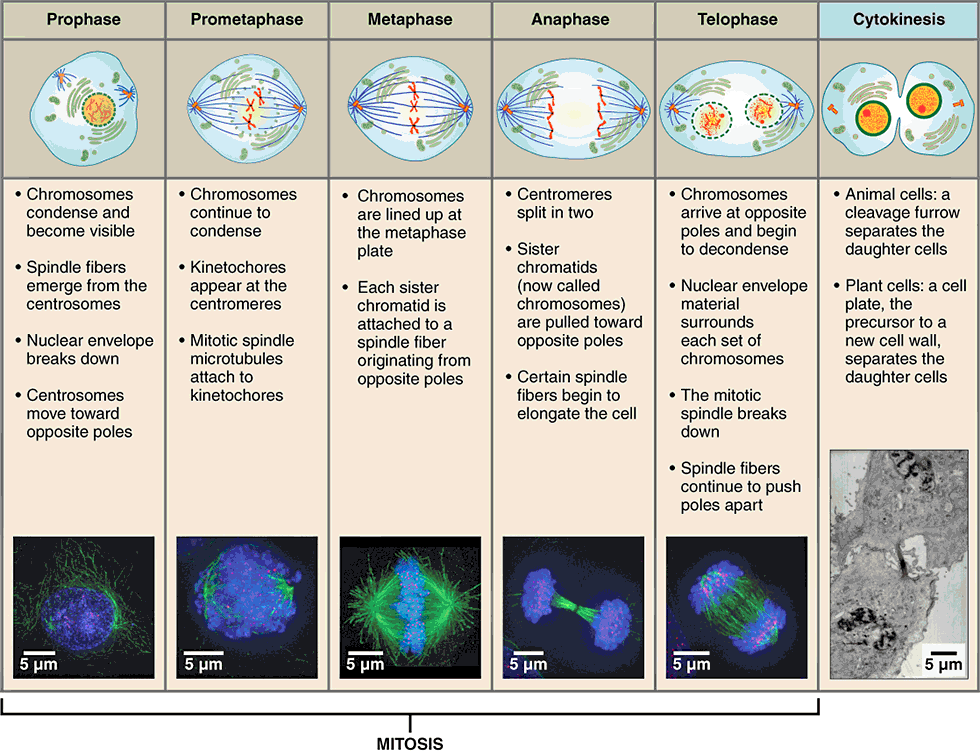
mitotic spindle
network of microtubules, originating from centrioles, that arranges and pulls apart chromosomes during mitosis
metaphase
second stage of mitosis, characterized by the linear alignment of sister chromatids in the center of the cell
“middle”:
spindle fibers attached to the kinetochore begin pulling on the chromosome
double-stranded chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell called the metaphase plate
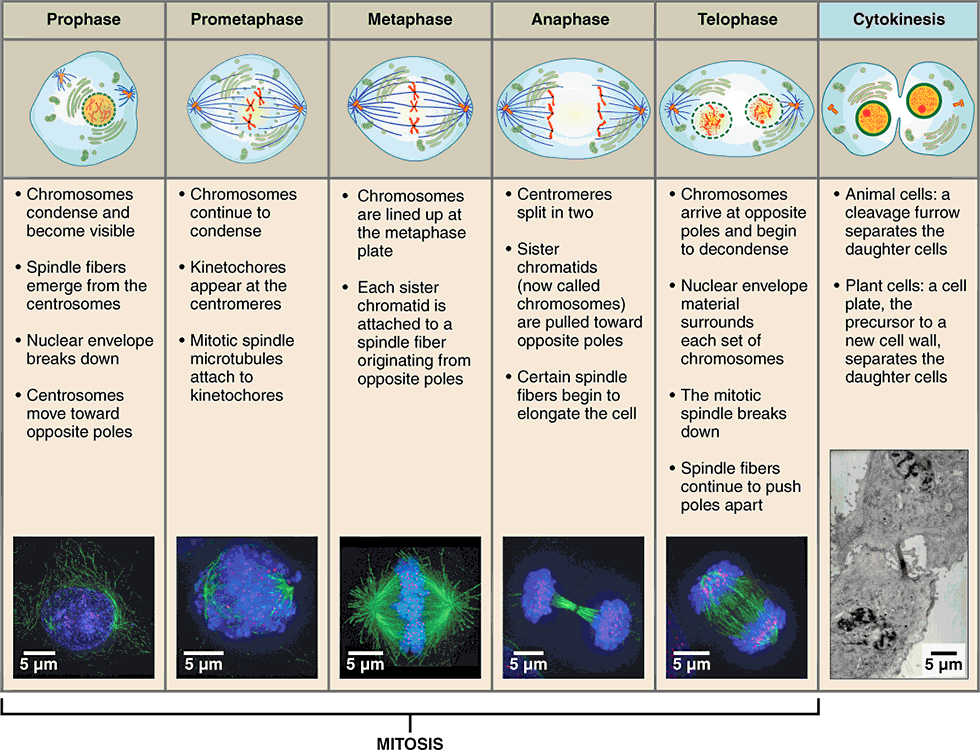
metaphase plate
linear alignment of sister chromatids in the center of the cell, which takes place during metaphase
anaphase
third stage of mitosis, during which sister chromatids separate into two new nuclear regions of a dividing cell
“apart”:
chromatids get pulled apart
single-stranded chromosomes migrate to opposite ends of the cell
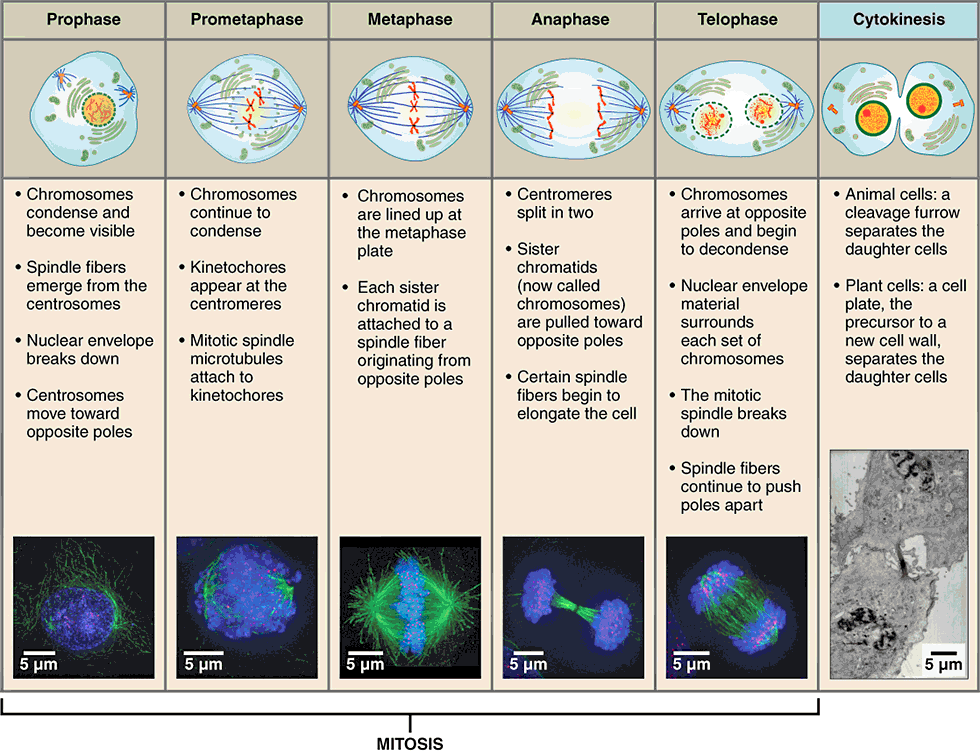
telophase
final stage of mitosis, preceding cytokinesis, characterized by the formation of two new daughter nuclei
reverse of prophase:
nuclear membrane reforms
single-stranded chromosomes decondense and disappear
spindle fibers break down
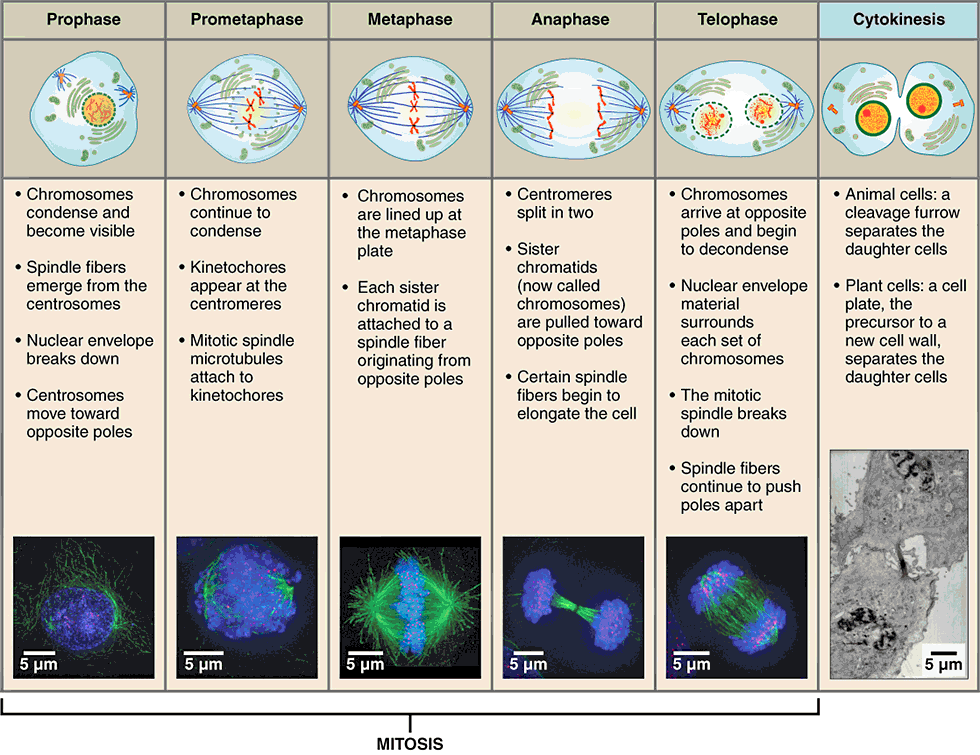
cytokinesis
final stage in cell division, where the cytoplasm divides to form two separate daughter cells
division of cytoplasm into two cells
telophase is the end of nuclear division but overlaps cytokinesis
creates cleavage furrow around the equator of cell
cell eventually pinches in two
completion of cytokinesis marks the end of cell division
cleavage furrow
contractile ring that forms around a cell during cytokinesis that pinches the cell into two halves
daughter cells
two daughter cells are produced and each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell