Gross Anatomy - Neuroanatomy
1/379
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
380 Terms
c. Medial Longitudinal Fissure
This fissure is where the falx cerebri projects into:
a. Lateral Fissure (Sylvian)
b. Central Fissure (Rolando)
c. Medial Longitudinal Fissure
d. Parieto-Occipital Fissure
Longitudinal / Sagittal Fissure
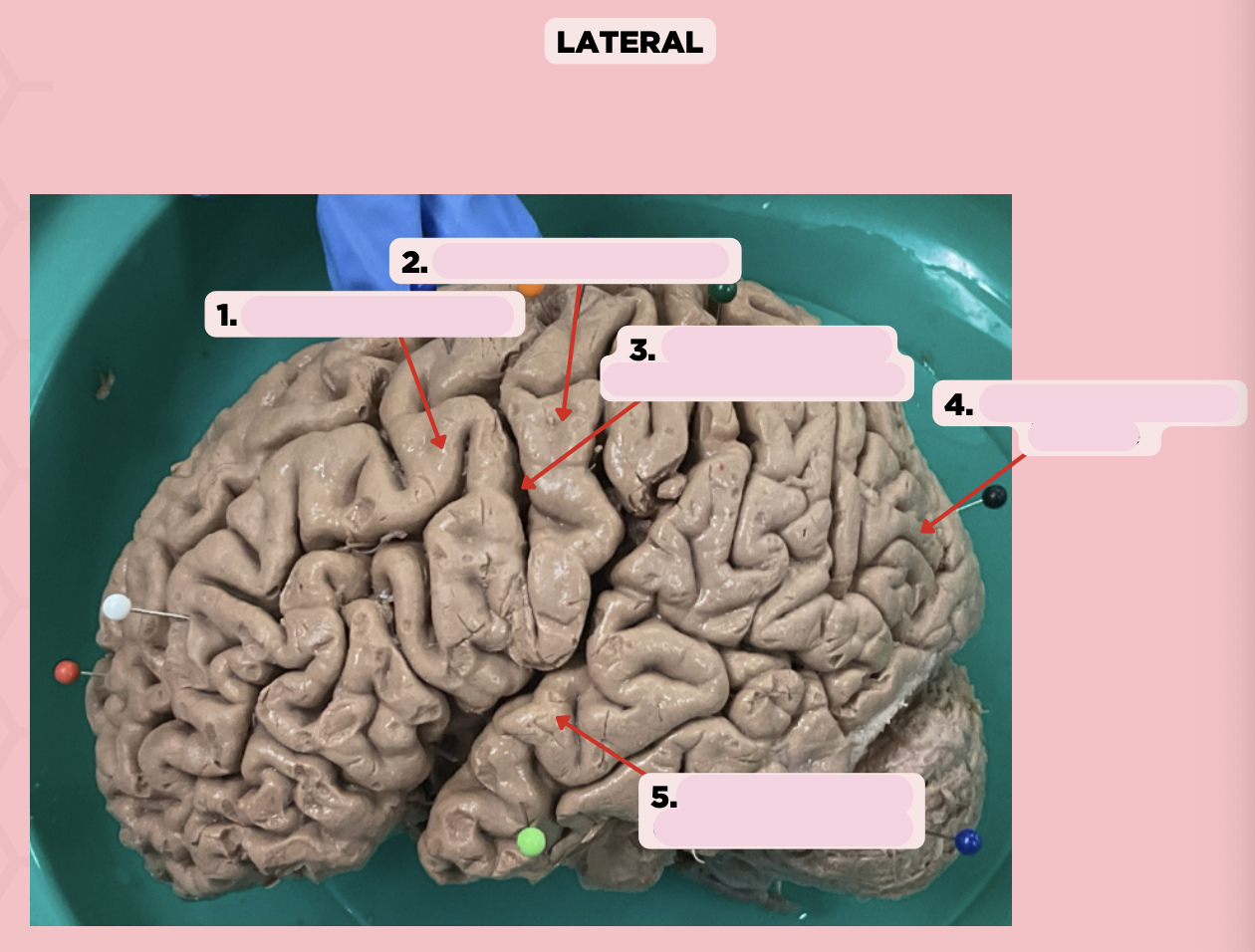
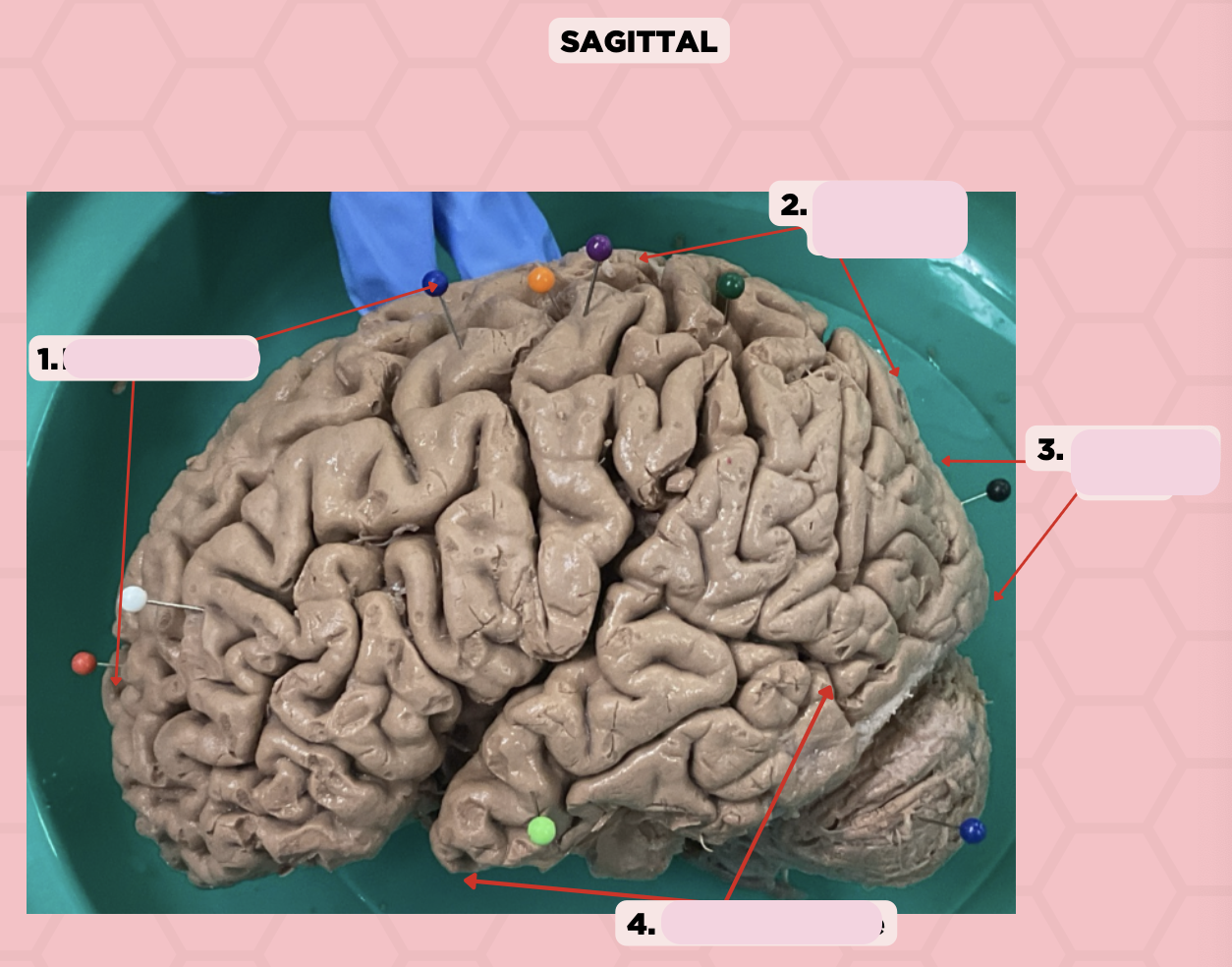
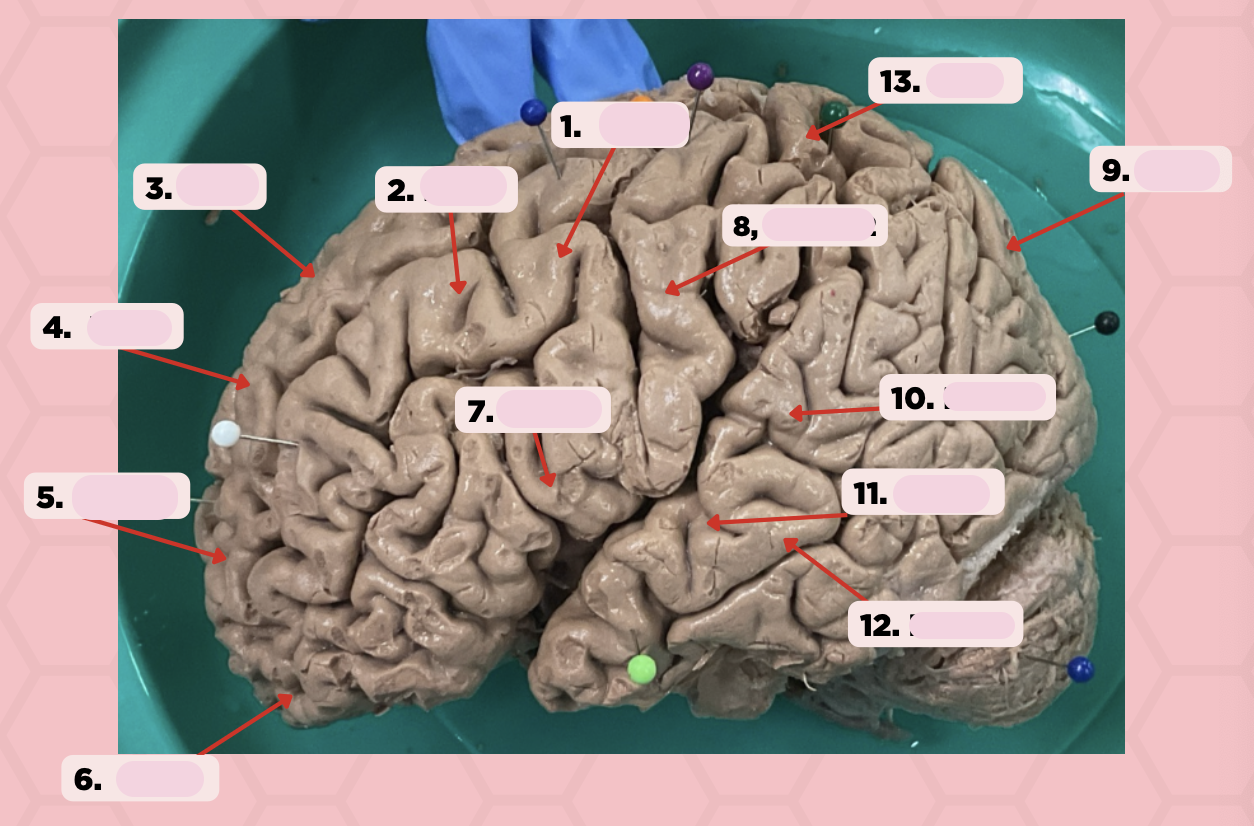
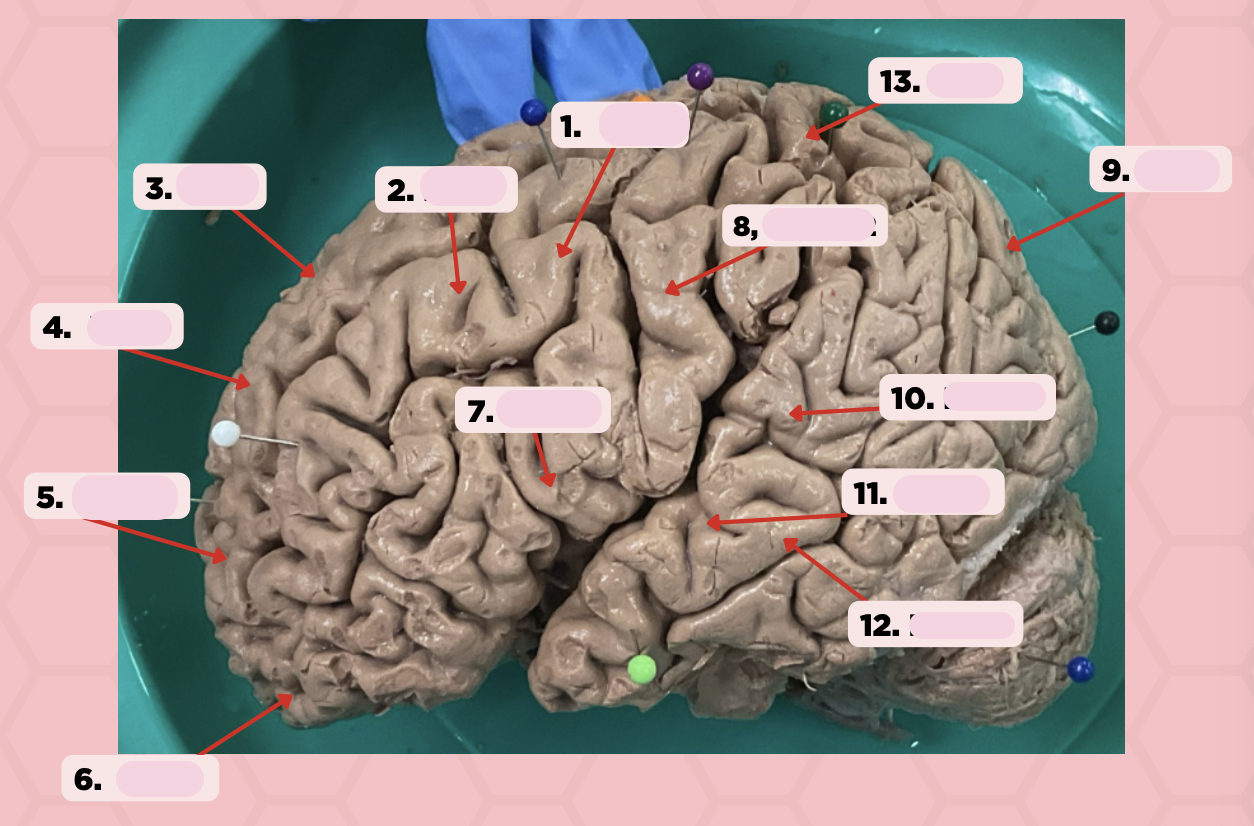
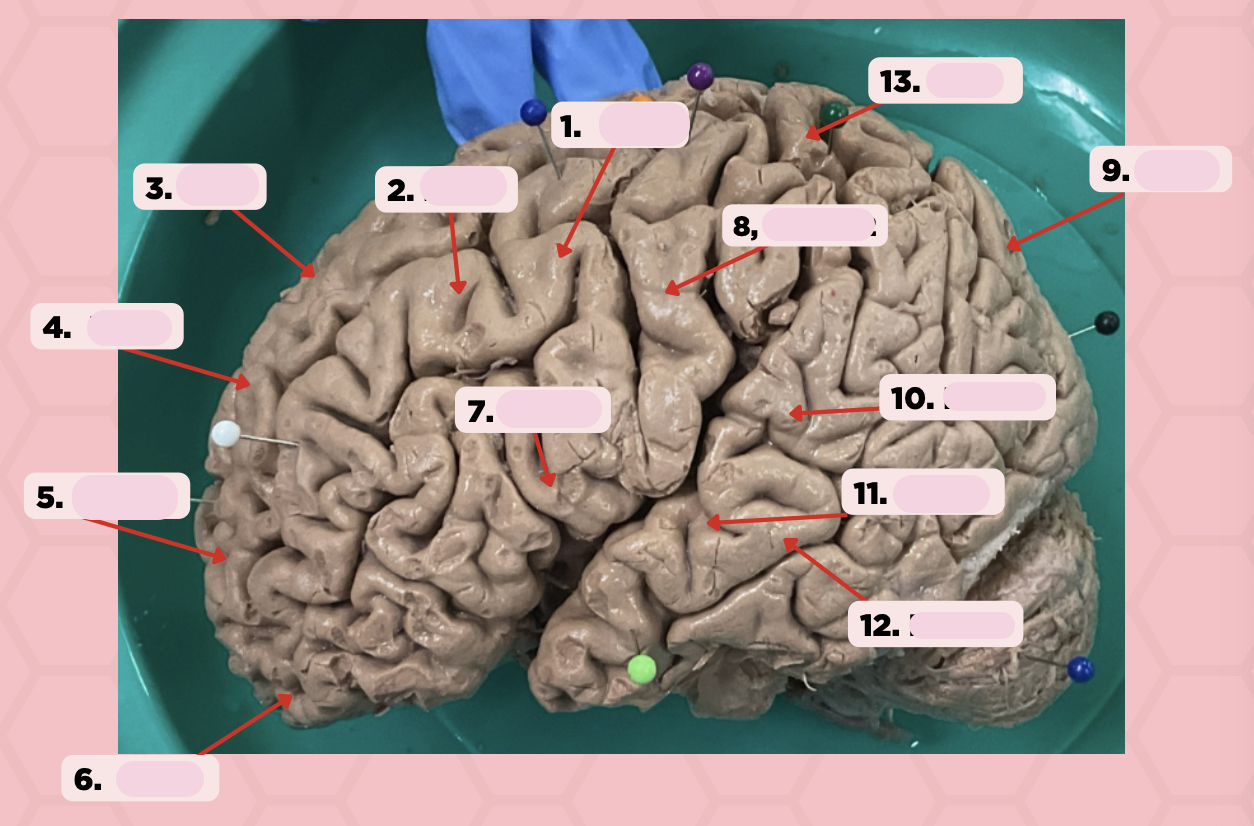
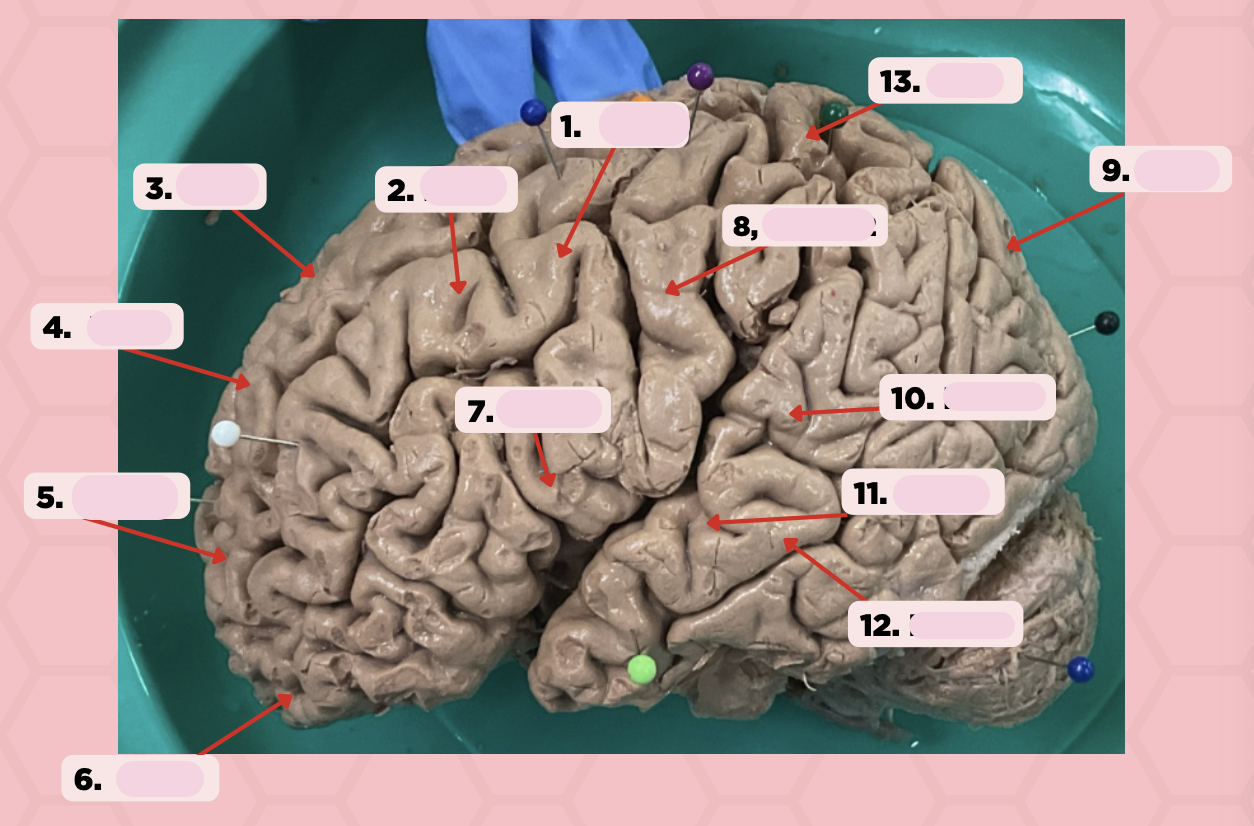
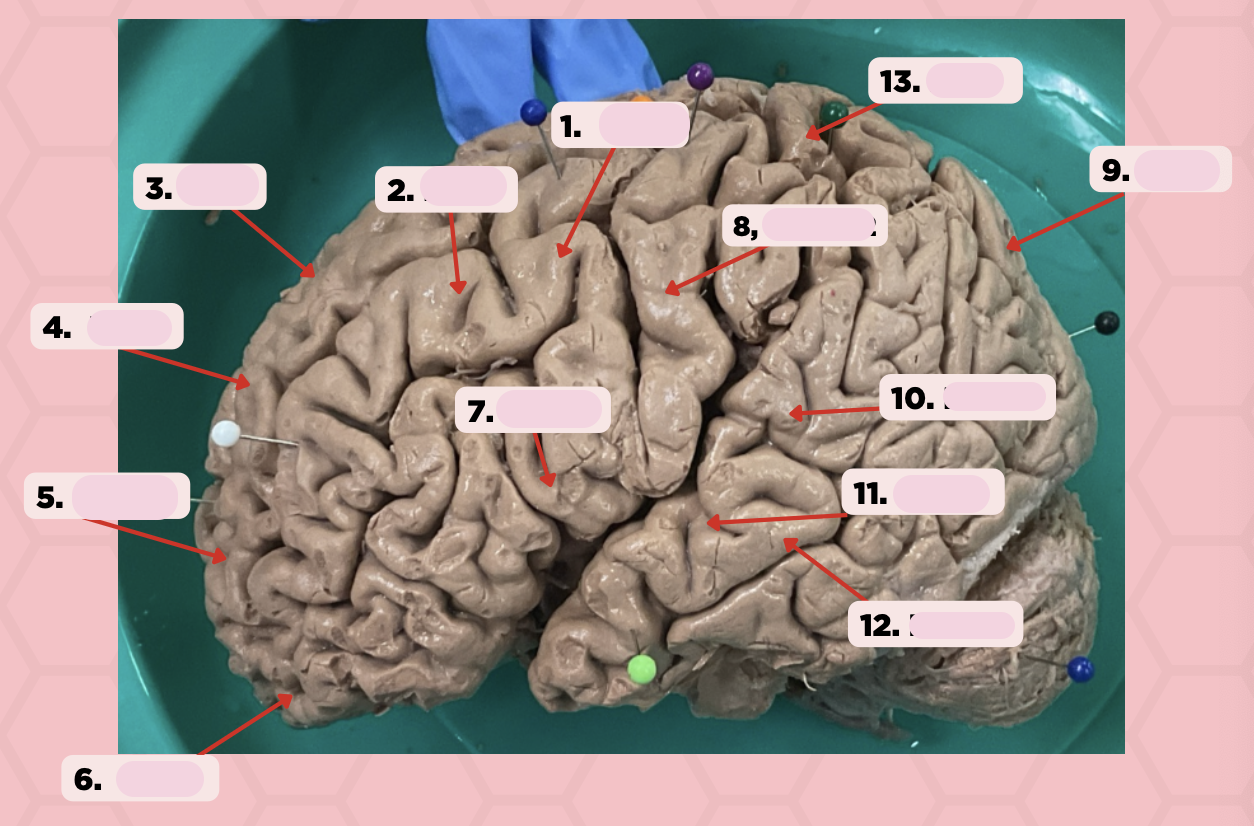
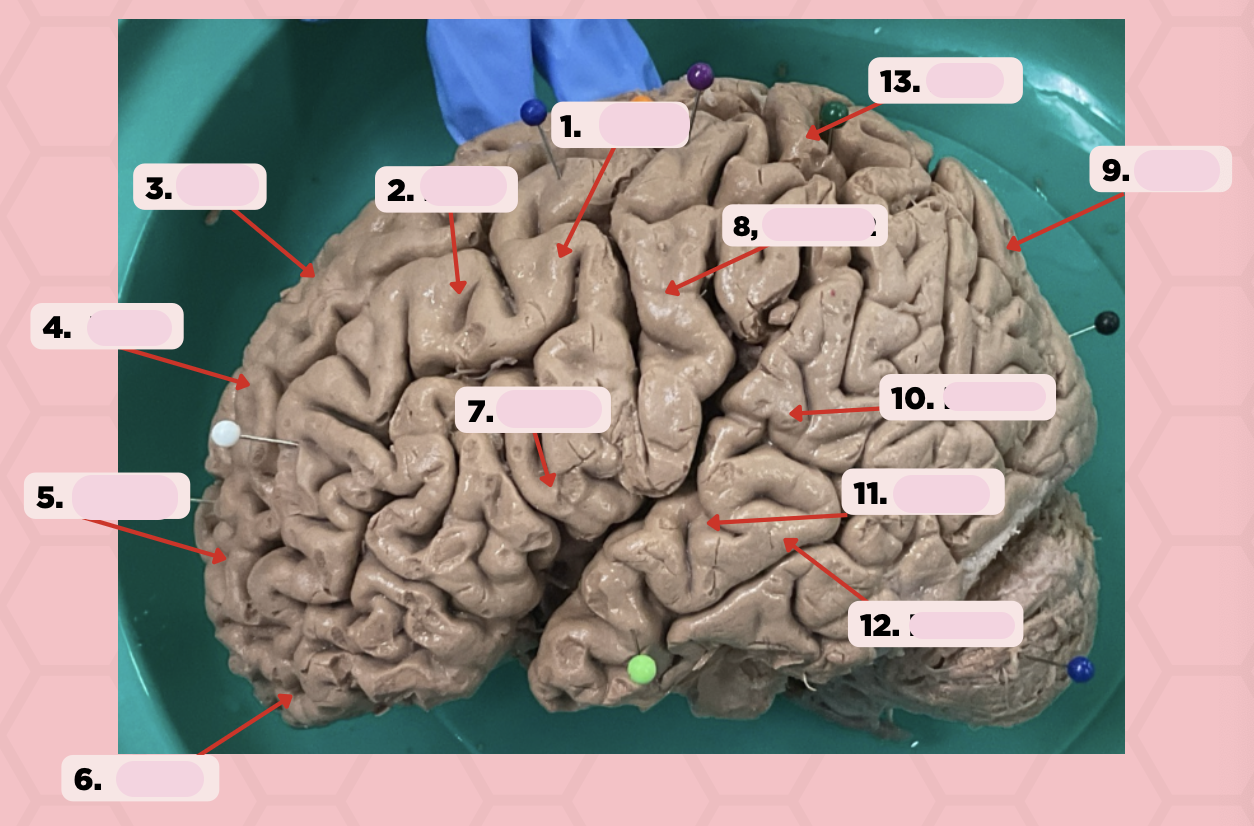
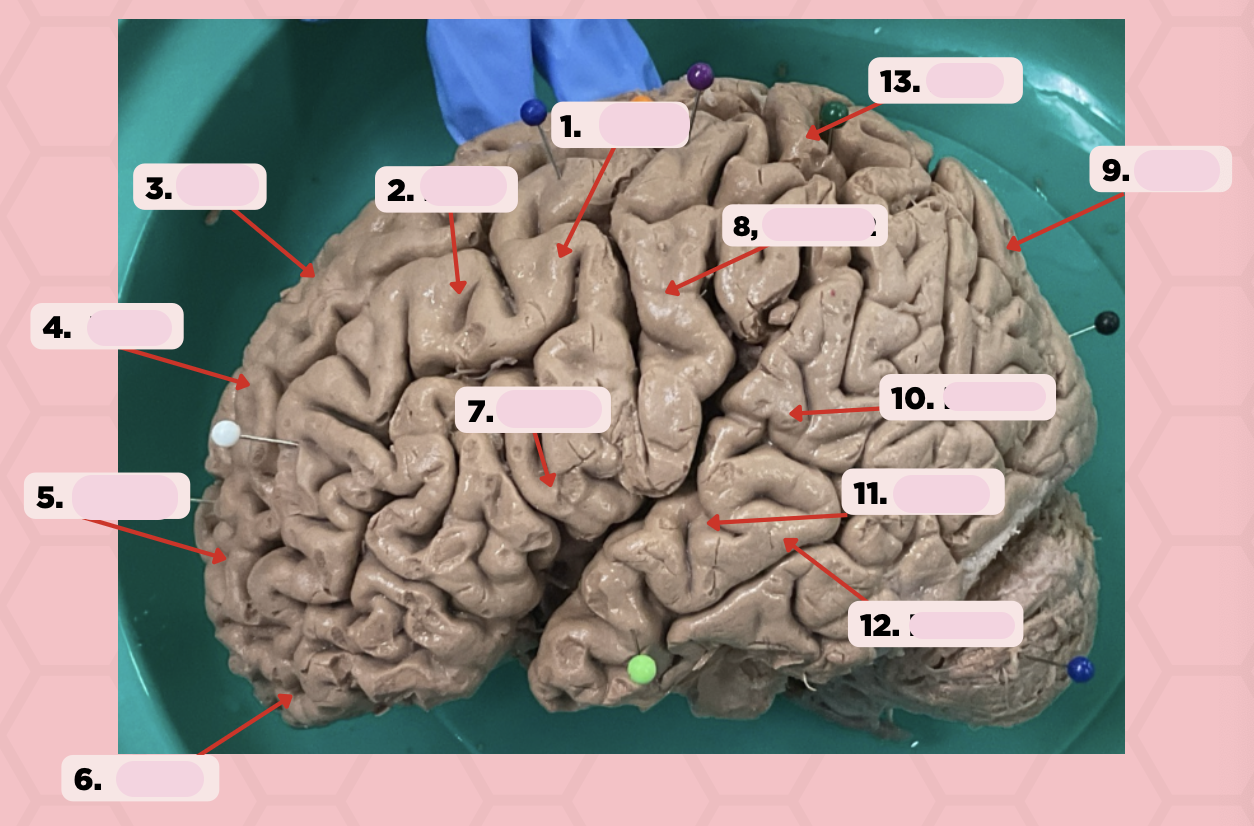
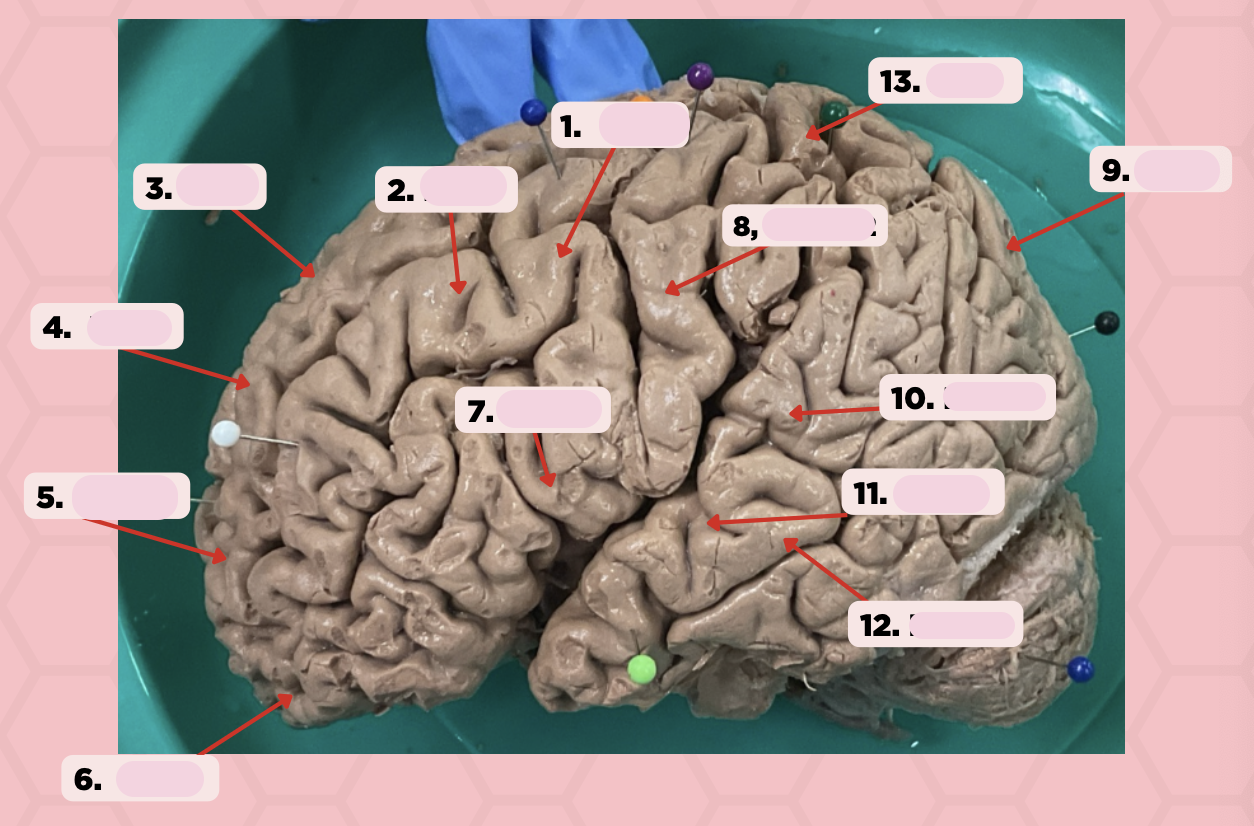
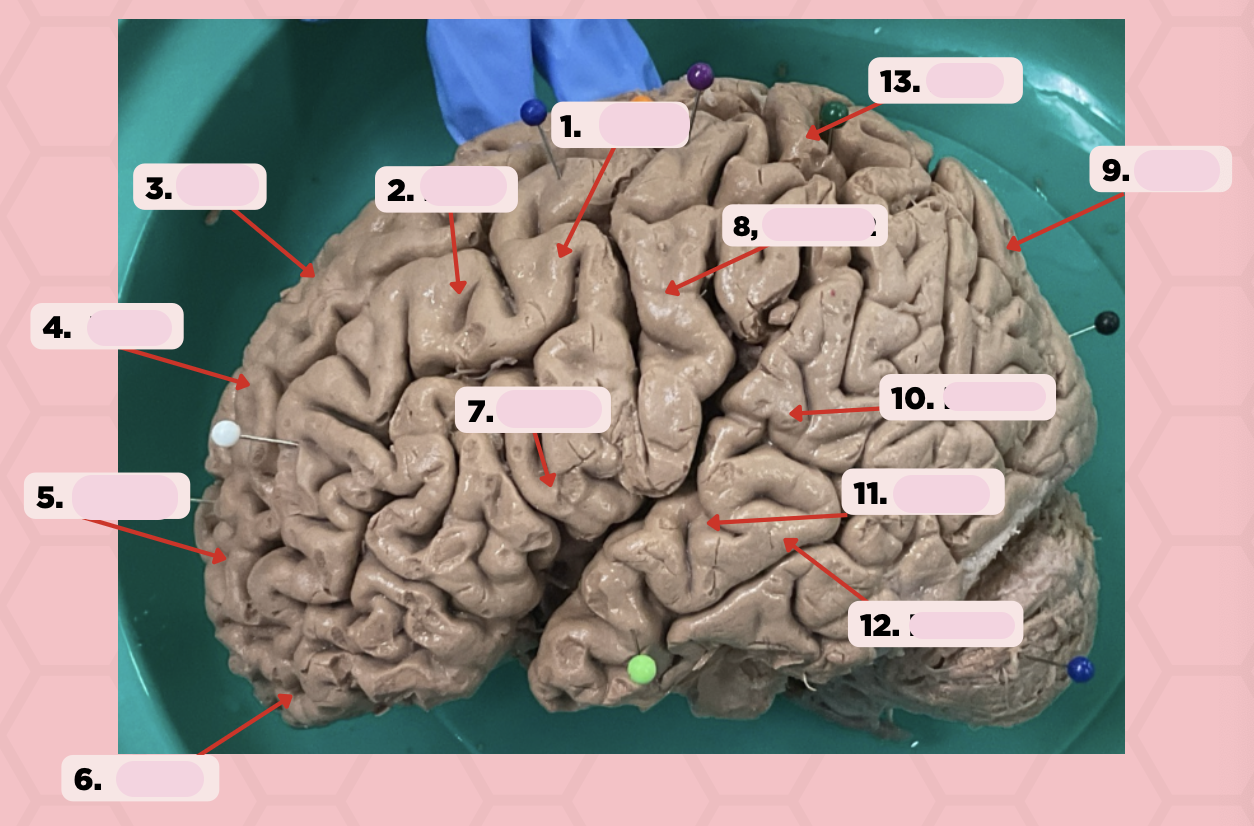
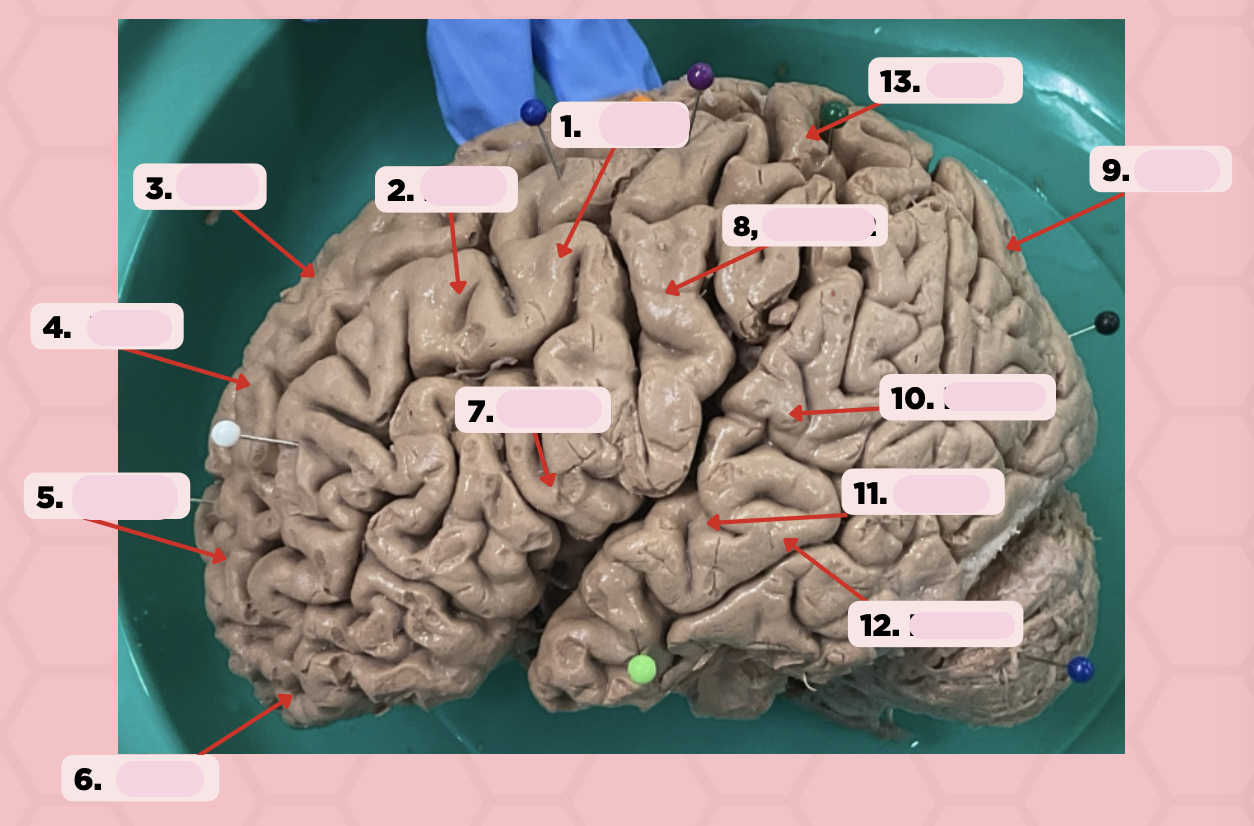
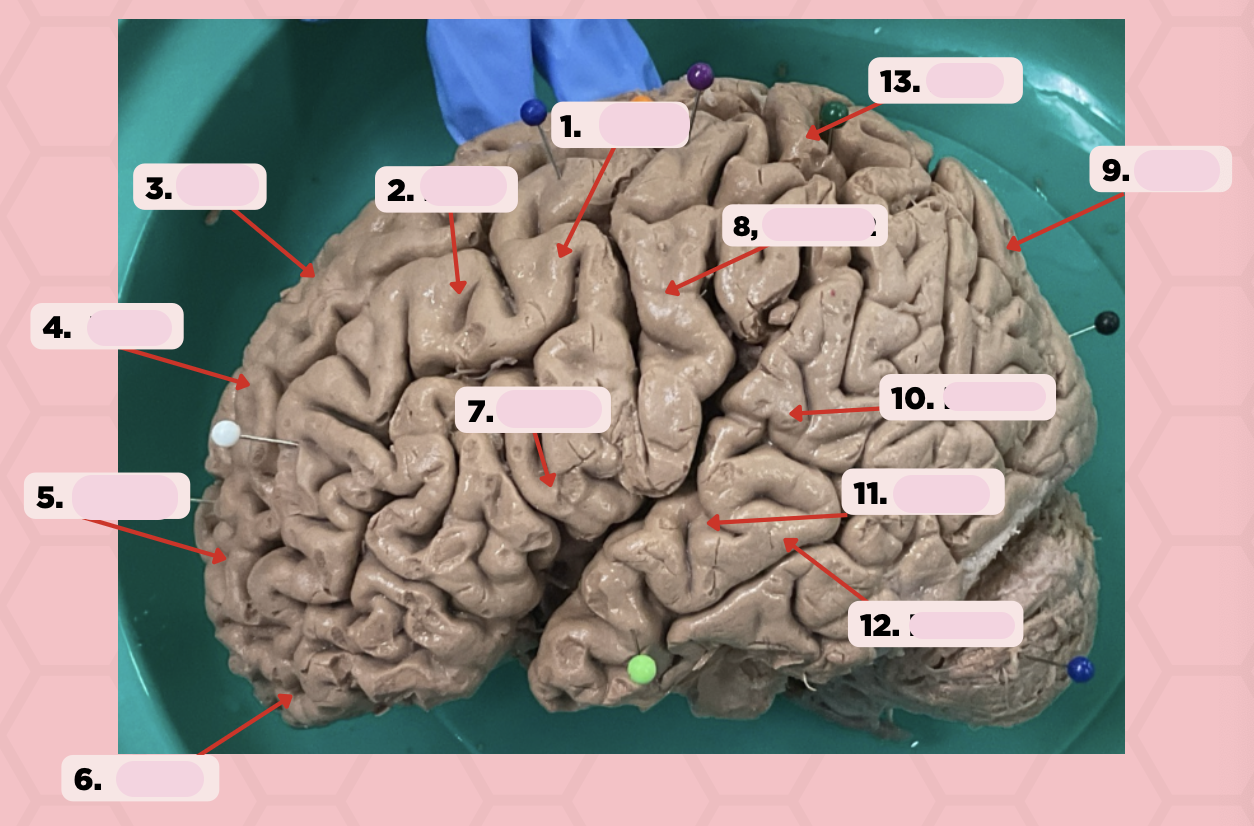
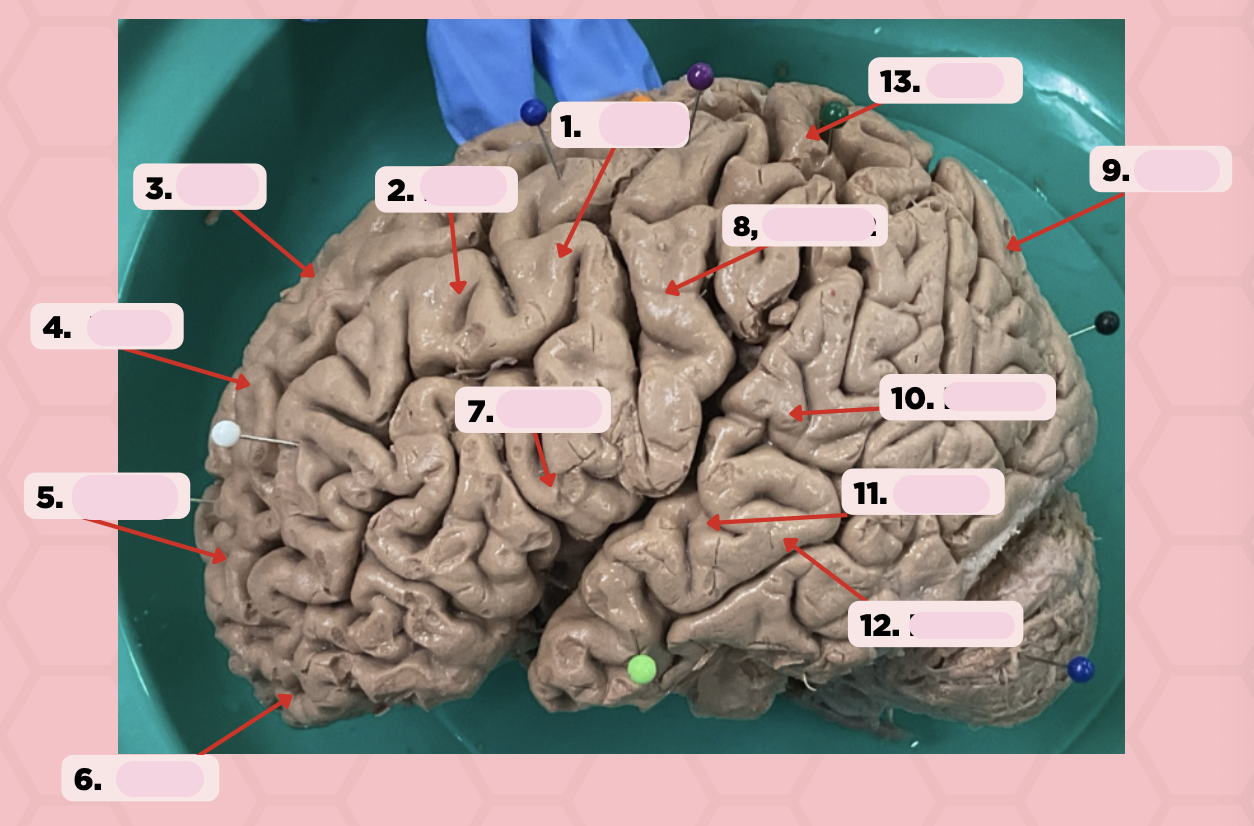
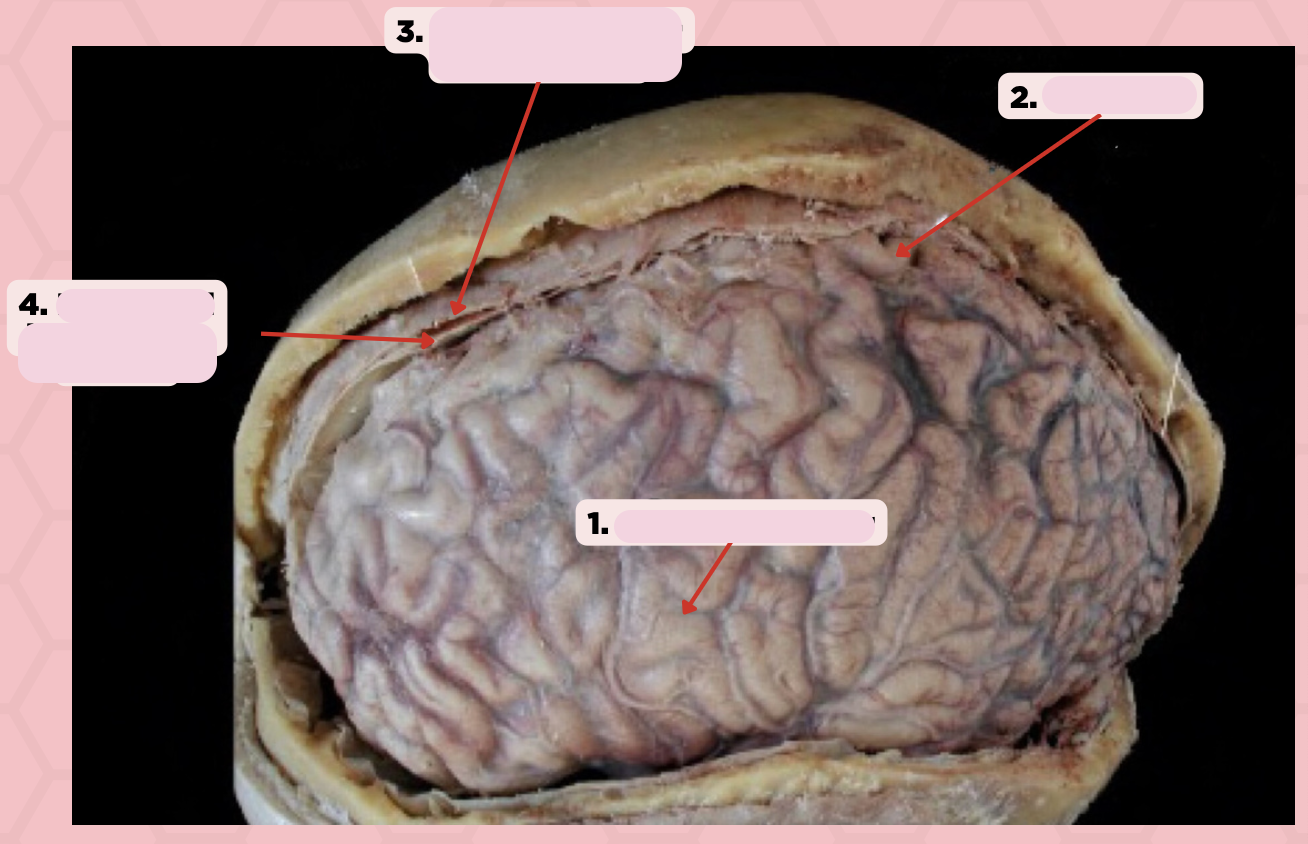
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
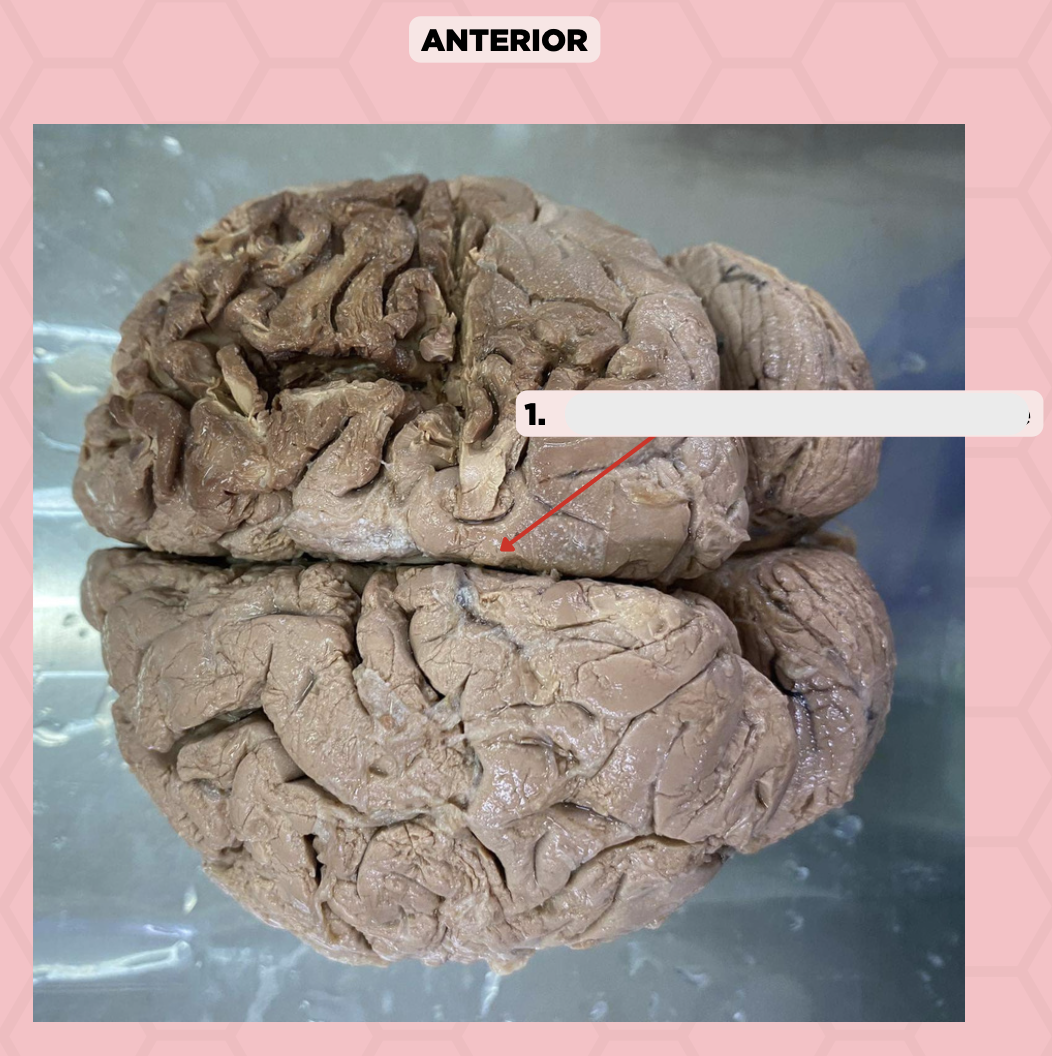
a. Pre-central gyrus
It is where BA 4 is located
a. Pre-central gyrus
b. Post-central gyrus
c. Central sulcus
d. Pareto-occipital fissure
d. Lateral fissure
It separates the frontoparietal lobe and temporal lobe
a. Post-central gyrus
b. Central sulcus
c. Pareto-occipital fissure
d. Lateral fissure
a. Post-central gyrus
It is part of the parietal lobe and located behind the central sulcus
a. Post-central gyrus
b. Central sulcus
c. Pareto-occipital fissure
d. Lateral fissure
b. Central sulcus
This line separates the frontal lobe and parietal lobe
a. Post-central gyrus
b. Central sulcus
c. Pareto-occipital fissure
d. Lateral fissure
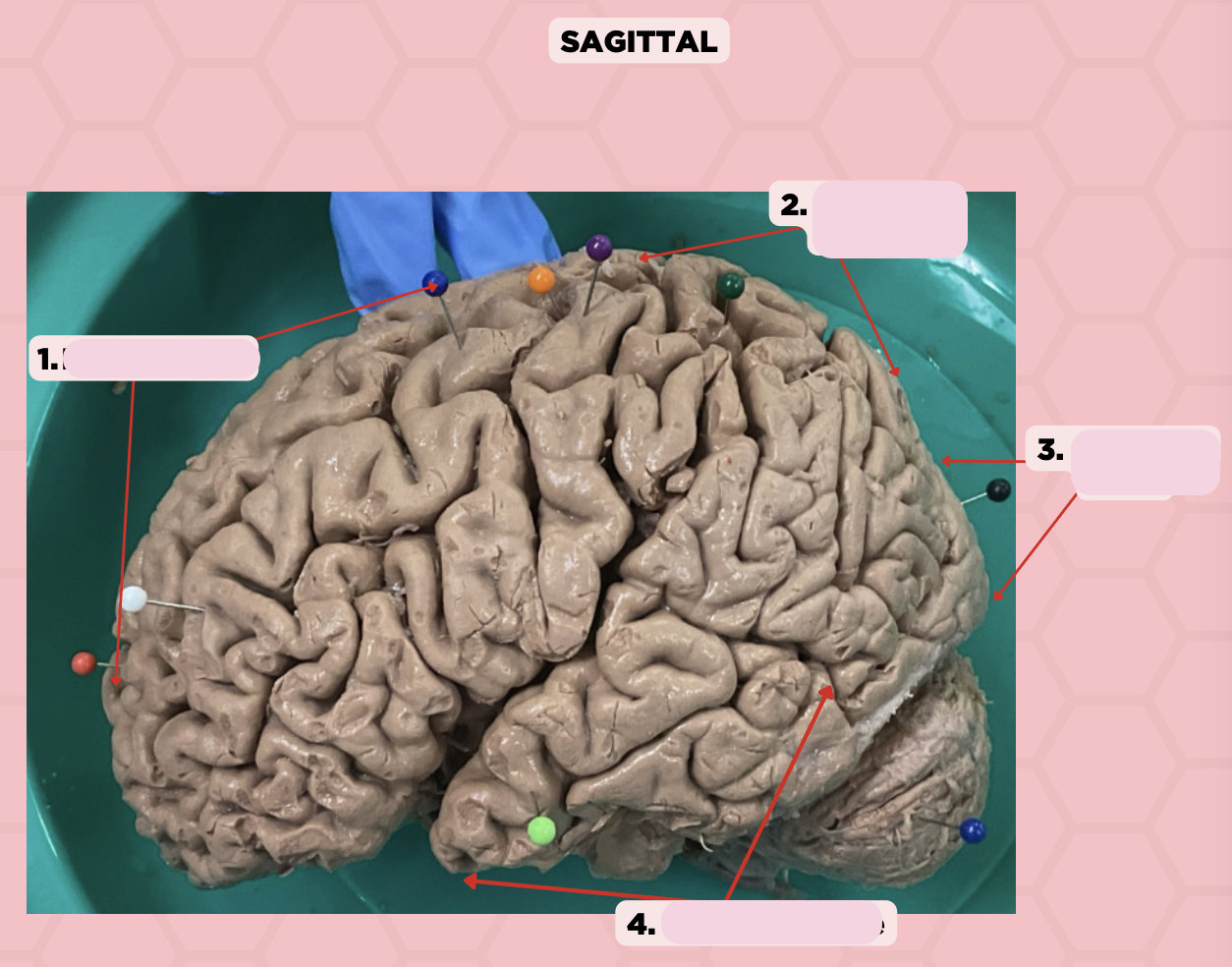
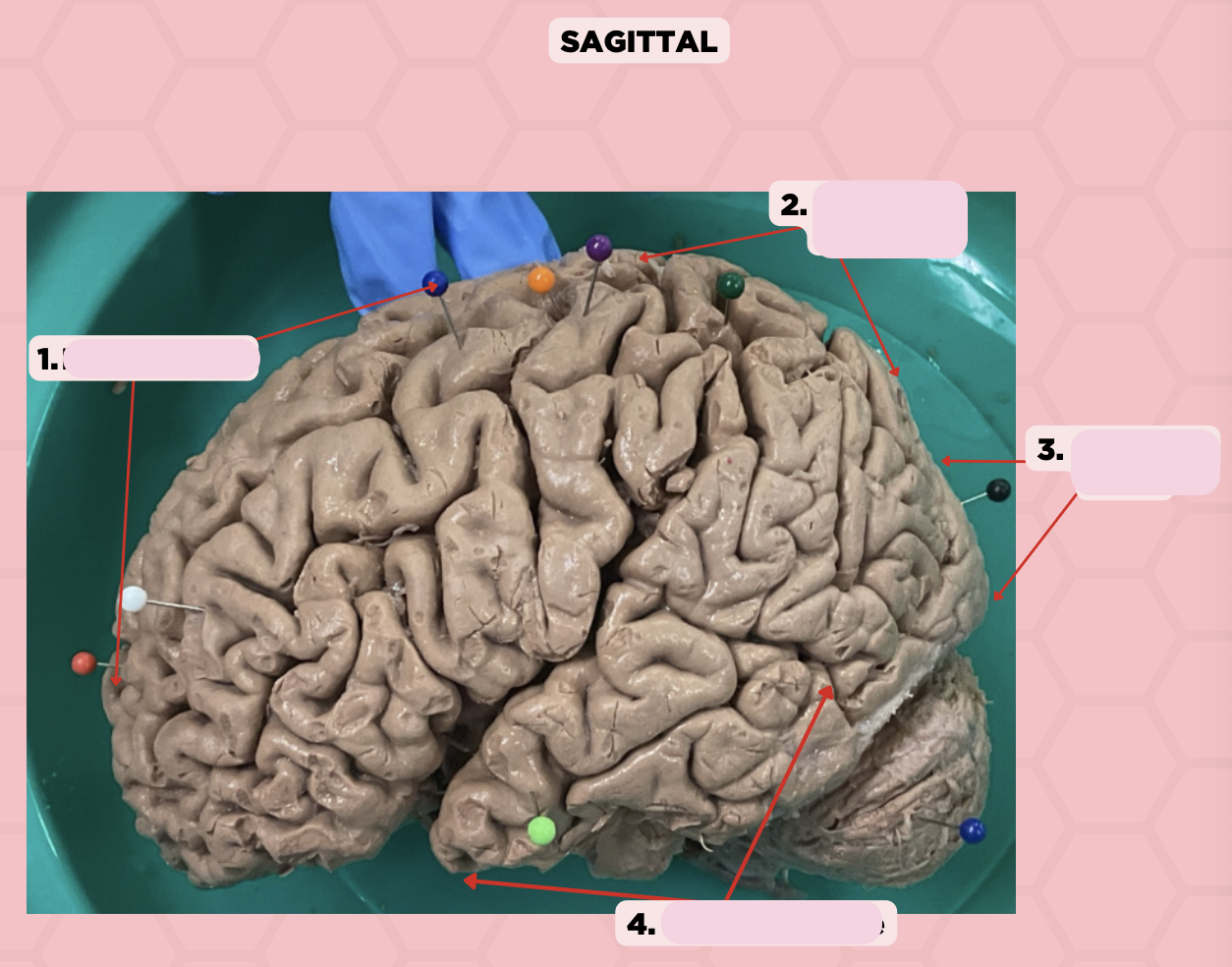
Pre-Central Gyrus
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
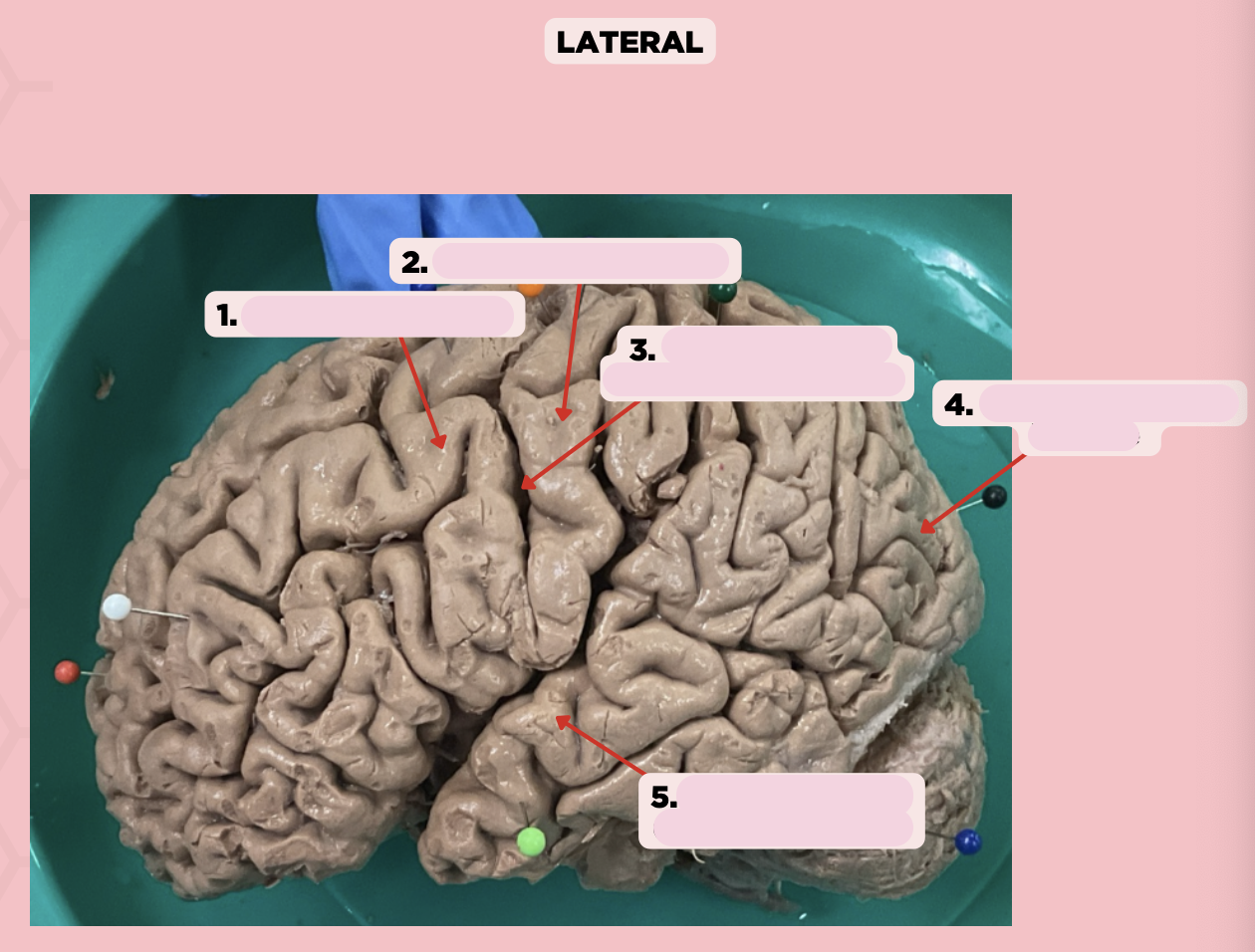
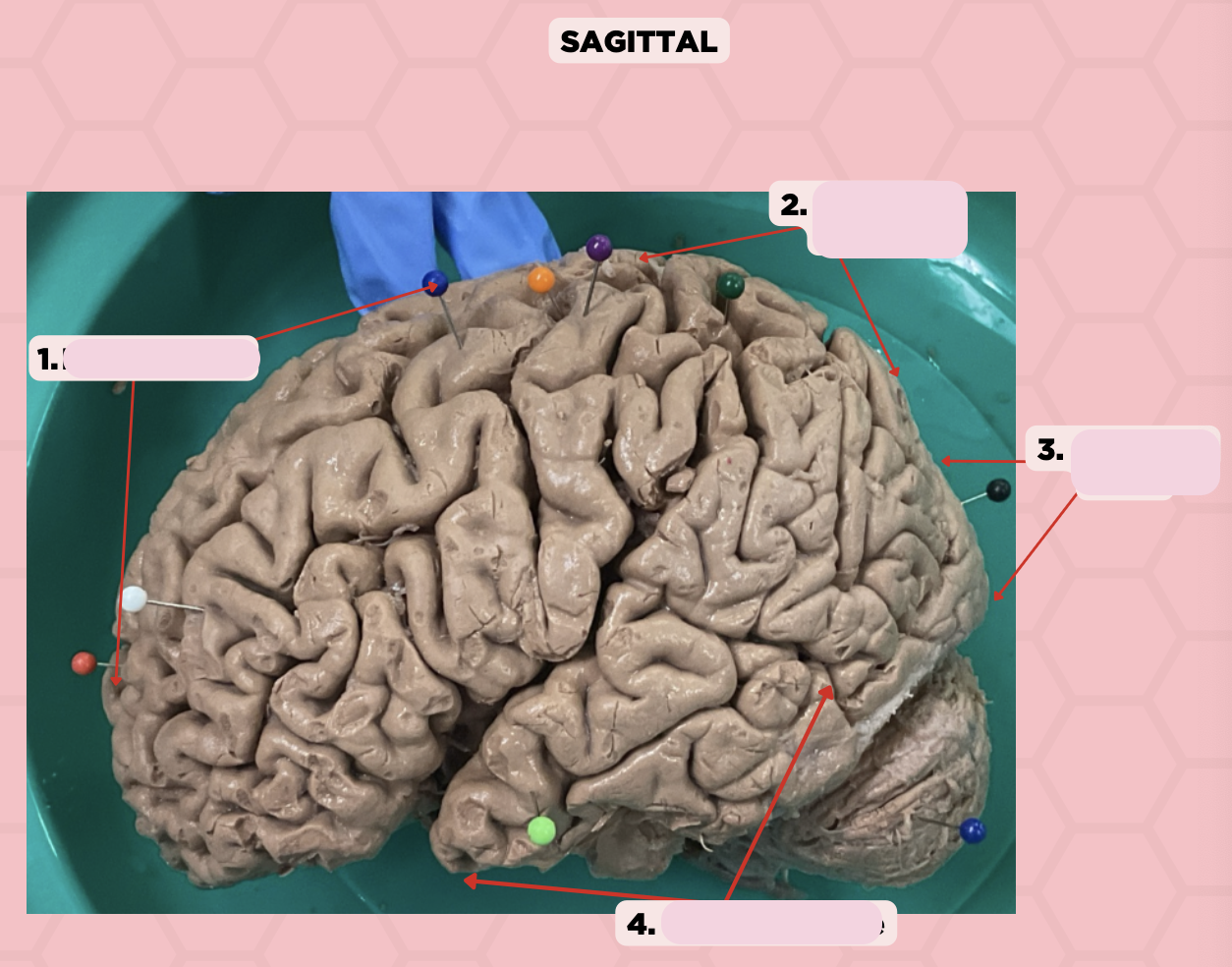
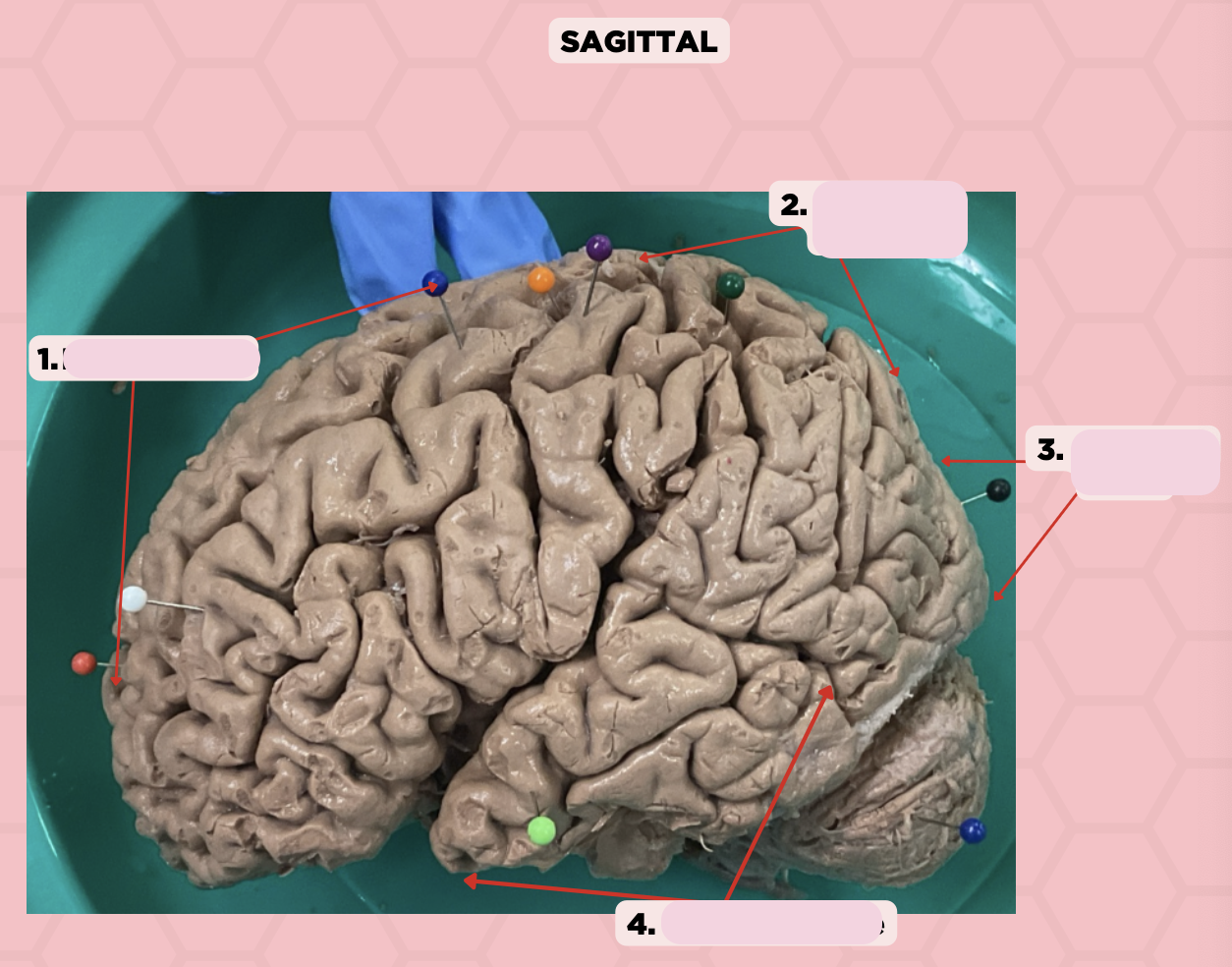
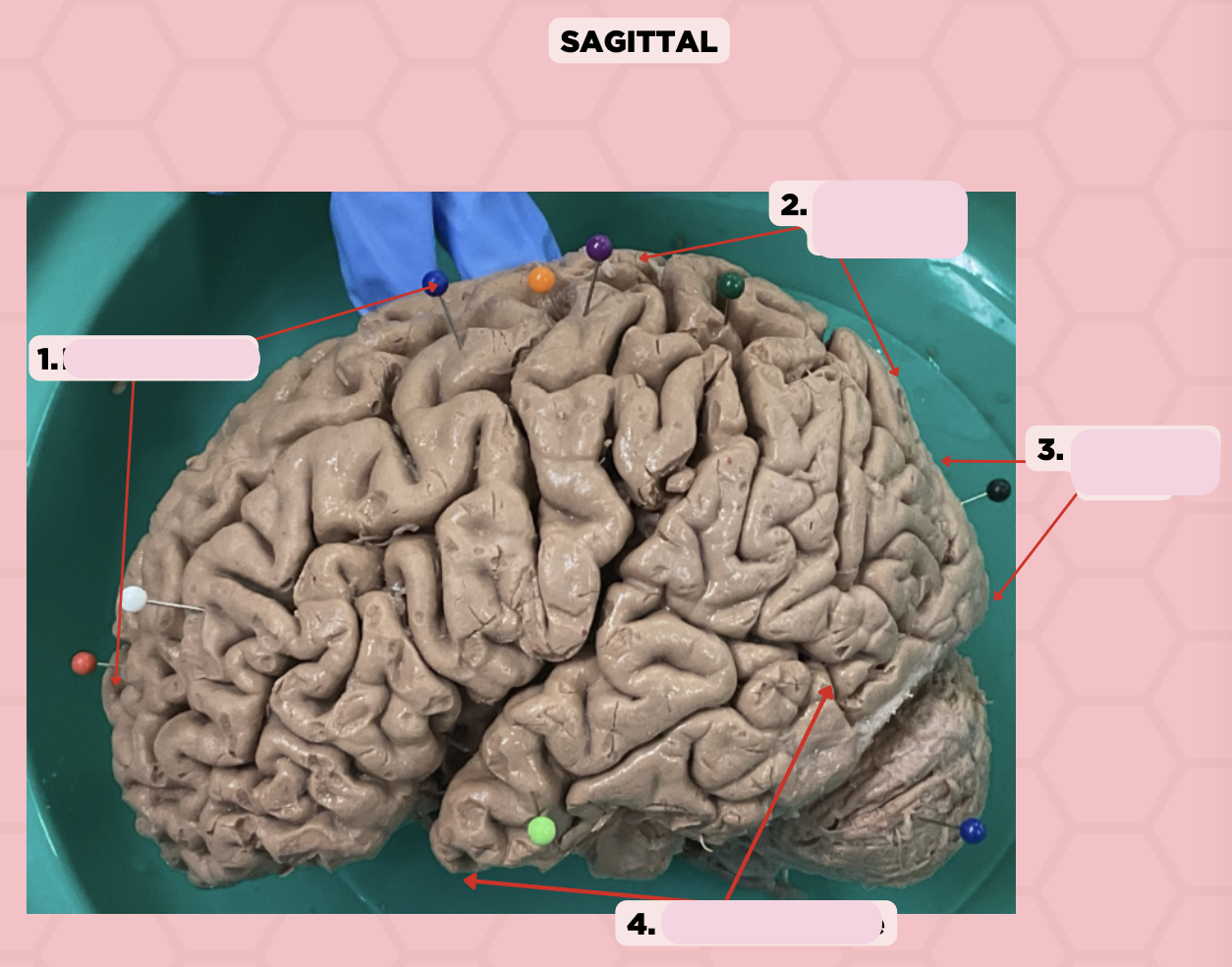
Post-Central Gyrus
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
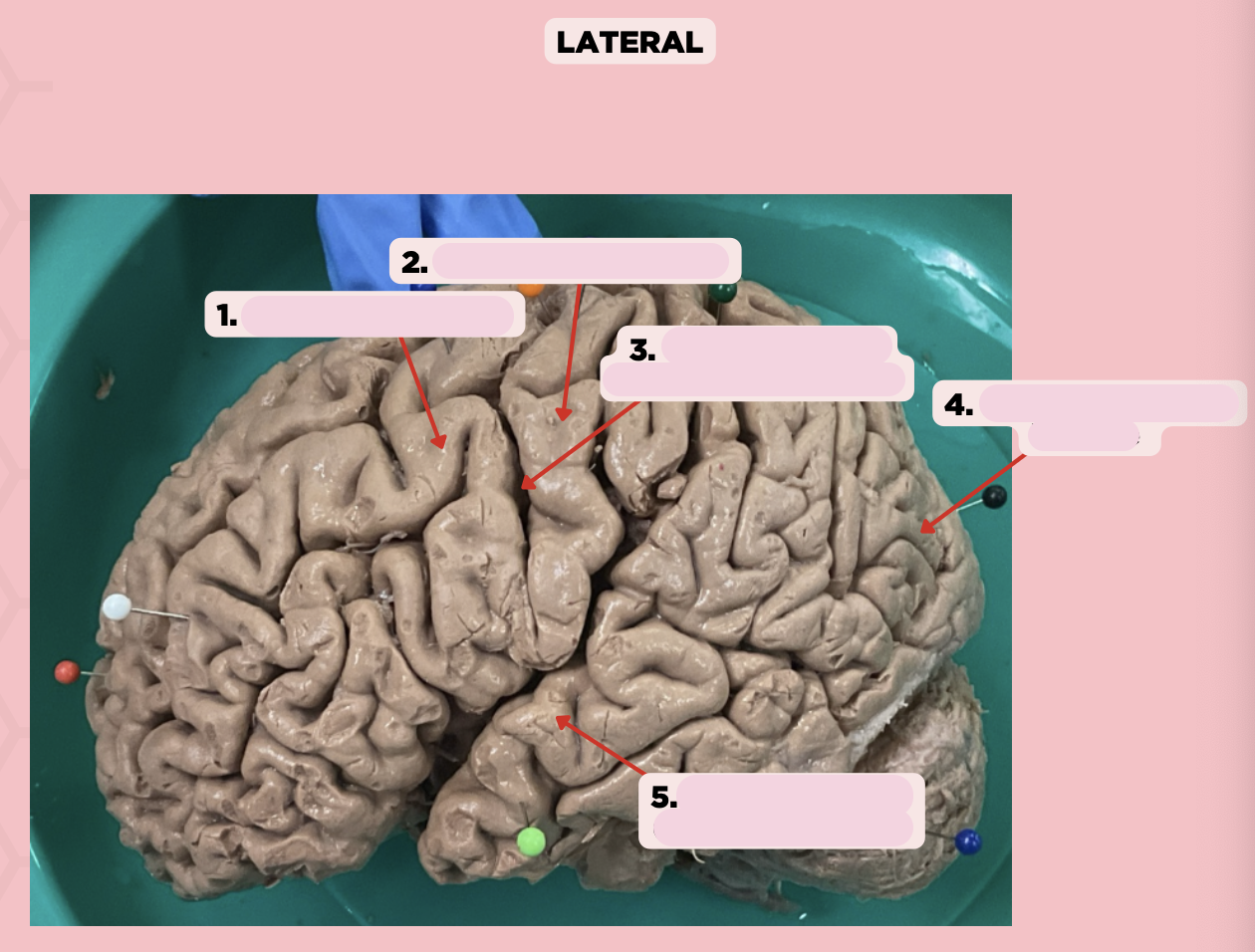
Central Sulcus (Sulcus of Rolando)
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
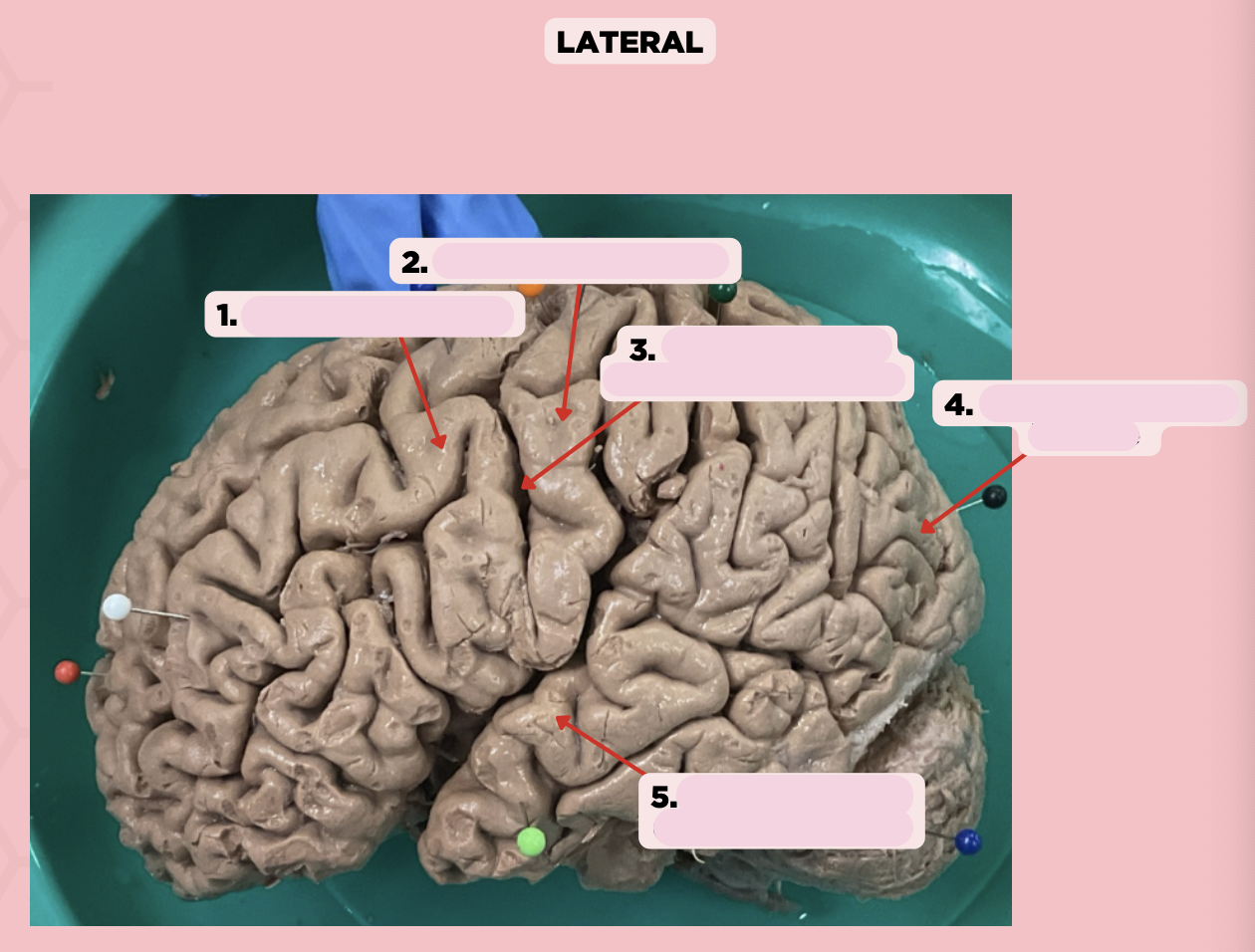
Pareto-Occipital Fissure
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
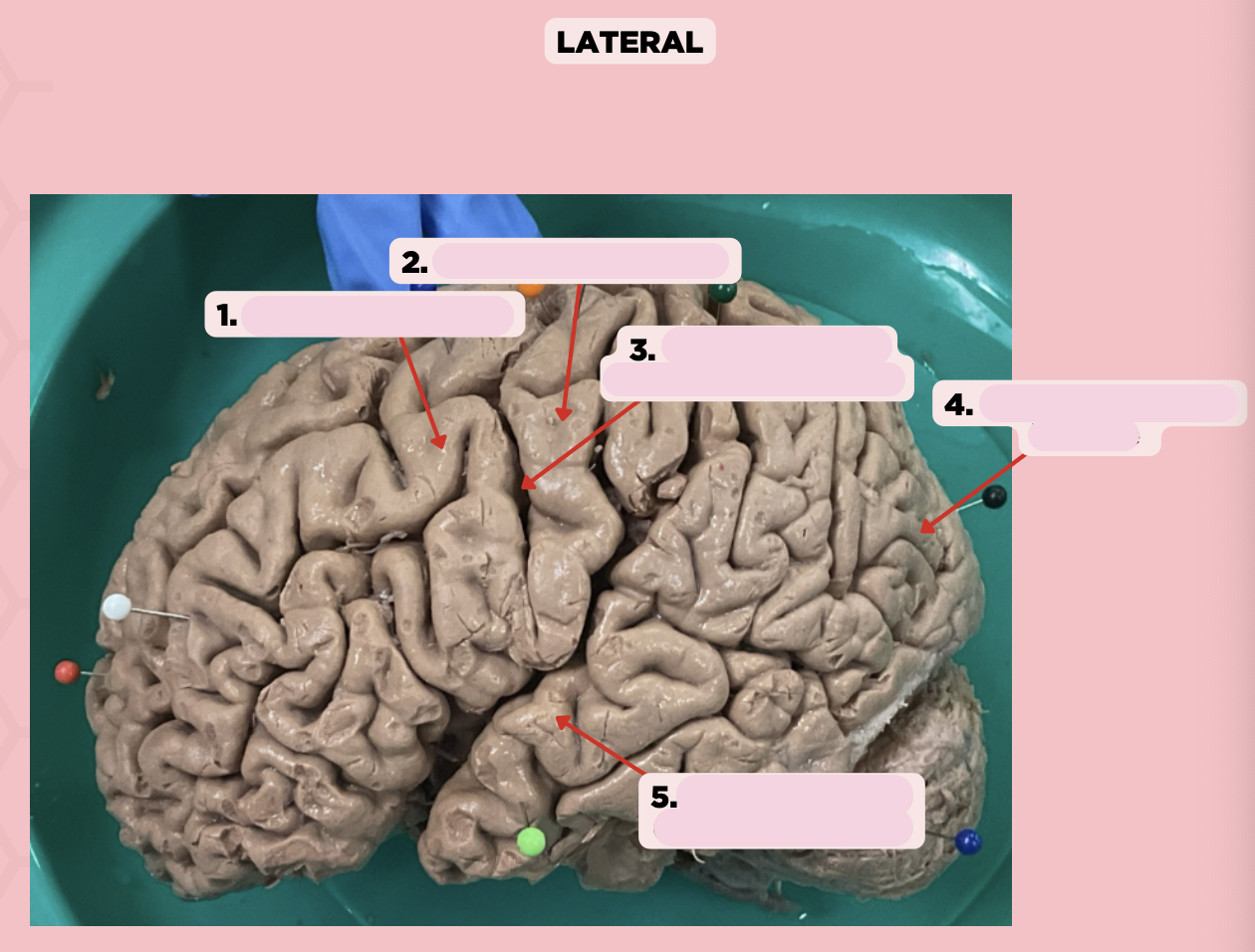
Lateral Fissure (Sylvian Fissure)
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
d. Parieto-Occipital Fissure
This fissure (Pin #1) of the brain is more prominent on the medial surface of the posterior cerebrum
a. Lateral Fissure
b. Central Fissure
c. Medial Longitudinal Fissure
d. Parieto-Occipital Fissure
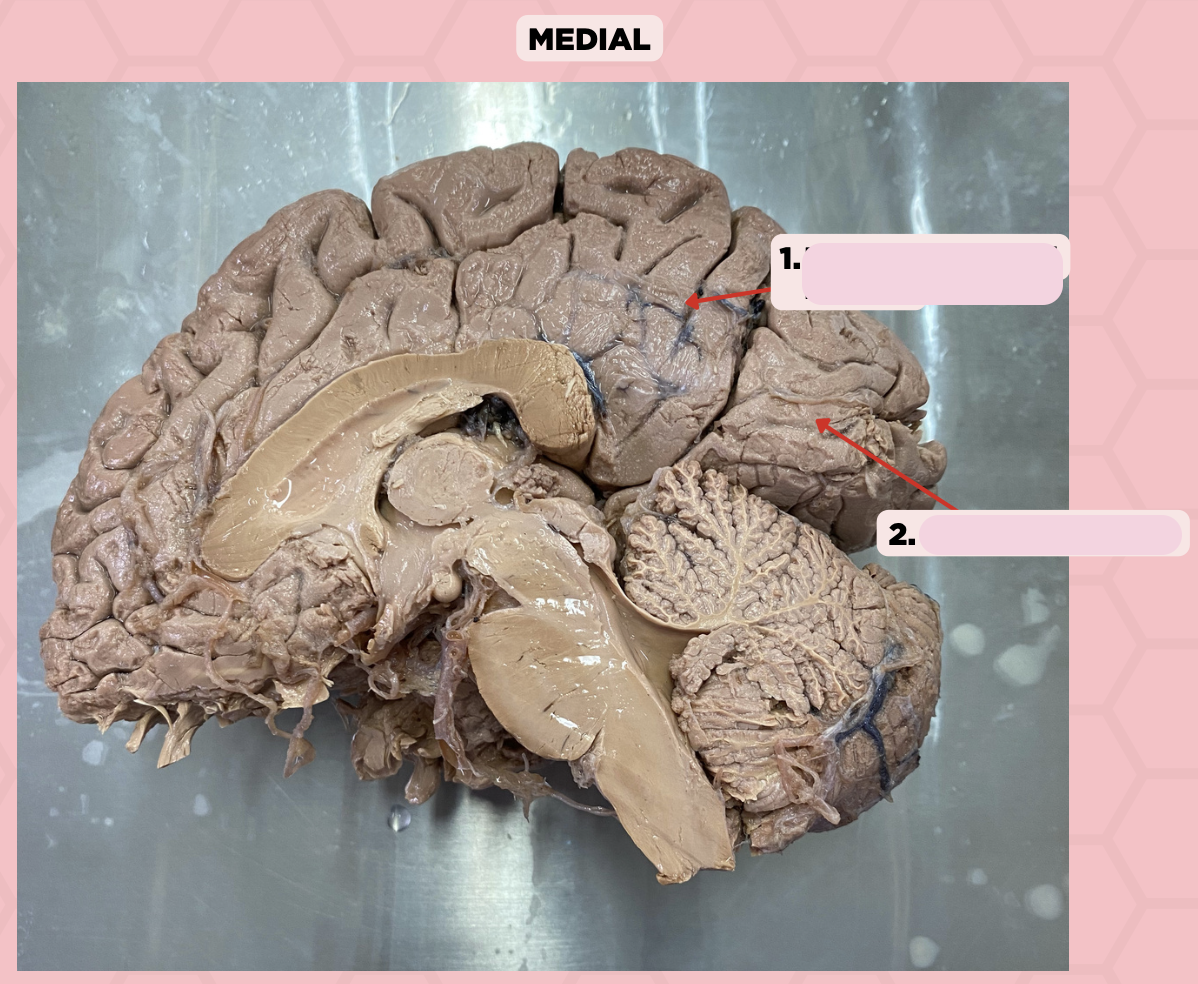
c. Calcarine Fissure
Damage to the gyri surrounding this fissure (Pin #2) could potentially lead to visual impairment and/or blindness
a. Central Fissure
b. Parieto-Occipital Fissure
c. Calcarine Fissure
d. Lateral Fissure
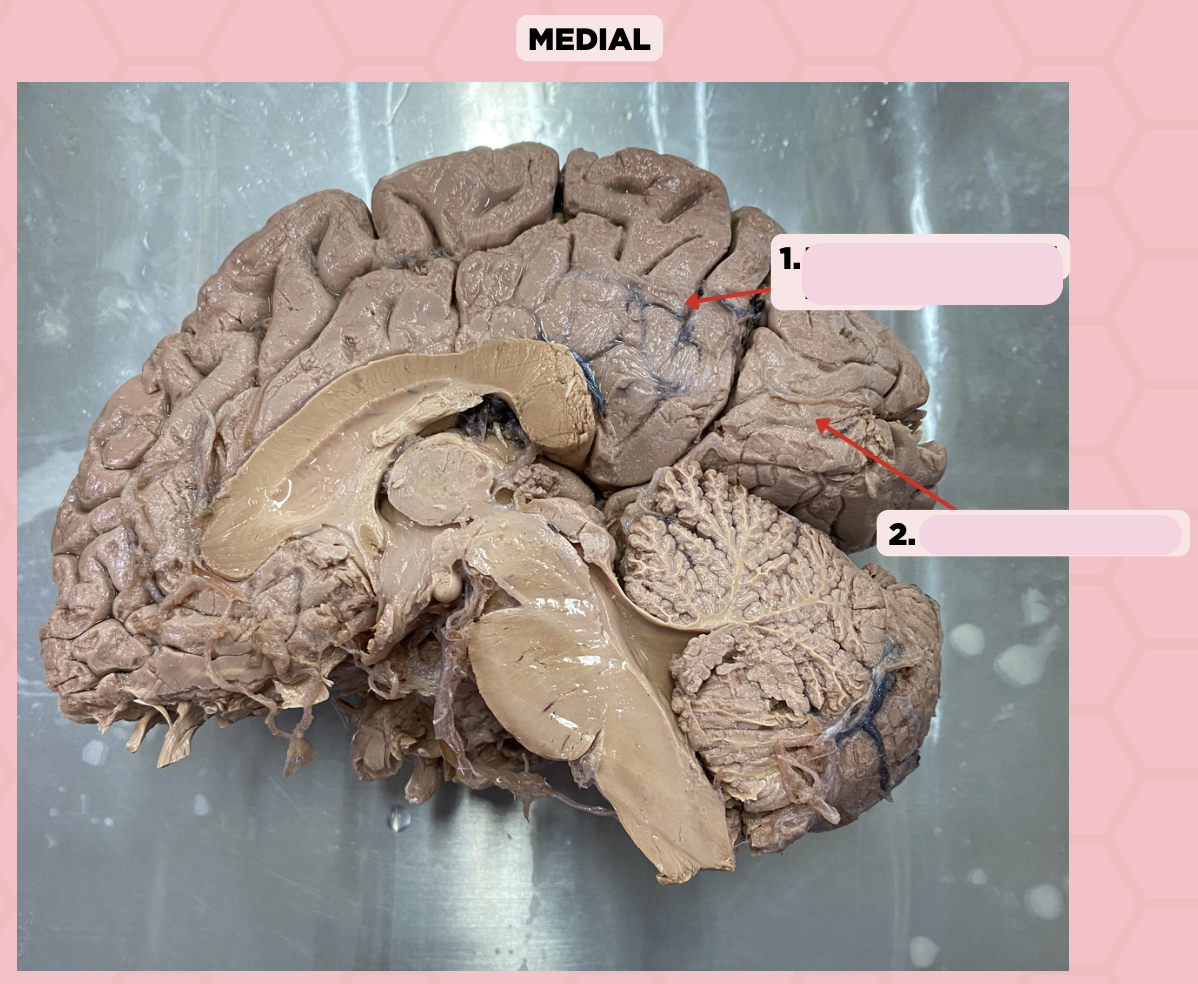
Parieto-Occipital Fissure
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
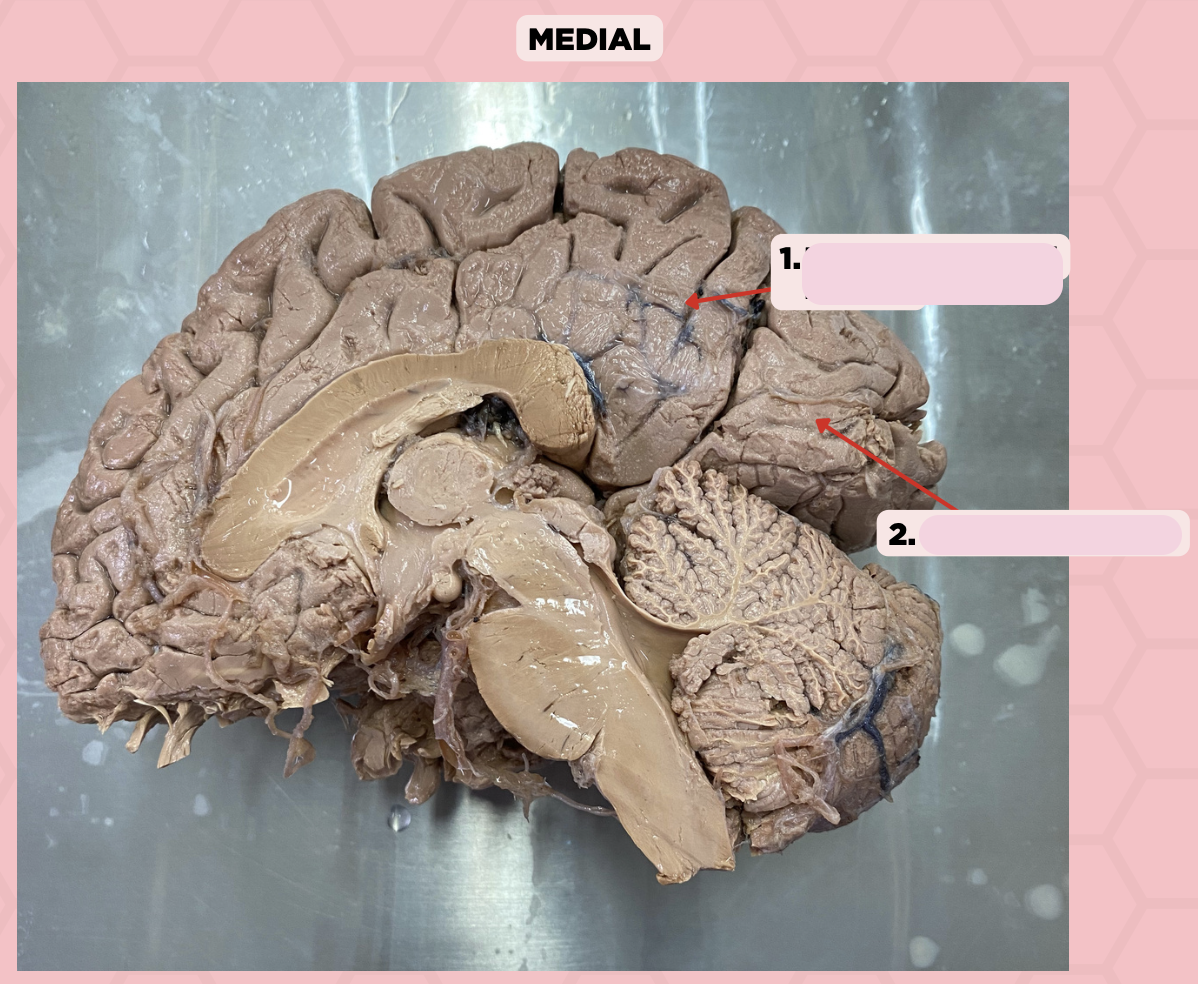
Calcarine Sulcus
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
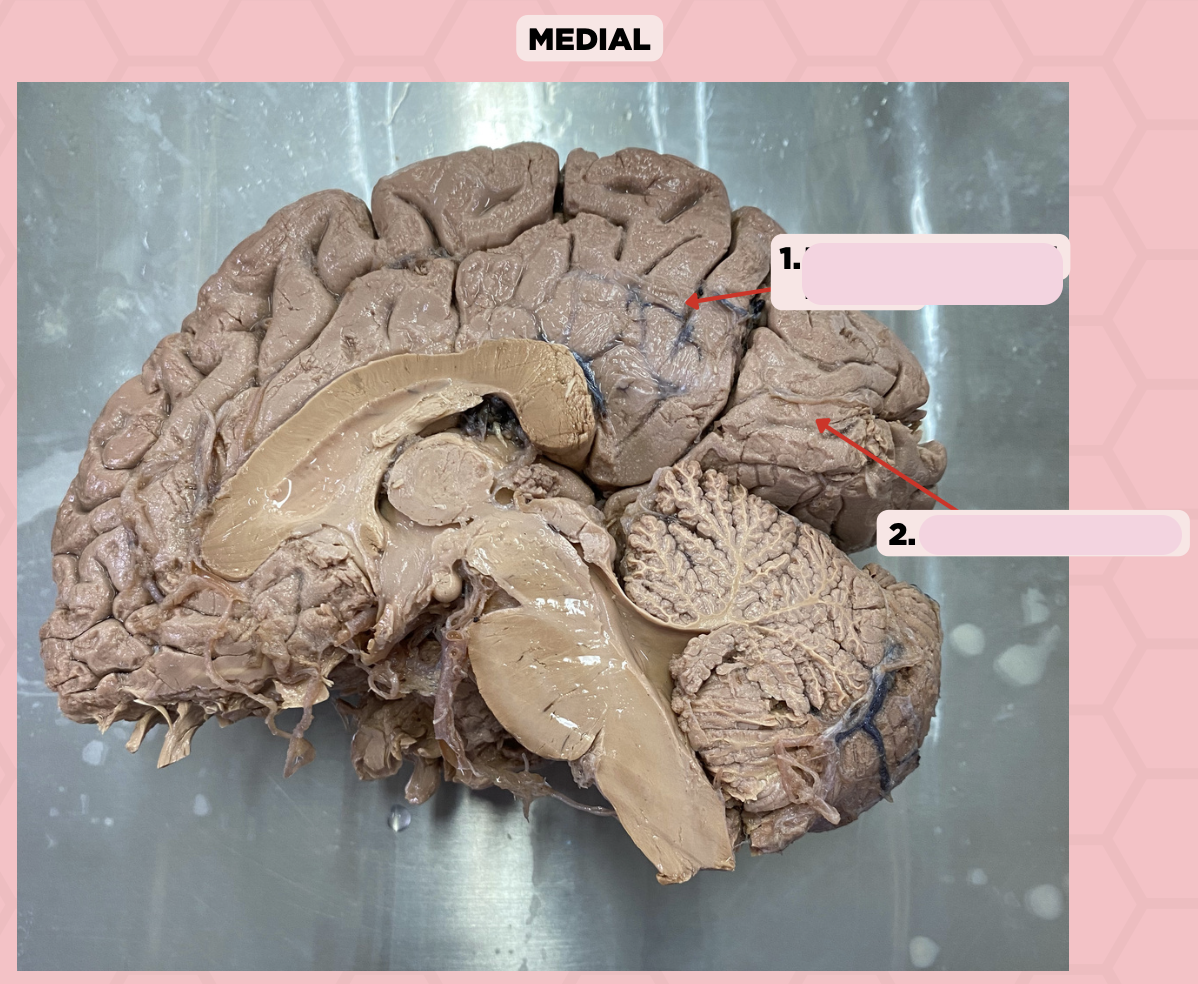
b. Parietal
A patient presents with impaired sensations (pain, proprioception, and temperature) on his extremities. Which of the following lobes spanned by Pin #2 may be damaged based on the symptoms present?
a. Temporal
b. Parietal
c. Occipital
d. Frontal
d. Frontal
Fibers from the corticospinal and corticobulbar tract will originate from a specific Brodmann Area located in which lobe of the brain spanned by Pin #1?
a. Temporal
b. Parietal
c. Occipital
d. Frontal
Frontal Lobe
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
Parietal Lobe
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
Occipital Lobe
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
Temporal Lobe
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
b. Anterior Cerebral Artery
A patient with notable lower extremity weakness indicating potential damage to Brodmann Area 4 (Pin #1) specifically, the medial side of the motor homunculus may have had a ruptured:
a. Posterior Cerebral Artery
b. Anterior Cerebral Artery
c. Middle Cerebral Artery
d. Internal Carotid Artery
b. Area 9,10,11 - Frontal Lobe
A patient from a vehicular accident presents with intact motor and sensory function yet had difficulty complying when asked to perform complex tasks. This is a problem with which Brodmann Area and Lobe of the brain (Pins #4,5,6):
a. Area 42 - Temporal Lobe
b. Area 9,10,11 - Frontal Lobe
c. Area 17 - Occipital Lobe
d. Area 3,1,2 - Parietal Lobe
c. Area. 3,1,2
Fibers of the ascending sensory pathways such as the spinothalamic and medial lemniscus pathway will eventually reach this area of the cerebrum (Pin #8):
a. Area 6
b. Area 4
c. Area. 3,1,2
d. None of the above
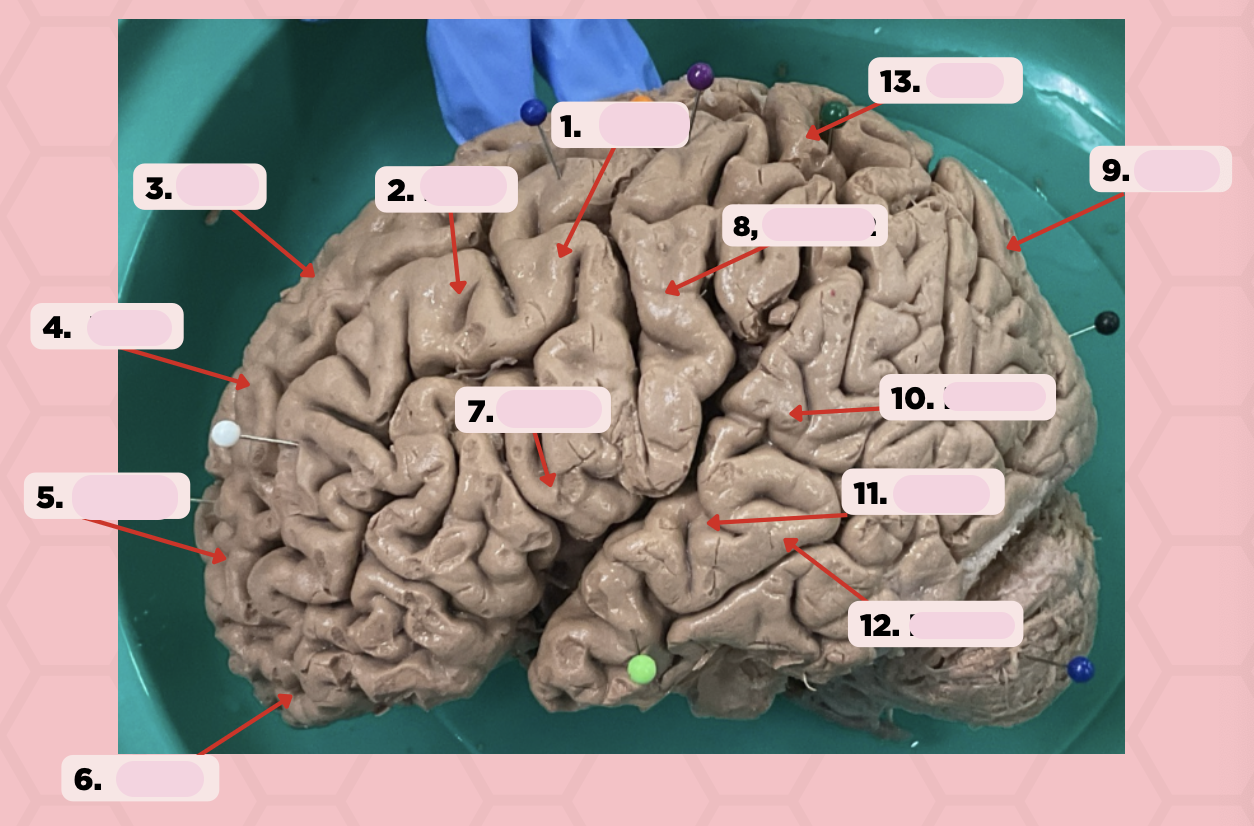
BA 4
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
BA 6
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
BA 8
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
BA 9
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
BA 10
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
BA 11
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
BA 44
Identify the structure labeled as 7.
BA 3, 1, 2
Identify the structure labeled as 8.
BA 13
Identify the structure labeled as 9.
BA 22
Identify the structure labeled as 10.
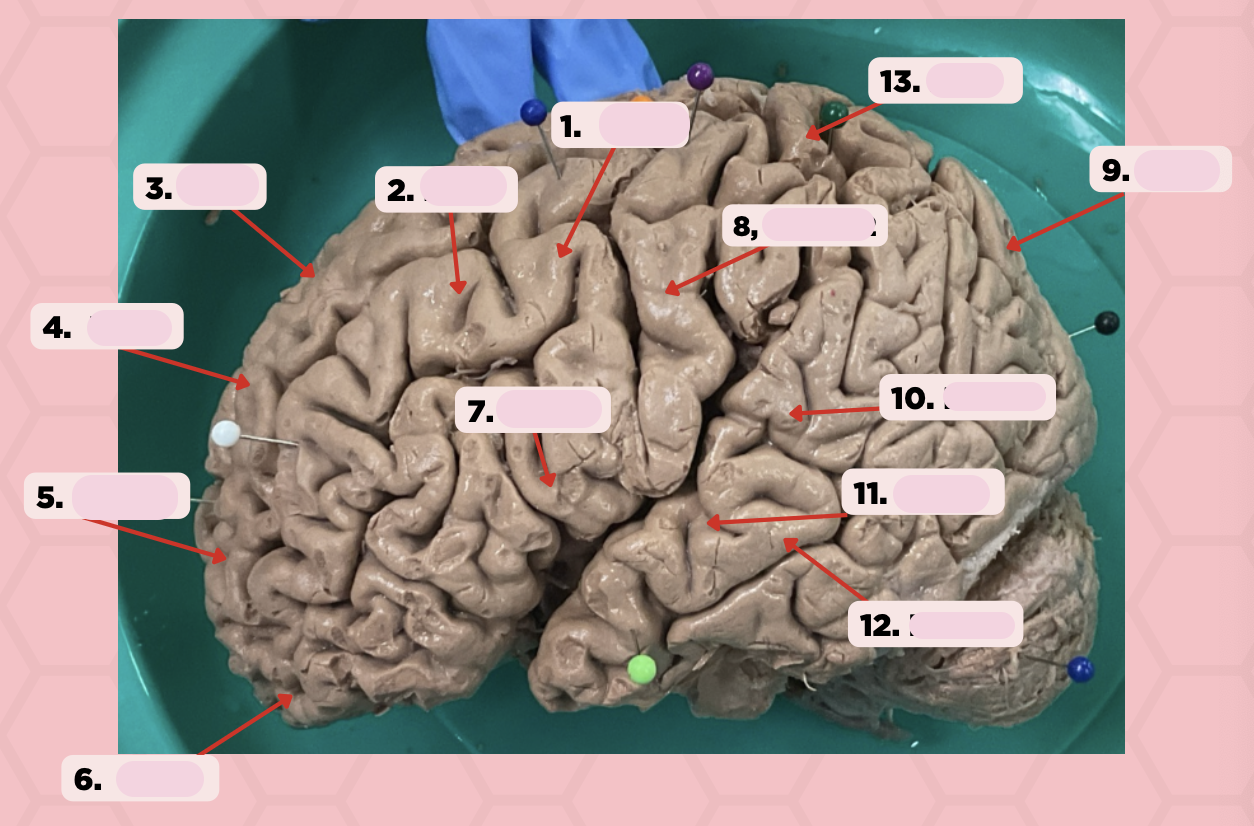
BA 41
Identify the structure labeled as 11.
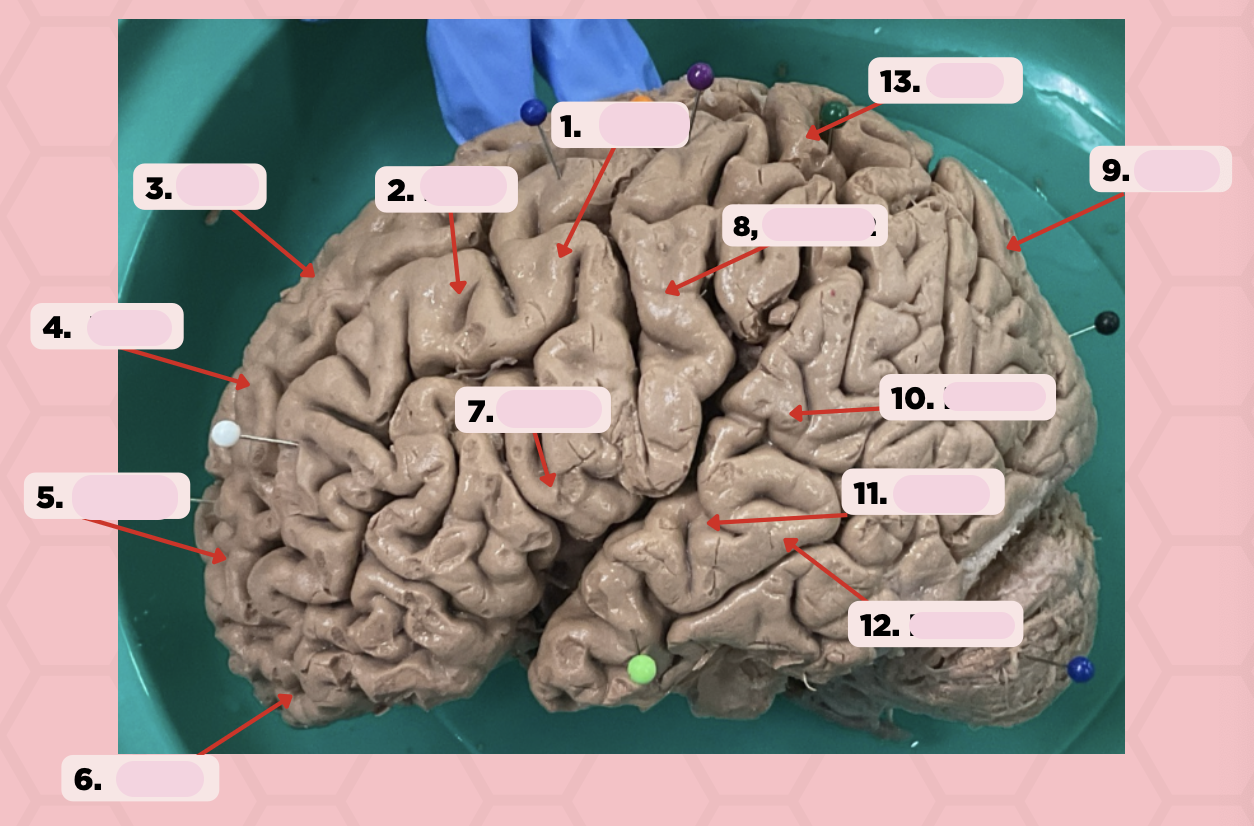
BA 42
Identify the structure labeled as 12.
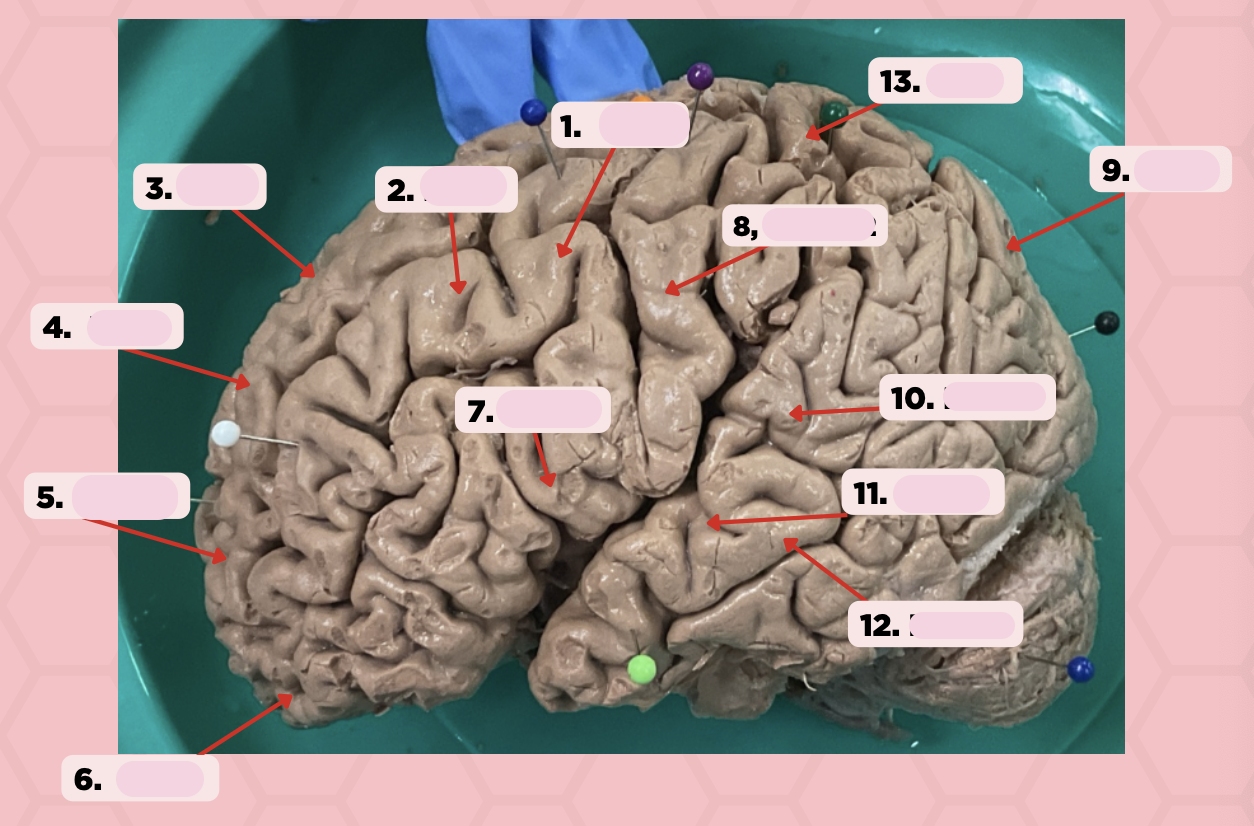
BA 8
Identify the structure labeled as 13.
c. Visual Impairment
Damage to Area 17 (Pin #2) may present with the following symptoms in a patient:
a. Lower extremity weakness
b. Upper extremity weakness
c. Visual Impairment
d. Impaired sensations from the limbs and trunk
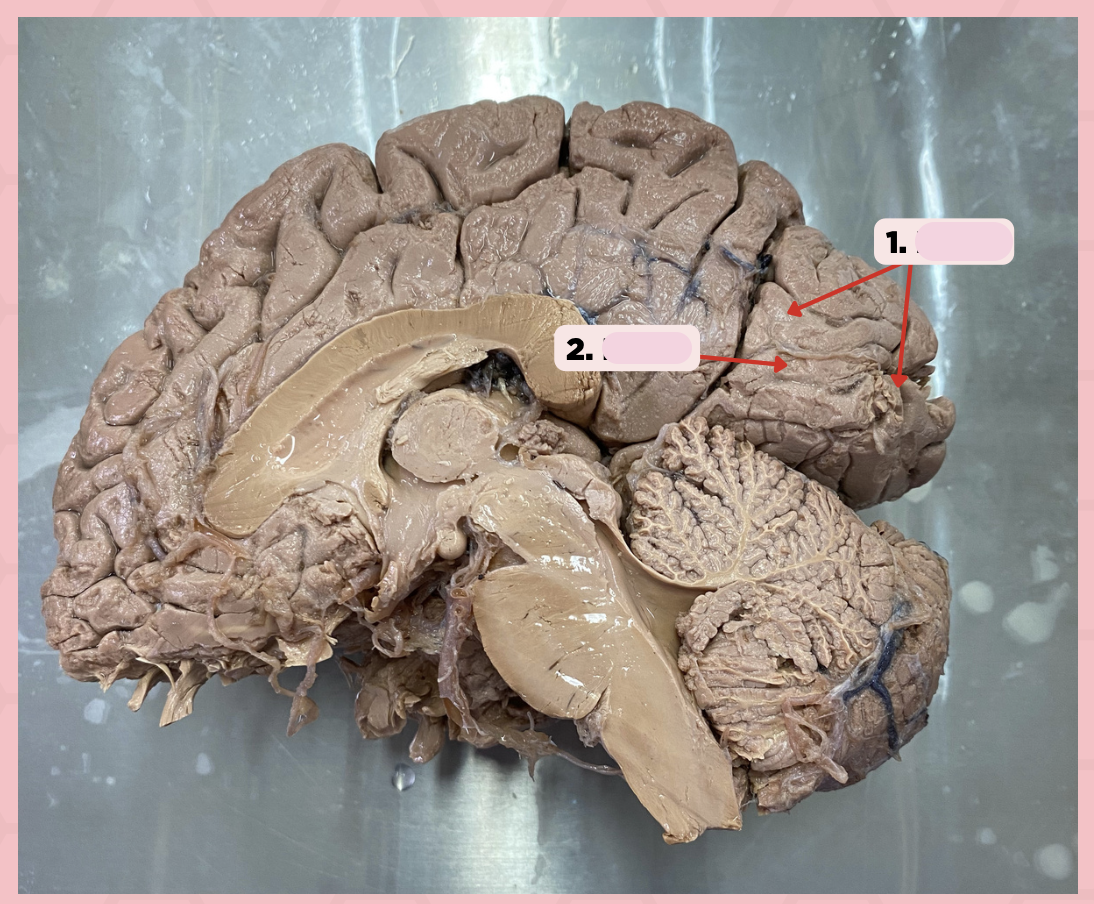
c. Analysis, interpretation, and recognition of visual stimuli
Area 18 (Pin #1) is concerned with the following functions:
a. Horizontal eye gaze
b. Conscious awareness of auditory stimulus
c. Analysis, interpretation, and recognition of visual stimuli
d. Analysis of somatosensory sensation
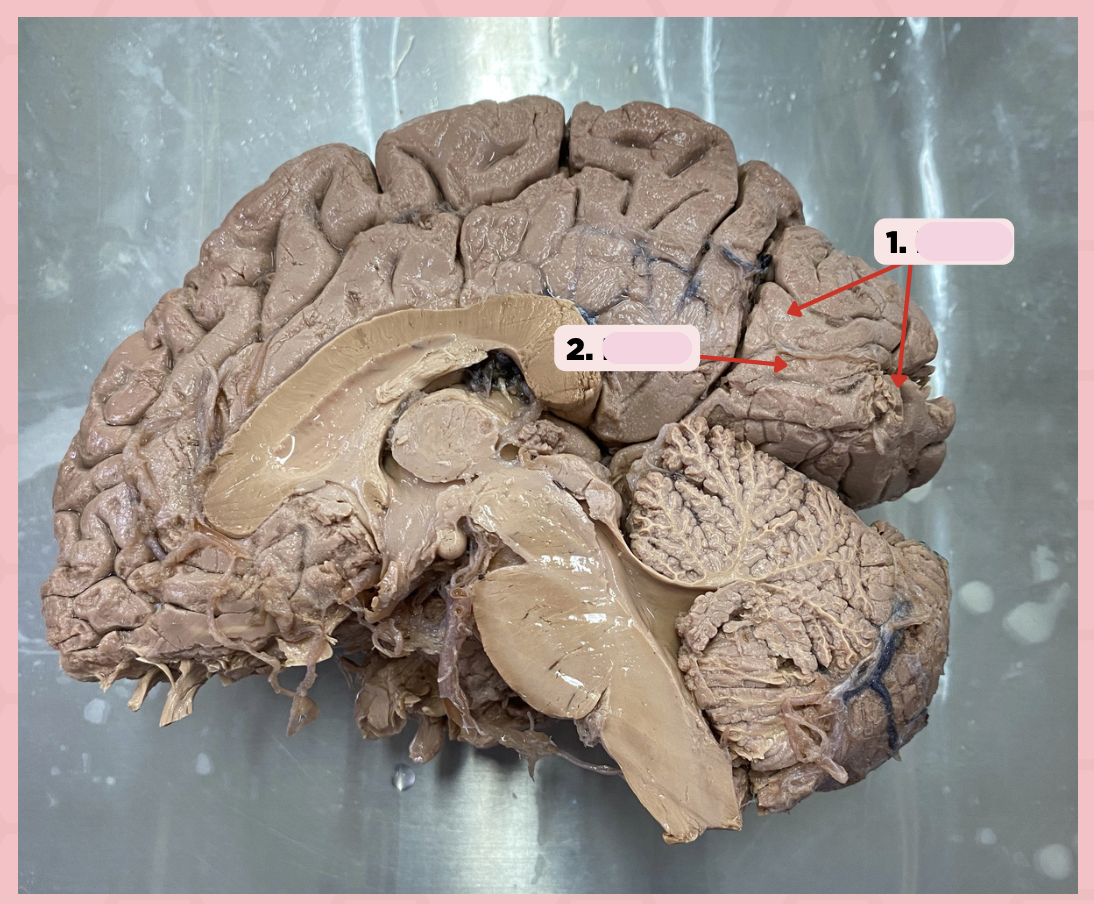
BA 18
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
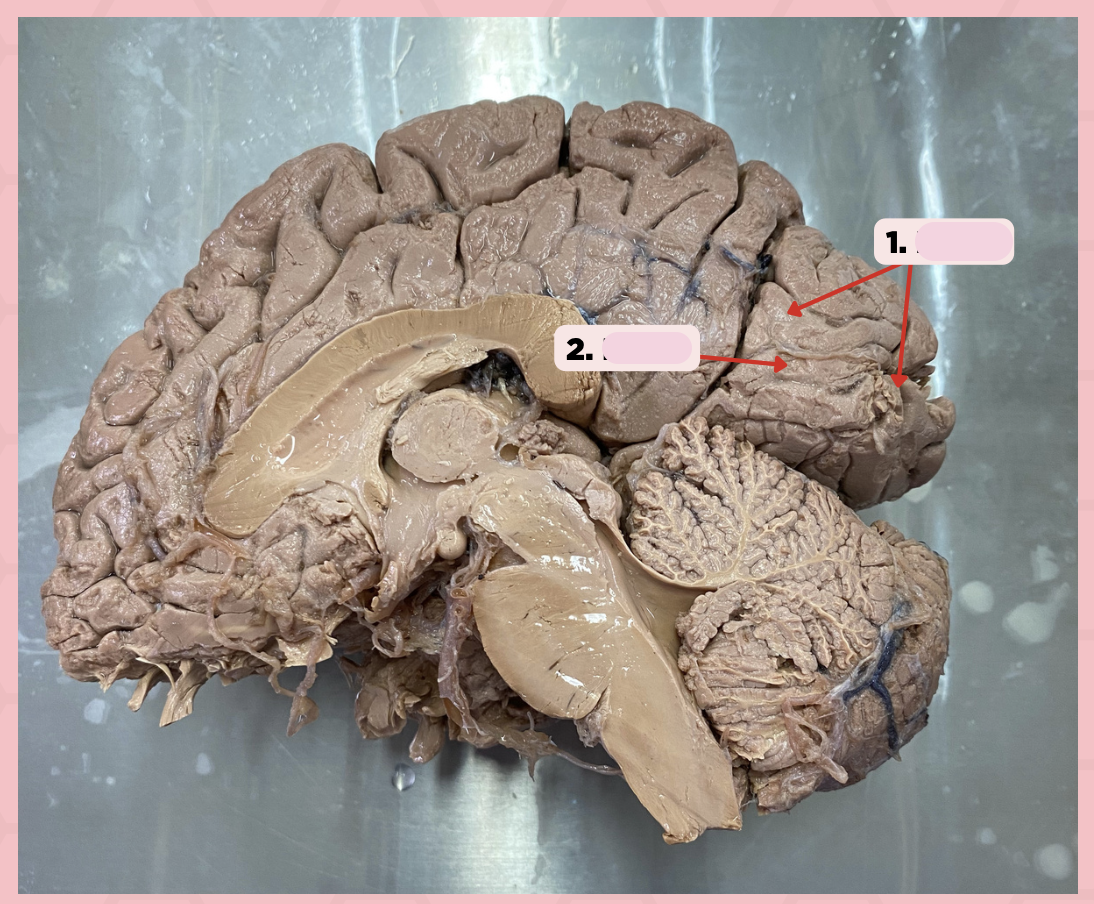
BA 17
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
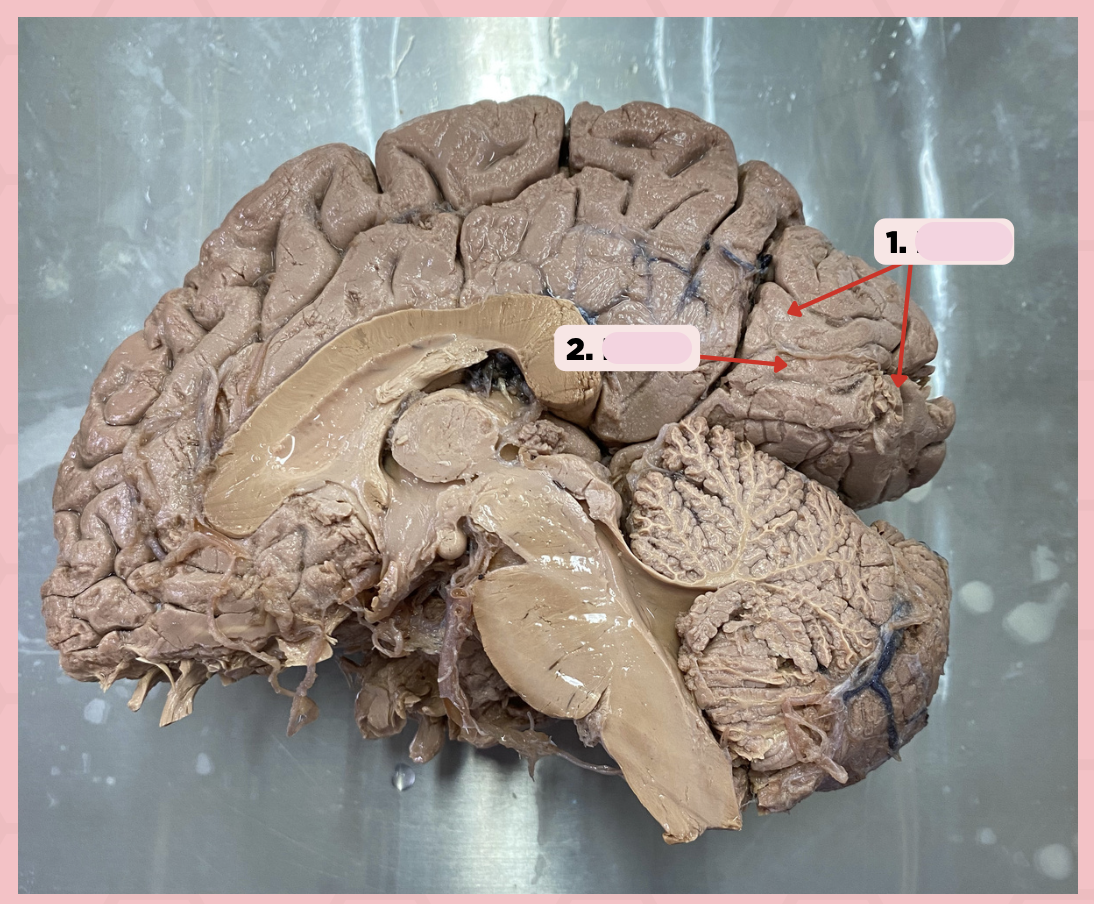
b. Commissural Fibers
The corpus callosum (Pin #2) is a type of:
a. Association Fibers
b. Commissural Fibers
c. Projection Fibers
d. None of the above
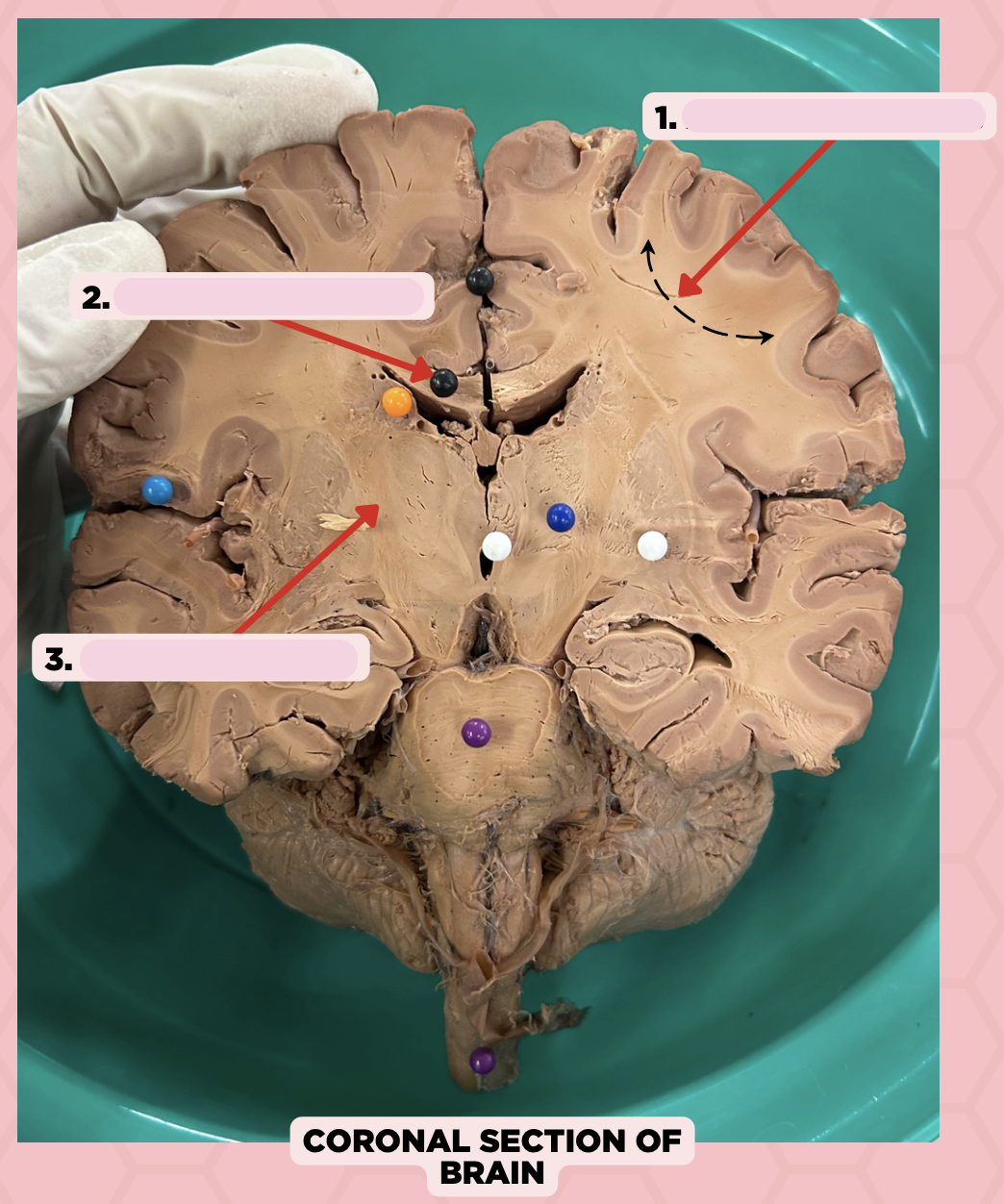
b. Pin 2- Commissural Fibers
All of the following will not traverse hemispheres EXCEPT:
a. Pin 1 - Association Fibers
b. Pin 2- Commissural Fibers
c. Pin 3- Projection Fibers
d. None of the above
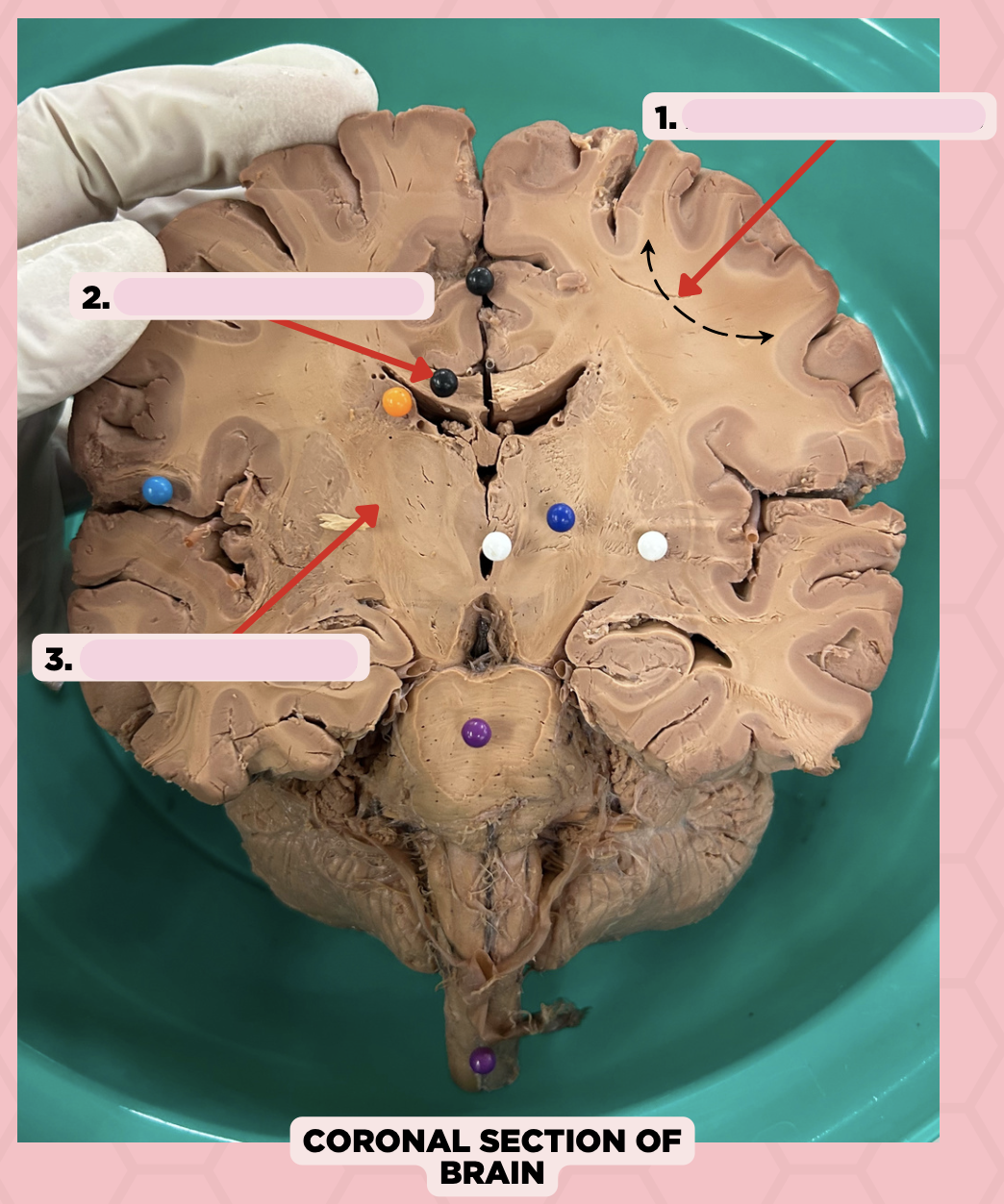
Association Fibers
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
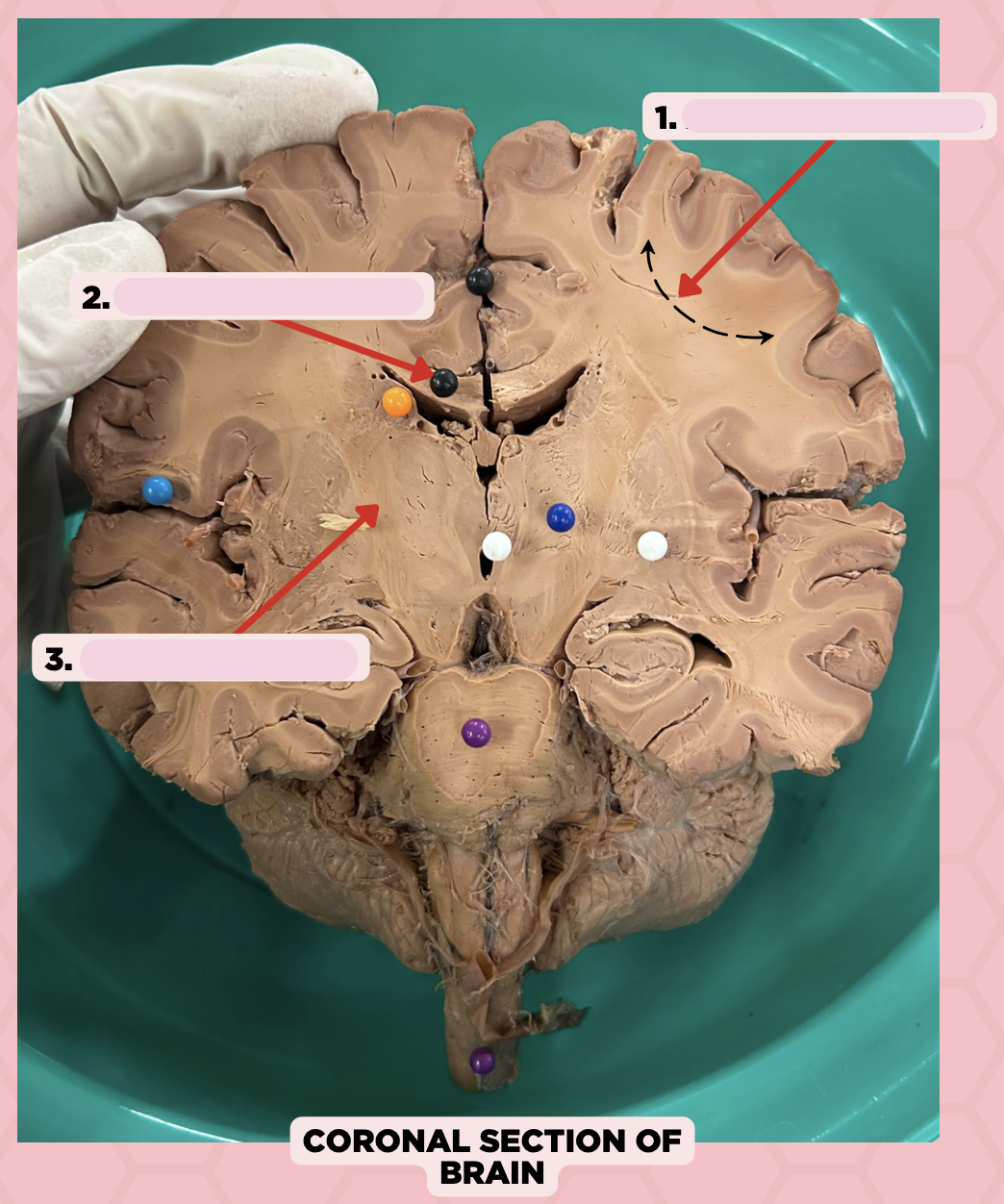
Commissural Fibers
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
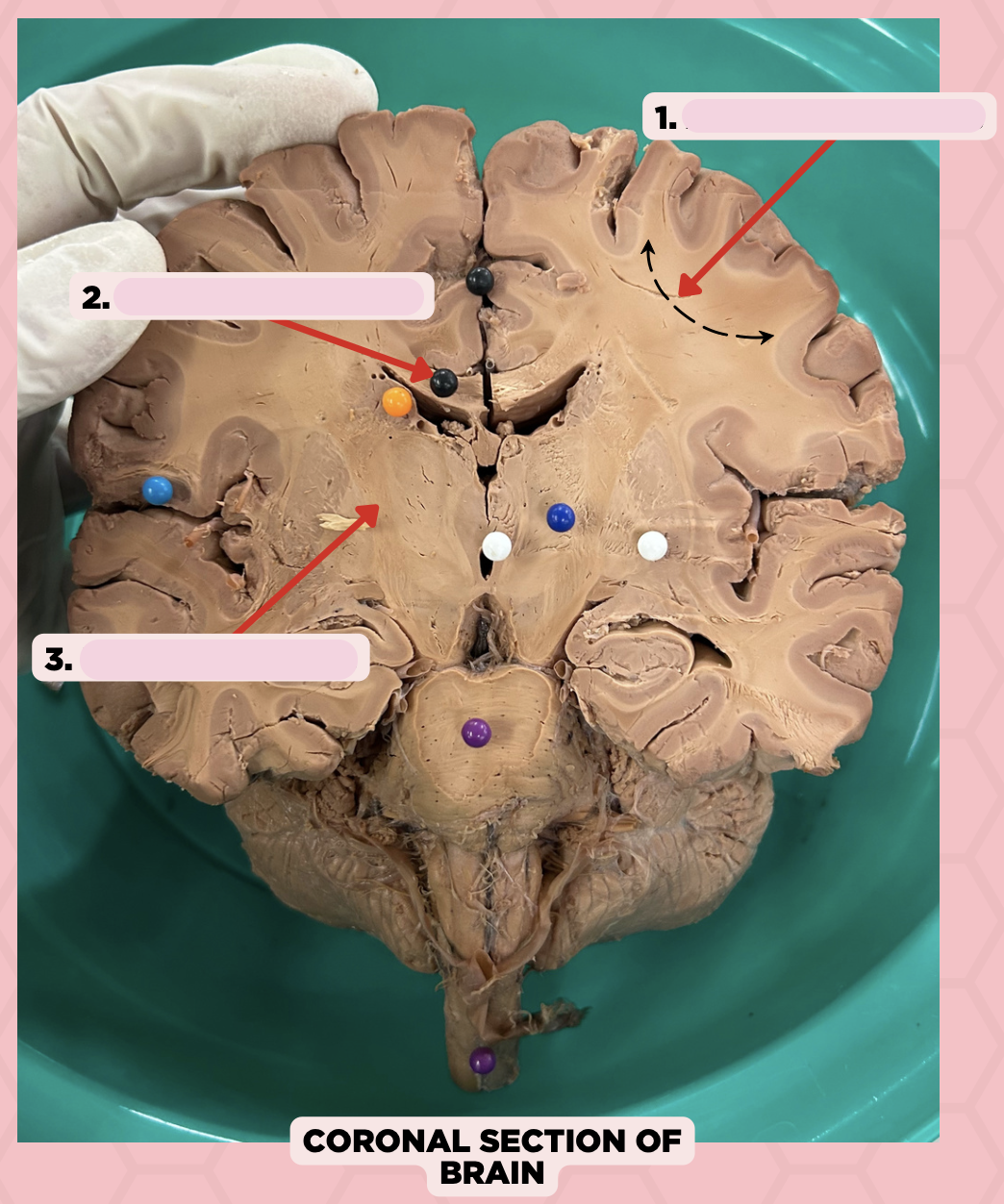
Projection Fibers
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
d. External Carotid Artery
Which of the following arteries is NOT involved in the Circle of Willis?
a. Anterior communicating artery
b. Posterior communicating artery
c. Internal Carotid Artery
d. External Carotid Artery
a. Middle Cerebral
Which among the pointed structures is the largest branch of the internal carotid artery and most commonly occluded in an ischemic stroke?
a. Middle Cerebral
b. Basilar
c. Vertebral
d. Anterior Cerebral
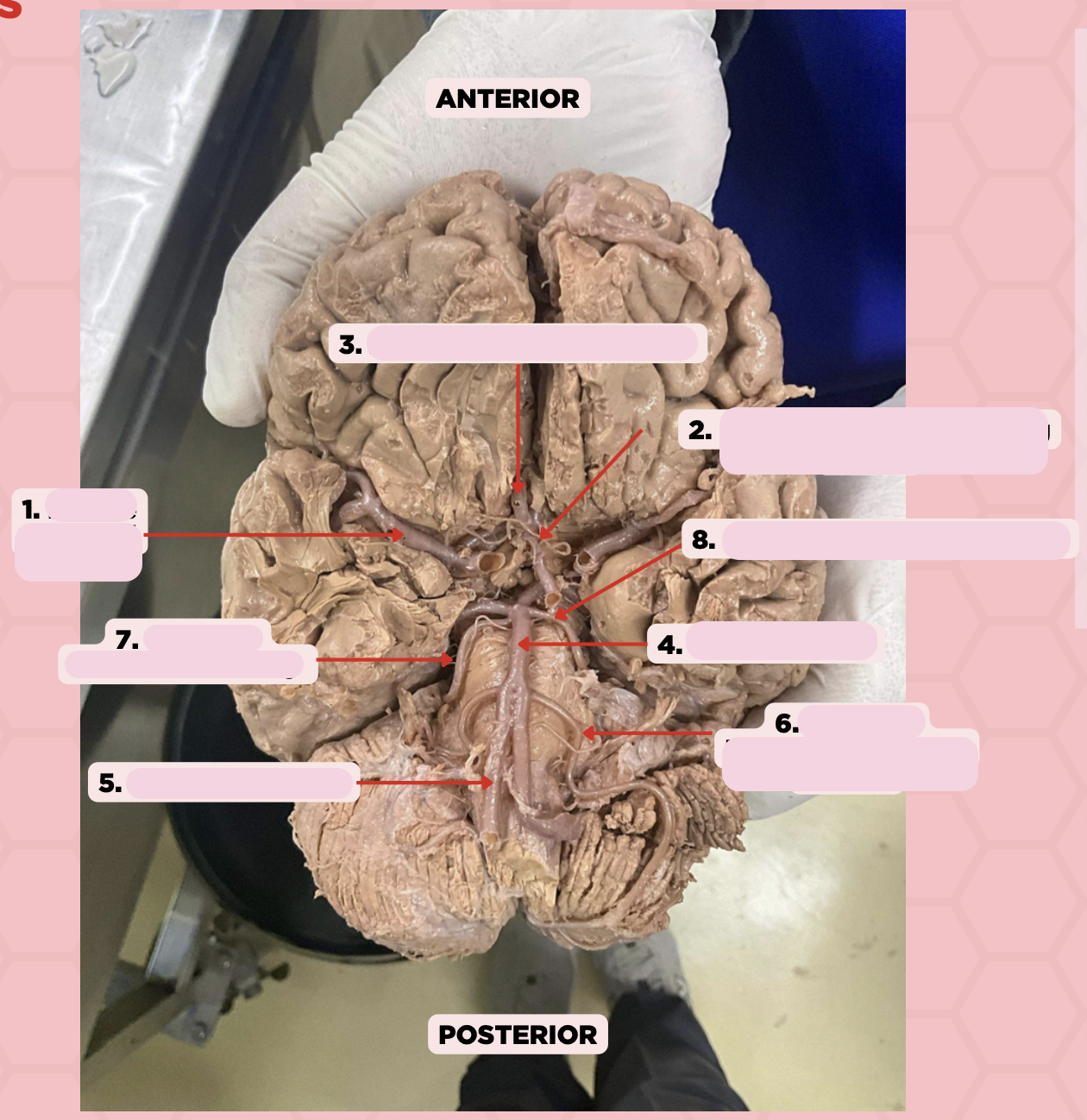
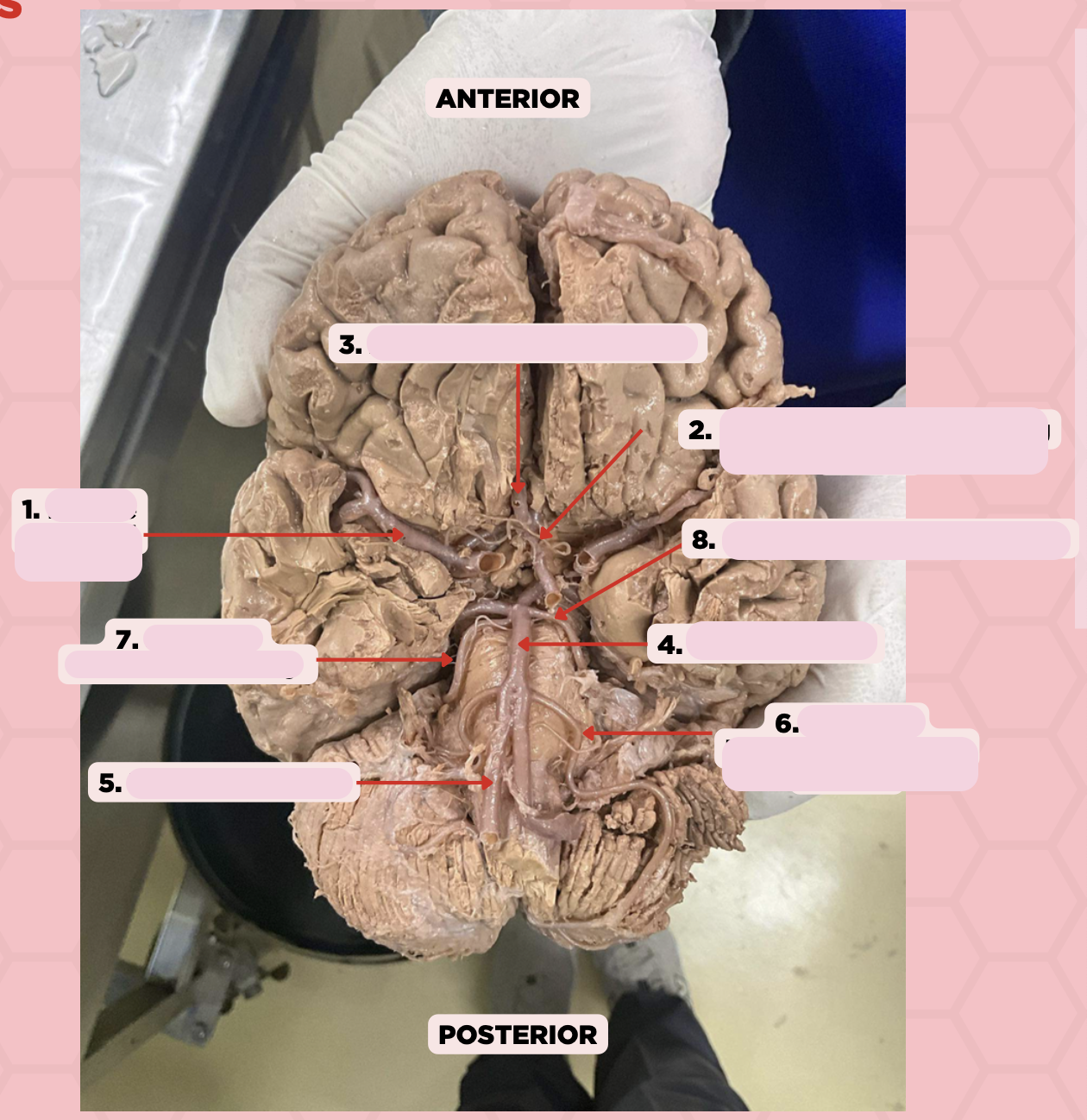
Middle Cerebral Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
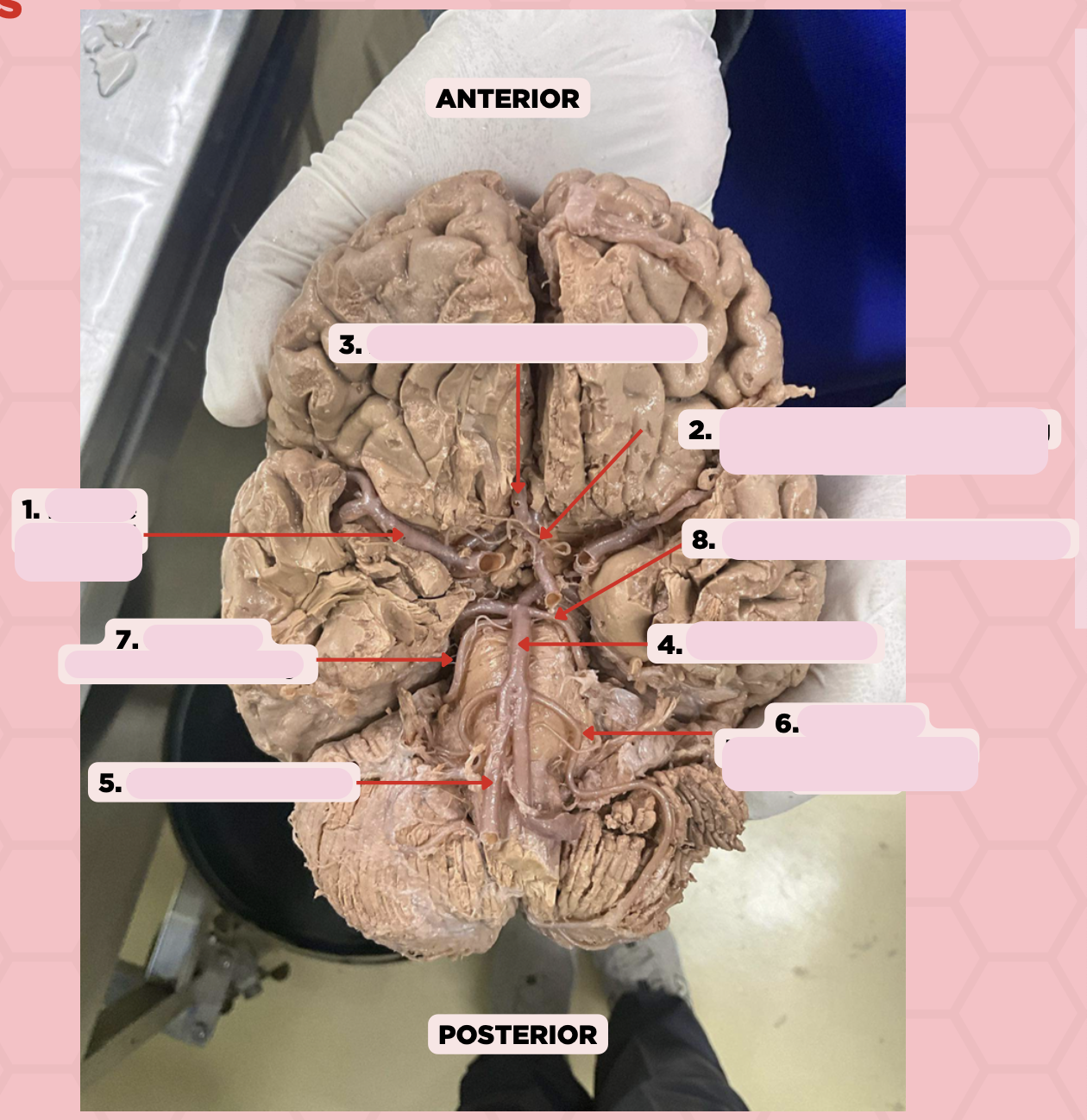
Anterior Communicating Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
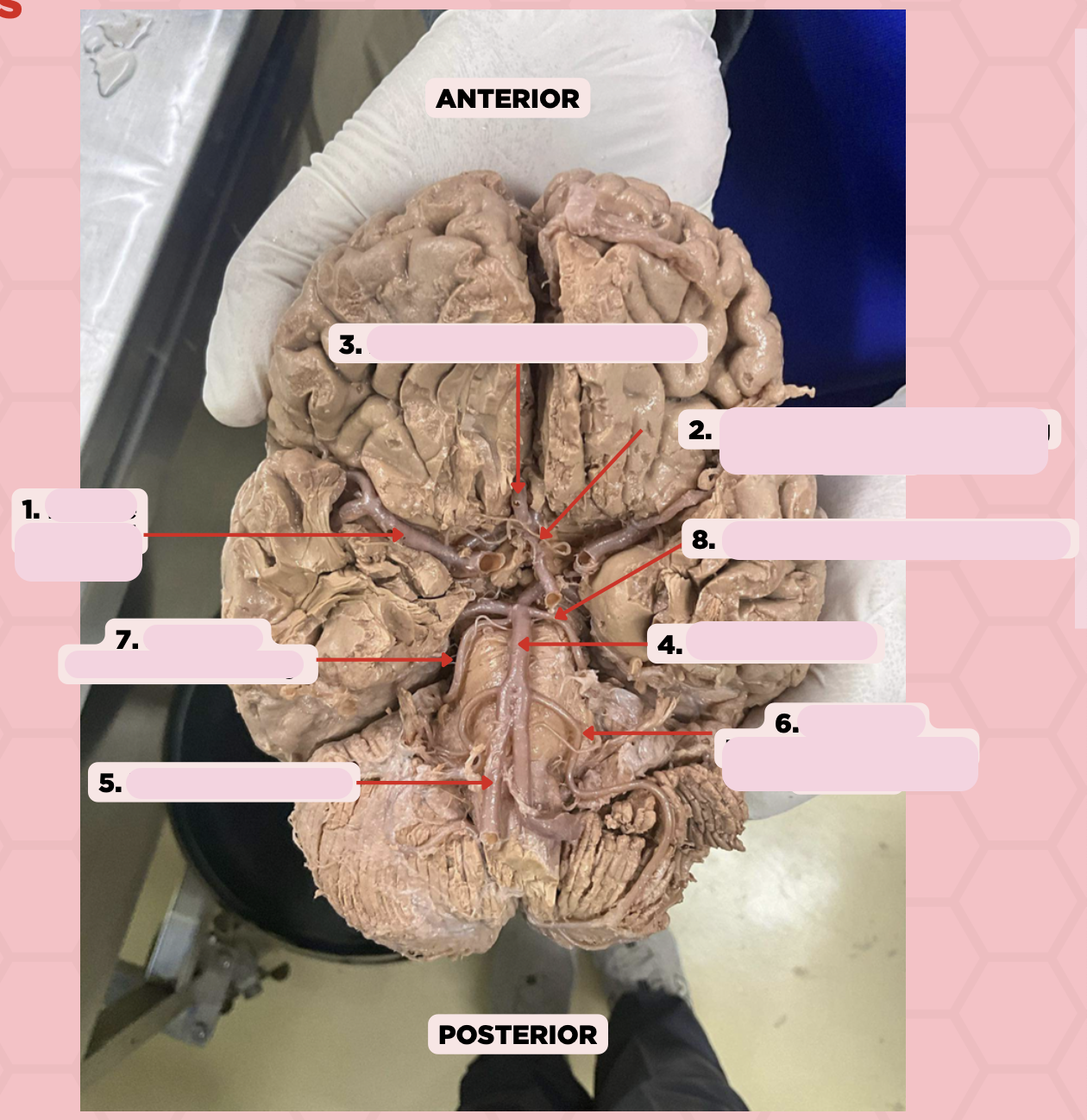
Anterior Cerebral Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
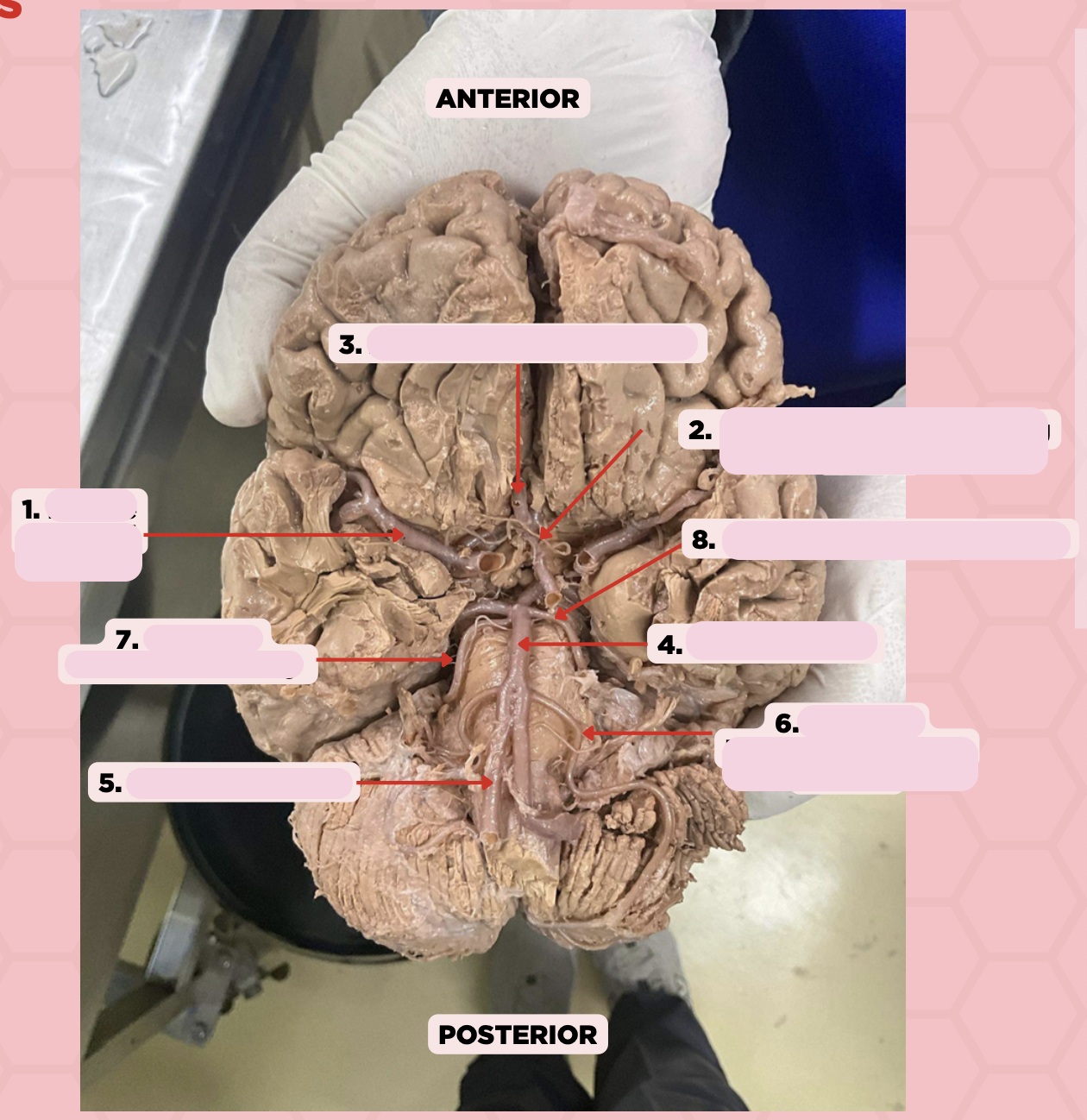
Basilar Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
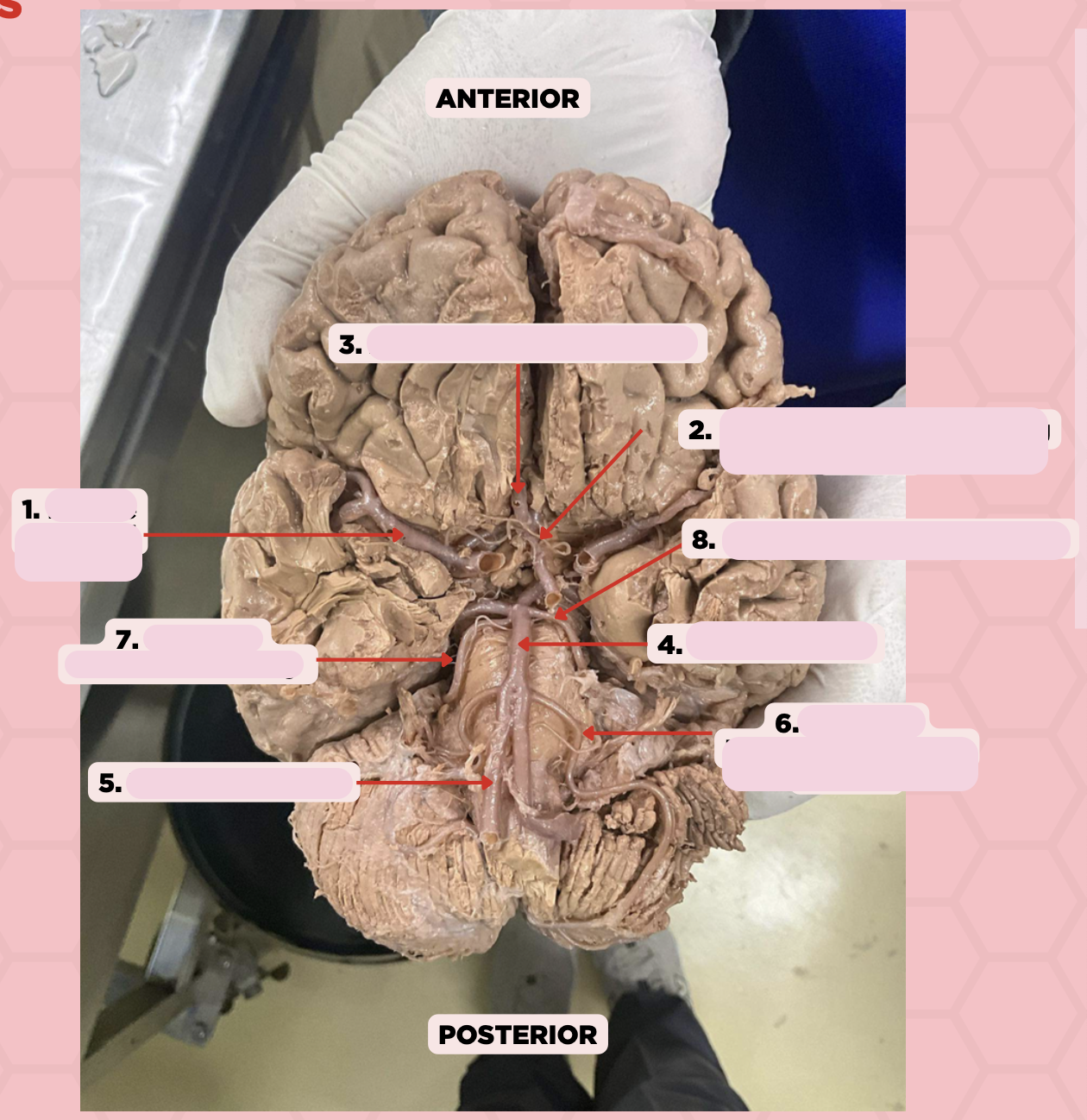
Vertebral Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 5.

Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
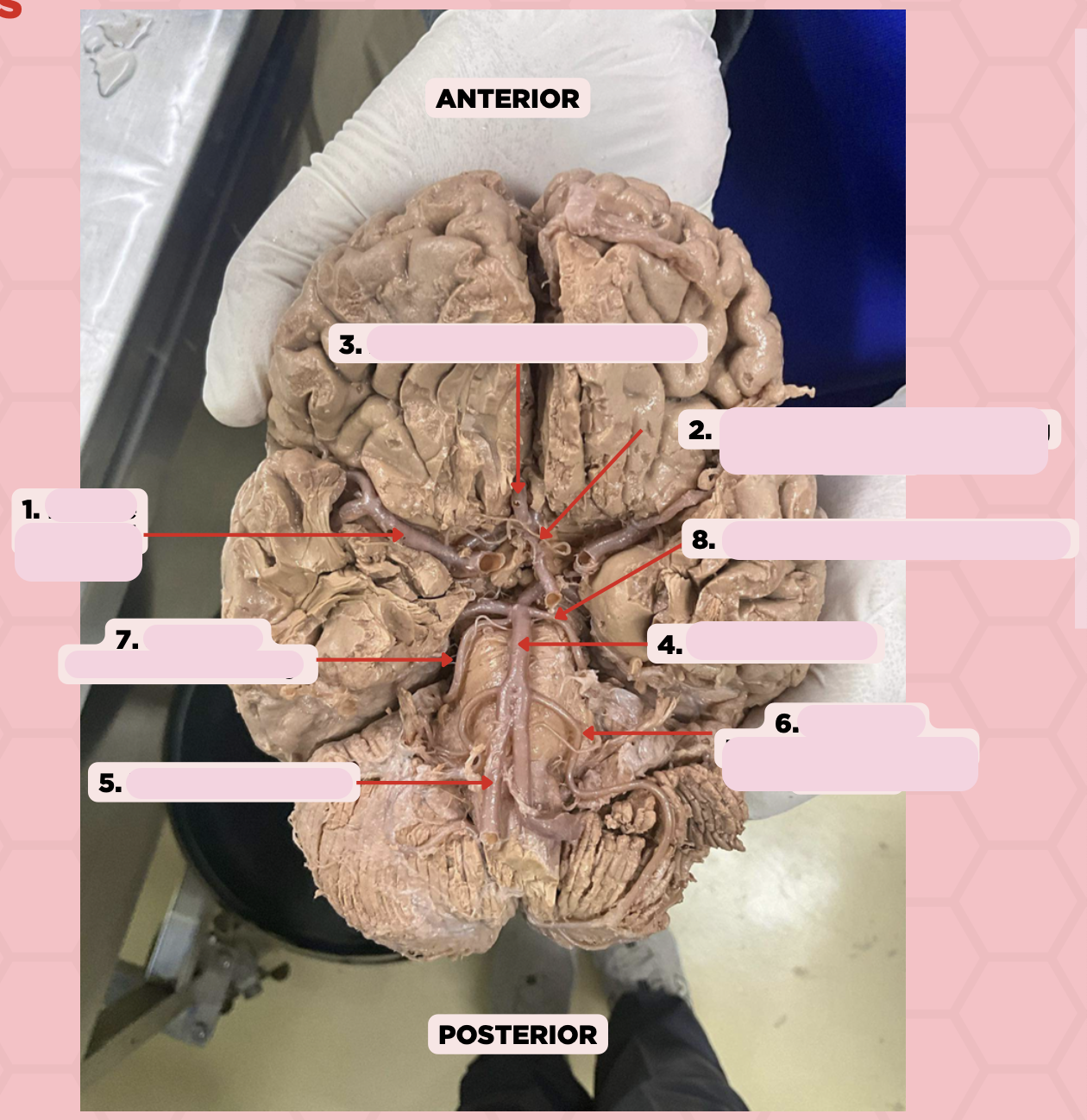
Superior Cerebellar Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 7.
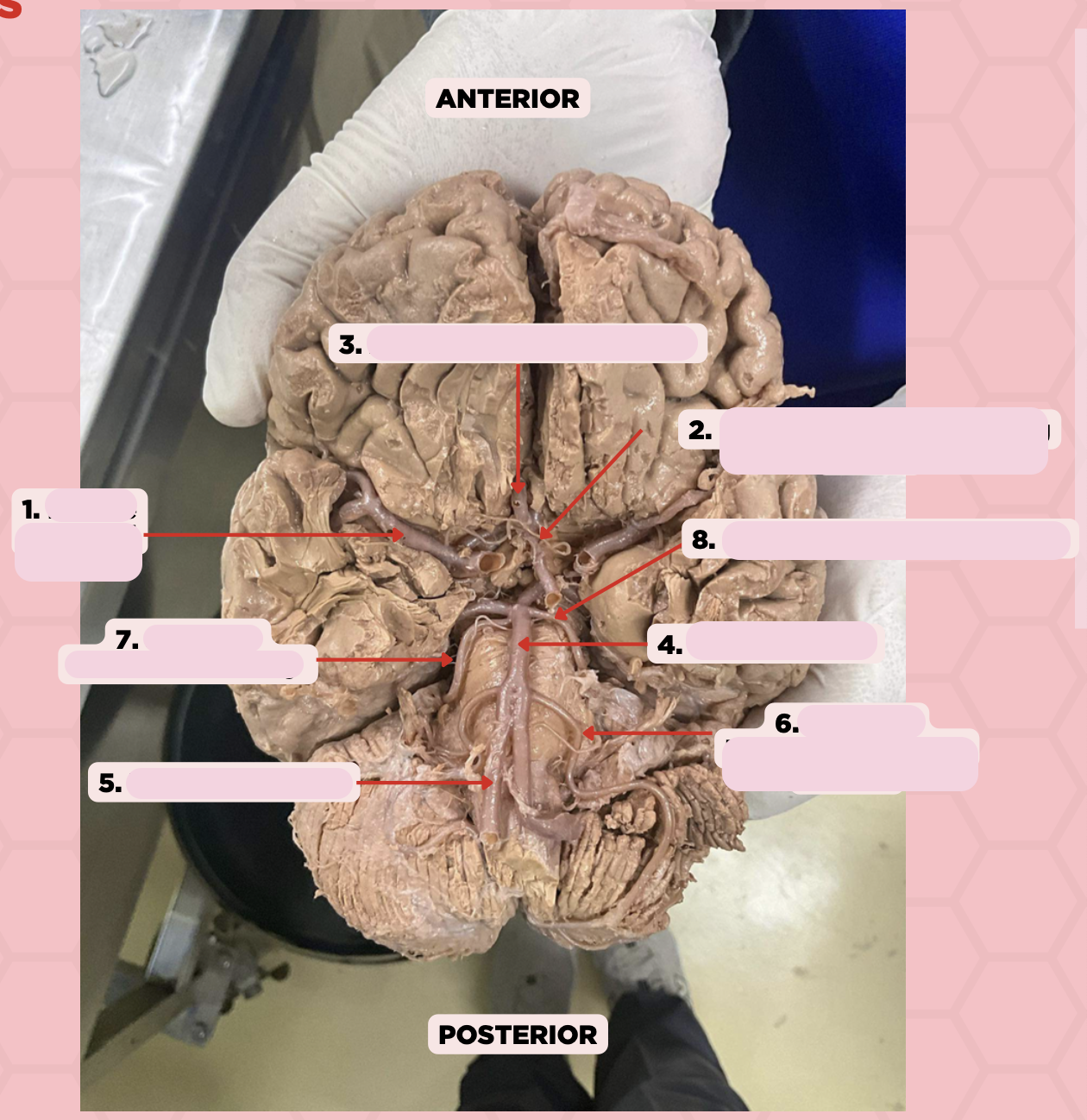
Posterior Cerebral Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 8.
c. Dural venous sinus
What structure is formed by the intervening space where the periosteal layer (outer dura) and meningeal layer (inner dura) of the dura mater separate from each other?
a. Subdural space
b. Cavernous sinus
c. Dural venous sinus
d. Subarachnoid space
b. Subdural hemorrhage
What type of hemorrhage allows bleeding into the potential space between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater?
a. Epidural hemorrhage
b. Subdural hemorrhage
c. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
d. None of the above
c. Pia mater
Which of the following meninges is tightly associated with the surface of the brain which lines the various sulci?
a. Dura mater
b. Arachnoid mater
c. Pia mater
d. None of the above
a. Cerebrospinal fluid
Which of the following is the main component of the subarachnoid space?
a. Cerebrospinal fluid
b. Blood
c. Proteins
d. Serum
Arachnoid Mater
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
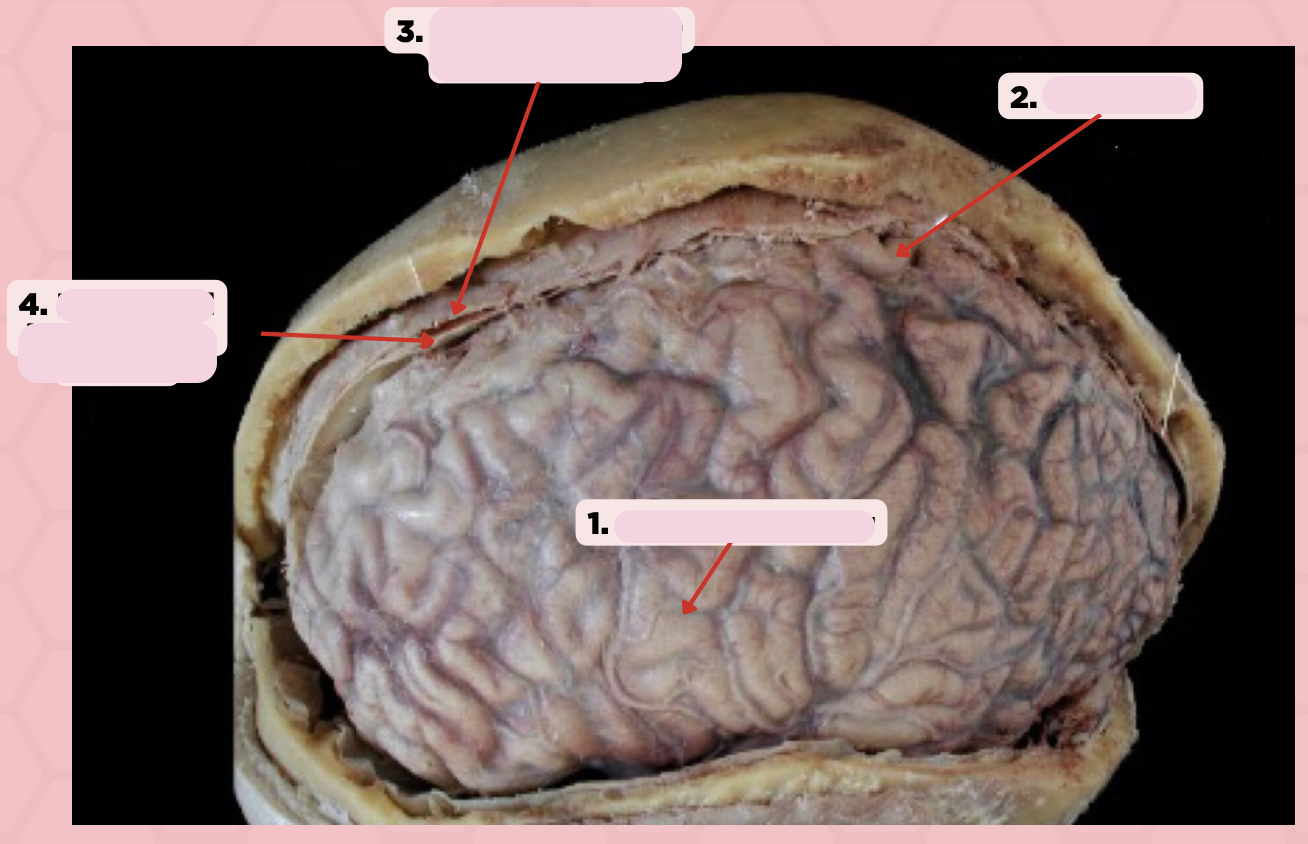
Pia Mater
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
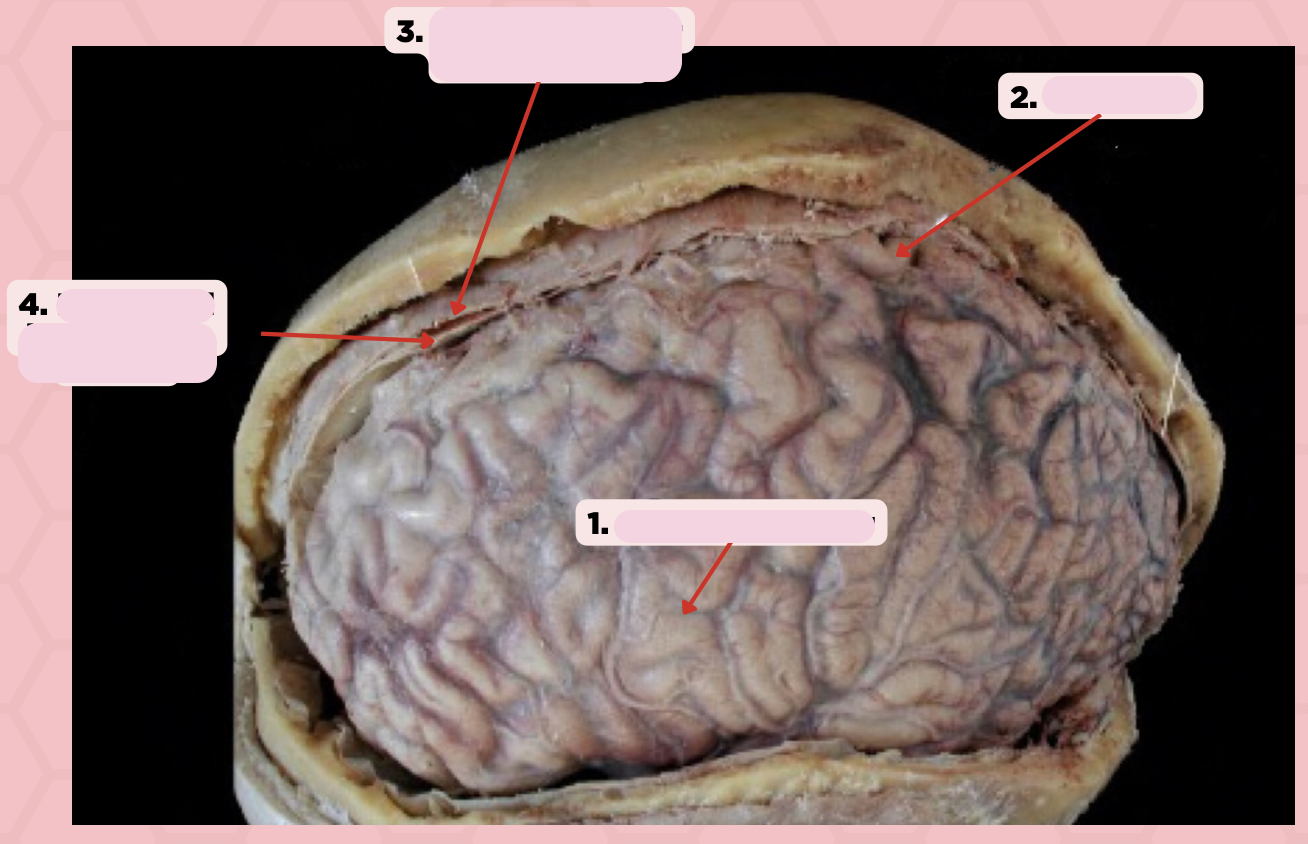
Periosteal Layer (Dura Mater)
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
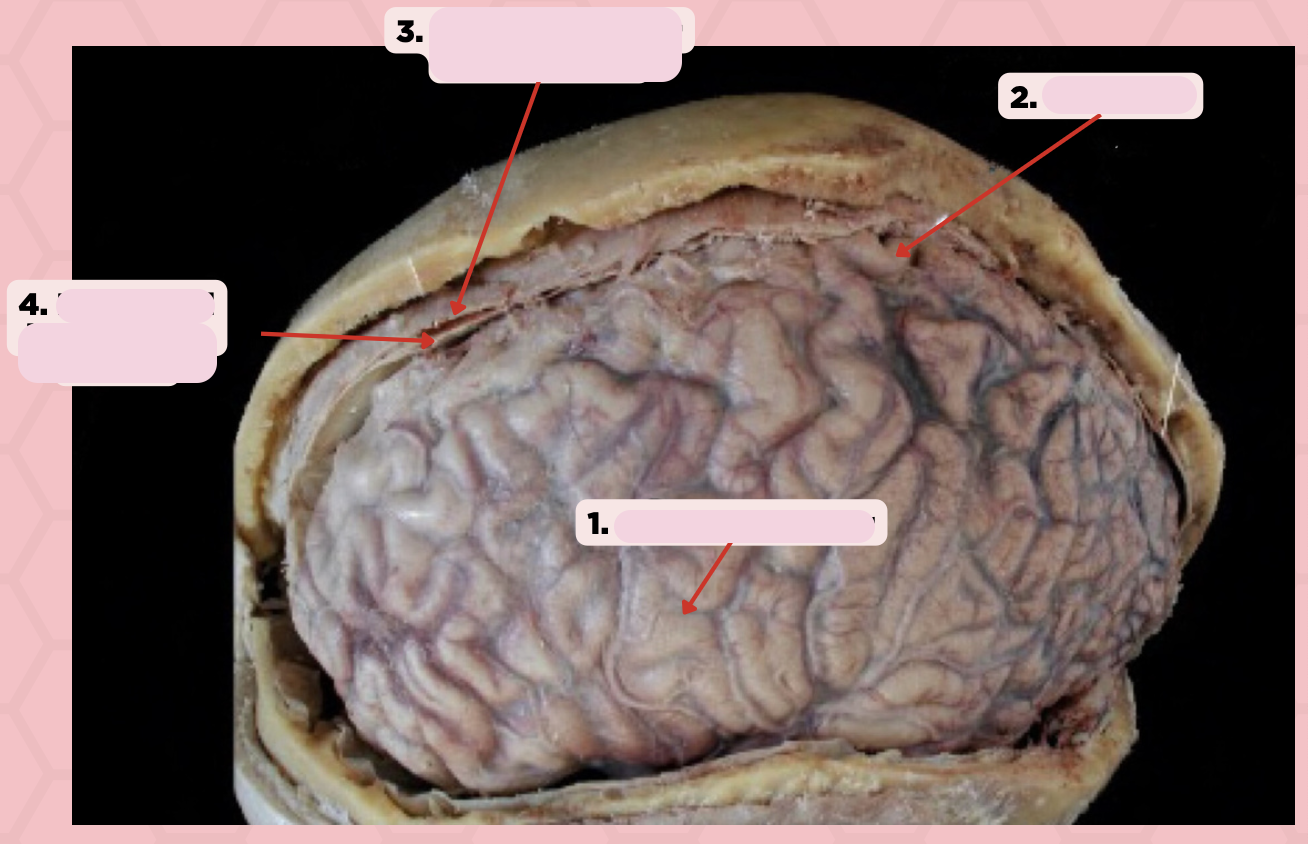
Meningeal Layer (Dura Mater)
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
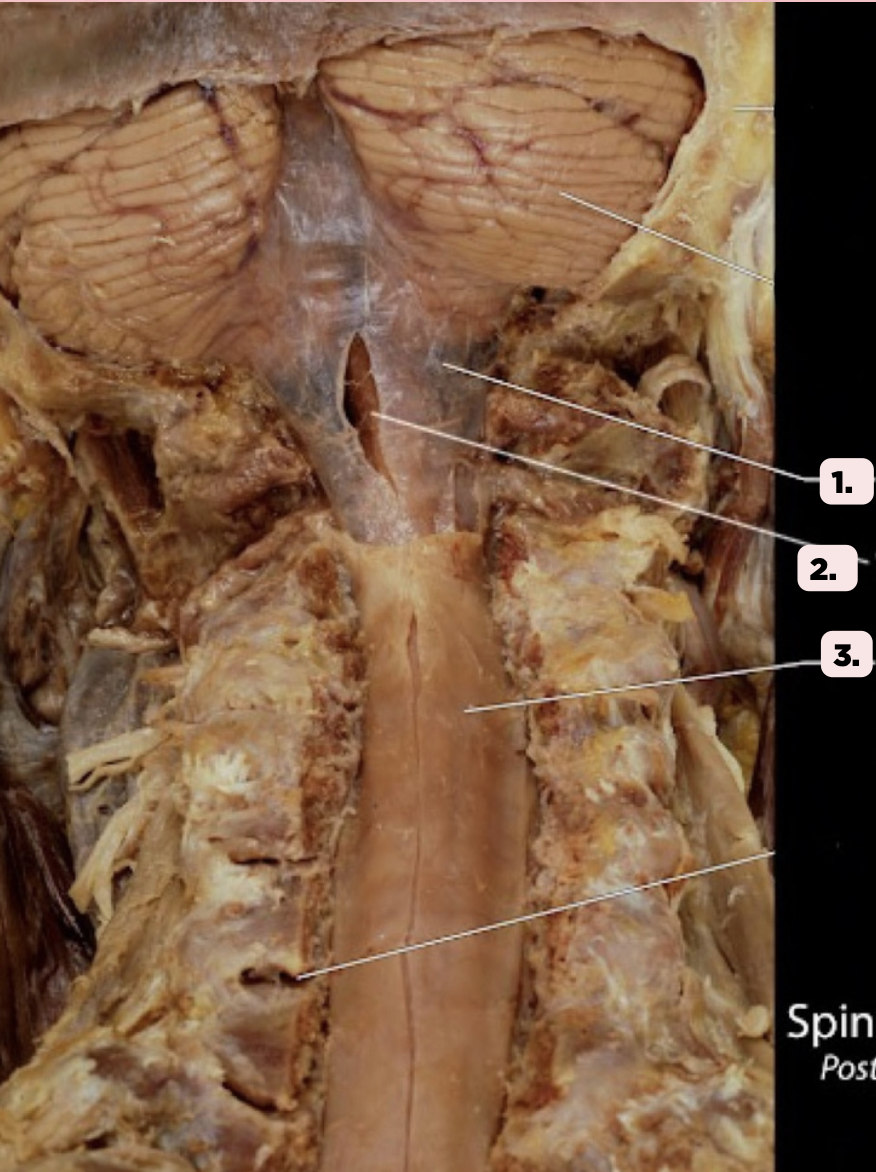
b. Filum Terminale
Pin #2 ends as a prolongation in the spinal cord attaching the conus medullaris to the back of the coccyx. This structure is known as the?
a. Spinal Cord
b. Filum Terminale
c. Lumbar Plexus
d. None of the above
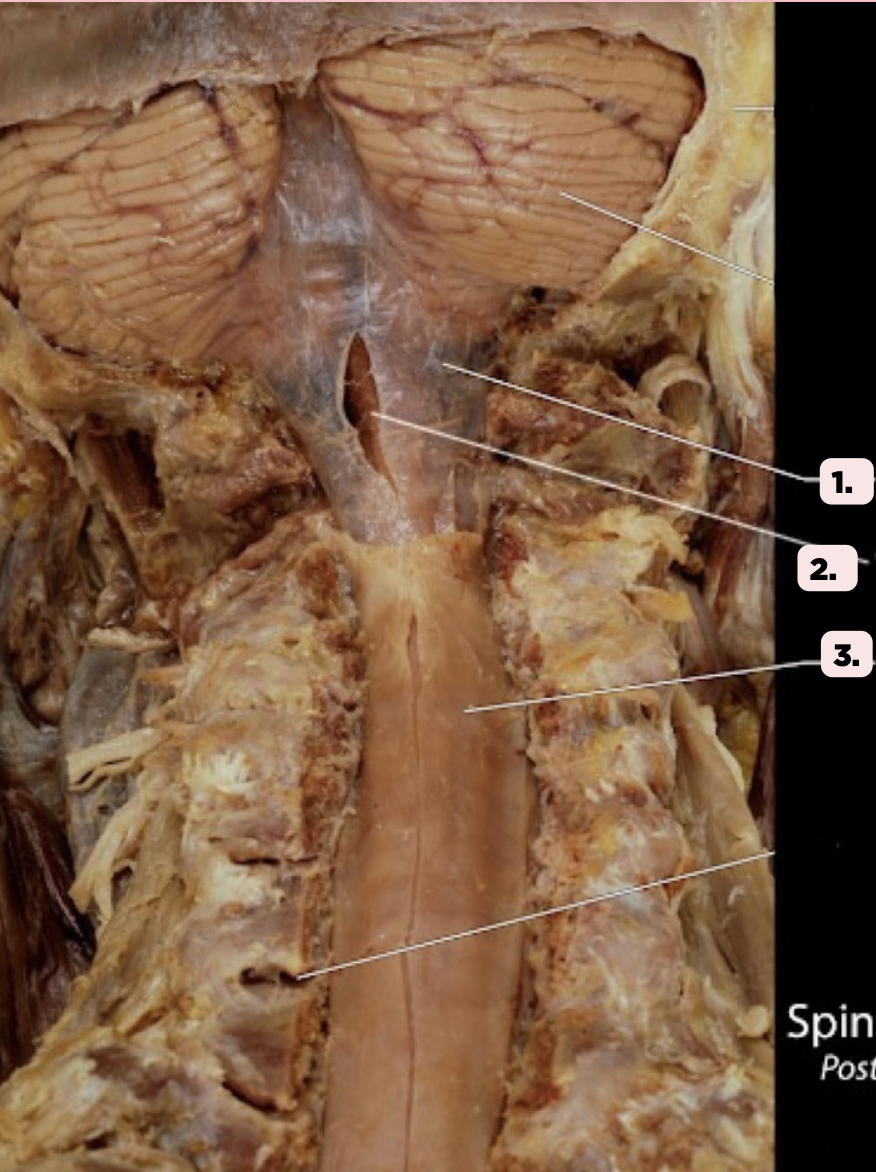
Arachnoid Mater
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
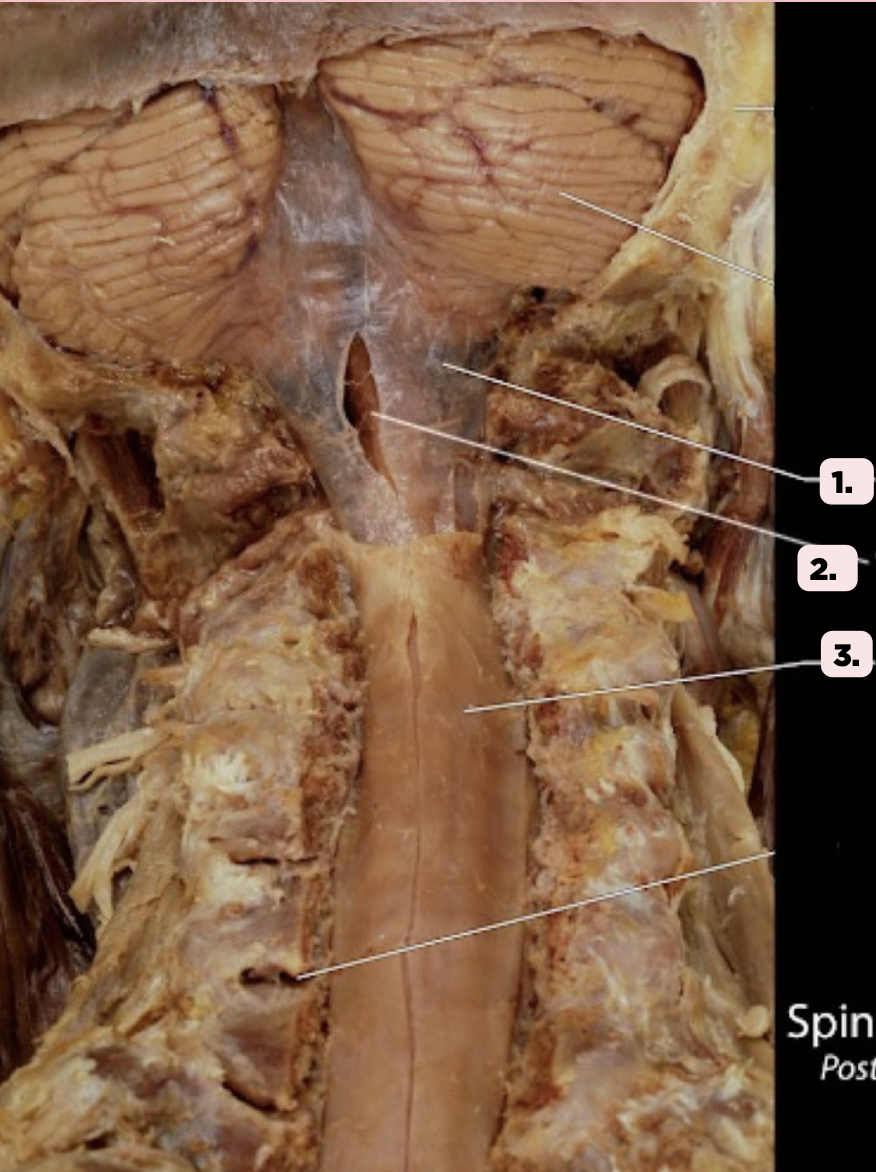
Pia Mater
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
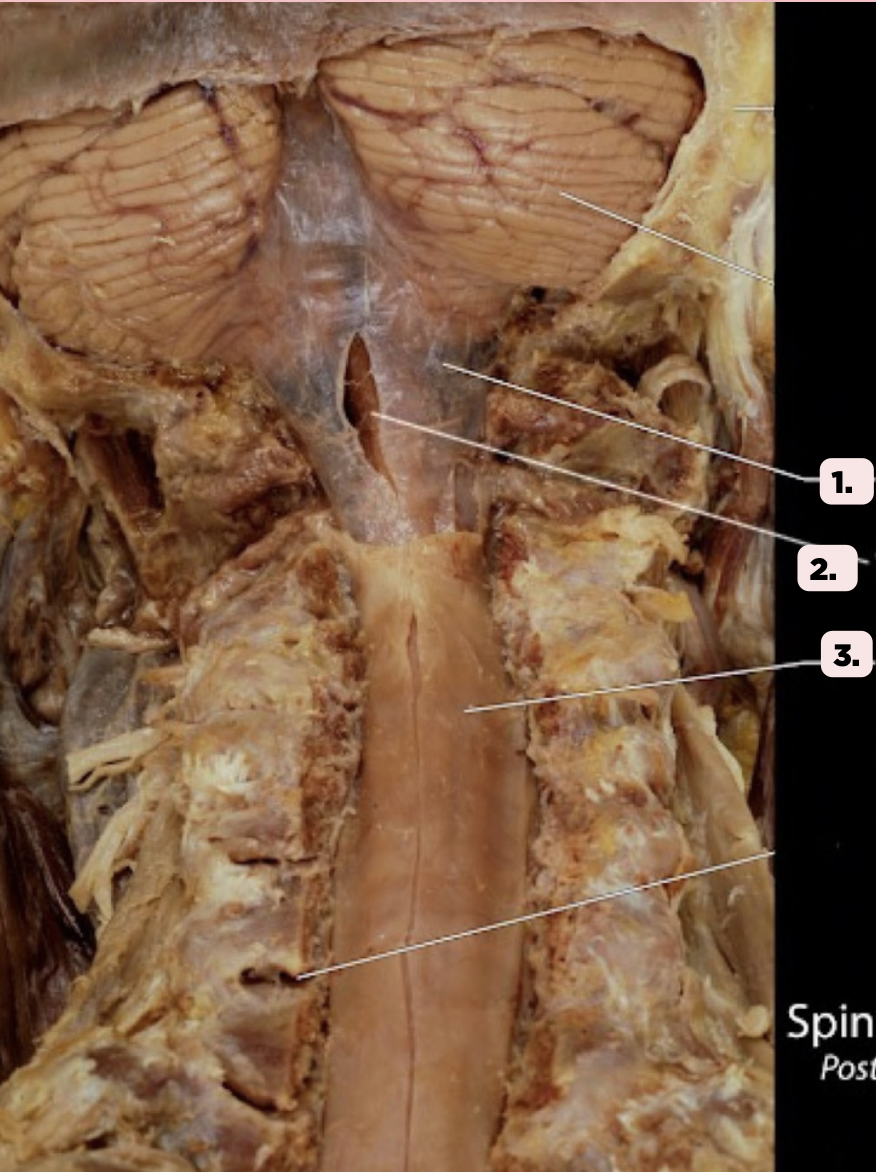
Spinal Dura
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
d. Internal Jugular Vein
Where does the straight sinus ultimately drain into after emptying into the left, right, and transverse sinus?
a. Great Cerebral Vein (of Galen)
b. Occipital Sinus
c. Cavernous Sinus
d. Internal Jugular Vein
b. Subdural hematoma
What type of intercranial injury is a result of the rupture of the bridging veins that connects superficial veins in the subarachnoid space with the venous sinuses?
a. Epidural hematoma
b. Subdural hematoma
c. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
d. Intracerebral hemorrhage
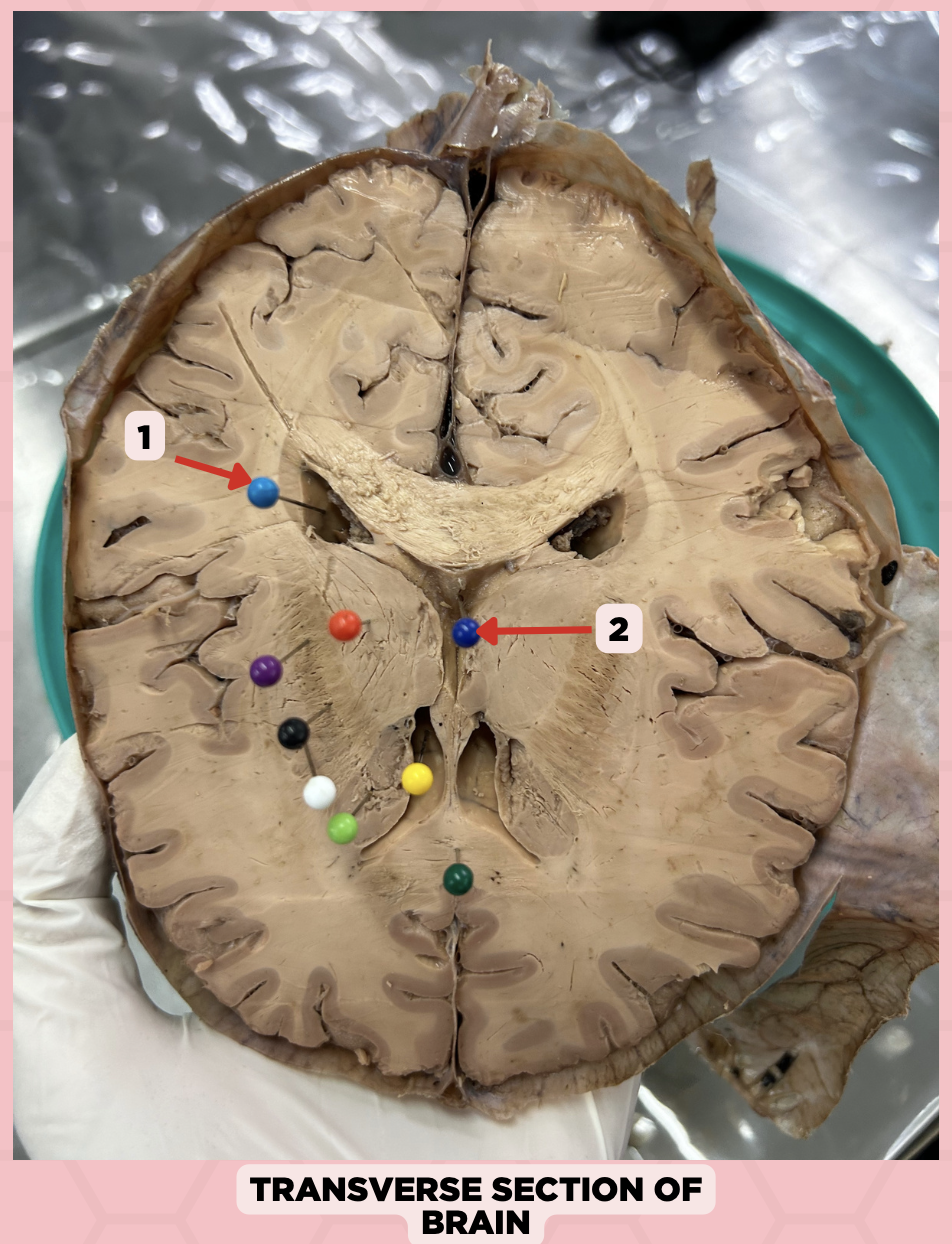
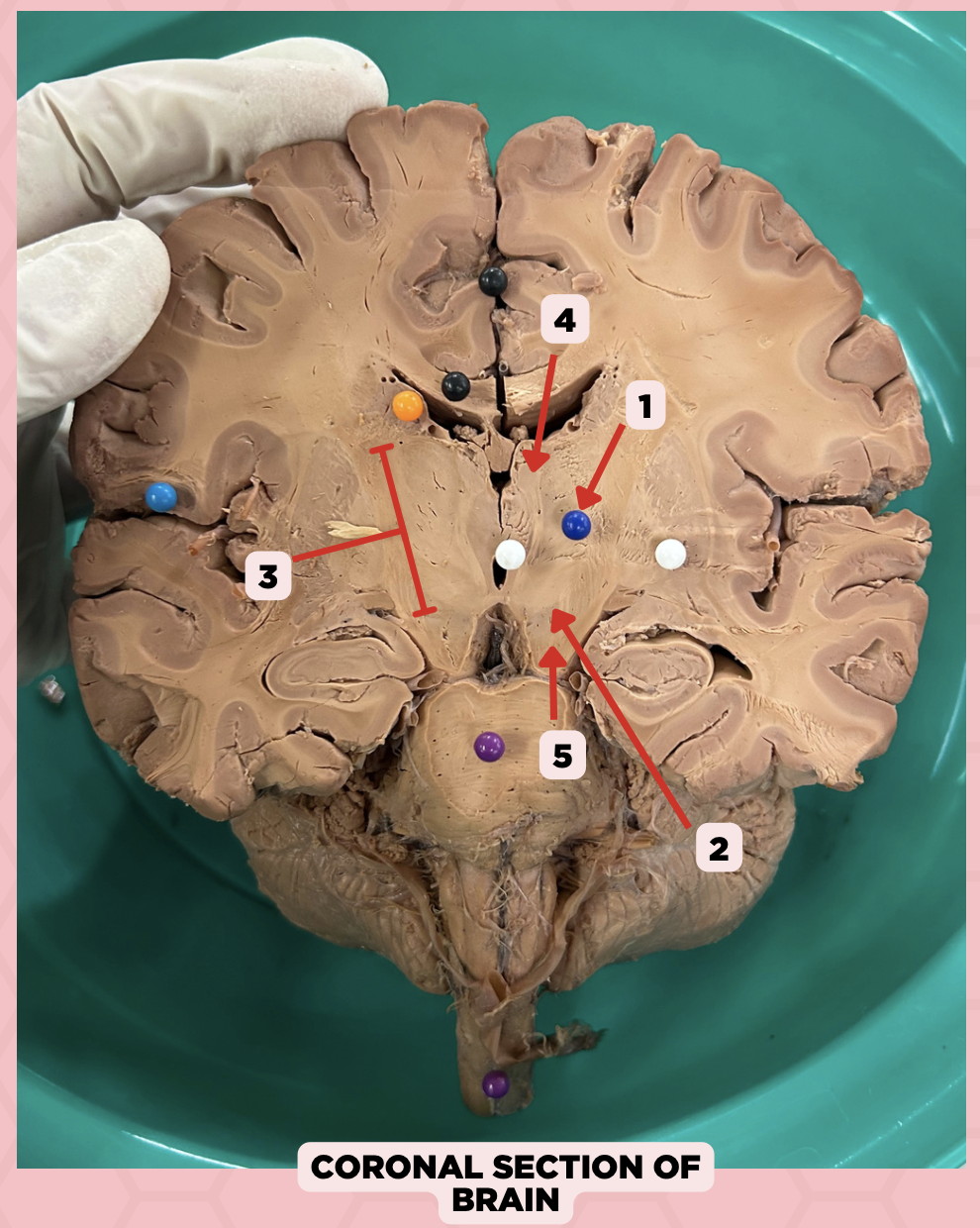
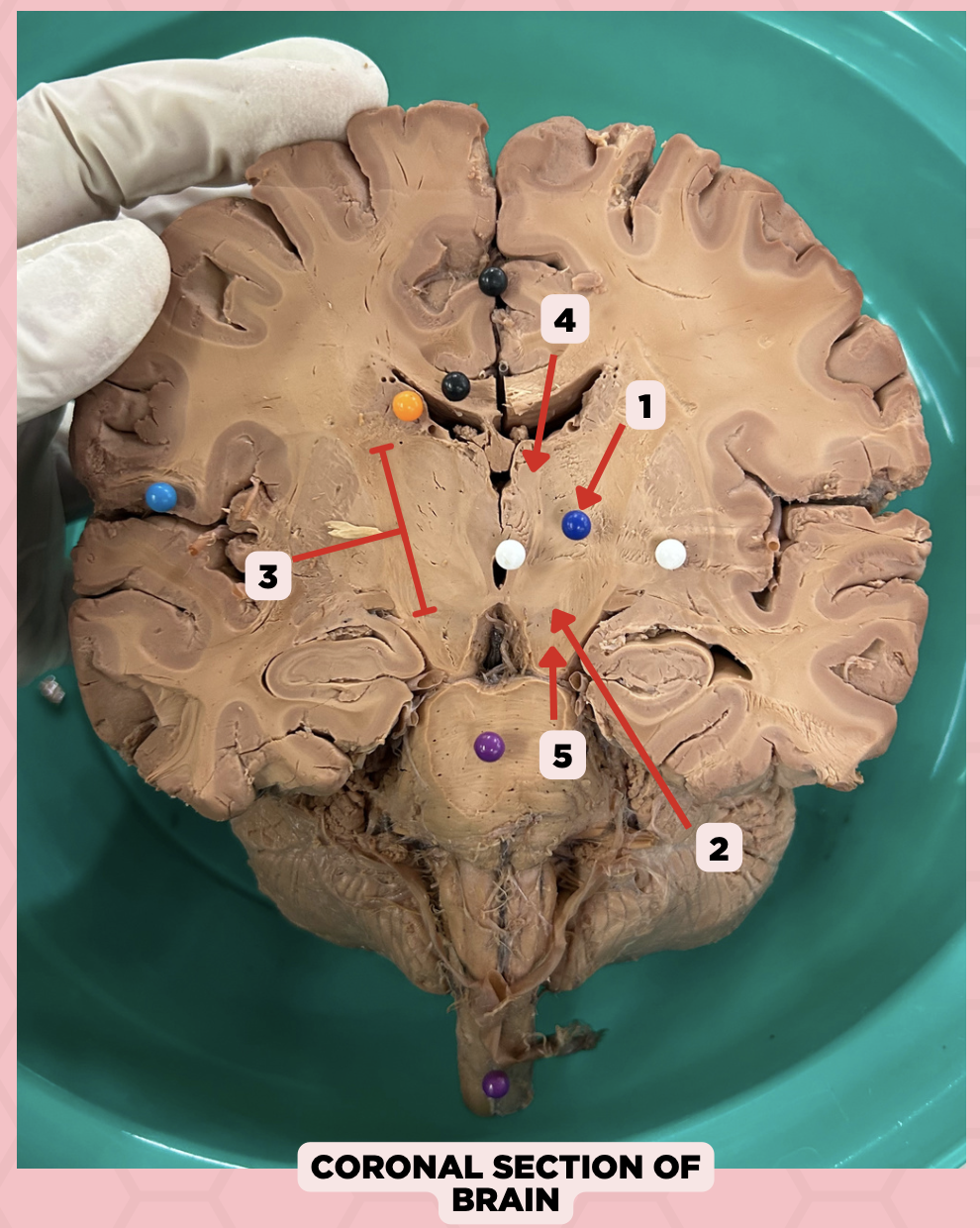
c. Foramen of Monro
What structure connects #1 and #2?
a. Cerebral aqueduct
b. Corpus callosum
c. Foramen of Monro
d. Fourth ventricle
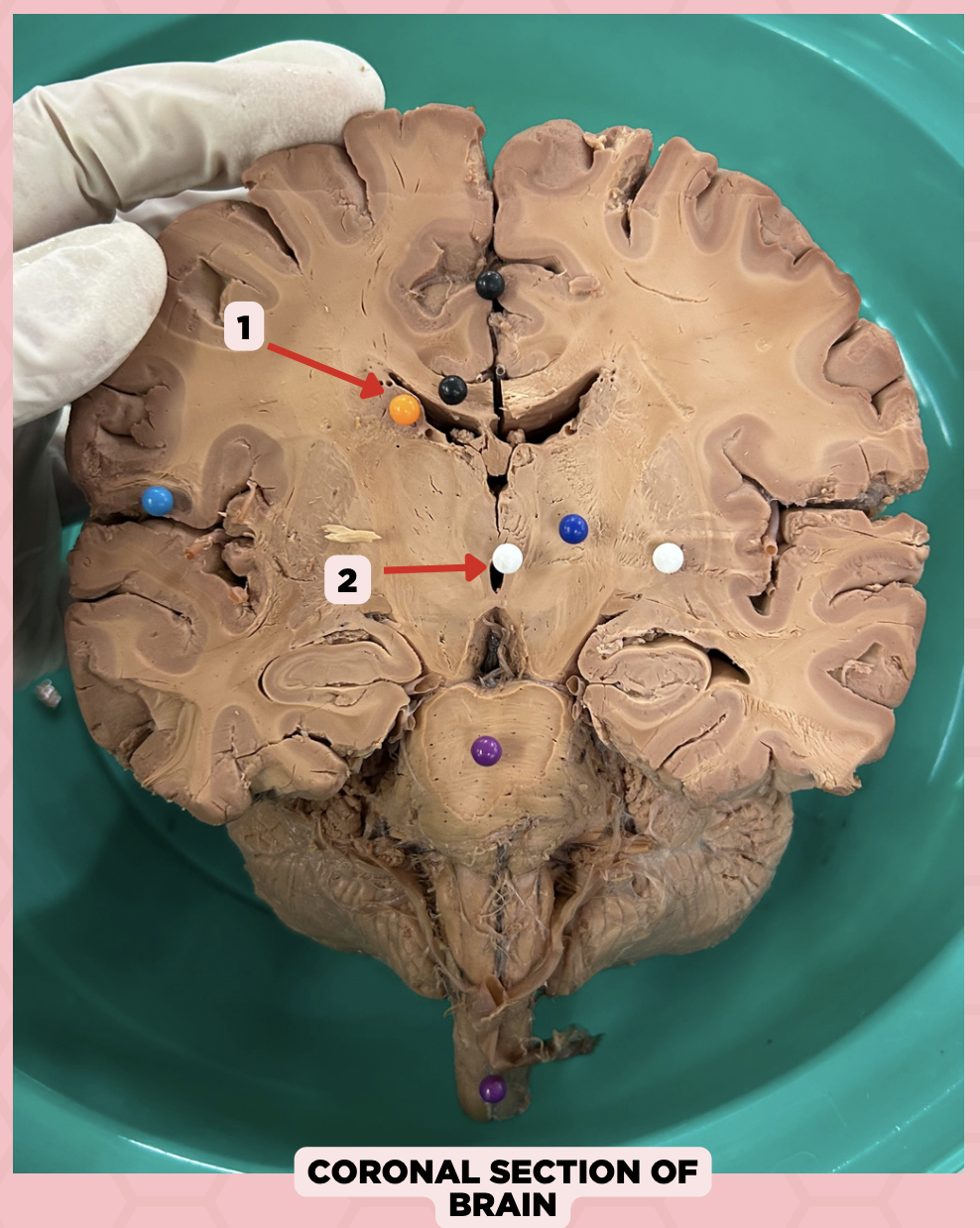
b. Between two thalami
Where is structure #2 located?
a. Midbrain
b. Between two thalami
c. Level of pons and cerebellum
d. Level of medulla and spinal cord
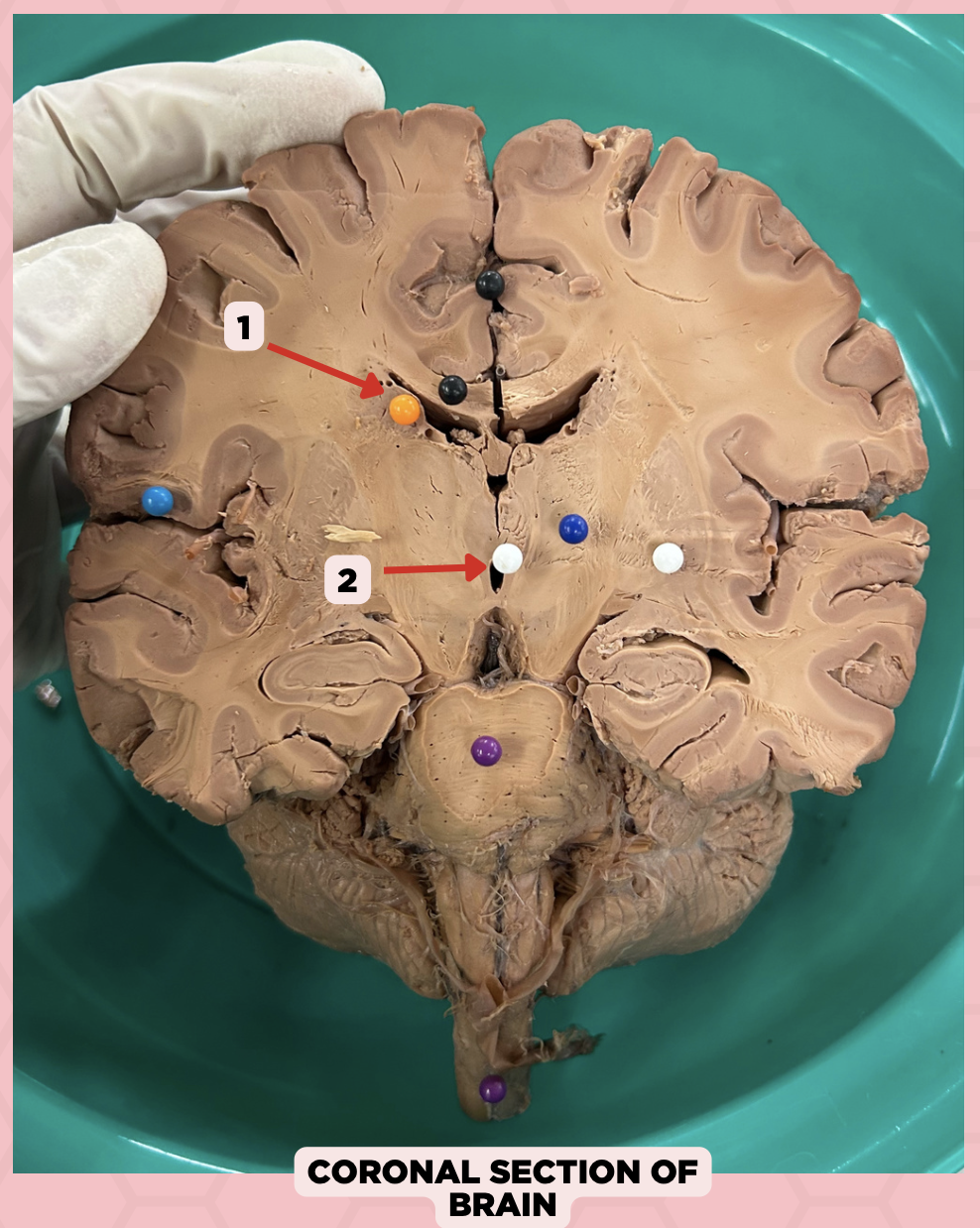
Lateral Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
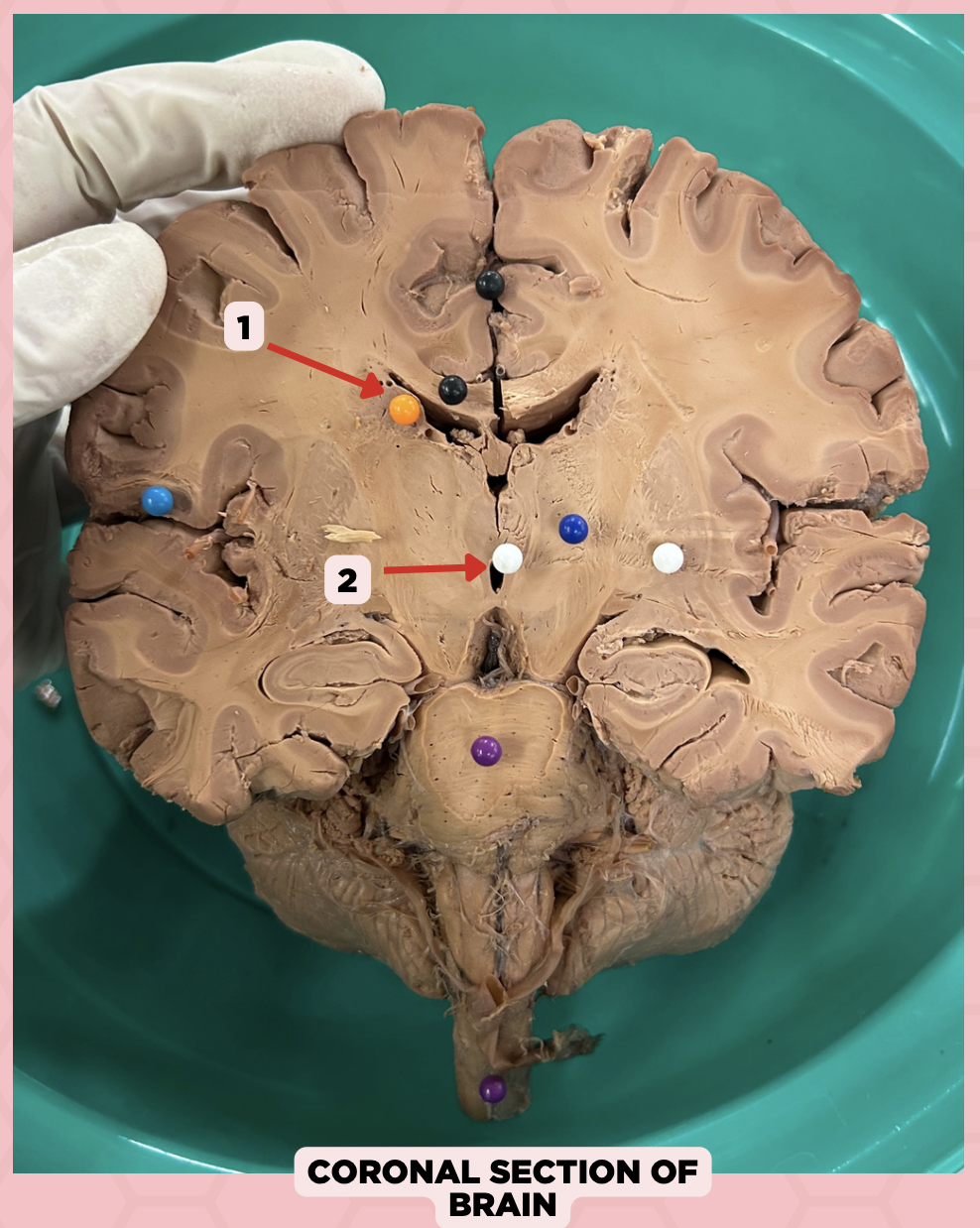
Third Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
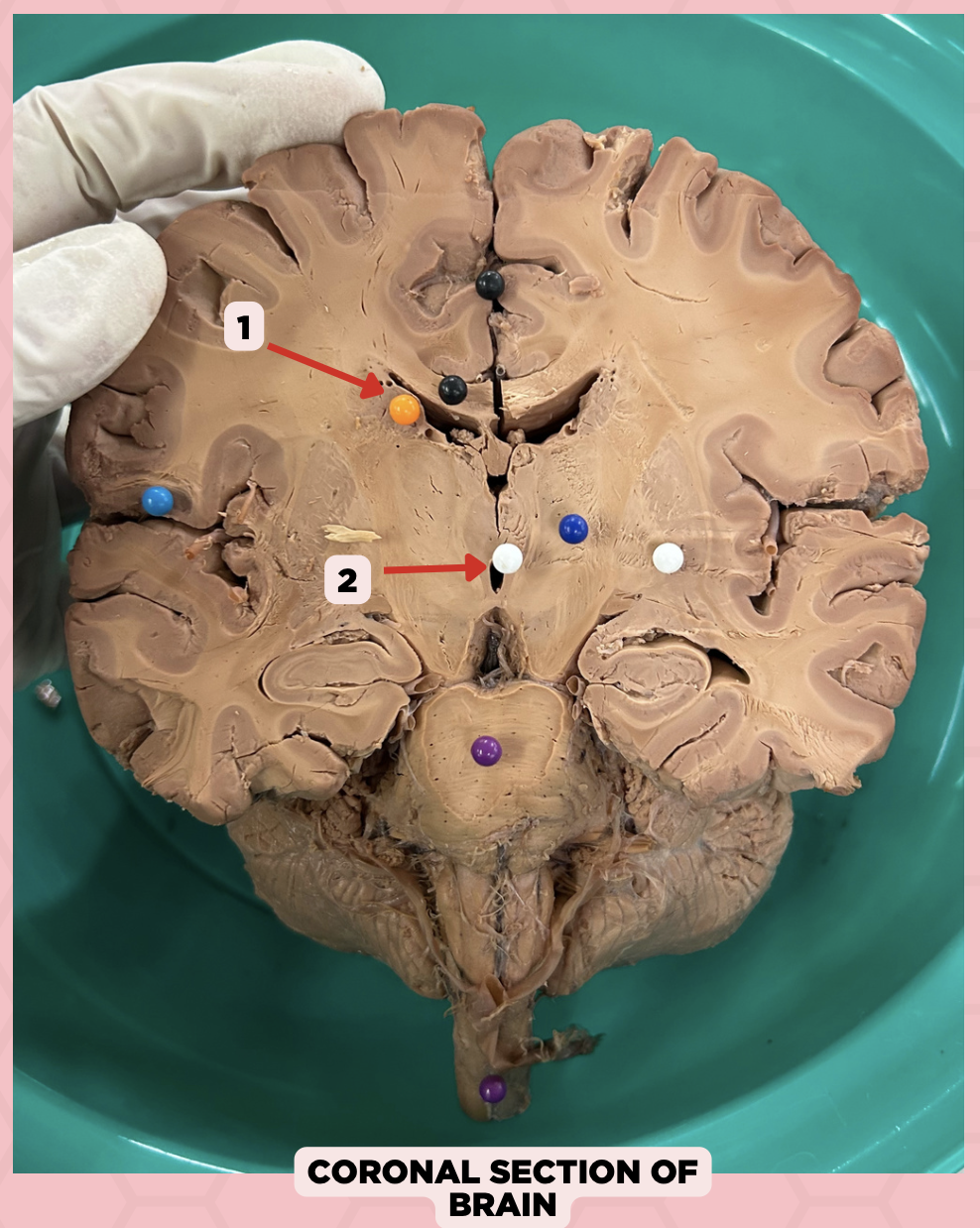
d. Cerebral Hemispheres
The pointed structure (Pin #1) is one of the ventricular systems of the brain found at the level of the?
a. Midbrain
b. Pons
c. Medulla
d. Cerebral Hemispheres
c. 4th Ventricle
The pointed structure (Pin #2) is connected via the Cerebral Aqueduct of Sylvius to which of the following ventricular system?
a. Lateral Ventricles
b. 3rd Ventricle
c. 4th Ventricle
d. Central Canal
Lateral Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
Third Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
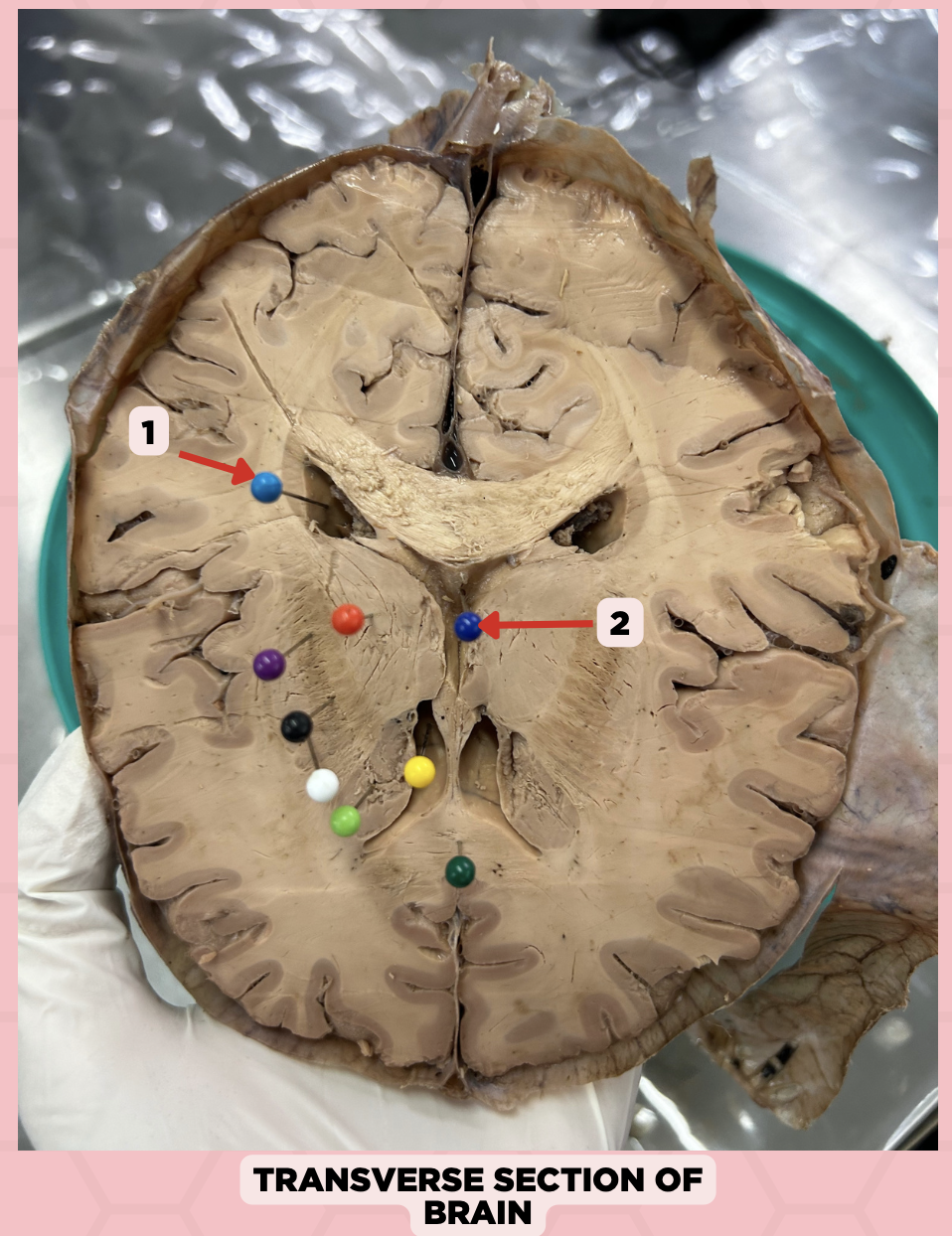
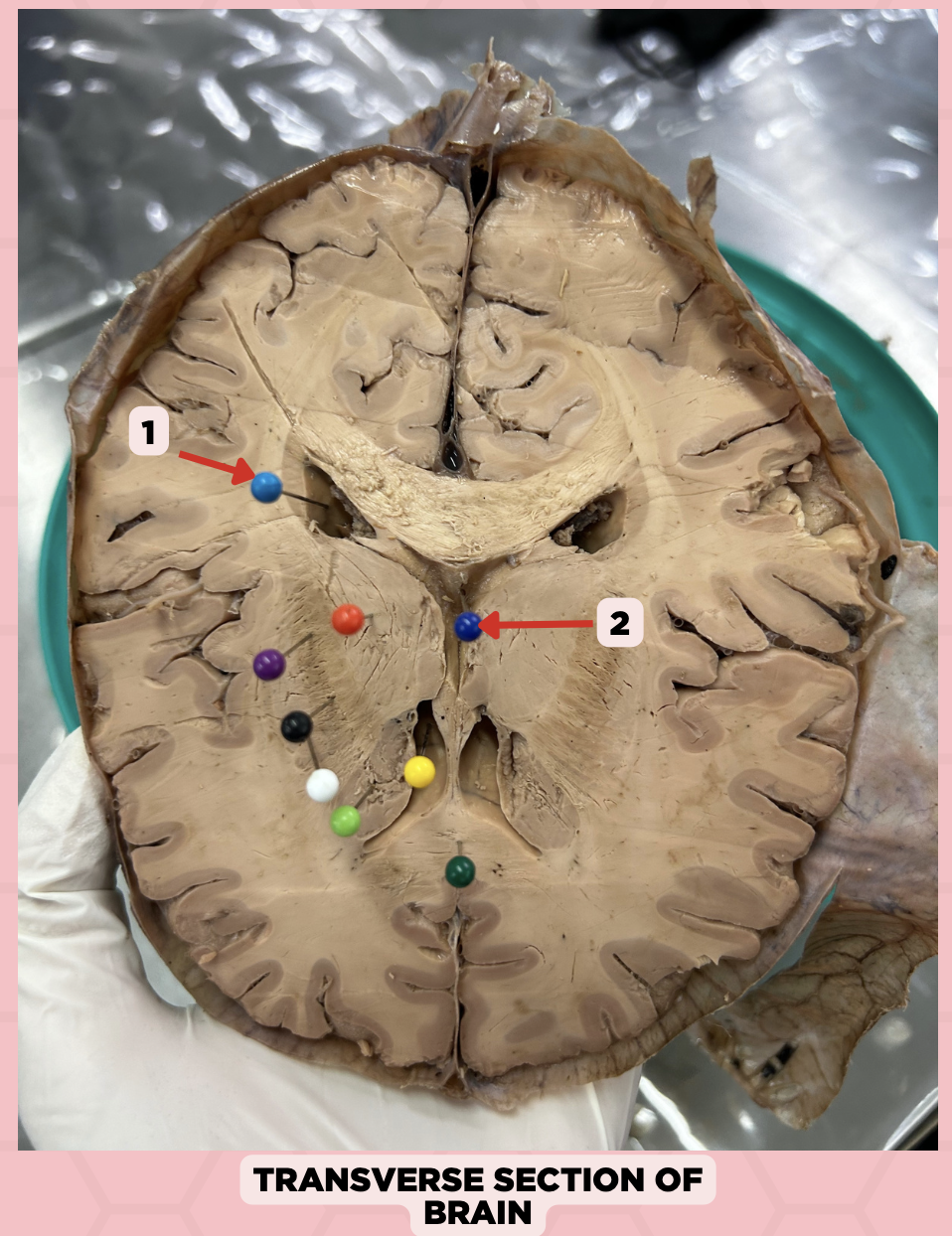
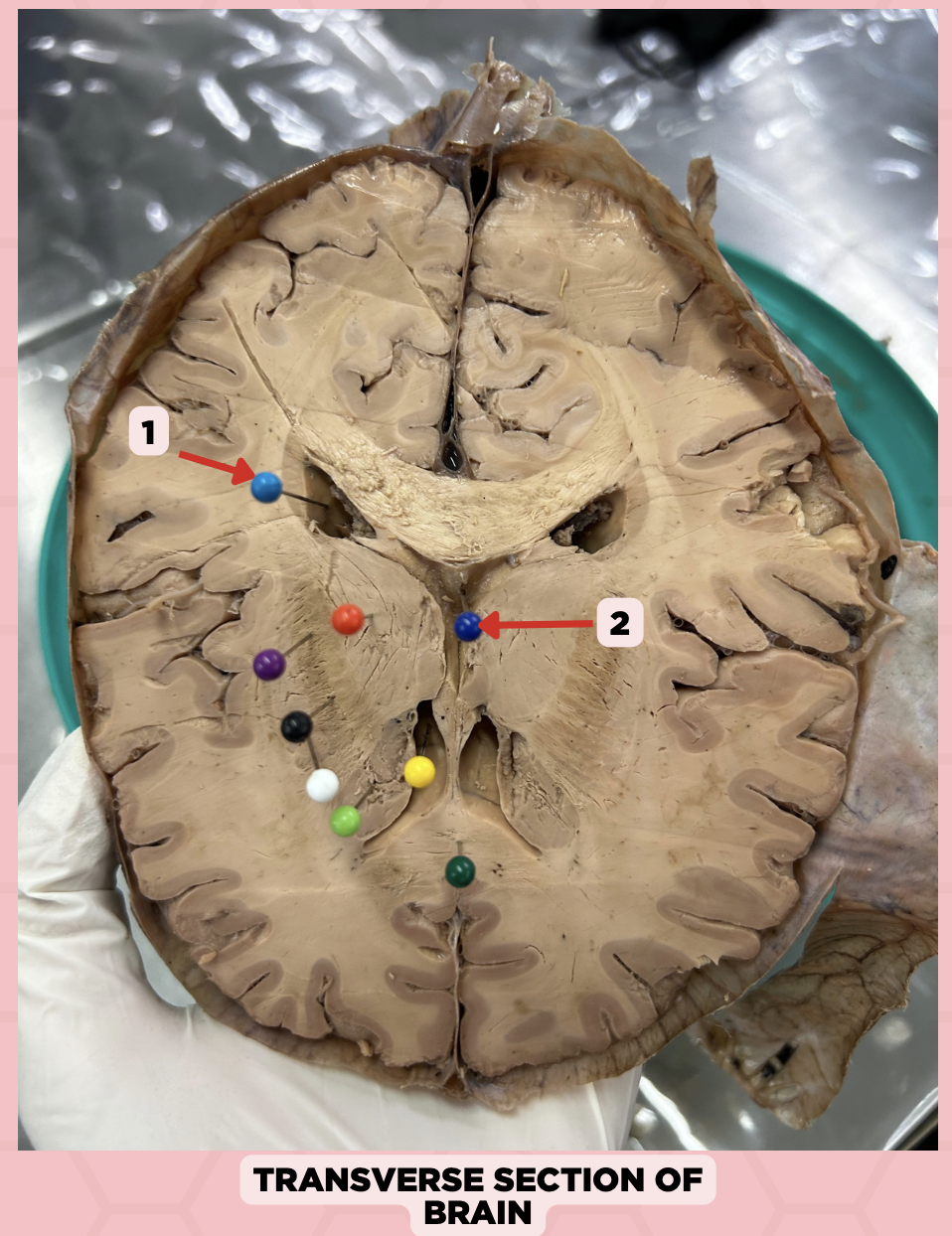
b. Midbrain
The structure separating Pin #2 from Pin #3 can be found at the level of the:
a. Cerebrum
b. Midbrain
c. Pons
d. Medulla
b. Non-communicating Hydrocephalus
Upon receiving the imaging result of a patient with hydrocephalus, you found that there is an obstruction between Pin #2 and Pin #3. This is diagnosed as?
a. Communicating Hydrocephalus
b. Non-communicating Hydrocephalus
c. Both
d. Cannot be determined
Lateral Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
Fourth Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
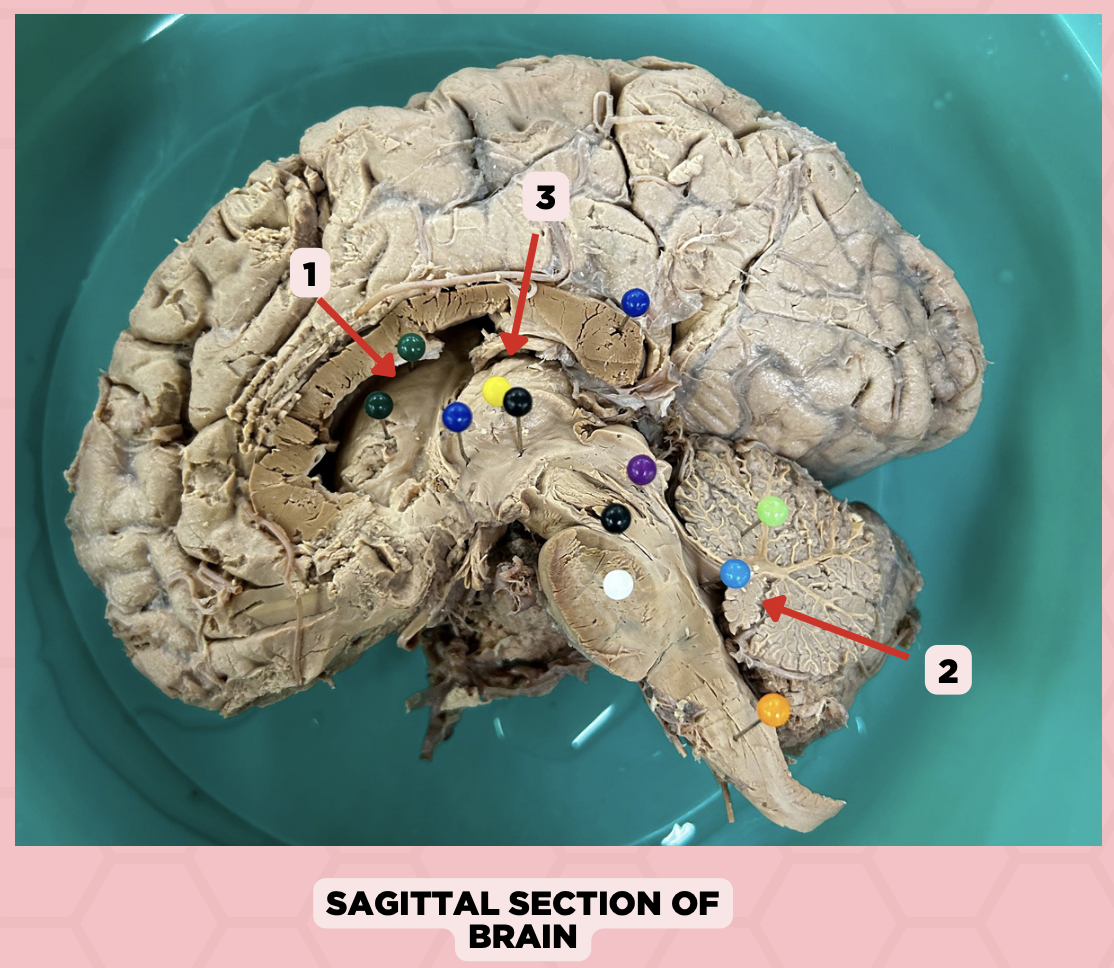
Third Ventricle
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
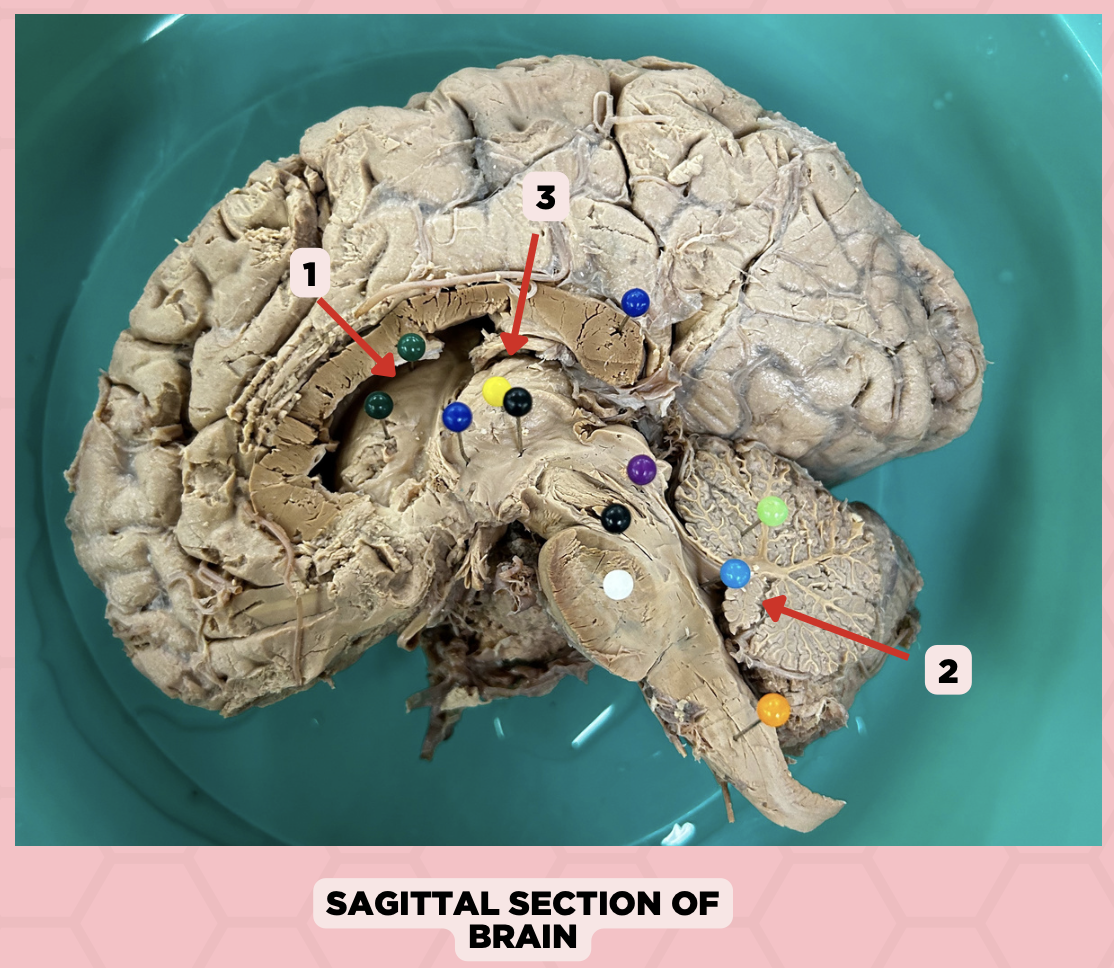
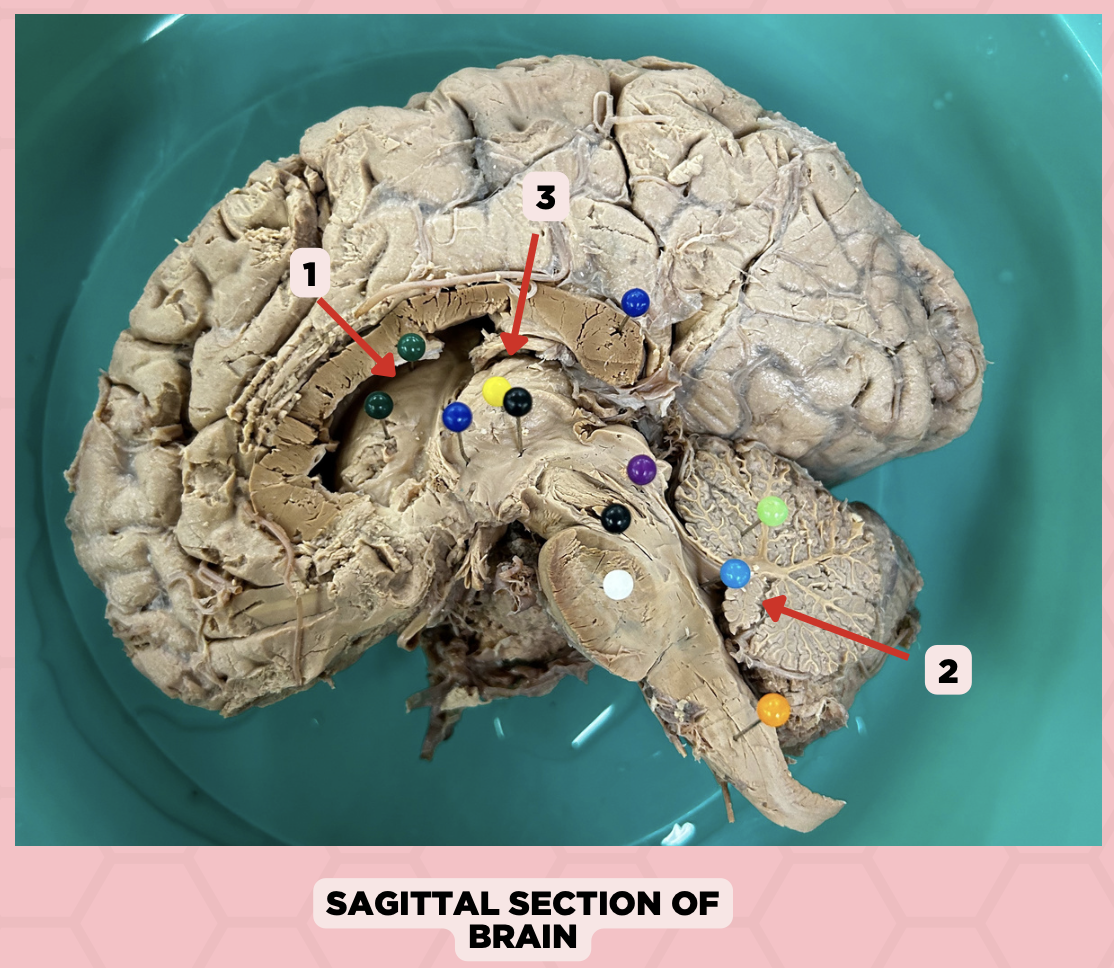
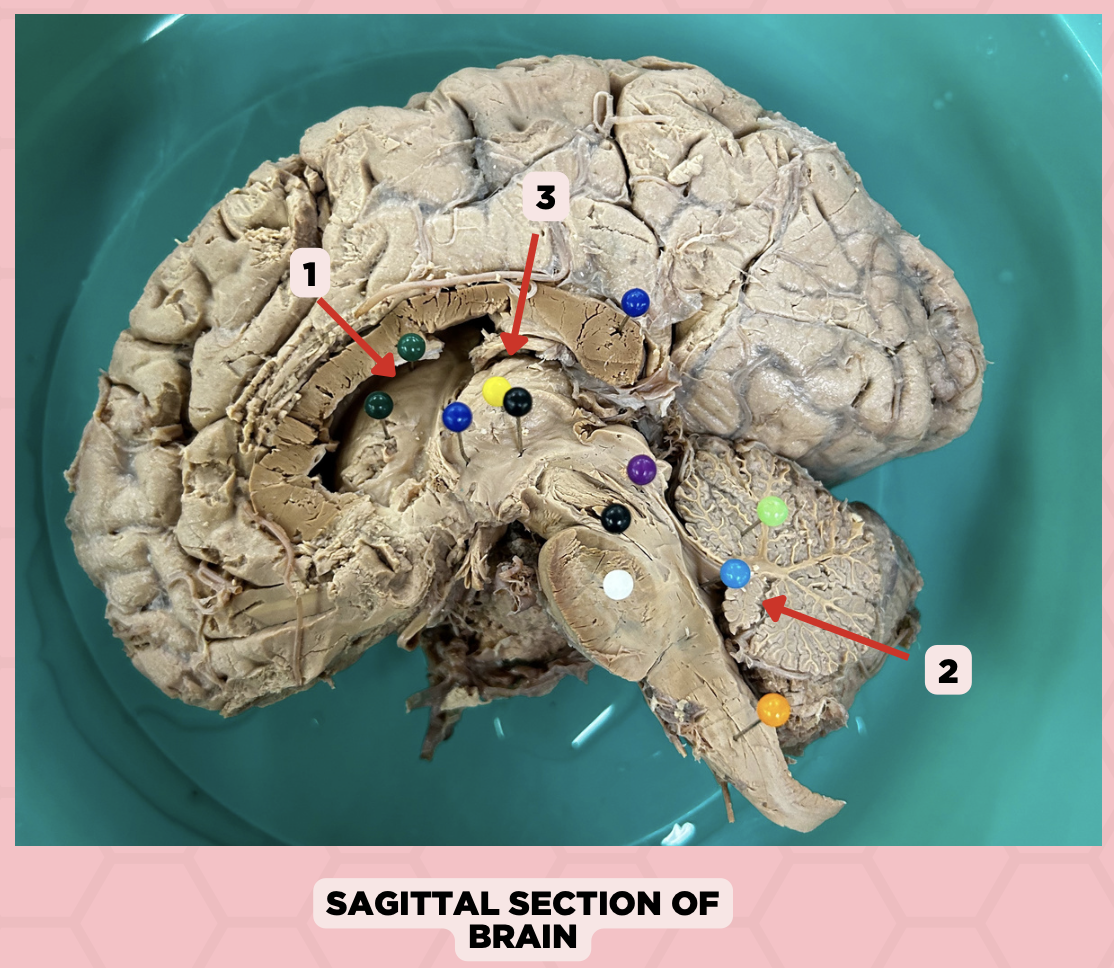
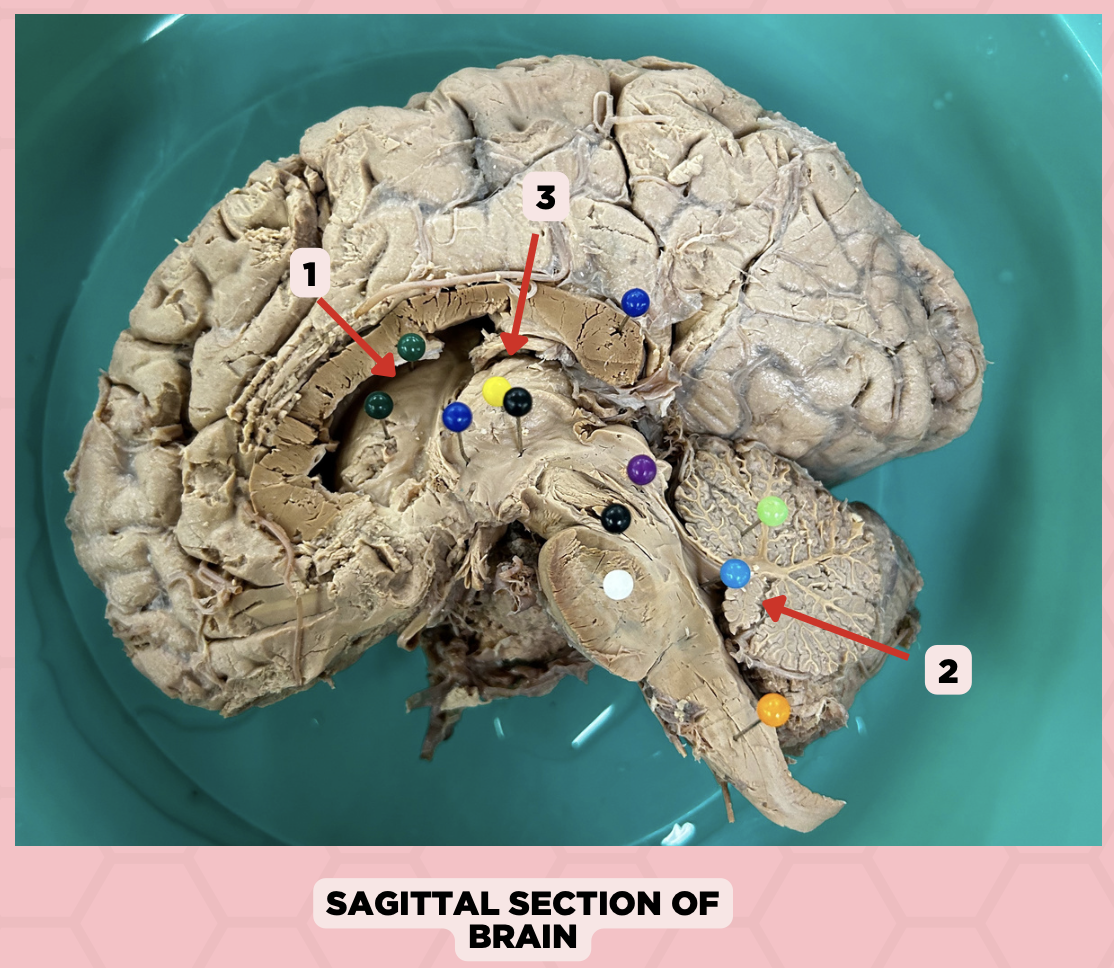
a. Weakness of the arm, trunk, or leg
Damage or lesion on the posterior limb of #3 manifests as:
a. Weakness of the arm, trunk, or leg
b. Loss of vision
c. Facial weakness
d. Loss of hearing
c. Pineal gland
What important structure is found in structure #4?
a. Pituitary gland
b. Amygdala
c. Pineal gland
d. Hippocampus
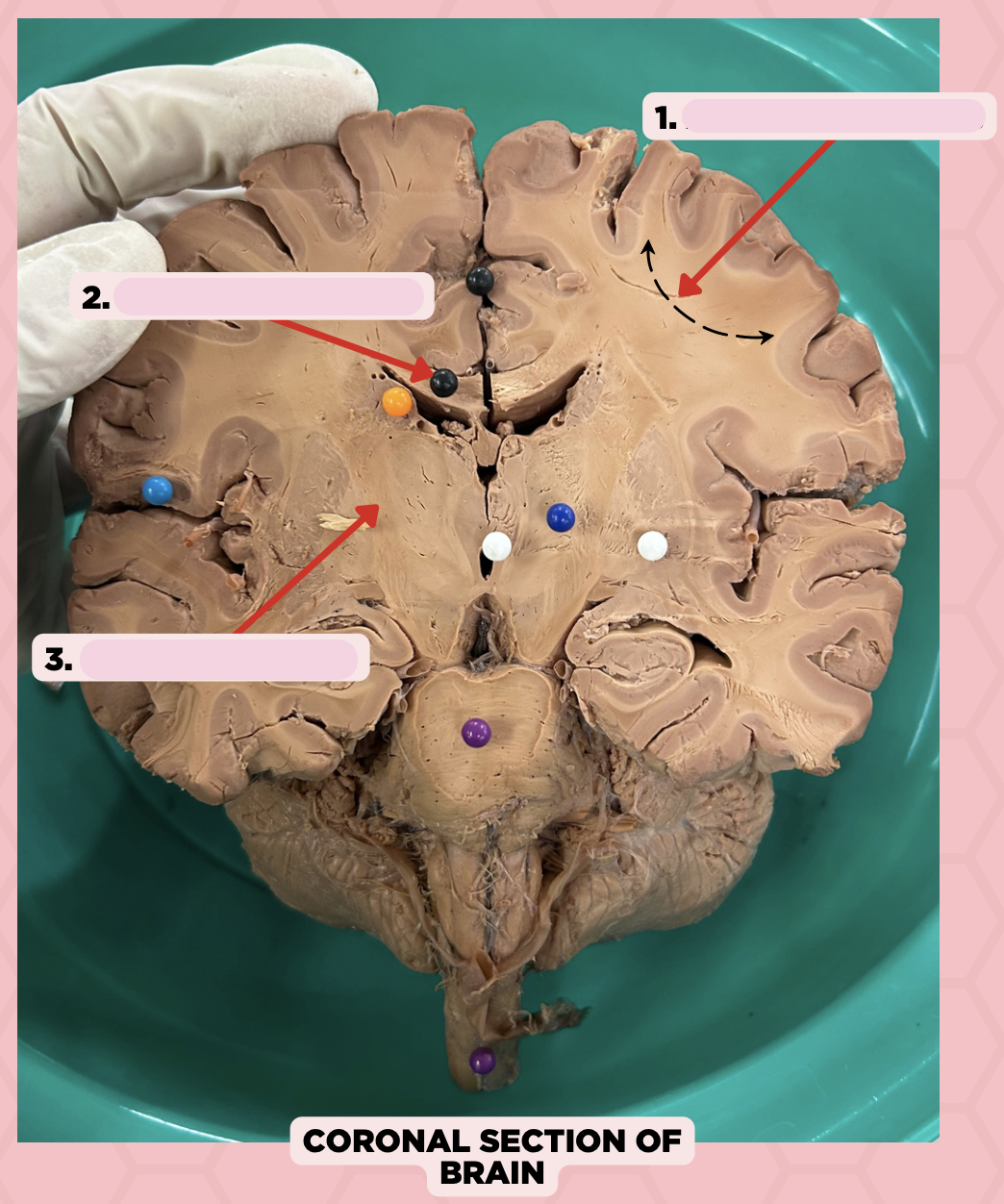
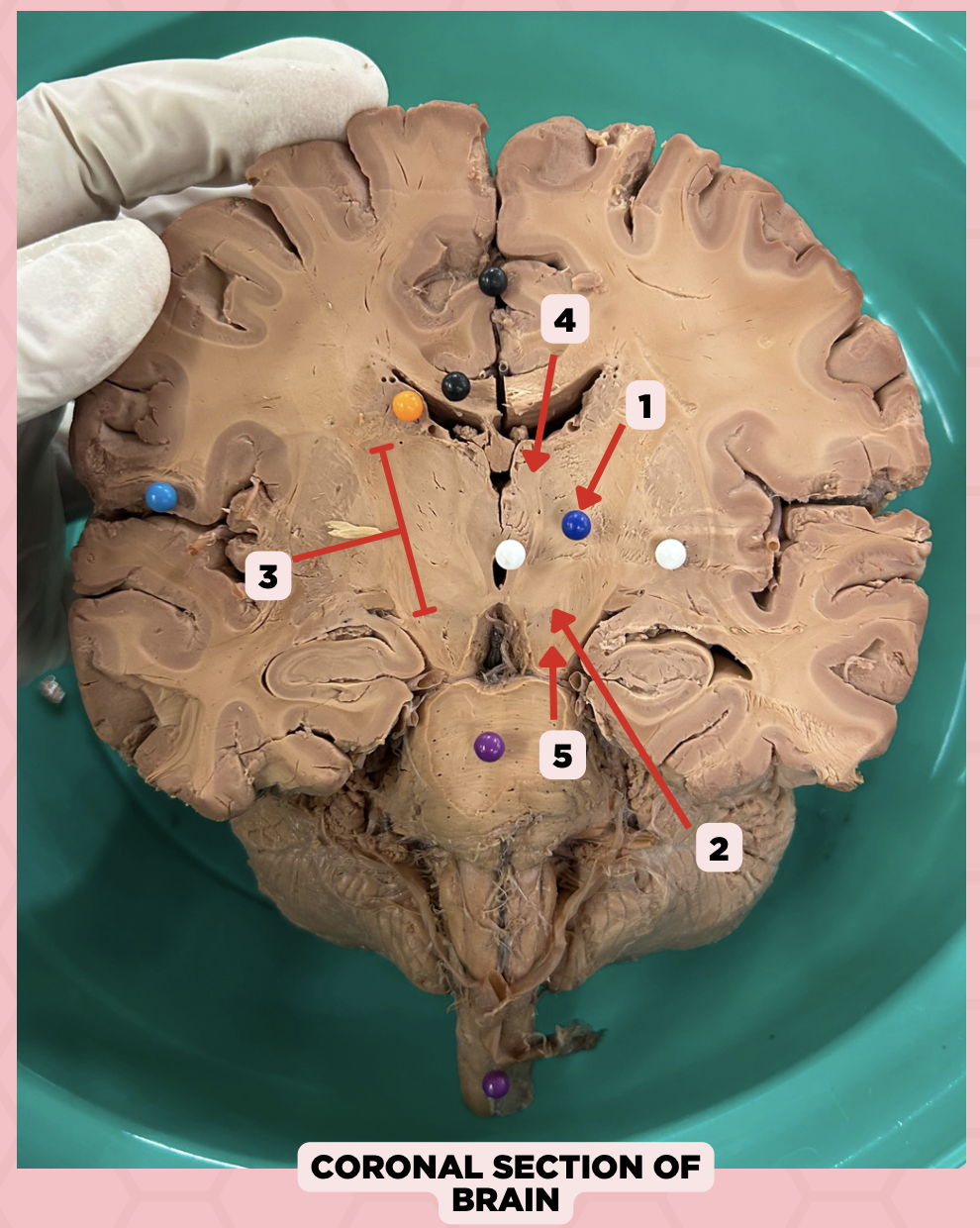
Thalamus
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
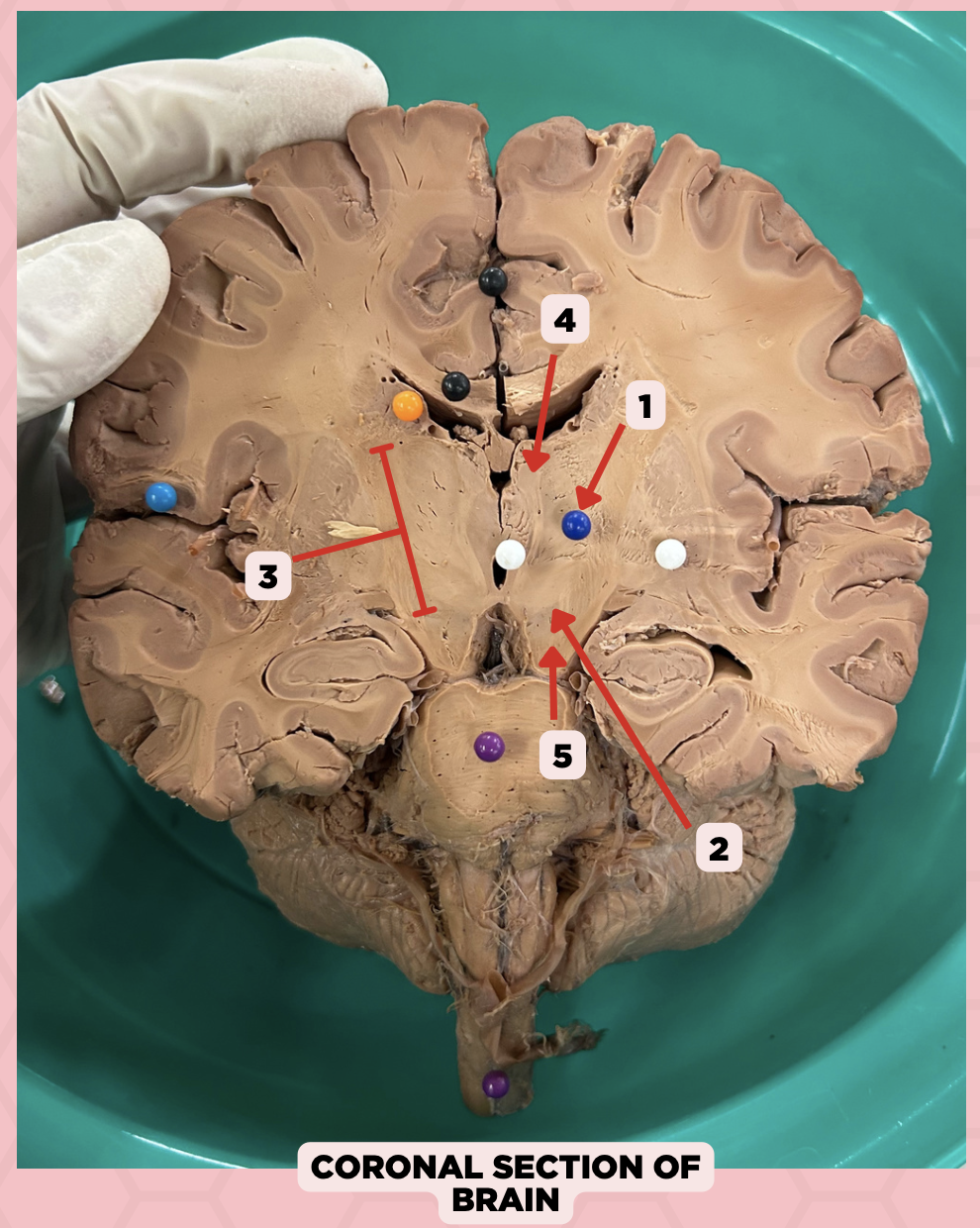
Subthalamus
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
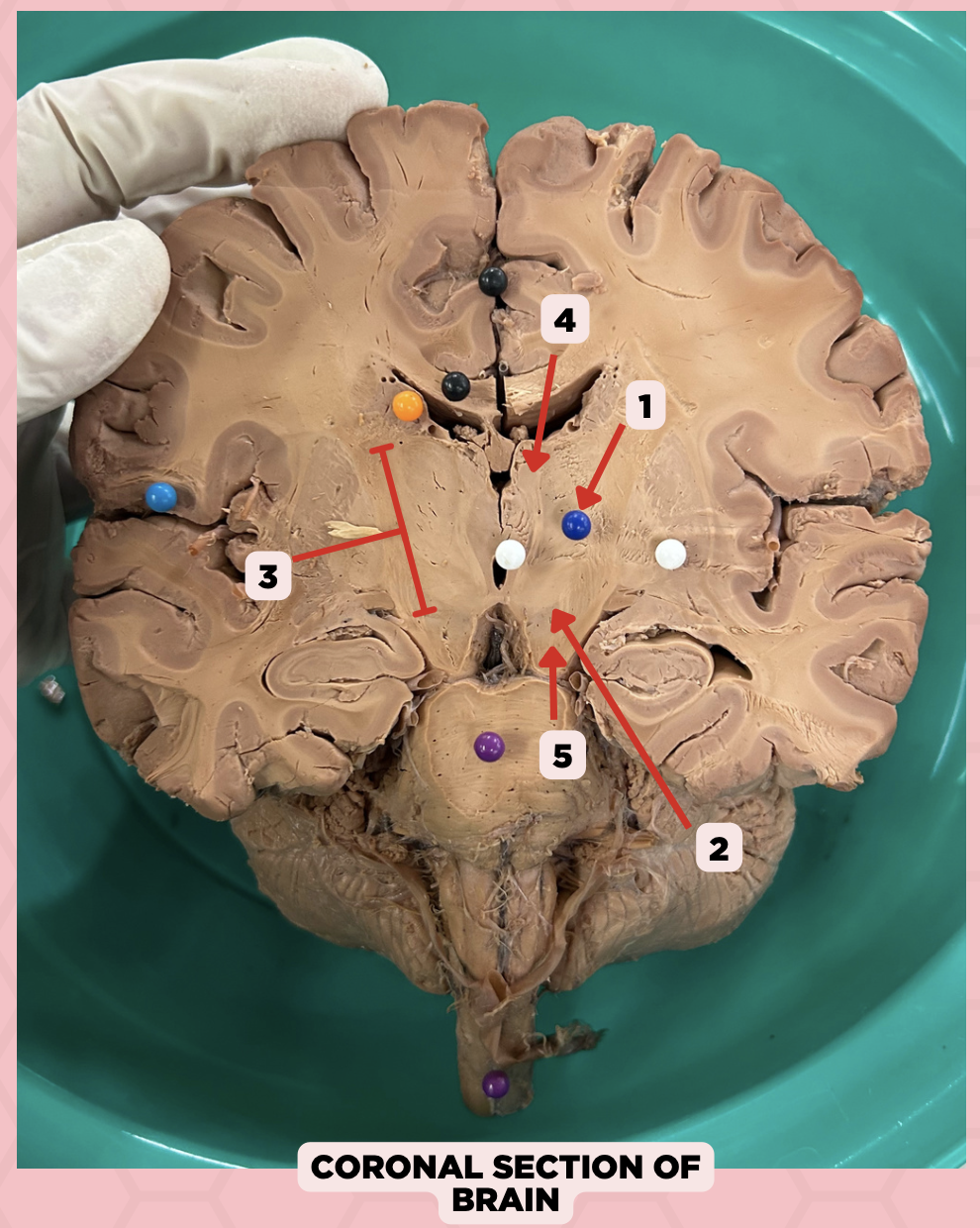
Internal Capsule
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
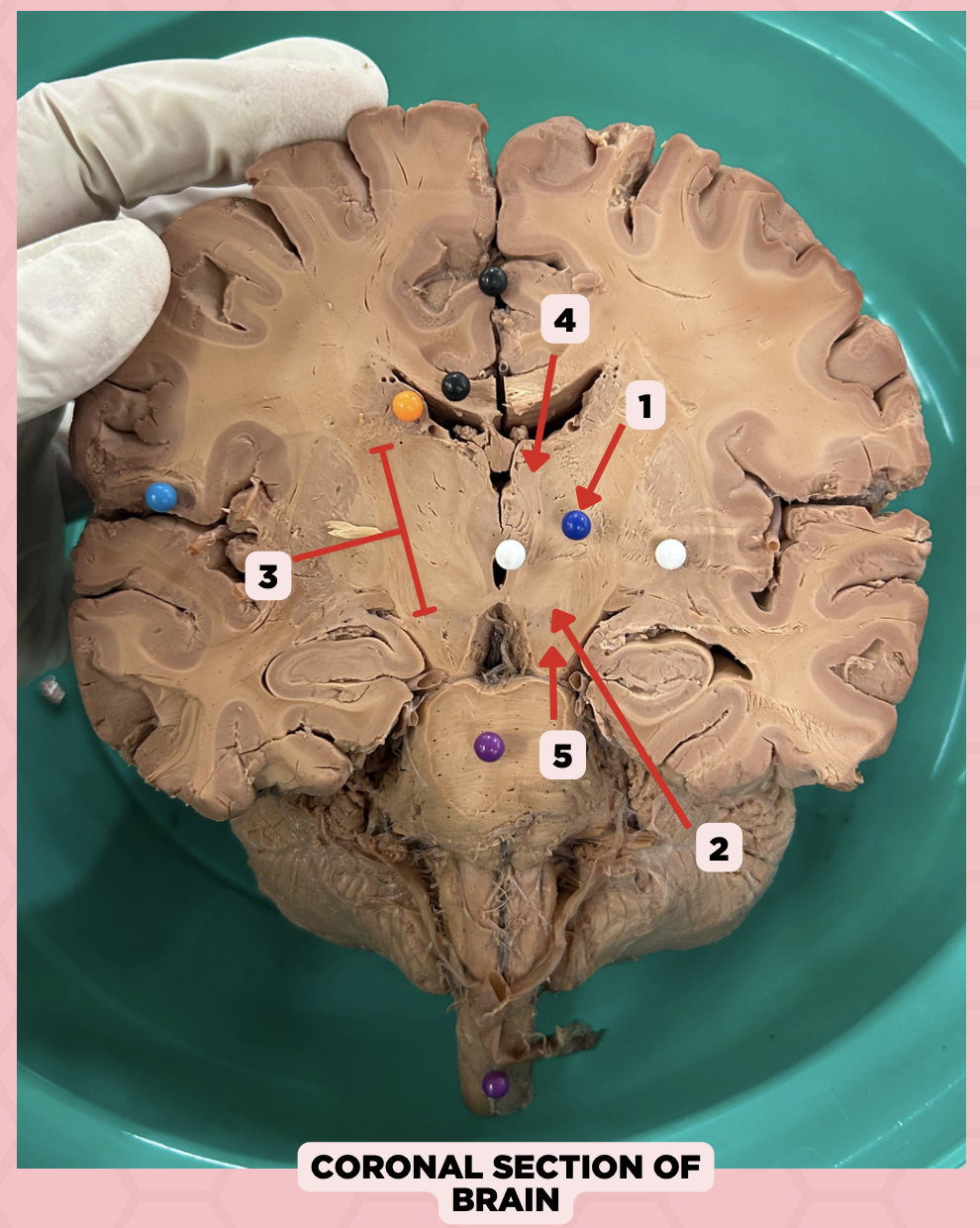
Epithalamus
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
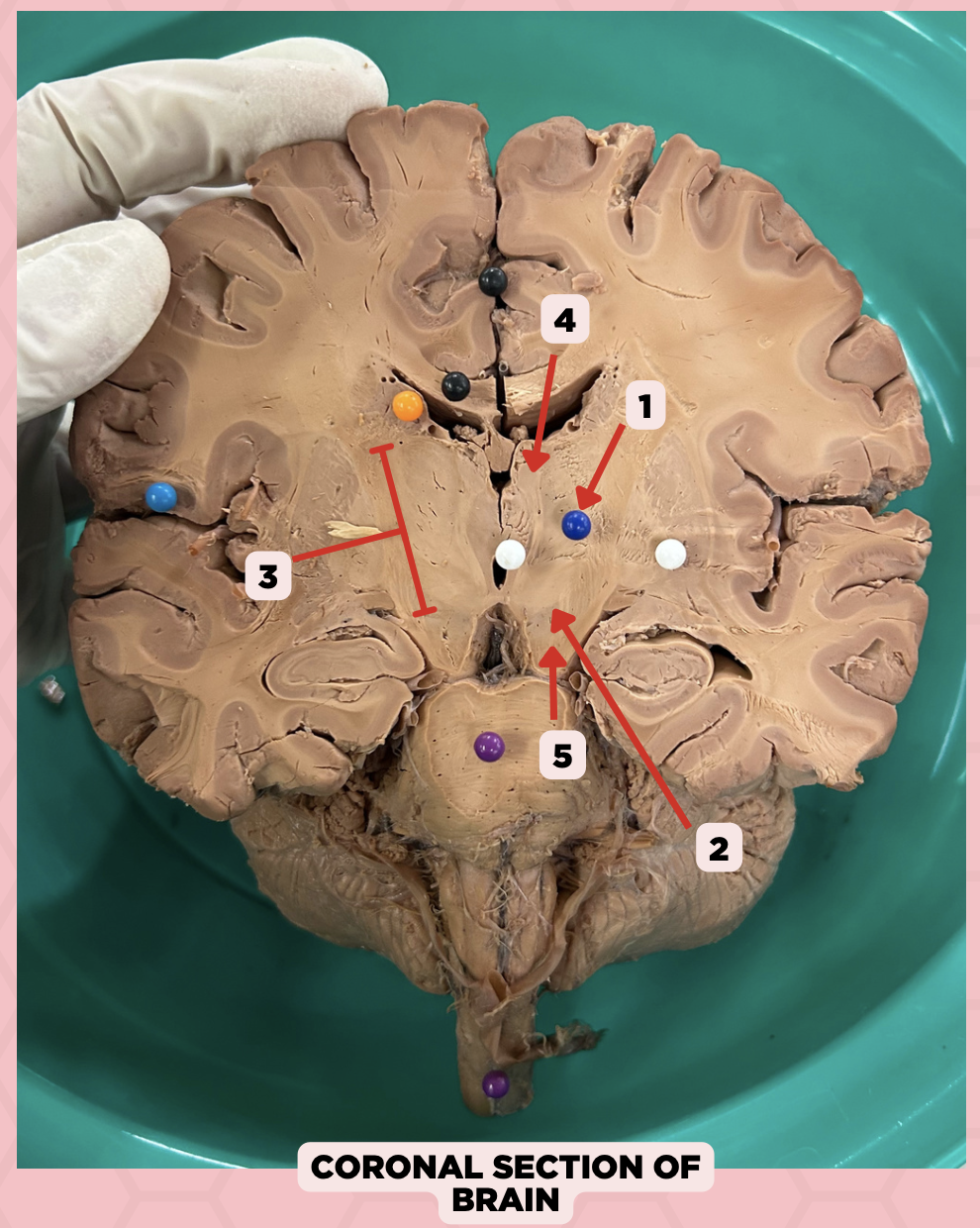
Hypothalamus
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
Dominant hemisphere
The speech area is in found in what hemisphere?
Broca’s Area
Area that allows to understand (speech comprehension)
Wernicke’s Area
Area that allows to speak (speech expression or fluency)
Arcuate Fasciculus
Another anatomical structure related to speech. These are association fibers connecting the two speech areas. A normal arcuate fasciculus gives a person the ability to repeat a language (speech repetition)
Aphasia
A communication disorder that affects a person’s ability to speak, understand language, read, and write
Broca’s Aphasia
Patient has comprehension but no fluency nor repetition
Broca’s Aphasia
Patient has comprehension but no fluency nor repetition
Conduction Aphasia
Patient has comprehension and fluency but cannot repeat
Global Aphasia
Patient has no comprehension, fluency, and repetition. Only stares.
Dysarhthia
Nervous system damage causes the muscles that produce speech to become paralyzed or weakened.