Cytology and Histology: Key Concepts and Diagnostic Criteria in Gynecological Cytopathology
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is cytology and its main advantage?
The study of individual cells without tissue architecture. Main Advantage: Minimally invasive, cheaper, and faster than histology.
What is the main limitation of cytology compared to histology?
It Cannot confirm invasion; only histology can definitively verify 'Invasive Cancer.' Since cells are detached, it is not possible to ascertain whether the basement membrane has been breached; only histological examination can confirm "Invasive Cancer."
What is the N:C ratio?
The ratio of Nuclear size to cytoplasmic size; an increased N: C ratio is the hallmark of malignancy or high-grade dysplasia. (the "blue" nucleus grows while the "pink/green" cytoplasm shrinks).
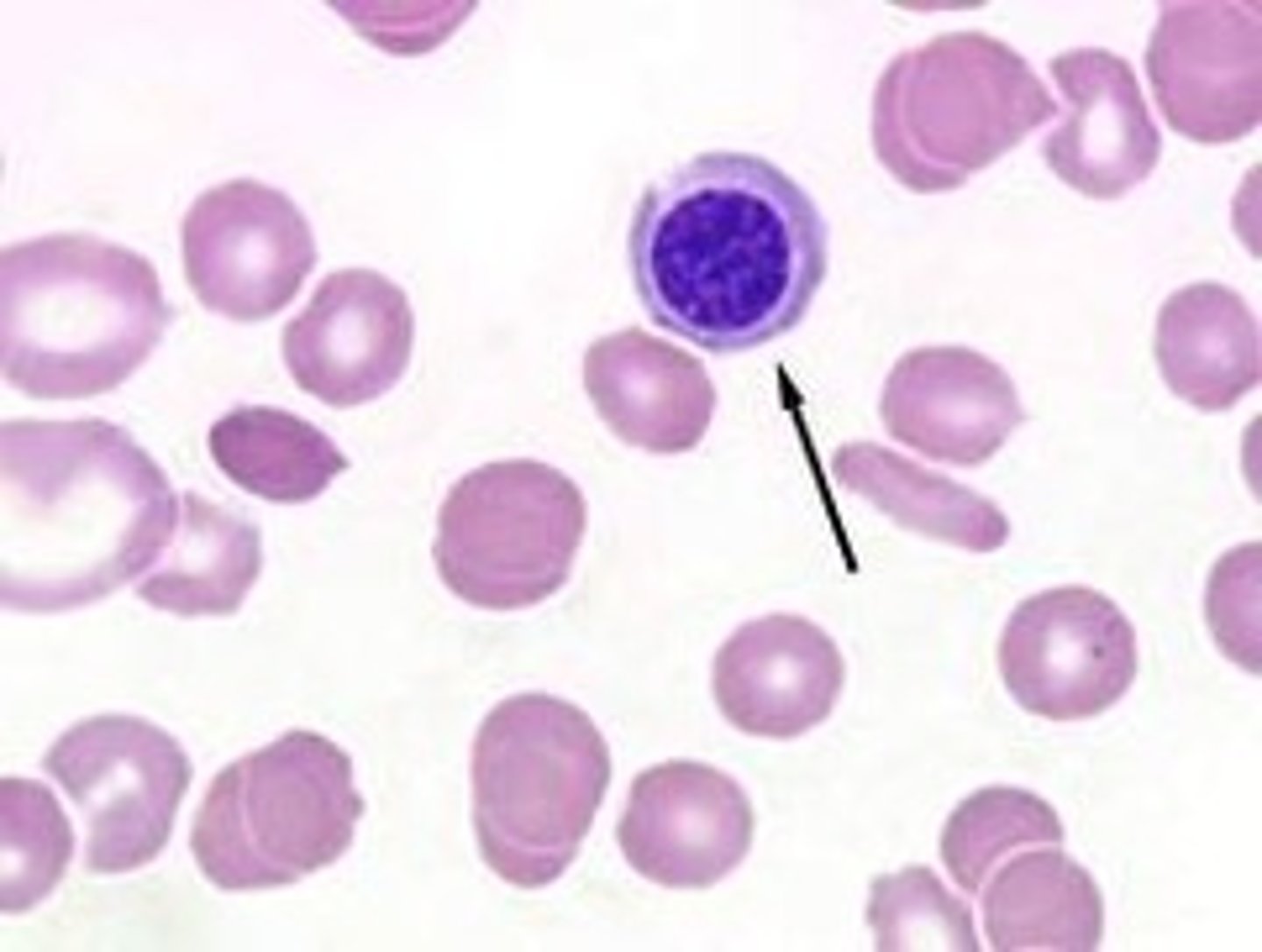
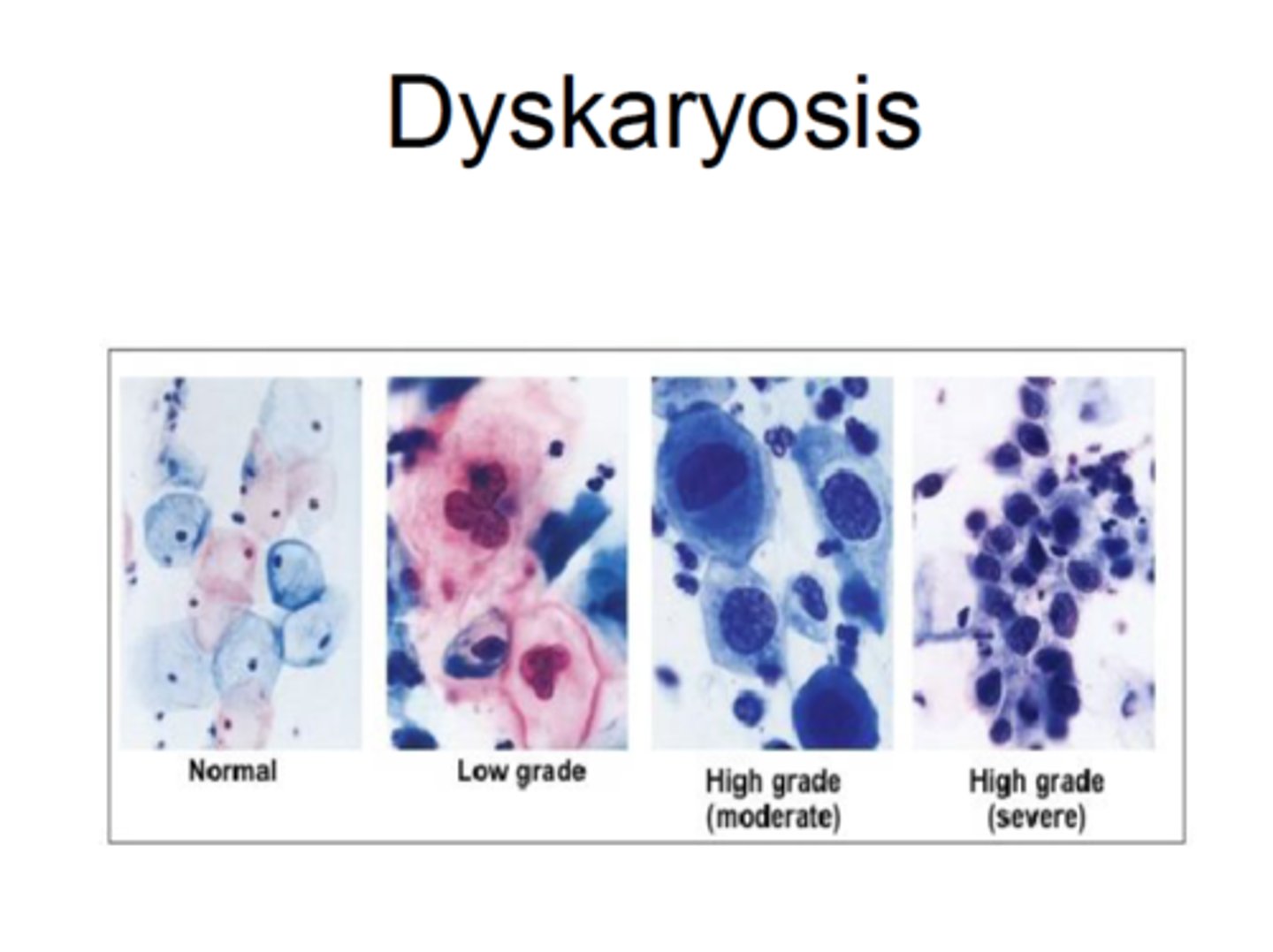
What is Dyskaryosis?
The cytological term for an abnormal nuclear appearance (enlargement, irregularity, hyperchromasia) in epithelial cells
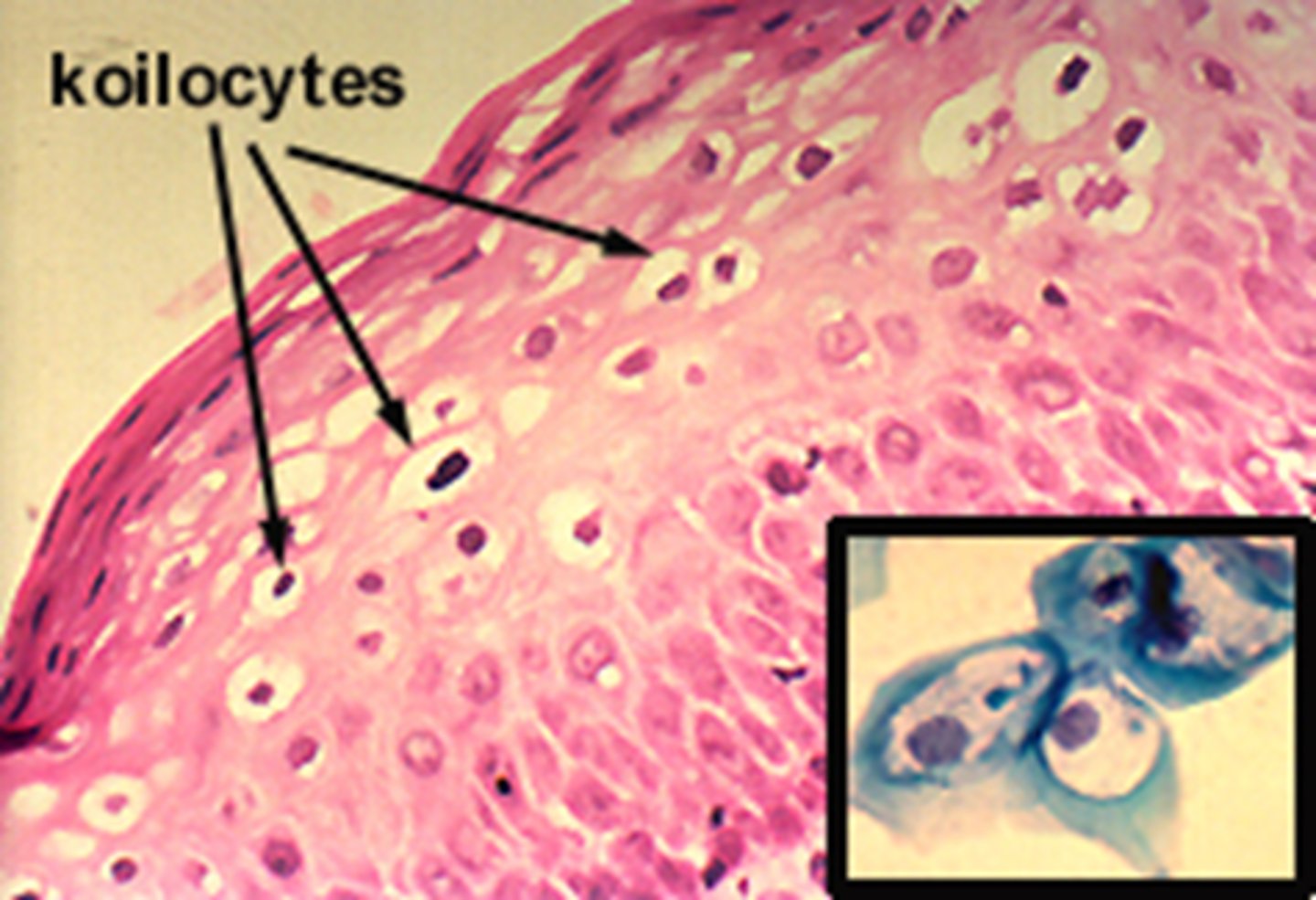
What are Koilocytes?
Squamous cells showing the 'signature' of HPV infection, characterized by a large, dark, irregular nucleus surrounded by a clear halo.
What are the 'Big 3' criteria for diagnosing Dyskaryosis?
1. Nuclear Enlargement (Increased N:C ratio). 2. Hyperchromasia (Nucleus becomes very dark/dense). 3. Irregular Chromatin (DNA looks clumpy).
How do LSIL and HSIL relate to CIN grades?
LSIL (Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion) = CIN 1; HSIL (High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion) = CIN 2 and CIN 3.
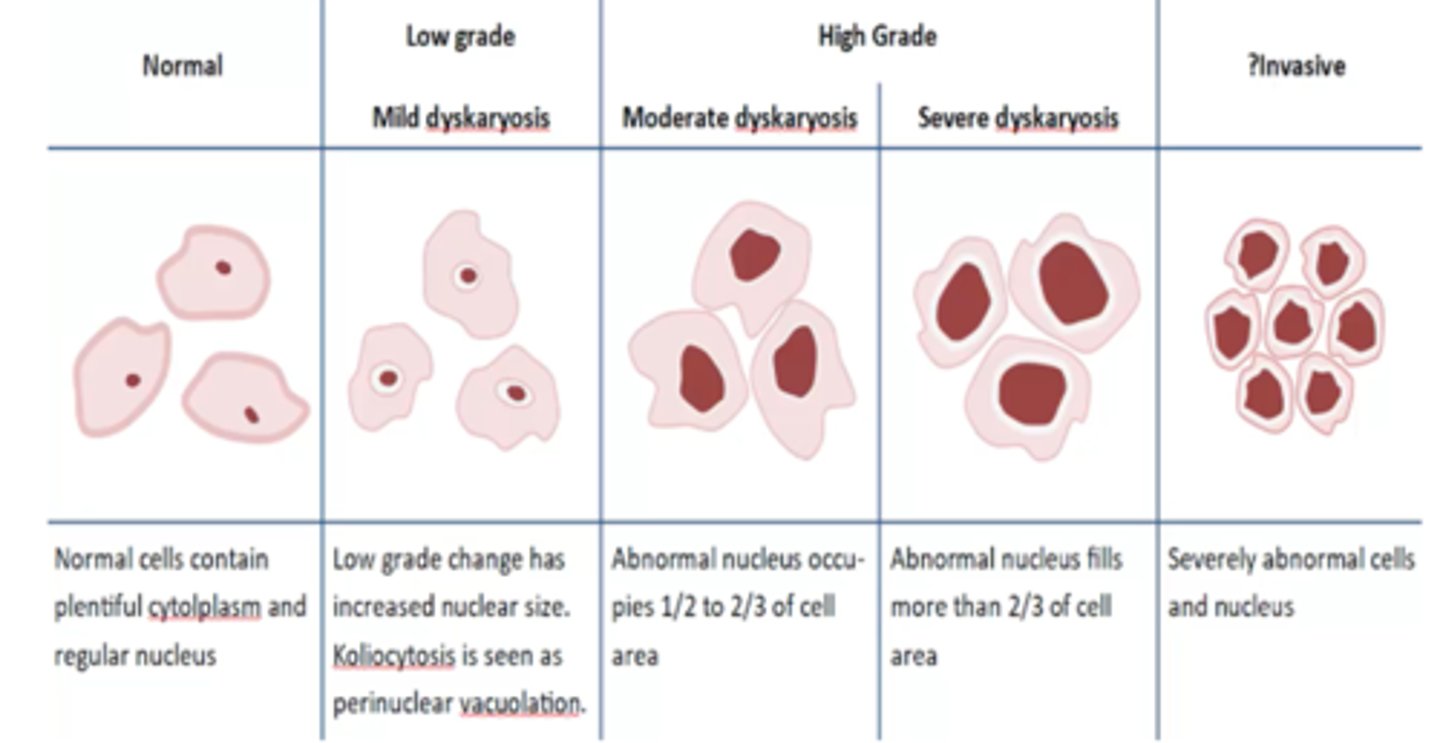
Describe the N:C ratio for 'Mild Dyskaryosis' (LSIL).
The nucleus is enlarged but occupies less than 1/3 of the total cell area.
Describe the N:C ratio for 'Moderate Dyskaryosis' (HSIL).
The nucleus occupies 1/2 to 2/3 of the cell area..This is a "High-Risk" lesion
Describe the N:C ratio for 'Severe Dyskaryosis' (HSIL).
The nucleus occupies more than 2/3 of the cell area.
What is the 'Papanicolaou (Pap) Stain'?
A polychromatic stain is used to show nuclear detail. Blue/Purple: Nuclei (via Hematoxylin).
Pink/Green/Orange: Cytoplasm (showing how mature the cell is).
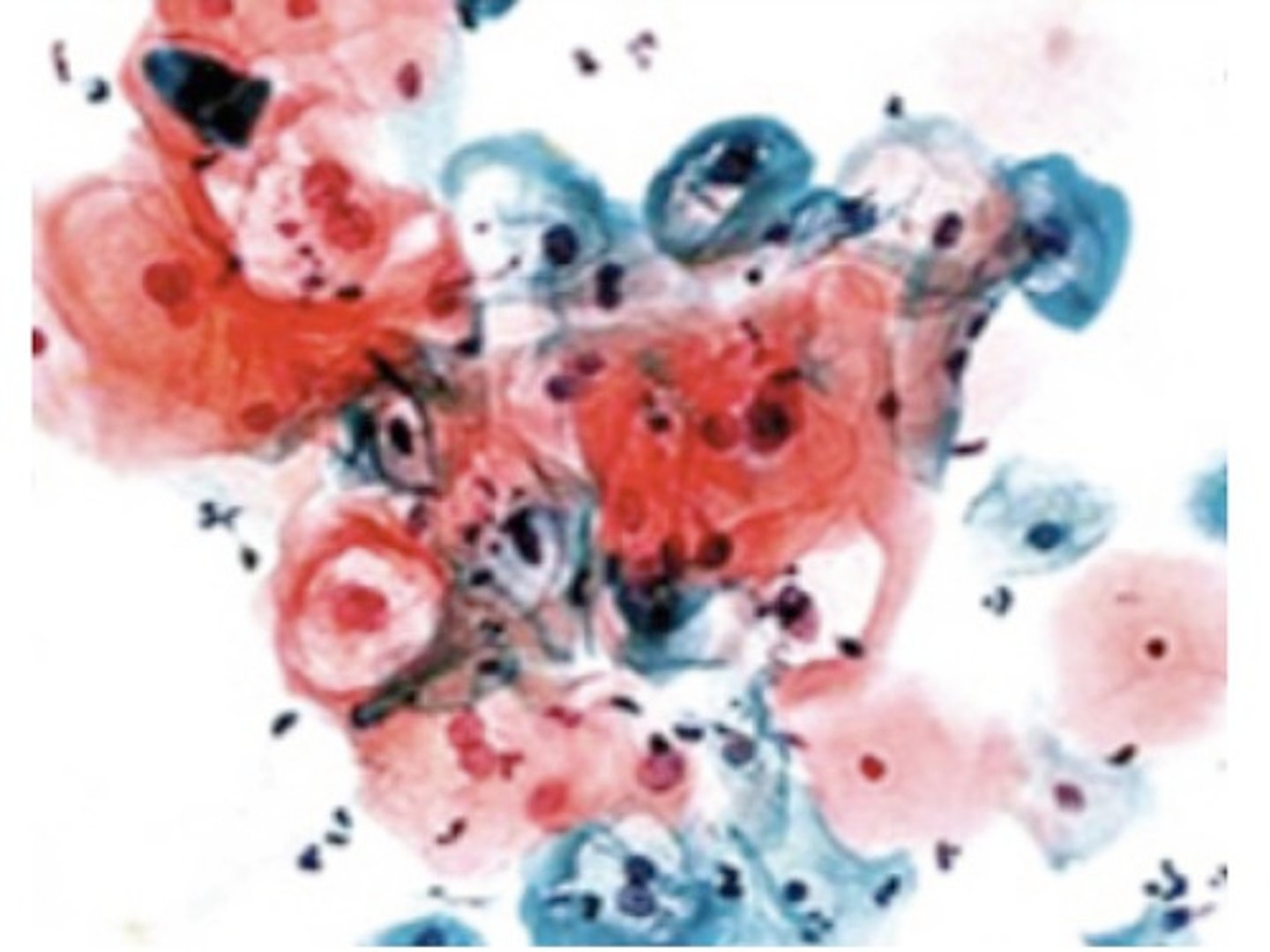

What does the color blue/purple indicate in Pap stain?
Nuclei (via Hematoxylin).
What does the color pink/green/orange indicate in Pap stain?
Cytoplasm, showing how mature the cell is.
What is Liquid Based Cytology (LBC)?
A preparation method where cells are collected in a preservative vial rather than smeared directly. Advantage: It filters out blood, mucus, and inflammatory cells to provide a clean "monolayer" of cells.
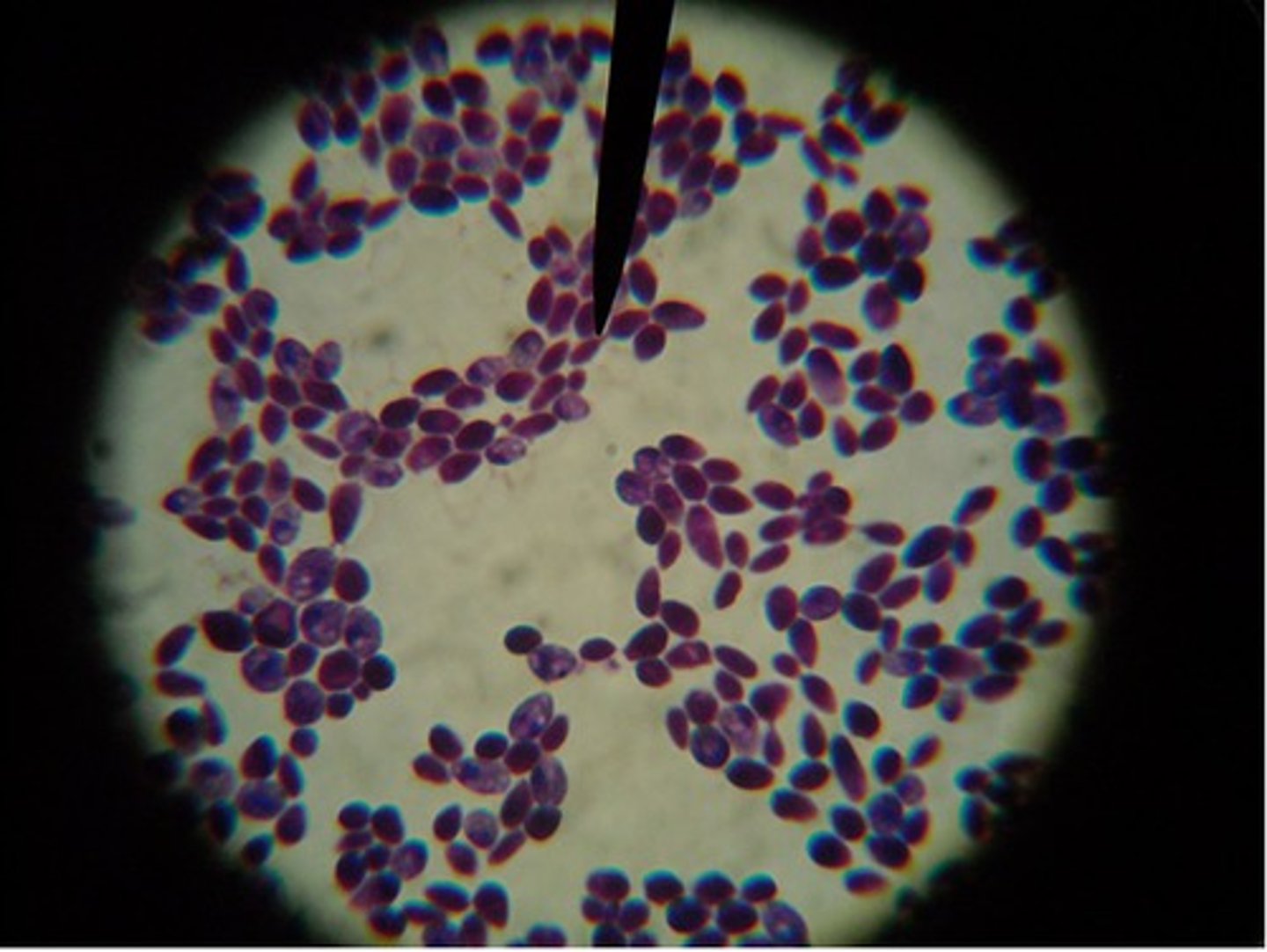
What does 'Candida albicans' look like in a Pap smear?
Budding yeast (blastoconidia)
Pseudohyphae (elongated chains of yeast cells)
What does 'Actinomyces' look like in a Pap smear?
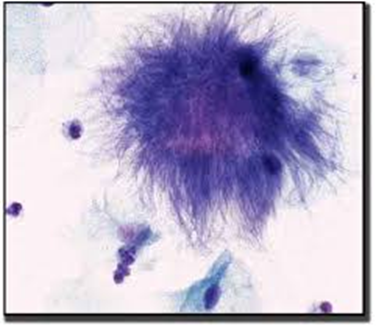
Large, dark, fuzzy clumps of bacteria that look like 'Dust Bunnies.'
Can cytology 'Stage' cancer?
No, staging requires histology and imaging.
What is the UK Triage Logic for an 'Inadequate' sample?
If inadequate, the patient is invited back for a repeat; if it happens three times, they are referred to Colposcopy.