5 - The Mitotic Cell Cycle 👩👩👧👦
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Describe the changes that occur during prophase in an animal cell. (4)
1) condensation of chromatin
2) chromosomes visible as two sister chromatids joined by a centromere
3) spindle formation / microtubules assemble
4) centrioles move to opposite poles
5) disappearance of nucleolus
6) breakdown of nuclear envelope
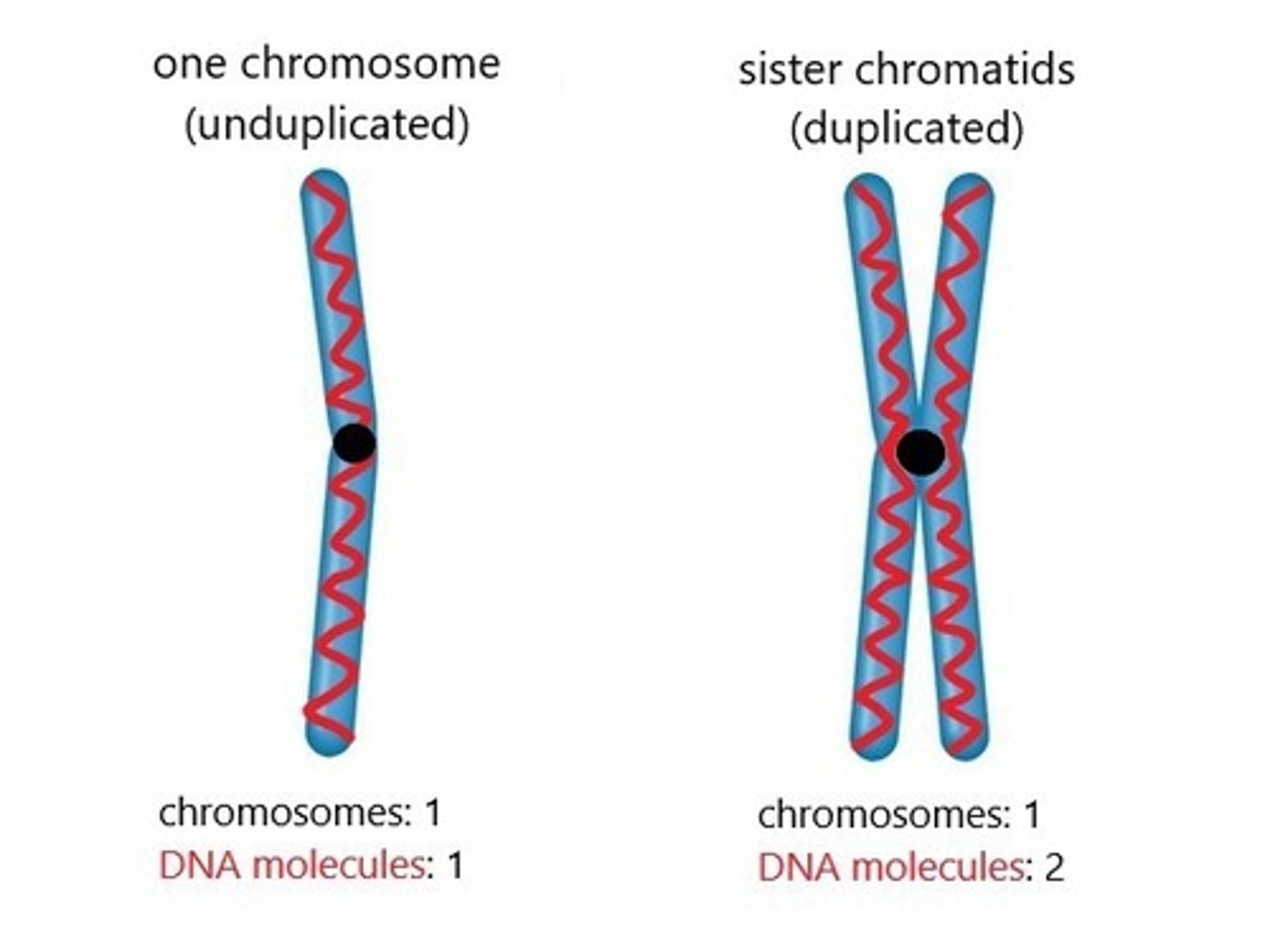
Chromatid
one half of a duplicated chromosome
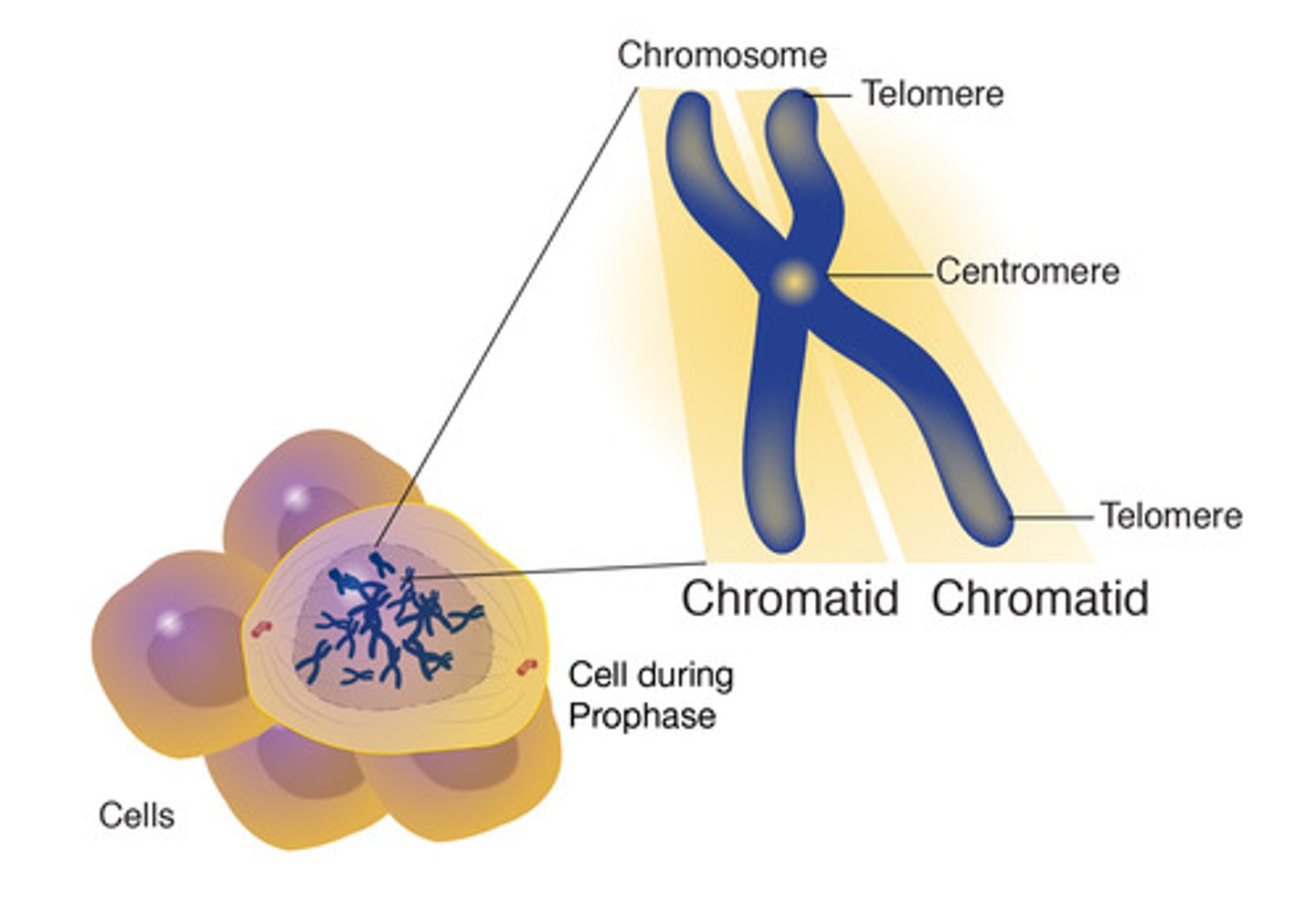
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of nucleic acids and proteins that contain genes
histone proteins
Proteins which package dna one nucleosomes
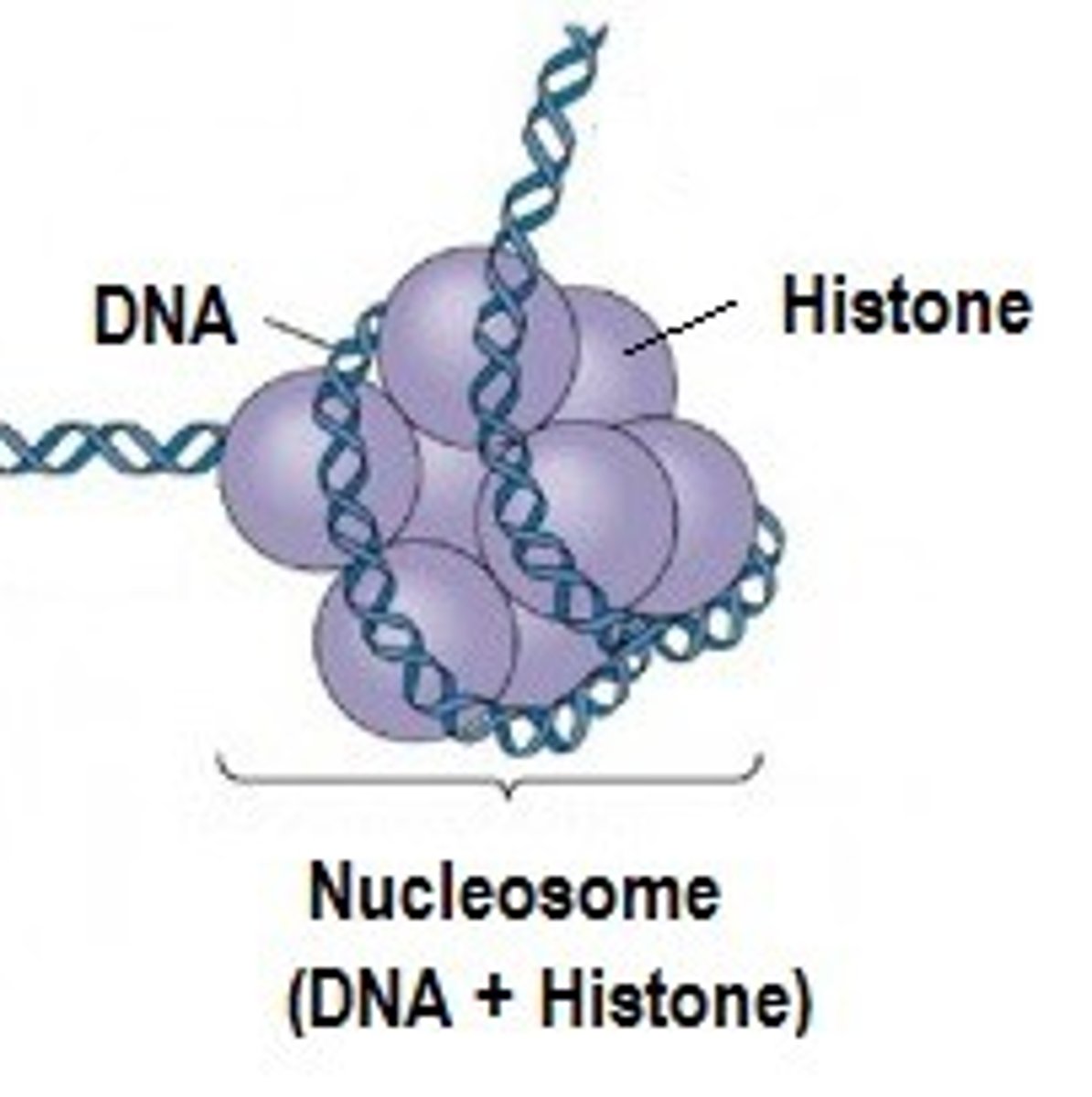
Chromatin
Combination of DNA and proteins
Each chromatid contains how many DNA molecules?
1
Size of DNA molecule
2nm
Why mitosis is carried out instead of meiosis
1) maintains genetic stability by producing genetically identical cells
2) ensures cells retain function
3) maintains chromosome number
Nucleosome
- 11 nm wide by 6 nm long
- made of 8 histone molecules
- DNA is wrapped outside the base cylinder making 1 2/3 turns before linking to next histone
Function of telomeres
1) permit continued replication
2) prevent loss of genes
Telomeres
Repeated DNA sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes and are needed for successful division
How telomeres permit continued replication
1) copying enzyme telomerase stops a little short of the end of DNA
2) repeated bases are added which don't have useful info but allow telomerase to complete copying meaningful DNA
Mitosis
Nuclear division that produces two genetically identical daughter cells
Interphase consists of
G1, S, and G2 phases
G1 phase
cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles
S phase
- synthesis of dna
- dna in the nucleus replicated so that each chromosome consists of two identical chromatids
G2 phase
- cell continues to grow
- the new dna is checked and any errors are corrected
- preparations are made to start cell division eg sharp increase in the production of Tubulin is observed which is needed to make microtubules for mitotic spindle
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division
M phase (mitosis)
Production of genetically identical cells
- growth
- cell replacement
- repair of tissues
- asexual reproduction
- immune response (cloning of B and T lymphocytes)
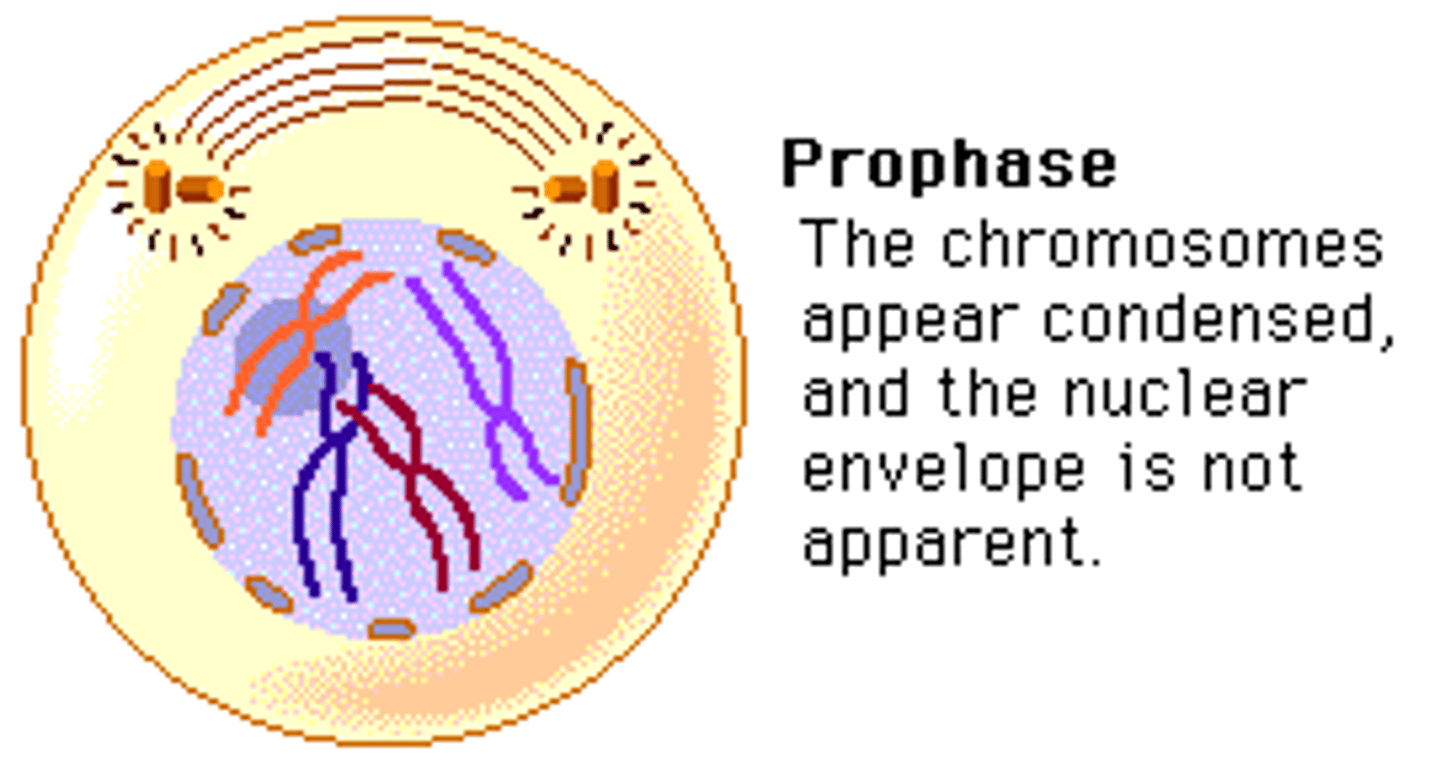
Prophase
- chromatin starts to condense
- nuclear envelope and nucleolus disappears
- centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell and form piles of mitotic spindle
- asters and spindle fibres form
Metaphase
- centrosomes are at cell poles and organise production of spindle fibres
- chromosomes line up across equator of spindle
Anaphase
Chromatids are pulled apart by the contraction of spindle fibres and move to opposite poles of the cell
Telophase
- nuclear envelope and nucleolus reforms
- nucleus divides
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
cytokinesis in plant cells
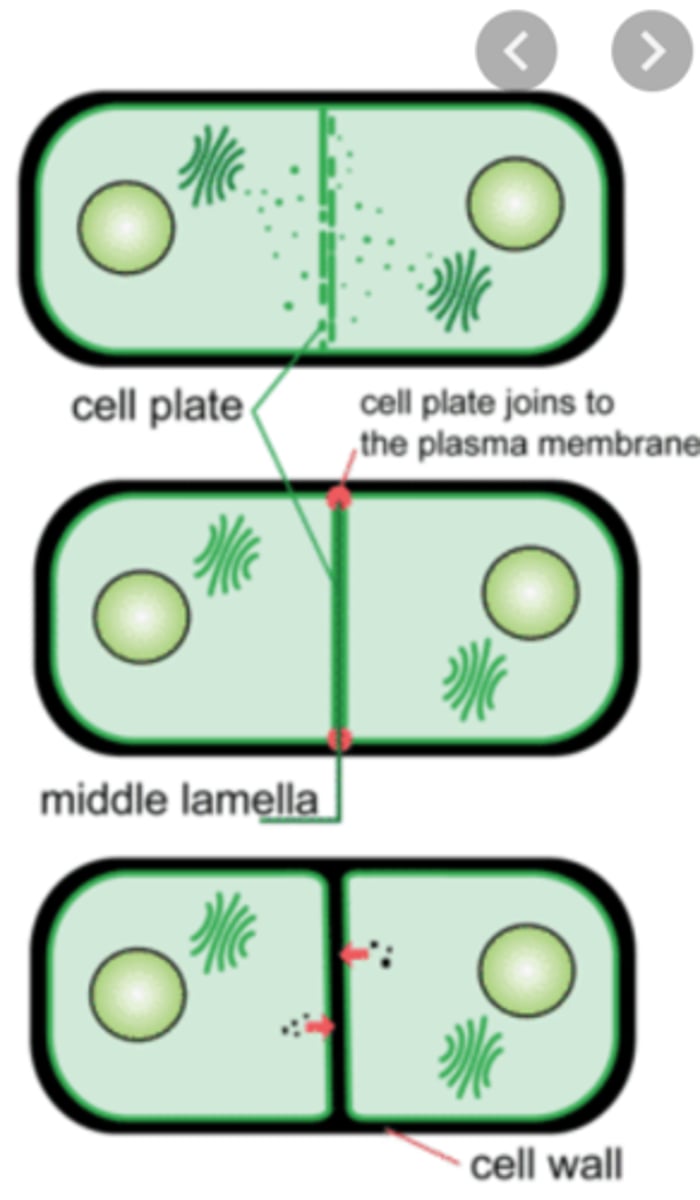
1) cell plate forms across equator of the cell / cellulose cell wall laid down
2) cytoplasm is divided into two
Cytokinesis in animal cells
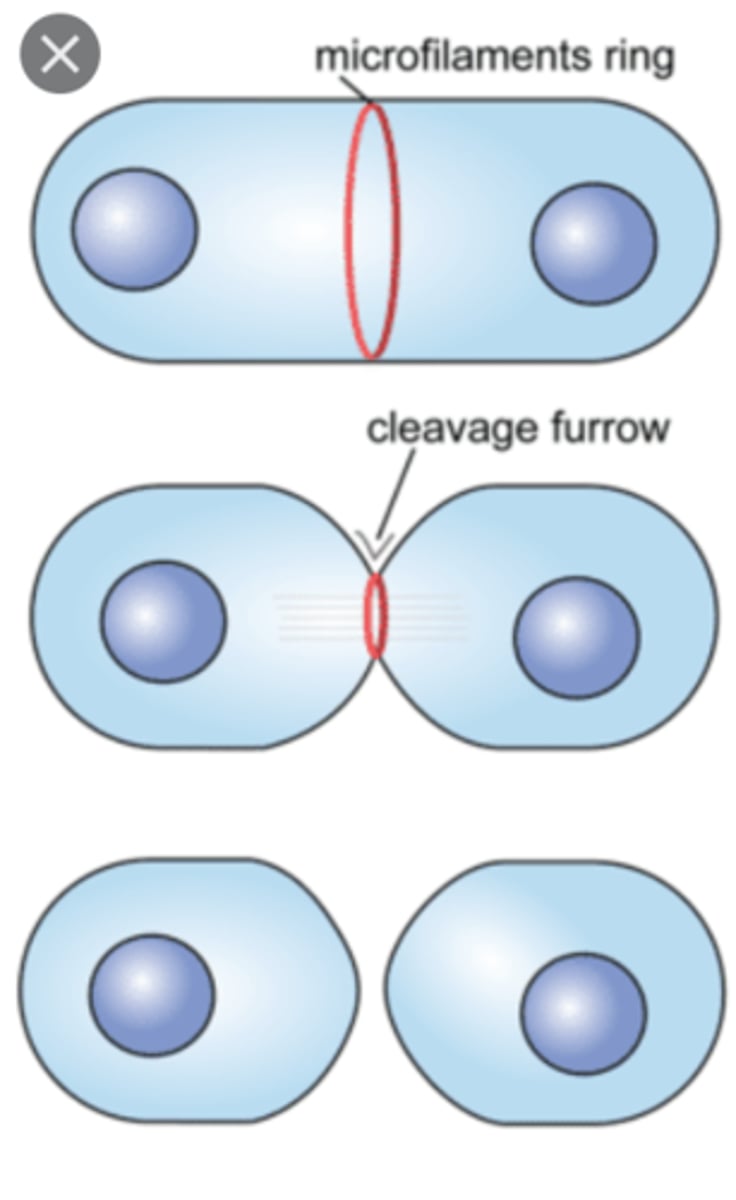
1) contractile ring forms pushing equator of cell inwards forming cleavage furrow
2) it deepens as actin filaments in ring contract and eventually splits into two membranes
Differences in plant and animal cells mitosis
1) plant cells don't have any visible centriole or aster
2) daughter cells get separated by cell plate in plants
Centromere
- Site of attachment of spindle microtubules
- Each metaphase chromosome has two kinetochores at its centromere
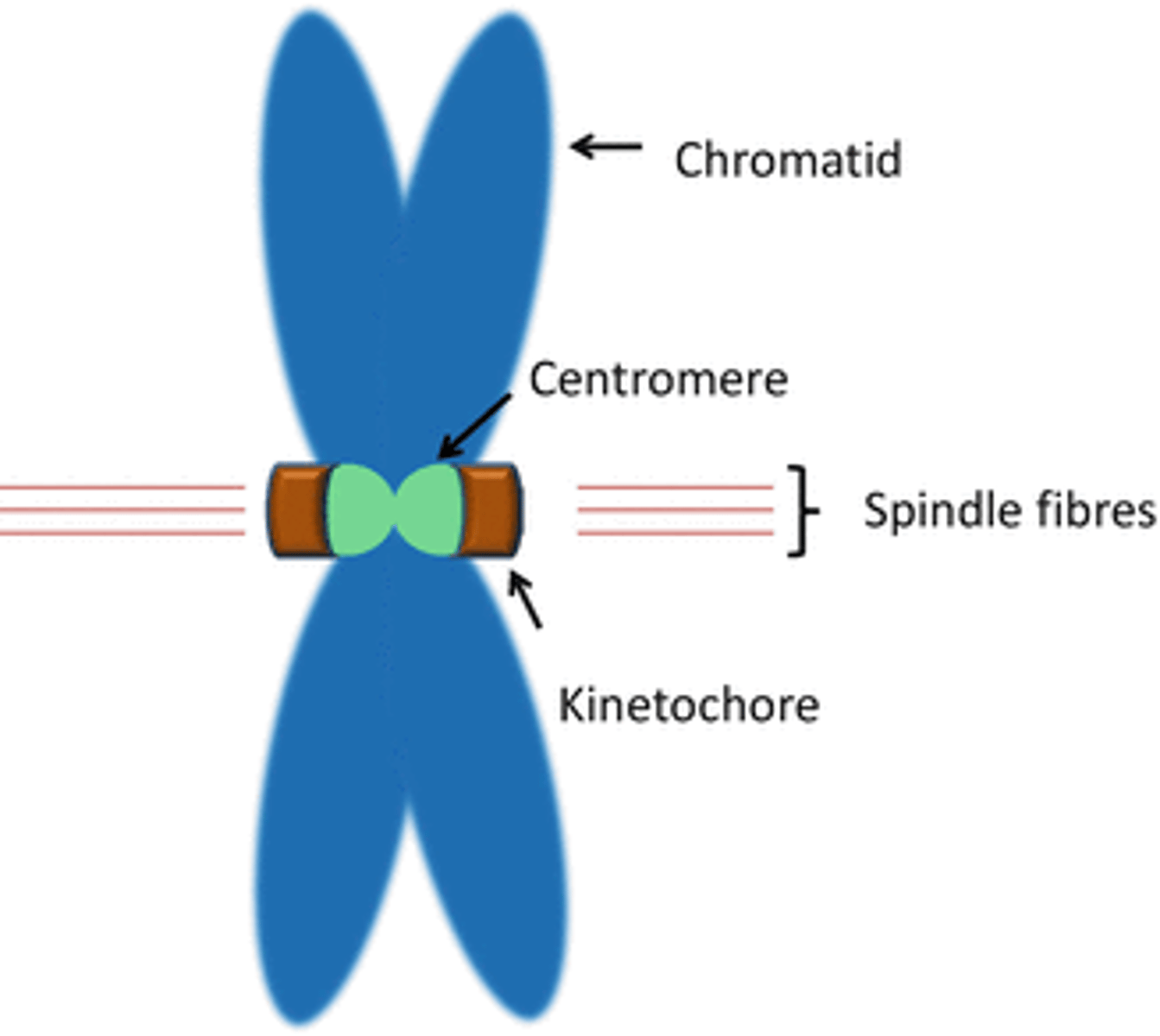
kinetochore
A structure of proteins attached to the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle.
Centrosomes
- Present at the poles of the spindle
- An organelle found in animal cells that acts as an MTOC for construction of the spindle
Stem cells
Cells that can divide an unlimited number of times via mitosis
Cellular changes that occur in development of cancer
1) mutation occurs in gene that controls cell division leading to formation of oncogene from protooncogene
2) this causes uncontrolled division
3) coordination of cell cycle is lost (cell does not respond to or receive signals that tell it to stop dividing)
4) loss of function and lack of specialisation occurs
5) a tumour is formed, an irregular mass of cells showing an abnormal change in shape
Roles of centrioles during mitosis
1) act as MTOCs
2) assemble / form spindle fibres during prophase
3) contraction of spindle fibres during anaphase separates sister chromatids
State the substances used to synthesise DNA during the S phase. [3]
1. ATP
2. activated / free nucleotides
3. DNA polymerase
4. DNA ligase
Describe the behaviour of the nuclear envelope during mitosis. [2]
breakdowns at prophase into vesicles, vesicles fuse to form new membranes around both sets of daughter chromosomes in telophase