A level WJEC Biology unit 1.1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/57
Last updated 2:36 PM on 11/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Definition of a monosaccharide
one sugar
2
New cards
two types of glucose
alpha glucose and beta glucose
3
New cards
what is triose important for?
important in respiration
4
New cards
what is pentose important for?
important within nucleotides
5
New cards
what is hexose important for? and name an example
respiration, glucose is an example of this. Monomers are linked to make dimers and polymers
6
New cards
Name three disaccharides
Sucrose, Maltose, and Lactose
7
New cards
What are polysaccharides?
Large complex polymers. They are long chains of polysaccharides
8
New cards
What are inorganic ions?
Inorganic ions only have no more than one carbon atom
9
New cards
What are calcium ions useful for?
Making bones and teeth hard
10
New cards
What are magnesium ions useful for?
Found within chlorophyll, making them vital for efficient photosynthesis
11
New cards
What are iron ions useful for?
found within haemoglobin in red blood cells, enabling the efficient transport of oxygen
12
New cards
What are phosphate ions useful for?
Component of nucleic acids (DNA + RNA) and ATP
13
New cards
What are nitrate ions useful for?
making nucleotides such as DNA and the nitrogen is used for amino acid formation
14
New cards
What is meant by a polar molecule?
electrons are not shared equally
15
New cards
How is water a polar molecule?
The oxygen end contains more electrons (negatively charged) and the hydrogen is positively charged
16
New cards
How will dipole water molecules bind?
They will bind together forming hydrogen bonds
17
New cards
What is cohesion in water?
Many water molecules together form a lattice and is strong. Hence cohesion is present
18
New cards
What are some properties of water?
Solvent, Transport medium, Chemical reactions, Density
19
New cards
What are lipids?
They are triglycerides (fats and oils)
They contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Insoluble in water (polar)
Soluble in other solvents such as ethanol
They contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Insoluble in water (polar)
Soluble in other solvents such as ethanol
20
New cards
What is glycerol?
Alcohol
21
New cards
What are fatty acids?
Organic molecules containing long hydrocarbons chains and have a -COOH group.
22
New cards
What bonds are found in lipids?
Ester bonds
23
New cards
What are saturated fats?
Saturated fats carry the maximum number of hydrogen atoms and have no double bonds between neighbouring carbon atoms with the hydrocarbon tail. They are solid, animal lipids tend to be saturated. Solid at room temperature.
24
New cards
What are unsaturated fats?
Unsaturated fats have double bonds on the C=C atoms. This produces a kink in the chain. They don't contain maximum number of hydrogen atoms. Most oils are unsaturated. Meaning the melt more easily. Liquid at room temperature.
25
New cards
How do lipids link to heart disease?
Fatty deposits are main causes of heart disease such as atherosclerosis and high blood tension. Lipids combine with protein to make lipoproteins
26
New cards
Product of high saturated fats building up
If high saturated fats or LDL (low density lipoproteins) build up. This leads to atheroma build up in coronary arteries restricting blood flow and oxygen to heart tissue. This can lead to angina and a myocardial infraction. (If arteries become blocked).
27
New cards
Product of high unsaturated fats building up
Higher proportions of unsaturated fats more HDL (high density lipoproteins) which carry harmful fats to the liver to be disposed of. Higher ratio of HDL:LDL, lower risk of CHD and cardiovascular disease.
28
New cards
What are phospholipids?
Two fatty acid tails and a phosphate group (replacing the third fatty acid) phosphate group is soluble in water Hydrophilic head and two hydrophilic tails
29
New cards
What is a protein
Proteins contain only carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Proteins are made of monomers called amino acids. There are 20 types of amino acids which make up code for thousands of different proteins. The protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids in the chain. Shape determines function.
30
New cards
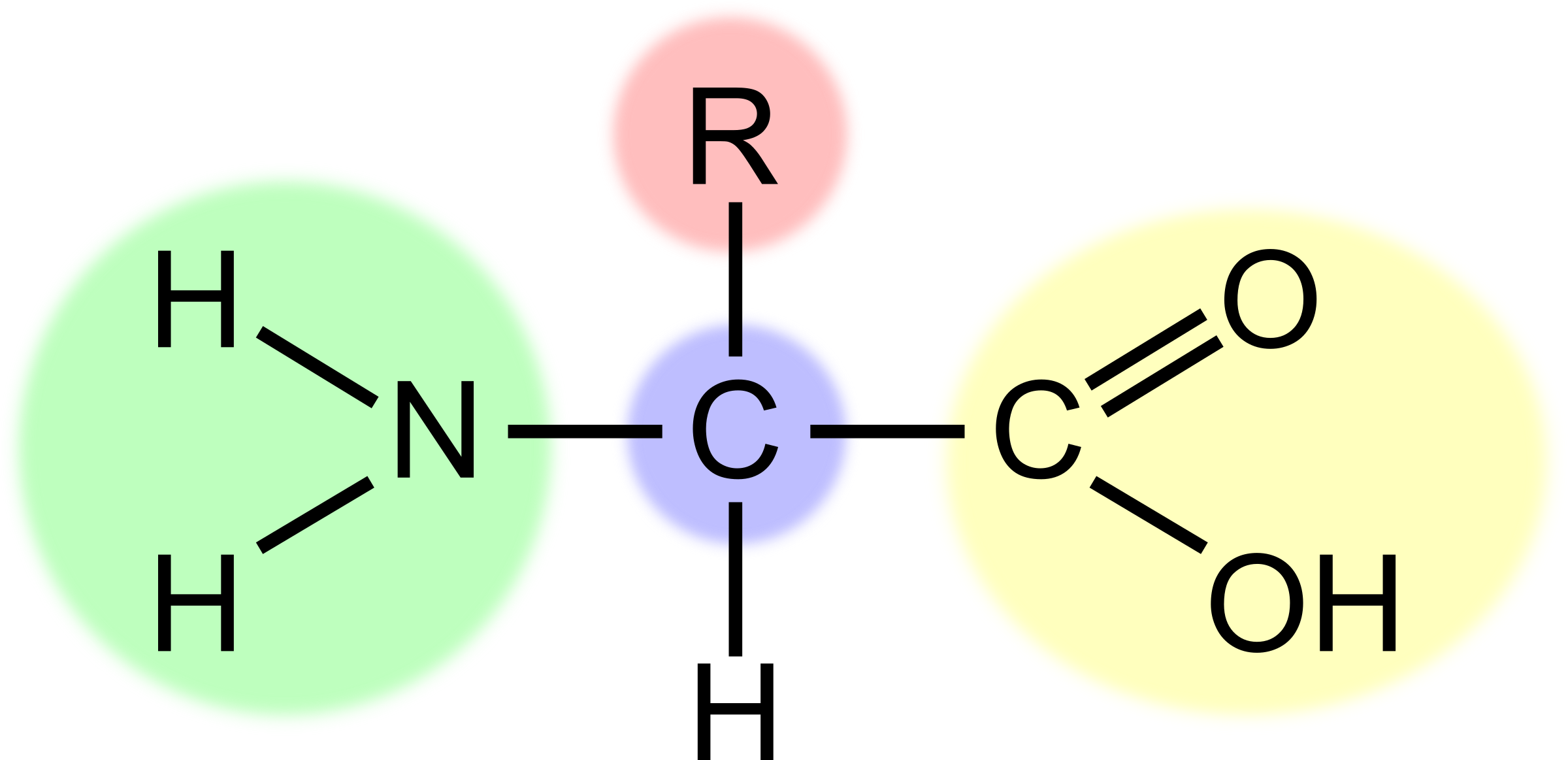
What is the part highlighted in green?
The amino group (-NH2) alkaline
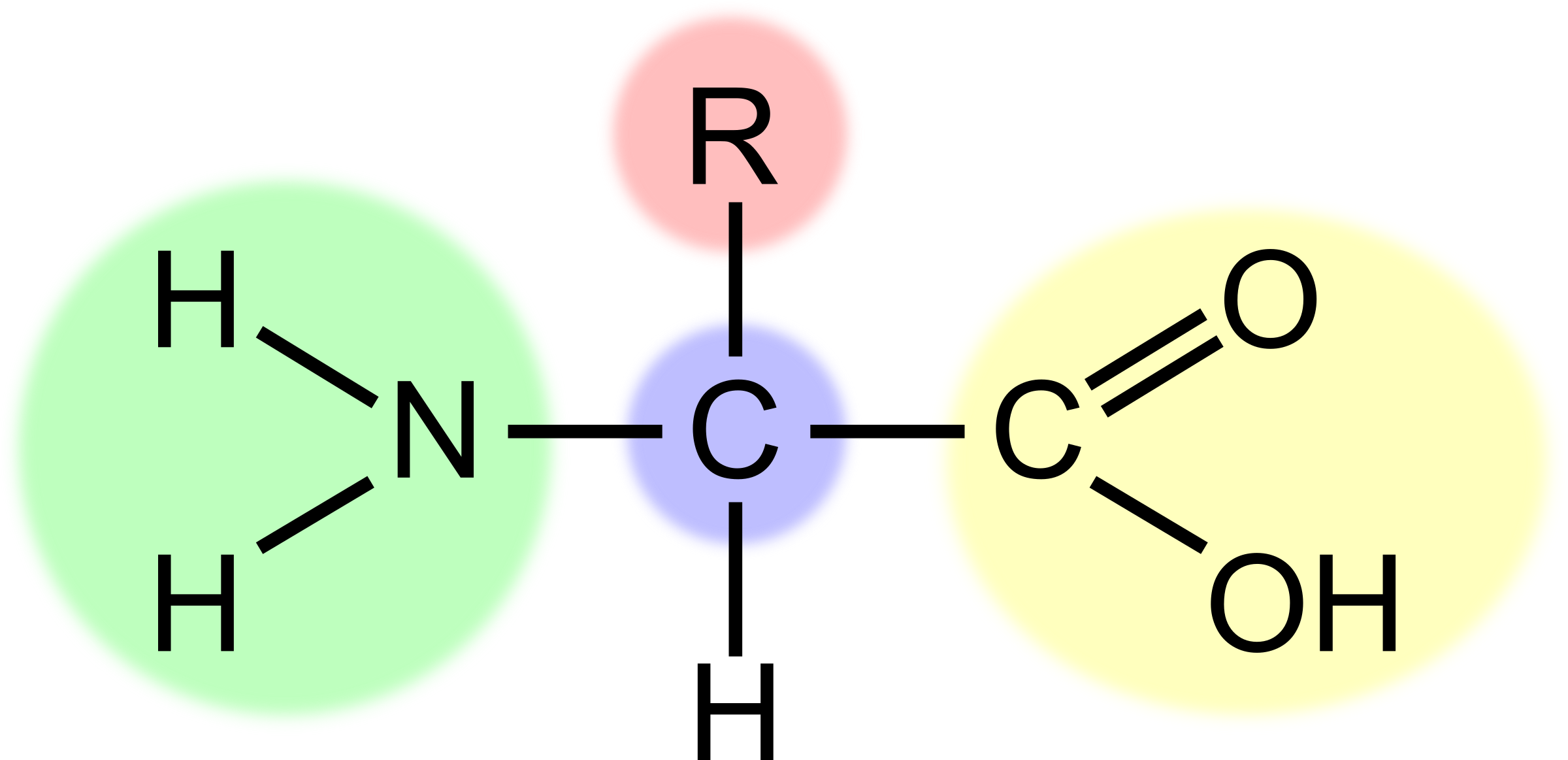
31
New cards
What is the part highlighted in red?
The R group, variable group of atoms
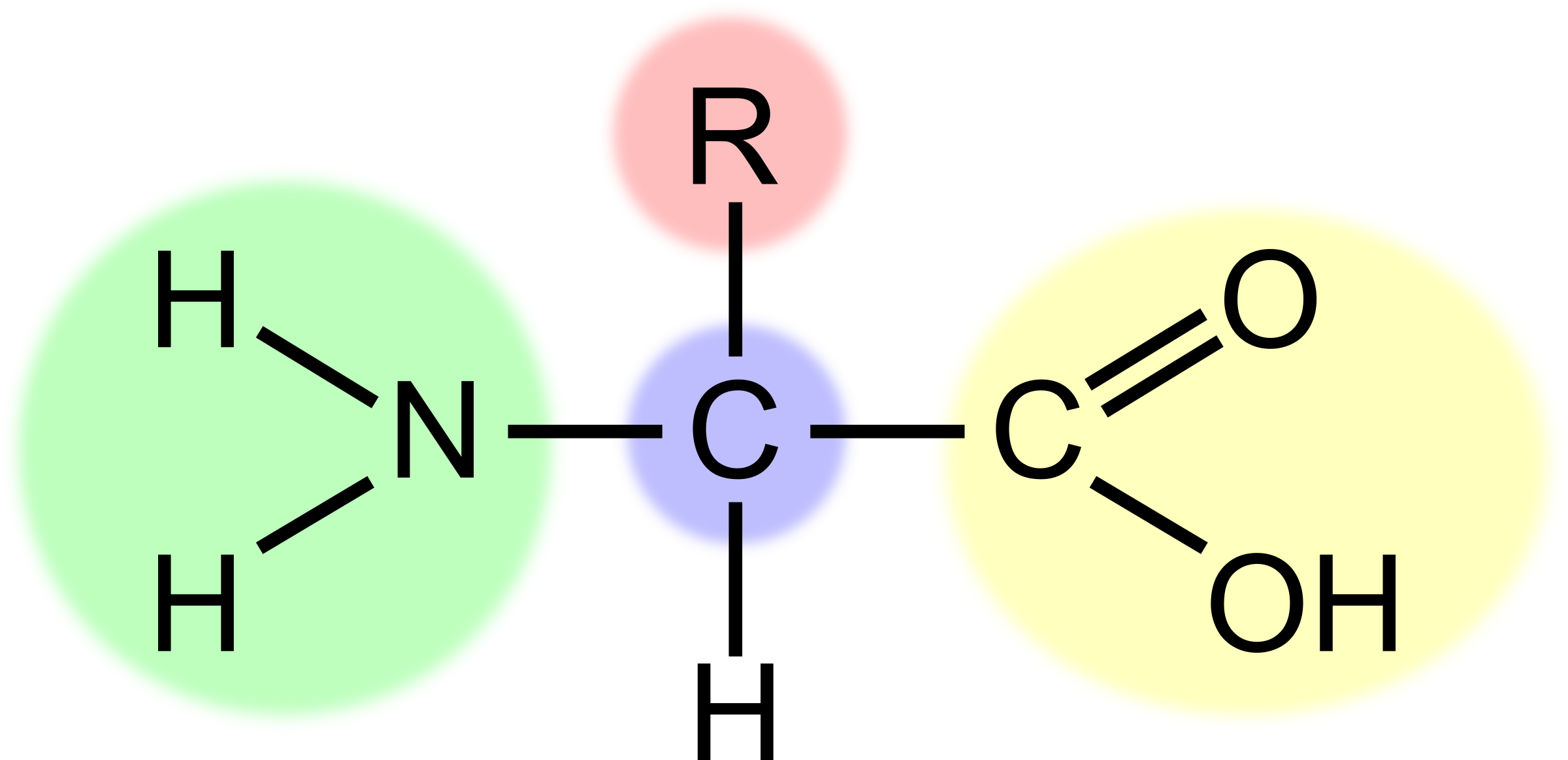
32
New cards
What is the part highlighted in blue?
The central carbon
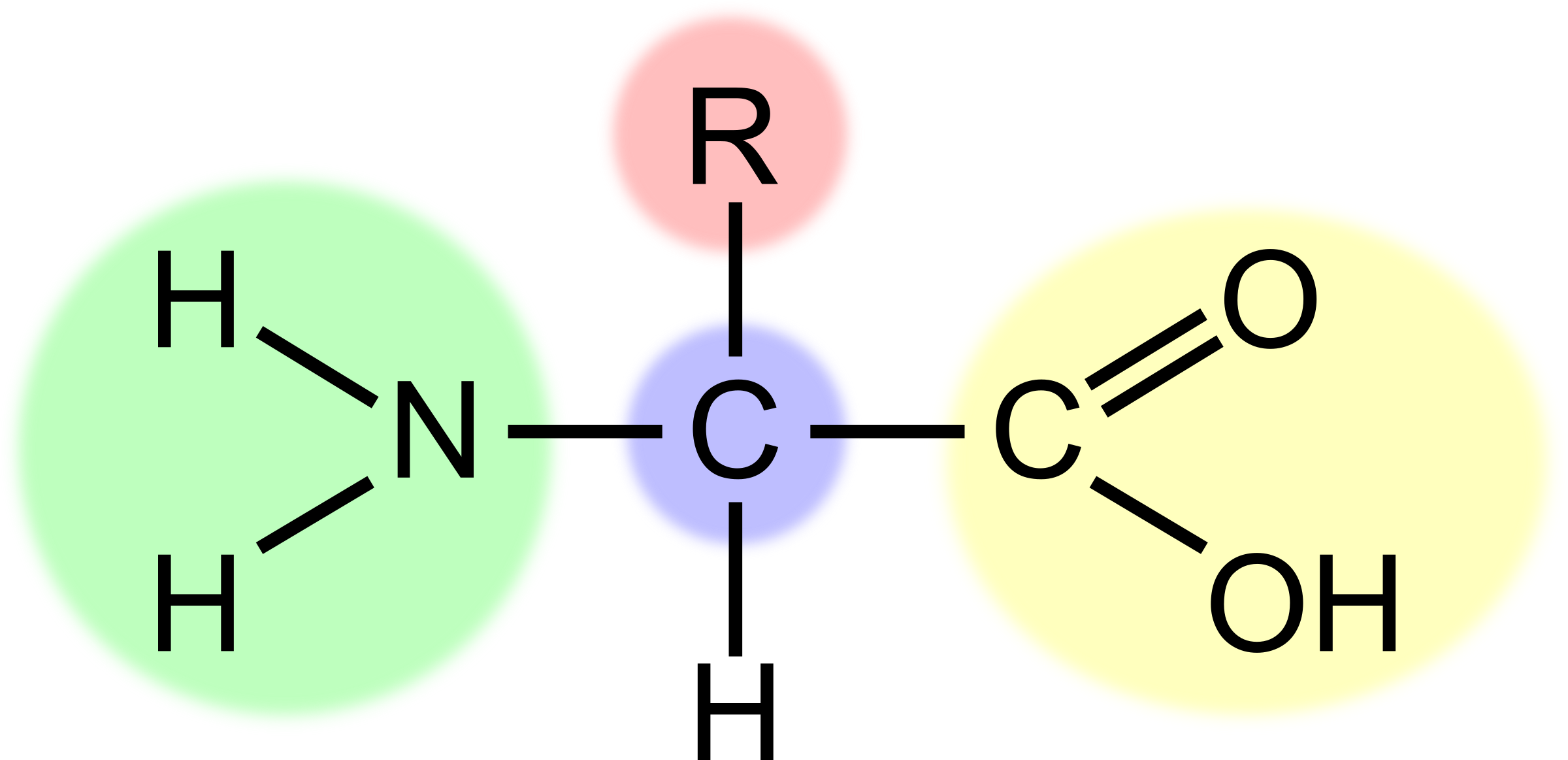
33
New cards
What is the part highlighted in yellow?
The carboxyl group (-COOH) acidic
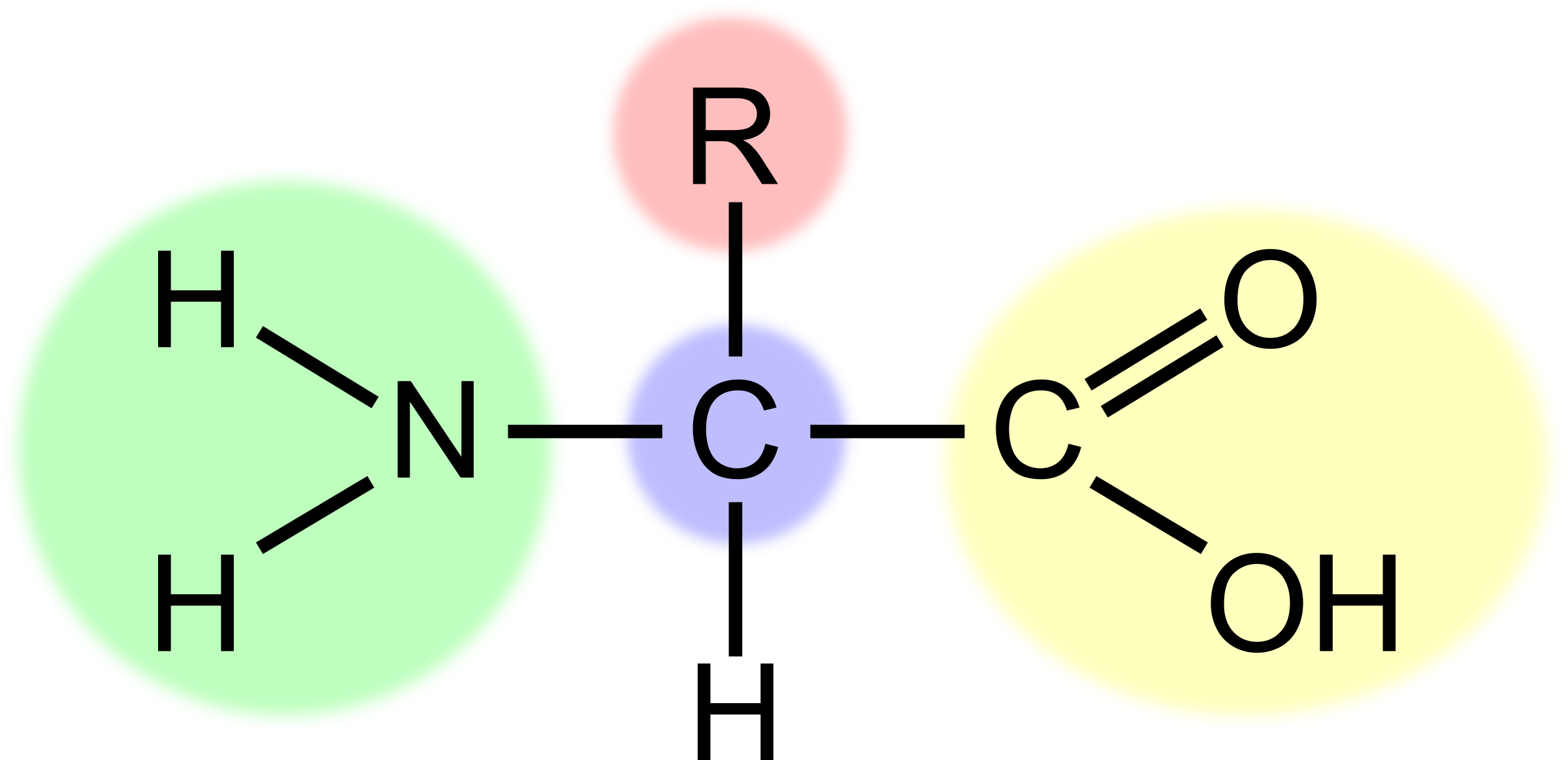
34
New cards
What is the H?
Hydrogen atom
35
New cards
How are dipeptides and polypeptides formed?
Amino group reacts with carboxyl group (condensation reaction) peptide bond is formed and water eliminated.
36
New cards
What are the four levels of structure of protein?
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
37
New cards
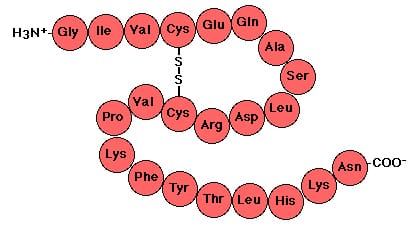
What are primary proteins?
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. Determined by DNA. Held with peptide bonds.
38
New cards
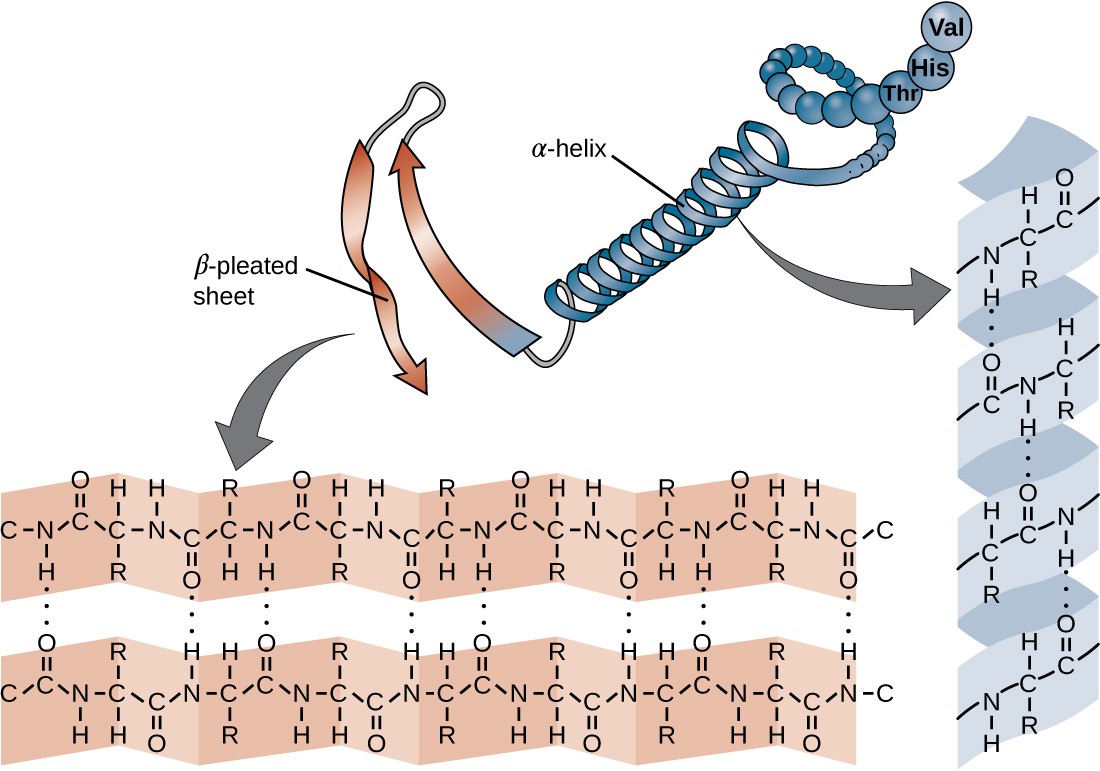
What are secondary proteins?
Hydrogen bonds twist and fold and form an alpha helix (single strand) or beta pleated sheets (two strands). Increase stability and amino acid fold into repeating pattern.
39
New cards
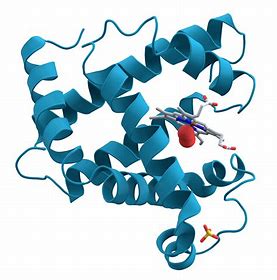
What are tertiary proteins?
Alpha helix folded and twisted further. 3D structure. Bonded by ionic, disulphide, covalent, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonds. These maintain the structure and shape. Enzymes have a tertiary structure. Bonds also maintain active site shape.
40
New cards
What are quaternary proteins?
Combination of two or more tertiary polypeptide chains and non-protein groups (haem group). Held together by non-covalent bonds (hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions) and also covalent disulphide bonds. Form large complex molecules such as haemoglobin. Haemoglobin has four peptide chains.
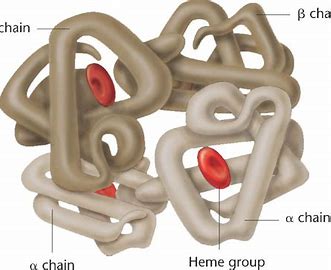
41
New cards
What is meant by globular classification?
Compact
folded in 3D shape
can be tertiary or quaternary
soluble in water
enzymes are globular
folded in 3D shape
can be tertiary or quaternary
soluble in water
enzymes are globular
42
New cards
What is meant by fibrous classification?
Polypeptide in parallel sheets/ chains with numerous cross linkages
insoluble in water, strong and tough
structural functions
Keratin is fibrous
insoluble in water, strong and tough
structural functions
Keratin is fibrous
43
New cards
What is a conisation reaction
Joins monomers together to form polymers. Water and bonds are formed
44
New cards
What is a hydrolysis reaction
Polymers broken down back into monomers. Requires water and breaks bonds.
45
New cards
What is starch
Most commonly found in photosynthesising cells, in leaves, and storage cells in seeds and organs. It is compacted and dense, insoluble grains stored in special organelles called amyloplasts.
46
New cards
What does starch consist of
Two different polysaccharides, amylose and amylopectin.
47
New cards
What is amylose?
a long chain of alpha glucose molecules joined together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
48
New cards
What is amylopectin?
a long chain of alpha glucose molecules joined together with 1,4 glycosidic bonds but with the occasional 1,6 glycosidic bond. The additional 1,6 bonds cause amylopectin to have side branches with more accessible ends
49
New cards
Why can amylose only be broken down slowly
it only has two accessible ends
50
New cards
why can amylopectin be broken down faster
is has many accessible ends
51
New cards
is amylose used as a long- or short-term store of energy?
long term store, as it can only be broken down slowly
52
New cards
is amylopectin used as a long- or short-term store of energy?
short term store, as it can be broken down quickly
53
New cards
What role does cellulose have?
A structural role within organisms such as plants
54
New cards
What is cellulose composed of?
many thousands of beta glucose molecules joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
55
New cards
What does cellulose do to cells
makes them turgid
56
New cards
What is chitin?
a large structural polysaccharide made from chains of modified glucose. Chitin is found in the exoskeleton of insects, the cell walls of fungi and certain hard structures in invertebrates and fish
57
New cards
What is the role of chitin?
Protects and gives mechanical support to soft bodied organisms.
58
New cards
What are some properties of chitin?
Translucent
Resilient
Tough
Resilient
Tough