233 Unit 8 Exam (Part 1) - Spinal Cord and Reflexes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
subarachnoid space
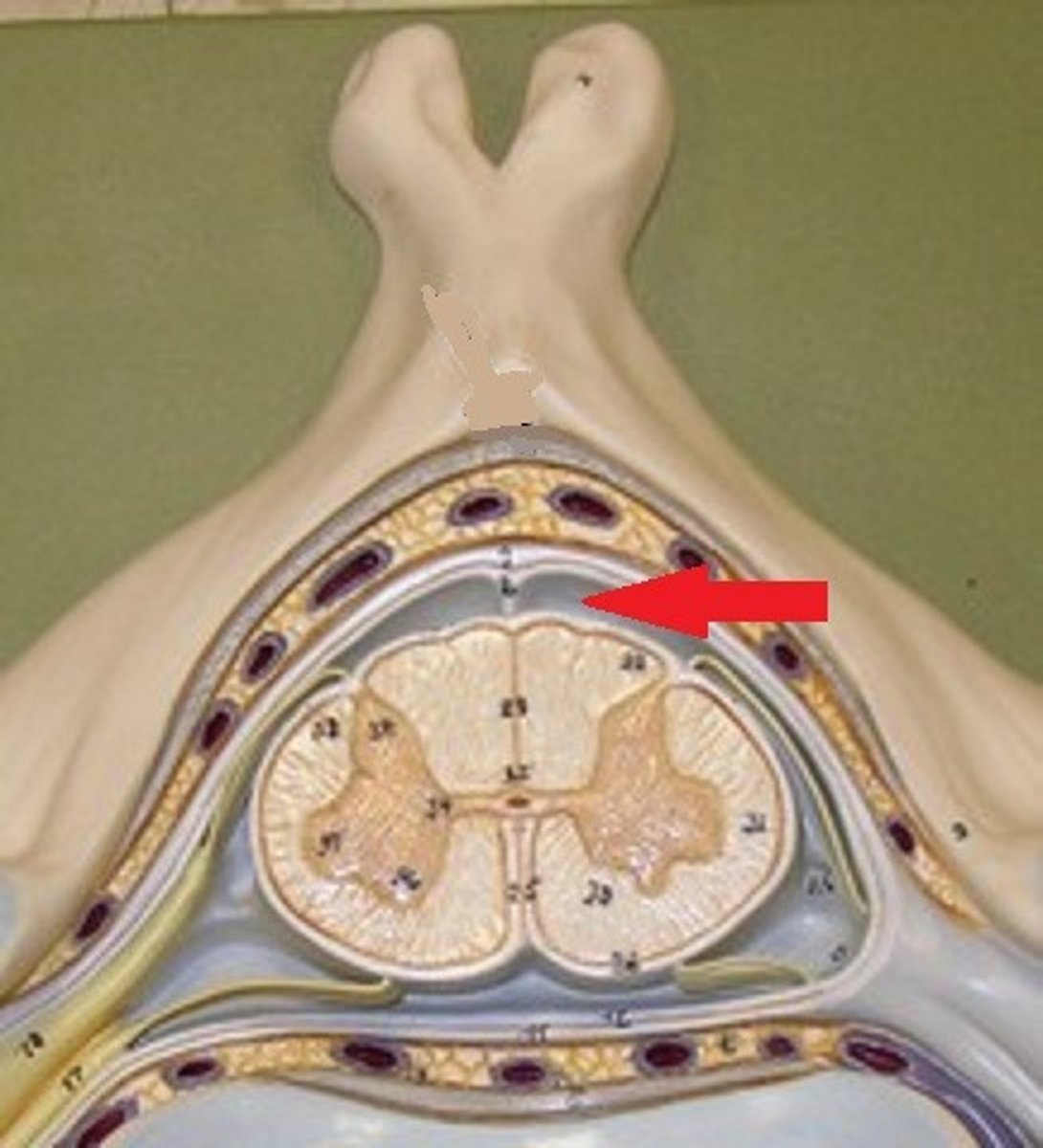
Where CSF flows--a space beneath the arachnoid membrane (and above the pia mater) that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
Sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron - Identification
Identification
spinal cord functions
1) Carries sensory nerve impulses from the sensory receptors to the brain.
2) Carries motor nerve impulses from the brain to the effectors.
3) It serves as a reflex center.

ganglia
Collections of neuron cell bodies outside the central nervous system (CNS)
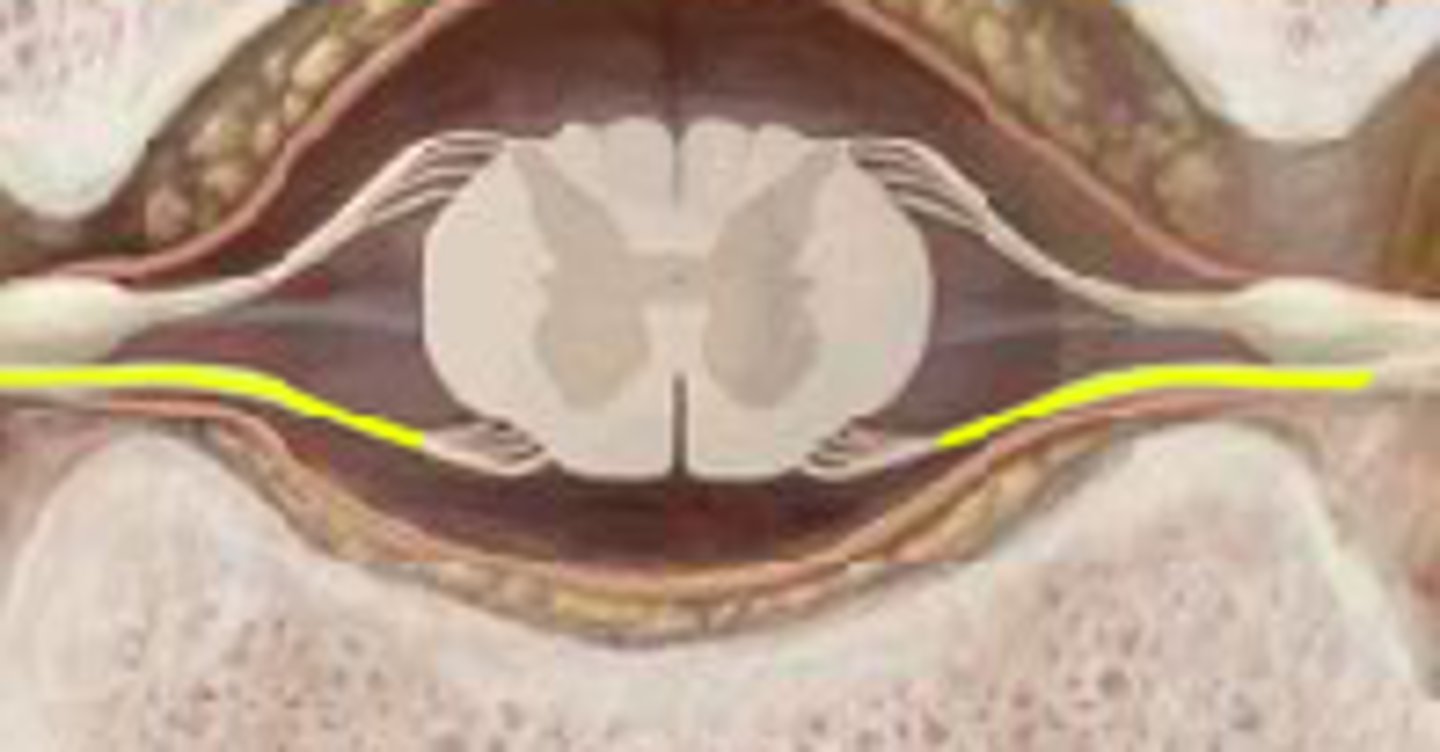
ventral root of spinal nerve
responsible for motor output (contain axons of EFFERENT motor neurons)
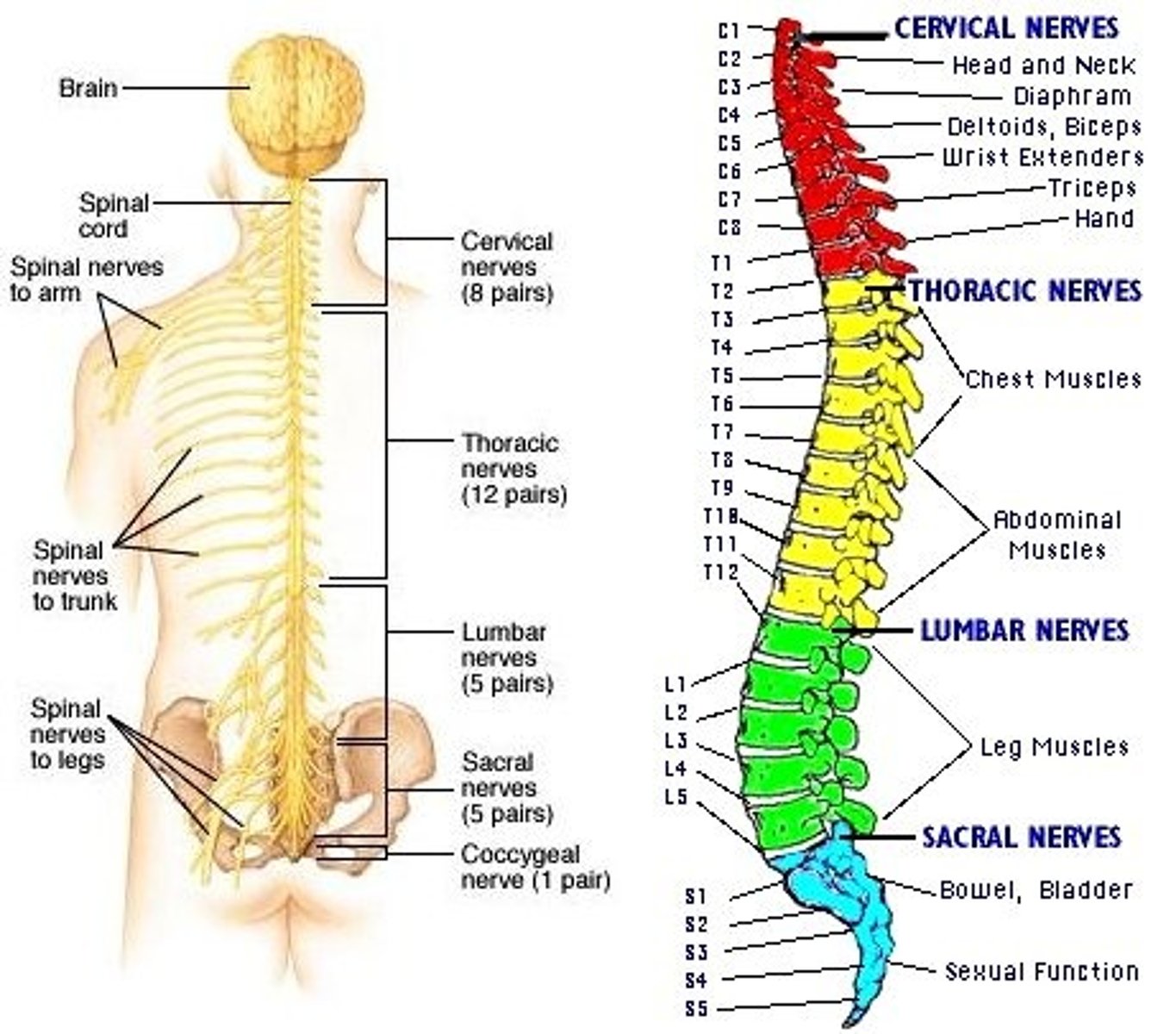
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31 pairs (62 in all)
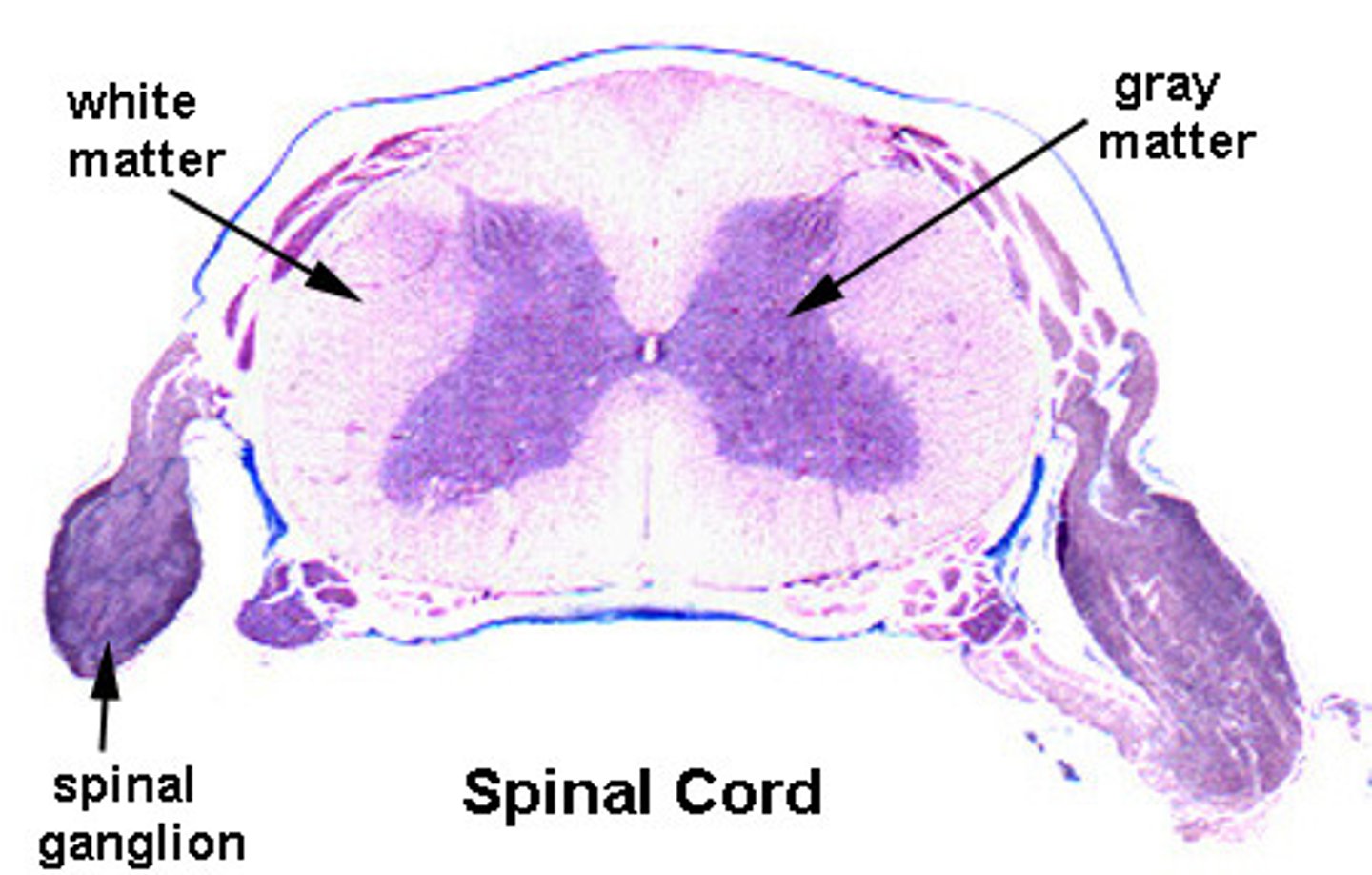
white matter of spinal cord
Composed mostly of myelinated axons.
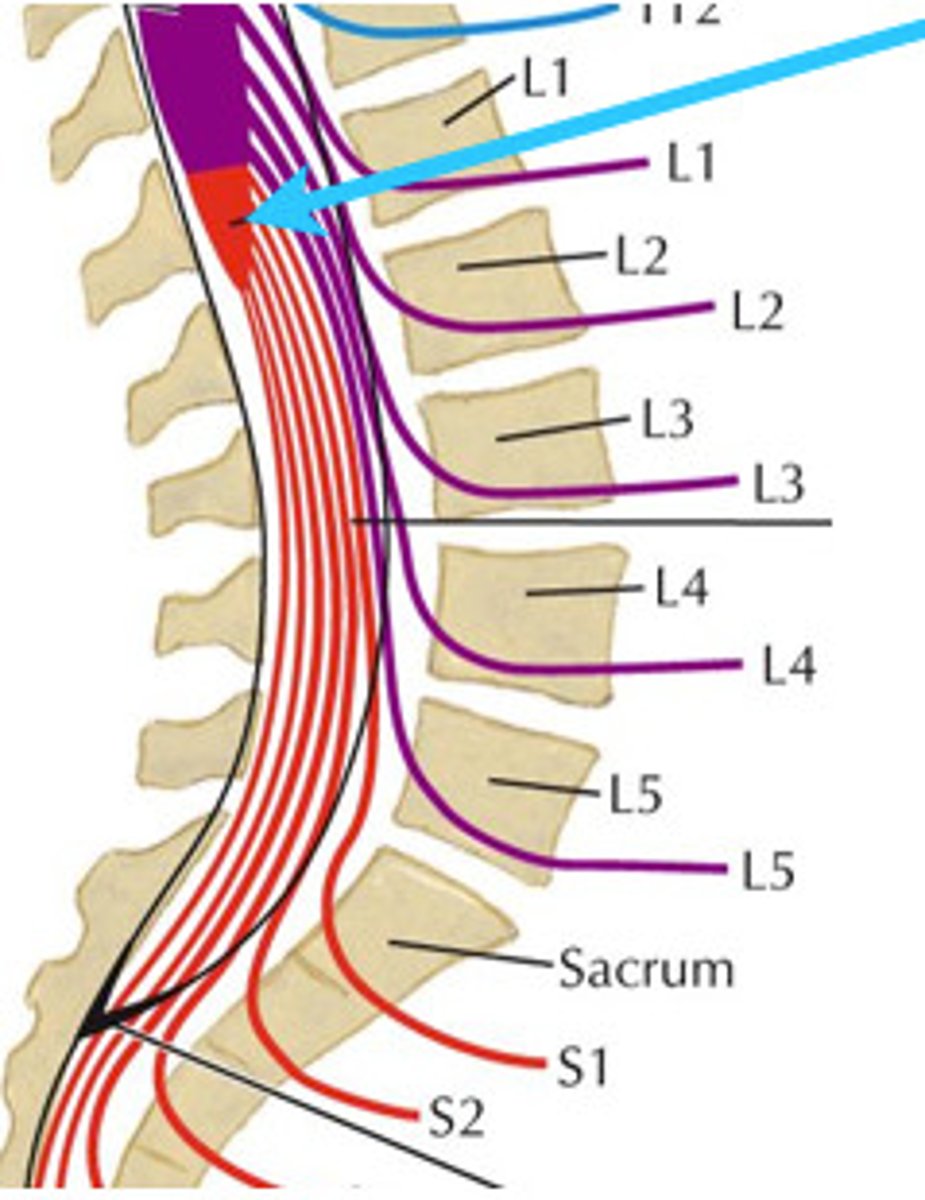
Where does the spinal cord terminate?
It usually ends at Lumbar Vertebra #1 or #2
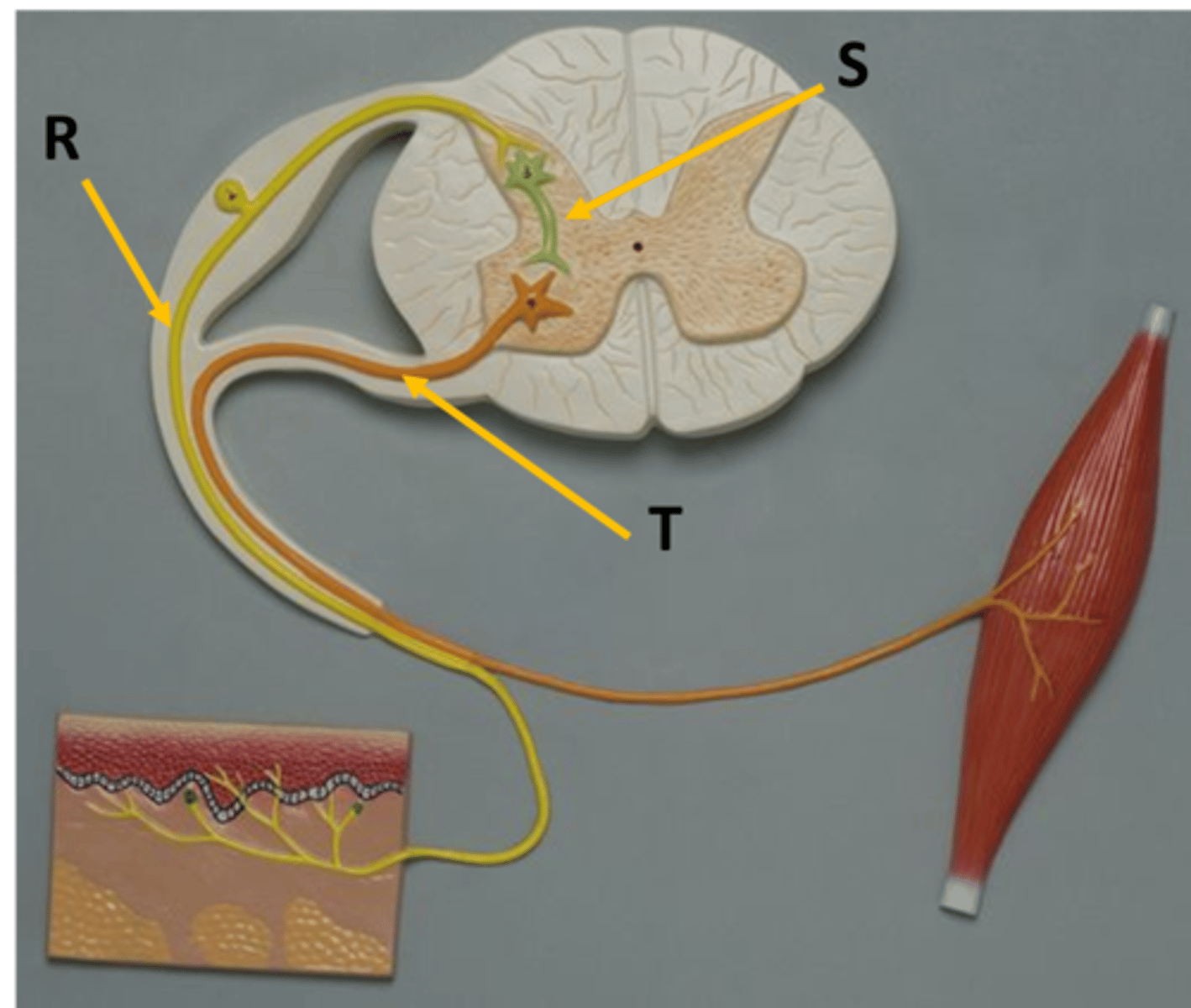
Which is the sensory/ afferent pathway?
C (pathway ID)
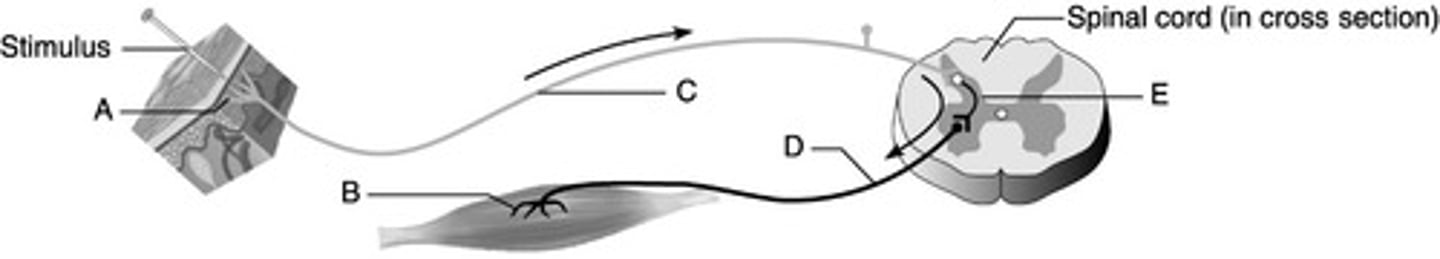
B (pathway ID)
Which is the effector?
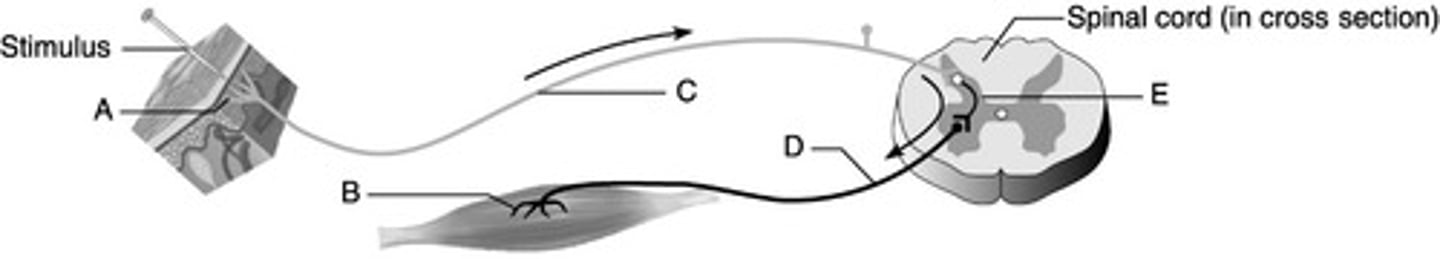
E (Image ID)
Which represents the interneuron?
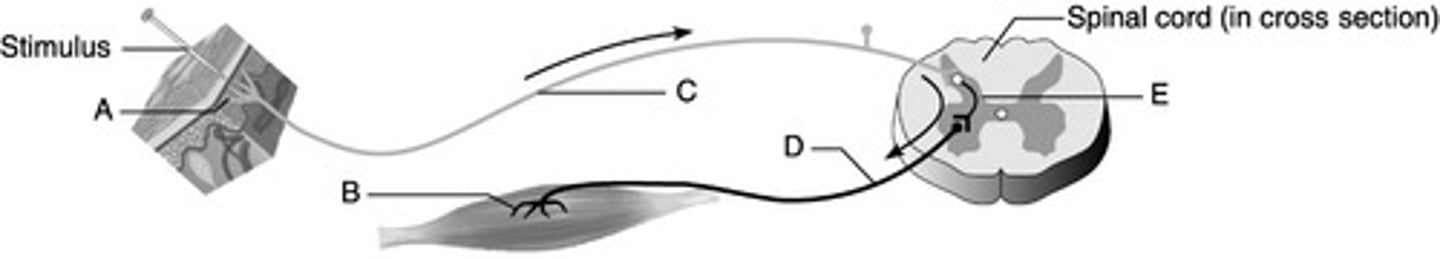
Reflex Centers - characteristics
1) Reflexes are involuntary.
2) Reflex responses are rapid.
3) Reflex responses are predictable.
4) Reflexes responses benefit the body
monosynaptic reflex
Reflex pathway with NO INTERNEURON--only one synapse between the sensory and motor neurons (ex: knee-jerk).
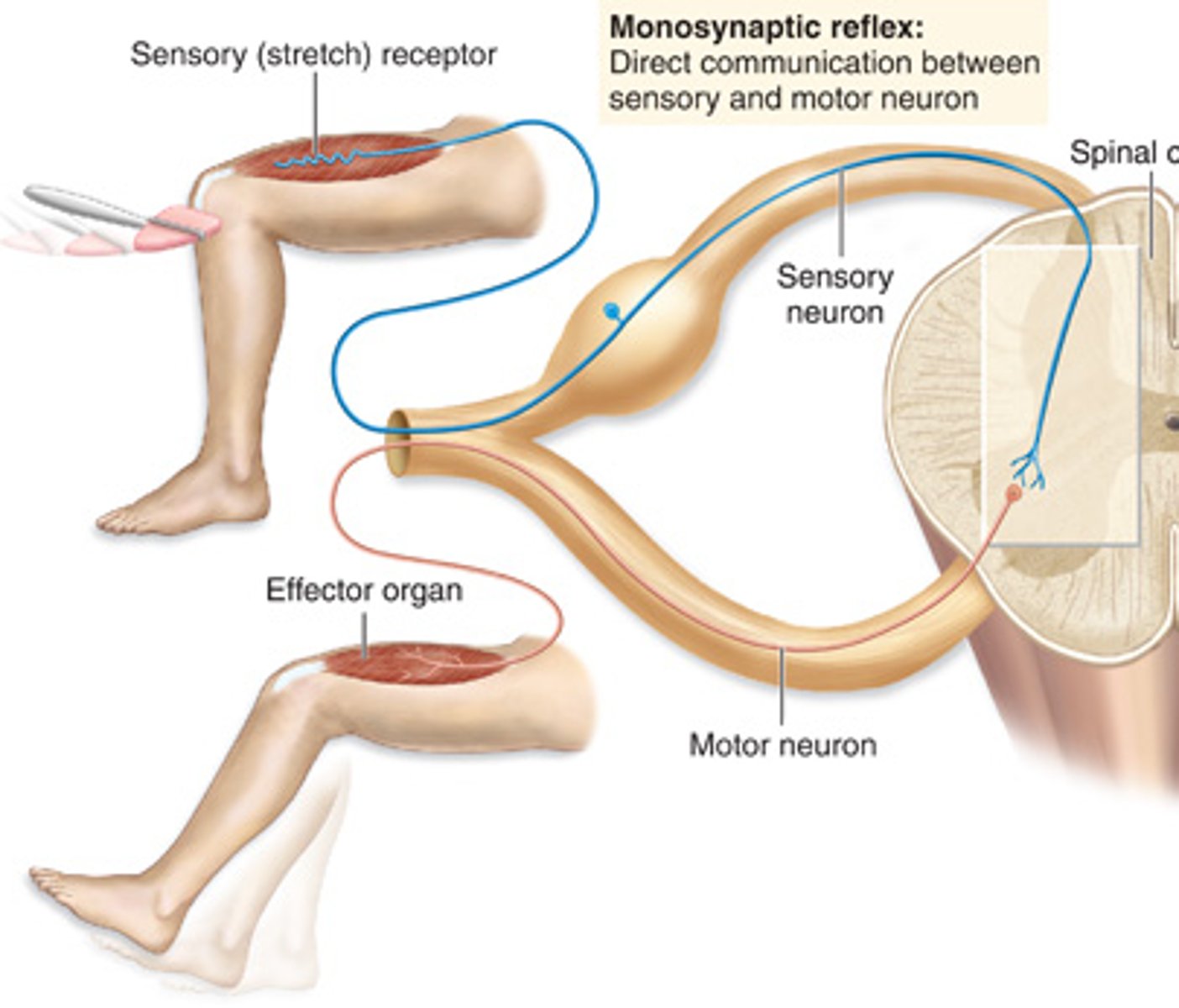
Spinal nerves are __________.
both sensory and motor
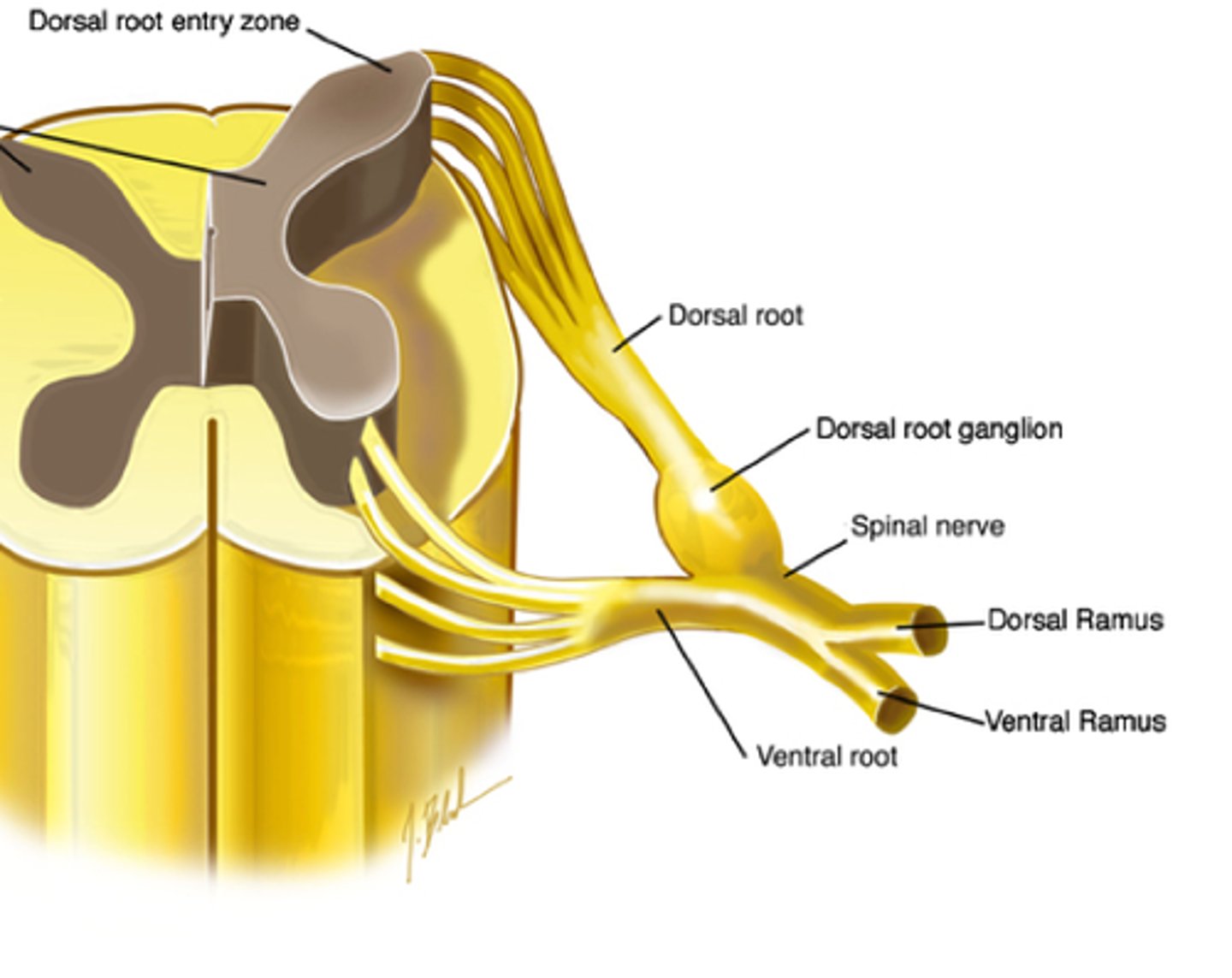
What does the dorsal root ganglion contain?
cell bodies of sensory neurons
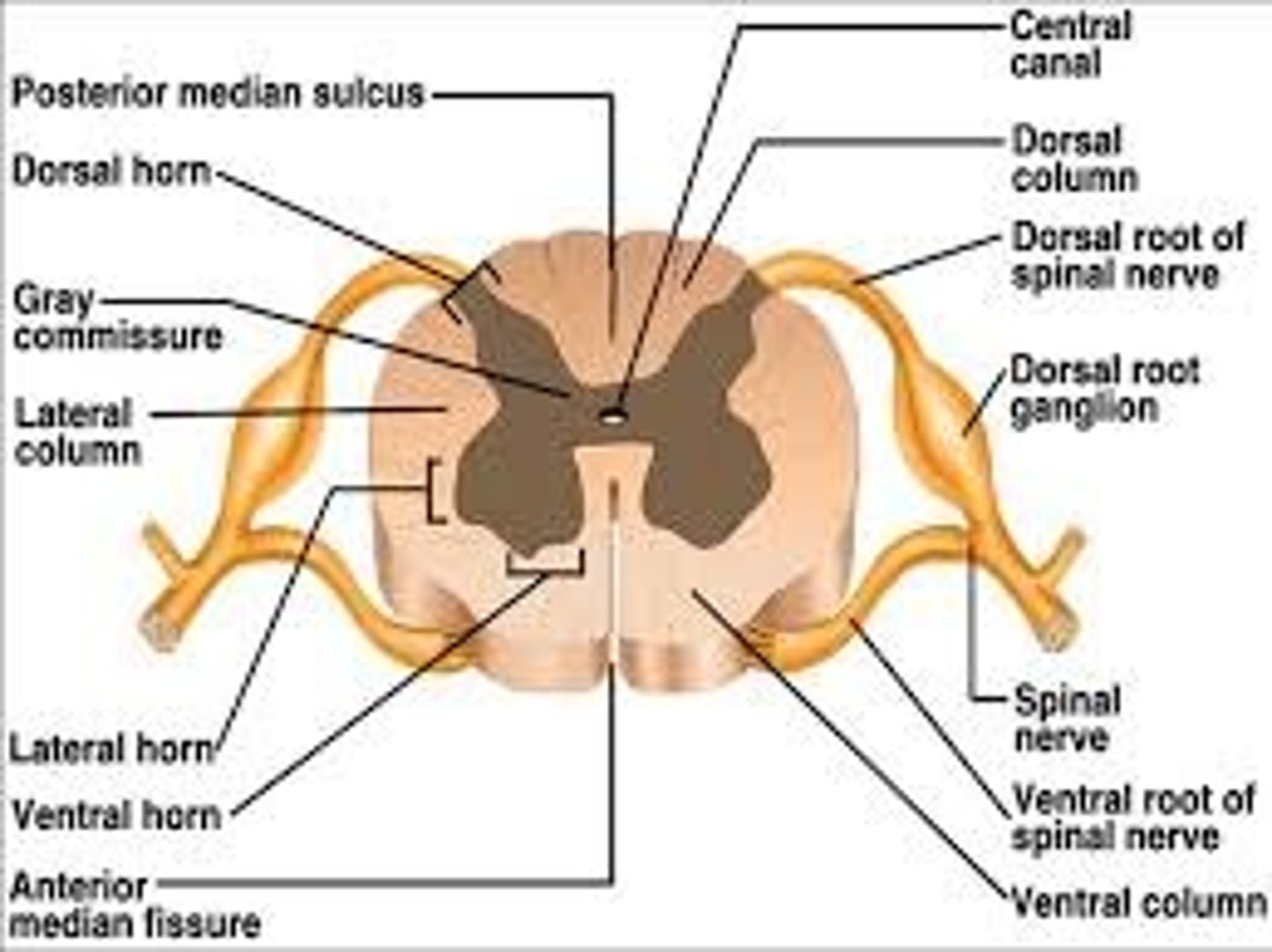
Which structure sends motor signals to muscles of the back, and receives sensory information from the skin of the back?
posterior ramus
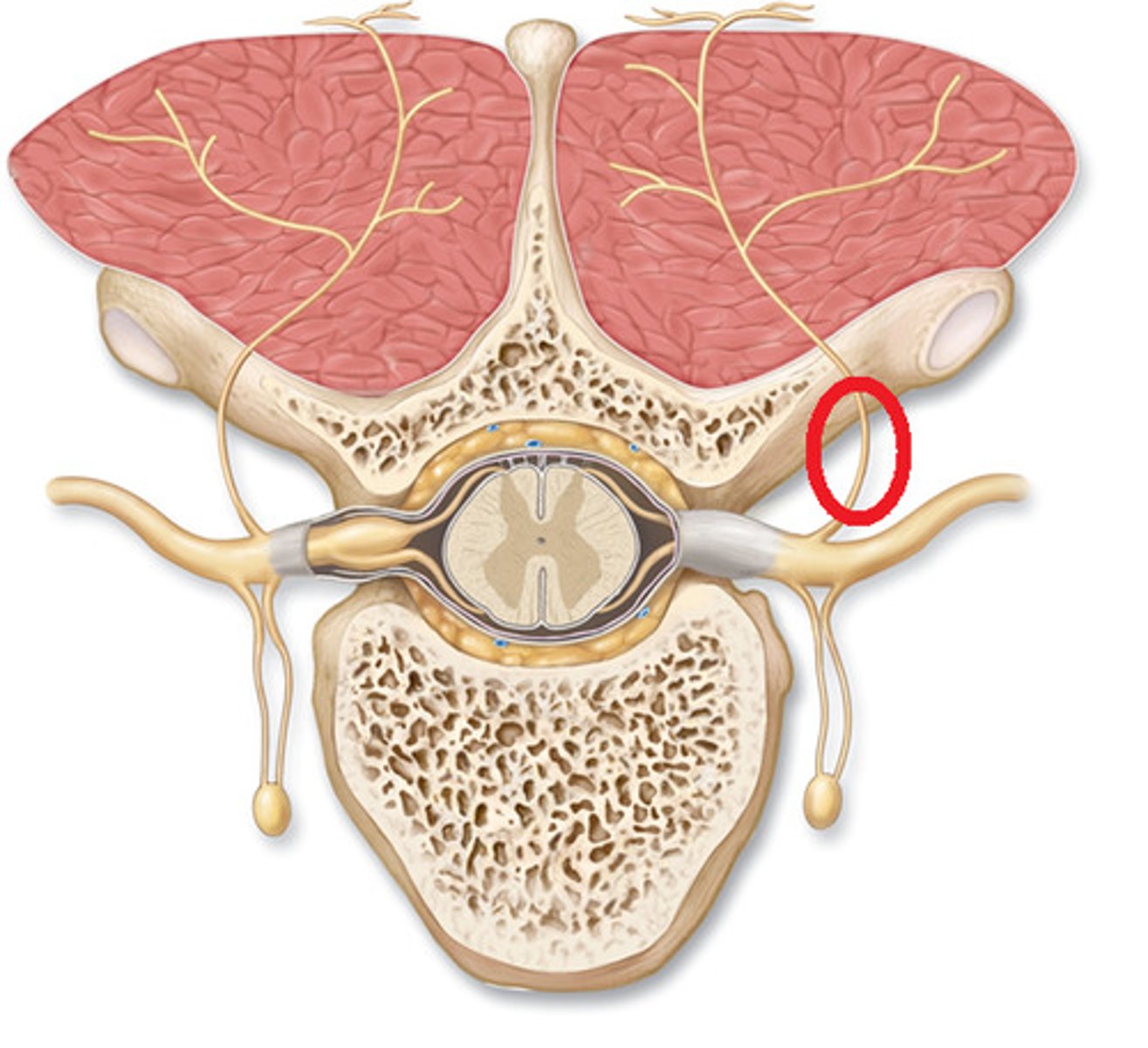
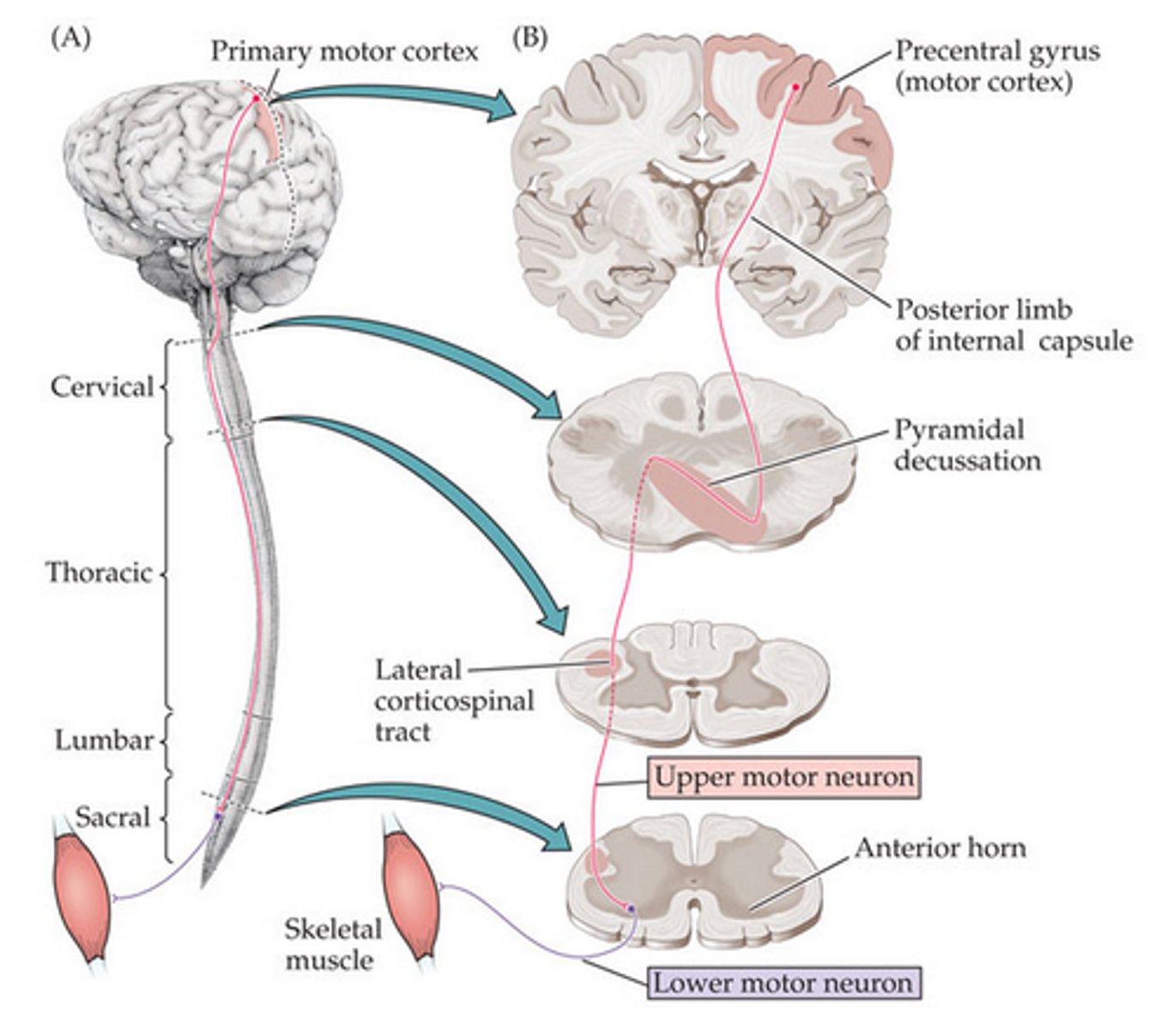
Which tracts in the spinal cord are likely damaged if you can feel sensations from your leg but cannot move your leg?
Corticospinal tract (descending tract) If you can feel sensations from your leg but cannot move your leg, this suggests that DESCENDING motor pathways are damaged while ASCENDING sensory pathways are intact.
Which tracts in the spinal cord are likely damaged if you can move your leg but cannot feel sensations?
sensory tracts --ascending tracts (Spinothalamic tract and dorsal columns)
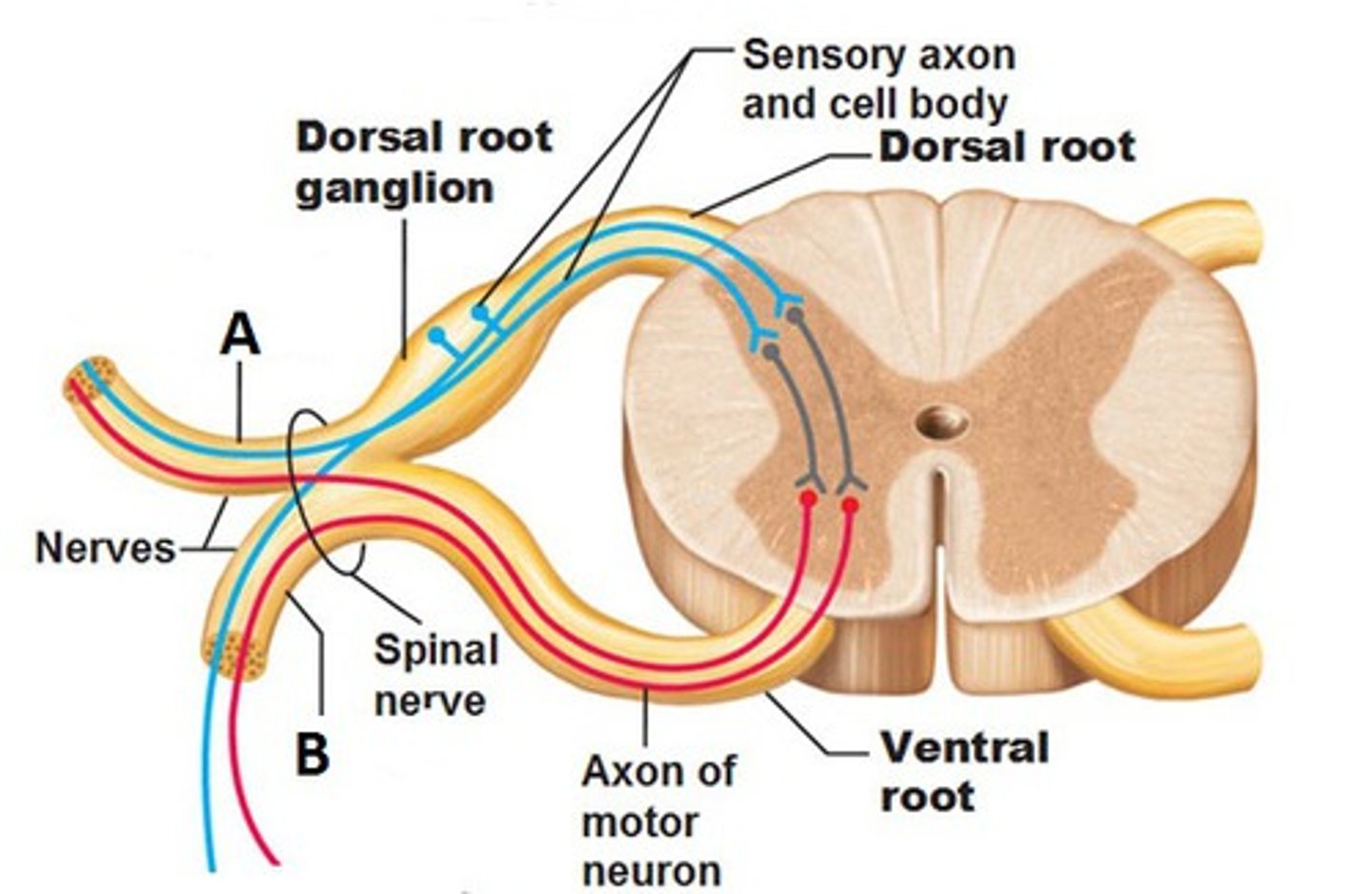
What would happen if the dorsal root of a spinal nerve is severed?
sensory / afferent input would be blocked
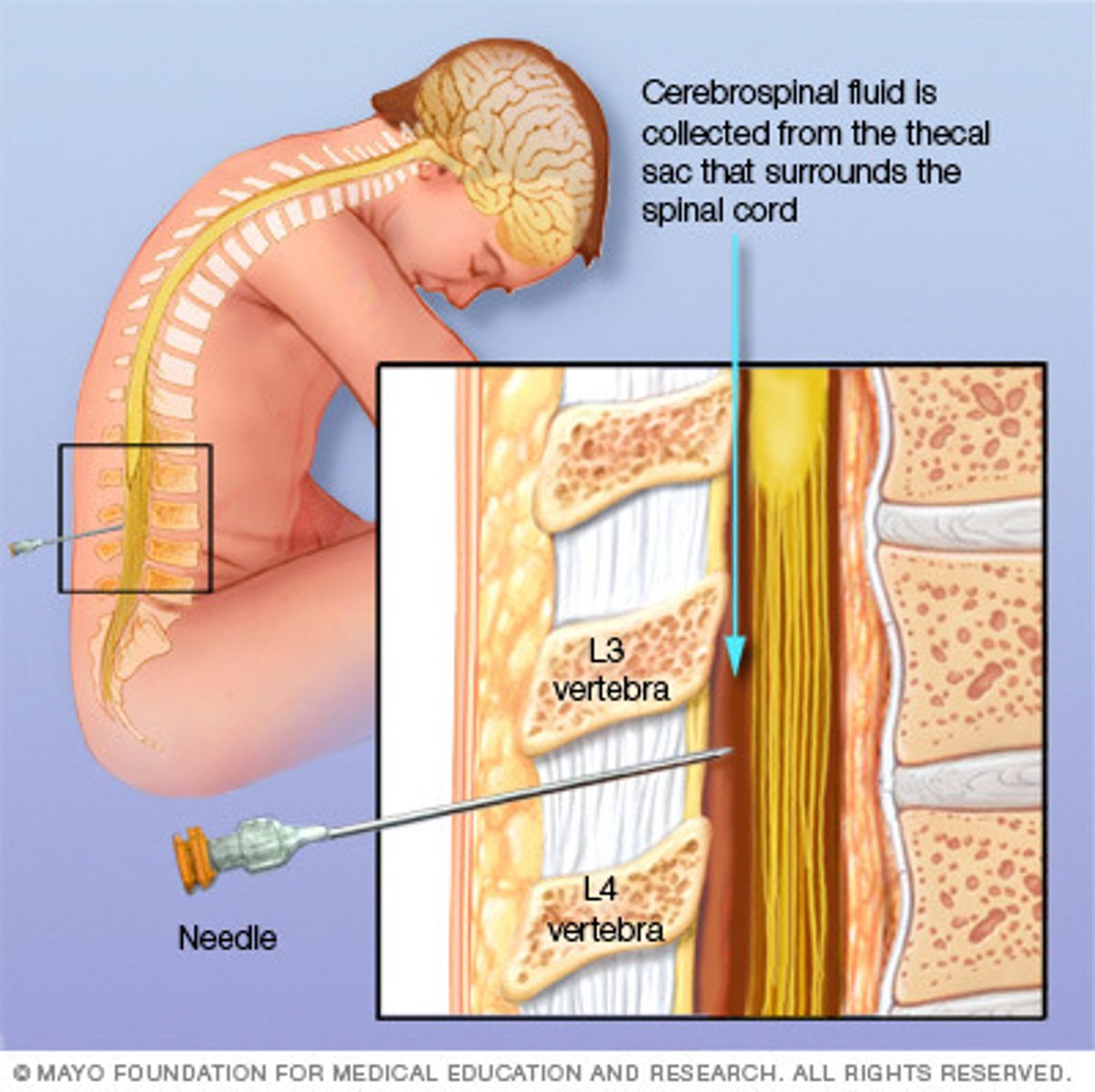
Where are spinal taps of cerebrospinal fluid drawn?
subarachnoid space
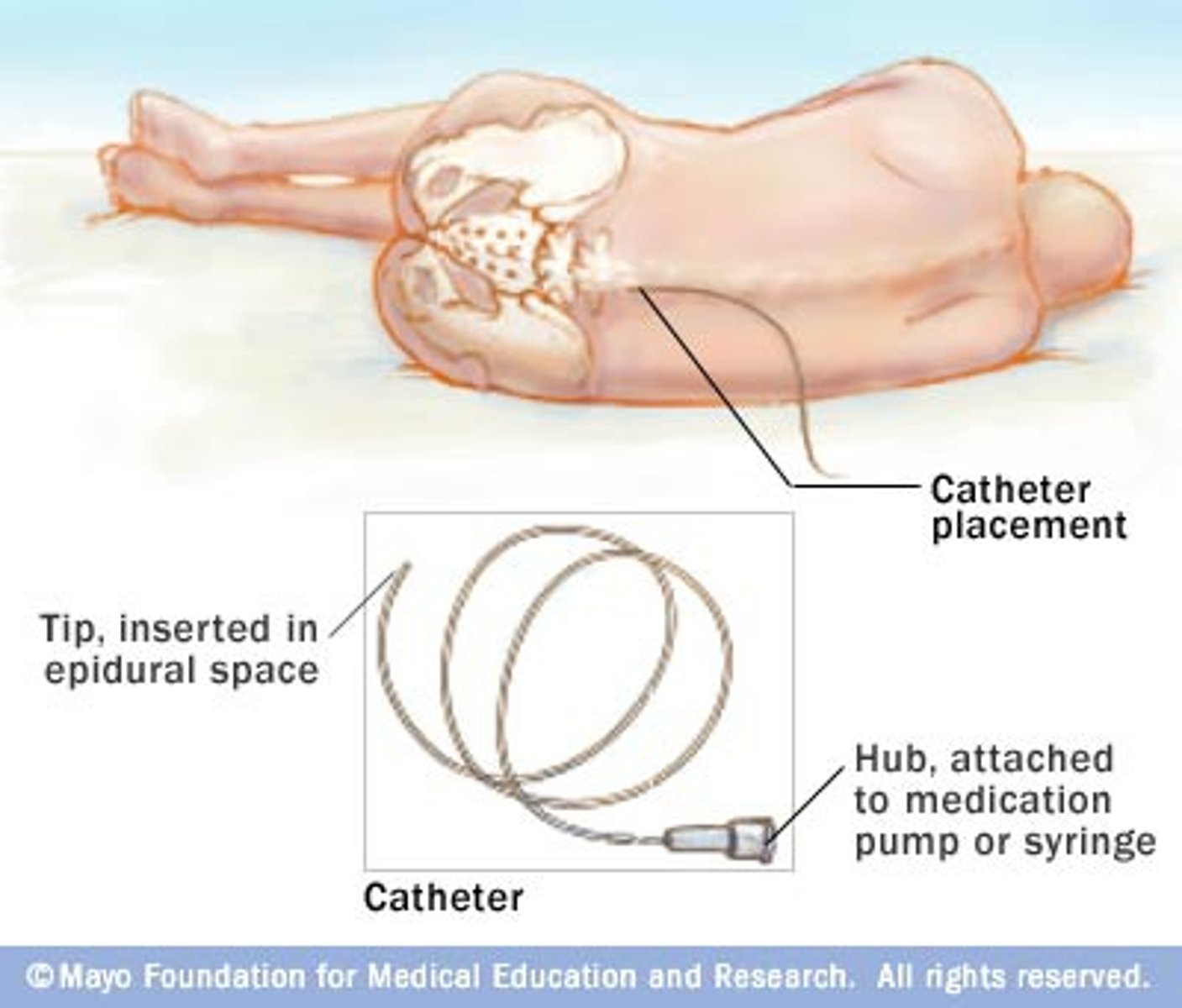
Epidural anesthesia is often used in childbirth during labor because it ________.
it can be adjusted and extended if needed
Which nerve controls movement of the diaphragm, affects respiration, and results in hiccups when it spasms?
phrenic
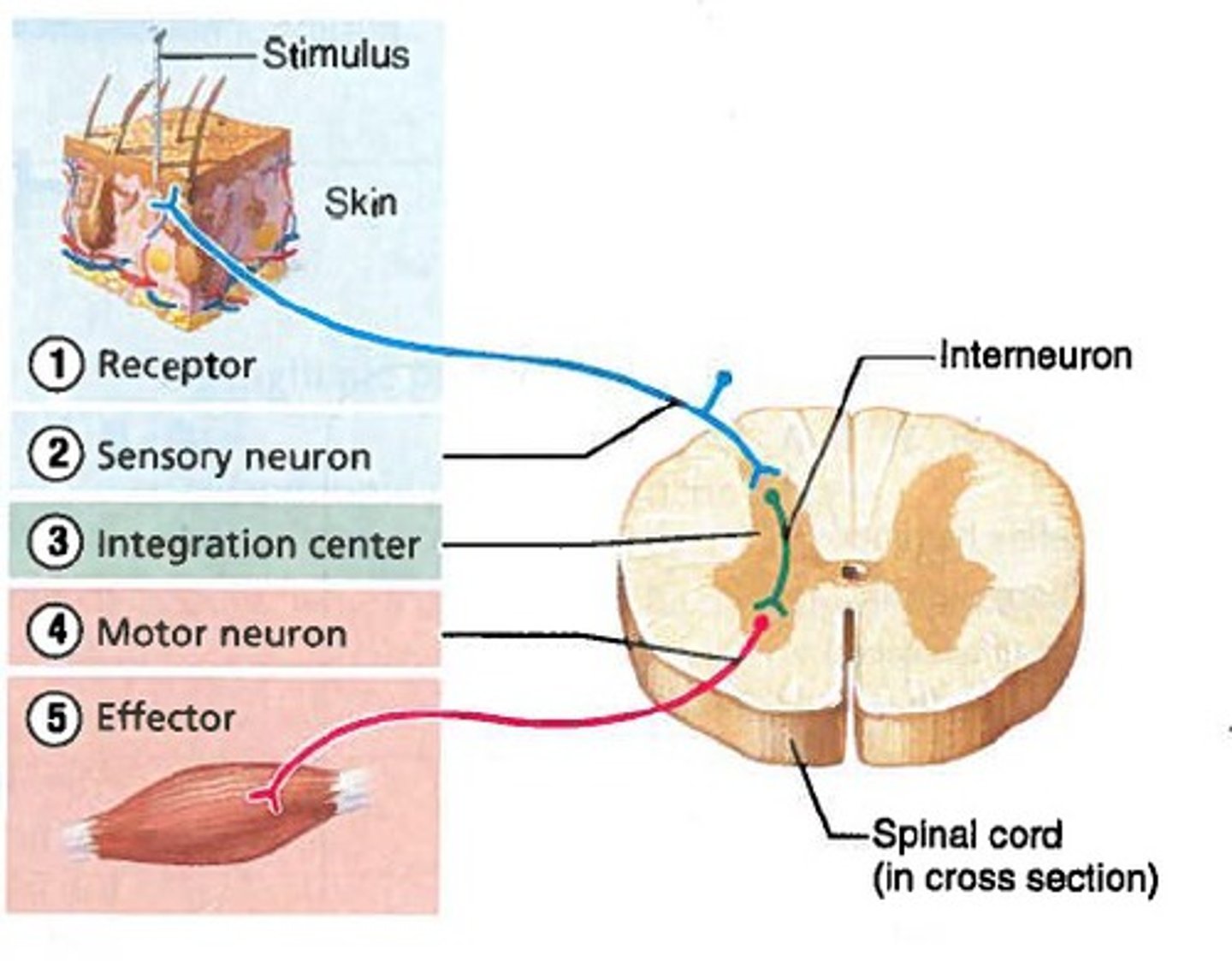
Be able to place the events of a reflex arc in order.
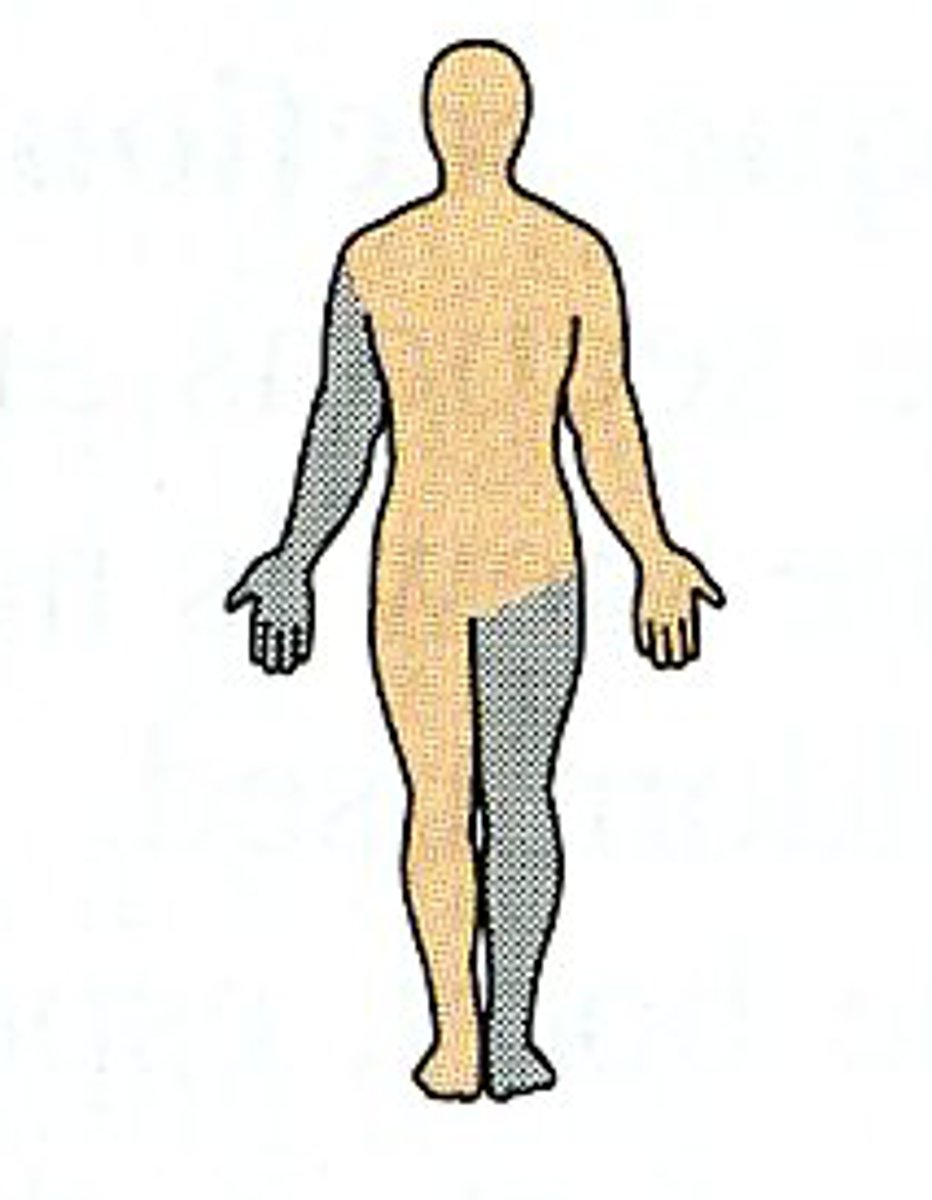
Reflexes that activate muscles on the opposite side of the body as the stimulus are called _______.
contralateral
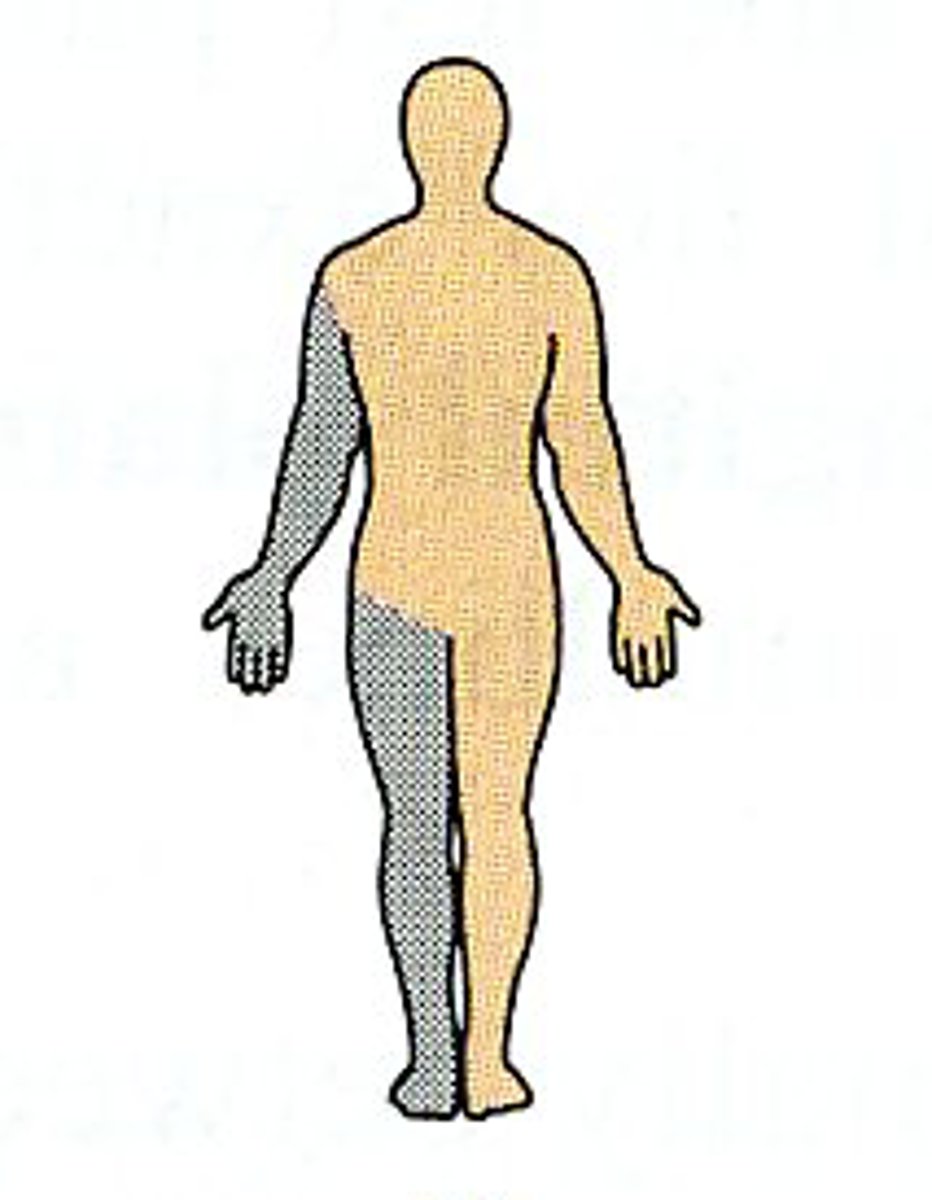
Reflexes that activate muscles on the same side of the body as the stimulus are called _______.
ipsilateral
Reflexes that control the most rapid, stereotyped motor responses to stimuli, such as the patellar stretch reflex, are termed ________.
monosynaptic reflexes
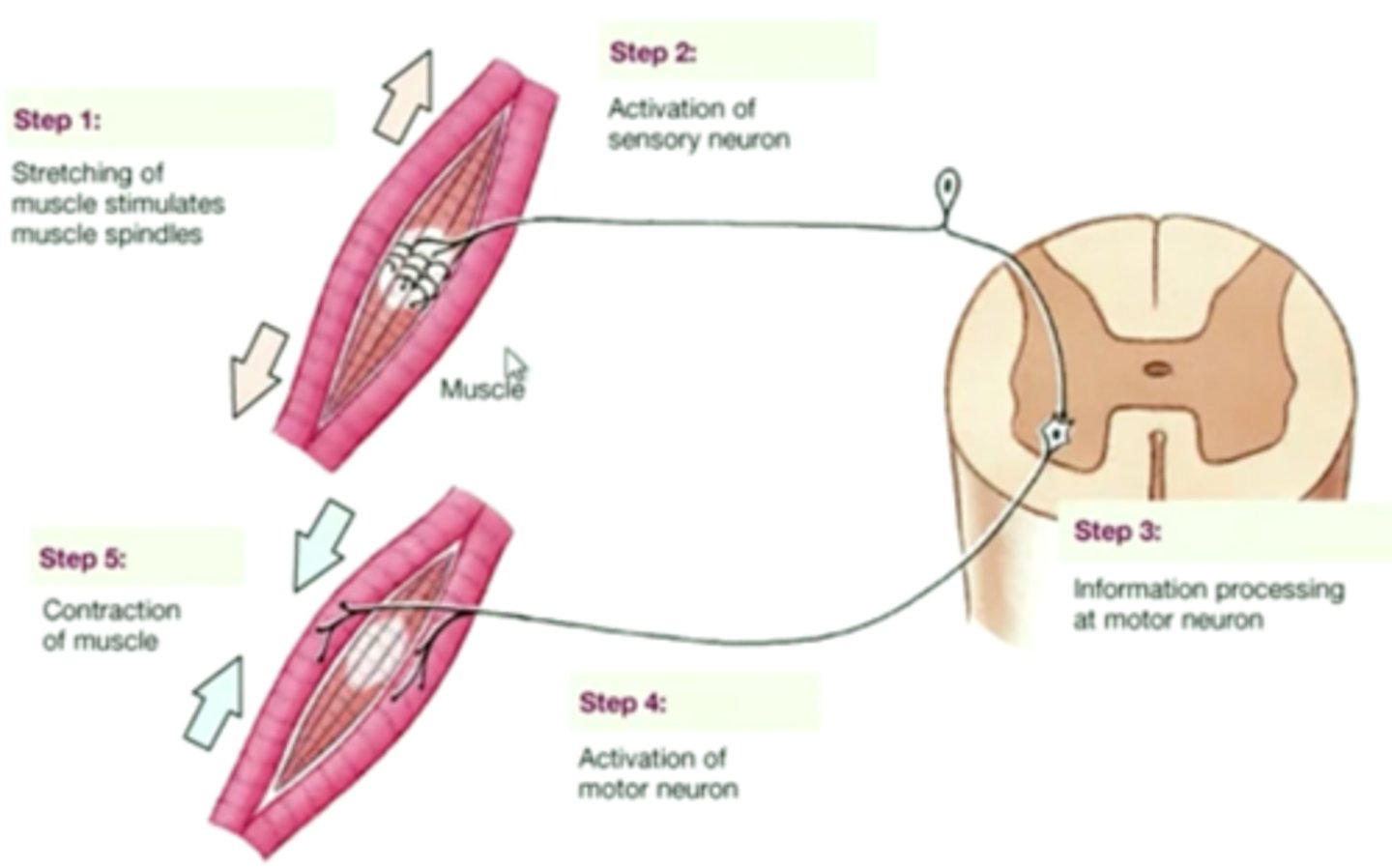
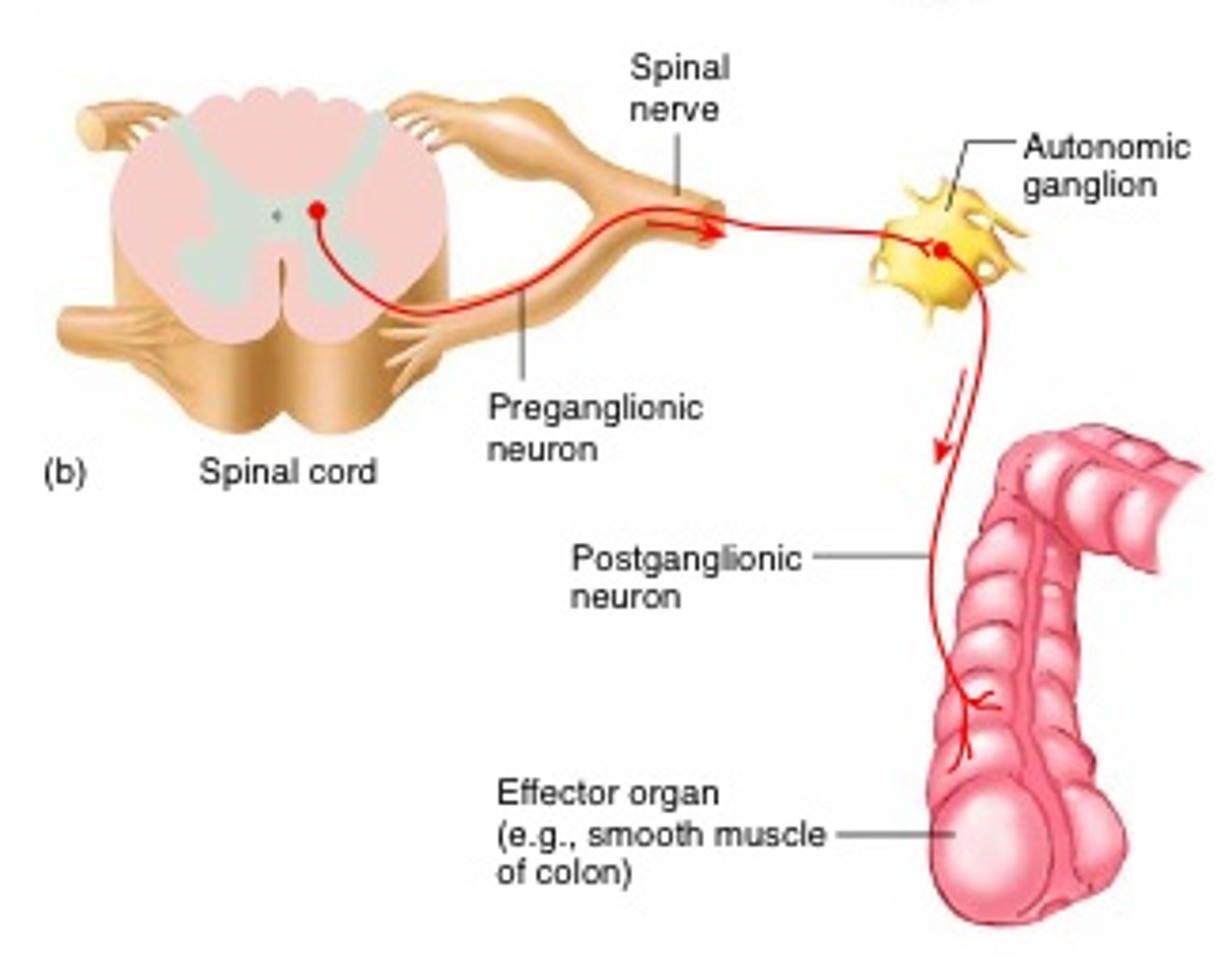
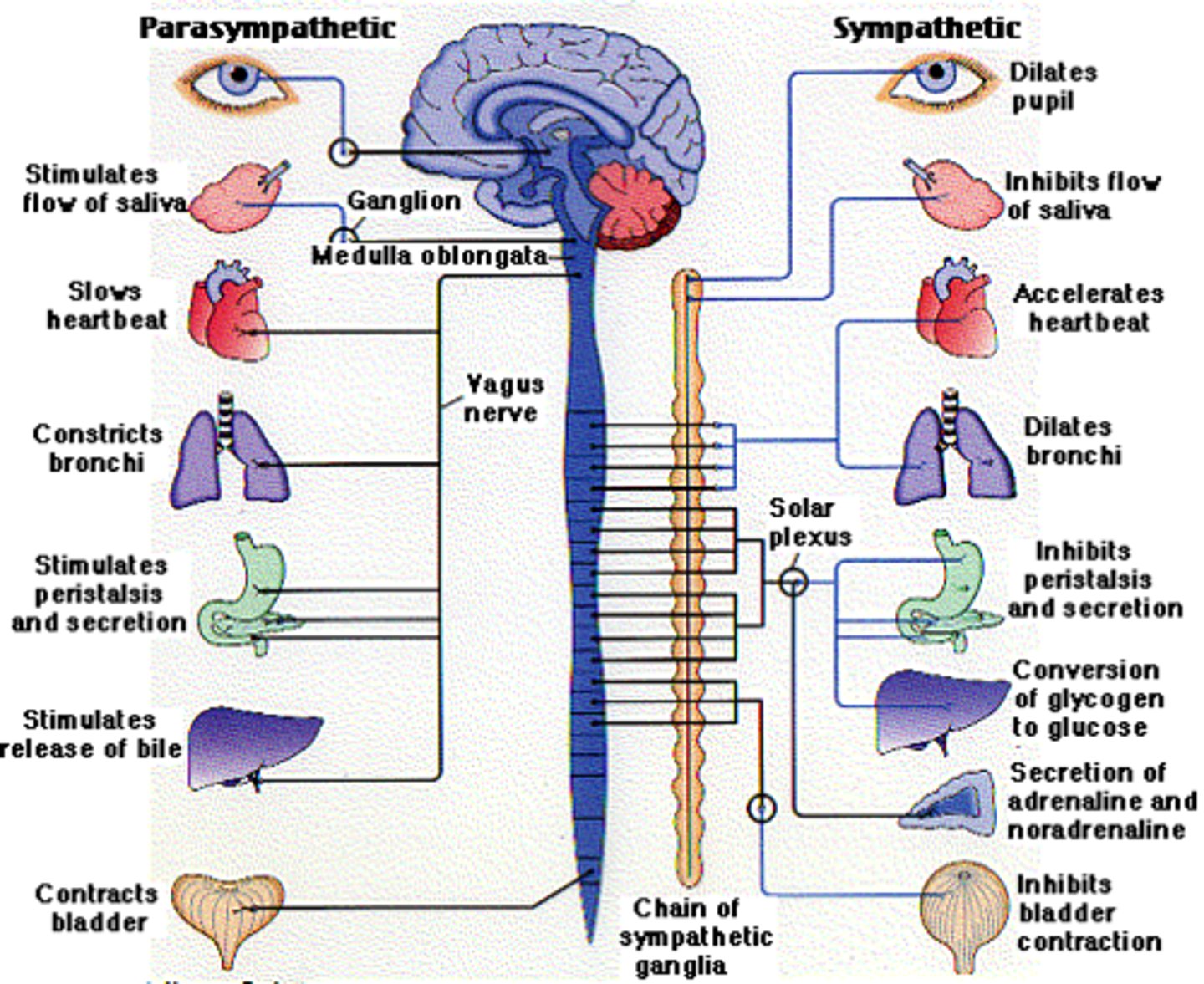
Reflexes that innervate the internal organs and digestive tract are classified as ____________.
autonomic
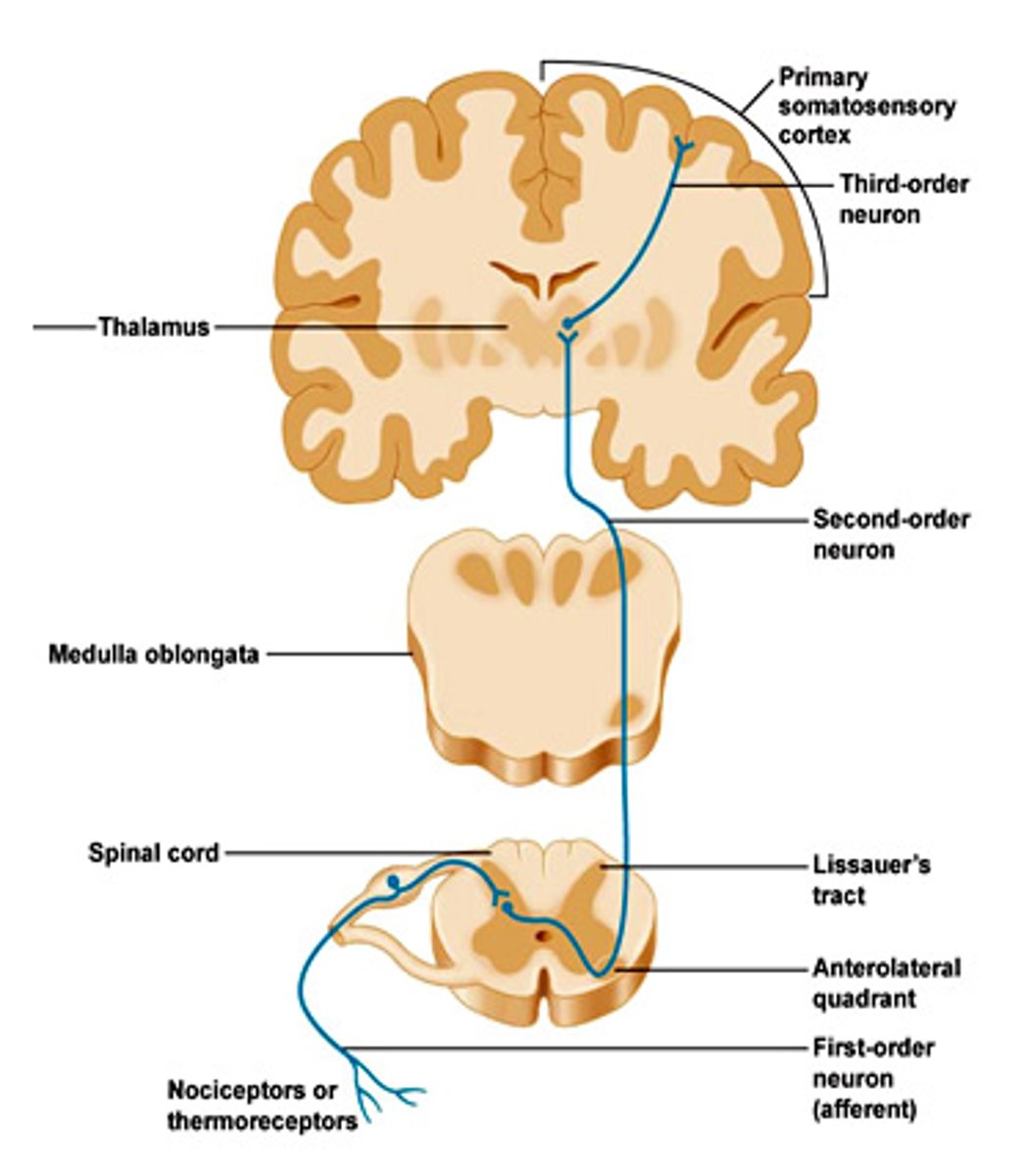
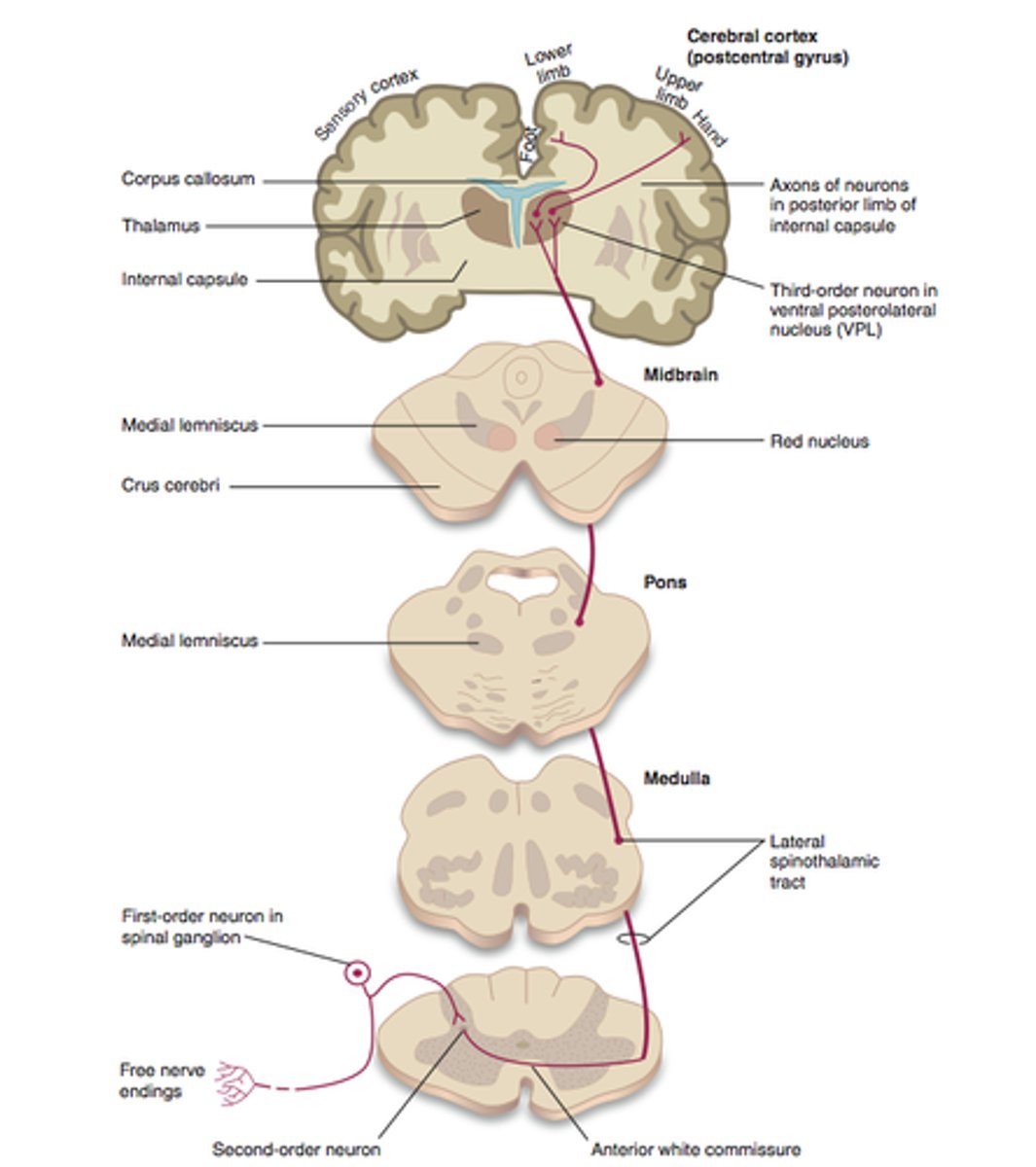
Which of the tract carries pain and temperature sensations?
spinothalamic tract
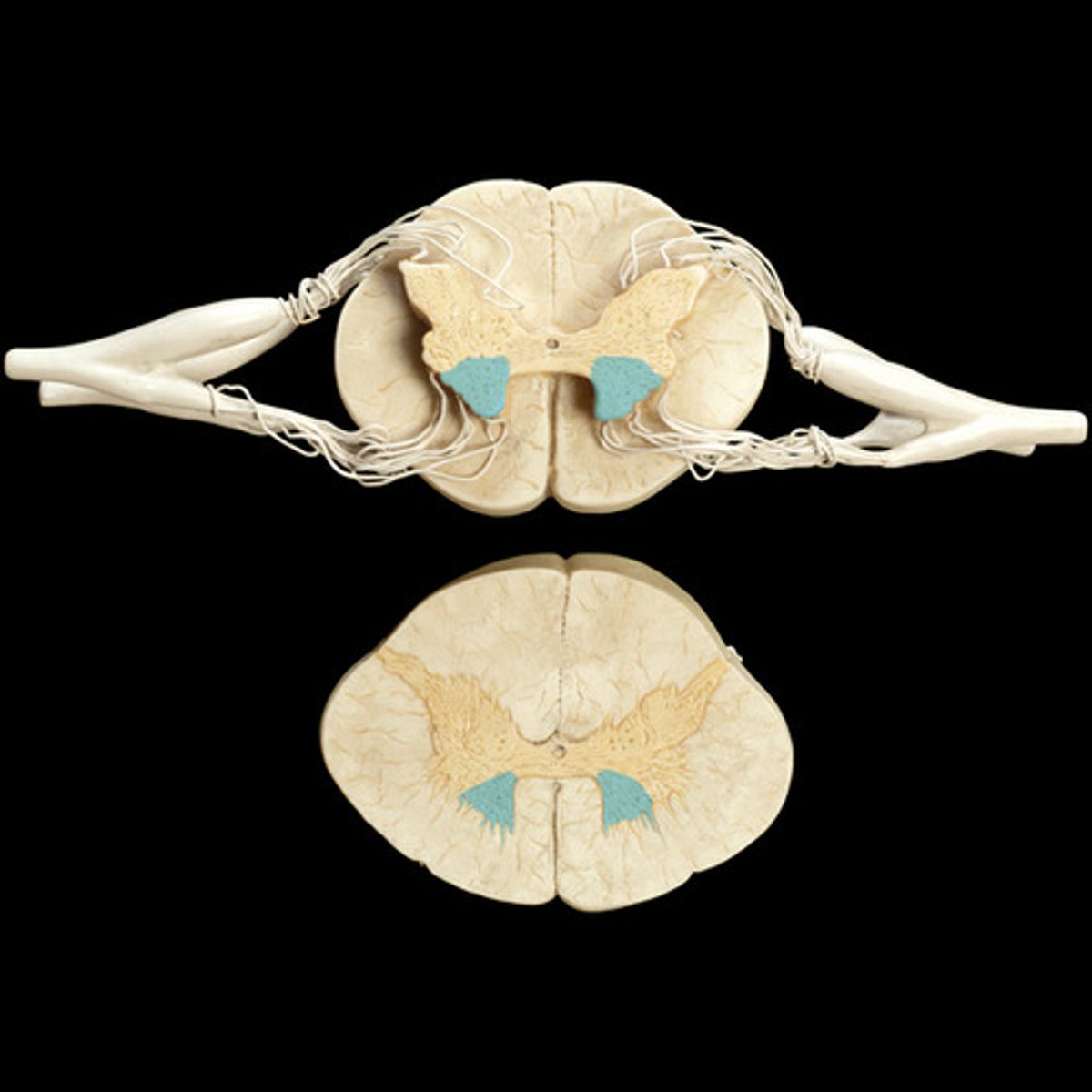
Which part of the spinal cord contains motor neuron cell bodies?
Ventral gray horn
The cauda equina is composed of ________.
spinal nerve roots in the sacral region
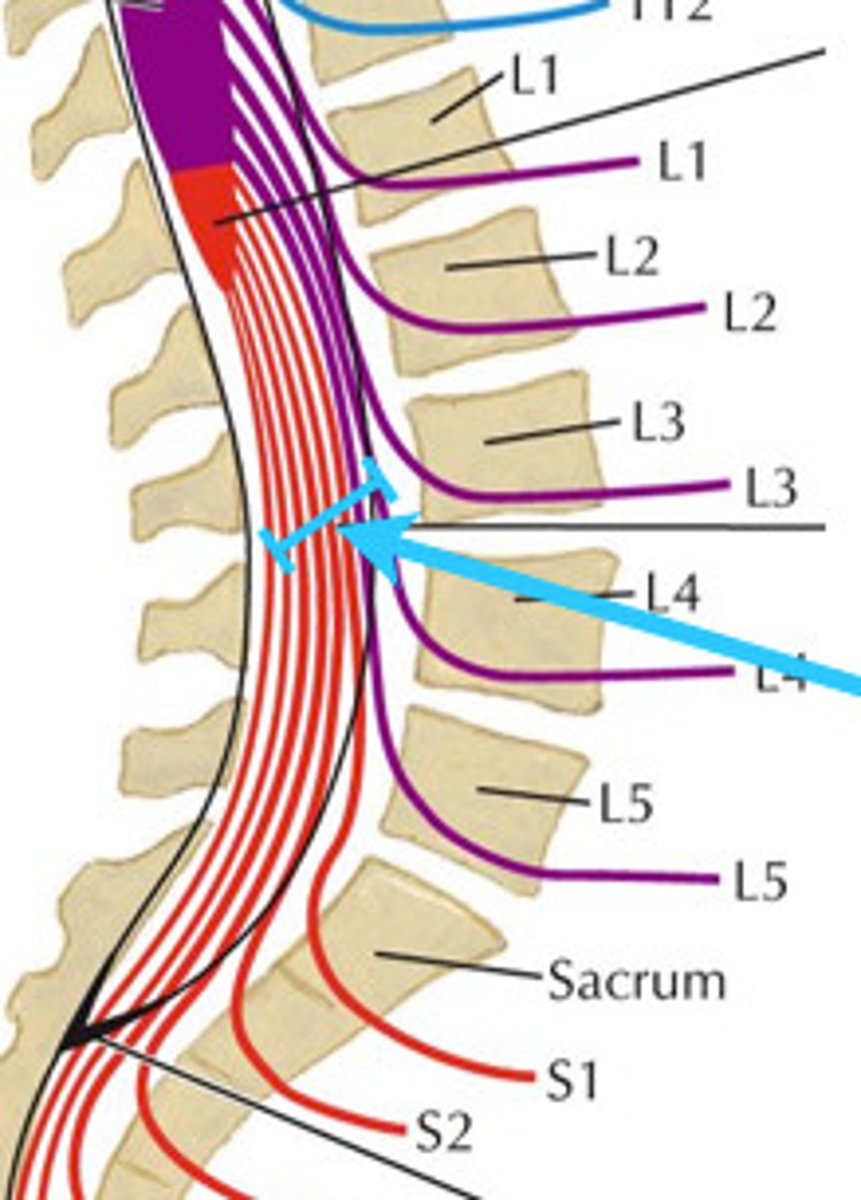
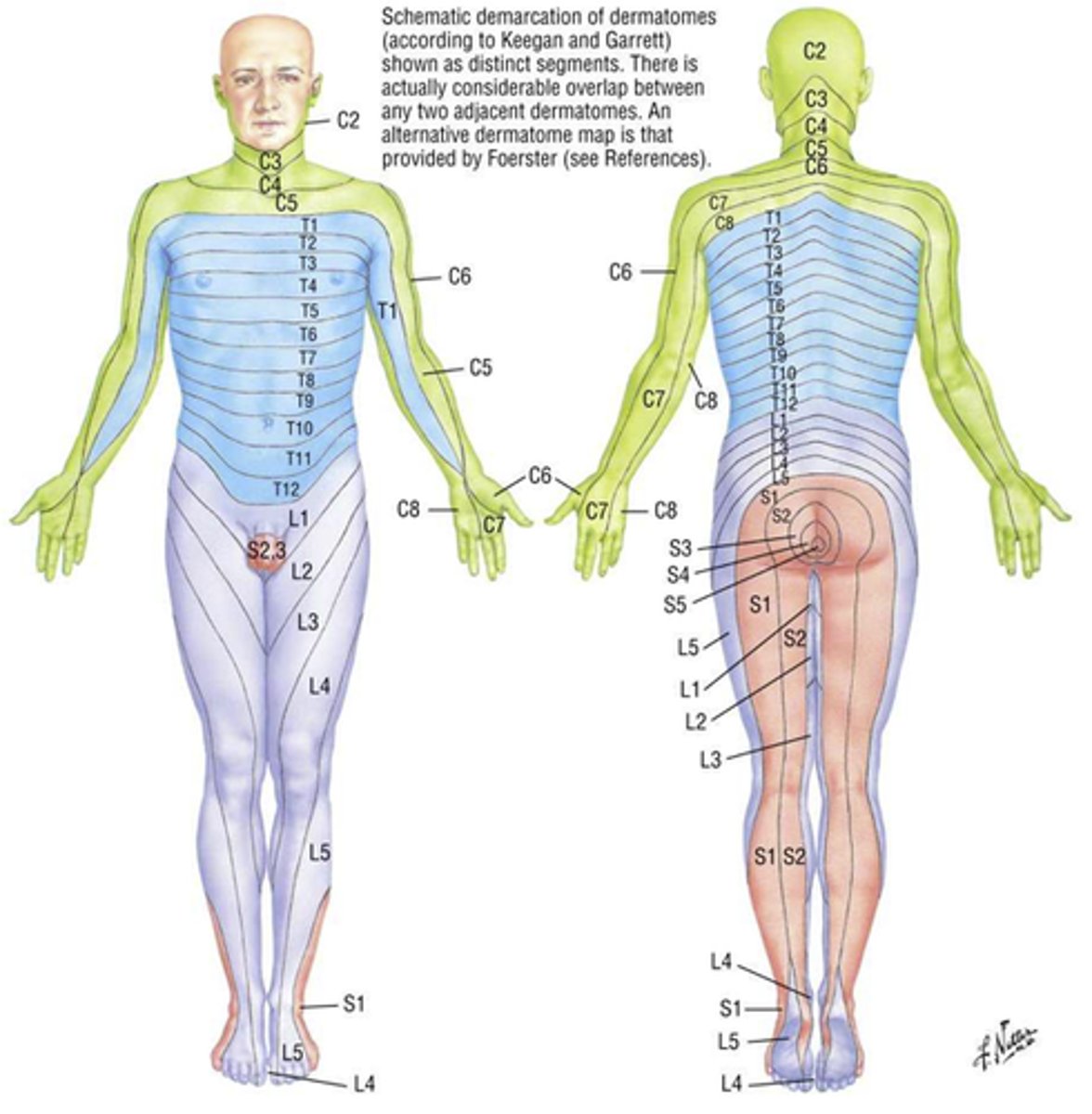
dermatome
A region of skin innervated by a single spinal nerve