CSI exam 2
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hair fibers + paint + soil + drugs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Can a human hair be individualized by morphology alone?
No - it is not possible yet. morphology alone = class characteristics.
What allows partial individualization of hair?
Isolating and characterizing DNA in hair.
Hair without a follicle provides what type of characteristics?
Class characteristics.
Hair with a follicle provides what type of characteristics?
Individual characteristics (nuclear DNA).
What are the 3 layers of the hair shaft?
Medulla (center), cortex (middle w/ pigment), Cuticle (outer)
In which direction do cuticle scales point?
Toward the tip of the hair.
Why is the shaft the most examined part of the hair?
Because roots (with nuclear DNA) are harder to obtained at crime scenes (degradation + shed hairs lack the follicular tag)
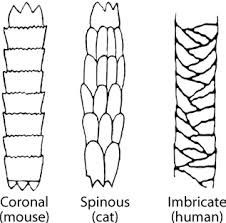
What are the 3 cuticle patterns?
Coronal, Spinous, Imbricate.
Coronal scales look like
A stack of paper cups
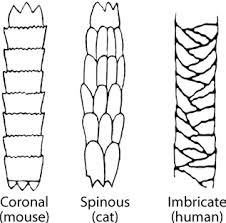
Spinous scales look like
Petal-like/ triangular, protruding.
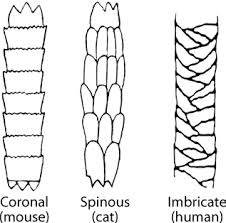
Imbricate scales look like
Flattened, overlapping scales with narrow margins.
why is the cortex important?
It contains pigment granules - color, shape, and distribution are key comparison points.
What is the medullary index for humans vs animals?
Humans smaller or equal to 1/3, animals bigger than or equal to 1/2.