Visual System
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KIN 4571 Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
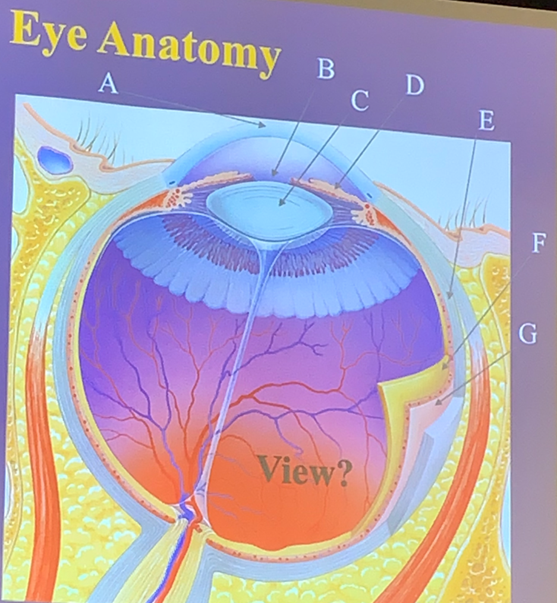
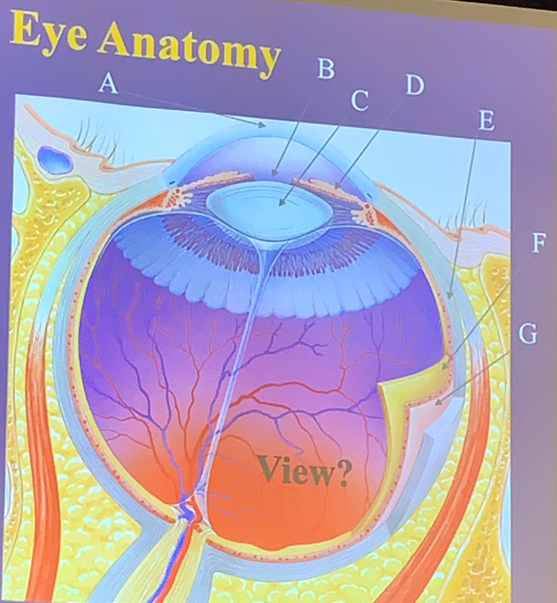
Pupil
The hole in the central iris that allows light to enter the eye.
B
What letter is the pupil?
Iris
Muscles that regulate the amount of light entering the eye, consisting of circular fibers for constriction and radial fibers for dilation.
D
What letter is the iris?
Constriction
Bright light

Relaxed
Normal light

Dilation
Dim light

Sclera
The white part of the eye that shapes and protects it.
E
What letter is the sclera?
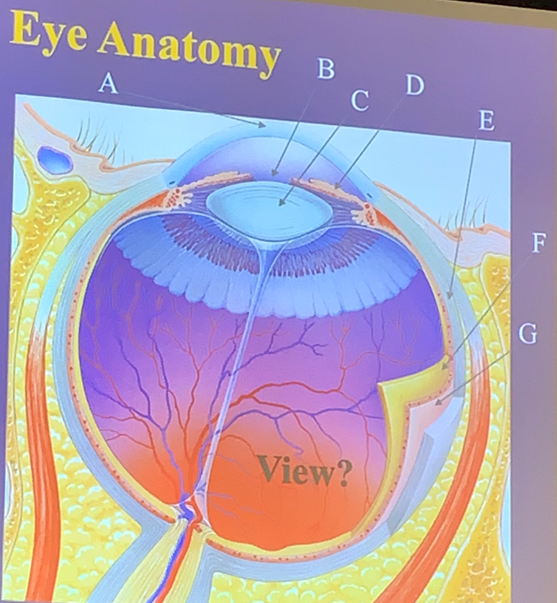
Lens
The part of the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina.
C
What letter is the lens?
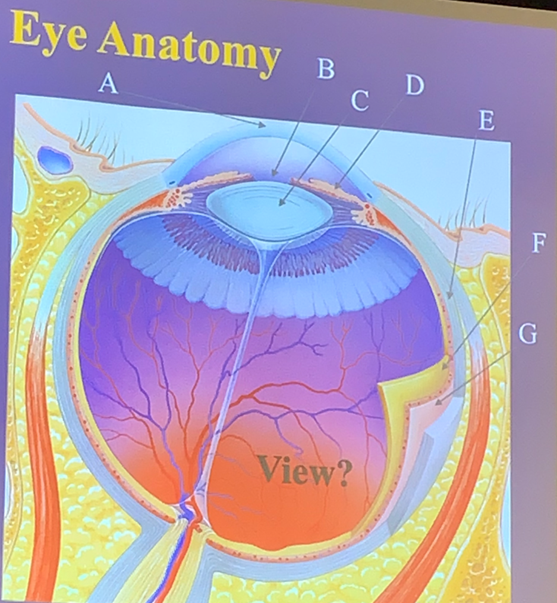
Cornea
The transparent covering of the iris that helps focus light.
A
What letter is the cornea?
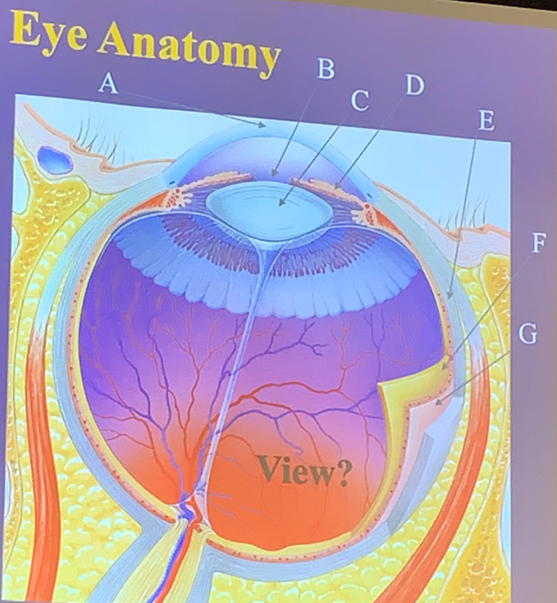
Choroid
The layer that lies within the sclera, providing nutrients to the retina through blood vessels.
G
What letter is the choroid?
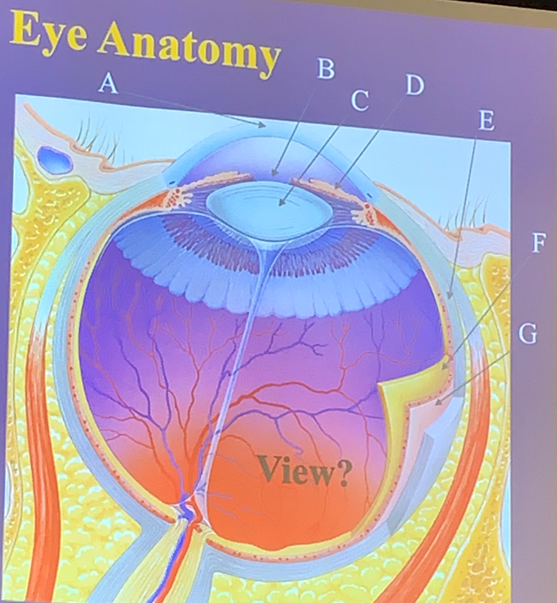
Retina
The layer lining 3/4 of the eyeball, containing photoreceptors like rods and cones and starting the visual pathway.
F
What letter is the retina?
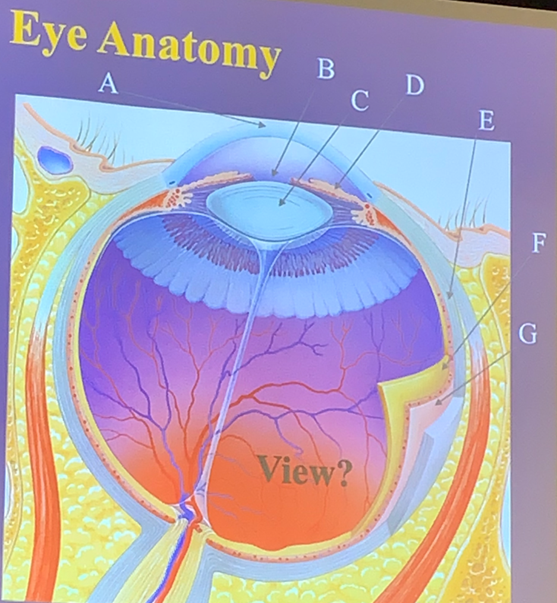
Optic Disc
The start of the optic nerve (CN II); an area on the retina with no photoreceptors.
optic disc
What is the green mark?
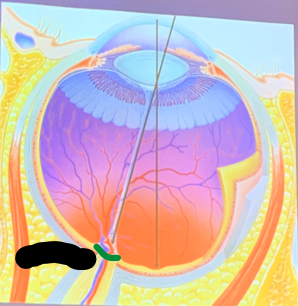
Fovea
The area of the retina with the largest number of cones, providing the clearest vision.
fovea
What is the circled structure?
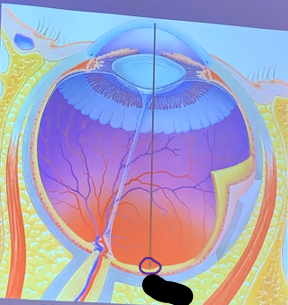
lateral
The fovea is located _______ to the optic disc, thus making the “blind spot” for the left eye on the left side
Blind Spot
The area on the retina without photoreceptors; corresponding to the optic disc.
left
The left eye blind spot is on what side?
right
The right eye blind spot is on what side?
Monocular Vision
The visual field with one eye open, resulting in a field of 160 degrees wide by 135 degrees high.
Binocular Vision
The visual field with both eyes open, resulting in a wider field of 200 degrees wide by 135 degrees high.
Binocular Overlap
The area in the visual field where the images from both eyes overlap, allowing for depth perception and a more accurate perception of objects. The field of view is 120 degrees wide by 135 degrees high.
height; width
________ of the visual field does NOT change, but ________ gets bigger.
retina, optic disc, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus (Thalamus), optic radiations, primary visual area (Occipital lobe)
order of visual pathway
bilateral
The visual pathway is _________
Dorsal Stream
The visual processing pathway that answers the question 'where/how?' regarding objects. It is about the “action”. Ex. when seeing a football being thrown, this pathway would answer how fast the football is going and where.
dorsal stream
What is the green part?
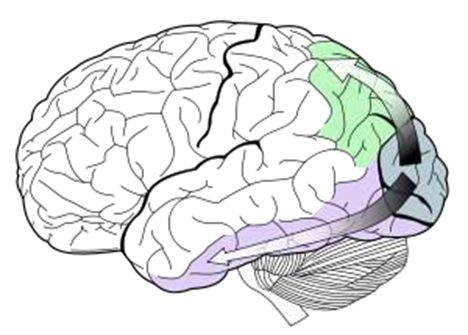
Ventral Stream
The visual processing pathway that answers the question 'what?' regarding objects. It is about the “perceptual”. Ex. when seeing a football being thrown, this pathway would answer that it is a football.
ventral stream
What is the purple part?
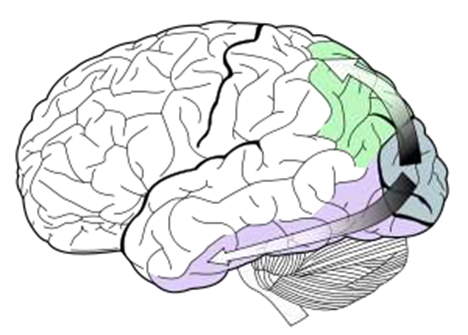
medially
If an image hits _________, it will cross at the optic chiasm
laterally
If an image hits _________, it will not cross at the optic chiasm and stay ipsilateral
left
The right field is processed by the ______ brain
right
The left field is processed by the ______ brain
Optic Chiasm
The point where optic nerve fibers cross over; crucial for visual information processing.
Optic Tract
The pathway carrying visual information from the optic chiasm to the lateral geniculate nucleus.
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
The relay center in the thalamus for visual information, part of the visual pathway.
Optic Radiations
The pathways that carry visual information from the lateral geniculate nucleus to the primary visual area.
Primary Visual Area
The area in the occipital lobe that processes visual information.
right eye
Damage to the right optic nerve causes a loss of vision in the _________
lateral; left; right
Damage to the optic chiasm will cause a loss of vision in the _______ side of both eyes (______ side of left eye and _______ side of right eye)
left
Damage to the right optic tract causes a loss of vision in the _______ side of both eyes