IB ESS SL
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB environmental systems and societies- terms and vocab from topic 1-8
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
Ecological footprint
a model that can be used to estimate the demands that a human population places on the environment. It is a measure of the amount of land that is needed to support a population.
The EF considers two aspects:
* **Biocapacity**: this is the earth’s bioproductive land and sea. Ex: includes forests, cropland, pastures and fisheries.
* **Demand**: considers the amount of bioproductive land we need to provide our resources and space for infrastructure and absorb the waste.
The EF considers two aspects:
* **Biocapacity**: this is the earth’s bioproductive land and sea. Ex: includes forests, cropland, pastures and fisheries.
* **Demand**: considers the amount of bioproductive land we need to provide our resources and space for infrastructure and absorb the waste.
2
New cards
transfers
move energy or matter from one place to another without changing it in any way.
3
New cards
transformations
move energy and matter and change it’s state or form. Ex:
* Water changes state from solid, to liquid to gas (matter).
* Incoming light is transformed into heat as it is re-radiated from the earth’s surface (energy).
* Energy is converted into matter during photosynthesis.
* Water changes state from solid, to liquid to gas (matter).
* Incoming light is transformed into heat as it is re-radiated from the earth’s surface (energy).
* Energy is converted into matter during photosynthesis.
4
New cards
open system
**exchanges matter and energy** with its surroundings.
5
New cards
closed system
**exchanges energy** __**but not**__ **matter** with its surroundings.
6
New cards
Isolated system
**exchanges neither energy nor matter** with its surroundings.
7
New cards
maximum sustainable yield
the optimum harvest that can be obtained yearly without affecting the standing stock and its ability to replenish itself
8
New cards
Bioaccumulation
the increase in the concentration of a pollutant in an organism as it absorbs or it ingests it from its environment.
takes place in a single organism over the span of its life, resulting in a higher concentration in older individuals.
takes place in a single organism over the span of its life, resulting in a higher concentration in older individuals.
9
New cards
Biomagnification
the increase in the concentration of a pollutant as it moves up through the food chain. (think consumption of DDT in fish)
takes place as chemicals transfer from lower trophic levels to higher trophic levels within a food web, resulting in a higher concentration in apex predators.
takes place as chemicals transfer from lower trophic levels to higher trophic levels within a food web, resulting in a higher concentration in apex predators.
10
New cards
Biocapacity
The biological capacity of an area/region/country to generate the resources and absorb the wastes of a given population.
11
New cards
Biodiversity
the variety of all life on earth. It includes genetic diversity, species diversity and habitat diversity.
12
New cards
NPP
represents the amount of usable biomass in an ecosystem.
Takes into account respiratory losses (R) and is shown as the following equation:
NPP = GPP – R
Takes into account respiratory losses (R) and is shown as the following equation:
NPP = GPP – R
13
New cards
GPP
all the biomass produced by primary producers in a given amount of time (before any of it is used for respiration)
GPP = NPP + R
GPP = NPP + R
14
New cards
NSP
Leftover energy after respiration
NSP = GSP – R
NSP = GSP – R
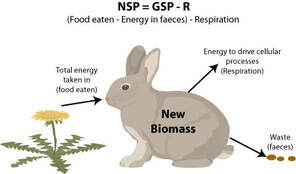
15
New cards
GSP
represents the total amount of energy or biomass used by consumers.
16
New cards
natural capital
natural resources that produce sustainable natural income of goods and services. Ex: forests, fisheries, fertile lands etc
17
New cards
natural income
the yield from natural capital. Ex: timber, fruit produce, etc.
18
New cards
k strategist
Have less offspring, but spend more time caring for them. Quality > quantity. Offspring grow up slower. More common in climax communities. Ex: horses, elephants, whales, etc.
Think “K” for “Kare”. Because they care for their offspring.
Think “K” for “Kare”. Because they care for their offspring.
19
New cards
r strategist
Quantity > quality of offspring. Lots of offspring, grow up fast. Most of these animals are prey, or have some threat that makes it hard for their young to survive. Ex: rabbits, mice, insects, etc
20
New cards
climax community
The final stage of succession. This is a steady state equilibrium with the climate and/or the soil. Won’t change unless there is a disaster.
21
New cards
zonation
The change in a vegetation community along an environmental slope. The change may be caused by changes in altitude, depth of water, tidal level, distance from the shore etc. These types of changes are spatial and are determined by changes in the abiotic factors.
22
New cards
succession
The predictable change in a vegetation community over time. It starts with a pioneer community. During this stage, the ecological community will change in composition.
23
New cards
BOD (Biochemical oxygen demand)
the measure of the amount of dissolved oxygen used to breakdown the organic material in a body of water. It’s an indirect measure of the amount organic material in the water.
24
New cards
Biotic index
determine water quality by observing the organisms living there. high biodiversity = likely clean water
25
New cards
Photochemical smog
occurs when sunlight activates reactions between (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) resulting in the formation of ozone and peroxyacyl nitrates (PAN).
mostly likely to be formed under the following conditions:
* High emissions of pollutants
* Cities
* traffic
* High levels of sunlight
* Calm or light winds
* Dry weather conditions
* Hills/mountains
* thermal inversion
mostly likely to be formed under the following conditions:
* High emissions of pollutants
* Cities
* traffic
* High levels of sunlight
* Calm or light winds
* Dry weather conditions
* Hills/mountains
* thermal inversion
26
New cards
Limiting factors
the resources in the environment that limit the growth, abundance and distribution of organisms/populations in an ecosystem. Ex: water, food, sunlight, temperature, etc.
27
New cards
point source pollution
a single identifiable source of pollution. Ex: a specific factory, smokestacks, water treatment plant, etc.
28
New cards
non-point source pollution
pollution from diffuse sources. Difficult to monitor and control. Ex: polluted water from runoff, acid rain, road salt, fertilizer, etc.